Efficiency of adaptive mesh algorithms
|
|
|
- William Daniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Efficiency of adaptive mesh algorithms Jörn Behrens KlimaCampus, Universität Hamburg Model for adaptive efficiency 10 8 = 0.75, = 0.50,!= 3.00, = 10.00! Assumptions: Tree refinement (binary tree here) Overheads for o refinement criterion o Less efficient numerics o Mesh management Refinement area as fraction Computational work = no. of unknowns! : Area of refinement large (α=3/4) Overheads large: number of cells/work uniform adaptive level of refinement o Refinement criterion (χ=1/2 of a computational step) o Numerics slow (ω= 10 times slower as uniform comp.) o Mesh management demanding (µ= 3 times a comp. step) 1
2 Model for adaptive efficiency small adaptive area! Now: Area of refinement small (α=1/10) Rest unchanged 10 8 = 0.10, = 0.50,!= 3.00, = number of cells/work uniform adaptive level of refinement Model for adaptive efficiency small adaptive area! Now: Area of refinement large (α=3/4) But efficient grid management and numerics! 10 8 = 0.75, = 0.10,!= 0.50, = number of cells/work uniform adaptive level of refinement 2
3 Simulation Codes! Finite element code based on P1NC-P1 FEM pair! Discontinuous Galerkin code based on linear or quadratic triangular discr. FEM Equations (non-linear SWE): Momentum in advection form Continuity in flux form (mass conservation!) Right hand side:! Coriolis! Bottom friction! Eddy diffusion 3
4 FEM Boundary conditions (solid) Boundary conditions (open) Boundary conditions (inundation) Extrapolation of wave height Extrapolation based on neighbors Lynnet, Wu, Liu, 2002 FEM Time discretization (leap-frog): Robert-Aselin type filter Simple Damping Low-order 4
5 FEM Space discretization (P1NC-P1): Conforming linear for ζ and H: Non-Conforming linear for v Hanert et al. (2005) Advection Projection (P1 advection) Androsov, J.B., Danilov (2011) DG Equations in flux form (non-linear SWE): with 5
6 DG Flux-limited explicit RK time stepping Girlado, Hesthaven, Warburton (2002) Zhang, Xia, Zhu (2011) Beisiegel (2012) Model Problem Gravity wave propagation in simple domain Model Domain Initial values 6
7 Efficiency metrics Metrics for adaptive efficiency can be based on! # DOFs! Convergence! Computing time! Scalability (single node)! Overhead DOF based metrics # DOFs for given resolution! Depends on size of high resolution domain (fraction of total area)! Depends on efficiency of refinement criterion! Coarse level 8, fine level ! Ratio:
8 DOF based metrics # DOFs for given error! Depends on size of high resolution domain (fraction of total area)! Depends on efficiency of refinement criterion Numerical Methods: DG A grid independent numerical method A. Müller (2009/2012) 8
9 Convergence based metrics Convergence over # DOFs Convergence based metrics Error with fixed #DOFs! Depends on size of high resolution domain (fraction of total area)! Depends on efficiency of refinement criterion cells uniform cells uniform 9
10 Time based metrics Computing time for given resolution! Depends on size of high resolution domain (fraction of total area) FEM: Adaptive: 15.8 s Uniform: 173 s DG: Adaptive: 302 s Uniform: 6484 s Time based metrics Computing time for given error! Depends on size of high resolution domain (fraction of total area)! Related to DOFs for given error Error: 10-7 Adaptive: 6.1 s (5k nodes) Uniform: s (66k nodes) 10
11 Time based metrics Error for given computing time! Depends on size of high resolution domain (fraction of total area)! Related to DOFs for given error Computing time: 230 s Adaptive: 4.7e-4 Uniform: 1.8e-3 Time based metrics Computing time per node! Measures efficiency of data structures... 11
12 Scaling metrics Scaling of DOFs over resolution! Related to highest possible resolution Scaling metrics Time scaling over resolution! Related to time to solution 12
13 Scaling metrics Time scaling over error! Related to time to solution of certain accuracy! depends on covergence and refinement criterion Measuring the overhead Time for adaptation vs. total time step time Shallow Water Dx: Total computing time: 1050 s Time per step: 4.5 s Time for adaptation: 0.12 s Fraction: 3% Semi-Lagrangia Advection Dx: Total computing time: 226s Time per step: 15.2 s Time for adaptation: 10.7 s Fraction: 70% 13
14 Ongoing!! Diverse Metrics! Efficiency with respect to parallelization...! Efficiency with respect to cache efficiency... 14
Klima-Exzellenz in Hamburg
 Klima-Exzellenz in Hamburg Adaptive triangular meshes for inundation modeling 19.10.2010, University of Maryland, College Park Jörn Behrens KlimaCampus, Universität Hamburg Acknowledging: Widodo Pranowo,
Klima-Exzellenz in Hamburg Adaptive triangular meshes for inundation modeling 19.10.2010, University of Maryland, College Park Jörn Behrens KlimaCampus, Universität Hamburg Acknowledging: Widodo Pranowo,
Dependency of tsunami simulations on advection scheme, grid resolution, bottom friction and topography
 IMUM-2010, MIT, 17-20 August Dependency of tsunami simulations on advection scheme, grid resolution, bottom friction and topography C. Wekerle, S. Harig, W. Pranowo, A. Androsov, A. Fuchs, N. Rakowsky,
IMUM-2010, MIT, 17-20 August Dependency of tsunami simulations on advection scheme, grid resolution, bottom friction and topography C. Wekerle, S. Harig, W. Pranowo, A. Androsov, A. Fuchs, N. Rakowsky,
Parallel Adaptive Tsunami Modelling with Triangular Discontinuous Galerkin Schemes
 Parallel Adaptive Tsunami Modelling with Triangular Discontinuous Galerkin Schemes Stefan Vater 1 Kaveh Rahnema 2 Jörn Behrens 1 Michael Bader 2 1 Universität Hamburg 2014 PDES Workshop 2 TU München Partial
Parallel Adaptive Tsunami Modelling with Triangular Discontinuous Galerkin Schemes Stefan Vater 1 Kaveh Rahnema 2 Jörn Behrens 1 Michael Bader 2 1 Universität Hamburg 2014 PDES Workshop 2 TU München Partial
Development of an operational tsunami model for inclusion into the Indian Ocean Tsunami Early Warning System (GITEWS)
 Development of an operational tsunami model for inclusion into the Indian Ocean Tsunami Early Warning System (GITEWS) Jörn Behrens for Polar and Marine Research Acknowledge contributions by Alexey Androsov,
Development of an operational tsunami model for inclusion into the Indian Ocean Tsunami Early Warning System (GITEWS) Jörn Behrens for Polar and Marine Research Acknowledge contributions by Alexey Androsov,
Testing refinement criteria in adaptive Discontinuous Galerkin simulations of dry atmospheric convection
 Testing refinement criteria in adaptive Discontinuous Galerkin simulations of dry atmospheric convection Andreas Müller a,, Jörn Behrens b, Francis X. Giraldo c, Volkmar Wirth a a Institute for Atmospheric
Testing refinement criteria in adaptive Discontinuous Galerkin simulations of dry atmospheric convection Andreas Müller a,, Jörn Behrens b, Francis X. Giraldo c, Volkmar Wirth a a Institute for Atmospheric
Homogenization and numerical Upscaling. Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow
 Homogenization and numerical Upscaling Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow Insa Neuweiler Institute of Hydromechanics, University of Stuttgart Outline Block 1: Introduction and Repetition Homogenization
Homogenization and numerical Upscaling Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow Insa Neuweiler Institute of Hydromechanics, University of Stuttgart Outline Block 1: Introduction and Repetition Homogenization
AMR Multi-Moment FVM Scheme
 Chapter 4 AMR Multi-Moment FVM Scheme 4.1 Berger s AMR scheme An AMR grid with the hierarchy of Berger s AMR scheme proposed in [13] for CFD simulations is given in Fig.4.1 as a simple example for following
Chapter 4 AMR Multi-Moment FVM Scheme 4.1 Berger s AMR scheme An AMR grid with the hierarchy of Berger s AMR scheme proposed in [13] for CFD simulations is given in Fig.4.1 as a simple example for following
University of Reading. Discretization On Non-uniform Meshes: Tests solving shallow-water equations
 University of Reading School of Mathematics, Meteorology and Physics Discretization On Non-uniform Meshes: Tests solving shallow-water equations By FAWZI B ALBUSAIDI August 2008 This dissertation is submitted
University of Reading School of Mathematics, Meteorology and Physics Discretization On Non-uniform Meshes: Tests solving shallow-water equations By FAWZI B ALBUSAIDI August 2008 This dissertation is submitted
Partial Differential Equations
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Partial Differential Equations Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Motivation various dynamic effects and physical processes are described
Simulation in Computer Graphics Partial Differential Equations Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Motivation various dynamic effects and physical processes are described
Lecture 1: Finite Volume WENO Schemes Chi-Wang Shu
 Lecture 1: Finite Volume WENO Schemes Chi-Wang Shu Division of Applied Mathematics Brown University Outline of the First Lecture General description of finite volume schemes for conservation laws The WENO
Lecture 1: Finite Volume WENO Schemes Chi-Wang Shu Division of Applied Mathematics Brown University Outline of the First Lecture General description of finite volume schemes for conservation laws The WENO
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems
 1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
Fluent User Services Center
 Solver Settings 5-1 Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring Stability Accelerating Convergence Accuracy Grid Independence Adaption Appendix: Background Finite Volume
Solver Settings 5-1 Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring Stability Accelerating Convergence Accuracy Grid Independence Adaption Appendix: Background Finite Volume
Literature Report. Daniël Pols. 23 May 2018
 Literature Report Daniël Pols 23 May 2018 Applications Two-phase flow model The evolution of the momentum field in a two phase flow problem is given by the Navier-Stokes equations: u t + u u = 1 ρ p +
Literature Report Daniël Pols 23 May 2018 Applications Two-phase flow model The evolution of the momentum field in a two phase flow problem is given by the Navier-Stokes equations: u t + u u = 1 ρ p +
Advective and conservative semi-lagrangian schemes on uniform and non-uniform grids
 Advective and conservative semi-lagrangian schemes on uniform and non-uniform grids M. Mehrenberger Université de Strasbourg and Max-Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik 5 September 2013 M. Mehrenberger (UDS
Advective and conservative semi-lagrangian schemes on uniform and non-uniform grids M. Mehrenberger Université de Strasbourg and Max-Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik 5 September 2013 M. Mehrenberger (UDS
Comparison between adaptive and uniform discontinuous Galerkin simulations in dry 2D bubble experiments
 Calhoun: The NPS Institutional Archive DSpace Repository Faculty and Researchers Faculty and Researchers Collection 2012-11-08 Comparison between adaptive and uniform discontinuous Galerkin simulations
Calhoun: The NPS Institutional Archive DSpace Repository Faculty and Researchers Faculty and Researchers Collection 2012-11-08 Comparison between adaptive and uniform discontinuous Galerkin simulations
Optimization of HOM Couplers using Time Domain Schemes
 Optimization of HOM Couplers using Time Domain Schemes Workshop on HOM Damping in Superconducting RF Cavities Carsten Potratz Universität Rostock October 11, 2010 10/11/2010 2009 UNIVERSITÄT ROSTOCK FAKULTÄT
Optimization of HOM Couplers using Time Domain Schemes Workshop on HOM Damping in Superconducting RF Cavities Carsten Potratz Universität Rostock October 11, 2010 10/11/2010 2009 UNIVERSITÄT ROSTOCK FAKULTÄT
Asynchronous OpenCL/MPI numerical simulations of conservation laws
 Asynchronous OpenCL/MPI numerical simulations of conservation laws Philippe HELLUY 1,3, Thomas STRUB 2. 1 IRMA, Université de Strasbourg, 2 AxesSim, 3 Inria Tonus, France IWOCL 2015, Stanford Conservation
Asynchronous OpenCL/MPI numerical simulations of conservation laws Philippe HELLUY 1,3, Thomas STRUB 2. 1 IRMA, Université de Strasbourg, 2 AxesSim, 3 Inria Tonus, France IWOCL 2015, Stanford Conservation
f xx + f yy = F (x, y)
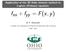 Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
The Shallow Water Equations and CUDA
 The Shallow Water Equations and CUDA Alexander Pöppl December 9 th 2015 Tutorial: High Performance Computing - Algorithms and Applications, December 9 th 2015 1 Last Tutorial Discretized Heat Equation
The Shallow Water Equations and CUDA Alexander Pöppl December 9 th 2015 Tutorial: High Performance Computing - Algorithms and Applications, December 9 th 2015 1 Last Tutorial Discretized Heat Equation
CGT 581 G Fluids. Overview. Some terms. Some terms
 CGT 581 G Fluids Bedřich Beneš, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Technology Overview Some terms Incompressible Navier-Stokes Boundary conditions Lagrange vs. Euler Eulerian approaches
CGT 581 G Fluids Bedřich Beneš, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Technology Overview Some terms Incompressible Navier-Stokes Boundary conditions Lagrange vs. Euler Eulerian approaches
Unstructured grid modelling
 Unstructured grid modelling Intercomparison between several finite element and finite volume approaches to model the North Sea tides Silvia Maßmann 1, Alexey Androsov 1, Sergey Danilov 1 and Jens Schröter
Unstructured grid modelling Intercomparison between several finite element and finite volume approaches to model the North Sea tides Silvia Maßmann 1, Alexey Androsov 1, Sergey Danilov 1 and Jens Schröter
The Shallow Water Equations and CUDA
 The Shallow Water Equations and CUDA HPC - Algorithms and Applications Alexander Pöppl Technical University of Munich Chair of Scientific Computing January 11 th 2017 Last Tutorial Discretized Heat Equation
The Shallow Water Equations and CUDA HPC - Algorithms and Applications Alexander Pöppl Technical University of Munich Chair of Scientific Computing January 11 th 2017 Last Tutorial Discretized Heat Equation
The Shallow Water Equations and CUDA
 The Shallow Water Equations and CUDA Oliver Meister December 17 th 2014 Tutorial Parallel Programming and High Performance Computing, December 17 th 2014 1 Last Tutorial Discretized Heat Equation System
The Shallow Water Equations and CUDA Oliver Meister December 17 th 2014 Tutorial Parallel Programming and High Performance Computing, December 17 th 2014 1 Last Tutorial Discretized Heat Equation System
WAVE PATTERNS, WAVE INDUCED FORCES AND MOMENTS FOR A GRAVITY BASED STRUCTURE PREDICTED USING CFD
 Proceedings of the ASME 2011 30th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2011 June 19-24, 2011, Rotterdam, The Netherlands OMAE2011-49593 WAVE PATTERNS, WAVE INDUCED FORCES
Proceedings of the ASME 2011 30th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2011 June 19-24, 2011, Rotterdam, The Netherlands OMAE2011-49593 WAVE PATTERNS, WAVE INDUCED FORCES
Homework 4A Due November 7th IN CLASS
 CS207, Fall 2014 Systems Development for Computational Science Cris Cecka, Ray Jones Homework 4A Due November 7th IN CLASS Previously, we ve developed a quite robust Graph class to let us use Node and
CS207, Fall 2014 Systems Development for Computational Science Cris Cecka, Ray Jones Homework 4A Due November 7th IN CLASS Previously, we ve developed a quite robust Graph class to let us use Node and
Coupled Simulation of Flow and Body Motion Using Overset Grids. Eberhard Schreck & Milovan Perić
 Coupled Simulation of Flow and Body Motion Using Overset Grids Eberhard Schreck & Milovan Perić Contents Dynamic Fluid-Body Interaction (DFBI) model in STAR-CCM+ Overset grids method in STAR-CCM+ Advantages
Coupled Simulation of Flow and Body Motion Using Overset Grids Eberhard Schreck & Milovan Perić Contents Dynamic Fluid-Body Interaction (DFBI) model in STAR-CCM+ Overset grids method in STAR-CCM+ Advantages
Realistic Animation of Fluids
 Realistic Animation of Fluids p. 1/2 Realistic Animation of Fluids Nick Foster and Dimitri Metaxas Realistic Animation of Fluids p. 2/2 Overview Problem Statement Previous Work Navier-Stokes Equations
Realistic Animation of Fluids p. 1/2 Realistic Animation of Fluids Nick Foster and Dimitri Metaxas Realistic Animation of Fluids p. 2/2 Overview Problem Statement Previous Work Navier-Stokes Equations
lecture 8 Groundwater Modelling -1
 The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Water Resources Msc. Groundwater Hydrology- ENGC 6301 lecture 8 Groundwater Modelling -1 Instructor: Dr. Yunes Mogheir
The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Water Resources Msc. Groundwater Hydrology- ENGC 6301 lecture 8 Groundwater Modelling -1 Instructor: Dr. Yunes Mogheir
Retrospect on the tsunami simulation efforts for the German-Indonesian Tsunami Early Warning System
 Retrospect on the tsunami simulation efforts for the German-Indonesian Tsunami Early Warning System Natalja Rakowsky, Alexey Androsov, Annika Fuchs, Sven Harig, Antonia Immerz, Jörn Behrens, Wolfgang Hiller,
Retrospect on the tsunami simulation efforts for the German-Indonesian Tsunami Early Warning System Natalja Rakowsky, Alexey Androsov, Annika Fuchs, Sven Harig, Antonia Immerz, Jörn Behrens, Wolfgang Hiller,
Parallel Algorithms: Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) method and its implementation
 Parallel Algorithms: Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) method and its implementation Massimiliano Guarrasi m.guarrasi@cineca.it Super Computing Applications and Innovation Department AMR - Introduction Solving
Parallel Algorithms: Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) method and its implementation Massimiliano Guarrasi m.guarrasi@cineca.it Super Computing Applications and Innovation Department AMR - Introduction Solving
ADAPTIVE FINITE ELEMENT
 Finite Element Methods In Linear Structural Mechanics Univ. Prof. Dr. Techn. G. MESCHKE SHORT PRESENTATION IN ADAPTIVE FINITE ELEMENT Abdullah ALSAHLY By Shorash MIRO Computational Engineering Ruhr Universität
Finite Element Methods In Linear Structural Mechanics Univ. Prof. Dr. Techn. G. MESCHKE SHORT PRESENTATION IN ADAPTIVE FINITE ELEMENT Abdullah ALSAHLY By Shorash MIRO Computational Engineering Ruhr Universität
A Semi-Lagrangian Discontinuous Galerkin (SLDG) Conservative Transport Scheme on the Cubed-Sphere
 A Semi-Lagrangian Discontinuous Galerkin (SLDG) Conservative Transport Scheme on the Cubed-Sphere Ram Nair Computational and Information Systems Laboratory (CISL) National Center for Atmospheric Research
A Semi-Lagrangian Discontinuous Galerkin (SLDG) Conservative Transport Scheme on the Cubed-Sphere Ram Nair Computational and Information Systems Laboratory (CISL) National Center for Atmospheric Research
Adaptive numerical methods
 METRO MEtallurgical TRaining On-line Adaptive numerical methods Arkadiusz Nagórka CzUT Education and Culture Introduction Common steps of finite element computations consists of preprocessing - definition
METRO MEtallurgical TRaining On-line Adaptive numerical methods Arkadiusz Nagórka CzUT Education and Culture Introduction Common steps of finite element computations consists of preprocessing - definition
Integral Equation Methods for Vortex Dominated Flows, a High-order Conservative Eulerian Approach
 Integral Equation Methods for Vortex Dominated Flows, a High-order Conservative Eulerian Approach J. Bevan, UIUC ICERM/HKUST Fast Integral Equation Methods January 5, 2016 Vorticity and Circulation Γ =
Integral Equation Methods for Vortex Dominated Flows, a High-order Conservative Eulerian Approach J. Bevan, UIUC ICERM/HKUST Fast Integral Equation Methods January 5, 2016 Vorticity and Circulation Γ =
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis
 Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
ACCURACY OF NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF HEAT DIFFUSION EQUATION
 Scientific Research of the Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science ACCURACY OF NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF HEAT DIFFUSION EQUATION Ewa Węgrzyn-Skrzypczak, Tomasz Skrzypczak Institute of Mathematics, Czestochowa
Scientific Research of the Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science ACCURACY OF NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF HEAT DIFFUSION EQUATION Ewa Węgrzyn-Skrzypczak, Tomasz Skrzypczak Institute of Mathematics, Czestochowa
Finite Element Convergence for Time-Dependent PDEs with a Point Source in COMSOL 4.2
 Finite Element Convergence for Time-Dependent PDEs with a Point Source in COMSOL 4.2 David W. Trott and Matthias K. Gobbert Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore County,
Finite Element Convergence for Time-Dependent PDEs with a Point Source in COMSOL 4.2 David W. Trott and Matthias K. Gobbert Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore County,
Coupling of STAR-CCM+ to Other Theoretical or Numerical Solutions. Milovan Perić
 Coupling of STAR-CCM+ to Other Theoretical or Numerical Solutions Milovan Perić Contents The need to couple STAR-CCM+ with other theoretical or numerical solutions Coupling approaches: surface and volume
Coupling of STAR-CCM+ to Other Theoretical or Numerical Solutions Milovan Perić Contents The need to couple STAR-CCM+ with other theoretical or numerical solutions Coupling approaches: surface and volume
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4399 Efficiency and performances
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4399 Efficiency and performances
Animation of Fluids. Animating Fluid is Hard
 Animation of Fluids Animating Fluid is Hard Too complex to animate by hand Surface is changing very quickly Lots of small details In short, a nightmare! Need automatic simulations AdHoc Methods Some simple
Animation of Fluids Animating Fluid is Hard Too complex to animate by hand Surface is changing very quickly Lots of small details In short, a nightmare! Need automatic simulations AdHoc Methods Some simple
Discontinuous Galerkin Sparse Grid method for Maxwell s equations
 Discontinuous Galerkin Sparse Grid method for Maxwell s equations Student: Tianyang Wang Mentor: Dr. Lin Mu, Dr. David L.Green, Dr. Ed D Azevedo, Dr. Kwai Wong Motivation u We consider the Maxwell s equations,
Discontinuous Galerkin Sparse Grid method for Maxwell s equations Student: Tianyang Wang Mentor: Dr. Lin Mu, Dr. David L.Green, Dr. Ed D Azevedo, Dr. Kwai Wong Motivation u We consider the Maxwell s equations,
Development of a Maxwell Equation Solver for Application to Two Fluid Plasma Models. C. Aberle, A. Hakim, and U. Shumlak
 Development of a Maxwell Equation Solver for Application to Two Fluid Plasma Models C. Aberle, A. Hakim, and U. Shumlak Aerospace and Astronautics University of Washington, Seattle American Physical Society
Development of a Maxwell Equation Solver for Application to Two Fluid Plasma Models C. Aberle, A. Hakim, and U. Shumlak Aerospace and Astronautics University of Washington, Seattle American Physical Society
Corrected/Updated References
 K. Kashiyama, H. Ito, M. Behr and T. Tezduyar, "Massively Parallel Finite Element Strategies for Large-Scale Computation of Shallow Water Flows and Contaminant Transport", Extended Abstracts of the Second
K. Kashiyama, H. Ito, M. Behr and T. Tezduyar, "Massively Parallel Finite Element Strategies for Large-Scale Computation of Shallow Water Flows and Contaminant Transport", Extended Abstracts of the Second
A Multiscale Non-hydrostatic Atmospheric Model for Regional and Global Applications
 A Multiscale Non-hydrostatic Atmospheric Model for Regional and Global Applications James D. Doyle 1, Frank Giraldo 2, Saša Gaberšek 1 1 Naval Research Laboratory, Monterey, CA, USA 2 Naval Postgraduate
A Multiscale Non-hydrostatic Atmospheric Model for Regional and Global Applications James D. Doyle 1, Frank Giraldo 2, Saša Gaberšek 1 1 Naval Research Laboratory, Monterey, CA, USA 2 Naval Postgraduate
Control Volume Finite Difference On Adaptive Meshes
 Control Volume Finite Difference On Adaptive Meshes Sanjay Kumar Khattri, Gunnar E. Fladmark, Helge K. Dahle Department of Mathematics, University Bergen, Norway. sanjay@mi.uib.no Summary. In this work
Control Volume Finite Difference On Adaptive Meshes Sanjay Kumar Khattri, Gunnar E. Fladmark, Helge K. Dahle Department of Mathematics, University Bergen, Norway. sanjay@mi.uib.no Summary. In this work
3-D Wind Field Simulation over Complex Terrain
 3-D Wind Field Simulation over Complex Terrain University Institute for Intelligent Systems and Numerical Applications in Engineering Congreso de la RSME 2015 Soluciones Matemáticas e Innovación en la
3-D Wind Field Simulation over Complex Terrain University Institute for Intelligent Systems and Numerical Applications in Engineering Congreso de la RSME 2015 Soluciones Matemáticas e Innovación en la
On the thickness of discontinuities computed by THINC and RK schemes
 The 9th Computational Fluid Dynamics Symposium B7- On the thickness of discontinuities computed by THINC and RK schemes Taku Nonomura, ISAS, JAXA, Sagamihara, Kanagawa, Japan, E-mail:nonomura@flab.isas.jaxa.jp
The 9th Computational Fluid Dynamics Symposium B7- On the thickness of discontinuities computed by THINC and RK schemes Taku Nonomura, ISAS, JAXA, Sagamihara, Kanagawa, Japan, E-mail:nonomura@flab.isas.jaxa.jp
ATM 298, Spring 2013 Lecture 4 Numerical Methods: Horizontal DiscreDzaDons April 10, Paul A. Ullrich (HH 251)
 ATM 298, Spring 2013 Lecture 4 Numerical Methods: Horizontal DiscreDzaDons April 10, 2013 Paul A. Ullrich (HH 251) paullrich@ucdavis.edu Outline 1. Introduction / Motivation 2. Finite Difference Methods
ATM 298, Spring 2013 Lecture 4 Numerical Methods: Horizontal DiscreDzaDons April 10, 2013 Paul A. Ullrich (HH 251) paullrich@ucdavis.edu Outline 1. Introduction / Motivation 2. Finite Difference Methods
The Development of a Volume-of-Fluid Interface Tracking Method for Modeling Problems in Mantle Convection
 The Development of a Volume-of-Fluid Interface Tracking Method for Modeling Problems in Mantle Convection Jonathan Robey 1 September 12, 2016 1 Funded in part by a GAANN Fellowship 1 Motivation Mantle
The Development of a Volume-of-Fluid Interface Tracking Method for Modeling Problems in Mantle Convection Jonathan Robey 1 September 12, 2016 1 Funded in part by a GAANN Fellowship 1 Motivation Mantle
Three Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow Over Spillways
 Three Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow Over Spillways Latif Bouhadji ASL-AQFlow Inc., Sidney, British Columbia, Canada Email: lbouhadji@aslenv.com ABSTRACT Turbulent flows over a spillway
Three Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow Over Spillways Latif Bouhadji ASL-AQFlow Inc., Sidney, British Columbia, Canada Email: lbouhadji@aslenv.com ABSTRACT Turbulent flows over a spillway
Technical Report TR
 Technical Report TR-2015-09 Boundary condition enforcing methods for smoothed particle hydrodynamics Arman Pazouki 1, Baofang Song 2, Dan Negrut 1 1 University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, 53706-1572,
Technical Report TR-2015-09 Boundary condition enforcing methods for smoothed particle hydrodynamics Arman Pazouki 1, Baofang Song 2, Dan Negrut 1 1 University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, 53706-1572,
Advanced Numerical Methods for Numerical Weather Prediction
 Advanced Numerical Methods for Numerical Weather Prediction Francis X. Giraldo Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943-5502 phone: (831) 656-4882 fax: (831) 656-4769 e-mail: giraldo@nrlmry.navy.mil
Advanced Numerical Methods for Numerical Weather Prediction Francis X. Giraldo Naval Research Laboratory Monterey, CA 93943-5502 phone: (831) 656-4882 fax: (831) 656-4769 e-mail: giraldo@nrlmry.navy.mil
Second International Workshop on Scientific Computing and Applications. Kananaskis, Canada, May 28 - June 1, 2000
 Second International Workshop on Scientific Computing and Applications. Kananaskis, Canada, May 28 - June 1, 2000 Program May 28 (Sunday) 19:00-21:00 Registration and reception Session Chairman: Y. Wong
Second International Workshop on Scientific Computing and Applications. Kananaskis, Canada, May 28 - June 1, 2000 Program May 28 (Sunday) 19:00-21:00 Registration and reception Session Chairman: Y. Wong
ALE and AMR Mesh Refinement Techniques for Multi-material Hydrodynamics Problems
 ALE and AMR Mesh Refinement Techniques for Multi-material Hydrodynamics Problems A. J. Barlow, AWE. ICFD Workshop on Mesh Refinement Techniques 7th December 2005 Acknowledgements Thanks to Chris Powell,
ALE and AMR Mesh Refinement Techniques for Multi-material Hydrodynamics Problems A. J. Barlow, AWE. ICFD Workshop on Mesh Refinement Techniques 7th December 2005 Acknowledgements Thanks to Chris Powell,
Shallow Water Equation simulation with Sparse Grid Combination Technique
 GUIDED RESEARCH Shallow Water Equation simulation with Sparse Grid Combination Technique Author: Jeeta Ann Chacko Examiner: Prof. Dr. Hans-Joachim Bungartz Advisors: Ao Mo-Hellenbrand April 21, 2017 Fakultät
GUIDED RESEARCH Shallow Water Equation simulation with Sparse Grid Combination Technique Author: Jeeta Ann Chacko Examiner: Prof. Dr. Hans-Joachim Bungartz Advisors: Ao Mo-Hellenbrand April 21, 2017 Fakultät
Chapter 6. Semi-Lagrangian Methods
 Chapter 6. Semi-Lagrangian Methods References: Durran Chapter 6. Review article by Staniford and Cote (1991) MWR, 119, 2206-2223. 6.1. Introduction Semi-Lagrangian (S-L for short) methods, also called
Chapter 6. Semi-Lagrangian Methods References: Durran Chapter 6. Review article by Staniford and Cote (1991) MWR, 119, 2206-2223. 6.1. Introduction Semi-Lagrangian (S-L for short) methods, also called
High-order methods for the next generation of computational engineering software
 High-order methods for the next generation of computational engineering software Rubén Sevilla Zienkiewicz Centre for Computational Engineering College of Engineering Swansea University Swansea Wales,
High-order methods for the next generation of computational engineering software Rubén Sevilla Zienkiewicz Centre for Computational Engineering College of Engineering Swansea University Swansea Wales,
Offshore Platform Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) Simulation
 Offshore Platform Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) Simulation Ali Marzaban, CD-adapco Murthy Lakshmiraju, CD-adapco Nigel Richardson, CD-adapco Mike Henneke, CD-adapco Guangyu Wu, Chevron Pedro M. Vargas,
Offshore Platform Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) Simulation Ali Marzaban, CD-adapco Murthy Lakshmiraju, CD-adapco Nigel Richardson, CD-adapco Mike Henneke, CD-adapco Guangyu Wu, Chevron Pedro M. Vargas,
Summary of the C2.3 test case results
 1st International Workshop on High-Order CFD Methods, Nashville, January 7-8, 2012 Institute of Aerodynamics and Flow Technology German Aerospace Center 8. Jan. 2012 1 / 19 Test case C2.3 Compressible
1st International Workshop on High-Order CFD Methods, Nashville, January 7-8, 2012 Institute of Aerodynamics and Flow Technology German Aerospace Center 8. Jan. 2012 1 / 19 Test case C2.3 Compressible
Parallel Computing For Finite Element Models of Surface Water Flow. Srinivas Chippada, Clint N. Dawson, Mary F. Wheeler, Monica L.
 TICAM REPORT 96-40 August 1996 Parallel Computing For Finite Element Models of Surface Water Flow Srinivas Chippada, Clint N. Dawson, Mary F. Wheeler, Monica L. Martinez PARALLEL COMPUTING FOR FINITE ELEMENT
TICAM REPORT 96-40 August 1996 Parallel Computing For Finite Element Models of Surface Water Flow Srinivas Chippada, Clint N. Dawson, Mary F. Wheeler, Monica L. Martinez PARALLEL COMPUTING FOR FINITE ELEMENT
Mesh refinement in FE-micromagnetics for multi-domain Nd 2 Fe 14 B particles
 Version 3.0 98-09-11 Mesh refinement in FE-micromagnetics for multi-domain Nd 2 Fe 14 B particles W. Scholz, T. Schrefl, J. Fidler Institute of Applied and Technical Physics, Vienna University of Technology,
Version 3.0 98-09-11 Mesh refinement in FE-micromagnetics for multi-domain Nd 2 Fe 14 B particles W. Scholz, T. Schrefl, J. Fidler Institute of Applied and Technical Physics, Vienna University of Technology,
Michal A. Kopera a,, Francis X. Giraldo a
 Analysis of Adaptive Mesh Refinement for IMEX Discontinuous Galerkin Solutions of the Compressible Euler Equations with Application to Atmospheric Simulations Michal A. Kopera a,, Francis X. Giraldo a
Analysis of Adaptive Mesh Refinement for IMEX Discontinuous Galerkin Solutions of the Compressible Euler Equations with Application to Atmospheric Simulations Michal A. Kopera a,, Francis X. Giraldo a
OpenFOAM in Wave and Offshore CFD
 OpenFOAM in Wave and Offshore CFD Capabilities of the Naval Hydro Pack Hrvoje Jasak Wikki Ltd. United Kingdom Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, Uni Zagreb, Croatia University of
OpenFOAM in Wave and Offshore CFD Capabilities of the Naval Hydro Pack Hrvoje Jasak Wikki Ltd. United Kingdom Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, Uni Zagreb, Croatia University of
Computational Astrophysics 5 Higher-order and AMR schemes
 Computational Astrophysics 5 Higher-order and AMR schemes Oscar Agertz Outline - The Godunov Method - Second-order scheme with MUSCL - Slope limiters and TVD schemes - Characteristics tracing and 2D slopes.
Computational Astrophysics 5 Higher-order and AMR schemes Oscar Agertz Outline - The Godunov Method - Second-order scheme with MUSCL - Slope limiters and TVD schemes - Characteristics tracing and 2D slopes.
Von Neumann Analysis for Higher Order Methods
 1. Introduction Von Neumann Analysis for Higher Order Methods Von Neumann analysis is a widely used method to study how an initial wave is propagated with certain numerical schemes for a linear wave equation
1. Introduction Von Neumann Analysis for Higher Order Methods Von Neumann analysis is a widely used method to study how an initial wave is propagated with certain numerical schemes for a linear wave equation
CFD Best Practice Guidelines: A process to understand CFD results and establish Simulation versus Reality
 CFD Best Practice Guidelines: A process to understand CFD results and establish Simulation versus Reality Judd Kaiser ANSYS Inc. judd.kaiser@ansys.com 2005 ANSYS, Inc. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Overview
CFD Best Practice Guidelines: A process to understand CFD results and establish Simulation versus Reality Judd Kaiser ANSYS Inc. judd.kaiser@ansys.com 2005 ANSYS, Inc. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Overview
WESTFÄLISCHE WILHELMS-UNIVERSITÄT MÜNSTER
 MÜNSTER Adaptive Discretization of Liftings for Curvature Regularization SIAM Conference on Imaging Science 2016, Albuquerque, NM Ulrich Hartleif, Prof. Dr. Benedikt Wirth May 23, 2016 Outline MÜNSTER
MÜNSTER Adaptive Discretization of Liftings for Curvature Regularization SIAM Conference on Imaging Science 2016, Albuquerque, NM Ulrich Hartleif, Prof. Dr. Benedikt Wirth May 23, 2016 Outline MÜNSTER
Lecture 2 Unstructured Mesh Generation
 Lecture 2 Unstructured Mesh Generation MIT 16.930 Advanced Topics in Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations Per-Olof Persson (persson@mit.edu) February 13, 2006 1 Mesh Generation Given a
Lecture 2 Unstructured Mesh Generation MIT 16.930 Advanced Topics in Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations Per-Olof Persson (persson@mit.edu) February 13, 2006 1 Mesh Generation Given a
Realtime Water Simulation on GPU. Nuttapong Chentanez NVIDIA Research
 1 Realtime Water Simulation on GPU Nuttapong Chentanez NVIDIA Research 2 3 Overview Approaches to realtime water simulation Hybrid shallow water solver + particles Hybrid 3D tall cell water solver + particles
1 Realtime Water Simulation on GPU Nuttapong Chentanez NVIDIA Research 2 3 Overview Approaches to realtime water simulation Hybrid shallow water solver + particles Hybrid 3D tall cell water solver + particles
Modeling Khowr-e Musa Multi-Branch Estuary Currents due to the Persian Gulf Tides Using NASIR Depth Average Flow Solver
 Journal of the Persian Gulf (Marine Science)/Vol.1/No.1/September 2010/6/45-50 Modeling Khowr-e Musa Multi-Branch Estuary Currents due to the Persian Gulf Tides Using NASIR Depth Average Flow Solver Sabbagh-Yazdi,
Journal of the Persian Gulf (Marine Science)/Vol.1/No.1/September 2010/6/45-50 Modeling Khowr-e Musa Multi-Branch Estuary Currents due to the Persian Gulf Tides Using NASIR Depth Average Flow Solver Sabbagh-Yazdi,
multi-moments moments or multi-moment moment constraints:
 Isaac Newton Institute for Mathematical Sciences Program on Multiscale Numerics for the Atmosphere and Ocean Cambridge, Nov. 16, 2012 High order finite volume methods using multi-moments moments or multi-moment
Isaac Newton Institute for Mathematical Sciences Program on Multiscale Numerics for the Atmosphere and Ocean Cambridge, Nov. 16, 2012 High order finite volume methods using multi-moments moments or multi-moment
Ocean Simulations using MPAS-Ocean
 Ocean Simulations using MPAS-Ocean Mark Petersen and the MPAS-Ocean development team Los Alamos National Laboratory U N C L A S S I F I E D Slide 1 Progress on MPAS-Ocean in 2010 MPAS-Ocean is a functioning
Ocean Simulations using MPAS-Ocean Mark Petersen and the MPAS-Ocean development team Los Alamos National Laboratory U N C L A S S I F I E D Slide 1 Progress on MPAS-Ocean in 2010 MPAS-Ocean is a functioning
Finite Element Method. Chapter 7. Practical considerations in FEM modeling
 Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
Acceleration of a Python-based Tsunami Modelling Application via CUDA and OpenHMPP
 Acceleration of a Python-based Tsunami Modelling Application via CUDA and OpenHMPP Zhe Weng and Peter Strazdins*, Computer Systems Group, Research School of Computer Science, The Australian National University
Acceleration of a Python-based Tsunami Modelling Application via CUDA and OpenHMPP Zhe Weng and Peter Strazdins*, Computer Systems Group, Research School of Computer Science, The Australian National University
A COMPARISON OF VARIOUS NODAL DISCONTINUOUS GALERKIN METHODS FOR THE 3D EULER EQUATIONS
 ECCOMAS Congress 2016 VII European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering M. Papadrakakis, V. Papadopoulos, G. Stefanou, V. Plevris (eds.) Crete Island, Greece, 5 10 June
ECCOMAS Congress 2016 VII European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering M. Papadrakakis, V. Papadopoulos, G. Stefanou, V. Plevris (eds.) Crete Island, Greece, 5 10 June
Semi-Conservative Schemes for Conservation Laws
 Semi-Conservative Schemes for Conservation Laws Rosa Maria Pidatella 1 Gabriella Puppo, 2 Giovanni Russo, 1 Pietro Santagati 1 1 Università degli Studi di Catania, Catania, Italy 2 Università dell Insubria,
Semi-Conservative Schemes for Conservation Laws Rosa Maria Pidatella 1 Gabriella Puppo, 2 Giovanni Russo, 1 Pietro Santagati 1 1 Università degli Studi di Catania, Catania, Italy 2 Università dell Insubria,
Channel Routing & Lakes/Reservoirs in WRF-Hydro
 Channel Routing & Lakes/Reservoirs in WRF-Hydro L. Read, D. Yates National Center for Atmospheric Research Channel Routing Channel Routing Methods Set in hydro.namelist with the channel_option = 1, 2 or
Channel Routing & Lakes/Reservoirs in WRF-Hydro L. Read, D. Yates National Center for Atmospheric Research Channel Routing Channel Routing Methods Set in hydro.namelist with the channel_option = 1, 2 or
High-Order Numerical Algorithms for Steady and Unsteady Simulation of Viscous Compressible Flow with Shocks (Grant FA )
 High-Order Numerical Algorithms for Steady and Unsteady Simulation of Viscous Compressible Flow with Shocks (Grant FA9550-07-0195) Sachin Premasuthan, Kui Ou, Patrice Castonguay, Lala Li, Yves Allaneau,
High-Order Numerical Algorithms for Steady and Unsteady Simulation of Viscous Compressible Flow with Shocks (Grant FA9550-07-0195) Sachin Premasuthan, Kui Ou, Patrice Castonguay, Lala Li, Yves Allaneau,
Marine Hydrodynamics Solver in OpenFOAM
 Marine Hydrodynamics Solver in OpenFOAM p. 1/14 Marine Hydrodynamics Solver in OpenFOAM Hrvoje Jasak and Henrik Rusche h.jasak@wikki.co.uk, h.rusche@wikki.co.uk Wikki, United Kingdom and Germany 4 December
Marine Hydrodynamics Solver in OpenFOAM p. 1/14 Marine Hydrodynamics Solver in OpenFOAM Hrvoje Jasak and Henrik Rusche h.jasak@wikki.co.uk, h.rusche@wikki.co.uk Wikki, United Kingdom and Germany 4 December
Higher Order Adaptive and Parallel Simulations Including Dynamic Load Balancing with the Software Package DUNE
 Higher Order Adaptive and Parallel Simulations Including Dynamic Load Balancing with the Software Package DUNE Andreas Dedner 1, Robert Klöfkorn 2, and Dietmar Kröner 3 1 Abteilung für Angewandte Mathematik,
Higher Order Adaptive and Parallel Simulations Including Dynamic Load Balancing with the Software Package DUNE Andreas Dedner 1, Robert Klöfkorn 2, and Dietmar Kröner 3 1 Abteilung für Angewandte Mathematik,
Nonoscillatory Central Schemes on Unstructured Triangular Grids for Hyperbolic Systems of Conservation Laws
 Nonoscillatory Central Schemes on Unstructured Triangular Grids for Hyperbolic Systems of Conservation Laws Ivan Christov 1,* Bojan Popov 1 Peter Popov 2 1 Department of Mathematics, 2 Institute for Scientific
Nonoscillatory Central Schemes on Unstructured Triangular Grids for Hyperbolic Systems of Conservation Laws Ivan Christov 1,* Bojan Popov 1 Peter Popov 2 1 Department of Mathematics, 2 Institute for Scientific
DISCONTINUOUS GALERKIN SHALLOW WATER SOLVER ON CUDA ARCHITECTURES
 9 th International Conference on Hydroinformatics HIC 2010, Tianjin, CHINA DISCONTINUOUS GALERKIN SHALLOW WATER SOLVER ON CUDA ARCHITECTURES D. SCHWANENBERG Operational Water Management, Deltares, Rotterdamseweg
9 th International Conference on Hydroinformatics HIC 2010, Tianjin, CHINA DISCONTINUOUS GALERKIN SHALLOW WATER SOLVER ON CUDA ARCHITECTURES D. SCHWANENBERG Operational Water Management, Deltares, Rotterdamseweg
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE SHALLOW WATER EQUATIONS USING A TIME-CENTERED SPLIT-IMPLICIT METHOD
 18th Engineering Mechanics Division Conference (EMD007) NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE SHALLOW WATER EQUATIONS USING A TIME-CENTERED SPLIT-IMPLICIT METHOD Abstract S. Fu University of Texas at Austin, Austin,
18th Engineering Mechanics Division Conference (EMD007) NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE SHALLOW WATER EQUATIONS USING A TIME-CENTERED SPLIT-IMPLICIT METHOD Abstract S. Fu University of Texas at Austin, Austin,
Third Order WENO Scheme on Three Dimensional Tetrahedral Meshes
 COMMUNICATIONS IN COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS Vol. 5, No. 2-4, pp. 86-848 Commun. Comput. Phys. February 29 Third Order WENO Scheme on Three Dimensional Tetrahedral Meshes Yong-Tao Zhang 1, and Chi-Wang Shu
COMMUNICATIONS IN COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS Vol. 5, No. 2-4, pp. 86-848 Commun. Comput. Phys. February 29 Third Order WENO Scheme on Three Dimensional Tetrahedral Meshes Yong-Tao Zhang 1, and Chi-Wang Shu
Simulation in Computer Graphics. Deformable Objects. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Deformable Objects Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction forces performance collision handling visualization University
Simulation in Computer Graphics Deformable Objects Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction forces performance collision handling visualization University
Solver Settings. Introductory FLUENT Training ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
 Solver Settings Introductory FLUENT Training 2006 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 2006 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 5-2 Outline Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring
Solver Settings Introductory FLUENT Training 2006 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 2006 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 5-2 Outline Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring
Adaptive-Mesh-Refinement Pattern
 Adaptive-Mesh-Refinement Pattern I. Problem Data-parallelism is exposed on a geometric mesh structure (either irregular or regular), where each point iteratively communicates with nearby neighboring points
Adaptive-Mesh-Refinement Pattern I. Problem Data-parallelism is exposed on a geometric mesh structure (either irregular or regular), where each point iteratively communicates with nearby neighboring points
Recent developments for the multigrid scheme of the DLR TAU-Code
 www.dlr.de Chart 1 > 21st NIA CFD Seminar > Axel Schwöppe Recent development s for the multigrid scheme of the DLR TAU-Code > Apr 11, 2013 Recent developments for the multigrid scheme of the DLR TAU-Code
www.dlr.de Chart 1 > 21st NIA CFD Seminar > Axel Schwöppe Recent development s for the multigrid scheme of the DLR TAU-Code > Apr 11, 2013 Recent developments for the multigrid scheme of the DLR TAU-Code
Finite Volume Discretization on Irregular Voronoi Grids
 Finite Volume Discretization on Irregular Voronoi Grids C.Huettig 1, W. Moore 1 1 Hampton University / National Institute of Aerospace Folie 1 The earth and its terrestrial neighbors NASA Colin Rose, Dorling
Finite Volume Discretization on Irregular Voronoi Grids C.Huettig 1, W. Moore 1 1 Hampton University / National Institute of Aerospace Folie 1 The earth and its terrestrial neighbors NASA Colin Rose, Dorling
Modeling icing using cartesian grids, penalization & level sets
 Introduction State of the art The proposed approach Proof of concept Modeling icing using cartesian grids, penalization & level sets Héloïse Beaugendre IMB Institut de Mathématiques de Bordeaux - INRIA
Introduction State of the art The proposed approach Proof of concept Modeling icing using cartesian grids, penalization & level sets Héloïse Beaugendre IMB Institut de Mathématiques de Bordeaux - INRIA
AMATOS A FLEXIBLE ENGINE FOR ADAPTIVE GRID COMPUTATIONS
 AMATOS A FLEXIBLE ENGINE FOR ADAPTIVE GRID COMPUTATIONS Abstract. amatos stands for Adaptive Mesh generator for Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulations. It is a software library that eases to a great extend
AMATOS A FLEXIBLE ENGINE FOR ADAPTIVE GRID COMPUTATIONS Abstract. amatos stands for Adaptive Mesh generator for Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulations. It is a software library that eases to a great extend
Simulation in Computer Graphics. Particles. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Particles Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction particle motion finite differences system of first order ODEs second
Simulation in Computer Graphics Particles Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction particle motion finite differences system of first order ODEs second
On the high order FV schemes for compressible flows
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (2007) 453-460 On the high order FV schemes for compressible flows J. Fürst a, a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, CTU in Prague, Karlovo nám. 13, 121 35 Praha, Czech
Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (2007) 453-460 On the high order FV schemes for compressible flows J. Fürst a, a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, CTU in Prague, Karlovo nám. 13, 121 35 Praha, Czech
QUASI-3D SOLVER OF MEANDERING RIVER FLOWS BY CIP-SOROBAN SCHEME IN CYLINDRICAL COORDINATES WITH SUPPORT OF BOUNDARY FITTED COORDINATE METHOD
 QUASI-3D SOLVER OF MEANDERING RIVER FLOWS BY CIP-SOROBAN SCHEME IN CYLINDRICAL COORDINATES WITH SUPPORT OF BOUNDARY FITTED COORDINATE METHOD Keisuke Yoshida, Tadaharu Ishikawa Dr. Eng., Tokyo Institute
QUASI-3D SOLVER OF MEANDERING RIVER FLOWS BY CIP-SOROBAN SCHEME IN CYLINDRICAL COORDINATES WITH SUPPORT OF BOUNDARY FITTED COORDINATE METHOD Keisuke Yoshida, Tadaharu Ishikawa Dr. Eng., Tokyo Institute
Mass-flux parameterization in the shallow convection gray zone
 Mass-flux parameterization in the shallow convection gray zone LACE stay report Toulouse Centre National de Recherche Meteorologique, 15. September 2014 26. September 2014 Scientific supervisor: Rachel
Mass-flux parameterization in the shallow convection gray zone LACE stay report Toulouse Centre National de Recherche Meteorologique, 15. September 2014 26. September 2014 Scientific supervisor: Rachel
Comparison Between Numerical & PIV Experimental Results for Gas-Solid Flow in Ducts
 Fabio Kasper Comparison Between Numerical & PIV Experimental Results for Gas-Solid Flow in Ducts Rodrigo Decker, Oscar Sgrott Jr., Henry F. Meier Waldir Martignoni Agenda Introduction The Test Bench Case
Fabio Kasper Comparison Between Numerical & PIV Experimental Results for Gas-Solid Flow in Ducts Rodrigo Decker, Oscar Sgrott Jr., Henry F. Meier Waldir Martignoni Agenda Introduction The Test Bench Case
Algebraic Flux Correction Schemes for High-Order B-Spline Based Finite Element Approximations
 Algebraic Flux Correction Schemes for High-Order B-Spline Based Finite Element Approximations Numerical Analysis group Matthias Möller m.moller@tudelft.nl 7th DIAM onderwijs- en onderzoeksdag, 5th November
Algebraic Flux Correction Schemes for High-Order B-Spline Based Finite Element Approximations Numerical Analysis group Matthias Möller m.moller@tudelft.nl 7th DIAM onderwijs- en onderzoeksdag, 5th November
The 3D DSC in Fluid Simulation
 The 3D DSC in Fluid Simulation Marek K. Misztal Informatics and Mathematical Modelling, Technical University of Denmark mkm@imm.dtu.dk DSC 2011 Workshop Kgs. Lyngby, 26th August 2011 Governing Equations
The 3D DSC in Fluid Simulation Marek K. Misztal Informatics and Mathematical Modelling, Technical University of Denmark mkm@imm.dtu.dk DSC 2011 Workshop Kgs. Lyngby, 26th August 2011 Governing Equations
C. A. D. Fraga Filho 1,2, D. F. Pezzin 1 & J. T. A. Chacaltana 1. Abstract
 Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XIII 15 A numerical study of heat diffusion using the Lagrangian particle SPH method and the Eulerian Finite-Volume method: analysis of convergence,
Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XIII 15 A numerical study of heat diffusion using the Lagrangian particle SPH method and the Eulerian Finite-Volume method: analysis of convergence,
ALE Adaptive Mesh Refinement in LS-DYNA
 12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference FSI/ALE(2) ALE Adaptive Mesh Refinement in LS-DYNA Nicolas AQUELET Livermore Software Technology Corp. 7374 Las Positas Rd Livermore CA94550 aquelet@lstc.com
12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference FSI/ALE(2) ALE Adaptive Mesh Refinement in LS-DYNA Nicolas AQUELET Livermore Software Technology Corp. 7374 Las Positas Rd Livermore CA94550 aquelet@lstc.com
