Chapter 7 Assignment due Wednesday, May 24
|
|
|
- Laurence Washington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 due Wednesday, May 24 Calculating Probabilities for Normal Distributions Overview What you re going to do in this assignment is use an online applet to calculate: probabilities associated with given -scores or data values, and -scores or data values associated with given probabilities. You will do these calculations for both: the standard normal distribution, and a non-standard normal distribution. How to Use the Applet Here is the website for the applet (I will include the link on the Assignments page also): I have currently tested the applet with Internet Explorer 11. If you have troubles getting it to work, then try a different browser, such as Moilla Firefox or Google Chrome, both of which are free downloads, and I just tested them both. Or, give me a call if you have a problem running it, and I will try to help. The help may involve you trying it on another computer. Actually I have never had any complaints from students in the past about this particular applet not working.
2 So, once you get to the website, wait for a few (or several) seconds while the applet loads. Once it loads, the page should hopefully look like this. Use this button to calculate a probability from a -score or data value. Input the mean, standard deviation, and the -score(s) or data value(s), hit correct button. The output is the area, and the graph will show where the area is (according to your input). The top button (Area from a value) is what you will use to calculate the probabilities when you are given a data value or a -score. The value shown in the yellow box at the bottom of the first distribution: Area (probability) is the answer for this portion; remember that probability = area. In other words, the area above a -score of 1.96 =
3 If you hit the second button (Value from an area), the input and output regions will change like this: Use this button to calculate a - score or data value from a given area. Input the mean, standard deviation, and the area. Choose the correct button, and the -scores(s) or data value(s), and the graph will show where the area is (according to your input). The second button (Value from an area) is what you will use if you are given a probability (area), and want to calculate the associated data value or -score. If you click that button, the yellow box will change and give you four options to enter the area. Once you make that selection the answer will appear immediately to the right of the option (Above, Below, ). The answer(s) will be the -scores or data values. So again: use top button on applet to go from -scores/values to probabilities use bottom button on applet to go from probabilities/areas to - scores/values.
4 Looking at either part of the applet, you can see that the default is for the standard normal distribution, since the mean = 0 and the standard deviation = 1. You will use this for problems 1-3, and for problem 4 you will input a different mean and standard deviation. Make sure that you hit the Recalculate button every time you change an input to the applet! Other than this, I m NOT going to give you a detailed step-by-step procedure on how to use the applet, because I think it s pretty self-explanatory, and you should be able to just play around with it and figure it out. I will include some specific pointers in the problems below. One suggestion would be to try reproducing the problems that we did in class, to verify that you are using the applet correctly and getting the same answers. Since you are also going to do the problems by hand (using Table V), I would suggest the following: Draw the figures by hand first, and calculate your probabilities or data values THEN verify by using the applet if the figure does not at all match what you drew, then you re either using the applet incorrectly, or you drew it wrong to begin with. However, I will give the following CAUTION for using the applet: ONLY input the values that are given in the problem statements. Do NOT calculate something by hand, or look it up in the table, and then use that value as input to the applet. The Table V result and the Applet Result should be completely independent of each other!
5 Problems: Note that you are going to do all of these problems using two methods: 1. by hand, using Table V look-up method (make SURE you know how to do this, it s how you ll have to do it on the test!) 2. with the applet Therefore, you have the perfect opportunity to check your own answers, since the results from both methods should be approximately the same. If there is a large discrepancy, then go back and check because you have done one (or both) incorrectly. Note: DO NOT round off your answers from the Applet. 1. Determine the total area under the standard normal curve: a. that lies to the left of = 1.38 b. that lies to the right of = 1.22 c. that lies between = 0.89 and = 0.57 d. to the left of = 0.96 or to the right of = 2.22 (note: you can use the Outside button for this one) 2. Find the -score such that the area under the standard normal curve to its left is In other words, find the 17 th percentile, P17, which is the - score separating the bottom 17% of the -scores from the top 83%. So in other words, you want to use the bottom button on the applet, to find the value from an area. 3. Find the -scores (two of them) that separate the middle 47% of the distribution from the area in the tails of the standard normal distribution. Again, you want to use the bottom button on the applet, to find the value from an area. You can use either the Between or the Outside button, but be careful that you put in the correct area that corresponds to that option. Check that your results match your hand results from Table V.
6 4. For this problem, you are going to use the Body Data data set which is preloaded into STATDISK, 13 th edition. HOWEVER! the data file in STATDISK is a mixture of male and female data. I sorted it out according to gender, and saved the data into two different Excel files. Pick the file that corresponds to YOU! Therefore, ladies will be using one file and guys will be using a different file. Ladies: Body_data_women_pulse (147 data values) Guys: Body_data_men_pulse (153 data values) The variable that you will be looking at is the pulse rate, in beats per minute. Therefore, take your own resting pulse rate for one minute and record that on the Answer sheet. The Excel files contain the pulse rate data for a sample of 153 men and 147 women in the respective files, and the original source is from the National Center for Health Statistics. Copy the column of pulse rate data to STATDISK, and make a histogram to verify that the data is approximately normal. Make sure to add a title and x-axis label with measurement units, and print out the histogram. Use STATDISK to find the Descriptive Statistics for the data set. Note: make sure that you have copied all 153 (men) or 147 (women) data values over. Because the data is approximately normal, we can use the mean and the standard deviation of the data to model the variable pulse rate as a normal distribution. Do NOT round off the mean or the standard deviation, use all of the digits from the STATDISK calculation for both your hand calculations and as input to the applet. Note: answer each of the questions below with respect to the data set YOU are using either the Men s or the Women s. You don t need to do both! a. Using the Empirical Rule, calculate the minimum and maximum usual values for the pulse rates, in bpm. Along the x-axis of your histogram, mark and label the approximate locations of the mean, the minimum and maximum usual values, and also your own pulse rate.
7 b. Men: Based on the result in part a, would a man with a pulse rate of 95 bpm be considered unusual? Explain why or why not. Women: Based on the result in part a, would a woman with a pulse rate of 95 bpm be considered unusual? Explain why or why not. c. Using the normal model, what proportion of men or women have a pulse rate greater than 85 bpm? d. What proportion of men s or women s pulse rates are between 60 and 90 bpm? e. Find the fourth decile of the pulse rates, in other words the pulse rate (in bpm) that separates the bottom 40% of pulse rates from the top 60%. f. Using the normal model, determine the interval of pulse rates that make up the middle 80% of the pulse rates. g. Based on your pulse rate measurement, what percentile are you in? (round to the nearest percent) h. Is your pulse rate unusual? Explain why or why not. What You Need to Turn In: Print out the following table, fill it out, and turn it in (5 pages total). Histogram from STATDISK, including a title and x-axis label, and with the values marked and labeled as noted in problem 4a. For the Table V column, SHOW ALL OF YOUR HAND CALCULATIONS (for many problems, these will be minimal)! For the Applet result, do not round off the answers! For each Figure on the Answer Sheet, just make a rough sketch showing the appropriate shaded region for the problem. Include any applicable measurement units with your answers (this only applies to question 4).
8 Prob. # 1a. Figure (just a rough sketch) Table V Result (and any work if applicable) Applet Result (do not round off) 1b. 1c.
9 Prob. # 1d. Figure (just a rough sketch) Table V Result (and any work if applicable) Applet Result (do not round off) 2. 3.
10 4. Does the STATDISK histogram indicate that a normal distribution could be used as a model for the variable? (yes or no) List the mean (do not round off): List the standard deviation (do not round off): (bpm) (bpm) List your pulse rate: (bpm) 4a. Minimum usual value = (bpm) Maximum usual value = (bpm) 4b. Men: Based on the result in part a, would a man with a pulse rate of 95 bpm be considered unusual? Explain why or why not. Women: Based on the result in part a, would a woman with a pulse rate of 95 bpm be considered unusual? Explain why or why not. Prob. # 4c. Figure (just a rough sketch) Table V Result (and any work if applicable) Applet Result (do not round off)
11 Prob. # 4d. Figure (just a rough sketch) Table V Result (and any work if applicable) Applet Result (do not round off) 4e. 4f.
12 Prob. # 4g. Figure (just a rough sketch) Table V Result (and any work if applicable) Applet Result (do not round off) 4h. Unusual or not? Explain.
Chapter 7 Assignment SOLUTIONS WOMEN: Plus, add your pulse rate to the histogram.
 Instructor: Linda C. Stephenson WOMEN: Plus, add your pulse rate to the histogram. Instructor: Linda C. Stephenson MEN: Plus, add your pulse rate to the histogram. 1a. For z = -1.17: P (below) = 0.1210
Instructor: Linda C. Stephenson WOMEN: Plus, add your pulse rate to the histogram. Instructor: Linda C. Stephenson MEN: Plus, add your pulse rate to the histogram. 1a. For z = -1.17: P (below) = 0.1210
Chapter 7 Assignment SOLUTIONS WOMEN:
 SOLUTIONS WOMEN: MEN: 1a. For z -0.79: P (below) 0.2148 1b. For z 1.46: 0.9279 P(above) 1 0.9279 0.0721 1c. For z 1.23: 0.1093 For z 1.65: 0.9505 P(between) 0.9505 0.1093 0.8412 1d. For z 0.71: 0.2389
SOLUTIONS WOMEN: MEN: 1a. For z -0.79: P (below) 0.2148 1b. For z 1.46: 0.9279 P(above) 1 0.9279 0.0721 1c. For z 1.23: 0.1093 For z 1.65: 0.9505 P(between) 0.9505 0.1093 0.8412 1d. For z 0.71: 0.2389
Measures of Position
 Measures of Position In this section, we will learn to use fractiles. Fractiles are numbers that partition, or divide, an ordered data set into equal parts (each part has the same number of data entries).
Measures of Position In this section, we will learn to use fractiles. Fractiles are numbers that partition, or divide, an ordered data set into equal parts (each part has the same number of data entries).
Chapter 3 Analyzing Normal Quantitative Data
 Chapter 3 Analyzing Normal Quantitative Data Introduction: In chapters 1 and 2, we focused on analyzing categorical data and exploring relationships between categorical data sets. We will now be doing
Chapter 3 Analyzing Normal Quantitative Data Introduction: In chapters 1 and 2, we focused on analyzing categorical data and exploring relationships between categorical data sets. We will now be doing
Chapter 2 Assignment (due Thursday, April 19)
 (due Thursday, April 19) Introduction: The purpose of this assignment is to analyze data sets by creating histograms and scatterplots. You will use the STATDISK program for both. Therefore, you should
(due Thursday, April 19) Introduction: The purpose of this assignment is to analyze data sets by creating histograms and scatterplots. You will use the STATDISK program for both. Therefore, you should
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe
 Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe Section 1.3 Homework Answers Assignment 5 1.80 If you ask a computer to generate "random numbers between 0 and 1, you uniform will
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe Section 1.3 Homework Answers Assignment 5 1.80 If you ask a computer to generate "random numbers between 0 and 1, you uniform will
Prepare a stem-and-leaf graph for the following data. In your final display, you should arrange the leaves for each stem in increasing order.
 Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
appstats6.notebook September 27, 2016
 Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model Objectives: 1.Students will calculate and interpret z scores. 2.Students will compare/contrast values from different distributions using
Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model Objectives: 1.Students will calculate and interpret z scores. 2.Students will compare/contrast values from different distributions using
Chapter 2 Assignment (due Thursday, October 5)
 (due Thursday, October 5) Introduction: The purpose of this assignment is to analyze data sets by creating histograms and scatterplots. You will use the STATDISK program for both. Therefore, you should
(due Thursday, October 5) Introduction: The purpose of this assignment is to analyze data sets by creating histograms and scatterplots. You will use the STATDISK program for both. Therefore, you should
The main issue is that the mean and standard deviations are not accurate and should not be used in the analysis. Then what statistics should we use?
 Chapter 4 Analyzing Skewed Quantitative Data Introduction: In chapter 3, we focused on analyzing bell shaped (normal) data, but many data sets are not bell shaped. How do we analyze quantitative data when
Chapter 4 Analyzing Skewed Quantitative Data Introduction: In chapter 3, we focused on analyzing bell shaped (normal) data, but many data sets are not bell shaped. How do we analyze quantitative data when
23.2 Normal Distributions
 1_ Locker LESSON 23.2 Normal Distributions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: S-ID.4 Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate
1_ Locker LESSON 23.2 Normal Distributions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: S-ID.4 Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate
Normal Distribution. 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution
 Normal Distribution 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution 1 /20 Homework Read Sec 6-4. Discussion question p316 Do p316 probs 1-10, 16-22, 31, 32, 34-37, 39 2 /20 3 /20 Objective Find the probabilities
Normal Distribution 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution 1 /20 Homework Read Sec 6-4. Discussion question p316 Do p316 probs 1-10, 16-22, 31, 32, 34-37, 39 2 /20 3 /20 Objective Find the probabilities
Section 10.4 Normal Distributions
 Section 10.4 Normal Distributions Random Variables Suppose a bank is interested in improving its services to customers. The manager decides to begin by finding the amount of time tellers spend on each
Section 10.4 Normal Distributions Random Variables Suppose a bank is interested in improving its services to customers. The manager decides to begin by finding the amount of time tellers spend on each
Math 120 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency
 Math 1 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency lowest value + highest value midrange The word average: is very ambiguous and can actually refer to the mean,
Math 1 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency lowest value + highest value midrange The word average: is very ambiguous and can actually refer to the mean,
1. The Normal Distribution, continued
 Math 1125-Introductory Statistics Lecture 16 10/9/06 1. The Normal Distribution, continued Recall that the standard normal distribution is symmetric about z = 0, so the area to the right of zero is 0.5000.
Math 1125-Introductory Statistics Lecture 16 10/9/06 1. The Normal Distribution, continued Recall that the standard normal distribution is symmetric about z = 0, so the area to the right of zero is 0.5000.
Ch6: The Normal Distribution
 Ch6: The Normal Distribution Introduction Review: A continuous random variable can assume any value between two endpoints. Many continuous random variables have an approximately normal distribution, which
Ch6: The Normal Distribution Introduction Review: A continuous random variable can assume any value between two endpoints. Many continuous random variables have an approximately normal distribution, which
Data Analysis & Probability
 Unit 5 Probability Distributions Name: Date: Hour: Section 7.2: The Standard Normal Distribution (Area under the curve) Notes By the end of this lesson, you will be able to Find the area under the standard
Unit 5 Probability Distributions Name: Date: Hour: Section 7.2: The Standard Normal Distribution (Area under the curve) Notes By the end of this lesson, you will be able to Find the area under the standard
Distributions of random variables
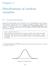 Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
 CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is how the data is spread or distributed over the range of the data values. This is one of
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is how the data is spread or distributed over the range of the data values. This is one of
What s Normal Anyway?
 Name Class Problem 1 A Binomial Experiment 1. When rolling a die, what is the theoretical probability of rolling a 3? 2. When a die is rolled 100 times, how many times do you expect that a 3 will be rolled?
Name Class Problem 1 A Binomial Experiment 1. When rolling a die, what is the theoretical probability of rolling a 3? 2. When a die is rolled 100 times, how many times do you expect that a 3 will be rolled?
CHAPTER 6. The Normal Probability Distribution
 The Normal Probability Distribution CHAPTER 6 The normal probability distribution is the most widely used distribution in statistics as many statistical procedures are built around it. The central limit
The Normal Probability Distribution CHAPTER 6 The normal probability distribution is the most widely used distribution in statistics as many statistical procedures are built around it. The central limit
Introduction to Minitab 1
 Introduction to Minitab 1 We begin by first starting Minitab. You may choose to either 1. click on the Minitab icon in the corner of your screen 2. go to the lower left and hit Start, then from All Programs,
Introduction to Minitab 1 We begin by first starting Minitab. You may choose to either 1. click on the Minitab icon in the corner of your screen 2. go to the lower left and hit Start, then from All Programs,
4. Descriptive Statistics: Measures of Variability and Central Tendency
 4. Descriptive Statistics: Measures of Variability and Central Tendency Objectives Calculate descriptive for continuous and categorical data Edit output tables Although measures of central tendency and
4. Descriptive Statistics: Measures of Variability and Central Tendency Objectives Calculate descriptive for continuous and categorical data Edit output tables Although measures of central tendency and
Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data
 Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.2 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition - For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution
Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.2 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition - For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
MAT 155. Z score. August 31, S3.4o3 Measures of Relative Standing and Boxplots
 MAT 155 Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College Chapter 3 Statistics for Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Data 3 1 Review and Preview 3 2 Measures of Center 3 3 Measures of Variation 3 4 Measures
MAT 155 Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College Chapter 3 Statistics for Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Data 3 1 Review and Preview 3 2 Measures of Center 3 3 Measures of Variation 3 4 Measures
Normal Curves and Sampling Distributions
 Normal Curves and Sampling Distributions 6 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Section 6.2 Standard Units and Areas Under the Standard Normal Distribution Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights
Normal Curves and Sampling Distributions 6 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Section 6.2 Standard Units and Areas Under the Standard Normal Distribution Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights
The standard deviation 1 n
 The standard deviation 1 SD = (xj x) n 2 The SD gives a measure of how the data are clustered around the mean. If the SD is larger, then the data are more spread out we are more likely to find data that
The standard deviation 1 SD = (xj x) n 2 The SD gives a measure of how the data are clustered around the mean. If the SD is larger, then the data are more spread out we are more likely to find data that
The Normal Distribution & z-scores
 & z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
& z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
Frequency Distributions and Descriptive Statistics in SPS
 230 Combs Building 859.622.3050 studentcomputing.eku.edu studentcomputing@eku.edu Frequency Distributions and Descriptive Statistics in SPSS In this tutorial, we re going to work through a sample problem
230 Combs Building 859.622.3050 studentcomputing.eku.edu studentcomputing@eku.edu Frequency Distributions and Descriptive Statistics in SPSS In this tutorial, we re going to work through a sample problem
CHAPTER 2: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Lecture Notes for Introductory Statistics 1. Daphne Skipper, Augusta University (2016)
 CHAPTER 2: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Lecture Notes for Introductory Statistics 1 Daphne Skipper, Augusta University (2016) 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is
CHAPTER 2: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Lecture Notes for Introductory Statistics 1 Daphne Skipper, Augusta University (2016) 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
2.1: Frequency Distributions and Their Graphs
 2.1: Frequency Distributions and Their Graphs Frequency Distribution - way to display data that has many entries - table that shows classes or intervals of data entries and the number of entries in each
2.1: Frequency Distributions and Their Graphs Frequency Distribution - way to display data that has many entries - table that shows classes or intervals of data entries and the number of entries in each
Normal Data ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning
 Normal Data ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning Histogram for Different Sample Sizes For a small sample, the choice of class (group) size dramatically affects how the histogram appears. Say we
Normal Data ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning Histogram for Different Sample Sizes For a small sample, the choice of class (group) size dramatically affects how the histogram appears. Say we
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
CHAPTER 2: Describing Location in a Distribution
 CHAPTER 2: Describing Location in a Distribution 2.1 Goals: 1. Compute and use z-scores given the mean and sd 2. Compute and use the p th percentile of an observation 3. Intro to density curves 4. More
CHAPTER 2: Describing Location in a Distribution 2.1 Goals: 1. Compute and use z-scores given the mean and sd 2. Compute and use the p th percentile of an observation 3. Intro to density curves 4. More
STA Module 4 The Normal Distribution
 STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA /25/12. Module 4 The Normal Distribution. Learning Objectives. Let s Look at Some Examples of Normal Curves
 STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
Creating a Histogram Creating a Histogram
 Creating a Histogram Another great feature of Excel is its ability to visually display data. This Tip Sheet demonstrates how to create a histogram and provides a general overview of how to create graphs,
Creating a Histogram Another great feature of Excel is its ability to visually display data. This Tip Sheet demonstrates how to create a histogram and provides a general overview of how to create graphs,
Make sure to keep all graphs in same excel file as your measures.
 Project Part 2 Graphs. I. Use Excel to make bar graph for questions 1, and 5. II. Use Excel to make histograms for questions 2, and 3. III. Use Excel to make pie graphs for questions 4, and 6. IV. Use
Project Part 2 Graphs. I. Use Excel to make bar graph for questions 1, and 5. II. Use Excel to make histograms for questions 2, and 3. III. Use Excel to make pie graphs for questions 4, and 6. IV. Use
Assignment 3 due Thursday Oct. 11
 Instructor Linda C. Stephenson due Thursday Oct. 11 GENERAL NOTE: These assignments often build on each other what you learn in one assignment may be carried over to subsequent assignments. If I have already
Instructor Linda C. Stephenson due Thursday Oct. 11 GENERAL NOTE: These assignments often build on each other what you learn in one assignment may be carried over to subsequent assignments. If I have already
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers HW 34. Sketch
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers HW 34. Sketch
Chapter 2 Ratios, Percents, Simple Equations, and Ratio-Proportion
 Chapter 2 Ratios, Percents, Simple Equations, and Ratio-Proportion PROBLEM Decimal Fraction Percent Ratio 1. 0.05 2. 3. 45% 4. 1. Complete row 1 in the table above., 5%, 1:20 DIF: Application REF: Ratios
Chapter 2 Ratios, Percents, Simple Equations, and Ratio-Proportion PROBLEM Decimal Fraction Percent Ratio 1. 0.05 2. 3. 45% 4. 1. Complete row 1 in the table above., 5%, 1:20 DIF: Application REF: Ratios
Averages and Variation
 Averages and Variation 3 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1-1 Section 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency: Mode, Median, and Mean Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1-2 Focus
Averages and Variation 3 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1-1 Section 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency: Mode, Median, and Mean Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1-2 Focus
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 2. Section 1: Describing Location in a Distribution
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 2 Section 1: Describing Location in a Distribution Suppose you earned an 86 on a statistics quiz. The question is: should you be satisfied with this score? What if it is the
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 2 Section 1: Describing Location in a Distribution Suppose you earned an 86 on a statistics quiz. The question is: should you be satisfied with this score? What if it is the
Week 7: The normal distribution and sample means
 Week 7: The normal distribution and sample means Goals Visualize properties of the normal distribution. Learning the Tools Understand the Central Limit Theorem. Calculate sampling properties of sample
Week 7: The normal distribution and sample means Goals Visualize properties of the normal distribution. Learning the Tools Understand the Central Limit Theorem. Calculate sampling properties of sample
Math 14 Lecture Notes Ch. 6.1
 6.1 Normal Distribution What is normal? a 10-year old boy that is 4' tall? 5' tall? 6' tall? a 25-year old woman with a shoe size of 5? 7? 9? an adult alligator that weighs 200 pounds? 500 pounds? 800
6.1 Normal Distribution What is normal? a 10-year old boy that is 4' tall? 5' tall? 6' tall? a 25-year old woman with a shoe size of 5? 7? 9? an adult alligator that weighs 200 pounds? 500 pounds? 800
Chapter 5: The normal model
 Chapter 5: The normal model Objective (1) Learn how rescaling a distribution affects its summary statistics. (2) Understand the concept of normal model. (3) Learn how to analyze distributions using the
Chapter 5: The normal model Objective (1) Learn how rescaling a distribution affects its summary statistics. (2) Understand the concept of normal model. (3) Learn how to analyze distributions using the
Section 7.2: Applications of the Normal Distribution
 Section 7.2: Applications of the Normal Distribution Objectives By the end of this lesson, you will be able to... 1. find and interpret the area under a normal curve 2. find the value of a normal random
Section 7.2: Applications of the Normal Distribution Objectives By the end of this lesson, you will be able to... 1. find and interpret the area under a normal curve 2. find the value of a normal random
The Normal Distribution
 14-4 OBJECTIVES Use the normal distribution curve. The Normal Distribution TESTING The class of 1996 was the first class to take the adjusted Scholastic Assessment Test. The test was adjusted so that the
14-4 OBJECTIVES Use the normal distribution curve. The Normal Distribution TESTING The class of 1996 was the first class to take the adjusted Scholastic Assessment Test. The test was adjusted so that the
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
The Normal Distribution
 The Normal Distribution Lecture 20 Section 6.3.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 28, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, 2011 1 / 41 Outline
The Normal Distribution Lecture 20 Section 6.3.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 28, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, 2011 1 / 41 Outline
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers
 IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
A Quick Introduction to R
 Math 4501 Fall 2012 A Quick Introduction to R The point of these few pages is to give you a quick introduction to the possible uses of the free software R in statistical analysis. I will only expect you
Math 4501 Fall 2012 A Quick Introduction to R The point of these few pages is to give you a quick introduction to the possible uses of the free software R in statistical analysis. I will only expect you
Exploration: Multiplying Fractions & Decimals Using an Area Model
 Exploration: Multiplying Fractions & Decimals Using an Area Model REPRESENT MULTIPLICATION SITUATIONS INVOLVING FRACTIONS & DECIMALS WITH MODELS INCLUDING PICTURES IDENTIFY FACTORS OF POSITIVE INTEGERS
Exploration: Multiplying Fractions & Decimals Using an Area Model REPRESENT MULTIPLICATION SITUATIONS INVOLVING FRACTIONS & DECIMALS WITH MODELS INCLUDING PICTURES IDENTIFY FACTORS OF POSITIVE INTEGERS
Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary
 1 Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary Z-score: Is the distance of each data value from the mean in standard deviation Standardizes data values Standardization changes the mean and the standard deviation: o Z
1 Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary Z-score: Is the distance of each data value from the mean in standard deviation Standardizes data values Standardization changes the mean and the standard deviation: o Z
So..to be able to make comparisons possible, we need to compare them with their respective distributions.
 Unit 3 ~ Modeling Distributions of Data 1 ***Section 2.1*** Measures of Relative Standing and Density Curves (ex) Suppose that a professional soccer team has the money to sign one additional player and
Unit 3 ~ Modeling Distributions of Data 1 ***Section 2.1*** Measures of Relative Standing and Density Curves (ex) Suppose that a professional soccer team has the money to sign one additional player and
Unit 8: Normal Calculations
 Unit 8: Normal Calculations Prerequisites This unit requires familiarity with basic facts about normal distributions, which are covered in Unit 7, Normal Curves. In addition, students need some background
Unit 8: Normal Calculations Prerequisites This unit requires familiarity with basic facts about normal distributions, which are covered in Unit 7, Normal Curves. In addition, students need some background
Data organization. So what kind of data did we collect?
 Data organization Suppose we go out and collect some data. What do we do with it? First we need to figure out what kind of data we have. To illustrate, let s do a simple experiment and collect the height
Data organization Suppose we go out and collect some data. What do we do with it? First we need to figure out what kind of data we have. To illustrate, let s do a simple experiment and collect the height
Section 6.3: Measures of Position
 Section 6.3: Measures of Position Measures of position are numbers showing the location of data values relative to the other values within a data set. They can be used to compare values from different
Section 6.3: Measures of Position Measures of position are numbers showing the location of data values relative to the other values within a data set. They can be used to compare values from different
4.3, Math 1410 Name: And now for something completely different... Well, not really.
 4.3, Math 1410 Name: And now for something completely different... Well, not really. How derivatives affect the shape of a graph. Please allow me to offer some explanation as to why the first couple parts
4.3, Math 1410 Name: And now for something completely different... Well, not really. How derivatives affect the shape of a graph. Please allow me to offer some explanation as to why the first couple parts
BIOL Gradation of a histogram (a) into the normal curve (b)
 (التوزيع الطبيعي ( Distribution Normal (Gaussian) One of the most important distributions in statistics is a continuous distribution called the normal distribution or Gaussian distribution. Consider the
(التوزيع الطبيعي ( Distribution Normal (Gaussian) One of the most important distributions in statistics is a continuous distribution called the normal distribution or Gaussian distribution. Consider the
Distributions of Continuous Data
 C H A P T ER Distributions of Continuous Data New cars and trucks sold in the United States average about 28 highway miles per gallon (mpg) in 2010, up from about 24 mpg in 2004. Some of the improvement
C H A P T ER Distributions of Continuous Data New cars and trucks sold in the United States average about 28 highway miles per gallon (mpg) in 2010, up from about 24 mpg in 2004. Some of the improvement
Today s Topics. Percentile ranks and percentiles. Standardized scores. Using standardized scores to estimate percentiles
 Today s Topics Percentile ranks and percentiles Standardized scores Using standardized scores to estimate percentiles Using µ and σ x to learn about percentiles Percentiles, standardized scores, and the
Today s Topics Percentile ranks and percentiles Standardized scores Using standardized scores to estimate percentiles Using µ and σ x to learn about percentiles Percentiles, standardized scores, and the
Example 1. Find the x value that has a left tail area of.1131 P ( x <??? ) =. 1131
 Section 6 4D: Finding a Value of x with a Given tail arae Label the shaded area for both graphs. Find the value for z and label the z axis. Find the value for x for the given area under the normal curve
Section 6 4D: Finding a Value of x with a Given tail arae Label the shaded area for both graphs. Find the value for z and label the z axis. Find the value for x for the given area under the normal curve
UNIT 1A EXPLORING UNIVARIATE DATA
 A.P. STATISTICS E. Villarreal Lincoln HS Math Department UNIT 1A EXPLORING UNIVARIATE DATA LESSON 1: TYPES OF DATA Here is a list of important terms that we must understand as we begin our study of statistics
A.P. STATISTICS E. Villarreal Lincoln HS Math Department UNIT 1A EXPLORING UNIVARIATE DATA LESSON 1: TYPES OF DATA Here is a list of important terms that we must understand as we begin our study of statistics
Measures of Central Tendency. A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set.
 Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean the sum of all data values divided by the number of values in
Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean the sum of all data values divided by the number of values in
Section 1.2. Displaying Quantitative Data with Graphs. Mrs. Daniel AP Stats 8/22/2013. Dotplots. How to Make a Dotplot. Mrs. Daniel AP Statistics
 Section. Displaying Quantitative Data with Graphs Mrs. Daniel AP Statistics Section. Displaying Quantitative Data with Graphs After this section, you should be able to CONSTRUCT and INTERPRET dotplots,
Section. Displaying Quantitative Data with Graphs Mrs. Daniel AP Statistics Section. Displaying Quantitative Data with Graphs After this section, you should be able to CONSTRUCT and INTERPRET dotplots,
Chapter 6: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
 Chapter 6: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Random Sampling Numerical Summaries Stem-n-Leaf plots Histograms, and Box plots Time Sequence Plots Normal Probability Plots Sections 6-1 to 6-5, and 6-7 Random Sampling
Chapter 6: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Random Sampling Numerical Summaries Stem-n-Leaf plots Histograms, and Box plots Time Sequence Plots Normal Probability Plots Sections 6-1 to 6-5, and 6-7 Random Sampling
AP Statistics. Study Guide
 Measuring Relative Standing Standardized Values and z-scores AP Statistics Percentiles Rank the data lowest to highest. Counting up from the lowest value to the select data point we discover the percentile
Measuring Relative Standing Standardized Values and z-scores AP Statistics Percentiles Rank the data lowest to highest. Counting up from the lowest value to the select data point we discover the percentile
Econ 3790: Business and Economics Statistics. Instructor: Yogesh Uppal
 Econ 3790: Business and Economics Statistics Instructor: Yogesh Uppal Email: yuppal@ysu.edu Chapter 8: Interval Estimation Population Mean: Known Population Mean: Unknown Margin of Error and the Interval
Econ 3790: Business and Economics Statistics Instructor: Yogesh Uppal Email: yuppal@ysu.edu Chapter 8: Interval Estimation Population Mean: Known Population Mean: Unknown Margin of Error and the Interval
Chapter 2: Statistical Models for Distributions
 Chapter 2: Statistical Models for Distributions 2.2 Normal Distributions In Chapter 2 of YMS, we learn that distributions of data can be approximated by a mathematical model known as a density curve. In
Chapter 2: Statistical Models for Distributions 2.2 Normal Distributions In Chapter 2 of YMS, we learn that distributions of data can be approximated by a mathematical model known as a density curve. In
a. divided by the. 1) Always round!! a) Even if class width comes out to a, go up one.
 Probability and Statistics Chapter 2 Notes I Section 2-1 A Steps to Constructing Frequency Distributions 1 Determine number of (may be given to you) a Should be between and classes 2 Find the Range a The
Probability and Statistics Chapter 2 Notes I Section 2-1 A Steps to Constructing Frequency Distributions 1 Determine number of (may be given to you) a Should be between and classes 2 Find the Range a The
CHAPTER 1. Introduction. Statistics: Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, presenting and interpreting data.
 1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction Statistics: Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, presenting and interpreting data. Variable: Any characteristic of a person or thing that can be expressed
1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction Statistics: Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, presenting and interpreting data. Variable: Any characteristic of a person or thing that can be expressed
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions
 Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
Excel 2010 with XLSTAT
 Excel 2010 with XLSTAT J E N N I F E R LE W I S PR I E S T L E Y, PH.D. Introduction to Excel 2010 with XLSTAT The layout for Excel 2010 is slightly different from the layout for Excel 2007. However, with
Excel 2010 with XLSTAT J E N N I F E R LE W I S PR I E S T L E Y, PH.D. Introduction to Excel 2010 with XLSTAT The layout for Excel 2010 is slightly different from the layout for Excel 2007. However, with
9.1 Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Date: 2. Decide whether to use a solid line or dotted line:
 9.1 Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Date: Key Ideas: Example Solve the inequality by graphing 3y 2x 6. steps 1. Rearrange the inequality so it s in mx ± b form. Don t forget to flip the inequality
9.1 Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Date: Key Ideas: Example Solve the inequality by graphing 3y 2x 6. steps 1. Rearrange the inequality so it s in mx ± b form. Don t forget to flip the inequality
MAT 110 WORKSHOP. Updated Fall 2018
 MAT 110 WORKSHOP Updated Fall 2018 UNIT 3: STATISTICS Introduction Choosing a Sample Simple Random Sample: a set of individuals from the population chosen in a way that every individual has an equal chance
MAT 110 WORKSHOP Updated Fall 2018 UNIT 3: STATISTICS Introduction Choosing a Sample Simple Random Sample: a set of individuals from the population chosen in a way that every individual has an equal chance
Probability and Statistics. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Probability and Statistics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 14.6 Descriptive Statistics (Graphical) Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Data in Categories Histograms
Probability and Statistics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 14.6 Descriptive Statistics (Graphical) Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Data in Categories Histograms
Section 2.2 Normal Distributions. Normal Distributions
 Section 2.2 Normal Distributions Normal Distributions One particularly important class of density curves are the Normal curves, which describe Normal distributions. All Normal curves are symmetric, single-peaked,
Section 2.2 Normal Distributions Normal Distributions One particularly important class of density curves are the Normal curves, which describe Normal distributions. All Normal curves are symmetric, single-peaked,
L E A R N I N G O B JE C T I V E S
 2.2 Measures of Central Location L E A R N I N G O B JE C T I V E S 1. To learn the concept of the center of a data set. 2. To learn the meaning of each of three measures of the center of a data set the
2.2 Measures of Central Location L E A R N I N G O B JE C T I V E S 1. To learn the concept of the center of a data set. 2. To learn the meaning of each of three measures of the center of a data set the
Lecture Slides. Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition. by Mario F. Triola. and the Triola Statistics Series. Section 6.2-1
 Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Section 6.2-1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard
Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Section 6.2-1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard
Unit 1 Review of BIOSTATS 540 Practice Problems SOLUTIONS - Stata Users
 BIOSTATS 640 Spring 2018 Review of Introductory Biostatistics STATA solutions Page 1 of 13 Key Comments begin with an * Commands are in bold black I edited the output so that it appears here in blue Unit
BIOSTATS 640 Spring 2018 Review of Introductory Biostatistics STATA solutions Page 1 of 13 Key Comments begin with an * Commands are in bold black I edited the output so that it appears here in blue Unit
Sections 4.3 and 4.4
 Sections 4.3 and 4.4 Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 205: Elementary Statistics for the Biological and Life Sciences 1 / 32 4.3 Areas under normal densities Every
Sections 4.3 and 4.4 Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 205: Elementary Statistics for the Biological and Life Sciences 1 / 32 4.3 Areas under normal densities Every
Central Limit Theorem Sample Means
 Date Central Limit Theorem Sample Means Group Member Names: Part One Review of Types of Distributions Consider the three graphs below. Match the histograms with the distribution description. Write the
Date Central Limit Theorem Sample Means Group Member Names: Part One Review of Types of Distributions Consider the three graphs below. Match the histograms with the distribution description. Write the
Excel Tips and FAQs - MS 2010
 BIOL 211D Excel Tips and FAQs - MS 2010 Remember to save frequently! Part I. Managing and Summarizing Data NOTE IN EXCEL 2010, THERE ARE A NUMBER OF WAYS TO DO THE CORRECT THING! FAQ1: How do I sort my
BIOL 211D Excel Tips and FAQs - MS 2010 Remember to save frequently! Part I. Managing and Summarizing Data NOTE IN EXCEL 2010, THERE ARE A NUMBER OF WAYS TO DO THE CORRECT THING! FAQ1: How do I sort my
Measures of Central Tendency
 Page of 6 Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean The sum of all data values divided by the number of
Page of 6 Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean The sum of all data values divided by the number of
Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution. Measures of center and spread. Features of the normal distribution
 Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution Reading: Section 1.3 Density curves An example: GRE scores Measures of center and spread The normal distribution Features of the normal
Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution Reading: Section 1.3 Density curves An example: GRE scores Measures of center and spread The normal distribution Features of the normal
Saving Internet Searches and Resources
 Saving Internet Searches and Resources You and your students will find many resources on the Internet. Sometimes there is a graphic that is perfect for a presentation or project. Or, there may be some
Saving Internet Searches and Resources You and your students will find many resources on the Internet. Sometimes there is a graphic that is perfect for a presentation or project. Or, there may be some
Unit 0: Extending Algebra 1 Concepts
 1 What is a Function? Unit 0: Extending Algebra 1 Concepts Definition: ---Function Notation--- Example: f(x) = x 2 1 Mapping Diagram Use the Vertical Line Test Interval Notation A convenient and compact
1 What is a Function? Unit 0: Extending Algebra 1 Concepts Definition: ---Function Notation--- Example: f(x) = x 2 1 Mapping Diagram Use the Vertical Line Test Interval Notation A convenient and compact
Density Curve (p52) Density curve is a curve that - is always on or above the horizontal axis.
 1.3 Density curves p50 Some times the overall pattern of a large number of observations is so regular that we can describe it by a smooth curve. It is easier to work with a smooth curve, because the histogram
1.3 Density curves p50 Some times the overall pattern of a large number of observations is so regular that we can describe it by a smooth curve. It is easier to work with a smooth curve, because the histogram
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
Use the Move tool to drag A around and see how the automatically constructed objects (like G or the perpendicular and parallel lines) are updated.
 Math 5335 Fall 2015 Lab #0: Installing and using GeoGebra This semester you will have a number of lab assignments which require you to use GeoGebra, a dynamic geometry program. GeoGebra lets you explore
Math 5335 Fall 2015 Lab #0: Installing and using GeoGebra This semester you will have a number of lab assignments which require you to use GeoGebra, a dynamic geometry program. GeoGebra lets you explore
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
Lesson 18-1 Lesson Lesson 18-1 Lesson Lesson 18-2 Lesson 18-2
 Topic 18 Set A Words survey data Topic 18 Set A Words Lesson 18-1 Lesson 18-1 sample line plot Lesson 18-1 Lesson 18-1 frequency table bar graph Lesson 18-2 Lesson 18-2 Instead of making 2-sided copies
Topic 18 Set A Words survey data Topic 18 Set A Words Lesson 18-1 Lesson 18-1 sample line plot Lesson 18-1 Lesson 18-1 frequency table bar graph Lesson 18-2 Lesson 18-2 Instead of making 2-sided copies
Winstats Instruction Sheet
 Winstats Instruction Sheet I. Installing Winstats on your Computer A. Go to the Peanut Software homepage. Either go directly to http://math.exeter.edu/rparris/default.html or Google Peanut Software. B.
Winstats Instruction Sheet I. Installing Winstats on your Computer A. Go to the Peanut Software homepage. Either go directly to http://math.exeter.edu/rparris/default.html or Google Peanut Software. B.
Introduction to SPSS
 Introduction to SPSS Purpose The purpose of this assignment is to introduce you to SPSS, the most commonly used statistical package in the social sciences. You will create a new data file and calculate
Introduction to SPSS Purpose The purpose of this assignment is to introduce you to SPSS, the most commonly used statistical package in the social sciences. You will create a new data file and calculate
Your Name: Section: 2. To develop an understanding of the standard deviation as a measure of spread.
 Your Name: Section: 36-201 INTRODUCTION TO STATISTICAL REASONING Computer Lab #3 Interpreting the Standard Deviation and Exploring Transformations Objectives: 1. To review stem-and-leaf plots and their
Your Name: Section: 36-201 INTRODUCTION TO STATISTICAL REASONING Computer Lab #3 Interpreting the Standard Deviation and Exploring Transformations Objectives: 1. To review stem-and-leaf plots and their
MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY
 11.1 Find Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion STATISTICS Numerical values used to summarize and compare sets of data MEASURE OF CENTRAL TENDENCY A number used to represent the center or middle
11.1 Find Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion STATISTICS Numerical values used to summarize and compare sets of data MEASURE OF CENTRAL TENDENCY A number used to represent the center or middle
Descriptive Statistics, Standard Deviation and Standard Error
 AP Biology Calculations: Descriptive Statistics, Standard Deviation and Standard Error SBI4UP The Scientific Method & Experimental Design Scientific method is used to explore observations and answer questions.
AP Biology Calculations: Descriptive Statistics, Standard Deviation and Standard Error SBI4UP The Scientific Method & Experimental Design Scientific method is used to explore observations and answer questions.
