lecture 8 Groundwater Modelling -1
|
|
|
- Amy McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Water Resources Msc. Groundwater Hydrology- ENGC 6301 lecture 8 Groundwater Modelling -1 Instructor: Dr. Yunes Mogheir (ymogheir@mail.iugaza.edu) Semester: 1st/
2 Equation and Analytical Solutions Groundwater Flow Groundwater System A groundwater system is essential three dimensional, consisting of -water bearing layers (aquifers), - The flux exchange between layers is determined by the piezometric heads and the horizontal and vertical permeability. -the separating layers are continuously and impervious then each water bearing layer or aquifer is a groundwater system in itself.
3 Equation and Analytical Solutions Groundwater Flow Groundwater System Although groundwater flow and transport is essential three dimensional, groundwater systems may be schematized to two and one-dimensional systems. -A three dimensional flow approach (3D) is applied in advanced and detailed studies, in particular for the determination of flow patterns in relation to convective flow and related advective solute transport. -Two-dimensional areal flow (2D) is usually characterized in the horizontal x-y plain. The flow in the vertical z-direction is neglected
4 Equation and Analytical Solutions Groundwater Flow Groundwater System Although groundwater flow and transport is essential three dimensional, groundwater systems may be schematized to two and one-dimensional systems. -A three dimensional flow approach (3D) is applied in advanced and detailed studies, in particular for the determination of flow patterns in relation to convective flow and related advective solute transport. -Two-dimensional areal flow (2D) is usually characterized in the horizontal x-y plain. The flow in the vertical z-direction is neglected
5 GENERAL FLOW EQUATIONS THREE DIMENSIONAL FLOW EQUATION The groundwater flow or flux mass balance consists of three major components 1. Induced flow by the spatial differences in hydraulic head, usually called Darcy flow. 2. Forced flow is represented as volumetric external inflow from sources and sinks. 3. Storage flow, induced by a change of water levels or piezometric head
6 GENERAL FLOW EQUATIONS THREE DIMENSIONAL FLOW EQUATION 1. Induced flow or Darcy Flow The net Darcy inflow in x-direction 3D the darcy inflow
7 GENERAL FLOW EQUATIONS THREE DIMENSIONAL FLOW EQUATION Source and Sink Sources : are external forced inflows like natural percolation from the unsaturated zone and artificial recharge from surface waters and recharge wells. Sinks are outflows from the control volume, like natural drainage and well discharges Where is the control volume
8 GENERAL FLOW EQUATIONS THREE DIMENSIONAL FLOW EQUATION Storage Flow The change in piezometric level induces a change in storage. Where is the specific storage The 3D general flow mass balance :
9 GENERAL FLOW EQUATIONS THREE DIMENSIONAL FLOW EQUATION The 3D general flow mass balance :
10 GENERAL FLOW EQUATIONS The 2D case the aquifer thickness H is accounted for : where q 2i and q 20 (m3/m2/d) are aerial fluxes like percolation and seepage through confining layers, and S s. is the elastic storage (storage coefficient ) for confined aquifers
11 Recharge is the forced external inflow into the groundwater system. Recharge can be specified as -a fixed rate at a specific location (m3/day), - a linear inflow along a line (m 3 /m/d) or as -a diffuse inflow over a specific area (m 3 /m 2 /d). Storage flow in a phreatic aquifer (unconfined) results from the filling of the void space in fractures and fissures (rock) or in between the grains (soil) In confined aquifer, the change in storage is determined as:
12 The general 2-D groundwater flow is
13 Leakage or seepage is induced flow through semi-permeable layers, in general the interaction between aquifers. Or Interaction between surface water bodies (rivers, lakes) and the groundwater system is also an induced flow, the reverse process is called drainage For Unconfined aquifer
14 Interaction with surface water is essential induced flow
15 SOLUTION METHODS Modelling is the representation of the physical reality by means of analogons, physical scale models and mathematical methods. Selection of solution methods in mathematical modelling of groundwater flow and transport depends on the physical conditions, complexity of the problem and preference of the user. 1. Analytical methods or 'exact' solutions, where the hydraulic head, flow (q, v) and concentrations of constituents (c) are solved by integration in time and space. (homogeneous and uniform problems.) 2. Semi-analytical methods, where general analytical solutions are superimposed and finally solved in time by numerical integration. simplified two-dimensional areal cases applied in preliminary design studies.
16 SOLUTION METHODS 3. Numerical methods where the hydraulic head and flow are computed in time and space at discrete points of a projected network. Provide mathematical solutions for almost all groundwater flow problems, and is most applicable in non-homogeneous and multi-dimensional flow. 4. Boundary element methods and analytical element methods where conditions specified at the boundaries fit the real boundary conditions. Their complexity limit their application to real world problems.
17 Modelling Errors When making modelling, errors are introduced. These errors relate to : -the simplification of reality, -basic assumptions, -data accuracy, -schematization and selected computational method. Types of errors can be subdivided as: - physical system errors introduced by the simplification and schematization of the physical reality to a conceptual model and related parameters -mathematical errors by expressing the physical system behaviour by differential equations -numerical errors due to transform of differential into numerical equations - computational errors due to convergence and computer inaccuracies.
18 Analytical Methods Analytical methods provide -an quick solution for the simplified problem, - often serves as a verification of solutions of more complex problems obtained by numerical computer oriented methods. -For the applications of these methods see examples 3.4.1, 3.4.2, and 3.4.4
19 Example Steady flow in a uniform confined aquifer, including infiltration.
20 Example Steady flow in a uniform confined aquifer, including infiltration. infiltration Linear Head
21 Example Steady flow in a uniform confined aquifer, including infiltration.
22 NUMERICAL METHODS Applied In : - complex problems, especially under varying conditions in space (inhomogeneous hydrogeological conditions) and in time (varying boundary conditions, unsteady flow), numerical methods have proven their general applicability. -Convective transport and related advective solute contaminant transport can be simulated using numerical methods, - but particle tracking like the method of characteristics are preferred for reasons of numerical stability.
23 NUMERICAL METHODS In groundwater modeling three methods are applied: -Finite Difference Methods (FDM), including cell or block centred methods - Finite Element Methods (FEM) -Polygon based Difference or Integrated methods. In these methods: - the dependent variables,(the head and concentrations), are defined at discrete points (grid system) in space and time, where analytical solutions provide continuous solutions.
24 NUMERICAL METHODS -the solution is an approximation to the exact solution, and its accuracy depends on the selected numerical procedure and the specification of the hydrogeological parameters. The smaller the user selected steps in space and time, the more detailed and exact the obtained solution. -In numerical modeling the domain is overlain by a rectangular, triangular or quadrangular grid -Around each node an impact area or cell can be defined for which the node is representative.
25 NUMERICAL METHODS
26 Solution Procedures -For each node and related impact area the governing differential equation, based on conservation of mass, is transformed to a difference equation which relates the hydraulic head at the node itself and the heads at the surrounding nodes. (Discretization). -Depending on the selected scheme the set of equations can be independent of each other (explicit) or interrelated (implicit). -Explicit methods are solved using standard substitution methods. For reasons of stability and accuracy, they are not often applied.
27 Implicit Solution Procedures Solution methods can be divided into: 1. Direct solutions, where the set of equations is solved as a complete matrix (Gaussian elimination, Cholesky decomposition and Matrix inversion). >>> require large storage capacity and long computational time. 2. Indirect or iterative solutions, where equation after equation is solved, using trial start values. The speed and accuracy of the solution procedure highly depends on these initial values. Computed values are corrected until sufficient accuracy is reached. (Gauss-Seidl substitution, Successive over-relaxation and Conjugate Gradient methods).
28 Implicit Solution Procedures Numerical models generate errors concerning 1. Accuracy defining how well the final difference equation represents the actual physical situation. 2. Efficiency concerning the computational effort in setting up the model and computation time. 3. Stability addressing to have a solution at all. Implicit numerical schemes like cell methods and FEM in general show a high rate of stability. Stability is highly dependent on the user selected time and space interval
29 General Guide Lines for Grid System A critical step in modeling is the design of a grid. The finer the grid, the more accurate the solution. -Define grid nodes at well locations or the centre of a well field Nodal parameters must be representative for the related impact area -Define the boundary accurately, even if the grid has to be expanded to cover distant boundaries. -Avoid large spacing next to small ones. -Refine the grid in areas with a rapid spatial changes in heads and geohydrologic parameters like transmissivity.
Groundwater hydraulics numerical modelling
 Groundwater hydraulics numerical modelling Martin Šanda, B673 martin.sanda@fsv.cvut.cz Martina Sobotková, B609 martina.sobotkova@fsv.cvut.cz CTU in Prague, FCE, Dept. of Irrigation, Drainage and landscape
Groundwater hydraulics numerical modelling Martin Šanda, B673 martin.sanda@fsv.cvut.cz Martina Sobotková, B609 martina.sobotkova@fsv.cvut.cz CTU in Prague, FCE, Dept. of Irrigation, Drainage and landscape
Groundwater in Hydrologic Cycle
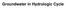 Groundwater in Hydrologic Cycle Types of Terrestrial Water Surface Water Soil Moisture Ground water Pores Full of Combination of Air and Water Unsaturated Zone / Zone of Aeration / Vadose (Soil Water)
Groundwater in Hydrologic Cycle Types of Terrestrial Water Surface Water Soil Moisture Ground water Pores Full of Combination of Air and Water Unsaturated Zone / Zone of Aeration / Vadose (Soil Water)
Training Manual FEFLOW 7.1
 Training Manual FEFLOW 7.1 Groundwater Modeling with FEFLOW 7.1 August 24, 2017 DHI WASY GmbH Groundwater Modelling Centre FEFLOW Services Contents 3 Contents Preface i 0.1 Scope and structure of this
Training Manual FEFLOW 7.1 Groundwater Modeling with FEFLOW 7.1 August 24, 2017 DHI WASY GmbH Groundwater Modelling Centre FEFLOW Services Contents 3 Contents Preface i 0.1 Scope and structure of this
CAPTURE ZONE MODELING USING THE WELLHEAD ANALYTIC ELEMENT MODEL (WhAEM) S.R. Kraemer, H.M. Haitjema, O.D.L. Strack 1
 Kraemer, S.R, H.M. Haitjema, O.D.L. Strack, 1994. Capture zone modeling using the WhAEM (wellhead analytic element model), In: Analytic Element Modeling of Groundwater Flow, Proceedings of the International
Kraemer, S.R, H.M. Haitjema, O.D.L. Strack, 1994. Capture zone modeling using the WhAEM (wellhead analytic element model), In: Analytic Element Modeling of Groundwater Flow, Proceedings of the International
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems
 1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
Period #10: Multi dimensional Fluid Flow in Soils (II)
 Period #10: Multi dimensional Fluid Flow in Soils (II) A. Review Our objective is to solve multi dimensional fluid flow problems in soils. Last time, mass conservation and Darcy s Law were used to derive
Period #10: Multi dimensional Fluid Flow in Soils (II) A. Review Our objective is to solve multi dimensional fluid flow problems in soils. Last time, mass conservation and Darcy s Law were used to derive
Developer s Tips. Groundwater analysis using Slide
 Developer s Tips Groundwater analysis using Slide In this article we introduce the new groundwater/seepage analysis module, which was built into version 5.0 of Slide. The groundwater module uses a finite
Developer s Tips Groundwater analysis using Slide In this article we introduce the new groundwater/seepage analysis module, which was built into version 5.0 of Slide. The groundwater module uses a finite
Sımultaneous estımatıon of Aquifer Parameters and Parameter Zonations using Genetic Algorithm
 Sımultaneous estımatıon of Aquifer Parameters and Parameter Zonations using Genetic Algorithm M.Tamer AYVAZ Visiting Graduate Student Nov 20/2006 MULTIMEDIA ENVIRONMENTAL SIMULATIONS LABORATORY (MESL)
Sımultaneous estımatıon of Aquifer Parameters and Parameter Zonations using Genetic Algorithm M.Tamer AYVAZ Visiting Graduate Student Nov 20/2006 MULTIMEDIA ENVIRONMENTAL SIMULATIONS LABORATORY (MESL)
Prof. B.S. Thandaveswara. The computation of a flood wave resulting from a dam break basically involves two
 41.4 Routing The computation of a flood wave resulting from a dam break basically involves two problems, which may be considered jointly or seperately: 1. Determination of the outflow hydrograph from the
41.4 Routing The computation of a flood wave resulting from a dam break basically involves two problems, which may be considered jointly or seperately: 1. Determination of the outflow hydrograph from the
A Semi-Analytical Particle Tracking Algorithm for Arbitrary Unstructured Grids
 A Semi-Analytical Particle Tracking Algorithm for Arbitrary Unstructured Grids by Muhammad Ramadhan A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree
A Semi-Analytical Particle Tracking Algorithm for Arbitrary Unstructured Grids by Muhammad Ramadhan A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree
Partial Differential Equations
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Partial Differential Equations Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Motivation various dynamic effects and physical processes are described
Simulation in Computer Graphics Partial Differential Equations Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Motivation various dynamic effects and physical processes are described
Determination of Free Surface in Steady-State Seepage through a Dam with Toe Drain by the Boundary Element Method
 Determination of Free Surface in Steady-State Seepage through a Dam with Toe Drain by the Boundary Element Method Somchart Chantasiriwan Faculty of Engineering, Thammasat University, Rangsit Campus, Pathum
Determination of Free Surface in Steady-State Seepage through a Dam with Toe Drain by the Boundary Element Method Somchart Chantasiriwan Faculty of Engineering, Thammasat University, Rangsit Campus, Pathum
8 Modeling Fractured Rock
 8 Modeling Fractured Rock Groundwater flow and chemical transport models can help to characterize and remediate fractured rock sites at all scales. It is critical that any modeling be performed by modelers
8 Modeling Fractured Rock Groundwater flow and chemical transport models can help to characterize and remediate fractured rock sites at all scales. It is critical that any modeling be performed by modelers
MODFLOW UZF Package The MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) Package Interface in GMS
 v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial The MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) Package Interface in GMS Objectives This tutorial explains how to use the MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) package and compares it to
v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial The MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) Package Interface in GMS Objectives This tutorial explains how to use the MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) package and compares it to
Comparison of parameter estimation algorithms in hydrological modelling
 Calibration and Reliability in Groundwater Modelling: From Uncertainty to Decision Making (Proceedings of ModelCARE 2005, The Hague, The Netherlands, June 2005). IAHS Publ. 304, 2006. 67 Comparison of
Calibration and Reliability in Groundwater Modelling: From Uncertainty to Decision Making (Proceedings of ModelCARE 2005, The Hague, The Netherlands, June 2005). IAHS Publ. 304, 2006. 67 Comparison of
GeoStudio Product Details
 Product Details I. Purchasing Options Universal Professional Standard Vadose Basic Student (Free) Feature Comparison Finite Element Integration No limit 500 elements 500 elements Analysis Methods Ordinary
Product Details I. Purchasing Options Universal Professional Standard Vadose Basic Student (Free) Feature Comparison Finite Element Integration No limit 500 elements 500 elements Analysis Methods Ordinary
Tutorial 1. Getting Started
 Tutorial 1 Getting Started Table of Contents Objective 2 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Input Data Preparation and Main Menu Options. 2 Step 1: Create New Project... 2 Step 2: Define Base Grid Size
Tutorial 1 Getting Started Table of Contents Objective 2 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Input Data Preparation and Main Menu Options. 2 Step 1: Create New Project... 2 Step 2: Define Base Grid Size
Integrated Groundwater Surface Water Modeling of the Green Swamp, Florida
 Integrated Groundwater Surface Water Modeling of the Green Swamp, Florida Data Management Challenges and Opportunities Peter J. Singhofen, P.E. Gordon L. McClung, P.E Streamline Technologies, Inc. 1900
Integrated Groundwater Surface Water Modeling of the Green Swamp, Florida Data Management Challenges and Opportunities Peter J. Singhofen, P.E. Gordon L. McClung, P.E Streamline Technologies, Inc. 1900
Visual MODFLOW Premium with MODFLOW SURFACT
 Visual MODFLOW Premium with MODFLOW SURFACT A Step-by-Step Tutorial for the MODFLOW-SURFACT Trial Version Waterloo Hydrogeologic TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction..............................................
Visual MODFLOW Premium with MODFLOW SURFACT A Step-by-Step Tutorial for the MODFLOW-SURFACT Trial Version Waterloo Hydrogeologic TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction..............................................
Airport Tutorial - Contaminant Transport Modeling. Visual MODFLOW Flex. Integrated Conceptual & Numerical Groundwater Modeling
 Airport Tutorial - Contaminant Transport Modeling Visual MODFLOW Flex Integrated Conceptual & Numerical Groundwater Modeling Airport Tutorial: Numerical Modeling with Transport The following example is
Airport Tutorial - Contaminant Transport Modeling Visual MODFLOW Flex Integrated Conceptual & Numerical Groundwater Modeling Airport Tutorial: Numerical Modeling with Transport The following example is
Homogenization and numerical Upscaling. Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow
 Homogenization and numerical Upscaling Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow Insa Neuweiler Institute of Hydromechanics, University of Stuttgart Outline Block 1: Introduction and Repetition Homogenization
Homogenization and numerical Upscaling Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow Insa Neuweiler Institute of Hydromechanics, University of Stuttgart Outline Block 1: Introduction and Repetition Homogenization
Integrated 2D Surface-Groundwater Modeling of the Green Swamp, Florida
 Integrated 2D Surface-Groundwater Modeling of the Green Swamp, Florida Peter J. Singhofen, P.E. Gordon L. McClung, P.E Streamline Technologies, Inc. 1900 Town Plaza Ct. Winter Springs, FL 32708 407-679-1696
Integrated 2D Surface-Groundwater Modeling of the Green Swamp, Florida Peter J. Singhofen, P.E. Gordon L. McClung, P.E Streamline Technologies, Inc. 1900 Town Plaza Ct. Winter Springs, FL 32708 407-679-1696
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis
 Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
Objectives Build a 3D mesh and a FEMWATER flow model using the conceptual model approach. Run the model and examine the results.
 v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Build a FEMWATER model to simulate flow Objectives Build a 3D mesh and a FEMWATER flow model using the conceptual model approach. Run the model and examine the results. Prerequisite
v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Build a FEMWATER model to simulate flow Objectives Build a 3D mesh and a FEMWATER flow model using the conceptual model approach. Run the model and examine the results. Prerequisite
Verification Manual. 1D / 2D / 3D Contaminant Transport Modeling Software. SoilVision Systems Ltd. Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada
 1D / 2D / 3D Contaminant Transport Modeling Software Verification Manual Written by: Robert Thode, P.Eng., B.Sc.G.E. Edited by: Murray Fredlund, P.Eng., Ph.D. SoilVision Systems Ltd. Saskatoon, Saskatchewan,
1D / 2D / 3D Contaminant Transport Modeling Software Verification Manual Written by: Robert Thode, P.Eng., B.Sc.G.E. Edited by: Murray Fredlund, P.Eng., Ph.D. SoilVision Systems Ltd. Saskatoon, Saskatchewan,
Automatic Mesh Refinement In The SVFlux And ChemFlux Software Packages
 Automatic Mesh Refinement In The SVFlux And ChemFlux Software Packages Murray Fredlund, SoilVision Systems Ltd., Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada Jason Stianson, SoilVision Systems Ltd., Saskatoon, Saskatchewan,
Automatic Mesh Refinement In The SVFlux And ChemFlux Software Packages Murray Fredlund, SoilVision Systems Ltd., Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada Jason Stianson, SoilVision Systems Ltd., Saskatoon, Saskatchewan,
MIDAS Geotechnical Training Series
 MIDAS Geotechnical Training Series Fully Coupled vs Consolidation Analysis Seongwan Bae Angel F. Martinez MIDAS Information Technology Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform
MIDAS Geotechnical Training Series Fully Coupled vs Consolidation Analysis Seongwan Bae Angel F. Martinez MIDAS Information Technology Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform
GFLOW and WhAEM Solver Verifications. H.M. Haitjema
 GFLOW and WhAEM Solver Verifications H.M. Haitjema 2 Contents 1 CODE VERIFICATIONS 5 1.1 WELL IN A UNIFORM FLOW.................. 8 1.1.1 Residence times........................ 9 1.2 SINK OR SOURCE DISC......................
GFLOW and WhAEM Solver Verifications H.M. Haitjema 2 Contents 1 CODE VERIFICATIONS 5 1.1 WELL IN A UNIFORM FLOW.................. 8 1.1.1 Residence times........................ 9 1.2 SINK OR SOURCE DISC......................
Tutorial 7. Water Table and Bedrock Surface
 Tutorial 7 Water Table and Bedrock Surface Table of Contents Objective. 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Data Input. 2 Step 1: Open Adaptive Groundwater Input (.agw) File. 2 Step 2: Assign Material
Tutorial 7 Water Table and Bedrock Surface Table of Contents Objective. 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Data Input. 2 Step 1: Open Adaptive Groundwater Input (.agw) File. 2 Step 2: Assign Material
Chapter 5 Computer Modeling of Groundwater Flow
 Chapter 5 Computer Modeling of Groundwater Flow 5-1. General a. Chapter organization. In Chapter 3, an overview of planning and management considerations in performing a groundwater site characterization
Chapter 5 Computer Modeling of Groundwater Flow 5-1. General a. Chapter organization. In Chapter 3, an overview of planning and management considerations in performing a groundwater site characterization
v. 9.2 GMS 9.2 Tutorial MODFLOW MNW2 Package Use the MNW2 package with the sample problem and a conceptual model Prerequisite Tutorials
 v. 9.2 GMS 9.2 Tutorial Use the MNW2 package with the sample problem and a conceptual model Objectives Learn how to use the MNW2 package in GMS and compare it to the WEL package. Both packages can be used
v. 9.2 GMS 9.2 Tutorial Use the MNW2 package with the sample problem and a conceptual model Objectives Learn how to use the MNW2 package in GMS and compare it to the WEL package. Both packages can be used
Water seepage through a dam: A finite element approach
 Water seepage through a dam: A finite element approach Ashley B. Pitcher Student Number 250098269 AM466b Final Project (Undergraduate) University of Western Ontario April 15, 2005 Abstract We consider
Water seepage through a dam: A finite element approach Ashley B. Pitcher Student Number 250098269 AM466b Final Project (Undergraduate) University of Western Ontario April 15, 2005 Abstract We consider
Overview of main GFLOW features
 Overview of main GFLOW features Updated: April 8, 2016 The GFLOW GUI contains many tools to efficiently design and manage a groundwater flow model. The most prominent are listed below. Note: The documents
Overview of main GFLOW features Updated: April 8, 2016 The GFLOW GUI contains many tools to efficiently design and manage a groundwater flow model. The most prominent are listed below. Note: The documents
MODFLOW Lake Package GMS TUTORIALS
 GMS TUTORIALS MODFLOW Lake Package This tutorial illustrates the steps involved in using the Lake (LAK3) Package as part of a MODFLOW simulation. The Lake Package is a more sophisticated alternative to
GMS TUTORIALS MODFLOW Lake Package This tutorial illustrates the steps involved in using the Lake (LAK3) Package as part of a MODFLOW simulation. The Lake Package is a more sophisticated alternative to
Tutorial 6. Pumping Well and River
 Tutorial 6 Pumping Well and River Table of Contents Objective. 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Data Input. 2 Step 1: Open Adaptive Groundwater Input (.agw) File. 2 Step 2: Pumping Well Design Database
Tutorial 6 Pumping Well and River Table of Contents Objective. 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Data Input. 2 Step 1: Open Adaptive Groundwater Input (.agw) File. 2 Step 2: Pumping Well Design Database
M T 3 D. By C. Zheng S.S. Papadopulos & Associates, Inc Rockville, Maryland 20852
 M T 3 D A Modular Three-Dimensional Transport Model for Simulation of Advection, Dispersion and Chemical Reaction of Contaminants in Groundwater Systems By C. Zheng S.S. Papadopulos & Associates, Inc Rockville,
M T 3 D A Modular Three-Dimensional Transport Model for Simulation of Advection, Dispersion and Chemical Reaction of Contaminants in Groundwater Systems By C. Zheng S.S. Papadopulos & Associates, Inc Rockville,
Transient Groundwater Analysis
 Transient Groundwater Analysis 18-1 Transient Groundwater Analysis A transient groundwater analysis may be important when there is a time-dependent change in pore pressure. This will occur when groundwater
Transient Groundwater Analysis 18-1 Transient Groundwater Analysis A transient groundwater analysis may be important when there is a time-dependent change in pore pressure. This will occur when groundwater
Tutorial 7 Finite Element Groundwater Seepage. Steady state seepage analysis Groundwater analysis mode Slope stability analysis
 Tutorial 7 Finite Element Groundwater Seepage Steady state seepage analysis Groundwater analysis mode Slope stability analysis Introduction Within the Slide program, Slide has the capability to carry out
Tutorial 7 Finite Element Groundwater Seepage Steady state seepage analysis Groundwater analysis mode Slope stability analysis Introduction Within the Slide program, Slide has the capability to carry out
INVERSE PROBLEMS IN GROUNDWATER MODELING
 INVERSE PROBLEMS IN GROUNDWATER MODELING Theory and Applications of Transport in Porous Media Series Editor: Jacob Bear, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel Volume 6 The titles published
INVERSE PROBLEMS IN GROUNDWATER MODELING Theory and Applications of Transport in Porous Media Series Editor: Jacob Bear, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel Volume 6 The titles published
f xx + f yy = F (x, y)
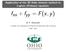 Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
v MODFLOW Stochastic Modeling, Parameter Randomization GMS 10.3 Tutorial
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial MODFLOW Stochastic Modeling, Parameter Randomization Run MODFLOW in Stochastic (Monte Carlo) Mode by Randomly Varying Parameters Objectives Learn how to develop a stochastic (Monte
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial MODFLOW Stochastic Modeling, Parameter Randomization Run MODFLOW in Stochastic (Monte Carlo) Mode by Randomly Varying Parameters Objectives Learn how to develop a stochastic (Monte
Three-dimensional finite-volume ELLAM implementation
 Three-dimensional finite-volume ELLAM implementation C.I. Heberton & T.F. Russell University of Colorado at Denver, Denver, Colorado, United States L.F. Konikow & G.Z. Hornberger U.S. Geological Survey,
Three-dimensional finite-volume ELLAM implementation C.I. Heberton & T.F. Russell University of Colorado at Denver, Denver, Colorado, United States L.F. Konikow & G.Z. Hornberger U.S. Geological Survey,
2D & 3D Semi Coupled Analysis Seepage-Stress-Slope
 D & D Semi Coupled Analysis Seepage-Stress-Slope MIDASoft Inc. Angel Francisco Martinez Civil Engineer MIDASoft NY office Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform Finite Element
D & D Semi Coupled Analysis Seepage-Stress-Slope MIDASoft Inc. Angel Francisco Martinez Civil Engineer MIDASoft NY office Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 6-bit platform Finite Element
CFD-1. Introduction: What is CFD? T. J. Craft. Msc CFD-1. CFD: Computational Fluid Dynamics
 School of Mechanical Aerospace and Civil Engineering CFD-1 T. J. Craft George Begg Building, C41 Msc CFD-1 Reading: J. Ferziger, M. Peric, Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics H.K. Versteeg, W. Malalasekara,
School of Mechanical Aerospace and Civil Engineering CFD-1 T. J. Craft George Begg Building, C41 Msc CFD-1 Reading: J. Ferziger, M. Peric, Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics H.K. Versteeg, W. Malalasekara,
Modeling Ground Water Problems Using the Complex Polynomial Method
 Modeling Ground Water Problems Using the Complex Polynomial Method A. W. Bohannon and T. V. Hromadka, AS-0020 Abstract Numerical methods for solving the governing partial differential equations involved
Modeling Ground Water Problems Using the Complex Polynomial Method A. W. Bohannon and T. V. Hromadka, AS-0020 Abstract Numerical methods for solving the governing partial differential equations involved
SEAWAT Tutorial - Elder Model
 SEAWAT Tutorial - Elder Model Introduction Saltwater intrusion is a common occurrence along coastlines throughout the world. Saltwater is denser than freshwater, and consequently will tend to migrate inland
SEAWAT Tutorial - Elder Model Introduction Saltwater intrusion is a common occurrence along coastlines throughout the world. Saltwater is denser than freshwater, and consequently will tend to migrate inland
Comparison of different solvers for two-dimensional steady heat conduction equation ME 412 Project 2
 Comparison of different solvers for two-dimensional steady heat conduction equation ME 412 Project 2 Jingwei Zhu March 19, 2014 Instructor: Surya Pratap Vanka 1 Project Description The purpose of this
Comparison of different solvers for two-dimensional steady heat conduction equation ME 412 Project 2 Jingwei Zhu March 19, 2014 Instructor: Surya Pratap Vanka 1 Project Description The purpose of this
MODFLOW Model Calibration
 GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS MODFLOW Model Calibration 1 Introduction An important part of any groundwater modeling exercise is the model calibration process. In order for a groundwater model to be used in any type
GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS MODFLOW Model Calibration 1 Introduction An important part of any groundwater modeling exercise is the model calibration process. In order for a groundwater model to be used in any type
IMPROVING THE NUMERICAL ACCURACY OF HYDROTHERMAL RESERVOIR SIMULATIONS USING THE CIP SCHEME WITH THIRD-ORDER ACCURACY
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 2012 SGP-TR-194 IMPROVING THE NUMERICAL ACCURACY OF HYDROTHERMAL
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 2012 SGP-TR-194 IMPROVING THE NUMERICAL ACCURACY OF HYDROTHERMAL
GMS 10.4 Tutorial RT3D Instantaneous Aerobic Degradation
 v. 10.4 GMS 10.4 Tutorial Objectives Simulate the reaction for instantaneous aerobic degradation of hydrocarbons using a predefined user reaction package. Prerequisite Tutorials MT2DMS Grid Approach Required
v. 10.4 GMS 10.4 Tutorial Objectives Simulate the reaction for instantaneous aerobic degradation of hydrocarbons using a predefined user reaction package. Prerequisite Tutorials MT2DMS Grid Approach Required
GGU-2D-SSFLOW. Modelling of groundwater flow using finite elements in two-dimensional systems VERSION 11. Last revision: July 2018
 Modelling of groundwater flow using finite elements in two-dimensional systems GGU-2D-SSFLOW VERSION 11 Last revision: July 2018 Copyright: Prof. Dr. Johann Buß Technical implementation and sales: Civilserve
Modelling of groundwater flow using finite elements in two-dimensional systems GGU-2D-SSFLOW VERSION 11 Last revision: July 2018 Copyright: Prof. Dr. Johann Buß Technical implementation and sales: Civilserve
1. Mathematical Modelling
 1. describe a given problem with some mathematical formalism in order to get a formal and precise description see fundamental properties due to the abstraction allow a systematic treatment and, thus, solution
1. describe a given problem with some mathematical formalism in order to get a formal and precise description see fundamental properties due to the abstraction allow a systematic treatment and, thus, solution
Using GIS for hierarchial refinement of MODFLOW models
 HydroGÏS 96: Application of Geographic Information Systems in Hydrology and Water Resources Management (Proceedings of the Vienna Conference, April 1996). IAHS Publ. no. 235, 1996. 535 Using GIS for hierarchial
HydroGÏS 96: Application of Geographic Information Systems in Hydrology and Water Resources Management (Proceedings of the Vienna Conference, April 1996). IAHS Publ. no. 235, 1996. 535 Using GIS for hierarchial
RT3D Instantaneous Aerobic Degradation
 GMS TUTORIALS RT3D Instantaneous Aerobic Degradation This tutorial illustrates the steps involved in performing a reactive transport simulation using the RT3D model. Several types of contaminant reactions
GMS TUTORIALS RT3D Instantaneous Aerobic Degradation This tutorial illustrates the steps involved in performing a reactive transport simulation using the RT3D model. Several types of contaminant reactions
Tutorial: Airport Numerical Model with Transport
 Tutorial: Visual MODFLOW Flex 5.0 Integrated Conceptual & Numerical Groundwater Modeling Software 1 1 Visual MODFLOW Flex 5.0 The following example walks through creating a numerical model with groundwater
Tutorial: Visual MODFLOW Flex 5.0 Integrated Conceptual & Numerical Groundwater Modeling Software 1 1 Visual MODFLOW Flex 5.0 The following example walks through creating a numerical model with groundwater
Improving the Senior Level Hydraulic Engineering Design Course (CE 474) By Means of Computer Assisted Instruction
 Improving the Senior Level Hydraulic Engineering Design Course (CE 474) By Means of Computer Assisted Instruction Rolando Bravo 1 Abstract- This paper presents the development of spreadsheet software at
Improving the Senior Level Hydraulic Engineering Design Course (CE 474) By Means of Computer Assisted Instruction Rolando Bravo 1 Abstract- This paper presents the development of spreadsheet software at
The Finite Element Method
 The Finite Element Method A Practical Course G. R. Liu and S. S. Quek Chapter 1: Computational modeling An overview 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION PHYSICAL PROBLEMS IN ENGINEERING COMPUTATIONAL MODELLING USING
The Finite Element Method A Practical Course G. R. Liu and S. S. Quek Chapter 1: Computational modeling An overview 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION PHYSICAL PROBLEMS IN ENGINEERING COMPUTATIONAL MODELLING USING
HYDRUS (2D/3D) Software Package for Simulating the Two- and Three-Dimensional Movement of Water, Heat, and Multiple Solutes
 HYDRUS (2D/3D) Software Package for Simulating the Two- and Three-Dimensional Movement of Water, Heat, and Multiple Solutes in Variably-Saturated Media User Manual Version 1.02 March 2007 PC-Progress,
HYDRUS (2D/3D) Software Package for Simulating the Two- and Three-Dimensional Movement of Water, Heat, and Multiple Solutes in Variably-Saturated Media User Manual Version 1.02 March 2007 PC-Progress,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4399 Efficiency and performances
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4399 Efficiency and performances
Contents. I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1
 page v Preface xiii I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1 1 Some model PDEs 3 1.1 Laplace s equation; elliptic BVPs... 3 1.1.1 Physical experiments modeled by Laplace s equation... 5 1.2 Other
page v Preface xiii I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1 1 Some model PDEs 3 1.1 Laplace s equation; elliptic BVPs... 3 1.1.1 Physical experiments modeled by Laplace s equation... 5 1.2 Other
Tutorial 9. Changing the Global Grid Resolution
 Tutorial 9 Changing the Global Grid Resolution Table of Contents Objective and Overview 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Changing the Global Grid Resolution.. 2 Step 1: Open Adaptive Groundwater
Tutorial 9 Changing the Global Grid Resolution Table of Contents Objective and Overview 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Changing the Global Grid Resolution.. 2 Step 1: Open Adaptive Groundwater
Groundwater flow modelling (450008)
 Groundwater flow modelling (450008) Computer laboratories dr. V.E.A. Post Contents Part I: Python 1 1 Calculating heads 5 1.1 Solution methods.......................... 5 1.1.1 Gauss-Seidel iteration
Groundwater flow modelling (450008) Computer laboratories dr. V.E.A. Post Contents Part I: Python 1 1 Calculating heads 5 1.1 Solution methods.......................... 5 1.1.1 Gauss-Seidel iteration
v Prerequisite Tutorials Required Components Time
 v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial MODFLOW Stochastic Modeling, Parameter Randomization Run MODFLOW in Stochastic (Monte Carlo) Mode by Randomly Varying Parameters Objectives Learn how to develop a stochastic (Monte
v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial MODFLOW Stochastic Modeling, Parameter Randomization Run MODFLOW in Stochastic (Monte Carlo) Mode by Randomly Varying Parameters Objectives Learn how to develop a stochastic (Monte
GMS 8.3 Tutorial MODFLOW LAK Package Use the MODFLOW Lake (LAK3) package to simulate mine dewatering
 v. 8.3 GMS 8.3 Tutorial Use the MODFLOW Lake (LAK3) package to simulate mine dewatering Objectives Learn the steps involved in using the MODFLOW Lake (LAK3) package interface in GMS. Use the LAK3 package
v. 8.3 GMS 8.3 Tutorial Use the MODFLOW Lake (LAK3) package to simulate mine dewatering Objectives Learn the steps involved in using the MODFLOW Lake (LAK3) package interface in GMS. Use the LAK3 package
Dynamic data integration and stochastic inversion of a two-dimensional confined aquifer
 Hydrology Days 2013 Dynamic data integration and stochastic inversion of a two-dimensional confined aquifer Dongdong Wang 1 Ye Zhang 1 Juraj Irsa 1 Abstract. Much work has been done in developing and applying
Hydrology Days 2013 Dynamic data integration and stochastic inversion of a two-dimensional confined aquifer Dongdong Wang 1 Ye Zhang 1 Juraj Irsa 1 Abstract. Much work has been done in developing and applying
MODFLOW Conceptual Model Approach II Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques
 v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques 00 Objectives The conceptual model approach involves using the GIS tools in the Map module to develop
v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques 00 Objectives The conceptual model approach involves using the GIS tools in the Map module to develop
NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY FOR FLOW PATTERN CHANGES INDUCED BY SINGLE GROYNE
 NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY FOR FLOW PATTERN CHANGES INDUCED BY SINGLE GROYNE Jungseok Ho 1, Hong Koo Yeo 2, Julie Coonrod 3, and Won-Sik Ahn 4 1 Research Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering,
NUMERICAL MODELING STUDY FOR FLOW PATTERN CHANGES INDUCED BY SINGLE GROYNE Jungseok Ho 1, Hong Koo Yeo 2, Julie Coonrod 3, and Won-Sik Ahn 4 1 Research Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering,
Seepage_CSM8. A spreadsheet tool implementing the Finite Difference Method (FDM) for the solution of twodimensional steady-state seepage problems.
 Seepage_CSM8 A spreadsheet tool implementing the Finite Difference Method (FDM) for the solution of twodimensional steady-state seepage problems. USER S MANUAL J. A. Knappett (2012) This user s manual
Seepage_CSM8 A spreadsheet tool implementing the Finite Difference Method (FDM) for the solution of twodimensional steady-state seepage problems. USER S MANUAL J. A. Knappett (2012) This user s manual
Metro Model 3 User Manual and Tutorial Guide. March, 2014
 Metro Model 3 User Manual and Tutorial Guide March, 2014 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Tutorial 1: Navigating Metro Model 3 in Groundwater Vistas... 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Model Units and Grid...
Metro Model 3 User Manual and Tutorial Guide March, 2014 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Tutorial 1: Navigating Metro Model 3 in Groundwater Vistas... 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Model Units and Grid...
Fluent User Services Center
 Solver Settings 5-1 Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring Stability Accelerating Convergence Accuracy Grid Independence Adaption Appendix: Background Finite Volume
Solver Settings 5-1 Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring Stability Accelerating Convergence Accuracy Grid Independence Adaption Appendix: Background Finite Volume
MODFLOW - Conceptual Model Approach
 GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS MODFLOW - Conceptual Model Approach 1 Introduction Two approaches can be used to construct a MODFLOW simulation in GMS: the grid approach or the conceptual model approach. The grid approach
GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS MODFLOW - Conceptual Model Approach 1 Introduction Two approaches can be used to construct a MODFLOW simulation in GMS: the grid approach or the conceptual model approach. The grid approach
VALIDATION VERSION 2.50
 VALIDATION VERSION 2.50 8ANALYTIC & COMPUTATIONAL RESEARCH, INC. 1985-1994 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED - NOTIFICATION OF COPYRIGHT - The PORFLOW J software package, including this documentation, is a proprietary
VALIDATION VERSION 2.50 8ANALYTIC & COMPUTATIONAL RESEARCH, INC. 1985-1994 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED - NOTIFICATION OF COPYRIGHT - The PORFLOW J software package, including this documentation, is a proprietary
GMS 10.0 Tutorial MODFLOW Conceptual Model Approach II Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques
 v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques 00 Objectives The conceptual model approach involves using the GIS tools in the Map Module to develop
v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques 00 Objectives The conceptual model approach involves using the GIS tools in the Map Module to develop
GeoStudio Product Details
 Product Details I. Purchasing Options Universal Professional Standard Basic Student (Free) Feature Comparison Finite Element Integration No limit 500 elements 500 elements Analysis Ordinary Yes Yes Yes
Product Details I. Purchasing Options Universal Professional Standard Basic Student (Free) Feature Comparison Finite Element Integration No limit 500 elements 500 elements Analysis Ordinary Yes Yes Yes
Kansas Geological Survey
 Kansas Geological Survey Recent MODFLOW developments for groundwater modeling Ashok KC and Marios Sophocleous Case Study P=0.0055 m/day T=0.001 m/day E=0.0005 m/day 100 m 98 m -4 m 3 /day 95 m 25 m 25
Kansas Geological Survey Recent MODFLOW developments for groundwater modeling Ashok KC and Marios Sophocleous Case Study P=0.0055 m/day T=0.001 m/day E=0.0005 m/day 100 m 98 m -4 m 3 /day 95 m 25 m 25
GEO-SLOPE International Ltd, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Lysimeters
 1 Introduction Lysimeters This steady state SEEP/W example illustrates how to model a lysimeter from construction of the model to interpretation of the results. Lysimeters are used to measure flow through
1 Introduction Lysimeters This steady state SEEP/W example illustrates how to model a lysimeter from construction of the model to interpretation of the results. Lysimeters are used to measure flow through
Finite Element Method. Chapter 7. Practical considerations in FEM modeling
 Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
SOIL PEMEABILITY AND SEEPAGE
 SOIL PEMEABILITY AND SEEPAGE The elevation head (z) is equal to the vertical distance of the point above the datum. The pressure head (p/γ w)is equal to the head indicated by a piezometer with its tip
SOIL PEMEABILITY AND SEEPAGE The elevation head (z) is equal to the vertical distance of the point above the datum. The pressure head (p/γ w)is equal to the head indicated by a piezometer with its tip
I/O format for 2D Steady Seepage Flow Analysis
 I/O format for 2D Steady Seepage Flow Analysis (f90 FEM SEEP.f90) December 2, 2012 1. Outline of a program f90 FEM SEEP.f90 This is a program for 2D Steady Seepage Flow Analysis. This program can not treat
I/O format for 2D Steady Seepage Flow Analysis (f90 FEM SEEP.f90) December 2, 2012 1. Outline of a program f90 FEM SEEP.f90 This is a program for 2D Steady Seepage Flow Analysis. This program can not treat
What is new in GFLOW 2.1.0?
 What is new in GFLOW 2.1.0? Users that are upgrading from an earlier version of GFLOW (previously named GFLOW 2000) should read this document, since some paradigms of the earlier versions have been modified.
What is new in GFLOW 2.1.0? Users that are upgrading from an earlier version of GFLOW (previously named GFLOW 2000) should read this document, since some paradigms of the earlier versions have been modified.
Mathematical model of Baltic artesian basin version V0. Juris Seņņikovs
 Mathematical model of Baltic artesian basin version V0 Juris Seņņikovs Laboratory for Mathematical Modelling of Environmental and Technological Processes UNIVERSITY OF LATVIA Introduction Structure of
Mathematical model of Baltic artesian basin version V0 Juris Seņņikovs Laboratory for Mathematical Modelling of Environmental and Technological Processes UNIVERSITY OF LATVIA Introduction Structure of
Second International Workshop on Scientific Computing and Applications. Kananaskis, Canada, May 28 - June 1, 2000
 Second International Workshop on Scientific Computing and Applications. Kananaskis, Canada, May 28 - June 1, 2000 Program May 28 (Sunday) 19:00-21:00 Registration and reception Session Chairman: Y. Wong
Second International Workshop on Scientific Computing and Applications. Kananaskis, Canada, May 28 - June 1, 2000 Program May 28 (Sunday) 19:00-21:00 Registration and reception Session Chairman: Y. Wong
SEEP2D & GMS: Simple Tools for Solving a Variety of Seepage Problems. Clarissa Hansen, ERDC-CHL
 SEEP2D & GMS: Simple Tools for Solving a Variety of Seepage Problems Clarissa Hansen, ERDC-CHL CHL Fred Tracy, ERDC-ITL Eileen Glynn, ERDC-GSL Cary Talbot, ERDC-CHL CHL Earl Edris,, ERDC-CHL CHL SEEP2D
SEEP2D & GMS: Simple Tools for Solving a Variety of Seepage Problems Clarissa Hansen, ERDC-CHL CHL Fred Tracy, ERDC-ITL Eileen Glynn, ERDC-GSL Cary Talbot, ERDC-CHL CHL Earl Edris,, ERDC-CHL CHL SEEP2D
PCRasterMODFLOW. Groundwater models within PCRaster. Oliver Schmitz, Utrecht University <o.schmitz at geo.uu.nl>
 PCRasterMODFLOW Groundwater models within PCRaster Oliver Schmitz, Utrecht University PCRasterMODFLOW: Groundwater models within PCRaster by Oliver Schmitz Table of Contents 1.
PCRasterMODFLOW Groundwater models within PCRaster Oliver Schmitz, Utrecht University PCRasterMODFLOW: Groundwater models within PCRaster by Oliver Schmitz Table of Contents 1.
GMS 9.1 Tutorial MODFLOW Conceptual Model Approach II Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques
 v. 9.1 GMS 9.1 Tutorial Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques 00 Objectives The conceptual model approach involves using the GIS tools in the Map module to develop
v. 9.1 GMS 9.1 Tutorial Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques 00 Objectives The conceptual model approach involves using the GIS tools in the Map module to develop
International Journal of Civil & Environmental Engineering IJCEE-IJENS Vol: 14 No: 03 17
 International Journal of Civil & Environmental Engineering IJCEE-IJENS Vol: 14 No: 03 17 Numerical Solution for Diffusion Waves equation using Coupled Finite Difference and Differential Quadrature Methods
International Journal of Civil & Environmental Engineering IJCEE-IJENS Vol: 14 No: 03 17 Numerical Solution for Diffusion Waves equation using Coupled Finite Difference and Differential Quadrature Methods
v GMS 10.0 Tutorial MODFLOW Grid Approach Build a MODFLOW model on a 3D grid Prerequisite Tutorials None Time minutes
 v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Build a MODFLOW model on a 3D grid Objectives The grid approach to MODFLOW pre-processing is described in this tutorial. In most cases, the conceptual model approach is more powerful
v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Build a MODFLOW model on a 3D grid Objectives The grid approach to MODFLOW pre-processing is described in this tutorial. In most cases, the conceptual model approach is more powerful
Stability with FE Pore-Water Pressure
 1 Introduction Stability with FE Pore-Water Pressure One of the most powerful features of GeoStudio is the smooth integration that exists between all the individual programs. For simple pore-water pressure
1 Introduction Stability with FE Pore-Water Pressure One of the most powerful features of GeoStudio is the smooth integration that exists between all the individual programs. For simple pore-water pressure
Solve Non-Linear Parabolic Partial Differential Equation by Spline Collocation Method
 Solve Non-Linear Parabolic Partial Differential Equation by Spline Collocation Method P.B. Choksi 1 and A.K. Pathak 2 1 Research Scholar, Rai University,Ahemdabad. Email:pinalchoksey@gmail.com 2 H.O.D.
Solve Non-Linear Parabolic Partial Differential Equation by Spline Collocation Method P.B. Choksi 1 and A.K. Pathak 2 1 Research Scholar, Rai University,Ahemdabad. Email:pinalchoksey@gmail.com 2 H.O.D.
A mass-conservative version of the semi- Lagrangian semi-implicit HIRLAM using Lagrangian vertical coordinates
 A mass-conservative version of the semi- Lagrangian semi-implicit HIRLAM using Lagrangian vertical coordinates Peter Hjort Lauritzen Atmospheric Modeling & Predictability Section National Center for Atmospheric
A mass-conservative version of the semi- Lagrangian semi-implicit HIRLAM using Lagrangian vertical coordinates Peter Hjort Lauritzen Atmospheric Modeling & Predictability Section National Center for Atmospheric
Connecting 1D and 2D Domains
 Connecting 1D and 2D Domains XP Solutions has a long history of Providing original, high-performing software solutions Leading the industry in customer service and support Educating our customers to be
Connecting 1D and 2D Domains XP Solutions has a long history of Providing original, high-performing software solutions Leading the industry in customer service and support Educating our customers to be
DR. SHUGUANG LI AND ASSOCIATES INTERACTIVE GROUNDWATER MODELING (IGW) TUTORIALS Version 5.0P
 DR. SHUGUANG LI AND ASSOCIATES INTERACTIVE GROUNDWATER MODELING (IGW) TUTORIALS Version 5.0P Dr. Shuguang Li and Associates at Michigan State University IGW Tutorials for Version 5.0P Copyright 2006 by
DR. SHUGUANG LI AND ASSOCIATES INTERACTIVE GROUNDWATER MODELING (IGW) TUTORIALS Version 5.0P Dr. Shuguang Li and Associates at Michigan State University IGW Tutorials for Version 5.0P Copyright 2006 by
APPENDIX B STEP-BY-STEP APPLICATIONS OF THE FEMWATER-LHS
 APPENDIX B STEP-BY-STEP APPLICATIONS OF THE FEMWATER-LHS Steady Two-Dimensional Drainage Problem 1. Double-click on the Argus ONE icon to open Argus ONE. 2. From the PIEs menu found along the top of the
APPENDIX B STEP-BY-STEP APPLICATIONS OF THE FEMWATER-LHS Steady Two-Dimensional Drainage Problem 1. Double-click on the Argus ONE icon to open Argus ONE. 2. From the PIEs menu found along the top of the
MODFLOW - SWI2 Package, Two-Aquifer System. A Simple Example Using the MODFLOW SWI2 (Seawater Intrusion) Package
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial A Simple Example Using the MODFLOW SWI2 (Seawater Intrusion) Package Objectives Become familiar with the interface to the MODFLOW SWI2 package in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials MODFLOW
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial A Simple Example Using the MODFLOW SWI2 (Seawater Intrusion) Package Objectives Become familiar with the interface to the MODFLOW SWI2 package in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials MODFLOW
v. 9.2 GMS 9.2 Tutorial MODFLOW Managing Transient Data Creating transient MODFLOW models with time-varying inputs Prerequisite Tutorials
 v. 9.2 GMS 9.2 Tutorial Creating transient MODFLOW models with time-varying inputs Objectives GMS provides a powerful suite of tools for inputting and managing transient data. These tools allow all data
v. 9.2 GMS 9.2 Tutorial Creating transient MODFLOW models with time-varying inputs Objectives GMS provides a powerful suite of tools for inputting and managing transient data. These tools allow all data
v MODFLOW Grid Approach Build a MODFLOW model on a 3D grid GMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisite Tutorials None
 v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Build a MODFLOW model on a 3D grid Objectives The grid approach to MODFLOW pre-processing is described in this tutorial. In most cases, the conceptual model approach is more powerful
v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Build a MODFLOW model on a 3D grid Objectives The grid approach to MODFLOW pre-processing is described in this tutorial. In most cases, the conceptual model approach is more powerful
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 36
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 In last class, we have derived element equations for two d elasticity problems
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 In last class, we have derived element equations for two d elasticity problems
New Mexico Tech Hyd 510
 Numerics Motivation Modeling process (JLW) To construct a model we assemble and synthesize data and other information to formulate a conceptual model of the situation. The model is conditioned on the science
Numerics Motivation Modeling process (JLW) To construct a model we assemble and synthesize data and other information to formulate a conceptual model of the situation. The model is conditioned on the science
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING
 CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
MAE 3130: Fluid Mechanics Lecture 5: Fluid Kinematics Spring Dr. Jason Roney Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
 MAE 3130: Fluid Mechanics Lecture 5: Fluid Kinematics Spring 2003 Dr. Jason Roney Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Outline Introduction Velocity Field Acceleration Field Control Volume and System Representation
MAE 3130: Fluid Mechanics Lecture 5: Fluid Kinematics Spring 2003 Dr. Jason Roney Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Outline Introduction Velocity Field Acceleration Field Control Volume and System Representation
