Mobile Digital Filter Design Toolbox
|
|
|
- Jeffry Wiggins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mobile Digital Filter Deign Toolbox Somak Sukittanon and Joh Pott Univerity of Tenneee at Martin Department of Engineering Martin, TN USA Abtract! Mobile device have become very ueful in many field a portable computation device. They function a data analyi and collection tool. Though they have become common place in many field, there are few application in the area of Digital Signal Proceing (DSP). In thi paper, we have developed a filter deign toolbox for mobile device, particularly ios device. Thi toolbox allow for the deign of filter of uer pecified order and type, export of filter coefficient via , frequency and impule repone plotting, and real time filtered playback. The limited memory and proceing power of the device required pecial mathematic for the filter deign to be derived. I. INTRODUCTION Digital ignal proceing (DSP) i common in today technical world and can be found in many application. Audio data manipulation relie heavily on DSP in the digital age for filtering data, digitization, and analyi. Power ytem alo rely on DSP for application uch a better detecting AC current frequencie. Filter deign, an advanced topic in DSP, i a vital tool that i ued in many field. Currently, filter deign i done motly on dektop computer platform with program uch a Matlab or the open ource alternative Octave. Both offer powerful tool for digital ignal proceing. Smaller ytem for DSP implementation have been developed before for microproceor, and now mobile device. Mobile device are becoming the preferred computational device for many different field, even though they lack the power of a traditional dektop computer. In Phyic [1], data collecting tool uch a compae and high reolution camera are being connected to mobile device to analyze data. In chemitry, the ToiChem application [] i enhancing and reinforcing topic covered in organic chemitry. Mobile application [3] have been developed to help tudent learn introductory programming concept in the engineering field. One of the mot utilized device for thee type of application i the Apple ipad/iphone, which run the ios. The primary difference between the ipad and iphone i the creen ize. Thee device ue the Cocoa Touch programming, which i baed on Objective-C language. Thee device differ from their dektop counterpart in that multiple application cannot be diplayed imultaneouly on the creen, and are limited to one uer interface at a time. The device are alo limited to the memory available to application, and application cannot acce anything that would require adminitrator privilege on a typical dektop. Mobile device offer much more portability than dektop, but uffer from a limited creen ize a a reult. Though mobile device have proliferated thee many field, DSP i till a relatively untouched area on mobile device. One uch application i ijdsp [4], an iphone application that allow the uer to do data filtering and analyi uing graphical block diagram. Matlab [5] alo offer a mobile application, but i chained via internet to the power of a dektop computer. In thi paper we develop a filter deign toolbox for mobile device. The mathematic developed had to be compatible with the limited memory and proceing power of thee device. It provide filter deign, real time playback, and frequency/impule repone plotting. Verion of thi toolbox were created for the iphone and ipad. II. SOFTWARE DESIGN Thi ection decribe the IIR filter deign with Biquad form uing Bilinear tranformation. There are 3 tep, i.e. Lowpa prototype deign, frequency tranformation, and bilinear tranformation. The derivation for mobile implementation i dicued. Thi new method fit for the mall memory contrain on the mobile device and yield the ame reult a other PC oftware, e.g. Matlab Fdatool. A. Analog Prototype Lowpa Filter The goal of thi tep i to deign the analog lowpa filter with cutoff frequency equal to one. The final equation, uing any deign, will be in thi form, where N B i the number of biquad (econd order) tate. N Bi 1 b H () = G k 0 + b k1 + b k (1) a k 0 k=0 + a k1 + a k Three method were deigned in the tool, i.e. Butterworth, Chebyhev I and II, to etimate, B, and A parameter. Given the filter order N, the implified tranfer function H () for Butterworth and Chebyhev I filter can be expreed a following: N 1 G H () = 1 ( + a) r aco N +1 N π + kπ (). k=0 N + p k For the Butterworth filter, ince pole location are located on the unit circle, a,, become one in the equation (). For the Chebyhev I, ince the pole are not placed on the unit circle but intead form an oval hape center at the origin, a,, parameter dep on the ripple magnitude of the paband. For both cae, if the order N i an odd
2 number, r become one and when the order N i even, r become zero. Given the paband ripple magnitude in linear cale, the ret of parameter can be etimated by p k α = 1+ = a co N +1 N π + kπ N + b in N +1 N π + kπ N, where R p R p 1 parameter are 0.5 db (or 1.1 in linear cale) and 30 db (or 1000 in linear cale) for Chebyhev I and II, repectively. (a) a = 1 N α N ( 1 α ) b = 1 N α + N ( 1 α ). (3) Finally, the gain of Chebyhev I filter i computed. G = a r N ( R p ) r 1 1 p k k=0 (4) For Chebyhev II, the ripple occur in the topband frequency. Given the topband ripple magnitude in linear cale, the implified H () of the Chebyhev II can be expreed a following: H () = N 1 G + k=1 ( k 1)π co N 1 e r 3N k=n+1 Γ = ( R + R 1) 1 N c k = Γ 1 Γ d k = Γ +1 Γ c k c k + d + 1 k c k + d k in (k 1)π N, where co (k 1)π N (5) where e i equal to with k = 3N +. Finally, the gain of Chebyhev II filter i computed by the ratio of the product of all and the product of all, 1 G = a k b k. Once the mathematic are k k implified to be uitable for a mobile OS, the implementation wa executed in ios (iphone/ipad) ytem. Fig. 1 how the output of the prototype lowpa filter order 10 (5 biquad) from an ipad app. Thee reult are identical to Matlab Fdatool. Each row of the SOS matrix contain B and A parameter for each biquad. The firt 3 number are B parameter and the ret are A parameter. The ripple (b) (c) Fig. 1. Screenhot of analog lowpa prototype output from ios implementation uing (a) Butterworth, (b) Chebyhev I, and (c) Chebyhev II method. All the reult are identical with Matlab. B. Frequency Tranformation The goal of thi tep i to tranform the lowpa filter with cut-off at one to one of four filter type, i.e. lowpa, highpa, bandpa, bandtop, at the deired cut-off frequency. The final form after tranformation to lowpa and highpa filter will be in thi form. H () = f (u) N b H (u) = G k 0 u Bi 1 + b k1 u + b k (6) a k 0 u + a k1 u + Note that the gain and number of biquad doe not change during thi tep. The final output are till in the biquad form. The implementation in thi tep i to etimate and parameter. After derivation, the olution become a imple ubtitution of the previou tep. For the lowpa filter with cut-off frequency Hz, the mapping equation can be expreed a b k0 a k0 k=0 a k = b k0 b k1 = b k1 Ω b k = b k Ω (7). = a k0 a k1 = a k1 Ω a k = a k Ω On the other hand, for highpa frequency with cut-off frequency Hz, the mapping equation can be expreed a b k0 a k0 = b k b k1 = b k1 Ω b k = b k0 Ω (8). = a k a k1 = a k1 Ω a k = a k0 Ω For the bandpa and bandtop, the final form after tranformation i in the fourth order. The decompoition back to biquad form will be applied after bilinear
3 tranformation in the next tep. For the frequency tranformation of the bandpa filter with cut-off frequency Hz. and bandwidth Hz., can be expreed a following: H () = = f (u) N b H 4 (u) = G k 0 u 4 + b k1 u 3 + b k u Bi 1 + b k 3 u + b k 4 a k 0 u 4 + a k1 u 3 + a k u k=0 + a k 3 u + a k 4 (9). The mapping function for the bandpa filter can be expreed a following. b k0 = b k0 b k1 = b k1 Δ b k b k3 b k 4 = b k0 Ω + b k Δ = b k1 ΔΩ = b k0 Ω 4 a k0 = a k0 a k1 = a k1 Δ a k a k3 a k 4 = a k0 Ω + a k Δ = a k1 ΔΩ = a k0 Ω 4 (10) For the mapping function of the bandtop filter, the equation i imply the interchange between, and, of the bandpa filter. b k0 = b k b k1 = b k1 Δ b k b k3 b k 4 = b k Ω + b k0 Δ = b k1 ΔΩ = b k Ω 4 a k0 = a k a k1 = a k1 Δ a k a k3 a k 4 = a k Ω + a k0 Δ = a k1 ΔΩ = a k Ω 4 (11) The cut-off frequency and bandwidth are the prewrapping frequency. Given the ampling frequency and deired cut-off frequency in digital domain, the prewrapping frequency i etimated by Ω = F tan( π F c F ). When uing them in bandpa and bandtop, The cut-off frequency i the geometric mean of the high and low prewrapping frequencie, and the bandwidth i the difference between two frequencie. C. Bilinear Tranformation The goal of thi final tep i to tranform from analog domain to digital domain (z domain). For the lowpa and highpa biquad, the final form i imilar to the previou tep, except the mapping function i different. Again the gain and number of biquad doe not change during thi tep. H (u) u= f (z 1 ) N Bi 1 ˆbk H (z) = G 0 + ˆb k1 z 1 + ˆb k z (1) â k 0 + â k1 z 1 + â k z k=0 The mapping function for the biquad form uing bilinear tranformation can be expreed a following: ˆb 0 = 4b 0 F + b 1 F + b ˆb 1 = 8b 0 F + b ˆb = 4b 0 F b 1 F + b â 0 = 4a 0 F + a 1 F + a â 1 = 8a 0 F + a â = 4a 0 F a 1 F + a For the bandpa and bandtop, ince they are fourth order, the tranformation can be expreed a following: H 4 (u) u= f (z 1 ) H (z) = G N Bi 1 k=0 (13). ˆbk 0 + ˆb k1 z 1 + ˆb k z + ˆb k 3 z 3 + ˆb k 4 z 4 â k 0 + â k1 z 1 + â k z + â k 3 z 3 + â k 4 z 4 The mapping function for the fourth form uing bilinear tranformation can be expreed a following. ˆb k0 = 16b k0 ˆb k1 = 64b k0 ˆb k = 96b k0 ˆb k3 = 64b k0 ˆb k 4 = 16b k0 F 4 + 8b k1 F 4 16b k1 F 3 + 4b k F 4 8b k F + 6b k 4 F 4 +16b k1 F 4 8b k1 F + b k3 F + b k 4 F 3 + 4b k3 F + 4b k 4 F 3 4b k3 F + 4b k 4 F 3 + 4b k F b k3 F + b k 4 (15). For the A parameter, the mapping function i the ame fahion of the above equation by interchanging b to a term. Once the bilinear tranformation i finihed, the decompoition back to biquad i applied. The tak i done by finding 4 root of B and A parameter and pairing the ame complex conjugate term. Thi will make the number of biquad double. The final normalization i done by making and equal to one. Fig. how the reult of digital IIR filter running on an iphone. Fig.. Screenhot of digital IIR filter from ios implementation: (a) Highpa filter uing Butterworth order 10 with cut-off 4000 Hz, and (b) Bandpa filter uing Chebyhev II order 4 with cut-off 1000 and 4000 Hz. Both filter have the ampling frequency Hz. (a) (b) (14).
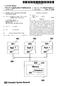
4 Fig. 3. Screenhot of mobile digital filter deign toolbox on ios device: (a) main menu on an iphone app where the uer can chooe each method, (b) the ytem where the uer can the deign coefficient in floating and fixed point format, and (c) graphing on an ipad app. III. RESULTS Thi mobile digital filtering toolbox wa implemented on ios device, both iphone and ipad. The ios SDK verion 4.3 wa ued in thi project. The OS i compried of 4 layer including the core OS, Core Service, Media, and Cocoa Touch layer. Mot of the program in thi paper were implemented uing Cocoa Touch and Objective-C code. Cocoa Touch i the et of Objective-C framework that provide the building block for ios application. Contained are all the uer interface widget, event and event loop management, API to repond to touch, geture, movement, acce to the camera, file ytem, and other device feature. Fig. 3 illutrate the creenhot of mobile app running on both device. Due to the creen ize, the additional feature uch a real-time audio playback, frequency repone plotting are not implemented in every device. On the ipad app (DSP Aitant app [6] on the app tore ), the program can plot the impule and frequency repone of the deigning filter. The reult can be hown in both floating and fixed point format (16 bit) and ent out via . The iphone app (DSP digital filter app [7] on the app tore ) function identically to the ipad app, except it doe not plot. The iphone program can alo playback the audio paed thru the filter in real-time. Uer can turn on/off the filter function in real-time. Thi mobile tool can alo etimate FIR filter coefficient, which we did not dicu the deign in thi paper. There are 6 different type, e.g. ame 4 type a IIR and the additional Hibert, Differentiator, of FIR filter and 8 window type, e.g. Kaier, Gauian, Hann, that can be elected. The plotting, function, both fixed and floating format, are imilar to IIR tool. The implementation on Android mobile i ongoing. IV. CONCLUSION A filter deign toolbox wa deigned and implemented for mobile device. Different verion were created for the iphone and ipad device becaue of difference in creen ize. The iphone verion allow a uer to deign a filter and filter real time audio playback. The ipad verion i identical, with addition of plotting function for both impule and frequency repone. There are multiple filter type and window that can be implemented in the ytem. The toolbox upport the deign of both FIR and IIR filter type. Once a filter i deigned, the application allow uer to the filter coefficient in a format that can be implemented in Matlab, along with the order, type of filter and other pertinent information. REFERENCES [1] ipad App demontration with phyic profeor Mike Cavagnero, [] Mai Yin Toi, Dekhane, S., ToiChem: A Mobile Application to Facilitate Student Learning in Organic Chemitry, IEEE ICALT, page , 011 [3] Mahmoud, Q.H.; Popowicz, P., A mobile application development approach to teaching introductory programming, IEEE Frontier in Education, page T4F-1 - T4F-6, 010. [4] Jinru Liu, et al., iphone/ipad baed interactive laboratory for ignal proceing in mobile device, ASEE, 011. [5] [6] [7]
5 6/7/1 1:4 PM /Uer/ukitta/Dektop/ButterAnalog.m 1 of 1 function [Bc,Ac,G] = ButterAnalog(N); %% Uage: [Bc,Ac,G] = ButterAnalog(N); %% Deign the normalized analog butterworth filter prototype with OMEGA = 1 %% input i N (order): calar %% output Biquad coefficient with B, A, vector and G %%%%%%%%%%%%% STEP 1 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%% Create a output martix %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Ac = zero(ceil(n/),3); %% prepare the matrix Bc = zero(ceil(n/),3); %% prepare the matrix G = 1; %%%%%%%%%%%%% STEP %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%% make the incomplete biquad if N = odd %%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%% STEP 3 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%% Compute the complete biquad %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% for k = 0:floor(N/) 1 Bc(k+1,3) = 1; %% the numerator i alway 1/Ac Ac(k+1,1) = 1; %% ^ Ac(k+1,3) = 1; %% 1 Ac(k+1,) = *co(((n+1)*pi/(*n))+k*pi/n); if (rem(n,) == 1) %% coefficient for, even cae k = floor(n/); Bc(k+1,3) = 1; %% the numerator i alway 1/Ac Ac(k+1,1) = 0; %% ^ Ac(k+1,3) = 1; %% 1 Ac(k+1,) = 1;
6 6/7/1 1:3 PM /Uer/ukitta/Dektop/Cheby1Analog.m 1 of 1 function [Bc,Ac,G] = Cheby1Analog(N,Rp); %% uage: [Bc,Ac,G] = Cheby1Analog(N,Rp); %% deign the normalized analog cheby1 filter prototype %% input i N (order): calar %% Rp: ripple value, default at 0.5 %% output i SOS (B,A) and Gain for biquad: matrix %% make a default for Rp if nargin == 1 Rp = 0.5; Rp = 10^(Rp/10); %% linear %%%%%% Create a output martix %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Ac = zero(ceil(n/),3); %% prepare the matrix Bc = zero(ceil(n/),3); %% prepare the matrix G = 1; %%%%%%%%%%%%% STEP 1 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%% Compute the parameter %%%%%% %% compute alpha alpha = (1+qrt(Rp))/qrt(Rp 1); %% compute a and b a = (1/)*((alpha^(1/N)) ((1/alpha)^(1/N))); b = (1/)*((alpha^(1/N))+((1/alpha)^(1/N))); %%%%%%%%%%%%% STEP,3 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%% Make a biquad and find G %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %% tart to compute biquad for k = 0:floor(N/) 1 %% elect the left hand pole, N/ pole tart with k=0 pr = a*co((n+1)*pi/(*n) + k*pi/n); pii = b*in((n+1)*pi/(*n) + k*pi/n); Bc(k+1,3) = 1; %% the numerator i alway 1. Ac(k+1,1) = 1; %% pair with conjugate pole, S^ Ac(k+1,) = *pr; %% *re{p}s Ac(k+1,3) = (pr.^)+(pii.^); %% ab(p)^ G = G*Ac(k+1,3); if (rem(n,) == 1) k = floor(n/); Bc(k+1,3) = 1; %% the numerator i alway 1. Ac(k+1,1) = 0; %% pair with conjugate pole, S^ Ac(k+1,) = 1; %% *re{p}s Ac(k+1,3) = a; %% ab(p)^ G = (G*(a)^(rem(N,)))/(Rp)^((1 rem(n,))/);
7 6/7/1 1:3 PM /Uer/ukitta/Dektop/ChebyAnalog.m 1 of 1 function [Bc,Ac,G] = ChebyAnalog(N,R) %% uage: [Bc,Ac,G] = ChebyAnalog(N,R); %% deign the normalized analog cheby filter prototype %% input i N (order): calar %% R: ripple value, default at 30 %% output i SOS (B,A) and Gain for biquad: matrix %% make a default for Rp if nargin == 1 R = 30; W = 1; R = 10^(R/10); gm = (qrt(r)+qrt(r 1)); Gr = gm^(1/n); G = 1; ctr = 1; for k = N+1:floor(3*N/); a = in(((*k) 1)*pi/(*N)); b = co(((*k) 1)*pi/(*N)); a = a*((gr^) 1)/(*Gr); b = b*((gr^)+1)/(*gr); Ac(ctr,:) = [1 *a/(a*a+b*b) 1/(a*a+b*b)]; G = G*Ac(ctr,3); ctr = ctr+1; if (rem(n,) == 1) k = floor((3*n+)/); a = in(((*k) 1)*pi/(*N)); a = a*((gr^) 1)/(*Gr); Ac(ctr,:) = [0 1 1/a]; G = G*Ac(ctr,3); ctr = 1; for k = 1:floor(N/) b = co(((*k) 1)*pi/(*N)); Bc(ctr,:) = [1 0 1/(b*b)]; G = G/Bc(ctr,3); ctr = ctr+1; %% tet code with built in matlab code %% [BB,AA] = cheby(n,30,1, ); %% [SOS,G] = tfo(bb,aa)
8 6/7/1 1:7 PM /Uer/ukitta/De.../LowpaToLowpa.m 1 of 1 function [Bt,At] = LowpaToLowpa(B,A,Omega); %% Uage: [Bt,At] = LowpaToLowpa(B,A,Omega); %% mapping a prototype LP to a pecific LP with correct cutoff frequency. %% input are B, A vector (1 by 3) for each biquad tate, Omega i freq cutoff. %% output are Bt, At vector (1 by 3) for each biquad tate. b0 = B(1); %% ^ b1 = B(); %% b = B(3); %% 1 a0 = A(1); %% ^ a1 = A(); %% a = A(3); %% 1 if (a0 == 0) Bt(1) = 0; Bt() = b1; Bt(3) = b*omega; At(1) = 0; At() = a1; At(3) = a*omega; ele Bt(1) = b0; Bt() = b1*omega; Bt(3) = b*omega*omega; At(1) = a0; At() = a1*omega; At(3) = a*omega*omega; %% incomplete biquad %% complete biquad
9 6/7/1 1:8 PM /Uer/ukitta/De.../LowpaToHighpa.m 1 of 1 function [Bt,At] = LowpaToHighpa(B,A,Omega); %% Uage: [Bt,At] = LowpaToHighpa(B,A,Omega); %% mapping a prototype LP to a pecific HP with correct cutoff frequency. %% input are B, A vector (1 by 3) for each biquad tate, Omega i freq cutoff. %% output are Bt, At vector (1 by 3) for each biquad tate. b0 = B(1); %% ^ b1 = B(); %% b = B(3); %% 1 a0 = A(1); %% ^ a1 = A(); %% a = A(3); %% 1 if (a0 == 0) Bt(1) = 0; Bt() = b; Bt(3) = b1*omega; At(1) = 0; At() = a; At(3) = a1*omega; ele Bt(1) = b; Bt() = b1*omega; Bt(3) = b0*omega*omega; At(1) = a; At() = a1*omega; At(3) = a0*omega*omega; %% incomplete biquad %% complete biquad
10 6/7/1 1:9 PM /Uer/ukitta/De.../LowpaToBandpa.m 1 of 1 function [Bt,At] = LowpaToBandpa(B,A,Omega,BW); %% Uage: [Bt,At] = LowpaToBandpa(B,A,Omega,BW); %% mapping a prototype LP to a pecific BP with correct cutoff frequency. %% input are B, A vector (1 by 3) for each biquad tate, Omega i freq cutoff and BW i bandwidth. %% output are Bt, At vector (1 by 3) for each biquad tate. b0 = B(1); %% ^ b1 = B(); %% b = B(3); %% 1 a0 = A(1); %% ^ a1 = A(); %% a = A(3); %% 1 if (a0 == 0) %% incomplete biquad Bt(1) = 0; Bt() = 0; Bt(3) = b1; Bt(4) = b*bw; Bt(5) = b1*omega*omega; At(1) = 0; At() = 0; At(3) = a1; At(4) = a*bw; At(5) = a1*omega*omega; ele %% complete biquad Bt(1) = b0; Bt() = b1*bw; Bt(3) = (*b0*omega*omega)+(b*bw*bw); Bt(4) = b1*bw*omega*omega; Bt(5) = b0*(omega^4); At(1) = a0; At() = a1*bw; At(3) = (*a0*omega*omega)+(a*bw*bw); At(4) = a1*bw*omega*omega; At(5) = a0*(omega^4);
11 6/7/1 1:9 PM /Uer/ukitta/De.../LowpaToBandtop.m 1 of 1 function [Bt,At] = LowpaToBandtop(B,A,Omega,BW); %% Uage: [Bt,At] = LowpaToBandtop(B,A,Omega,BW); %% mapping a prototype LP to a pecific BP with correct cutoff frequency. %% input are B, A vector (1 by 3) for each biquad tate, Omega i freq cutoff and BW i bandwidth. %% output are Bt, At vector (1 by 3) for each biquad tate. b0 = B(1); %% ^ b1 = B(); %% b = B(3); %% 1 a0 = A(1); %% ^ a1 = A(); %% a = A(3); %% 1 if (a0 == 0) %% incomplete biquad Bt(1) = 0; Bt() = 0; Bt(3) = b; Bt(4) = b1*bw; Bt(5) = b*(omega^); At(1) = 0; At() = 0; At(3) = a; At(4) = a1*bw; At(5) = a*(omega^); ele %% complete biquad Bt(1) = b; Bt() = b1*bw; Bt(3) = (*b*omega*omega)+(b0*bw*bw); Bt(4) = b1*bw*omega*omega; Bt(5) = b*(omega^4); At(1) = a; At() = a1*bw; At(3) = (*a*omega*omega)+(a0*bw*bw); At(4) = a1*bw*omega*omega; At(5) = a*(omega^4);
12 6/7/1 1:31 PM /Uer/ukitta/.../BilinearZTranform.m 1 of 1 function [bb,aa] = BilinearZTranform(B,A,F); %% uage: function [bb,aa] = BilinearZTranform(B,A,F); %% Bilinear tranform for order %% input i B,A : vector (1 by 3) %% F: a ampling rate %% output i bb and aa in z domain b0 = B(1); %% ^ b1 = B(); %% b = B(3); %% 1 a0 = A(1); %% ^ a1 = A(); %% a = A(3); %% 1 alp = *F; alp_q = alp^; if (a0 == 0) %% firt order bb(1) = (b1*alp)+b; bb() = ( b1*alp)+b; bb(3) = 0; aa(1) = (a1*alp)+a; aa() = ( a1*alp)+a; aa(3) = 0; ele %% econd order bb(1) = (4*b0*F*F)+(*b1*F)+b; bb() = ( 8*b0*F*F)+(*b); bb(3) = (4*b0*F*F) (*b1*f)+b; aa(1) = (4*a0*F*F)+(*a1*F)+a; aa() = ( 8*a0*F*F)+(*a); aa(3) = (4*a0*F*F) (*a1*f)+a; bb = bb/aa(1); %% normalize aa0 to be 1 aa = aa/aa(1);
13 6/7/1 1:31 PM /Uer/ukitta/.../BilinearZTranform4.m 1 of 1 function [bb,aa] = BilinearZTranform4(B,A,F); %% uage: function [bb,aa] = BilinearZTranform4(B,A,F); %% Bilinear tranform for order %% input i B,A : vector (1 by 5) %% F: a ampling rate %% output i bb and aa in z domain b0 = B(1); %% ^4 b1 = B(); %% ^3 b = B(3); %% ^ b3 = B(4); %% b4 = B(5); %% 1 a0 = A(1); %% ^4 a1 = A(); %% ^3 a = A(3); %% ^ a3 = A(4); %% a4 = A(5); %% 1 alp = *F; alp_ = alp^; alp_3 = alp^3; alp_4 = alp^4; if ((a0 == 0) && (a1 == 0)) %% econd order bb(1) = (b*alp_)+(b3*alp)+b4; bb() = ( *b*alp_)+(*b4); bb(3) = (b*alp_) (b3*alp)+b4; bb(4) = 0; bb(5) = 0; aa(1) = (a*alp_)+(a3*alp)+a4; aa() = ( *a*alp_)+(*a4); aa(3) = (a*alp_) (a3*alp)+a4; aa(4) = 0; aa(5) = 0; ele %% 4th order bb(1) = (16*b0*(F^4)) +(8*b1*(F^3)) +(4*b*(F^)) +(*b3*f) + b4; bb() = ( 64*b0*(F^4))+( 16*b1*(F^3))+0 +(4*b3*F) + (4*b4); bb(3) = (96*b0*(F^4)) +0 +( 8*b*(F^))+0 + (6*b4); bb(4) = ( 64*b0*(F^4))+(16*b1*(F^3))+0 (4*b3*F) + (4*b4); bb(5) = (16*b0*(F^4)) (8*b1*(F^3)) +(4*b*(F^)) (*b3*f) + b4; aa(1) = (a0*alp_4) +(a1*alp_3) +(a*alp_) +(a3*alp) + a4; aa() = ( 4*a0*alp_4)+( *a1*alp_3)+0 +(*a3*alp) + (4*a4); aa(3) = (6*a0*alp_4) +0 +( *a*alp_)+0 + (6*a4); aa(4) = ( 4*a0*alp_4)+(*a1*alp_3) +0 +( *a3*alp)+ (4*a4); aa(5) = (a0*alp_4) +( a1*alp_3) +(a*alp_) +( a3*alp) + a4; bb = bb/aa(1); %% normalize aa0 to be 1 aa = aa/aa(1);
Practical Analog and Digital Filter Design
 Practical Analog and Digital Filter Deign Artech Houe, Inc. Le Thede 004 Thi text i dedicated to my wife who keep me grounded, and to my grandchildren who know no bound. Content Preface xi Chapter Introduction
Practical Analog and Digital Filter Deign Artech Houe, Inc. Le Thede 004 Thi text i dedicated to my wife who keep me grounded, and to my grandchildren who know no bound. Content Preface xi Chapter Introduction
Laboratory Exercise 6
 Laboratory Exercie 6 Adder, Subtractor, and Multiplier The purpoe of thi exercie i to examine arithmetic circuit that add, ubtract, and multiply number. Each type of circuit will be implemented in two
Laboratory Exercie 6 Adder, Subtractor, and Multiplier The purpoe of thi exercie i to examine arithmetic circuit that add, ubtract, and multiply number. Each type of circuit will be implemented in two
ES205 Analysis and Design of Engineering Systems: Lab 1: An Introductory Tutorial: Getting Started with SIMULINK
 ES05 Analyi and Deign of Engineering Sytem: Lab : An Introductory Tutorial: Getting Started with SIMULINK What i SIMULINK? SIMULINK i a oftware package for modeling, imulating, and analyzing dynamic ytem.
ES05 Analyi and Deign of Engineering Sytem: Lab : An Introductory Tutorial: Getting Started with SIMULINK What i SIMULINK? SIMULINK i a oftware package for modeling, imulating, and analyzing dynamic ytem.
[N309] Feedforward Active Noise Control Systems with Online Secondary Path Modeling. Muhammad Tahir Akhtar, Masahide Abe, and Masayuki Kawamata
![[N309] Feedforward Active Noise Control Systems with Online Secondary Path Modeling. Muhammad Tahir Akhtar, Masahide Abe, and Masayuki Kawamata [N309] Feedforward Active Noise Control Systems with Online Secondary Path Modeling. Muhammad Tahir Akhtar, Masahide Abe, and Masayuki Kawamata](/thumbs/85/91884504.jpg) he 32nd International Congre and Expoition on Noie Control Engineering Jeju International Convention Center, Seogwipo, Korea, Augut 25-28, 2003 [N309] Feedforward Active Noie Control Sytem with Online
he 32nd International Congre and Expoition on Noie Control Engineering Jeju International Convention Center, Seogwipo, Korea, Augut 25-28, 2003 [N309] Feedforward Active Noie Control Sytem with Online
Distributed Packet Processing Architecture with Reconfigurable Hardware Accelerators for 100Gbps Forwarding Performance on Virtualized Edge Router
 Ditributed Packet Proceing Architecture with Reconfigurable Hardware Accelerator for 100Gbp Forwarding Performance on Virtualized Edge Router Satohi Nihiyama, Hitohi Kaneko, and Ichiro Kudo Abtract To
Ditributed Packet Proceing Architecture with Reconfigurable Hardware Accelerator for 100Gbp Forwarding Performance on Virtualized Edge Router Satohi Nihiyama, Hitohi Kaneko, and Ichiro Kudo Abtract To
MAT 155: Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Data Page 1 of NotesCh2-3.doc
 MAT 155: Decribing, Exploring, and Comparing Data Page 1 of 8 001-oteCh-3.doc ote for Chapter Summarizing and Graphing Data Chapter 3 Decribing, Exploring, and Comparing Data Frequency Ditribution, Graphic
MAT 155: Decribing, Exploring, and Comparing Data Page 1 of 8 001-oteCh-3.doc ote for Chapter Summarizing and Graphing Data Chapter 3 Decribing, Exploring, and Comparing Data Frequency Ditribution, Graphic
Floating Point CORDIC Based Power Operation
 Floating Point CORDIC Baed Power Operation Kazumi Malhan, Padmaja AVL Electrical and Computer Engineering Department School of Engineering and Computer Science Oakland Univerity, Rocheter, MI e-mail: kmalhan@oakland.edu,
Floating Point CORDIC Baed Power Operation Kazumi Malhan, Padmaja AVL Electrical and Computer Engineering Department School of Engineering and Computer Science Oakland Univerity, Rocheter, MI e-mail: kmalhan@oakland.edu,
Modeling of underwater vehicle s dynamics
 Proceeding of the 11th WEA International Conference on YTEM, Agio Nikolao, Crete Iland, Greece, July 23-25, 2007 44 Modeling of underwater vehicle dynamic ANDRZEJ ZAK Department of Radiolocation and Hydrolocation
Proceeding of the 11th WEA International Conference on YTEM, Agio Nikolao, Crete Iland, Greece, July 23-25, 2007 44 Modeling of underwater vehicle dynamic ANDRZEJ ZAK Department of Radiolocation and Hydrolocation
Digifort Standard. Architecture
 Digifort Standard Intermediate olution for intalling up to 32 camera The Standard verion provide the ideal reource for local and remote monitoring of up to 32 camera per erver and a the intermediate verion
Digifort Standard Intermediate olution for intalling up to 32 camera The Standard verion provide the ideal reource for local and remote monitoring of up to 32 camera per erver and a the intermediate verion
The norm Package. November 15, Title Analysis of multivariate normal datasets with missing values
 The norm Package November 15, 2003 Verion 1.0-9 Date 2002/05/06 Title Analyi of multivariate normal dataet with miing value Author Ported to R by Alvaro A. Novo . Original by Joeph
The norm Package November 15, 2003 Verion 1.0-9 Date 2002/05/06 Title Analyi of multivariate normal dataet with miing value Author Ported to R by Alvaro A. Novo . Original by Joeph
Laboratory Exercise 2
 Laoratory Exercie Numer and Diplay Thi i an exercie in deigning cominational circuit that can perform inary-to-decimal numer converion and inary-coded-decimal (BCD) addition. Part I We wih to diplay on
Laoratory Exercie Numer and Diplay Thi i an exercie in deigning cominational circuit that can perform inary-to-decimal numer converion and inary-coded-decimal (BCD) addition. Part I We wih to diplay on
Performance of a Robust Filter-based Approach for Contour Detection in Wireless Sensor Networks
 Performance of a Robut Filter-baed Approach for Contour Detection in Wirele Senor Network Hadi Alati, William A. Armtrong, Jr., and Ai Naipuri Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The Univerity
Performance of a Robut Filter-baed Approach for Contour Detection in Wirele Senor Network Hadi Alati, William A. Armtrong, Jr., and Ai Naipuri Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The Univerity
Laboratory Exercise 2
 Laoratory Exercie Numer and Diplay Thi i an exercie in deigning cominational circuit that can perform inary-to-decimal numer converion and inary-coded-decimal (BCD) addition. Part I We wih to diplay on
Laoratory Exercie Numer and Diplay Thi i an exercie in deigning cominational circuit that can perform inary-to-decimal numer converion and inary-coded-decimal (BCD) addition. Part I We wih to diplay on
A SIMPLE IMPERATIVE LANGUAGE THE STORE FUNCTION NON-TERMINATING COMMANDS
 A SIMPLE IMPERATIVE LANGUAGE Eventually we will preent the emantic of a full-blown language, with declaration, type and looping. However, there are many complication, o we will build up lowly. Our firt
A SIMPLE IMPERATIVE LANGUAGE Eventually we will preent the emantic of a full-blown language, with declaration, type and looping. However, there are many complication, o we will build up lowly. Our firt
Laboratory Exercise 6
 Laboratory Exercie 6 Adder, Subtractor, and Multiplier a a The purpoe of thi exercie i to examine arithmetic circuit that add, ubtract, and multiply number. Each b c circuit will be decribed in Verilog
Laboratory Exercie 6 Adder, Subtractor, and Multiplier a a The purpoe of thi exercie i to examine arithmetic circuit that add, ubtract, and multiply number. Each b c circuit will be decribed in Verilog
Laboratory Exercise 6
 Laboratory Exercie 6 Adder, Subtractor, and Multiplier The purpoe of thi exercie i to examine arithmetic circuit that add, ubtract, and multiply number. Each circuit will be decribed in Verilog and implemented
Laboratory Exercie 6 Adder, Subtractor, and Multiplier The purpoe of thi exercie i to examine arithmetic circuit that add, ubtract, and multiply number. Each circuit will be decribed in Verilog and implemented
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United State US 2011 0316690A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0316690 A1 Siegman (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR IDENTIFYING ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT
(19) United State US 2011 0316690A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0316690 A1 Siegman (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR IDENTIFYING ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT
( ) subject to m. e (2) L are 2L+1. = s SEG SEG Las Vegas 2012 Annual Meeting Page 1
 A new imultaneou ource eparation algorithm uing frequency-divere filtering Ying Ji*, Ed Kragh, and Phil Chritie, Schlumberger Cambridge Reearch Summary We decribe a new imultaneou ource eparation algorithm
A new imultaneou ource eparation algorithm uing frequency-divere filtering Ying Ji*, Ed Kragh, and Phil Chritie, Schlumberger Cambridge Reearch Summary We decribe a new imultaneou ource eparation algorithm
Lecture 14: Minimum Spanning Tree I
 COMPSCI 0: Deign and Analyi of Algorithm October 4, 07 Lecture 4: Minimum Spanning Tree I Lecturer: Rong Ge Scribe: Fred Zhang Overview Thi lecture we finih our dicuion of the hortet path problem and introduce
COMPSCI 0: Deign and Analyi of Algorithm October 4, 07 Lecture 4: Minimum Spanning Tree I Lecturer: Rong Ge Scribe: Fred Zhang Overview Thi lecture we finih our dicuion of the hortet path problem and introduce
AN ALGORITHM FOR RESTRICTED NORMAL FORM TO SOLVE DUAL TYPE NON-CANONICAL LINEAR FRACTIONAL PROGRAMMING PROBLEM
 RAC Univerity Journal, Vol IV, No, 7, pp 87-9 AN ALGORITHM FOR RESTRICTED NORMAL FORM TO SOLVE DUAL TYPE NON-CANONICAL LINEAR FRACTIONAL PROGRAMMING PROLEM Mozzem Hoain Department of Mathematic Ghior Govt
RAC Univerity Journal, Vol IV, No, 7, pp 87-9 AN ALGORITHM FOR RESTRICTED NORMAL FORM TO SOLVE DUAL TYPE NON-CANONICAL LINEAR FRACTIONAL PROGRAMMING PROLEM Mozzem Hoain Department of Mathematic Ghior Govt
A METHOD OF REAL-TIME NURBS INTERPOLATION WITH CONFINED CHORD ERROR FOR CNC SYSTEMS
 Vietnam Journal of Science and Technology 55 (5) (017) 650-657 DOI: 10.1565/55-518/55/5/906 A METHOD OF REAL-TIME NURBS INTERPOLATION WITH CONFINED CHORD ERROR FOR CNC SYSTEMS Nguyen Huu Quang *, Banh
Vietnam Journal of Science and Technology 55 (5) (017) 650-657 DOI: 10.1565/55-518/55/5/906 A METHOD OF REAL-TIME NURBS INTERPOLATION WITH CONFINED CHORD ERROR FOR CNC SYSTEMS Nguyen Huu Quang *, Banh
International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) ISSN: Vol. 2 Issue 5, May
 Intertage Pipeline VLI Architecture for 2-D DWT Ajinkya. Bankar 1,Bhavika. haha 2, P.K. Kadbe 3 E&TC Department, Pune Univerity 1,2,3 VPCOE Baramati Abtract In thi paper, a cheme for the deign of a high-pd
Intertage Pipeline VLI Architecture for 2-D DWT Ajinkya. Bankar 1,Bhavika. haha 2, P.K. Kadbe 3 E&TC Department, Pune Univerity 1,2,3 VPCOE Baramati Abtract In thi paper, a cheme for the deign of a high-pd
Laboratory Exercise 6
 Laboratory Exercie 6 Adder, Subtractor, and Multiplier The purpoe of thi exercie i to examine arithmetic circuit that add, ubtract, and multiply number. Each circuit will be decribed in VHL and implemented
Laboratory Exercie 6 Adder, Subtractor, and Multiplier The purpoe of thi exercie i to examine arithmetic circuit that add, ubtract, and multiply number. Each circuit will be decribed in VHL and implemented
A Basic Prototype for Enterprise Level Project Management
 A Baic Prototype for Enterprie Level Project Management Saurabh Malgaonkar, Abhay Kolhe Computer Engineering Department, Mukeh Patel School of Technology Management & Engineering, NMIMS Univerity, Mumbai,
A Baic Prototype for Enterprie Level Project Management Saurabh Malgaonkar, Abhay Kolhe Computer Engineering Department, Mukeh Patel School of Technology Management & Engineering, NMIMS Univerity, Mumbai,
Drawing Lines in 2 Dimensions
 Drawing Line in 2 Dimenion Drawing a traight line (or an arc) between two end point when one i limited to dicrete pixel require a bit of thought. Conider the following line uperimpoed on a 2 dimenional
Drawing Line in 2 Dimenion Drawing a traight line (or an arc) between two end point when one i limited to dicrete pixel require a bit of thought. Conider the following line uperimpoed on a 2 dimenional
Routing Definition 4.1
 4 Routing So far, we have only looked at network without dealing with the iue of how to end information in them from one node to another The problem of ending information in a network i known a routing
4 Routing So far, we have only looked at network without dealing with the iue of how to end information in them from one node to another The problem of ending information in a network i known a routing
SIMIT 7. Component Type Editor (CTE) User manual. Siemens Industrial
 SIMIT 7 Component Type Editor (CTE) Uer manual Siemen Indutrial Edition January 2013 Siemen offer imulation oftware to plan, imulate and optimize plant and machine. The imulation- and optimizationreult
SIMIT 7 Component Type Editor (CTE) Uer manual Siemen Indutrial Edition January 2013 Siemen offer imulation oftware to plan, imulate and optimize plant and machine. The imulation- and optimizationreult
Shortest Paths Problem. CS 362, Lecture 20. Today s Outline. Negative Weights
 Shortet Path Problem CS 6, Lecture Jared Saia Univerity of New Mexico Another intereting problem for graph i that of finding hortet path Aume we are given a weighted directed graph G = (V, E) with two
Shortet Path Problem CS 6, Lecture Jared Saia Univerity of New Mexico Another intereting problem for graph i that of finding hortet path Aume we are given a weighted directed graph G = (V, E) with two
Course Project: Adders, Subtractors, and Multipliers a
 In the name Allah Department of Computer Engineering 215 Spring emeter Computer Architecture Coure Intructor: Dr. Mahdi Abbai Coure Project: Adder, Subtractor, and Multiplier a a The purpoe of thi p roject
In the name Allah Department of Computer Engineering 215 Spring emeter Computer Architecture Coure Intructor: Dr. Mahdi Abbai Coure Project: Adder, Subtractor, and Multiplier a a The purpoe of thi p roject
Keywords Cloud Computing, Service Level Agreements (SLA), CloudSim, Monitoring & Controlling SLA Agent, JADE
 Volume 5, Iue 8, Augut 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Reearch in Computer Science and Software Engineering Reearch Paper Available online at: www.ijarce.com Verification of Agent
Volume 5, Iue 8, Augut 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Reearch in Computer Science and Software Engineering Reearch Paper Available online at: www.ijarce.com Verification of Agent
AUTOMATIC TEST CASE GENERATION USING UML MODELS
 Volume-2, Iue-6, June-2014 AUTOMATIC TEST CASE GENERATION USING UML MODELS 1 SAGARKUMAR P. JAIN, 2 KHUSHBOO S. LALWANI, 3 NIKITA K. MAHAJAN, 4 BHAGYASHREE J. GADEKAR 1,2,3,4 Department of Computer Engineering,
Volume-2, Iue-6, June-2014 AUTOMATIC TEST CASE GENERATION USING UML MODELS 1 SAGARKUMAR P. JAIN, 2 KHUSHBOO S. LALWANI, 3 NIKITA K. MAHAJAN, 4 BHAGYASHREE J. GADEKAR 1,2,3,4 Department of Computer Engineering,
Analyzing Hydra Historical Statistics Part 2
 Analyzing Hydra Hitorical Statitic Part Fabio Maimo Ottaviani EPV Technologie White paper 5 hnode HSM Hitorical Record The hnode i the hierarchical data torage management node and ha to perform all the
Analyzing Hydra Hitorical Statitic Part Fabio Maimo Ottaviani EPV Technologie White paper 5 hnode HSM Hitorical Record The hnode i the hierarchical data torage management node and ha to perform all the
Today s Outline. CS 561, Lecture 23. Negative Weights. Shortest Paths Problem. The presence of a negative cycle might mean that there is
 Today Outline CS 56, Lecture Jared Saia Univerity of New Mexico The path that can be trodden i not the enduring and unchanging Path. The name that can be named i not the enduring and unchanging Name. -
Today Outline CS 56, Lecture Jared Saia Univerity of New Mexico The path that can be trodden i not the enduring and unchanging Path. The name that can be named i not the enduring and unchanging Name. -
SLA Adaptation for Service Overlay Networks
 SLA Adaptation for Service Overlay Network Con Tran 1, Zbigniew Dziong 1, and Michal Pióro 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, École de Technologie Supérieure, Univerity of Quebec, Montréal, Canada
SLA Adaptation for Service Overlay Network Con Tran 1, Zbigniew Dziong 1, and Michal Pióro 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, École de Technologie Supérieure, Univerity of Quebec, Montréal, Canada
A Multi-objective Genetic Algorithm for Reliability Optimization Problem
 International Journal of Performability Engineering, Vol. 5, No. 3, April 2009, pp. 227-234. RAMS Conultant Printed in India A Multi-objective Genetic Algorithm for Reliability Optimization Problem AMAR
International Journal of Performability Engineering, Vol. 5, No. 3, April 2009, pp. 227-234. RAMS Conultant Printed in India A Multi-objective Genetic Algorithm for Reliability Optimization Problem AMAR
Operational Semantics Class notes for a lecture given by Mooly Sagiv Tel Aviv University 24/5/2007 By Roy Ganor and Uri Juhasz
 Operational emantic Page Operational emantic Cla note for a lecture given by Mooly agiv Tel Aviv Univerity 4/5/7 By Roy Ganor and Uri Juhaz Reference emantic with Application, H. Nielon and F. Nielon,
Operational emantic Page Operational emantic Cla note for a lecture given by Mooly agiv Tel Aviv Univerity 4/5/7 By Roy Ganor and Uri Juhaz Reference emantic with Application, H. Nielon and F. Nielon,
DAROS: Distributed User-Server Assignment And Replication For Online Social Networking Applications
 DAROS: Ditributed Uer-Server Aignment And Replication For Online Social Networking Application Thuan Duong-Ba School of EECS Oregon State Univerity Corvalli, OR 97330, USA Email: duongba@eec.oregontate.edu
DAROS: Ditributed Uer-Server Aignment And Replication For Online Social Networking Application Thuan Duong-Ba School of EECS Oregon State Univerity Corvalli, OR 97330, USA Email: duongba@eec.oregontate.edu
Representations and Transformations. Objectives
 Repreentation and Tranformation Objective Derive homogeneou coordinate tranformation matrice Introduce tandard tranformation - Rotation - Tranlation - Scaling - Shear Scalar, Point, Vector Three baic element
Repreentation and Tranformation Objective Derive homogeneou coordinate tranformation matrice Introduce tandard tranformation - Rotation - Tranlation - Scaling - Shear Scalar, Point, Vector Three baic element
Advanced Encryption Standard and Modes of Operation
 Advanced Encryption Standard and Mode of Operation G. Bertoni L. Breveglieri Foundation of Cryptography - AES pp. 1 / 50 AES Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) i a ymmetric cryptographic algorithm AES
Advanced Encryption Standard and Mode of Operation G. Bertoni L. Breveglieri Foundation of Cryptography - AES pp. 1 / 50 AES Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) i a ymmetric cryptographic algorithm AES
/06/$ IEEE 364
 006 IEEE International ympoium on ignal Proceing and Information Technology oie Variance Etimation In ignal Proceing David Makovoz IPAC, California Intitute of Technology, MC-0, Paadena, CA, 95 davidm@ipac.caltech.edu;
006 IEEE International ympoium on ignal Proceing and Information Technology oie Variance Etimation In ignal Proceing David Makovoz IPAC, California Intitute of Technology, MC-0, Paadena, CA, 95 davidm@ipac.caltech.edu;
Quadrilaterals. Learning Objectives. Pre-Activity
 Section 3.4 Pre-Activity Preparation Quadrilateral Intereting geometric hape and pattern are all around u when we tart looking for them. Examine a row of fencing or the tiling deign at the wimming pool.
Section 3.4 Pre-Activity Preparation Quadrilateral Intereting geometric hape and pattern are all around u when we tart looking for them. Examine a row of fencing or the tiling deign at the wimming pool.
A Novel Architecture for Real Time Implementation of Edge Detectors on FPGA
 IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Iue, Vol. 8, Iue 1, January 2011 193 A Novel Architecture for Real Time Implementation of Edge Detector on FPGA Sudeep K C 1 and Dr. Jharna Majumdar 2 1
IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Iue, Vol. 8, Iue 1, January 2011 193 A Novel Architecture for Real Time Implementation of Edge Detector on FPGA Sudeep K C 1 and Dr. Jharna Majumdar 2 1
Parallel MATLAB at FSU: Task Computing
 Parallel MATLAB at FSU: Tak John Burkardt Department of Scientific Florida State Univerity... 1:30-2:30 Thurday, 07 April 2011 499 Dirac Science Library... http://people.c.fu.edu/ jburkardt/preentation/...
Parallel MATLAB at FSU: Tak John Burkardt Department of Scientific Florida State Univerity... 1:30-2:30 Thurday, 07 April 2011 499 Dirac Science Library... http://people.c.fu.edu/ jburkardt/preentation/...
Trainable Context Model for Multiscale Segmentation
 Trainable Context Model for Multicale Segmentation Hui Cheng and Charle A. Bouman School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue Univerity Wet Lafayette, IN 47907-1285 {hui, bouman}@ ecn.purdue.edu
Trainable Context Model for Multicale Segmentation Hui Cheng and Charle A. Bouman School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue Univerity Wet Lafayette, IN 47907-1285 {hui, bouman}@ ecn.purdue.edu
Universität Augsburg. Institut für Informatik. Approximating Optimal Visual Sensor Placement. E. Hörster, R. Lienhart.
 Univerität Augburg à ÊÇÅÍÆ ËÀǼ Approximating Optimal Viual Senor Placement E. Hörter, R. Lienhart Report 2006-01 Januar 2006 Intitut für Informatik D-86135 Augburg Copyright c E. Hörter, R. Lienhart Intitut
Univerität Augburg à ÊÇÅÍÆ ËÀǼ Approximating Optimal Viual Senor Placement E. Hörter, R. Lienhart Report 2006-01 Januar 2006 Intitut für Informatik D-86135 Augburg Copyright c E. Hörter, R. Lienhart Intitut
Multi-Target Tracking In Clutter
 Multi-Target Tracking In Clutter John N. Sander-Reed, Mary Jo Duncan, W.B. Boucher, W. Michael Dimmler, Shawn O Keefe ABSTRACT A high frame rate (0 Hz), multi-target, video tracker ha been developed and
Multi-Target Tracking In Clutter John N. Sander-Reed, Mary Jo Duncan, W.B. Boucher, W. Michael Dimmler, Shawn O Keefe ABSTRACT A high frame rate (0 Hz), multi-target, video tracker ha been developed and
3D SMAP Algorithm. April 11, 2012
 3D SMAP Algorithm April 11, 2012 Baed on the original SMAP paper [1]. Thi report extend the tructure of MSRF into 3D. The prior ditribution i modified to atify the MRF property. In addition, an iterative
3D SMAP Algorithm April 11, 2012 Baed on the original SMAP paper [1]. Thi report extend the tructure of MSRF into 3D. The prior ditribution i modified to atify the MRF property. In addition, an iterative
Motion Control (wheeled robots)
 3 Motion Control (wheeled robot) Requirement for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground Definition of required motion -> peed control,
3 Motion Control (wheeled robot) Requirement for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground Definition of required motion -> peed control,
Building a Compact On-line MRF Recognizer for Large Character Set using Structured Dictionary Representation and Vector Quantization Technique
 202 International Conference on Frontier in Handwriting Recognition Building a Compact On-line MRF Recognizer for Large Character Set uing Structured Dictionary Repreentation and Vector Quantization Technique
202 International Conference on Frontier in Handwriting Recognition Building a Compact On-line MRF Recognizer for Large Character Set uing Structured Dictionary Repreentation and Vector Quantization Technique
Edits in Xylia Validity Preserving Editing of XML Documents
 dit in Xylia Validity Preerving diting of XML Document Pouria Shaker, Theodore S. Norvell, and Denni K. Peter Faculty of ngineering and Applied Science, Memorial Univerity of Newfoundland, St. John, NFLD,
dit in Xylia Validity Preerving diting of XML Document Pouria Shaker, Theodore S. Norvell, and Denni K. Peter Faculty of ngineering and Applied Science, Memorial Univerity of Newfoundland, St. John, NFLD,
Computer Arithmetic Homework Solutions. 1 An adder for graphics. 2 Partitioned adder. 3 HDL implementation of a partitioned adder
 Computer Arithmetic Homework 3 2016 2017 Solution 1 An adder for graphic In a normal ripple carry addition of two poitive number, the carry i the ignal for a reult exceeding the maximum. We ue thi ignal
Computer Arithmetic Homework 3 2016 2017 Solution 1 An adder for graphic In a normal ripple carry addition of two poitive number, the carry i the ignal for a reult exceeding the maximum. We ue thi ignal
Chapter 13 Non Sampling Errors
 Chapter 13 Non Sampling Error It i a general aumption in the ampling theory that the true value of each unit in the population can be obtained and tabulated without any error. In practice, thi aumption
Chapter 13 Non Sampling Error It i a general aumption in the ampling theory that the true value of each unit in the population can be obtained and tabulated without any error. In practice, thi aumption
SIMIT 7. Profinet IO Gateway. User Manual
 SIMIT 7 Profinet IO Gateway Uer Manual Edition January 2013 Siemen offer imulation oftware to plan, imulate and optimize plant and machine. The imulation- and optimizationreult are only non-binding uggetion
SIMIT 7 Profinet IO Gateway Uer Manual Edition January 2013 Siemen offer imulation oftware to plan, imulate and optimize plant and machine. The imulation- and optimizationreult are only non-binding uggetion
Comparison of Methods for Horizon Line Detection in Sea Images
 Comparion of Method for Horizon Line Detection in Sea Image Tzvika Libe Evgeny Gerhikov and Samuel Koolapov Department of Electrical Engineering Braude Academic College of Engineering Karmiel 2982 Irael
Comparion of Method for Horizon Line Detection in Sea Image Tzvika Libe Evgeny Gerhikov and Samuel Koolapov Department of Electrical Engineering Braude Academic College of Engineering Karmiel 2982 Irael
Generic Traverse. CS 362, Lecture 19. DFS and BFS. Today s Outline
 Generic Travere CS 62, Lecture 9 Jared Saia Univerity of New Mexico Travere(){ put (nil,) in bag; while (the bag i not empty){ take ome edge (p,v) from the bag if (v i unmarked) mark v; parent(v) = p;
Generic Travere CS 62, Lecture 9 Jared Saia Univerity of New Mexico Travere(){ put (nil,) in bag; while (the bag i not empty){ take ome edge (p,v) from the bag if (v i unmarked) mark v; parent(v) = p;
999 Computer System Network. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United State US 2006O1296.60A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Mueller et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2006 (54) METHOD AND COMPUTER SYSTEM FOR QUEUE PROCESSING (76) Inventor: Wolfgang
(19) United State US 2006O1296.60A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Mueller et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2006 (54) METHOD AND COMPUTER SYSTEM FOR QUEUE PROCESSING (76) Inventor: Wolfgang
Modelling the impact of cyber attacks on the traffic control centre of an urban automobile transport system by means of enhanced cybersecurity
 Modelling the impact of cyber attack on the traffic control centre of an urban automobile tranport ytem by mean of enhanced cyberecurity Yoana Ivanova 1,* 1 Bulgarian Academy of Science, Intitute of ICT,
Modelling the impact of cyber attack on the traffic control centre of an urban automobile tranport ytem by mean of enhanced cyberecurity Yoana Ivanova 1,* 1 Bulgarian Academy of Science, Intitute of ICT,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Dhar et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 NY (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 (19) United State US 2013 0145314A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0145314 A1 Dhar et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORCHANGEABLE (52) U.S. Cl. FOCUS
(19) United State US 2013 0145314A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0145314 A1 Dhar et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORCHANGEABLE (52) U.S. Cl. FOCUS
3D MODELLING WITH LINEAR APPROACHES USING GEOMETRIC PRIMITIVES
 MAKARA, TEKNOLOGI, VOL. 9, NO., APRIL 5: 3-35 3D MODELLING WITH LINEAR APPROACHES USING GEOMETRIC PRIMITIVES Mochammad Zulianyah Informatic Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, ARS International Univerity,
MAKARA, TEKNOLOGI, VOL. 9, NO., APRIL 5: 3-35 3D MODELLING WITH LINEAR APPROACHES USING GEOMETRIC PRIMITIVES Mochammad Zulianyah Informatic Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, ARS International Univerity,
INVERSE DYNAMIC SIMULATION OF A HYDRAULIC DRIVE WITH MODELICA. α Cylinder chamber areas ratio... σ Viscous friction coefficient
 Proceeding of the ASME 2013 International Mechanical Engineering Congre & Expoition IMECE2013 November 15-21, 2013, San Diego, California, USA IMECE2013-63310 INVERSE DYNAMIC SIMULATION OF A HYDRAULIC
Proceeding of the ASME 2013 International Mechanical Engineering Congre & Expoition IMECE2013 November 15-21, 2013, San Diego, California, USA IMECE2013-63310 INVERSE DYNAMIC SIMULATION OF A HYDRAULIC
DWH Performance Tuning For Better Reporting
 DWH Performance Tuning For Better Sandeep Bhargava Reearch Scholar Naveen Hemrajani Aociate Profeor Dineh Goyal Aociate Profeor Subhah Gander IT Profeional ABSTRACT: The concept of data warehoue deal in
DWH Performance Tuning For Better Sandeep Bhargava Reearch Scholar Naveen Hemrajani Aociate Profeor Dineh Goyal Aociate Profeor Subhah Gander IT Profeional ABSTRACT: The concept of data warehoue deal in
Analysis of slope stability
 Engineering manual No. 8 Updated: 02/2016 Analyi of lope tability Program: Slope tability File: Demo_manual_08.gt In thi engineering manual, we are going to how you how to verify the lope tability for
Engineering manual No. 8 Updated: 02/2016 Analyi of lope tability Program: Slope tability File: Demo_manual_08.gt In thi engineering manual, we are going to how you how to verify the lope tability for
Computer Aided Drafting, Design and Manufacturing Volume 25, Number 3, September 2015, Page 10
 Computer Aided Drafting, Deign and Manufacturing Volume 5, umber 3, September 015, Page 10 CADDM Reearch of atural Geture Recognition and Interactive Technology Compatible with YCbCr and SV Color Space
Computer Aided Drafting, Deign and Manufacturing Volume 5, umber 3, September 015, Page 10 CADDM Reearch of atural Geture Recognition and Interactive Technology Compatible with YCbCr and SV Color Space
Planning of scooping position and approach path for loading operation by wheel loader
 22 nd International Sympoium on Automation and Robotic in Contruction ISARC 25 - September 11-14, 25, Ferrara (Italy) 1 Planning of cooping poition and approach path for loading operation by wheel loader
22 nd International Sympoium on Automation and Robotic in Contruction ISARC 25 - September 11-14, 25, Ferrara (Italy) 1 Planning of cooping poition and approach path for loading operation by wheel loader
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O196031A1 (19) United State (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0196031 A1 Chen (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 16, 2003 (54) STORAGE CONTROLLER WITH THE DISK Related U.S. Application
US 2003O196031A1 (19) United State (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0196031 A1 Chen (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 16, 2003 (54) STORAGE CONTROLLER WITH THE DISK Related U.S. Application
Ethernet Peer-To-Peer Communication With Model 353 And Procidia i pac Controllers
 iemen Energy & utomation pplication ata Ethernet Peer-To-Peer Communication With odel 353 nd Procidia ipac Controller 353-113 Rev. 1 July Ethernet i a leading form of network communication that i often
iemen Energy & utomation pplication ata Ethernet Peer-To-Peer Communication With odel 353 nd Procidia ipac Controller 353-113 Rev. 1 July Ethernet i a leading form of network communication that i often
INTEGRATED BUSINESS PRINT SOLUTIONS FOR YOUR WORKGROUP
 INTEGRATED BUSINESS PRINT SOLUTIONS FOR YOUR WORKGROUP www.brother.eu l u p p l BROTHER S NEW PROFESSIONAL ALL-IN-ONE COLOUR LASER RANGE INTERGRATED PRINT SOLUTIONS FOR YOUR BUSINESS Brother undertand
INTEGRATED BUSINESS PRINT SOLUTIONS FOR YOUR WORKGROUP www.brother.eu l u p p l BROTHER S NEW PROFESSIONAL ALL-IN-ONE COLOUR LASER RANGE INTERGRATED PRINT SOLUTIONS FOR YOUR BUSINESS Brother undertand
Frequency Table Computation on Dataflow Architecture
 Frequency Table Computation on Dataflow Architecture P. Škoda *, V. Sruk **, and B. Medved Rogina * * Ruđer Bošković Intitute, Zagreb, Croatia ** Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing, Univerity
Frequency Table Computation on Dataflow Architecture P. Škoda *, V. Sruk **, and B. Medved Rogina * * Ruđer Bošković Intitute, Zagreb, Croatia ** Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing, Univerity
Aspects of Formal and Graphical Design of a Bus System
 Apect of Formal and Graphical Deign of a Bu Sytem Tiberiu Seceleanu Univerity of Turku, Dpt. of Information Technology Turku, Finland tiberiu.eceleanu@utu.fi Tomi Weterlund Turku Centre for Computer Science
Apect of Formal and Graphical Deign of a Bu Sytem Tiberiu Seceleanu Univerity of Turku, Dpt. of Information Technology Turku, Finland tiberiu.eceleanu@utu.fi Tomi Weterlund Turku Centre for Computer Science
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: Proceedings of the Working Conference on Advanced Visual Interfaces
 Aalborg Univeritet Software-Baed Adjutment of Mobile Autotereocopic Graphic Uing Static Parallax Barrier Paprocki, Martin Marko; Krog, Kim Srirat; Kritofferen, Morten Bak; Krau, Martin Publihed in: Proceeding
Aalborg Univeritet Software-Baed Adjutment of Mobile Autotereocopic Graphic Uing Static Parallax Barrier Paprocki, Martin Marko; Krog, Kim Srirat; Kritofferen, Morten Bak; Krau, Martin Publihed in: Proceeding
Focused Video Estimation from Defocused Video Sequences
 Focued Video Etimation from Defocued Video Sequence Junlan Yang a, Dan Schonfeld a and Magdi Mohamed b a Multimedia Communication Lab, ECE Dept., Univerity of Illinoi, Chicago, IL b Phyical Realization
Focued Video Etimation from Defocued Video Sequence Junlan Yang a, Dan Schonfeld a and Magdi Mohamed b a Multimedia Communication Lab, ECE Dept., Univerity of Illinoi, Chicago, IL b Phyical Realization
REVERSE KINEMATIC ANALYSIS OF THE SPATIAL SIX AXIS ROBOTIC MANIPULATOR WITH CONSECUTIVE JOINT AXES PARALLEL
 Proceeding of the ASME 007 International Deign Engineering Technical Conference & Computer and Information in Engineering Conference IDETC/CIE 007 September 4-7, 007 La Vega, Nevada, USA DETC007-34433
Proceeding of the ASME 007 International Deign Engineering Technical Conference & Computer and Information in Engineering Conference IDETC/CIE 007 September 4-7, 007 La Vega, Nevada, USA DETC007-34433
Service and Network Management Interworking in Future Wireless Systems
 Service and Network Management Interworking in Future Wirele Sytem V. Tountopoulo V. Stavroulaki P. Demeticha N. Mitrou and M. Theologou National Technical Univerity of Athen Department of Electrical Engineering
Service and Network Management Interworking in Future Wirele Sytem V. Tountopoulo V. Stavroulaki P. Demeticha N. Mitrou and M. Theologou National Technical Univerity of Athen Department of Electrical Engineering
E. Stanová. Key words: wire rope, strand of a rope, oval strand, geometrical model
 Te International Journal of TRANSPORT & LOGISTICS Medzinárodný čaopi DOPRAVA A LOGISTIKA ISSN 45-7X GEOMETRY OF OVAL STRAND CREATED OF n n n WIRES E. Stanová Abtract: Te paper deal wit te matematical geometric
Te International Journal of TRANSPORT & LOGISTICS Medzinárodný čaopi DOPRAVA A LOGISTIKA ISSN 45-7X GEOMETRY OF OVAL STRAND CREATED OF n n n WIRES E. Stanová Abtract: Te paper deal wit te matematical geometric
The Crank-Nicholson method for a nonlinear diffusion equation
 > retart; with(plot): with(linearalgebra): with(arraytool): The Crank-Nicholon method for a nonlinear diffuion equation The purpoe of thi workheet i to olve a diffuion equation involving nonlinearitie
> retart; with(plot): with(linearalgebra): with(arraytool): The Crank-Nicholon method for a nonlinear diffuion equation The purpoe of thi workheet i to olve a diffuion equation involving nonlinearitie
Keywords: Defect detection, linear phased array transducer, parameter optimization, phased array ultrasonic B-mode imaging testing.
 Send Order for Reprint to reprint@benthamcience.ae 488 The Open Automation and Control Sytem Journal, 2014, 6, 488-492 Open Acce Parameter Optimization of Linear Phaed Array Tranducer for Defect Detection
Send Order for Reprint to reprint@benthamcience.ae 488 The Open Automation and Control Sytem Journal, 2014, 6, 488-492 Open Acce Parameter Optimization of Linear Phaed Array Tranducer for Defect Detection
A Practical Model for Minimizing Waiting Time in a Transit Network
 A Practical Model for Minimizing Waiting Time in a Tranit Network Leila Dianat, MASc, Department of Civil Engineering, Sharif Univerity of Technology, Tehran, Iran Youef Shafahi, Ph.D. Aociate Profeor,
A Practical Model for Minimizing Waiting Time in a Tranit Network Leila Dianat, MASc, Department of Civil Engineering, Sharif Univerity of Technology, Tehran, Iran Youef Shafahi, Ph.D. Aociate Profeor,
Integration of Digital Test Tools to the Internet-Based Environment MOSCITO
 Integration of Digital Tet Tool to the Internet-Baed Environment MOSCITO Abtract Current paper decribe a new environment MOSCITO for providing acce to tool over the internet. The environment i built according
Integration of Digital Tet Tool to the Internet-Baed Environment MOSCITO Abtract Current paper decribe a new environment MOSCITO for providing acce to tool over the internet. The environment i built according
E-APPLAB #1
 E-APPLAB-93-069850 #1 Ultrafat tomography experiment etup at D-1 Beamline at CHESS The experiment etup conit of three major part: x-ray ource, injection chambe and detecto a hown chematically in Fig. EPAPS1a.
E-APPLAB-93-069850 #1 Ultrafat tomography experiment etup at D-1 Beamline at CHESS The experiment etup conit of three major part: x-ray ource, injection chambe and detecto a hown chematically in Fig. EPAPS1a.
See chapter 8 in the textbook. Dr Muhammad Al Salamah, Industrial Engineering, KFUPM
 Goal programming Objective of the topic: Indentify indutrial baed ituation where two or more objective function are required. Write a multi objective function model dla a goal LP Ue weighting um and preemptive
Goal programming Objective of the topic: Indentify indutrial baed ituation where two or more objective function are required. Write a multi objective function model dla a goal LP Ue weighting um and preemptive
Objects and Classes. The Big Picture. Classes. Objects. Some paradigms of programming:
 Object and Clae The Big Picture Some paradigm of programming: Imperative Programming ue explicit loop, conditional, variable Three paradigm of programming we cover in CS111. Functional Programming Ue function
Object and Clae The Big Picture Some paradigm of programming: Imperative Programming ue explicit loop, conditional, variable Three paradigm of programming we cover in CS111. Functional Programming Ue function
Dynamically Reconfigurable Neuron Architecture for the Implementation of Self- Organizing Learning Array
 Dynamically Reconfigurable Neuron Architecture for the Implementation of Self- Organizing Learning Array Januz A. Starzyk,Yongtao Guo, and Zhineng Zhu School of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science
Dynamically Reconfigurable Neuron Architecture for the Implementation of Self- Organizing Learning Array Januz A. Starzyk,Yongtao Guo, and Zhineng Zhu School of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science
Development of an atmospheric climate model with self-adapting grid and physics
 Intitute of Phyic Publihing Journal of Phyic: Conference Serie 16 (2005) 353 357 doi:10.1088/1742-6596/16/1/049 SciDAC 2005 Development of an atmopheric climate model with elf-adapting grid and phyic Joyce
Intitute of Phyic Publihing Journal of Phyic: Conference Serie 16 (2005) 353 357 doi:10.1088/1742-6596/16/1/049 SciDAC 2005 Development of an atmopheric climate model with elf-adapting grid and phyic Joyce
Select Operation (σ) It selects tuples that satisfy the given predicate from a relation (choose rows). Review : RELATIONAL ALGEBRA
 Review : RELATIONAL ALGEBRA Relational databae ytem are expected to be equipped with a query language that can ait it uer to query the databae intance. There are two kind of query language relational algebra
Review : RELATIONAL ALGEBRA Relational databae ytem are expected to be equipped with a query language that can ait it uer to query the databae intance. There are two kind of query language relational algebra
CSE 250B Assignment 4 Report
 CSE 250B Aignment 4 Report March 24, 2012 Yuncong Chen yuncong@c.ucd.edu Pengfei Chen pec008@ucd.edu Yang Liu yal060@c.ucd.edu Abtract In thi project, we implemented the recurive autoencoder (RAE) a decribed
CSE 250B Aignment 4 Report March 24, 2012 Yuncong Chen yuncong@c.ucd.edu Pengfei Chen pec008@ucd.edu Yang Liu yal060@c.ucd.edu Abtract In thi project, we implemented the recurive autoencoder (RAE) a decribed
Key Terms - MinMin, MaxMin, Sufferage, Task Scheduling, Standard Deviation, Load Balancing.
 Volume 3, Iue 11, November 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Reearch in Computer Science and Software Engineering Reearch Paper Available online at: www.ijarce.com Tak Aignment in
Volume 3, Iue 11, November 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Reearch in Computer Science and Software Engineering Reearch Paper Available online at: www.ijarce.com Tak Aignment in
An Active Stereo Vision System Based on Neural Pathways of Human Binocular Motor System
 Journal of Bionic Engineering 4 (2007) 185 192 An Active Stereo Viion Sytem Baed on Neural Pathway of Human Binocular Motor Sytem Yu-zhang Gu 1, Makoto Sato 2, Xiao-lin Zhang 2 1. Department of Advanced
Journal of Bionic Engineering 4 (2007) 185 192 An Active Stereo Viion Sytem Baed on Neural Pathway of Human Binocular Motor Sytem Yu-zhang Gu 1, Makoto Sato 2, Xiao-lin Zhang 2 1. Department of Advanced
Karen L. Collins. Wesleyan University. Middletown, CT and. Mark Hovey MIT. Cambridge, MA Abstract
 Mot Graph are Edge-Cordial Karen L. Collin Dept. of Mathematic Weleyan Univerity Middletown, CT 6457 and Mark Hovey Dept. of Mathematic MIT Cambridge, MA 239 Abtract We extend the definition of edge-cordial
Mot Graph are Edge-Cordial Karen L. Collin Dept. of Mathematic Weleyan Univerity Middletown, CT 6457 and Mark Hovey Dept. of Mathematic MIT Cambridge, MA 239 Abtract We extend the definition of edge-cordial
A New Approach to Pipeline FFT Processor
 A ew Approach to Pipeline FFT Proceor Shouheng He and Mat Torkelon Department of Applied Electronic, Lund Univerity S- Lund, SWEDE email: he@tde.lth.e; torkel@tde.lth.e Abtract A new VLSI architecture
A ew Approach to Pipeline FFT Proceor Shouheng He and Mat Torkelon Department of Applied Electronic, Lund Univerity S- Lund, SWEDE email: he@tde.lth.e; torkel@tde.lth.e Abtract A new VLSI architecture
A Study of a Variable Compression Ratio and Displacement Mechanism Using Design of Experiments Methodology
 A Study of a Variable Compreion Ratio and Diplacement Mechanim Uing Deign of Experiment Methodology Shugang Jiang, Michael H. Smith, Maanobu Takekohi Abtract Due to the ever increaing requirement for engine
A Study of a Variable Compreion Ratio and Diplacement Mechanim Uing Deign of Experiment Methodology Shugang Jiang, Michael H. Smith, Maanobu Takekohi Abtract Due to the ever increaing requirement for engine
Parameters, UVM, Coverage & Emulation Take Two and Call Me in the Morning
 Parameter, UVM, Coverage & Emulation Take Two and Call Me in the Morning Michael Horn Mentor Graphic Corporation Colorado, USA Mike_Horn@mentor.com Bryan Ramirez Mentor Graphic Corporation Colorado, USA
Parameter, UVM, Coverage & Emulation Take Two and Call Me in the Morning Michael Horn Mentor Graphic Corporation Colorado, USA Mike_Horn@mentor.com Bryan Ramirez Mentor Graphic Corporation Colorado, USA
SIMIT 7. What's New In SIMIT V7.1? Manual
 SIMIT 7 What' New In SIMIT V7.1? Manual Edition January 2013 Siemen offer imulation oftware to plan, imulate and optimize plant and machine. The imulation- and optimization-reult are only non-binding uggetion
SIMIT 7 What' New In SIMIT V7.1? Manual Edition January 2013 Siemen offer imulation oftware to plan, imulate and optimize plant and machine. The imulation- and optimization-reult are only non-binding uggetion
LinkGuide: Towards a Better Collection of Hyperlinks in a Website Homepage
 Proceeding of the World Congre on Engineering 2007 Vol I LinkGuide: Toward a Better Collection of Hyperlink in a Webite Homepage A. Ammari and V. Zharkova chool of Informatic, Univerity of Bradford anammari@bradford.ac.uk,
Proceeding of the World Congre on Engineering 2007 Vol I LinkGuide: Toward a Better Collection of Hyperlink in a Webite Homepage A. Ammari and V. Zharkova chool of Informatic, Univerity of Bradford anammari@bradford.ac.uk,
Stress-Blended Eddy Simulation (SBES) - A new Paradigm in hybrid RANS-LES Modeling
 Stre-Blended Eddy Simulation (SBES) - A new Paradigm in hybrid RANS-LES Modeling Menter F.R. ANSYS Germany GmbH Introduction It i oberved in many CFD imulation that RANS model how inherent technology limitation
Stre-Blended Eddy Simulation (SBES) - A new Paradigm in hybrid RANS-LES Modeling Menter F.R. ANSYS Germany GmbH Introduction It i oberved in many CFD imulation that RANS model how inherent technology limitation
A System Dynamics Model for Transient Availability Modeling of Repairable Redundant Systems
 International Journal of Performability Engineering Vol., No. 3, May 05, pp. 03-. RAMS Conultant Printed in India A Sytem Dynamic Model for Tranient Availability Modeling of Repairable Redundant Sytem
International Journal of Performability Engineering Vol., No. 3, May 05, pp. 03-. RAMS Conultant Printed in India A Sytem Dynamic Model for Tranient Availability Modeling of Repairable Redundant Sytem
TAM 212 Worksheet 3. Solutions
 Name: Group member: TAM 212 Workheet 3 Solution The workheet i concerned with the deign of the loop-the-loop for a roller coater ytem. Old loop deign: The firt generation of loop wa circular, a hown below.
Name: Group member: TAM 212 Workheet 3 Solution The workheet i concerned with the deign of the loop-the-loop for a roller coater ytem. Old loop deign: The firt generation of loop wa circular, a hown below.
Domain-Specific Modeling for Rapid System-Wide Energy Estimation of Reconfigurable Architectures
 Domain-Specific Modeling for Rapid Sytem-Wide Energy Etimation of Reconfigurable Architecture Seonil Choi 1,Ju-wookJang 2, Sumit Mohanty 1, Viktor K. Praanna 1 1 Dept. of Electrical Engg. 2 Dept. of Electronic
Domain-Specific Modeling for Rapid Sytem-Wide Energy Etimation of Reconfigurable Architecture Seonil Choi 1,Ju-wookJang 2, Sumit Mohanty 1, Viktor K. Praanna 1 1 Dept. of Electrical Engg. 2 Dept. of Electronic
Objects, Classes, and Inheritance
 Object, Clae, and Inheritance CS111 Computer Programming Department of Computer Science Welleley College The Big Picture Some paradigm of programming: o Imperative Programming Program pecified by conditional,
Object, Clae, and Inheritance CS111 Computer Programming Department of Computer Science Welleley College The Big Picture Some paradigm of programming: o Imperative Programming Program pecified by conditional,
Delaunay Triangulation: Incremental Construction
 Chapter 6 Delaunay Triangulation: Incremental Contruction In the lat lecture, we have learned about the Lawon ip algorithm that compute a Delaunay triangulation of a given n-point et P R 2 with O(n 2 )
Chapter 6 Delaunay Triangulation: Incremental Contruction In the lat lecture, we have learned about the Lawon ip algorithm that compute a Delaunay triangulation of a given n-point et P R 2 with O(n 2 )
Finite Elements Method in Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar developing process
 6th WSEAS International Conference on SYSTEM SCIENCE and SIMULATION in ENGINEERING, Venice, Italy, November 1-3, 007 63 Finite Element Method in Split Hopkinon Preure Bar developing proce ROTARIU ADRIAN
6th WSEAS International Conference on SYSTEM SCIENCE and SIMULATION in ENGINEERING, Venice, Italy, November 1-3, 007 63 Finite Element Method in Split Hopkinon Preure Bar developing proce ROTARIU ADRIAN
