Verification Procedures for Simulation of Fully Coupled Behavior of Porous Media
|
|
|
- Owen McGee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Verification Procedures for Simulation of Fully Coupled Behavior of Porous Media Boris, Panagiota Tasiopoulou, Mahdi Taiebat, Nima Tafazzoli, Mario Martinelli UCD, LBNL, NTUA, UBC, UCD, URoma USNCCM, Minneapolis, MN
2 Outline Introduction Verification and Validation Verification Saturated Soils Fully Coupled Formulation Verification Suite Summary
3 Outline Introduction Verification and Validation Verification Saturated Soils Fully Coupled Formulation Verification Suite Summary
4 Introduction Numerical analysts, designers need the best available tools for performance assessment (numerical predictions) Verification and validation process ensures accuracy of numerical predictions How much can (should) we trust model implementations (verification)? How much can (should) we trust numerical simulations (validation)? How good are our numerical predictions? The T experiments Focus on verification
5 Outline Introduction Verification and Validation Verification Saturated Soils Fully Coupled Formulation Verification Suite Summary
6 Verification Verification, Validation, Prediction Verification: provides evidence that the model is solved correctly. Validation: provides evidence that the correct model is solved. Prediction: use of computational model to foretell the state of a physical system under consideration under conditions for which the computational model has not been validated
7 Verification Role of Verification and Validation Reality Analysis Model Discovery and Building Model Validation Computer Simulation Mathematical Model Continuum Mathematics Programming Computer Implementation Discrete Mathematics Code Verification Oberkampf et al. Oden et al.
8 Verification Verification Verification: the process of determining that a model implementation accurately represents the developer s conceptual description and specification. Mathematics issue. Verification provides evidence that the model is solved correctly. Real World Conceptual Model Highly accurate solution Analytical solution Benchmark ODE solution Benchmark PDE solution Computational Model Computational Solution Experimental Data Unit Problems Benchmark Cases Subsystem Cases Complete System Verification Validation
9 Outline Introduction Verification and Validation Verification Saturated Soils Fully Coupled Formulation Verification Suite Summary
10 Fully Coupled Formulation Dynamic Equilibrium for Saturated, Coupled Systems Effective stress principle σ ij = σ ij + αδ ij p ; (p = /3σ kk ) Equilibrium of the mixture σ ij,j ρü i ρ f [ẅ i + ẇ j ẇ i,j ] + ρb i = ; (ρ = nρ f + ( n)ρ s ) Equilibrium of the fluid p,i R i ρ f ü i ρ f [ẅ i + ẇ j ẇ i,j ]/n + ρ f b i = ; (Darcy: nẇ j = Ki; i = h,j ; R i = k ij ẇ j ; k ij = K ij /ρ f g [m] 3 [s]/[kg]) Flow conservation ẇ i,i + α ε ii + ṗ/q + nρ f /ρ f + ṡ = ; /Q n/k f + ( n)/k s
11 Fully Coupled Formulation Fully Coupled u p U Formulation Formulation: fully coupled by Zienkiewicz and Shiomi 9), nonlinear dynamics by Argyris and Mlejnek (99) Physical, velocity proportional damping from solid fluid interaction (not using Rayleigh damping) Accelerations of pore fluid not neglected important for SFSI inertial forces of fluid allow liquefaction modeling Stable formulation for near incompressible pore fluid
12 Fully Coupled Formulation Finite Element Discretization + + (M s ) KijL (M f ) KijL (C ) KijL (C 2 ) KijL (C 2 ) LjiK (C 3 ) KijL ü Lj p N U Lj + u Lj ṗ N U Lj (K EP ) KijL (G ) KiM (G ) LjM P MN (G 2 ) LjM (G 2 ) KiL + u Lj p M U Lj = f solid Ki f fluid Ki
13 Fully Coupled Formulation Finite Element Discretization (M s ) KijL = NK u ( n)ρ sδ ij NL u dω ; (M f ) KijL = NK U nρ f δ ij NL U dω Ω Ω (C ) KijL = NK u n2 k ij NL u dω ; (C 2) KijL = NK u n2 k ij NL U dω Ω Ω (C 3 ) KijL = NK U n2 k ij NL U dω ; (K EP ) KijL = NK u,m D imjnnl,n u dω Ω Ω (G ) KiM = NK u,i (α n)np M dω ; (G 2) KiM = nnk U,i Np M dω Ω Ω P NM = N p N Q Np M dω Ω
14 Fully Coupled Formulation Finite Element Discretization f solid Ki = Γ t N u K n jσ ij dγ NK u (α n)n ipdγ Γ p + NK u ( n)ρ sb i dω f fluid Ki = nnk U n ipdγ Γ p + nnk U ρ f b i dω Ω Ω
15 Outline Introduction Verification and Validation Verification Saturated Soils Fully Coupled Formulation Verification Suite Summary
16 Verification Suite Code Verification Memory Function call arguments Code coverage Argument bounds Compiler warnings Computational Solution Verification Drilling of a well [Coussy ] The Case of a Spherical Cavity [Coussy ] Consolidation of a Soil Layer [Coussy 9] Line Injection of a fluid in a Reservoir [Coussy 9] Wave propagation, step displacement [Gajo and Mongiovi 9] Wave propagation, step velocity loading [de Boer et al. 93] Wave propagation, step force loading [Hiremath et al. ]
17 Vertical Consolidation Stresses (kpa) depth (m) 2 Effective Stresses Hydrostatic Pressures 2 Total Stresses 3 γ =. kn/m m Normalized Excess Pore Pressures Quicker dissipation towards the surface z/h = z/h =. 2 time (sec) z/h =.2 Numerical Analysis Normalized depth Normalized Excess Pore Pressure.2... T v = T.2 v =. T v =.2 T v =.... Numerical Analysis m Settlement of soil skeleton (m) Numerical Analysis. z = 9 m. z = m.2 z = 2 m.3 z =. 2 2 time (sec)
18 Vertical Consolidation: Normalized Excess Pore Pressure Numerical Analysis Normalized Excess Pore Pressures z/h = z/h = Time time factor (sec) T v z/h =.2
19 Shock Wave Propagation, Step Displacement x = Boundary Condition: δ (, t) = x -3 cm u x = U x = x -3 cm x. cm Semi-finite Soil column cm u x, U x ( -3 cm) No lateral flow. No lateral displacements. t (sec) (a) (b) (c)
20 Introduction Verification and Validation Saturated Soils Verification Suite Summary Shock Wave Propagation: Step Displacement x.. FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.32) FEM (Newmark, gamma=.7; beta=.).2 FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.32) FEM (Newmark, gamma=.7; beta=.) FEM (k = cm3s/g) FEM (k = cm3s/g). FEM (k = cm3s/g) (k = cm3s/g).2 (k = cm3s/g) x...2. FEM (k = cm3s/g) FEM (k = cm3s/g). FEM (k = cm3s/g). 3 (k = cm s/g) (k = cm3s/g).2.. x 2.. FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.32) FEM (Newmark, gamma=.7; beta=.).2 2 t [ sec] t [ sec] x.. FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.32) FEM (Newmark, gamma=.7; beta=.) FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.32) FEM (Newmark, gamma=.7; beta=.).2. 3 k = cm s/g x.. FEM (k = cm3s/g) (k = cm3s/g).2 (k = cm3s/g) (k = cm3s/g). 2 t [ sec] 3 k = cm s/g x FEM (k = cm3s/g) FEM (k = cm3s/g). t [ sec] t [ sec] FEM Vs x... k = cm3s/g..2 FEM Vs.2. FEM (k = cm3s/g). FEM (k = cm3s/g). FEM (k = cm3s/g).2 (k = cm3s/g) (k = cm3s/g) (k = cm3s/g) k = cm3s/g x 2... FEM (HHT, alpha=.) FEM (HHT, alpha=.3).2.. k = cm3s/g x 2... FEM (HHT, alpha=.) FEM (HHT, alpha=.3).2. t [ sec] t [ sec] k = cm3s/g x (k = cm3s/g) t [ sec] k = cm3s/g x t [ sec] x FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.32) FEM (Newmark, gamma=.7; beta=.).. (k = cm3s/g). t [ sec]..... FEM Vs. k = cm3s/g t [ sec] t [ sec] FEM Vs..2 FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.32) FEM (Newmark, gamma=.7; beta=.) t [ sec] k = cm s/g.. t [ sec]..2.. k = cm3s/g x.2 x FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.2) FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.32) t [ sec] k = cm3s/g x. t [ sec] x.2. k = cm3s/g.. x.2... FEM (HHT, alpha=.) FEM (HHT, alpha=.3).2. t [ sec] k = cm3s/g x. k = cm3s/g. FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.2) FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.32) FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.2) FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.32) x.2. k = cm3s/g... k = cm3s/g x FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.2) FEM (Newmark, gamma=.; beta=.32) x.2.2 k = cm3s/g. k = cm3s/g x. 2 t [ sec] k = cm3s/g x k = cm3s/g x. FEM (HHT, alpha=.) FEM (HHT, alpha=.3).2. t [ sec]... FEM (HHT, alpha=.) FEM (HHT, alpha=.3) FEM (HHT, alpha=.) FEM (HHT, alpha=.3) FEM (HHT, alpha=.) FEM (HHT, alpha=.3).2. t [ sec] t [ sec] k = cm3s/g x... FEM (HHT, alpha=.) FEM (HHT, alpha=.3).2. t [ sec] k = cm3s/g x k = cm3s/g 2 x... FEM (HHT, alpha=.) FEM (HHT, alpha=.3).2. t [ sec]... FEM (HHT, alpha=.) FEM (HHT, alpha=.3) 2.. FEM (HHT, alpha=.) FEM (HHT, alpha=.3). t [ sec] Jeremic t [ sec] t [ sec] FEM (HHT, alpha=.) FEM (HHT, alpha=.3).2. t [ sec] 2
21 Shock Wave Propagation: Porous Solid x FEM Vs.. FEM (k = cm 3 s/g) FEM (k = cm 3 s/g). FEM (k = cm 3 s/g) (k = cm 3 s/g).2 (k = cm 3 s/g) (k = cm 3 s/g) 2 t [ sec]
22 Shock Wave Propagation: Pore Fluid FEM Vs x FEM (k = cm 3 s/g) FEM (k = cm 3 s/g) FEM (k = cm 3 s/g) (k = cm 3 s/g).2 (k = cm 3 s/g) (k = cm 3 s/g) 2 t [ sec]
23 Outline Introduction Verification and Validation Verification Saturated Soils Fully Coupled Formulation Verification Suite Summary
24 Summary Importance of verification and validation for numerical predictions Numerical predictions under uncertainty Would you trust numerical simulations (for design/regulation/evaluation) if your program of choice (simulation tool) did not follow (extensive) verification and validation procedures?
Verification and Validation in Computational Geomechanics
 Verification and Validation in Computational Geomechanics Boris Mahdi Taiebat (UBC), Nima Tafazzoli, Panagiota Tasiopoulou Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of California, Davis
Verification and Validation in Computational Geomechanics Boris Mahdi Taiebat (UBC), Nima Tafazzoli, Panagiota Tasiopoulou Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of California, Davis
Challenges and Tools for Non-Linear SSI Analysis
 Challenges and Tools for Non-Linear SSI Analysis Boris University of California, Davis Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley UCB SSI Meeting, January 2013 Presentation Goals Briefly overview
Challenges and Tools for Non-Linear SSI Analysis Boris University of California, Davis Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley UCB SSI Meeting, January 2013 Presentation Goals Briefly overview
Earthquake Soil Structure Interaction (ESSI) Modeling and Simulation
 Earthquake Soil Structure Interaction (ESSI) Modeling and Simulation Boris Consulting Engineer, Jeremic Engineering Consultants Professor, University of California, Davis Faculty Scientist, Lawrence Berkeley
Earthquake Soil Structure Interaction (ESSI) Modeling and Simulation Boris Consulting Engineer, Jeremic Engineering Consultants Professor, University of California, Davis Faculty Scientist, Lawrence Berkeley
MIDAS Geotechnical Training Series
 MIDAS Geotechnical Training Series Fully Coupled vs Consolidation Analysis Seongwan Bae Angel F. Martinez MIDAS Information Technology Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform
MIDAS Geotechnical Training Series Fully Coupled vs Consolidation Analysis Seongwan Bae Angel F. Martinez MIDAS Information Technology Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform
Verification and Validation for Seismic Wave Propagation Problems
 Chapter 26 Verification and Validation for Seismic Wave Propagation Problems (1989-2-24-25-28-29-21-211-217-) (In collaboration with Dr. Nima Tafazzoli, Dr. Federico Pisanò, Mr. Kohei Watanabe and Mr.
Chapter 26 Verification and Validation for Seismic Wave Propagation Problems (1989-2-24-25-28-29-21-211-217-) (In collaboration with Dr. Nima Tafazzoli, Dr. Federico Pisanò, Mr. Kohei Watanabe and Mr.
Any analysis, static or dynamic, in a FEM follows a standard procedure as defined in fig.(9.1):
 Chapter 9 Model definition 9.1 Main features 9.1.1 Introduction Any analysis, static or dynamic, in a FEM follows a standard procedure as defined in fig.(9.1): The experimental sequence to perform in the
Chapter 9 Model definition 9.1 Main features 9.1.1 Introduction Any analysis, static or dynamic, in a FEM follows a standard procedure as defined in fig.(9.1): The experimental sequence to perform in the
Driven Cavity Example
 BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis
 Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
On Earthquake Soil Structure Interaction Modeling and Simulation
 On Earthquake Soil Structure Interaction Modeling and Simulation N. Tafazzoli, P. Tasiopoulou, J.A. Abell Mena, B. Kamrani, C.-G. Jeong, K. Watanabe, B. Aldridge, J. Anderson, F. Pisanò, M. Martinelli,
On Earthquake Soil Structure Interaction Modeling and Simulation N. Tafazzoli, P. Tasiopoulou, J.A. Abell Mena, B. Kamrani, C.-G. Jeong, K. Watanabe, B. Aldridge, J. Anderson, F. Pisanò, M. Martinelli,
Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian method for nonlinear problems of geomechanics
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian method for nonlinear problems of geomechanics To cite this article: M Nazem et al 2010 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian method for nonlinear problems of geomechanics To cite this article: M Nazem et al 2010 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
Imaging of flow in porous media - from optimal transport to prediction
 Imaging of flow in porous media - from optimal transport to prediction Eldad Haber Dept of EOS and Mathematics, UBC October 15, 2013 With Rowan Lars Jenn Cocket Ruthotto Fohring Outline Prediction is very
Imaging of flow in porous media - from optimal transport to prediction Eldad Haber Dept of EOS and Mathematics, UBC October 15, 2013 With Rowan Lars Jenn Cocket Ruthotto Fohring Outline Prediction is very
Stability Analysis of Particle Methods with Corrected Derivatives
 Stability Analysis of Particle Methods with Corrected Derivatives Shaoping iao and Ted Belytschko Northwestern University Supported by Office of Naval Research Outline: 1. Description of discretization
Stability Analysis of Particle Methods with Corrected Derivatives Shaoping iao and Ted Belytschko Northwestern University Supported by Office of Naval Research Outline: 1. Description of discretization
SPH: Why and what for?
 SPH: Why and what for? 4 th SPHERIC training day David Le Touzé, Fluid Mechanics Laboratory, Ecole Centrale de Nantes / CNRS SPH What for and why? How it works? Why not for everything? Duality of SPH SPH
SPH: Why and what for? 4 th SPHERIC training day David Le Touzé, Fluid Mechanics Laboratory, Ecole Centrale de Nantes / CNRS SPH What for and why? How it works? Why not for everything? Duality of SPH SPH
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems
 1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
Implicit Implementation of Material Point Method for Simulation of Incompressible Problems in Geomechanics
 Implicit Implementation of Material Point Method for Simulation of Incompressible Problems in Geomechanics Seyedfarzad Fatemizadeh M.Sc., Institute of Geotechnics (IGS), University of Stuttgart The Finite
Implicit Implementation of Material Point Method for Simulation of Incompressible Problems in Geomechanics Seyedfarzad Fatemizadeh M.Sc., Institute of Geotechnics (IGS), University of Stuttgart The Finite
On Earthquake Soil Structure Interaction Modeling and Simulation
 On Earthquake Soil Structure Interaction Modeling and Simulation N. Tafazzoli, J.A. Abell Mena, B. Kamrani, C.-G. Jeong, K. Watanabe, B. Aldridge, J. Anderson, F. Pisanò, M. Martinelli, K. Sett, B. Jeremić
On Earthquake Soil Structure Interaction Modeling and Simulation N. Tafazzoli, J.A. Abell Mena, B. Kamrani, C.-G. Jeong, K. Watanabe, B. Aldridge, J. Anderson, F. Pisanò, M. Martinelli, K. Sett, B. Jeremić
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 On the Use of Pore-Scale Computational Models for Two-Phase Porous-media Flows M.A. Celia, P.C Reeves, H.K. Dahle Environmental Engineering and Water Resources Program, Department of Civil Engineering
On the Use of Pore-Scale Computational Models for Two-Phase Porous-media Flows M.A. Celia, P.C Reeves, H.K. Dahle Environmental Engineering and Water Resources Program, Department of Civil Engineering
2.7 Cloth Animation. Jacobs University Visualization and Computer Graphics Lab : Advanced Graphics - Chapter 2 123
 2.7 Cloth Animation 320491: Advanced Graphics - Chapter 2 123 Example: Cloth draping Image Michael Kass 320491: Advanced Graphics - Chapter 2 124 Cloth using mass-spring model Network of masses and springs
2.7 Cloth Animation 320491: Advanced Graphics - Chapter 2 123 Example: Cloth draping Image Michael Kass 320491: Advanced Graphics - Chapter 2 124 Cloth using mass-spring model Network of masses and springs
Development of the Compliant Mooring Line Model for FLOW-3D
 Flow Science Report 08-15 Development of the Compliant Mooring Line Model for FLOW-3D Gengsheng Wei Flow Science, Inc. October 2015 1. Introduction Mooring systems are common in offshore structures, ship
Flow Science Report 08-15 Development of the Compliant Mooring Line Model for FLOW-3D Gengsheng Wei Flow Science, Inc. October 2015 1. Introduction Mooring systems are common in offshore structures, ship
3D Nearest-Nodes Finite Element Method for Solid Continuum Analysis
 Adv. Theor. Appl. Mech., Vol. 1, 2008, no. 3, 131-139 3D Nearest-Nodes Finite Element Method for Solid Continuum Analysis Yunhua Luo Department of Mechanical & Manufacturing Engineering, University of
Adv. Theor. Appl. Mech., Vol. 1, 2008, no. 3, 131-139 3D Nearest-Nodes Finite Element Method for Solid Continuum Analysis Yunhua Luo Department of Mechanical & Manufacturing Engineering, University of
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SHAKING TABLE TESTS ON DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF DRY SAND
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SHAKING TABLE TESTS ON DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF DRY SAND F. Jafarzadeh 1, D. Faghihi 2 and M. Ehsani 3 1 Assistant Professor, Civil Eng Dept, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SHAKING TABLE TESTS ON DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF DRY SAND F. Jafarzadeh 1, D. Faghihi 2 and M. Ehsani 3 1 Assistant Professor, Civil Eng Dept, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran,
The ECHO commands. Synopsis. Syntax
 The ECHO commands Synopsis The ECHO commands are used to control the verification or echo printing of various portions of the input data The ECHO commands have no effect on the results of an analysis Syntax
The ECHO commands Synopsis The ECHO commands are used to control the verification or echo printing of various portions of the input data The ECHO commands have no effect on the results of an analysis Syntax
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION
 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION 7 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION In this tutorial the influence of a vibrating source on its surrounding soil is studied.
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION 7 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A GENERATOR ON AN ELASTIC FOUNDATION In this tutorial the influence of a vibrating source on its surrounding soil is studied.
Mechanical Vibrations Chapter 8
 Mechanical Vibrations Chapter 8 Peter Avitabile Mechanical Engineering Department University of Massachusetts Lowell 1 Dr. Peter Avitabile Numerical Methods - Direct Integration The equation of motion
Mechanical Vibrations Chapter 8 Peter Avitabile Mechanical Engineering Department University of Massachusetts Lowell 1 Dr. Peter Avitabile Numerical Methods - Direct Integration The equation of motion
New developments in numerical modelling of pile installation
 New developments in numerical modelling of pile installation Nguyen Phuong, Frits van Tol, Alexander Rohe 18 September 2014 KIVI Geotechnical Lectures Evening TU Delft Displacement piles à installation
New developments in numerical modelling of pile installation Nguyen Phuong, Frits van Tol, Alexander Rohe 18 September 2014 KIVI Geotechnical Lectures Evening TU Delft Displacement piles à installation
A MULTI-DOMAIN ALE ALGORITHM FOR SIMULATING FLOWS INSIDE FREE-PISTON DRIVEN HYPERSONIC TEST FACILITIES
 A MULTI-DOMAIN ALE ALGORITHM FOR SIMULATING FLOWS INSIDE FREE-PISTON DRIVEN HYPERSONIC TEST FACILITIES Khalil Bensassi, and Herman Deconinck Von Karman Institute for Fluid Dynamics Aeronautics & Aerospace
A MULTI-DOMAIN ALE ALGORITHM FOR SIMULATING FLOWS INSIDE FREE-PISTON DRIVEN HYPERSONIC TEST FACILITIES Khalil Bensassi, and Herman Deconinck Von Karman Institute for Fluid Dynamics Aeronautics & Aerospace
A Novel Approach to High Speed Collision
 A Novel Approach to High Speed Collision Avril Slone University of Greenwich Motivation High Speed Impact Currently a very active research area. Generic projectile- target collision 11 th September 2001.
A Novel Approach to High Speed Collision Avril Slone University of Greenwich Motivation High Speed Impact Currently a very active research area. Generic projectile- target collision 11 th September 2001.
Inverse Analysis of Soil Parameters Based on Deformation of a Bank Protection Structure
 Inverse Analysis of Soil Parameters Based on Deformation of a Bank Protection Structure Yixuan Xing 1, Rui Hu 2 *, Quan Liu 1 1 Geoscience Centre, University of Goettingen, Goettingen, Germany 2 School
Inverse Analysis of Soil Parameters Based on Deformation of a Bank Protection Structure Yixuan Xing 1, Rui Hu 2 *, Quan Liu 1 1 Geoscience Centre, University of Goettingen, Goettingen, Germany 2 School
course outline basic principles of numerical analysis, intro FEM
 idealization, equilibrium, solutions, interpretation of results types of numerical engineering problems continuous vs discrete systems direct stiffness approach differential & variational formulation introduction
idealization, equilibrium, solutions, interpretation of results types of numerical engineering problems continuous vs discrete systems direct stiffness approach differential & variational formulation introduction
Period #10: Multi dimensional Fluid Flow in Soils (II)
 Period #10: Multi dimensional Fluid Flow in Soils (II) A. Review Our objective is to solve multi dimensional fluid flow problems in soils. Last time, mass conservation and Darcy s Law were used to derive
Period #10: Multi dimensional Fluid Flow in Soils (II) A. Review Our objective is to solve multi dimensional fluid flow problems in soils. Last time, mass conservation and Darcy s Law were used to derive
FEM techniques for interfacial flows
 FEM techniques for interfacial flows How to avoid the explicit reconstruction of interfaces Stefan Turek, Shu-Ren Hysing (ture@featflow.de) Institute for Applied Mathematics University of Dortmund Int.
FEM techniques for interfacial flows How to avoid the explicit reconstruction of interfaces Stefan Turek, Shu-Ren Hysing (ture@featflow.de) Institute for Applied Mathematics University of Dortmund Int.
Homogenization and numerical Upscaling. Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow
 Homogenization and numerical Upscaling Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow Insa Neuweiler Institute of Hydromechanics, University of Stuttgart Outline Block 1: Introduction and Repetition Homogenization
Homogenization and numerical Upscaling Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow Insa Neuweiler Institute of Hydromechanics, University of Stuttgart Outline Block 1: Introduction and Repetition Homogenization
Finite element method - tutorial no. 1
 Martin NESLÁDEK Faculty of mechanical engineering, CTU in Prague 11th October 2017 1 / 22 Introduction to the tutorials E-mail: martin.nesladek@fs.cvut.cz Room no. 622 (6th floor - Dept. of mechanics,
Martin NESLÁDEK Faculty of mechanical engineering, CTU in Prague 11th October 2017 1 / 22 Introduction to the tutorials E-mail: martin.nesladek@fs.cvut.cz Room no. 622 (6th floor - Dept. of mechanics,
INTEGRATION SCHEMES FOR THE TRANSIENT DYNAMICS OF NONLINEAR CABLE STRUCTURES
 6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 1115 June 2018, Glasgow, UK INTEGRATION SCHEMES FOR THE TRANSIENT DYNAMICS OF
6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 1115 June 2018, Glasgow, UK INTEGRATION SCHEMES FOR THE TRANSIENT DYNAMICS OF
2008 International ANSYS Conference Simulation of Densification in Granular Materials and Geomaterials
 2008 International ANSYS Conference Simulation of Densification in Granular Materials and Geomaterials Lewis Hartless, PE Principal Engineer Babcock & Wilcox lchartless@babcock.com 1 Overview An implicit
2008 International ANSYS Conference Simulation of Densification in Granular Materials and Geomaterials Lewis Hartless, PE Principal Engineer Babcock & Wilcox lchartless@babcock.com 1 Overview An implicit
CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 ME 475: Computer-Aided Design of Structures 1-1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Analysis versus Design 1.2 Basic Steps in Analysis 1.3 What is the Finite Element Method? 1.4 Geometrical Representation, Discretization
ME 475: Computer-Aided Design of Structures 1-1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Analysis versus Design 1.2 Basic Steps in Analysis 1.3 What is the Finite Element Method? 1.4 Geometrical Representation, Discretization
Developer s Tips. Groundwater analysis using Slide
 Developer s Tips Groundwater analysis using Slide In this article we introduce the new groundwater/seepage analysis module, which was built into version 5.0 of Slide. The groundwater module uses a finite
Developer s Tips Groundwater analysis using Slide In this article we introduce the new groundwater/seepage analysis module, which was built into version 5.0 of Slide. The groundwater module uses a finite
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE SHALLOW WATER EQUATIONS USING A TIME-CENTERED SPLIT-IMPLICIT METHOD
 18th Engineering Mechanics Division Conference (EMD007) NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE SHALLOW WATER EQUATIONS USING A TIME-CENTERED SPLIT-IMPLICIT METHOD Abstract S. Fu University of Texas at Austin, Austin,
18th Engineering Mechanics Division Conference (EMD007) NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE SHALLOW WATER EQUATIONS USING A TIME-CENTERED SPLIT-IMPLICIT METHOD Abstract S. Fu University of Texas at Austin, Austin,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY. Analyzing wind flow around the square plate using ADINA Project. Ankur Bajoria
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Analyzing wind flow around the square plate using ADINA 2.094 - Project Ankur Bajoria May 1, 2008 Acknowledgement I would like to thank ADINA R & D, Inc for the full
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Analyzing wind flow around the square plate using ADINA 2.094 - Project Ankur Bajoria May 1, 2008 Acknowledgement I would like to thank ADINA R & D, Inc for the full
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 111 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 111 (2015 ) 115 120 XXV R-S-P seminar, Theoretical Foundation of Civil Engineering (24RSP) (TFoCE 2015) Numerical simulation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 111 (2015 ) 115 120 XXV R-S-P seminar, Theoretical Foundation of Civil Engineering (24RSP) (TFoCE 2015) Numerical simulation
Control Volume Finite Difference On Adaptive Meshes
 Control Volume Finite Difference On Adaptive Meshes Sanjay Kumar Khattri, Gunnar E. Fladmark, Helge K. Dahle Department of Mathematics, University Bergen, Norway. sanjay@mi.uib.no Summary. In this work
Control Volume Finite Difference On Adaptive Meshes Sanjay Kumar Khattri, Gunnar E. Fladmark, Helge K. Dahle Department of Mathematics, University Bergen, Norway. sanjay@mi.uib.no Summary. In this work
Module 1: Introduction to Finite Element Analysis. Lecture 4: Steps in Finite Element Analysis
 25 Module 1: Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Lecture 4: Steps in Finite Element Analysis 1.4.1 Loading Conditions There are multiple loading conditions which may be applied to a system. The load
25 Module 1: Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Lecture 4: Steps in Finite Element Analysis 1.4.1 Loading Conditions There are multiple loading conditions which may be applied to a system. The load
A Wavelet-Based Method for Simulation of Seismic Wave Propagation
 AGU Fall Meeting, A Wavelet-Based Method for Simulation of Seismic Wave Propagation Tae-Kyung Hong & B.L.N. Kennett Research School of Earth Sciences The Australian National University Abstract Seismic
AGU Fall Meeting, A Wavelet-Based Method for Simulation of Seismic Wave Propagation Tae-Kyung Hong & B.L.N. Kennett Research School of Earth Sciences The Australian National University Abstract Seismic
A COUPLED FINITE VOLUME SOLVER FOR THE SOLUTION OF LAMINAR TURBULENT INCOMPRESSIBLE AND COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS
 A COUPLED FINITE VOLUME SOLVER FOR THE SOLUTION OF LAMINAR TURBULENT INCOMPRESSIBLE AND COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS L. Mangani Maschinentechnik CC Fluidmechanik und Hydromaschinen Hochschule Luzern Technik& Architektur
A COUPLED FINITE VOLUME SOLVER FOR THE SOLUTION OF LAMINAR TURBULENT INCOMPRESSIBLE AND COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS L. Mangani Maschinentechnik CC Fluidmechanik und Hydromaschinen Hochschule Luzern Technik& Architektur
Recent Developments in Computer Simulations and Visualization for Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering Problems Boris Jeremić
 Recent Developments in Computer Simulations and Visualization for Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering Problems Boris Jeremić Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California,
Recent Developments in Computer Simulations and Visualization for Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering Problems Boris Jeremić Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California,
SNAC: a tutorial. Eunseo Choi. July 29, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
 SNAC: a tutorial Eunseo Choi Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory July 29, 2010 What is SNAC? StGermaiN Analysis of Continua 2 of 20 What is SNAC? StGermaiN Analysis of Continua 3-D Version of FLAC 2 of 20
SNAC: a tutorial Eunseo Choi Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory July 29, 2010 What is SNAC? StGermaiN Analysis of Continua 2 of 20 What is SNAC? StGermaiN Analysis of Continua 3-D Version of FLAC 2 of 20
Offshore Platform Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) Simulation
 Offshore Platform Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) Simulation Ali Marzaban, CD-adapco Murthy Lakshmiraju, CD-adapco Nigel Richardson, CD-adapco Mike Henneke, CD-adapco Guangyu Wu, Chevron Pedro M. Vargas,
Offshore Platform Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) Simulation Ali Marzaban, CD-adapco Murthy Lakshmiraju, CD-adapco Nigel Richardson, CD-adapco Mike Henneke, CD-adapco Guangyu Wu, Chevron Pedro M. Vargas,
Continuum finite element analysis of strain localization in slopes
 Continuum finite element analysis of strain localization in slopes Richard A. Regueiro and Ronaldo I. Borja Department of Civil Engineering, Stanford University, USA ABSTRACT: This paper presents a continuum
Continuum finite element analysis of strain localization in slopes Richard A. Regueiro and Ronaldo I. Borja Department of Civil Engineering, Stanford University, USA ABSTRACT: This paper presents a continuum
PATCH TEST OF HEXAHEDRAL ELEMENT
 Annual Report of ADVENTURE Project ADV-99- (999) PATCH TEST OF HEXAHEDRAL ELEMENT Yoshikazu ISHIHARA * and Hirohisa NOGUCHI * * Mitsubishi Research Institute, Inc. e-mail: y-ishi@mri.co.jp * Department
Annual Report of ADVENTURE Project ADV-99- (999) PATCH TEST OF HEXAHEDRAL ELEMENT Yoshikazu ISHIHARA * and Hirohisa NOGUCHI * * Mitsubishi Research Institute, Inc. e-mail: y-ishi@mri.co.jp * Department
Modelling of Tunnels in 2D & 3D
 MIDAS Geotechnical Know-how Sharing Series November 28 th, 2017 (Tue) 10:00 ~ 11:00 AM (CET) Session 3. Modelling of Tunnels in 2D & 3D JaeSeok Yang Principal Geotechnical Engineer, MIDAS IT Integrated
MIDAS Geotechnical Know-how Sharing Series November 28 th, 2017 (Tue) 10:00 ~ 11:00 AM (CET) Session 3. Modelling of Tunnels in 2D & 3D JaeSeok Yang Principal Geotechnical Engineer, MIDAS IT Integrated
Possibility of Implicit LES for Two-Dimensional Incompressible Lid-Driven Cavity Flow Based on COMSOL Multiphysics
 Possibility of Implicit LES for Two-Dimensional Incompressible Lid-Driven Cavity Flow Based on COMSOL Multiphysics Masanori Hashiguchi 1 1 Keisoku Engineering System Co., Ltd. 1-9-5 Uchikanda, Chiyoda-ku,
Possibility of Implicit LES for Two-Dimensional Incompressible Lid-Driven Cavity Flow Based on COMSOL Multiphysics Masanori Hashiguchi 1 1 Keisoku Engineering System Co., Ltd. 1-9-5 Uchikanda, Chiyoda-ku,
Nonoscillatory Central Schemes on Unstructured Triangulations for Hyperbolic Systems of Conservation Laws
 Nonoscillatory Central Schemes on Unstructured Triangulations for Hyperbolic Systems of Conservation Laws Ivan Christov Bojan Popov Department of Mathematics, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas
Nonoscillatory Central Schemes on Unstructured Triangulations for Hyperbolic Systems of Conservation Laws Ivan Christov Bojan Popov Department of Mathematics, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas
LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA.
 12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference FSI/ALE(1) LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA Part 1 Facundo Del
12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference FSI/ALE(1) LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA Part 1 Facundo Del
14 Dec 94. Hydrocode Micro-Model Concept for Multi-Component Flow in Sediments Hans U. Mair
 Hydrocode Micro-Model Concept for Multi-Component Flow in Sediments Hans U. Mair mairh@asme.org Background Hydrocodes are Computational Mechanics tools that simulate the compressible dynamics (i.e., shock
Hydrocode Micro-Model Concept for Multi-Component Flow in Sediments Hans U. Mair mairh@asme.org Background Hydrocodes are Computational Mechanics tools that simulate the compressible dynamics (i.e., shock
Unstructured Mesh Generation for Implicit Moving Geometries and Level Set Applications
 Unstructured Mesh Generation for Implicit Moving Geometries and Level Set Applications Per-Olof Persson (persson@mit.edu) Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology http://www.mit.edu/
Unstructured Mesh Generation for Implicit Moving Geometries and Level Set Applications Per-Olof Persson (persson@mit.edu) Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology http://www.mit.edu/
GEOSTUDIO Tutorials Results and Procedure Comparison
 GEOSTUDIO Tutorials Results and Procedure Comparison Angel Francisco Martinez Application Engineer MIDAS IT Estados Unidos Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element
GEOSTUDIO Tutorials Results and Procedure Comparison Angel Francisco Martinez Application Engineer MIDAS IT Estados Unidos Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element
Characteristic Aspects of SPH Solutions
 Characteristic Aspects of SPH Solutions for Free Surface Problems: Source and Possible Treatment of High Frequency Numerical Oscillations of Local Loads. A. Colagrossi*, D. Le Touzé & G.Colicchio* *INSEAN
Characteristic Aspects of SPH Solutions for Free Surface Problems: Source and Possible Treatment of High Frequency Numerical Oscillations of Local Loads. A. Colagrossi*, D. Le Touzé & G.Colicchio* *INSEAN
FINITE ELEMENT MODELING OF TRANSIENT WAVE PHENOMENA AT
 FINITE ELEMENT MODELING OF TRANSIENT WAVE PHENOMENA AT SOLIDIFLUID INTERFACES T. Xue, W. Lord, S. Udpa, L. Udpa and M. Mina Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Iowa State University Ames,
FINITE ELEMENT MODELING OF TRANSIENT WAVE PHENOMENA AT SOLIDIFLUID INTERFACES T. Xue, W. Lord, S. Udpa, L. Udpa and M. Mina Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Iowa State University Ames,
Fluid structure interaction analysis: vortex shedding induced vibrations
 Fluid structure interaction analysis: vortex shedding induced vibrations N. Di Domenico, M. E. * University of Rome «Tor Vergata», Department of Enterprise Engineering «Mario Lucertini» A. Wade, T. Berg,
Fluid structure interaction analysis: vortex shedding induced vibrations N. Di Domenico, M. E. * University of Rome «Tor Vergata», Department of Enterprise Engineering «Mario Lucertini» A. Wade, T. Berg,
Purdue e-pubs. Purdue University. Jeongil Park Samsung Electronics Co. Nasir Bilal Purdue University. Douglas E. Adams Purdue University
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 26 Development of a Two-Dimensional Finite Element Model of a Suction Valve for Reduction
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 26 Development of a Two-Dimensional Finite Element Model of a Suction Valve for Reduction
Figure 2: Water Into Kerosene, Volume Fraction (Left) And Total Density Of Mixture (Right)
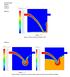 Jared Bottlinger MAE598 Project 3 11/16/17 Task 1 a) Figure 1: Volume Fraction Of Water At 0.4s Task 1 b) Figure 2: Water Into Kerosene, Volume Fraction (Left) And Total Density Of Mixture (Right) Task
Jared Bottlinger MAE598 Project 3 11/16/17 Task 1 a) Figure 1: Volume Fraction Of Water At 0.4s Task 1 b) Figure 2: Water Into Kerosene, Volume Fraction (Left) And Total Density Of Mixture (Right) Task
Example Simulations in OpenFOAM
 Example Simulations in OpenFOAM Hrvoje Jasak h.jasak@wikki.co.uk Wikki Ltd, United Kingdom FSB, University of Zagreb, Croatia 18/Nov/2005 Example Simulations in OpenFOAM p.1/26 Outline Objective Present
Example Simulations in OpenFOAM Hrvoje Jasak h.jasak@wikki.co.uk Wikki Ltd, United Kingdom FSB, University of Zagreb, Croatia 18/Nov/2005 Example Simulations in OpenFOAM p.1/26 Outline Objective Present
Introduction to the Finite Element Method (3)
 Introduction to the Finite Element Method (3) Petr Kabele Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Civil Engineering Czech Republic petr.kabele@fsv.cvut.cz people.fsv.cvut.cz/~pkabele 1 Outline
Introduction to the Finite Element Method (3) Petr Kabele Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Civil Engineering Czech Republic petr.kabele@fsv.cvut.cz people.fsv.cvut.cz/~pkabele 1 Outline
CS205b/CME306. Lecture 9
 CS205b/CME306 Lecture 9 1 Convection Supplementary Reading: Osher and Fedkiw, Sections 3.3 and 3.5; Leveque, Sections 6.7, 8.3, 10.2, 10.4. For a reference on Newton polynomial interpolation via divided
CS205b/CME306 Lecture 9 1 Convection Supplementary Reading: Osher and Fedkiw, Sections 3.3 and 3.5; Leveque, Sections 6.7, 8.3, 10.2, 10.4. For a reference on Newton polynomial interpolation via divided
Development of Hybrid Fluid Jet / Float Polishing Process
 COMSOL Conference - Tokyo 2013 Development of Hybrid Fluid Jet / Float Polishing Process A. Beaucamp, Y. Namba Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Chubu University, Japan Zeeko LTD, United Kingdom Research
COMSOL Conference - Tokyo 2013 Development of Hybrid Fluid Jet / Float Polishing Process A. Beaucamp, Y. Namba Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Chubu University, Japan Zeeko LTD, United Kingdom Research
Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown
 Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown 17-1 Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown When the water level at a dam drops, the stabilizing force due to the weight of the water is removed. If the dam material has a low permeability
Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown 17-1 Multi-Stage Rapid Drawdown When the water level at a dam drops, the stabilizing force due to the weight of the water is removed. If the dam material has a low permeability
ENHANCED STRUCTURE CAE SOLUTION WITH MOLDING EFFECT FOR AUTOMOTIVE PARTS
 ENHANCED STRUCTURE CAE SOLUTION WITH MOLDING EFFECT FOR AUTOMOTIVE PARTS Allen Y. Peng*, Wen-Hsien Yang, David C. Hsu CoreTech System Co., Ltd., HsinChu, Taiwan, ROC Abstract An increasing number of automotive
ENHANCED STRUCTURE CAE SOLUTION WITH MOLDING EFFECT FOR AUTOMOTIVE PARTS Allen Y. Peng*, Wen-Hsien Yang, David C. Hsu CoreTech System Co., Ltd., HsinChu, Taiwan, ROC Abstract An increasing number of automotive
SIMULATION OF A DETONATION CHAMBER TEST CASE
 SIMULATION OF A DETONATION CHAMBER TEST CASE Daniel Hilding Engineering Research Nordic AB Garnisonen I4, Byggnad 5 SE-582 10 Linköping www.erab.se daniel.hilding@erab.se Abstract The purpose of a detonation
SIMULATION OF A DETONATION CHAMBER TEST CASE Daniel Hilding Engineering Research Nordic AB Garnisonen I4, Byggnad 5 SE-582 10 Linköping www.erab.se daniel.hilding@erab.se Abstract The purpose of a detonation
Simulation of liquid cube fracture with SPH
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of liquid cube fracture with SPH To cite this article: M N Davydov 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 754 062001 View the article online for updates
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of liquid cube fracture with SPH To cite this article: M N Davydov 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 754 062001 View the article online for updates
Recent developments in simulation, optimization and control of flexible multibody systems
 Recent developments in simulation, optimization and control of flexible multibody systems Olivier Brüls Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering University of Liège o.bruls@ulg.ac.be Katholieke
Recent developments in simulation, optimization and control of flexible multibody systems Olivier Brüls Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering University of Liège o.bruls@ulg.ac.be Katholieke
Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus
 Tutorial 8. Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D, turbulent flow of a non-newtonian fluid. Turbulent
Tutorial 8. Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D, turbulent flow of a non-newtonian fluid. Turbulent
Diffpack- A Flexible Development Framework for the Numerical Modeling and Solution of Partial Differential Equations
 Diffpack- A Flexible Development Framework for the Numerical Modeling and Solution of Partial Differential Equations Peter Böhm, Frank Vogel Bratislava, July 25 th 2005 Outline inutech - Diffpack - an
Diffpack- A Flexible Development Framework for the Numerical Modeling and Solution of Partial Differential Equations Peter Böhm, Frank Vogel Bratislava, July 25 th 2005 Outline inutech - Diffpack - an
Computational methods - modelling and simulation
 Computational methods - modelling and simulation J. Pamin With thanks to: Authors of presented simulations C.A. Felippa (Univ. of Colorado at Boulder) www.colorado.edu/engineering/cas/courses.d/ifem.d
Computational methods - modelling and simulation J. Pamin With thanks to: Authors of presented simulations C.A. Felippa (Univ. of Colorado at Boulder) www.colorado.edu/engineering/cas/courses.d/ifem.d
2.5 D BEM modelisation of ground structure interaction
 paper ID: 510/p.1 2.5 D BEM modelisation of ground structure interaction Philippe JEAN CSTB, 24 rue Joseph Fourier, 38400 Saint Martin d Hères, France, jean@cstb.fr 2.5 D Green functions of continuous
paper ID: 510/p.1 2.5 D BEM modelisation of ground structure interaction Philippe JEAN CSTB, 24 rue Joseph Fourier, 38400 Saint Martin d Hères, France, jean@cstb.fr 2.5 D Green functions of continuous
NOISE PROPAGATION FROM VIBRATING STRUCTURES
 NOISE PROPAGATION FROM VIBRATING STRUCTURES Abstract R. Helfrich, M. Spriegel (INTES GmbH, Germany) Noise and noise exposure are becoming more important in product development due to environmental legislation.
NOISE PROPAGATION FROM VIBRATING STRUCTURES Abstract R. Helfrich, M. Spriegel (INTES GmbH, Germany) Noise and noise exposure are becoming more important in product development due to environmental legislation.
Validation of a Multi-physics Simulation Approach for Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter Design Application
 Validation of a Multi-physics Simulation Approach for Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter Design Application Setup Numerical Turbulence ing by March 15, 2015 Markets Insertion electromagnetic flowmeters
Validation of a Multi-physics Simulation Approach for Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter Design Application Setup Numerical Turbulence ing by March 15, 2015 Markets Insertion electromagnetic flowmeters
LS-DYNA CONTACT PROCEDURE ANALYSIS FOR SELECTED MECHANICAL SYSTEMS
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 22, No. 1 2015 LS-DYNA CONTACT PROCEDURE ANALYSIS FOR SELECTED MECHANICAL SYSTEMS Jerzy Małachowski, Jakub Bukala, Krzysztof Damaziak, Michał Tomaszewski
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 22, No. 1 2015 LS-DYNA CONTACT PROCEDURE ANALYSIS FOR SELECTED MECHANICAL SYSTEMS Jerzy Małachowski, Jakub Bukala, Krzysztof Damaziak, Michał Tomaszewski
Table of contents for: Waves and Mean Flows by Oliver Bühler Cambridge University Press 2009 Monographs on Mechanics. Contents.
 Table of contents for: Waves and Mean Flows by Oliver Bühler Cambridge University Press 2009 Monographs on Mechanics. Preface page 2 Part I Fluid Dynamics and Waves 7 1 Elements of fluid dynamics 9 1.1
Table of contents for: Waves and Mean Flows by Oliver Bühler Cambridge University Press 2009 Monographs on Mechanics. Preface page 2 Part I Fluid Dynamics and Waves 7 1 Elements of fluid dynamics 9 1.1
Olivier Brüls. Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering University of Liège
 Fully coupled simulation of mechatronic and flexible multibody systems: An extended finite element approach Olivier Brüls Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering University of Liège o.bruls@ulg.ac.be
Fully coupled simulation of mechatronic and flexible multibody systems: An extended finite element approach Olivier Brüls Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering University of Liège o.bruls@ulg.ac.be
USE OF V S30 TO REPRESENT LOCAL SITE CONDITIONS
 USE OF V S30 TO REPRESENT LOCAL SITE CONDITIONS Presented by I. M. Idriss, Professor Emeritus University of California at Davis e-mail: imidriss@aol.com Presented at the Session 6 on The V s30 Dialog How
USE OF V S30 TO REPRESENT LOCAL SITE CONDITIONS Presented by I. M. Idriss, Professor Emeritus University of California at Davis e-mail: imidriss@aol.com Presented at the Session 6 on The V s30 Dialog How
Verification and Validation in CFD and Heat Transfer: ANSYS Practice and the New ASME Standard
 Verification and Validation in CFD and Heat Transfer: ANSYS Practice and the New ASME Standard Dimitri P. Tselepidakis & Lewis Collins ASME 2012 Verification and Validation Symposium May 3 rd, 2012 1 Outline
Verification and Validation in CFD and Heat Transfer: ANSYS Practice and the New ASME Standard Dimitri P. Tselepidakis & Lewis Collins ASME 2012 Verification and Validation Symposium May 3 rd, 2012 1 Outline
IMPROVING THE NUMERICAL ACCURACY OF HYDROTHERMAL RESERVOIR SIMULATIONS USING THE CIP SCHEME WITH THIRD-ORDER ACCURACY
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 2012 SGP-TR-194 IMPROVING THE NUMERICAL ACCURACY OF HYDROTHERMAL
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 2012 SGP-TR-194 IMPROVING THE NUMERICAL ACCURACY OF HYDROTHERMAL
IMAGE ANALYSIS DEDICATED TO POLYMER INJECTION MOLDING
 Image Anal Stereol 2001;20:143-148 Original Research Paper IMAGE ANALYSIS DEDICATED TO POLYMER INJECTION MOLDING DAVID GARCIA 1, GUY COURBEBAISSE 2 AND MICHEL JOURLIN 3 1 European Polymer Institute (PEP),
Image Anal Stereol 2001;20:143-148 Original Research Paper IMAGE ANALYSIS DEDICATED TO POLYMER INJECTION MOLDING DAVID GARCIA 1, GUY COURBEBAISSE 2 AND MICHEL JOURLIN 3 1 European Polymer Institute (PEP),
Prediction Of Ship Shock Response & Damage w/ The Navy Enhanced Sierra Mechanics (NESM) Code. Dr. Tom Moyer, NSWC/CD Sr. Research Scientist
 Prediction Of Ship Shock Response & Damage w/ The Navy Enhanced Sierra Mechanics (NESM) Code Dr. Tom Moyer, NSWC/CD Sr. Research Scientist 1 U.S. Navy Need For Robust Shock/Damage M&S Capability Design
Prediction Of Ship Shock Response & Damage w/ The Navy Enhanced Sierra Mechanics (NESM) Code Dr. Tom Moyer, NSWC/CD Sr. Research Scientist 1 U.S. Navy Need For Robust Shock/Damage M&S Capability Design
OPENSEES Soil-Pile Interaction Study under Lateral Spread Loading
 OPENSEES Soil-Pile Interaction Study under Lateral Spread Loading Po-Lam - EarthMechanics Pedro Arduino UW Peter Mackenzie-Helnwein UW Overview Introduction Background & Common Practice 3D Analysis of
OPENSEES Soil-Pile Interaction Study under Lateral Spread Loading Po-Lam - EarthMechanics Pedro Arduino UW Peter Mackenzie-Helnwein UW Overview Introduction Background & Common Practice 3D Analysis of
Transactions on Information and Communications Technologies vol 15, 1997 WIT Press, ISSN
 Optimization of time dependent adaptive finite element methods K.-H. Elmer Curt-Risch-Institut, Universitat Hannover Appelstr. 9a, D-30167 Hannover, Germany Abstract To obtain reliable numerical solutions
Optimization of time dependent adaptive finite element methods K.-H. Elmer Curt-Risch-Institut, Universitat Hannover Appelstr. 9a, D-30167 Hannover, Germany Abstract To obtain reliable numerical solutions
Transient Groundwater Analysis
 Transient Groundwater Analysis 18-1 Transient Groundwater Analysis A transient groundwater analysis may be important when there is a time-dependent change in pore pressure. This will occur when groundwater
Transient Groundwater Analysis 18-1 Transient Groundwater Analysis A transient groundwater analysis may be important when there is a time-dependent change in pore pressure. This will occur when groundwater
Embankment design and soil settlement prediction D-SETTLEMENT
 Embankment design and soil settlement prediction D-SETTLEMENT Embankment design and soil settlement prediction D-SETTLEMENT General Peat and clay layers will compress significantly after embankment construction,
Embankment design and soil settlement prediction D-SETTLEMENT Embankment design and soil settlement prediction D-SETTLEMENT General Peat and clay layers will compress significantly after embankment construction,
Numerical Methods for (Time-Dependent) HJ PDEs
 Numerical Methods for (Time-Dependent) HJ PDEs Ian Mitchell Department of Computer Science The University of British Columbia research supported by National Science and Engineering Research Council of
Numerical Methods for (Time-Dependent) HJ PDEs Ian Mitchell Department of Computer Science The University of British Columbia research supported by National Science and Engineering Research Council of
CHAPTER 3. Elementary Fluid Dynamics
 CHAPTER 3. Elementary Fluid Dynamics - Understanding the physics of fluid in motion - Derivation of the Bernoulli equation from Newton s second law Basic Assumptions of fluid stream, unless a specific
CHAPTER 3. Elementary Fluid Dynamics - Understanding the physics of fluid in motion - Derivation of the Bernoulli equation from Newton s second law Basic Assumptions of fluid stream, unless a specific
Moment-rotation Behavior of Shallow Foundations with Fixed Vertical Load Using PLAXIS 3D
 6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand Moment-rotation Behavior of Shallow Foundations with Fixed Vertical Load Using PLAXIS 3D
6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 2015 Christchurch, New Zealand Moment-rotation Behavior of Shallow Foundations with Fixed Vertical Load Using PLAXIS 3D
The Finite Element Method
 The Finite Element Method A Practical Course G. R. Liu and S. S. Quek Chapter 1: Computational modeling An overview 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION PHYSICAL PROBLEMS IN ENGINEERING COMPUTATIONAL MODELLING USING
The Finite Element Method A Practical Course G. R. Liu and S. S. Quek Chapter 1: Computational modeling An overview 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION PHYSICAL PROBLEMS IN ENGINEERING COMPUTATIONAL MODELLING USING
A Study on Consolidation Behavior of Dredged Clay with Horizontal Drains
 A Study on Consolidation Behavior of Dredged Clay ith Horizontal Drains Y. S. Jang Dept of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Dongguk Universit Seoul, Korea ysang@dongguk.edu C. S. Park Geotechnical
A Study on Consolidation Behavior of Dredged Clay ith Horizontal Drains Y. S. Jang Dept of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Dongguk Universit Seoul, Korea ysang@dongguk.edu C. S. Park Geotechnical
Incompressible Viscous Flow Simulations Using the Petrov-Galerkin Finite Element Method
 Copyright c 2007 ICCES ICCES, vol.4, no.1, pp.11-18, 2007 Incompressible Viscous Flow Simulations Using the Petrov-Galerkin Finite Element Method Kazuhiko Kakuda 1, Tomohiro Aiso 1 and Shinichiro Miura
Copyright c 2007 ICCES ICCES, vol.4, no.1, pp.11-18, 2007 Incompressible Viscous Flow Simulations Using the Petrov-Galerkin Finite Element Method Kazuhiko Kakuda 1, Tomohiro Aiso 1 and Shinichiro Miura
CFD-DEM MODELING OF THE GRAVEL PACKING PROCESS DURING PETROLEUM HORIZONTAL WELL COMPLETIONS
 Mecánica Computacional Vol XXIX, págs. 8651-8659 (artículo completo) Eduardo Dvorkin, Marcela Goldschmit, Mario Storti (Eds.) Buenos Aires, Argentina, 15-18 Noviembre 2010 CFD-DEM MODELING OF THE GRAVEL
Mecánica Computacional Vol XXIX, págs. 8651-8659 (artículo completo) Eduardo Dvorkin, Marcela Goldschmit, Mario Storti (Eds.) Buenos Aires, Argentina, 15-18 Noviembre 2010 CFD-DEM MODELING OF THE GRAVEL
Comparison of Central and Upwind Flux Averaging in Overlapping Finite Volume Methods for Simulation of Super-Critical Flow with Shock Waves
 Proceedings of the 9th WSEAS International Conference on Applied Mathematics, Istanbul, Turkey, May 7, 6 (pp55665) Comparison of and Flux Averaging in Overlapping Finite Volume Methods for Simulation of
Proceedings of the 9th WSEAS International Conference on Applied Mathematics, Istanbul, Turkey, May 7, 6 (pp55665) Comparison of and Flux Averaging in Overlapping Finite Volume Methods for Simulation of
FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING
 14 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading. The building consists
14 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading. The building consists
A Sliding Block Analysis
 1 Introduction A Sliding Block Analysis This example simulates the sliding of a block on a rigid surface. The primary purpose of this example is to check the behavior of the slip (interface) elements in
1 Introduction A Sliding Block Analysis This example simulates the sliding of a block on a rigid surface. The primary purpose of this example is to check the behavior of the slip (interface) elements in
Analysis of Pile Behaviour due to Damped Vibration by Finite Element Method (FEM)
 ISSN 2395-1621 Analysis of Pile Behaviour due to Damped Vibration by Finite Element Method (FEM) #1 L.M.Sardesai, #2 G.A.Kadam 1 sardesaileena@rediffmail.com.com 2 ganeshkadam07@gmail.com #1 Mechanical
ISSN 2395-1621 Analysis of Pile Behaviour due to Damped Vibration by Finite Element Method (FEM) #1 L.M.Sardesai, #2 G.A.Kadam 1 sardesaileena@rediffmail.com.com 2 ganeshkadam07@gmail.com #1 Mechanical
Rocking Component of Earthquake Induced by Horizontal Motion in Irregular Form Foundation
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 121 Rocking Component of Earthquake Induced by Horizontal Motion in Irregular Form Foundation Tohru Jomen
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 121 Rocking Component of Earthquake Induced by Horizontal Motion in Irregular Form Foundation Tohru Jomen
