Describe Triangles. About the Math Professional Development 12.7 LESSON AT A GLANCE
|
|
|
- Hollie Washington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 12.7 LESSON Describe Triangles FOUS OHERENE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANE F R Focus: ommon ore State Standards 3.G.A.1 Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses, rectangles, and others) may share attributes (e.g., having four sides), and that the shared attributes can define a larger category (e.g., quadrilaterals). Recognize rhombuses, rectangles, and squares as examples of quadrilaterals, and draw examples of quadrilaterals that do not belong to any of these subcategories. MATHEMATIAL PRATIES (See ematical Practices in GO! in the Planning Guide for full text.) MP4 Model with mathematics. MP5 Use appropriate tools strategically. MP7 Look for and make use of structure. MP8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. F R oherence: Standards Across the Grades Before Grade 3 After 2.G.A.1 3.G.A.1 4.G.A.2 F R Rigor: Level 1: Understand oncepts...share and Show ( hecked Items) Level 2: Procedural Skills and Fluency...On Your Own, Practice and Homework Level 3: Applications...Think Smarter and Go Deeper Learning Objective Describe and compare triangles based on the number of sides that have equal length and by their angles. Language Objective Students draw and label a four panel cartoon to show how to use sides and angles to help you describe triangles. Materials Board, straws, scissors F R For more about how GO! fosters oherence within the ontent Standards and ematical Progressions for this chapter, see page 695J. About the Professional Development Why Teach This Interactive Student Edition As students describe and compare triangles based on sides and angles, they begin to develop a better understanding of the properties of triangles. Personal Trainer By exploring different triangles students can formulate conjectures about geometric properties and relationships. Students learn to develop and articulate clear mathematical arguments about why geometric relationships are true. For example: You can t make a triangle with two right angles, because if you start with a side across the bottom and make two right angles the sides go straight up and can t meet. These types of mathematical arguments help students verbalize what they have learned and make them better problem solvers. Professional Development Videos 735A hapter 12 on the Spot Video itools: Geometry
2 Daily Routines ommon ore Problem of the Day 12.7 One box has a mass of 96 grams. Another box has a mass of 115 grams. What is the mass of the boxes together? Vocabulary 211 grams Interactive Student Edition Multimedia Glossary e Fluency Builder ommon ore Fluency Standard 3.OA..7 Materials Number Wheels (see eteacher Resources) Multiplication Facts Practice Have students use a number wheel to practice multiplying by 8. Write 8 in the center of the number wheel and the numbers 2 9 in any order in the inner circle. Have students find and record the products in the outer circle Pages in Strategies and Practice for Skills and Facts Fluency provide additional fluency support for this lesson. 1 ENGAGE with the Interactive Student Edition Essential Question How can you use sides and angles to help you describe triangles? Making onnections Invite students to tell you what they know about triangles. How many sides does a triangle have? 3 How many angles does a triangle have? 3 Look around the room. Point out any triangles you see. Learning Activity What is the problem the students are trying to solve? onnect the story to the problem. Ask the following questions. How does Lucia want to describe the triangle? using its sides and angles Think of other shapes you've described, like quadrilaterals. How have you described their sides? Possible answers: parallel sides, sides of equal length How have you described angles? Possible answers: more than a right angle, less than a right angle Literacy and ematics View the lesson opener with the students. Then, choose one or more of the following activities to complete after they finish the lesson: Have students use dot paper to draw 3 to 5 different triangles. Have them write about the characteristics of the triangles. Have students draw a triangle on dot paper and then write a description of the triangle. Have students trade their description with a partner. The partner draws the triangle based on the description. Asks students to compare drawings to see if they match. How can you use sides and angles to help you describe triangles? 735B
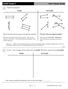
3 LESSON EXPLORE Unlock the Problem MATHEMATIAL PRATIES To introduce the lesson, have students watch the Real World Video, Shapes in Architecture. Activity MP4 Model with mathematics. The purpose of this activity is to help students understand the relationship between the lengths of the sides of a triangle. Students should recognize that if the length of two straws put together is not longer than the third straw, they cannot form a triangle. Make a triangle using 2 straws of equal length. What must be true of the length of the third straw in order to be able to form a triangle? It must be less than the length of the two equal-sized straws put together. Build a triangle using 3 straws of different lengths. Allow students time to share their work. Why could some of you build a triangle with 3 straws of different lengths? Possible answer: I could make a triangle because one of my straws is shorter than the other two straws put together. Use to help students recognize that a triangle can have 3 sides of equal length. MP6 Attend to precision. What types of angles do you see in the triangles that you made? Possible answers: right; greater than a right angle, less than a right angle Hands On 3.G.A.1 Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses, rectangles, and others) may share attributes (e.g., having four sides), and that the shared attributes can define a larger category (e.g., quadrilaterals). Recognize rhombuses, rectangles, and squares as examples of quadrilaterals, and draw examples of quadrilaterals that do not belong to any of these subcategories. Describe Triangles Essential Question How can you use sides and angles to help you describe triangles? Unlock the Problem How can you use straws of different lengths to make triangles? Activity Materials straws scissors Board 1. ompare the lengths of the sides. Describe when you can make a triangle. Possible description: 2. STEP 1 ut straws into different lengths. STEP 2 Find straw pieces that you can put together to make a triangle. Draw your triangle on the Board. STEP 3 Find straw pieces that you cannot put together to make a triangle. when two of the straw pieces put together are longer than the third piece, you can close up the straws to make a triangle. MATHEMATIAL PRATIE 1 Describe when you cannot make a triangle. Possible description: when two of the straw pieces put together are shorter than the third piece, you cannot close up the straws to make a triangle. 3. Explain how you can change the straw pieces in Step 3 to make a triangle. Possible explanation: you can exchange two longer pieces for the two shorter pieces. Geometry 3.G.A.1 MATHEMATIAL PRATIES MP1, MP2, MP6 Hands On MATHEMATIAL PRATIES 2 Reason Abstractly What if you have three straws of equal length? an you make a triangle? Yes; possible explanation: because two equal-length straw pieces put together would be longer than the third equal-length straw piece, you can close them up to make a triangle. hapter ELL Strategy: Illustrate Understanding The names of shapes tell students how many sides the shape should have. Restate the meanings of the prefixes in the words: triangle three quadrilateral four pentagon five hexagon six In pairs, have students write the names of the shapes on one side of an index card and write the meaning of the prefix underneath it. Have students draw an example of the shape on the back of the card. 735 hapter 12 Describe Triangles You can describe a triangle by its types of angles. 1 right angle. 1 angle greater than a right angle. 3 angles less than a right angle. Draw a line to match the description of the triangle(s). 1. One angle is a right angle. 2. One angle is greater than a right angle. 3. Three angles are less than a right angle. hapter Resources 2 Reteach 12.7 Enrich You can describe a triangle by the number of sides of equal length. 0 sides of the same length. 2 sides of the same length. 3 sides of the same length. Reteach 4. No sides are equal in length. 5. Two sides are equal in length. 6. Three sides are equal in length Reteach 3 Differentiated Instruction Sorting Triangles A description of a triangle is on each bucket. Write the letter of the triangle in all buckets that correctly describe it. Each triangle can go in at least two buckets. Some triangles can go in more than two buckets. A D Appears to have 1 right angle A, F 0 sides of equal length E, F B E 1 angle greater than a right angle, E Exactly 2 sides of equal length Exactly 2 angles less than a right angle A,, E, F F 3 sides of equal length A,, D B Sense or Nonsense? Beryl says the shape at the right will go in the first and last buckets because it has 1 right angle and 3 equal sides. Does her statement make sense? Explain. Enrich 3 angles less than a right angle B, D No. Possible explanation: the shape is not a triangle because it is not closed. hapter Resources Enrich
4 Ways to Describe Triangles What are two ways triangles can be described? 736 One Way A A B E Triangles can be described by the number of sides that are of equal length. Draw a line to match the description of the triangle(s). No sides are equal in length. Another Way Triangles can be described by the types of angles they have. Draw a line to match the description of the triangle(s). One angle is a right angle. B A E E Two sides are equal in length. One angle is greater than a right angle. No; possible explanation: if there were two right angles, the shape would have to have more than three sides and would no longer be a triangle. D B D Three sides are equal in length. D Three angles are less than a right angle. MATHEMATIAL PRATIES 2 Use Reasoning an a triangle have two right angles? Ways to Describe Triangles Students will learn how to describe triangles using the lengths of the sides and the types of angles. One Way This way focuses on describing triangles by the lengths of their sides. How can a ruler help you to describe a triangle based on its sides? I can use a ruler to measure the sides to see if any of them are the same length. Another Way This way focuses on describing triangles by the types of angles. Remind students of the types of angles. How can you use the corner of a sheet of paper to help you describe an angle in a triangle? I can use the square corner to find out if any of the angles are right angles. Draw a triangle like this one on the board. Have students describe the triangles they see. Possible answers: one triangle has three angles that are less than a right angle, and two triangles have one right angle. Use to explain that a shape with two right angles and three sides cannot be a closed shape. Do you think a triangle could have two angles that are greater than a right angle? Explain. No, if there were two angles greater than a right angle the shape would have to have more than three sides and would no longer be a triangle. Advanced Learners Materials ruler, Dot Paper (see eteacher Resources) Draw the following polygons on the board and have students draw them on square dot paper. Verbal / Linguistic Individual / Partner Then have students draw line segments from one vertex of each polygon to all other vertices. Have students describe and compare the triangles formed. Then challenge students to find the relationship between the number of triangles a polygon can be divided into and the number of sides the polygon has. The number of triangles is equal to the number of sides minus 2. OMMON ERRORS Error Students may not be able to identify sides of equal length or the types of angles. Example Students may not be able to identify sides of equal length in Exercise 1 or the types of angles in Exercises 2-4 on page 737. Springboard to Learning Remind students that they can always use a ruler to check the lengths of sides and they can always use a square corner to check the types of angles. 736
5 3 If Then EXPLAIN Share and Show MATH BOARD Quick heck MATH Use to check students understanding of how to describe triangles. an you explain another way to describe triangle G? Possible answers: triangle G has 2 sides of equal length. Use the checked exercises for Quick heck. a student misses the checked exercises RtI Differentiate Instruction with Reteach 12.7 Personal Trainer 3.G.A.1 RtI Tier 1 Activity (online) On Your Own If students complete the checked exercises correctly, they may continue with the On Your Own section. For Exercises 5 7, have students first analyze the angles in each triangle then focus on how the three side lengths compare. MP1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. Have students look at the triangles labeled L and M used in Exercises 5 7. Identify the largest angle and the longest side in each of the triangles. What do you notice about the relationship between the largest angle and the longest side? The longest side is opposite the largest angle. Share and Show F G H On Your Own K L MATH BOARD 1. Write the number of sides of equal length the triangle appears to have. 2 sides Use the triangles for 2 4. Write F, G, or H. 2. Triangle _ F has 1 right angle. 3. Triangle _ H has 1 angle greater than a right angle. 4. Triangle _ G has 3 angles less than a right angle. Use the triangles for 5 7. Write K, L, or M. Then complete the sentences. 5. Triangle _ M has 1 right angle and appears to have _ 2 sides of equal length. 6. Triangle _ K has 3 angles less than a right angle and appears to have _ 3 sides of equal length. 7. Triangle _ L has 1 angle greater than a right angle and appears to have _ 0 sides of equal length. M MATHEMATIAL PRATIES 8 Generalize Explain the ways you can describe a triangle. Possible explanation: triangles can be described by their sides or by their angles. hapter 12 Lesson hapter 12
6 MATHEMATIAL PRATIES OMMUNIA E ONSTRUT ARGUMENTS MATHEMATIAL 8. PRATIE 1 Make Sense of Problems Martin said a triangle can have two sides that are parallel. Does his statement make sense? Explain. No; possible explanation: a triangle has only 3 sides. If 2 sides were parallel, the shape would be an open shape. 4 ELABORATE Problem Solving Applications MATHEMATIAL PRATIES 9. DEEPER ompare Triangles R and S. How are they alike? How are they different? Possible explanation: alike both have 3 sides and 3 angles. Three angles are less than a right angle. Different Triangle R appears to have 3 sides of equal length, and R S MP1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. For Exercise 8 remind students that parallel lines do not intersect. Triangle S appears to have 2 sides of equal length. SMARTER 10. SMARTER Use a ruler to draw a straight line from one corner of this rectangle to the opposite corner. What shapes did you make? What do you notice about the shapes? 2 triangles; Possible answer: the triangles are the same size and same shape; each triangle has 1 right angle. Possible drawing. Exercise 10 requires students to decompose a polygon. on the Spot Video Tutor Use this video to help students model and solve this type of Think Smarter problem. 11. SMARTER Write the name of each triangle where it belongs in the table. Some triangles might belong in both parts of the table. Some triangles might not belong in either part. 738 Has 1 Right Angle L N P R Has at Least 2 Sides of Equal Length J O P Q R P J K M R N O Q L on the Spot videos are in the Interactive Student Edition and at SMARTER This item assesses a student s ability to classify triangles by their angles and sides. Students should examine each triangle individually and determine whether it belongs in either or both parts of the table. Students first should look for a right angle, and then look to see whether it has two or more equal sides. Some students might place a triangle in only one part of the table when it belongs in both parts if they do not clearly understand the directions of the problem. DIFFERENTIATED INSTRUTION INDEPENDENT ATIVITIES 5 EVALUATE Formative Assessment Activities lassification Act Students complete orange Activity ard 18 by classifying two-dimensional shapes based on their attributes. Differentiated enters Kit Activities Figure It Out Students complete blue Activity ard 18 by identifying two-dimensional shapes by their attributes. Essential Question Using the Language Objective Reflect Have students draw and label a four panel cartoon to answer the Essential Question. How can you use sides and angles to help you describe triangles? I can measure the sides of triangles to find out which sides, if any, have equal lengths. I can also find out if there is 1 right angle, 3 angles less than a right angle, or 1 angle greater than a right angle to describe a triangle. Journal WRITE Draw a triangle that has two sides of equal length and one right angle. 738
7 Practice and Homework Use the Practice and Homework pages to provide students with more practice of the concepts and skills presented in this lesson. Students master their understanding as they complete practice items and then challenge their critical thinking skills with Problem Solving. Use the Write section to determine student s understanding of content for this lesson. Encourage students to use their Journals to record their answers. Describe Triangles Use the triangles for 1 3. Write A, B, or. Then complete the sentences. A B 1. Triangle _ B has 3 angles less than a right angle and appears to have _ 3 sides of equal length. 2. Triangle _ has 1 right angle and appears to have _ 0 sides of equal length. 3. Triangle _ A has 1 angle greater than a right angle and appears to have _ 2 sides of equal length. Practice and Homework OMMON ORE STANDARD 3.G.A.1 Reason with shapes and their attributes. Problem Solving 4. Matthew drew the back of his tent. How many sides appear to be of equal length? 5. Sierra made the triangular picture frame shown. How many angles are greater than a right angle? 2 sides 6. WRITE Draw a triangle that has two sides of equal length and one right angle. heck students work. 0 angles hapter OMMON ON ORE PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT in Action The class is discussing ways to describe triangles. Amad: Lena: How can you describe a triangle? You can describe it by the number of sides of equal length. Very good. Besides using sides, is there another way to describe a triangle? By its angles. A triangle can have 1 right angle, 3 angles that are less than a right angle, or 1 angle that is greater than a right angle. Lena: Jonah: Lena, you just said that a triangle may have a right angle. Would a triangle ever have two right angles? Well, it might. No, wait. That wouldn t work. Two right angles would be like part of a square with a side missing. Good thinking. Is there any kind of angle that a triangle could have two of? It could have 2 angles less than a right angle. You re right! 739 hapter 12
8 Lesson heck (3.G.A.1) 1. How many angles less than a right angle does this triangle have? 3 angles 2. How many sides of equal length does this triangle appear to have? 2 sides ontinue concepts and skills practice with Lesson heck. Use Spiral Review to engage students in previously taught concepts and to promote content retention. ommon ore standards are correlated to each section. Spiral Review (3.NF.A.1, 3.MD.D.8, 3.G.A.1) 3. A quadrilateral has 4 right angles, 2 pairs of sides of equal length, and 2 pairs of opposite sides that are parallel. The pairs of opposite sides are not the same length. What quadrilateral could it be? 4. Mason drew a quadrilateral with only one pair of opposite sides that are parallel. What quadrilateral did Mason draw? Possible answers: rectangle or trapezoid trapezoid 5. Draw a rectangle that has an area of 8 square units and a perimeter of 12 units. What are the side lengths of the rectangle? 740 heck students drawings; 2 units and 4 units 6. What fraction of the square is shaded? 3_ 8 FOR MORE PRATIE GO TO THE Personal Trainer 740
Sort Two-Dimensional Shapes
 LESSON 12.1 Sort Two-Dimensional Shapes FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards Learning Objective 1.G.A.1 Distinguish between defining attributes (e.g., triangles
LESSON 12.1 Sort Two-Dimensional Shapes FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards Learning Objective 1.G.A.1 Distinguish between defining attributes (e.g., triangles
Hands On Three-Dimensional Shapes
 LESSON 11.1 Hands On Three-Dimensional Shapes FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards 1.G.A.1 Distinguish between defining attributes (e.g., triangles are closed
LESSON 11.1 Hands On Three-Dimensional Shapes FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards 1.G.A.1 Distinguish between defining attributes (e.g., triangles are closed
Investigate Understand Volume
 LESSON 11.6 Progress to Algebra Investigate Understand Volume FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards 5.MD.C.3b Recognize volume as an attribute of solid figures
LESSON 11.6 Progress to Algebra Investigate Understand Volume FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards 5.MD.C.3b Recognize volume as an attribute of solid figures
Investigate Explore Surface Area Using Nets
 LESSON 11.2 Investigate Explore Surface rea Using Nets OCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON T GLNCE C R ocus: Common Core State Standards Learning Objective 6.G..4 Represent three-dimensional figures using nets
LESSON 11.2 Investigate Explore Surface rea Using Nets OCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON T GLNCE C R ocus: Common Core State Standards Learning Objective 6.G..4 Represent three-dimensional figures using nets
ENGAGE. Daily Routines Common Core. Essential Question How can you find the volume of rectangular prisms with fractional edge lengths?
 LESSON.6 Algebra Volume of Rectangular Prisms FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards Learning Objective 6.G.A. Find the volume of a right rectangular prism with
LESSON.6 Algebra Volume of Rectangular Prisms FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards Learning Objective 6.G.A. Find the volume of a right rectangular prism with
Geometry. Students at Dommerich Elementary helped design and construct a mosaic to show parts of their community and local plants and animals.
 Geometry Describing and analyzing two-dimensional shapes Students at Dommerich Elementary helped design and construct a mosaic to show parts of their community and local plants and animals. 479 Make a
Geometry Describing and analyzing two-dimensional shapes Students at Dommerich Elementary helped design and construct a mosaic to show parts of their community and local plants and animals. 479 Make a
Objective: Compare and classify other polygons.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 5 3 7 Lesson 5 Objective: Compare and classify other polygons. Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (15
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 5 3 7 Lesson 5 Objective: Compare and classify other polygons. Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (15
15.4. PROBLEM SOLVING Three- Dimensional Solids? Are You Ready? Lesson Opener Making Connections. Resources. Essential Question
 5.4 PROBLEM SOLVING Three- Dimensional Solids? Essential Question How can making a model help you identify and describe attributes of three-dimensional solids? How can making a model help you identify
5.4 PROBLEM SOLVING Three- Dimensional Solids? Essential Question How can making a model help you identify and describe attributes of three-dimensional solids? How can making a model help you identify
The Grade 3 Common Core State Standards for Geometry specify that students should
 Students in third grade describe, analyze, and compare properties of two-dimensional shapes. They compare and classify shapes by their sides and angles, and they use these classifications to define shapes.
Students in third grade describe, analyze, and compare properties of two-dimensional shapes. They compare and classify shapes by their sides and angles, and they use these classifications to define shapes.
Lesson 4. Objective: Compare and classify quadrilaterals. Lesson Suggested Lesson Structure. Multiply by 4 (8 minutes)
 Lesson 4 3 7 Lesson 4 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (7 minutes) (31 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Lesson 4 3 7 Lesson 4 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (7 minutes) (31 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Describe Plane Shapes
 Lesson 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes You can use math words to describe plane shapes. point an exact position or location line endpoints line segment ray a straight path that goes in two directions without
Lesson 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes You can use math words to describe plane shapes. point an exact position or location line endpoints line segment ray a straight path that goes in two directions without
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 2016/2017 INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT
 HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 2016/2017 INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Third Grade Quarter 4 Unit 10: Geometry and Measurement Word Problems Approximately 40 Days Begin around March 27 th This 40-day final unit
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 2016/2017 INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Third Grade Quarter 4 Unit 10: Geometry and Measurement Word Problems Approximately 40 Days Begin around March 27 th This 40-day final unit
About Finish Line Mathematics 5
 Table of COntents About Finish Line Mathematics 5 Unit 1: Big Ideas from Grade 1 7 Lesson 1 1.NBT.2.a c Understanding Tens and Ones [connects to 2.NBT.1.a, b] 8 Lesson 2 1.OA.6 Strategies to Add and Subtract
Table of COntents About Finish Line Mathematics 5 Unit 1: Big Ideas from Grade 1 7 Lesson 1 1.NBT.2.a c Understanding Tens and Ones [connects to 2.NBT.1.a, b] 8 Lesson 2 1.OA.6 Strategies to Add and Subtract
Student Learning Targets for CCSS and Mathematical Practices
 Student and DUSD 3 rd Grade: Quarter 1 Unit Standards for Place Value and Comparing and Ordering Numbers 3.NBT.1 Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. M03-S1C3-01
Student and DUSD 3 rd Grade: Quarter 1 Unit Standards for Place Value and Comparing and Ordering Numbers 3.NBT.1 Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. M03-S1C3-01
Getting Ready to Teach Unit 6
 Getting Ready to Teach Unit 6 Learning Path in the Common Core Standards In this unit, students study the attributes of triangles, quadrilaterals, and other polygons. They find perimeter and area of various
Getting Ready to Teach Unit 6 Learning Path in the Common Core Standards In this unit, students study the attributes of triangles, quadrilaterals, and other polygons. They find perimeter and area of various
MCC5.G.3 Understand that attributes belonging to a category of two-dimensional figures also belong to all subcategories of that categories.
 Fifth Grade Mathematics Unit 6 CONSTRUCTING TASK: Property Lists of Quadrilaterals Adapted from Van De Walle, Teaching Student-Centered Math pg. 207 The purpose of this task is for students to become familiar
Fifth Grade Mathematics Unit 6 CONSTRUCTING TASK: Property Lists of Quadrilaterals Adapted from Van De Walle, Teaching Student-Centered Math pg. 207 The purpose of this task is for students to become familiar
In this task, students will investigate the attributes of quadrilaterals.
 PRACTICE TASK: Investigating Quadrilaterals In this task, students will investigate the attributes of quadrilaterals. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT MCC5.G.3 Understanding that attributes belonging
PRACTICE TASK: Investigating Quadrilaterals In this task, students will investigate the attributes of quadrilaterals. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT MCC5.G.3 Understanding that attributes belonging
Reason with shapes and their attributes.
 Grade 3 Geometry and Perimeter SDadfa;sdklfjas;Unit Overview Reason with shapes and their attributes. 1. Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses, rectangles, and others) may share
Grade 3 Geometry and Perimeter SDadfa;sdklfjas;Unit Overview Reason with shapes and their attributes. 1. Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses, rectangles, and others) may share
Objective: Use attributes to draw different polygons including triangles,
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 3 2 8 Lesson 3 Objective: Use attributes to draw different polygons including triangles, Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 3 2 8 Lesson 3 Objective: Use attributes to draw different polygons including triangles, Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
4 Mathematics Curriculum. Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1. Topic B: Angle Measurement... 4.B.1
 New York State Common Core 4 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1
New York State Common Core 4 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1
MATH - Grade 3 CUSD 303 Year Domain Cluster Standard Standard Skill Statement Resources Operations and Algebraic Thinking
 MATH - Grade 3 CUSD 303 Year 2012-2013 Domain Cluster Standard Standard Skill Statement Resources Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division 3.OA1
MATH - Grade 3 CUSD 303 Year 2012-2013 Domain Cluster Standard Standard Skill Statement Resources Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division 3.OA1
Mathematics Success Level E
 T877 [OBJECTIVE] The student will classify two-dimensional figures based on properties. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Lesson 29, knowledge of basic geometry terminology including: parallel sides, congruent sides,
T877 [OBJECTIVE] The student will classify two-dimensional figures based on properties. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Lesson 29, knowledge of basic geometry terminology including: parallel sides, congruent sides,
Classify two-dimensional figures in a hierarchy based on properties.
 rade Five Chapter 11 - eometry and Volume Overview & Support Standards: Classify two-dimensional figures into categories based on their properties. 5..3 Understand that attributes belonging to a category
rade Five Chapter 11 - eometry and Volume Overview & Support Standards: Classify two-dimensional figures into categories based on their properties. 5..3 Understand that attributes belonging to a category
Algebra Surface Area of Prisms
 LESSON.3 lgebra Surface rea of Prisms FOUS OHERENE RIGOR LESSON T GLNE F R Focus: ommon ore State Standards Learning Objective 6.G..4 Represent three-dimensional figures using nets made up of rectangles
LESSON.3 lgebra Surface rea of Prisms FOUS OHERENE RIGOR LESSON T GLNE F R Focus: ommon ore State Standards Learning Objective 6.G..4 Represent three-dimensional figures using nets made up of rectangles
Objective: Use attributes to draw different polygons including triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. (7 minutes) (5 minutes)
 Lesson 3 2 8 Lesson 3 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (6 minutes) (32 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Lesson 3 2 8 Lesson 3 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (6 minutes) (32 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Number and Operations - Fractions
 NF.1.3c Number and Operations - Fractions NF.1.3 NF.1.2b NF.1.2a Understand Fractions February 3 - February 20 NF.1.2 NF.1.1 Math! Lessons Develop understanding of fractions as numbers. Understand a fraction
NF.1.3c Number and Operations - Fractions NF.1.3 NF.1.2b NF.1.2a Understand Fractions February 3 - February 20 NF.1.2 NF.1.1 Math! Lessons Develop understanding of fractions as numbers. Understand a fraction
MISSOURI MATHEMATICS CORE ACADEMIC STANDARDS CROSSWALK TO MISSOURI GLES/CLES CONTENT ALIGNMENTS AND SHIFTS Grade 3 DRAFT
 Grade 3 Critical Areas In Grade 3, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: 1. developing understanding of multiplication and division and strategies for multiplication and division within
Grade 3 Critical Areas In Grade 3, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: 1. developing understanding of multiplication and division and strategies for multiplication and division within
Name Period Date GRADE 7: MATHEMATICS COMMON CORE SUPPLEMENT ANGLES, DRAWINGS, AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS
 Name Period Date 7-CORE3.1 Geometric Figures Measure and draw angles using a protractor. Review facts about interior angles of triangles and quadrilaterals. Find missing angle measures in geometric diagrams.
Name Period Date 7-CORE3.1 Geometric Figures Measure and draw angles using a protractor. Review facts about interior angles of triangles and quadrilaterals. Find missing angle measures in geometric diagrams.
Common Core. Mathematics Instruction
 014 Common Core Mathematics Instruction 7 Part 1: Introduction rea of Composed Figures Develop Skills and Strategies CCSS 7.G.B.6 In previous grades you learned that you can find the area of many different
014 Common Core Mathematics Instruction 7 Part 1: Introduction rea of Composed Figures Develop Skills and Strategies CCSS 7.G.B.6 In previous grades you learned that you can find the area of many different
Objective: Combine shapes to create a composite shape; create a new shape from composite shapes.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 2 8 Lesson 6 Objective: Combine shapes to create a composite shape; create a new shape Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 2 8 Lesson 6 Objective: Combine shapes to create a composite shape; create a new shape Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
Go to Grade 5 Everyday Mathematics Sample Lesson
 McGraw-Hill makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy of any information contained in this McGraw-Hill Material, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular
McGraw-Hill makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy of any information contained in this McGraw-Hill Material, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular
5 Mathematics Curriculum. Module Overview... i. Topic A: Concepts of Volume... 5.A.1
 5 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE 5 MODULE 5 Addition and Multiplication with Volume and Area GRADE 5 MODULE 5 Module Overview... i Topic A: Concepts of Volume... 5.A.1 Topic B:
5 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE 5 MODULE 5 Addition and Multiplication with Volume and Area GRADE 5 MODULE 5 Module Overview... i Topic A: Concepts of Volume... 5.A.1 Topic B:
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide Grade 3 (Draft) First Nine Weeks
 0 03 First Nine Weeks Big Ideas We are able to use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 0 or 00. What are the steps in rounding whole numbers? When would rounding be useful?.
0 03 First Nine Weeks Big Ideas We are able to use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 0 or 00. What are the steps in rounding whole numbers? When would rounding be useful?.
Math 3 - Lesson Title: Using the Coordinate Plane for Proofs
 Targeted Content Standard(s): Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. G.GPE.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove
Targeted Content Standard(s): Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. G.GPE.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove
Lesson 5 Post-Visit Circling the Bases
 Lesson 5 Post-Visit Circling the Bases Objective: Students will be able to: Review types and measurements of angles. Review types of polygons. Review formulas for perimeter and area. Time Required: 1 class
Lesson 5 Post-Visit Circling the Bases Objective: Students will be able to: Review types and measurements of angles. Review types of polygons. Review formulas for perimeter and area. Time Required: 1 class
6 Mathematics Curriculum
 New York State Common Core 6 Mathematics Curriculum GRADE GRADE 6 MODULE 5 Table of Contents 1 Area, Surface Area, and Volume Problems... 3 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)...
New York State Common Core 6 Mathematics Curriculum GRADE GRADE 6 MODULE 5 Table of Contents 1 Area, Surface Area, and Volume Problems... 3 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)...
9.2. Formulas for Volume. Are You Ready? Lesson Opener Making Connections. Resources. Essential Question. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
 9.2 Formulas for Volume? Essential Question How can you use formulas to find the volume of rectangular prisms? How can you use formulas to find the volume of rectangular prisms? Lesson Opener Making Connections
9.2 Formulas for Volume? Essential Question How can you use formulas to find the volume of rectangular prisms? How can you use formulas to find the volume of rectangular prisms? Lesson Opener Making Connections
Mathematics Curriculum
 6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
Math Services Align with the Common Core State Standards Mathematics (K 6)
 CORE Elementary Math Academy Alignment with Core State Standards CORE Elementary Math Academy emphasizes throughout each day the importance of teaching along the five proficiency strands identified by
CORE Elementary Math Academy Alignment with Core State Standards CORE Elementary Math Academy emphasizes throughout each day the importance of teaching along the five proficiency strands identified by
Name 8-6A. 1. What type of quadrilateral is shown below? A Rectangle B Trapezoid C Rhombus D Square. 2. What is true about every rhombus?
 Quick Check 1. What type of quadrilateral is shown below? A Rectangle B Trapezoid C Rhombus D Square 2. What is true about every rhombus? A All angles are equal. B All sides are equal. C Exactly one pair
Quick Check 1. What type of quadrilateral is shown below? A Rectangle B Trapezoid C Rhombus D Square 2. What is true about every rhombus? A All angles are equal. B All sides are equal. C Exactly one pair
15.2 Draw Quadrilaterals
 ? Name 15.2 Draw Quadrilaterals Essential Question How can you draw quadrilaterals? Geometry and Measurement 3.6.B Also 3.6.A MATHEMATICAL PROCESSES 3.1.D, 3.1.G Unlock the Problem Connect You have learned
? Name 15.2 Draw Quadrilaterals Essential Question How can you draw quadrilaterals? Geometry and Measurement 3.6.B Also 3.6.A MATHEMATICAL PROCESSES 3.1.D, 3.1.G Unlock the Problem Connect You have learned
Objective: Reason about attributes to construct quadrilaterals on square or triangular grid paper.
 Lesson 16 Objective: Reason about attributes to construct quadrilaterals on square or Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12
Lesson 16 Objective: Reason about attributes to construct quadrilaterals on square or Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12
CPSD: Grade 3 Mathematics. Module 4. area. Apx. 30 days Apx. 25 days Apx. 25 days Apx. 20 days Apx. 25 days Apx. 10 days 25 days
 CPSD: Grade 3 Mathematics Module 1 Module 2 Module 3 Module 4 Module 5 Module 6 Module 7 Properties of multiplication and division and solving problems with units of 2-5 and 10 Place value and problem
CPSD: Grade 3 Mathematics Module 1 Module 2 Module 3 Module 4 Module 5 Module 6 Module 7 Properties of multiplication and division and solving problems with units of 2-5 and 10 Place value and problem
Title: Identifying, Classifying, and Creating Quadrilaterals - Qualifying Quadrilaterals
 Title: Identifying, Classifying, and Creating Quadrilaterals - Qualifying Quadrilaterals Brief Overview: Through problem solving, oral and written communication, higher-order thinking and a variety of
Title: Identifying, Classifying, and Creating Quadrilaterals - Qualifying Quadrilaterals Brief Overview: Through problem solving, oral and written communication, higher-order thinking and a variety of
2nd Grade. 2D Shapes - Part 1 Angles and Sides. Slide 1 / 117 Slide 2 / 117. Slide 3 / 117. Slide 4 / 117. Slide 6 / 117.
 Slide 1 / 117 Slide 2 / 117 2nd Grade Geometry Presentation 1 2015-11-30 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 117 Table of ontents Presentation 1 2 Shapes - Sides and ngles - Part 1 2 Shapes - Part 2 Lab: 2 Shapes
Slide 1 / 117 Slide 2 / 117 2nd Grade Geometry Presentation 1 2015-11-30 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 117 Table of ontents Presentation 1 2 Shapes - Sides and ngles - Part 1 2 Shapes - Part 2 Lab: 2 Shapes
Common Core State Standards - Standards for Mathematical Practice
 Common Core State Standards - Standards for Mathematical Practice The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to develop
Common Core State Standards - Standards for Mathematical Practice The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to develop
3teacherchicks.blogspot.com
 Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division. 3.OA.1.Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example,
Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division. 3.OA.1.Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example,
Weeks 1 through 6 Aug. 6- Sept. 13 Weeks indicate introduction of standards
 1 Weeks 1 through 6 Aug. 6- Sept. 13 Weeks indicate introduction of standards Review Addition and Subtraction with Regrouping I can add numbers with regrouping. I can subtract numbers with regrouping.
1 Weeks 1 through 6 Aug. 6- Sept. 13 Weeks indicate introduction of standards Review Addition and Subtraction with Regrouping I can add numbers with regrouping. I can subtract numbers with regrouping.
The School District of Palm Beach County 3 rd Grade Mathematics Scope st Trimester
 1 st Trimester Measurement and Data (MD) MD.2.3 MD.2.4 Represent and interpret data. Draw a scaled picture graph and a scaled bar graph to represent a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two-step
1 st Trimester Measurement and Data (MD) MD.2.3 MD.2.4 Represent and interpret data. Draw a scaled picture graph and a scaled bar graph to represent a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two-step
The School District of Palm Beach County 3 rd Grade Mathematics Scope st Trimester
 1 st Trimester Measurement and Data (MD) MD.2.3 MD.2.4 Represent and interpret data. Draw a scaled picture graph and a scaled bar graph to represent a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two-step
1 st Trimester Measurement and Data (MD) MD.2.3 MD.2.4 Represent and interpret data. Draw a scaled picture graph and a scaled bar graph to represent a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two-step
The descriptions below provide an overview of the mathematical concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 4 th grade.
 Mathematics Grade 4 The descriptions below provide an overview of the mathematical concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 4 th grade. Operations and Algebraic Thinking Students build
Mathematics Grade 4 The descriptions below provide an overview of the mathematical concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 4 th grade. Operations and Algebraic Thinking Students build
Monroe County School District Elementary Pacing Guide
 Date Taught: Third Grade Unit 1: Number, Operations, and Base 10 Timeline: August5 - September 16 CMA: 3.NBT.2 Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value,
Date Taught: Third Grade Unit 1: Number, Operations, and Base 10 Timeline: August5 - September 16 CMA: 3.NBT.2 Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value,
Minnesota. Plainfield Public Schools Plainfield, New Jersey Grade 3 Pacing Guide. Volumes 1 and 2. Grade 3
 Plainfield Public Schools Plainfield, New Jersey Minnesota Volumes 1 and 2 Grade 3 2013 1. Computing with Whole Numbers 15 Days 3 days 3.OA.8 Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent
Plainfield Public Schools Plainfield, New Jersey Minnesota Volumes 1 and 2 Grade 3 2013 1. Computing with Whole Numbers 15 Days 3 days 3.OA.8 Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent
TOPIC 16 STUDY GUIDE LINES, ANGLES AND SHAPES
 Name: Teacher: TOPIC 16 STUDY GUIDE LINES, ANGLES AND SHAPES Study Guide Due: Test Date: Parents, 4th Graders are focusing on giving their best effort. One way to show that they are going above and beyond
Name: Teacher: TOPIC 16 STUDY GUIDE LINES, ANGLES AND SHAPES Study Guide Due: Test Date: Parents, 4th Graders are focusing on giving their best effort. One way to show that they are going above and beyond
3 RD GRADE MATH-COMMON CORE PACING GUIDE 1ST 9 WEEKS Standard I Can Statements Date
 3 RD GRADE MATH-COMMON CORE PACING GUIDE 1ST 9 WEEKS 2013-2014 Standard I Can Statements Date Taught Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) 3.OA.1. Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret
3 RD GRADE MATH-COMMON CORE PACING GUIDE 1ST 9 WEEKS 2013-2014 Standard I Can Statements Date Taught Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) 3.OA.1. Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret
Washington County School District Pacing Guide 3 rd Grade Math
 Dates August September October Enduring Skills/Understandings understanding of multiplication and division strategies for multiplication and division within 100. Subskill: Students use place value understanding
Dates August September October Enduring Skills/Understandings understanding of multiplication and division strategies for multiplication and division within 100. Subskill: Students use place value understanding
Geometry Sixth Grade
 Standard 6-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of shape, location, and movement within a coordinate system; similarity, complementary, and supplementary
Standard 6-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of shape, location, and movement within a coordinate system; similarity, complementary, and supplementary
Domain: Multiplication and Division Emphasis: Problem solving with multiplication and division. Third Grade
 Domain: Multiplication and Division Emphasis: Problem solving with multiplication and division Major Cluster (green): Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division. Major Cluster (green):
Domain: Multiplication and Division Emphasis: Problem solving with multiplication and division Major Cluster (green): Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division. Major Cluster (green):
Jackson County Schools Curriculum Pacing Guide
 Jackson County Schools Curriculum Pacing Guide - Third Grade 1st Nine Weeks 2nd Nine Weeks 3rd Nine Weeks 4th Nine Weeks Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Numbers and Operations in Base
Jackson County Schools Curriculum Pacing Guide - Third Grade 1st Nine Weeks 2nd Nine Weeks 3rd Nine Weeks 4th Nine Weeks Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Numbers and Operations in Base
Grade 3 Report Card Parent Support MATH Marking Period Expectations for Standards Based Report Card
 Grade 3 Report Card Parent Support MATH Marking Period Expectations for Standards Based Report Card Operations and Algebraic Thinking Standards 1st MP 2nd MP 3rd MP Represents and solves problems involving
Grade 3 Report Card Parent Support MATH Marking Period Expectations for Standards Based Report Card Operations and Algebraic Thinking Standards 1st MP 2nd MP 3rd MP Represents and solves problems involving
3.NBT.1 Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100.
 Date Taught: Monroe County School District Third Grade Unit 1: Number, Operations, and Base 10 Timeline: August 3 - September 28 CMA: September 24-28 3.NBT.2 Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using
Date Taught: Monroe County School District Third Grade Unit 1: Number, Operations, and Base 10 Timeline: August 3 - September 28 CMA: September 24-28 3.NBT.2 Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using
Monrovia School District Grade Three Common Core Math Pacing
 Trimester 3 Pretest (optional) March 29 Monrovia School District Grade Three Common Core Math Pacing 2017-2018 Trimester 3 Pretest Exam Use the information as an additional pacing tool to guide instruction.
Trimester 3 Pretest (optional) March 29 Monrovia School District Grade Three Common Core Math Pacing 2017-2018 Trimester 3 Pretest Exam Use the information as an additional pacing tool to guide instruction.
GRADE 5 UNIT 5 SHAPE AND COORDINATE GEOMETRY Established Goals: Standards
 GRADE 5 UNIT 5 SHAPE AND COORDINATE GEOMETRY Established Goals: Standards 5.NBT.7 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals to hundredths, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place
GRADE 5 UNIT 5 SHAPE AND COORDINATE GEOMETRY Established Goals: Standards 5.NBT.7 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals to hundredths, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place
Lesson 2 Pre-Visit A Diamond Filled with Shapes
 Lesson 2 Pre-Visit A Diamond Filled with Shapes Objective: Students will be able to: Define the term polygon. Recognize different polygons evident in baseball. Draw and identify different polygons. Time
Lesson 2 Pre-Visit A Diamond Filled with Shapes Objective: Students will be able to: Define the term polygon. Recognize different polygons evident in baseball. Draw and identify different polygons. Time
CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE
 School: Cumberland County Elementary School CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE Subject: Math Grade: Third Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: Weeks
School: Cumberland County Elementary School CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE Subject: Math Grade: Third Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: Weeks
Grade 4 CCSS Pacing Guide: Math Expressions
 Grade 4 CCSS Pacing Guide: Math Expressions Green : Areas of intensive focus, where students need fluent understanding and application of the core concepts (Approximately 70%) Blue : Rethinking and linking;
Grade 4 CCSS Pacing Guide: Math Expressions Green : Areas of intensive focus, where students need fluent understanding and application of the core concepts (Approximately 70%) Blue : Rethinking and linking;
Reteach. Chapter 14. Grade 4
 Reteach Chapter 14 Grade 4 Lesson 1 Reteach Draw Points, Lines, and Rays A point is an exact location that is represented by a dot. Example: point R R A line goes on forever in both directions. Example:
Reteach Chapter 14 Grade 4 Lesson 1 Reteach Draw Points, Lines, and Rays A point is an exact location that is represented by a dot. Example: point R R A line goes on forever in both directions. Example:
Objective: Build, identify, and analyze two dimensional shapes with specified attributes.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 2 2 8 Lesson 2 Objective: Build, identify, and analyze two dimensional shapes with specified Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 2 2 8 Lesson 2 Objective: Build, identify, and analyze two dimensional shapes with specified Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
Objective: Build, identify, and analyze two-dimensional shapes with specified attributes. (3 minutes) (9 minutes)
 Lesson 2 2 8 Lesson 2 Objective: Build, identify, and analyze two-dimensional shapes with specified Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total
Lesson 2 2 8 Lesson 2 Objective: Build, identify, and analyze two-dimensional shapes with specified Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total
Second Quarter Benchmark Expectations for Sections 4 and 5. Count orally by ones to 50. Count forward to 50 starting from numbers other than 1.
 Mastery Expectations For the Kindergarten Curriculum In Kindergarten, Everyday Mathematics focuses on procedures, concepts, and s in two critical areas: Representing and comparing whole numbers, initially
Mastery Expectations For the Kindergarten Curriculum In Kindergarten, Everyday Mathematics focuses on procedures, concepts, and s in two critical areas: Representing and comparing whole numbers, initially
Does a group of parallel line segments need to be the same length?
 1 Parallel Line Segments Parallel t Parallel What is the same about the groups of parallel line segments? They are always the same distance apart. They do not intersect each other. If you extend the line
1 Parallel Line Segments Parallel t Parallel What is the same about the groups of parallel line segments? They are always the same distance apart. They do not intersect each other. If you extend the line
3rd Grade Texas Math Crosswalk Document:
 New TX Math 3.1(A) apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace; 3.1(B) use a problem-solving model that incorporates analyzing given information, formulating a plan
New TX Math 3.1(A) apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace; 3.1(B) use a problem-solving model that incorporates analyzing given information, formulating a plan
Coordinate Geometry Lisa A. Over Robert Morris University Professor Trombetta EDUC 6400: Reading Across the Curriculum and ELL
 Coordinate Geometry Lisa A. Over Robert Morris University Professor Trombetta EDUC 6400: Reading Across the Curriculum and ELL Overview According to the PA State Standards for mathematics, students must
Coordinate Geometry Lisa A. Over Robert Morris University Professor Trombetta EDUC 6400: Reading Across the Curriculum and ELL Overview According to the PA State Standards for mathematics, students must
THE COMPETITIVE EDGE
 SAMPLE PAGES FOR THE READY EOG ASSESSMENT THE COMPETITIVE EDGE THIRD GRADE MATHEMATICS with COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS 2012 EDITION J ANE H EREFORD CPC CONTEMPORARY PUBLISHING COMPANY OF RALEIGH, INC.
SAMPLE PAGES FOR THE READY EOG ASSESSMENT THE COMPETITIVE EDGE THIRD GRADE MATHEMATICS with COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS 2012 EDITION J ANE H EREFORD CPC CONTEMPORARY PUBLISHING COMPANY OF RALEIGH, INC.
Grade K 8 Standards Grade 4
 Grade 4 In grade 4, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) developing understanding and fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing understanding of dividing to find quotients
Grade 4 In grade 4, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) developing understanding and fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing understanding of dividing to find quotients
Ratcheting Up the Three R s All SubjectsInstructional Unit Plan
 Subject: Mathematics Ratcheting Up the Three R s All SubjectsInstructional Unit Plan Estimated Length of Unit: 25 Beginning Date: April 24 Module: 6 Area, Surface, and Volume Problems Grade: 6 Projected
Subject: Mathematics Ratcheting Up the Three R s All SubjectsInstructional Unit Plan Estimated Length of Unit: 25 Beginning Date: April 24 Module: 6 Area, Surface, and Volume Problems Grade: 6 Projected
3rd Grade Standards Guide
 3rd Grade Standards Guide Table of Contents Content Page Number Overview to the Math Standards Guide 2-3 Geometry 4 Measurement & Data 4-6 Numbers & Operations Fractions 6-7 Numbers & Operations in Base
3rd Grade Standards Guide Table of Contents Content Page Number Overview to the Math Standards Guide 2-3 Geometry 4 Measurement & Data 4-6 Numbers & Operations Fractions 6-7 Numbers & Operations in Base
Casey County Schools- 3 rd Grade Math Map
 Week(s) Standard I can statement(s) Critical Vocabulary 3.MD.1 (Teach throughout the year) Resources Used throughout the year (math minutes, automaticity) Formative Assessment(s) (this will be left blank
Week(s) Standard I can statement(s) Critical Vocabulary 3.MD.1 (Teach throughout the year) Resources Used throughout the year (math minutes, automaticity) Formative Assessment(s) (this will be left blank
Quarter 1-Mid Quarter 1
 Domains Learning Goal/ SWBT Numbers and Operations in Base Ten Use place value understanding in properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. MAFS.3.NBT.1.1 : Use place value understanding
Domains Learning Goal/ SWBT Numbers and Operations in Base Ten Use place value understanding in properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. MAFS.3.NBT.1.1 : Use place value understanding
The Level 2 student is approaching proficient in applying mathematics knowledge/skills as specified in the standards.
 MATH GRADE 3 PLD Standard Below Proficient Approaching Proficient Proficient Highly Proficient The Level 1 student is below The Level 2 student is approaching The Level 3 student is proficient in applying
MATH GRADE 3 PLD Standard Below Proficient Approaching Proficient Proficient Highly Proficient The Level 1 student is below The Level 2 student is approaching The Level 3 student is proficient in applying
ame Date Class Practice A 11. What is another name for a regular quadrilateral with four right angles?
 ame Date Class Practice A Polygons Name each polygon. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Tell whether each polygon appears to be regular or not regular. 7. 8. 9. 10. What is another name for a regular triangle? 11. What
ame Date Class Practice A Polygons Name each polygon. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Tell whether each polygon appears to be regular or not regular. 7. 8. 9. 10. What is another name for a regular triangle? 11. What
GEOMETRY LESSON 5: POST-VISIT - CIRCLING THE BASES CIRCLING THE BASES. OBJECTIVE: Students will be able to: TIME REQUIRED: 1 class period
 POST-VISIT - OBJECTIVE: Students will be able to: Review types and measurements of angles. Review types of polygons. Review formulas for perimeter and area. TIME REQUIRED: 1 class period MATERIALS NEEDED:
POST-VISIT - OBJECTIVE: Students will be able to: Review types and measurements of angles. Review types of polygons. Review formulas for perimeter and area. TIME REQUIRED: 1 class period MATERIALS NEEDED:
Unit Goals Stage 1. Number of Days: 14 days 1/29/18-2/16/18
 Number of : 14 1/29/18-2/16/18 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Drawing on our knowledge of the definitions of special quadrilaterals and a few of their properties, students will now prove those properties
Number of : 14 1/29/18-2/16/18 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Drawing on our knowledge of the definitions of special quadrilaterals and a few of their properties, students will now prove those properties
Third Grade Math: I Can Statements
 Third Grade Math: I Can Statements Processes, Content Statements & Expectations (Disciplinary Knowledge) Operations and Algebraic Thinking 3.OA Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and
Third Grade Math: I Can Statements Processes, Content Statements & Expectations (Disciplinary Knowledge) Operations and Algebraic Thinking 3.OA Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Answer Key Lesson 11: Workshop: Shapes and Properties
 Answer Key esson 11: Use the nine Power Polygons below for Questions 1 and 2. 1. A. Sort the shapes with four sides into ox A. Sort the Shapes with one or more right angles into ox. Some shapes will go
Answer Key esson 11: Use the nine Power Polygons below for Questions 1 and 2. 1. A. Sort the shapes with four sides into ox A. Sort the Shapes with one or more right angles into ox. Some shapes will go
Grade 3. EDM Version 4. Everyday Math: Unit. Measurement and Geometry. Study Guide
 EDM Version 4 Grade 3 Everyday Math: Unit Measurement and Geometry. Study Guide Thank you! Catherine Wiist @ Abc123is4me http://www.teacherspayteachers.com/store/abc123is4me (All new products are discounted
EDM Version 4 Grade 3 Everyday Math: Unit Measurement and Geometry. Study Guide Thank you! Catherine Wiist @ Abc123is4me http://www.teacherspayteachers.com/store/abc123is4me (All new products are discounted
The descriptions below provide an overview of the mathematical concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 5 th grade.
 Mathematics Grade 5 The descriptions below provide an overview of the mathematical concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 5 th grade. Operations and Algebraic Thinking Students build
Mathematics Grade 5 The descriptions below provide an overview of the mathematical concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 5 th grade. Operations and Algebraic Thinking Students build
The descriptions below provide an overview of the mathematical concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 5 th grade.
 Mathematics Grade 5 The descriptions below provide an overview of the mathematical concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 5 th grade. Operations and Algebraic Thinking Students build
Mathematics Grade 5 The descriptions below provide an overview of the mathematical concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 5 th grade. Operations and Algebraic Thinking Students build
An angle that has a measure less than a right angle.
 Unit 1 Study Strategies: Two-Dimensional Figures Lesson Vocab Word Definition Example Formed by two rays or line segments that have the same 1 Angle endpoint. The shared endpoint is called the vertex.
Unit 1 Study Strategies: Two-Dimensional Figures Lesson Vocab Word Definition Example Formed by two rays or line segments that have the same 1 Angle endpoint. The shared endpoint is called the vertex.
CCSS Standard. CMSD Dynamic Pacing Guide 3 rd Grade Math I Can Statements + Introduced and Assessed Introduced First Nine Weeks
 3.NBT.1 Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. 3.OA.8 Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter
3.NBT.1 Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. 3.OA.8 Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Tiling the Plane
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: Tiling the Plane Let s look at tiling patterns and think about area. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Tilings Which pattern doesn t belong? 1 1.2: More Red, Green, or Blue? m.openup.org//6-1-1-2
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Tiling the Plane Let s look at tiling patterns and think about area. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Tilings Which pattern doesn t belong? 1 1.2: More Red, Green, or Blue? m.openup.org//6-1-1-2
Grade 4. Massachusetts Curriculum Framework for Mathematics 42
 Grade 4 Introduction In grade 4, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) developing understanding and fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing understanding of dividing
Grade 4 Introduction In grade 4, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) developing understanding and fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing understanding of dividing
Problem of the Month: William s Polygons
 Problem of the Month: William s Polygons The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Problem of the Month: William s Polygons The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Mathematics CMP3, Grade 7 Stretching and Shrinking Month: Nov-Dec, Weeks 11-14
 Standards for Mathematical Practice Critical Areas: Ratios and Proportions, Number System, Expressions and Equations Content Emphases for Grade 7 Major Cluster 70% of time Supporting Cluster 20% of Time
Standards for Mathematical Practice Critical Areas: Ratios and Proportions, Number System, Expressions and Equations Content Emphases for Grade 7 Major Cluster 70% of time Supporting Cluster 20% of Time
Ballston Spa Central School District The Common Core State Standards in Our Schools. Third Grade Math
 1 Ballston Spa Central School District The Common Core State s in Our Schools Third Grade Math Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division 3.OA.1.Interpret
1 Ballston Spa Central School District The Common Core State s in Our Schools Third Grade Math Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division 3.OA.1.Interpret
Objective: Construct perpendicular line segments on a rectangular grid.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 15 5 6 Lesson 15 Objective: Construct perpendicular line segments on a rectangular grid. Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Concept Development Student
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 15 5 6 Lesson 15 Objective: Construct perpendicular line segments on a rectangular grid. Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Concept Development Student
Houston County Schools Grade 4 Math
 Grade 4 Math Operations and Algebraic Thinking [OA] Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. Gain familiarity with factors and multiples. Generate and analyze patterns. Number and
Grade 4 Math Operations and Algebraic Thinking [OA] Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. Gain familiarity with factors and multiples. Generate and analyze patterns. Number and
Geometry. Standardized Practice Have students try the following problem.
 1 Students need a basic understanding of angles to learn the properties of twodimensional shapes. In this lesson, students use models to represent, measure, and classify angles. Objective Recognize types
1 Students need a basic understanding of angles to learn the properties of twodimensional shapes. In this lesson, students use models to represent, measure, and classify angles. Objective Recognize types
Mathematics. Unit 5: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane
 CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics CCGPS Coordinate Algebra Unit 5: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics CCGPS Coordinate Algebra Unit 5: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute
