Name: Unit 8 Beaumont Middle School 8th Grade, Advanced Algebra I T Q R U
|
|
|
- Todd Shelton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
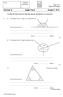
1 Unit 8 eaumont Middle School 8th Grade, dvanced lgebra I Name: P T Q R U S I can define ke terms and identif tpes of angles and adjacent angles. I can identif vertical, supplementar and complementar angles. I can determine the measure of an interior angle of a triangle given two angle measurements. I can determine an interior angle of a triangle given an interior and eterior angle measurement. I can use the sum of the interior angles of a polgon to determine measurements of angles. I can use the angle relationships involving parallel lines and transversals to determine the measures of corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, and alternate eterior angles. I can identif b name the parts of three dimensional shapes (vertices, lateral faces, bases). I can appl the volume formulas of right prisms, clinders, pramids, cones, and spheres. I can appl the formulas for volume to real-world and mathematical problems.
2 ~~ Unit 8, Page 2 ~~ ngles ngles are made up of two ras with a common endpoint, called the verte. Ras are named starting with the endpoint and then another point on the ra. Ra and ra share a common endpoint (). Notice that both ras are named starting with. Point is called the: The sides of the angle are: and ngles are usuall named b three capital letters. The middle letter names the. If onl one angle is located at a verte, then the angle can be named using the verte letter alone. nd if there is a lower case letter between the two sides, the angle can also be referred to using the lower case letter. The angle above can be named: NGLE MESURES protractor is used to measure angles. The protractor is divided evenl into a half circle of 180 degrees (180 ). When the middle of the bottom of the protractor is placed on the verte, and one of the ras of the angle is lined up with 0, the other ra of the angle crosses the protractor at the measure of the angle. The angle below has the ra pointing left lined up with 0 (the outside numbers), and the other ra of the angle crossed the protractor at 55. Tpes of ngles Tpe Tpe Tpe Tpe Measure Measure Measure Measure
3 ~~ Unit 8, Page 3 ~~ Using the protractor below, find the measure of the following angles. Then, tell what tpe of angle it is using the information above. # Question Measure Tpe of ngle 1 What is the measure of RF? 2 What is the measure of RF? 3 What is the measure of DRF? 4 What is the measure of RD? djacent ngles djacent ngles - djacent angles are two angles that have the same verte and share one ra as a side. The do not share space inside the angles. Figure D D ) D is adjacent to D. However, D is not adjacent to D because adjacent angles do not share an space inside the angle. Figure ) These two angles are not adjacent. The share a common ra but do not share the same verte. N S O T M Figure ) NOT is not adjacent to SOM. The share space inside the angles. (overlap)
4 ~~ Unit 8, Page 4 ~~ For each diagram below, name the angle that is adjacent to it. D 1) D is adjacent T U V Z 2) TUV is adjacent R S T P 3) SRP is adjacent J R Q P 4) PQR is adjacent to to to to Independent Practice Part 1: ircle the correct choice for each question.?
5 ~~ Unit 8, Page 5 ~~ Part 2: Fill in the blanks with the correct geometric term. 1) 2) 3) 4) The verte of OD in the drawing above is point 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) O Two acute angles in the figure are O and 10) Part 3: Find the measure of each angle. # Question Measure Tpe of ngle 1 What is the measure of RF? 2 What is the measure of ERF? 3 What is the measure of R? 4 What is the measure of KR? 5 What is the measure of R? 6 What is the measure of FR?
6 ~~ Unit 8, Page 6 ~~ Vertical ngles When two lines intersect, two pairs of VERTIL NGLES are formed. Vertical angles are not adjacent. Vertical angles are located across from each other, the share a common verte, and the sides of the angles are composed of opposite ras. Use a straight edge. Draw ra O opposite to ra O, and then draw ra O opposite to ra OD. Use what ou ve learned about the measure of straight angles to prove that the figure contains two pairs of congruent angles. OD O 45 D O Pairs of vertical angles alwas have the same measure. Vertical angles are (smbol hint ) ongruent means the have the. Set : In the diagram, name the second angle in each pair of vertical angles. Y Q R 1) YPV 4) VPT 2) QPR 5) RPT 3) SPT 6) VPS V P T S Set : Use the information given in the diagram to find the measure of each unknown vertical angle G Set Questions F D J H 1) m F = 2) m = 3) m KJ = 4) m G = 6) Figure above is a K 5) m J = 18) m = 7) The proper notation for the figure is 8) The sum of the angles in figure is + + =
7 ~~ Unit 8, Page 7 ~~ omplementar and Supplementar ngles Two angles are complementar if the sum of their angles measure 90. Two angles are supplementar if the sum of their angles measure 180. omplementar and supplementar angle pairs ma be adjacent, but do not need to be. linear pair is a pair of adjacent angles that are supplementar. elow, the angles marked 32 and 148 are a linear pair. Together, these angle pairs form a Sum = Sum = Sum = 148 Sum = Sum = Sum = These angles are: These angles are: PRTIE: alculate the measure of each unknown angle b a 140 c d 119 h e f g G F H O E D The sum of all the central angles = SET The sum of angles e + d + c = SET 1) m a = 5) m e = 2) m b = 6) m f = 9) m O = 10) m OD = 3)m c = 7) m g = 11)m EOF = 4) m d = 8) m h = 12) m OH =
8 ~~ Unit 8, Page 8 ~~ Independent Practice Part 1: In the diagram below, name the second angle in each pair of vertical angles. Set K M 1) MLN 4) GLM L N 2) KLH 5) KLM J H G 3) GLN 6) HLG Use the information given in the diagram to find the measure of each unknown vertical angle. Set 7) m = m p z w ) m = 9) m z = 10) m w = 11) m m = 12) m p = 13) + = 14) m + p = 15) w + z = 16) Each of the angle pairs in questions above are angles because their sum is. 17) The sum of the four angles located around ever point in the figure above =
9 ~~ Unit 8, Page 9 ~~ Interior ngles of a Triangle FT: The three interior angles of a triangle alwas add up to ⁰. Eample 1: 45⁰ 30⁰ 60⁰ 45⁰ 60⁰ 60⁰ 60⁰ 45⁰ + 45⁰ + = 30⁰ + 60⁰ + = 60⁰ + 60⁰ + 60⁰ = 3( ) = Eample 2: Find the missing angle in the triangle. 20⁰ Solution: Step 1: Write equation. 125⁰ 20⁰ + 125⁰ + = Step 2: ombine like terms. + = 180⁰ Step 3: Isolate. 145⁰ + = 180⁰ Step 4: State the solution. = Step 5: Use solution to answer the original question. The missing angle is Eample 3: Find the missing angle in the triangle. 42⁰
10 ~~ Unit 8, Page 10 ~~ Independent Practice Find the missing angle in the triangles. For each problem, show an equation and solve. 1) 40⁰ 2) 3) 80⁰ 32⁰ 45⁰ 4) 5) 6) 78⁰ 55⁰ 15⁰ 25⁰ 7) 8) 9) 60⁰ 36⁰ 30⁰ 30⁰ 10) Two equations required 11) 12) Two equations required 22⁰ z 38⁰ (2)⁰ (3 4)⁰ ( + 10)⁰ w 32⁰ 38⁰ z w: : z: : : : : : : z:
11 ~~ Unit 8, Page 11 ~~ Eterior ngles The eterior angle of a triangle is alwas equal to the sum of the opposite interior angles. Eample 1: Eamine the figures below. Find the measure of the missing angle. Figure Figure 62⁰ 60⁰ 58⁰ z 40⁰ 50⁰ 1) Sum s in triangle = 2) = 3) Sum of interior angles opposite of angle = + = 1) = 2) = z = 3) Sum of interior angles opposite of angle = Sum of interior angles opposite of angle z = Eample 2: Find the measure of and. Step 1: Use the rule for eterior angles to write equation. 120⁰ = + 120⁰ = 75⁰ + 45⁰ = 75⁰ 120⁰ Step 2: The sum of the interior angles of a triangle equals 180⁰, and supplements D, so either equation: SUM of INTERIOR NGLES 180⁰ = 75⁰ + 45⁰ + 180⁰ = 75⁰ + 45⁰ + SUPPLEMENTL NGLES 180⁰ = 120⁰ + 60⁰ = 180⁰ = 120⁰ + 60⁰ = Independent Practice
12 ~~ Unit 8, Page 12 ~~ Part 1: Find the measure of the missing angle measures. Show an equation for each angle. 1) 2) 102⁰ 50⁰ 105⁰ 38⁰ 3) 4) 28⁰ 55⁰ 110⁰ 81⁰ 5) 6) 33⁰ 122⁰ 39⁰ 119⁰ 7) w z (2 3) v 133⁰ 8) (2 + 45) 82⁰ 9) 64⁰ 84⁰ ( + 25) w v
13 Interior ngles of Polgons ~~ Unit 8, Page 13 ~~ n Interior ngle is an angle located inside a figure. Triangles: The interior angles of a TRINGLE add up to 180⁰. Interior ngles of POLYGONS 1) State the number of sides for each polgon. 2) From the given point at one verte, draw diagonals to find the number of non-overlapping triangles in each polgon. 3) Use the sum of angles in each triangle to determine the total sum of the interior angles of each figure. Number of sides = Number of s = SUM of int s = Number of sides = Number of s = SUM of int s = Number of sides = Number of s = SUM of int s = D Number of sides = Number of s = SUM of int s = E Number of sides = Number of s = SUM of int s =
14 ~~ Unit 8, Page 14 ~~ Number of sides = Number of s = SUM of int s = F If this polgon had 11 sides (that s an undecagon), then: G How man triangles? What would be the sum of the interior s? The General Rule Make a conjecture about how ou can calculate the sum of the interior angles of an polgon. Test our conjecture: Write an epression that ou could use to calculate the sum of the interior angles of an polgon using n for the number of sides. If the polgon was regular and ou know the sum of angles, how could ou find the measure of each angle?
15 ~~ Unit 8, Page 15 ~~ EXMPLE 1: What is the measure of each angle in a regular DEGON? NSWER: The measure of each angle in a regular decagon = EXMPLE 2; Find the measure of. EXMPLE 3: Find the measures of the missing angles. F Guided Practice: Eample 1: What is the measure of each angle in a regular 20-sided polgon? Eample 2: Find the measure of. Sum of the interior angles: Measure of each angle: Sum of the interior angles: Measure of :
16 ~~ Unit 8, Page 16 ~~ Eample 3: Find the measures of the missing angles. INDEPENDENT PRTIE lassif each polgon b its number of sides and state the sum of the interior angles. 1) 2) 3) lassif: Sum of the interior angles: lassif: Sum of the interior angles: lassif: Sum of the interior angles: 4) a polgon with 8 sides 5) a polgon with 5 sides lassif: Sum of the interior angles: lassif: Sum of the interior angles: What is the measure of each angle in the following regular polgons? 6) 7) Regular Pentagon Sum of the interior angles: Measure of each angle: Sum of the interior angles: Measure of each angle:
17 ~~ Unit 8, Page 17 ~~ Find the measure of the missing angles. 8) 9) Sum of the interior angles: Measure of : Sum of the interior angles: Measure of : 10) 11) Sum of the interior angles: Measure of : Sum of the interior angles: Measure of : 12) 13)
18 ~~ Unit 8, Page 18 ~~ orresponding, lternate Interior, and lternate Eterior ngles If two parallel lines are intersected b another line, how man angles are formed? Number them on the diagram. P T Q R U S PQ RS TU is a transversal The etra arrows on two of the lines mean the are. The line that intersects the two lines is called a. The number of angles formed is. The angles formed when parallel lines are cut b a transversal line have special relationships and are named according to those relationships with one another. ORRESPONDING NGLES Definition: Name the corresponding angles for the following. 1) 1 corresponds with 2) 2 corresponds with 3) 3 corresponds with 4) 4 corresponds with What do ou notice about the angle pairs above? omplete the sentence: If two angles are corresponding angles, then the are:
19 ~~ Unit 8, Page 19 ~~ LTERNTE INTERIOR NGLES Word attack To alternate means INterior means: Definition: Name the alternate interior angle for the following angles. 1) 3 is an alternate interior angle with 2) 4 is an alternate interior angle with How man pairs of alternate interior angles are possible? What do ou notice about the angle pairs above? omplete the sentence: If two angles are alternate interior angles, then the are: LTERNTE EXTERIOR NGLES Word attack To alternate means Eterior means: Definition: Name the alternate eterior angle for the following angles. 1) 1 is an alternate eterior angle with 2) 2 is an alternate eterior angle with How man pairs of alternate eterior angles are possible? What do ou notice about the angle pairs above? omplete the sentence: If two angles are alternate eterior angles, then the are: Look at the diagram below. For each pair of angles, state whether the are corresponding (), alternate interior (I), alternate eterior (E), vertical (V), or supplementar (S). s u w z F v E t D 1) u, 6) t, 11) t, u 2) w, s 7) w, z 12) w, 3) t, 8) v, w 13) w, s 4) s, t 9) v, z 14) s, v 5) w, 10) s, z 15), z 16) If m s = 110⁰, find the measure of the remaining angles. m v = m t = m u = m w = m = m = m z =
20 ~~ Unit 8, Page 20 ~~ INDEPENDENT PRTIE Part 1: 1) Parallel lines a and b when cut b transversal l form eight angles, as shown in the diagram below. Use the diagram to find the measures of each of the angles. l a b 108⁰ 1) m 1 = 3) m 3 = 5) m 5 = 7) m 7 = 2) m 2 = 4) m 4 = 6) m 6 = 8) m 8 = 108⁰ 2) Parallel lines a and b when cut b transversal l form eight angles, as shown in the diagram below. Use the diagram to find the measures of each of the angles. a b ⁰ 1 2 l 9) m 1 = 11) m 2 = 13) m 3 = 15) m 4 = 63⁰ 10) m 5 = 12) m 6 = 14) m 7 = 16) m 8 =
21 ~~ Unit 8, Page 21 ~~ Part 2: For each pair of angles, state whether the are corresponding (), alternate interior (I), alternate eterior (E), vertical (V), or supplementar (S) angles l m l m 1) 1 and 4 6) 6 and 5 11) 3 and 6 2) 2 and 6 7) 2 and 7 12) 4 and 8 3) 1 and 3 8) 1 and 2 13) 1 and 5 4) 5 and 8 9) 4 and 5 14) 2 and 3 5) 5 and 7 10) 6 and 8 15) 6 and 7 Parallel lines a and b when cut b transversal m form eight angles, as shown in the diagram below. Use the diagram below for problems 16 and ) m 2 = 17) m 4 = a b 121⁰ m Parallel lines a and b when cut b transversals m and n. Find all of the unknown angle measures. 18) m 18 = 19) m 19 = 20) m 20 = 21) m 21 = 22) m 22 = 23) m 23 = b 24) m 24 = 25) m 25 = 26) m 26 = 27) m 27 = 28) m 28 = 29) m 29 = n m a
22 Finding Unknown ngle Measures ~~ Unit 8, Page 22 ~~ We will use the angle relationships that are formed when two parallel lines are intersected b a transversal to find the measures of missing angles. ll of the angle relationships will either be supplementar or congruent. Eample : The pair of angles are either vertical angles, alternate interior angles, alternate eterior angles, or corresponding angles; so the are congruent. ll ou have to do is set up and solve an equation where the epressions are congruent. Once ou have solved for, substitute that value back into each epression to find the measure of each angle. #1 Relationship: Equation: = G = D = #2 Relationship: Equation: = D = HF = Eample : Each pair of angles are supplementar to each other, which means the angles add up to 180 o. ll ou have to do is set up and solve an equation where the epressions add up to equal 180 o. Once ou have solved for, substitute that value back into each epression to find the measure of each angle. #3 Relationship: Equation: = FD = HF =
23 ~~ Unit 8, Page 23 ~~ INDEPENDENT PRTIE Part 1: Find the measure of each missing angle in the parallel lines and transversals. Each pair of angles is either supplementar or congruent (vertical angles, alternate interior angles, alternate eterior angles, or corresponding angles). State the relationship, set up an appropriate equation and solve for. Once ou've solved for, substitute that value back into each epression to find the measure of each angle. Relationship: 1) Equation: 2) = EF = GFH = Relationship: Equation: = D = FH = 3) Relationship: Equation: = EF = FH = 4) Relationship: Equation: = EF = DF =
24 ~~ Unit 8, Page 24 ~~ 5) Relationship: Equation: = = FH = 6) Relationship: Equation: = = GFH = 7) Relationship: Equation: = D = EF = 8) Relationship: = = GFH = Equation: Part 2: Review lassif each polgon b its number of sides and state the sum of the interior angles. 1) 2) lassif: Sum of the interior angles: lassif: Sum of the interior angles:
25 ~~ Unit 8, Page 25 ~~ What is the measure of each angle in the following regular polgons? 3) 4) Regular Decagon Sum of the interior angles: Measure of each angle: Sum of the interior angles: Measure of each angle: Part 3: The following problems are multiple choice. ircle the letter indicating the best answer for each question. 1) 3) 2) 4)
Lines, angles, triangles, and More
 Unit 8 eaumont Middle School 8th Grade, 2016-2017 Introduction to lgebra Name: P R U T S Q Lines, angles, triangles, and More I can define key terms and identify types of angles and adjacent angles. I
Unit 8 eaumont Middle School 8th Grade, 2016-2017 Introduction to lgebra Name: P R U T S Q Lines, angles, triangles, and More I can define key terms and identify types of angles and adjacent angles. I
Grade 6 Math Circles February 29, D Geometry
 1 Universit of Waterloo Facult of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles Feruar 29, 2012 2D Geometr What is Geometr? Geometr is one of the oldest ranches in
1 Universit of Waterloo Facult of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles Feruar 29, 2012 2D Geometr What is Geometr? Geometr is one of the oldest ranches in
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 13: Angle Relationships and Transformations
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 13: Angle Relationships and Transformations Angle Relationships Sllabus Objectives: (7.1) The student will identif measures of complementar, supplementar, and vertical angles. (7.2)
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 13: Angle Relationships and Transformations Angle Relationships Sllabus Objectives: (7.1) The student will identif measures of complementar, supplementar, and vertical angles. (7.2)
Summer Dear Geometry Students and Parents:
 Summer 2018 Dear Geometry Students and Parents: Welcome to Geometry! For the 2018-2019 school year, we would like to focus your attention to the prerequisite skills and concepts for Geometry. In order
Summer 2018 Dear Geometry Students and Parents: Welcome to Geometry! For the 2018-2019 school year, we would like to focus your attention to the prerequisite skills and concepts for Geometry. In order
12.1. Angle Relationships. Identifying Complementary, Supplementary Angles. Goal: Classify special pairs of angles. Vocabulary. Complementary. angles.
 . Angle Relationships Goal: Classif special pairs of angles. Vocabular Complementar angles: Supplementar angles: Vertical angles: Eample Identifing Complementar, Supplementar Angles In quadrilateral PQRS,
. Angle Relationships Goal: Classif special pairs of angles. Vocabular Complementar angles: Supplementar angles: Vertical angles: Eample Identifing Complementar, Supplementar Angles In quadrilateral PQRS,
Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes
 Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess
Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess
Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes
 Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My
Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My
Are You Ready? Conditional Statements
 SKILL 88 onditional Statements Teaching Skill 88 Objective Determine whether a conditional statement is true, write its converse, and determine whether the converse is true. Review with students the different
SKILL 88 onditional Statements Teaching Skill 88 Objective Determine whether a conditional statement is true, write its converse, and determine whether the converse is true. Review with students the different
Section A Angle Facts Grade F D
 Name: Teacher ssessment Section ngle Facts Grade F IN THIS SETION NONE OF THE IGRMS RE RWN URTELY. 1. (a) The diagram shows 3 angles on a straight line. Not drawn accu Work out the value of. 60º 70º º..
Name: Teacher ssessment Section ngle Facts Grade F IN THIS SETION NONE OF THE IGRMS RE RWN URTELY. 1. (a) The diagram shows 3 angles on a straight line. Not drawn accu Work out the value of. 60º 70º º..
G7-3 Measuring and Drawing Angles and Triangles
 G7-3 Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles right angle acute angles obtuse angles 90 less than 90 more than 90 and less than 180 1. Without using a protractor, identify each angle as acute or obtuse.
G7-3 Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles right angle acute angles obtuse angles 90 less than 90 more than 90 and less than 180 1. Without using a protractor, identify each angle as acute or obtuse.
5 and Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
 Ch 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 3 1 Properties of Parallel Lines 3 Proving Lines Parallel 3 3 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 3 Parallel Lines and the Triangle Angles Sum Theorem 3 5 The Polgon
Ch 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 3 1 Properties of Parallel Lines 3 Proving Lines Parallel 3 3 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 3 Parallel Lines and the Triangle Angles Sum Theorem 3 5 The Polgon
Reteaching Inequalities in Two Triangles
 Name ate lass Inequalities in Two Triangles INV You have worked with segments and angles in triangles. Now ou will eplore inequalities with triangles. Hinge Theorem If two sides of one triangle are congruent
Name ate lass Inequalities in Two Triangles INV You have worked with segments and angles in triangles. Now ou will eplore inequalities with triangles. Hinge Theorem If two sides of one triangle are congruent
Geometry Review. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Geometr Review Multiple hoice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Tell whether the ordered pair (5, 3) is a solution of the sstem. a. es b. no 2. Solve Express
Geometr Review Multiple hoice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Tell whether the ordered pair (5, 3) is a solution of the sstem. a. es b. no 2. Solve Express
When two (or more) parallel lines are cut by a transversal, the following angle relationships are true:
 Lesson 8: Parallel Lines Two coplanar lines are said to be parallel if they never intersect. or any given point on the first line, its distance to the second line is equal to the distance between any other
Lesson 8: Parallel Lines Two coplanar lines are said to be parallel if they never intersect. or any given point on the first line, its distance to the second line is equal to the distance between any other
Geo Final Review 2014
 Period: ate: Geo Final Review 2014 Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. n angle measures 2 degrees more than 3 times its complement. Find the
Period: ate: Geo Final Review 2014 Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. n angle measures 2 degrees more than 3 times its complement. Find the
Boardworks Ltd KS3 Mathematics. S1 Lines and Angles
 1 KS3 Mathematics S1 Lines and Angles 2 Contents S1 Lines and angles S1.1 Labelling lines and angles S1.2 Parallel and perpendicular lines S1.3 Calculating angles S1.4 Angles in polygons 3 Lines In Mathematics,
1 KS3 Mathematics S1 Lines and Angles 2 Contents S1 Lines and angles S1.1 Labelling lines and angles S1.2 Parallel and perpendicular lines S1.3 Calculating angles S1.4 Angles in polygons 3 Lines In Mathematics,
a + b + c = 180 Example: 1. a = 2. b = 3. a = 4.1 Interior angles of a triangle. a = 180 So a = 1 3. Find the missing measurements.
 4.1 Interior angles of a triangle. b a a + b + c = 180 c Example: a 70 35 1 3. Find the missing measurements. a + 70 + 35 = 180 So a = 75 1. a = 2. b = a 3 4 6 6 1 4 b 3. a = 135 Triangle Sum onjecture:
4.1 Interior angles of a triangle. b a a + b + c = 180 c Example: a 70 35 1 3. Find the missing measurements. a + 70 + 35 = 180 So a = 75 1. a = 2. b = a 3 4 6 6 1 4 b 3. a = 135 Triangle Sum onjecture:
Unit 10 Study Guide: Plane Figures
 Unit 10 Study Guide: Plane Figures *Be sure to watch all videos within each lesson* You can find geometric shapes in art. Whether determining the amount of leading or the amount of glass needed for a piece
Unit 10 Study Guide: Plane Figures *Be sure to watch all videos within each lesson* You can find geometric shapes in art. Whether determining the amount of leading or the amount of glass needed for a piece
Example 1. Find the angle measure of angle b, using opposite angles.
 2..1 Exploring Parallel Lines Vertically opposite angles are equal When two lines intersect, the opposite angles are equal. Supplementary angles add to 180 Two (or more) adjacent angles on the same side
2..1 Exploring Parallel Lines Vertically opposite angles are equal When two lines intersect, the opposite angles are equal. Supplementary angles add to 180 Two (or more) adjacent angles on the same side
Reteaching Golden Ratio
 Name Date Class Golden Ratio INV 11 You have investigated fractals. Now ou will investigate the golden ratio. The Golden Ratio in Line Segments The golden ratio is the irrational number 1 5. c On the line
Name Date Class Golden Ratio INV 11 You have investigated fractals. Now ou will investigate the golden ratio. The Golden Ratio in Line Segments The golden ratio is the irrational number 1 5. c On the line
Glossary alternate interior angles absolute value function Example alternate exterior angles Example angle of rotation Example
 Glossar A absolute value function An absolute value function is a function that can be written in the form, where is an number or epression. alternate eterior angles alternate interior angles Alternate
Glossar A absolute value function An absolute value function is a function that can be written in the form, where is an number or epression. alternate eterior angles alternate interior angles Alternate
Geometry Notes - Unit 4 Congruence
 Geometry Notes - Unit 4 ongruence Triangle is a figure formed by three noncollinear points. lassification of Triangles by Sides Equilateral triangle is a triangle with three congruent sides. Isosceles
Geometry Notes - Unit 4 ongruence Triangle is a figure formed by three noncollinear points. lassification of Triangles by Sides Equilateral triangle is a triangle with three congruent sides. Isosceles
November 10, 2004 : Fax:
 Honors Geometry Issue Super Mathter November 0, 004 : 30-0-6030 Fax: 30--864 For class info, visit www.mathenglish.com irect your questions and comments to rli@smart4micro.com Name: Peter Lin Peter Lin
Honors Geometry Issue Super Mathter November 0, 004 : 30-0-6030 Fax: 30--864 For class info, visit www.mathenglish.com irect your questions and comments to rli@smart4micro.com Name: Peter Lin Peter Lin
Geometry Practice. 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles.
 Geometry Practice Name 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles. 2. Planes that meet to form right angles are called planes. 3. Lines that cross are called lines. 4.
Geometry Practice Name 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles. 2. Planes that meet to form right angles are called planes. 3. Lines that cross are called lines. 4.
Plot and connect the points in a coordinate plane to make a polygon. Name the polygon.
 . Start Thinking Find at least two objects in each of the following categories: circle, square, triangle, and rectangle (nonsquare). Use a table to compare each object of the same categor in the following
. Start Thinking Find at least two objects in each of the following categories: circle, square, triangle, and rectangle (nonsquare). Use a table to compare each object of the same categor in the following
7.1 Interior and Exterior Angles
 Name Class Date 7.1 Interior and Exterior ngles Essential Question: What can you say about the interior and exterior angles of a triangle and other polygons? G.6.D Verify theorems about the relationships
Name Class Date 7.1 Interior and Exterior ngles Essential Question: What can you say about the interior and exterior angles of a triangle and other polygons? G.6.D Verify theorems about the relationships
7.1 Interior and Exterior Angles
 Name Class Date 7.1 Interior and Exterior ngles Essential Question: What can you say about the interior and exterior angles of a triangle and other polygons? Resource Locker Explore 1 Exploring Interior
Name Class Date 7.1 Interior and Exterior ngles Essential Question: What can you say about the interior and exterior angles of a triangle and other polygons? Resource Locker Explore 1 Exploring Interior
Unit 8 Plane Geometry
 Unit 8 Plane Geometry Grade 9 pplied Lesson Outline *Note: This unit could stand alone and be placed anywhere in the course. IG PITURE Students will: investigate properties of geometric objects using dynamic
Unit 8 Plane Geometry Grade 9 pplied Lesson Outline *Note: This unit could stand alone and be placed anywhere in the course. IG PITURE Students will: investigate properties of geometric objects using dynamic
Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention 1-1 Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes
 1 Read to Go On? Skills Intervention 1-1 Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes Find these vocabular words in Lesson 1-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular point line plane collinear coplanar segment
1 Read to Go On? Skills Intervention 1-1 Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes Find these vocabular words in Lesson 1-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular point line plane collinear coplanar segment
Line: It s a straight arrangement of points that extends indefinitely in opposite directions.
 More Terminology and Notation: Plane: It s an infinitely large flat surface. Line: It s a straight arrangement of points that extends indefinitely in opposite directions. ollinear Points: Points that lie
More Terminology and Notation: Plane: It s an infinitely large flat surface. Line: It s a straight arrangement of points that extends indefinitely in opposite directions. ollinear Points: Points that lie
ANGLES See the Math Notes boxes in Lessons and for more information about angle relationships.
 CC1 Basic Definitions Defense Practice ANGLES 2.1.1 2.1.5 Applications of geometr in everda settings often involve the measures of angles. In this chapter we begin our stud of angle measurement. After
CC1 Basic Definitions Defense Practice ANGLES 2.1.1 2.1.5 Applications of geometr in everda settings often involve the measures of angles. In this chapter we begin our stud of angle measurement. After
Reteaching Exploring Angles of Polygons
 Name Date lass Eploring Angles of Polygons INV X 3 You have learned to identify interior and eterior angles in polygons. Now you will determine angle measures in regular polygons. Interior Angles Sum of
Name Date lass Eploring Angles of Polygons INV X 3 You have learned to identify interior and eterior angles in polygons. Now you will determine angle measures in regular polygons. Interior Angles Sum of
9-1. Translations. Vocabulary. Review. Vocabulary Builder. Use Your Vocabulary
 9- Translations Vocabular Review. Underline the correct word to complete the sentence. If two triangles are congruent, corresponding angle measures are the same/ different and corresponding side lengths
9- Translations Vocabular Review. Underline the correct word to complete the sentence. If two triangles are congruent, corresponding angle measures are the same/ different and corresponding side lengths
Ms. Nassif Mathematics. Guide. 2- Correction key. Example of an appropriate method. Area of the base. Volume of water
 1 2 2- orrection key Example of an appropriate method rea of the base Volume of water 568416 - Mathematics Guide 2 ( 19 16)( 19 12)( 19 10) = 3591 59.924... m 19 = rea of the base height 59.924 2 = 119.84
1 2 2- orrection key Example of an appropriate method rea of the base Volume of water 568416 - Mathematics Guide 2 ( 19 16)( 19 12)( 19 10) = 3591 59.924... m 19 = rea of the base height 59.924 2 = 119.84
Answer Key. 1.1 The Three Dimensions. Chapter 1 Basics of Geometry. CK-12 Geometry Honors Concepts 1. Answers
 1.1 The Three Dimensions 1. Possible answer: You need only one number to describe the location of a point on a line. You need two numbers to describe the location of a point on a plane. 2. vary. Possible
1.1 The Three Dimensions 1. Possible answer: You need only one number to describe the location of a point on a line. You need two numbers to describe the location of a point on a plane. 2. vary. Possible
GR 10 MATHS EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRY
 G 0 MTHS ULIN GOMTY Gr 0 Maths uclidean Geometr Geometr is a fun topic in which we work with lines angles triangles quadrilaterals polgons while we investigate and discover as much as we can for ourselves;
G 0 MTHS ULIN GOMTY Gr 0 Maths uclidean Geometr Geometr is a fun topic in which we work with lines angles triangles quadrilaterals polgons while we investigate and discover as much as we can for ourselves;
Unit 9 Study Guide. Multiple Choice (2 points) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Unit 9 Study Guide Multiple hoice (2 points) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the perimeter of each rectangle. 1. 38 m 18 m a. 684 m c. 56 m b. 94 m d.
Unit 9 Study Guide Multiple hoice (2 points) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the perimeter of each rectangle. 1. 38 m 18 m a. 684 m c. 56 m b. 94 m d.
Angles. Problems: A.! Name the vertex of the angle. What rays are the sides of the angle? C.! Give three other names of LJK.
 ngles page # Problems:. ngles. Name the vertex of the angle.. What rays are the sides of the angle? J. Give three other names of LJK.. Name the following angles with three letters: = = N M The remaining
ngles page # Problems:. ngles. Name the vertex of the angle.. What rays are the sides of the angle? J. Give three other names of LJK.. Name the following angles with three letters: = = N M The remaining
Geometry Basics * Rory Adams Free High School Science Texts Project Mark Horner Heather Williams. 1 Introduction. 2 Points and Lines
 OpenStax-NX module: m31494 1 Geometry asics * Rory dams Free High School Science Texts Project Mark Horner Heather Williams This work is produced by OpenStax-NX and licensed under the reative ommons ttribution
OpenStax-NX module: m31494 1 Geometry asics * Rory dams Free High School Science Texts Project Mark Horner Heather Williams This work is produced by OpenStax-NX and licensed under the reative ommons ttribution
9.1 Angle Relationships
 ? LESSON 9.1 ngle Relationships ESSENTIL QUESTION How can you use angle relationships to solve problems? Equations, epressions, and relationships 7.11. Write and solve equations using geometry concepts,
? LESSON 9.1 ngle Relationships ESSENTIL QUESTION How can you use angle relationships to solve problems? Equations, epressions, and relationships 7.11. Write and solve equations using geometry concepts,
Special Types of Angles
 Objectives: to determine measures of complementary, supplementary, and vertical angles to name or identify complementary, supplementary, adjacent, and vertical angles...to name, identify and/or determine
Objectives: to determine measures of complementary, supplementary, and vertical angles to name or identify complementary, supplementary, adjacent, and vertical angles...to name, identify and/or determine
Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms
 Unit 1 asics of Geometry Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically looks
Unit 1 asics of Geometry Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically looks
Convex polygon - a polygon such that no line containing a side of the polygon will contain a point in the interior of the polygon.
 Chapter 7 Polygons A polygon can be described by two conditions: 1. No two segments with a common endpoint are collinear. 2. Each segment intersects exactly two other segments, but only on the endpoints.
Chapter 7 Polygons A polygon can be described by two conditions: 1. No two segments with a common endpoint are collinear. 2. Each segment intersects exactly two other segments, but only on the endpoints.
Translations. Essential Question How can you translate a figure in a coordinate plane? A B
 . Translations Essential Question How can ou translate a figure in a coordinate plane? Translating a Triangle in a oordinate Plane USING TOOLS STRTEGILLY To be proficient in math, ou need to use appropriate
. Translations Essential Question How can ou translate a figure in a coordinate plane? Translating a Triangle in a oordinate Plane USING TOOLS STRTEGILLY To be proficient in math, ou need to use appropriate
= = The number system. Module. Glossary Math Tools... 33
 - > + > < - %. < + a = - = = b in. F - - Module The number sstem Lesson Rational and Irrational Numbers........ 8.NS. Lesson ompare and Order Numbers......... 8 8.NS., 8.NS. Lesson Estimate the Value of
- > + > < - %. < + a = - = = b in. F - - Module The number sstem Lesson Rational and Irrational Numbers........ 8.NS. Lesson ompare and Order Numbers......... 8 8.NS., 8.NS. Lesson Estimate the Value of
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Name Date Chapter 1 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 3 + ( 1) = 2. 10 11 = 3. 6 + 8 = 4. 9 ( 1) = 5. 12 ( 8) = 6. 15 7 = + = 8. 5 ( 15) 7. 12 3 + = 9. 1 12 = Find the area
Name Date Chapter 1 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 3 + ( 1) = 2. 10 11 = 3. 6 + 8 = 4. 9 ( 1) = 5. 12 ( 8) = 6. 15 7 = + = 8. 5 ( 15) 7. 12 3 + = 9. 1 12 = Find the area
Isometry: When the preimage and image are congruent. It is a motion that preserves the size and shape of the image as it is transformed.
 Chapter Notes Notes #36: Translations and Smmetr (Sections.1,.) Transformation: A transformation of a geometric figure is a change in its position, shape or size. Preimage: The original figure. Image:
Chapter Notes Notes #36: Translations and Smmetr (Sections.1,.) Transformation: A transformation of a geometric figure is a change in its position, shape or size. Preimage: The original figure. Image:
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships
 Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
To prove theorems using figures in the coordinate plane
 6-9 s Using Coordinate Geometr Content Standard G.GPE.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraicall. bjective To prove theorems using figures in the coordinate plane Better draw a diagram!
6-9 s Using Coordinate Geometr Content Standard G.GPE.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraicall. bjective To prove theorems using figures in the coordinate plane Better draw a diagram!
7.4 Start Thinking. 7.4 Warm Up. 7.4 Cumulative Review Warm Up
 7. Start Thinking rhombus and a square are both quadrilaterals with four congruent sides, but a square alwas contains four right angles. Examine the diagrams below and determine some other distinctive
7. Start Thinking rhombus and a square are both quadrilaterals with four congruent sides, but a square alwas contains four right angles. Examine the diagrams below and determine some other distinctive
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations
 Translations, Reflections, and Rotations The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Transformations Learning Targets: Perform transformations on and off the coordinate plane. Identif characteristics of transformations
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Transformations Learning Targets: Perform transformations on and off the coordinate plane. Identif characteristics of transformations
Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall October 9/10/11 Angles and Light
 Facult of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall 2018 - October 9/10/11 Angles and Light Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Toda we will be learning about angles.
Facult of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall 2018 - October 9/10/11 Angles and Light Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Toda we will be learning about angles.
Basics of Geometry Unit 1 - Notes. Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes.
 asics of Geometry Unit 1 - Notes Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically
asics of Geometry Unit 1 - Notes Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically
H Geo Final Review Packet Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 H Geo Final Review Packet Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which angle measures approximatel 7?.. In the figure below, what is the name of
H Geo Final Review Packet Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which angle measures approximatel 7?.. In the figure below, what is the name of
Ch 1 Note Sheet L2 Key.doc 1.1 Building Blocks of Geometry
 1.1 uilding locks of Geometry Read page 28. It s all about vocabulary and notation! To name something, trace the figure as you say the name, if you trace the figure you were trying to describe you re correct!
1.1 uilding locks of Geometry Read page 28. It s all about vocabulary and notation! To name something, trace the figure as you say the name, if you trace the figure you were trying to describe you re correct!
Ganado Unified School District 7 th Grade Mathematics
 Ganado Unified School District 7 th Grade Mathematics PACING Guide SY 2014-2015 Quarter 3 Week 1 Graphs Text Reference Concept : Use random sampling to draw inferences about population. 7.SP.A.1. Understand
Ganado Unified School District 7 th Grade Mathematics PACING Guide SY 2014-2015 Quarter 3 Week 1 Graphs Text Reference Concept : Use random sampling to draw inferences about population. 7.SP.A.1. Understand
Naming Angles. One complete rotation measures 360º. Half a rotation would then measure 180º. A quarter rotation would measure 90º.
 Naming Angles What s the secret for doing well in geometry? Knowing all the angles. An angle can be seen as a rotation of a line about a fixed point. In other words, if I were mark a point on a paper,
Naming Angles What s the secret for doing well in geometry? Knowing all the angles. An angle can be seen as a rotation of a line about a fixed point. In other words, if I were mark a point on a paper,
(Current Re nweb Grade)x.90 + ( finalexam grade) x.10 = semester grade
 2//2 5:7 PM Name ate Period This is your semester exam which is worth 0% of your semester grade. You can determine grade what-ifs by using the equation below. (urrent Re nweb Grade)x.90 + ( finalexam grade)
2//2 5:7 PM Name ate Period This is your semester exam which is worth 0% of your semester grade. You can determine grade what-ifs by using the equation below. (urrent Re nweb Grade)x.90 + ( finalexam grade)
Geometry Unit 4a - Notes Triangle Relationships
 Geometry Unit 4a - Notes Triangle Relationships This unit is broken into two parts, 4a & 4b. test should be given following each part. Triangle - a figure formed by three segments joining three noncollinear
Geometry Unit 4a - Notes Triangle Relationships This unit is broken into two parts, 4a & 4b. test should be given following each part. Triangle - a figure formed by three segments joining three noncollinear
Are You Ready? Triangle Sum Theorem
 SKILL 30 Triangle Sum Theorem Teaching Skill 30 Objective Use the Triangle Sum Theorem to find the measures of missing angles. Have students read the Triangle Sum Theorem. Point out that the theorem is
SKILL 30 Triangle Sum Theorem Teaching Skill 30 Objective Use the Triangle Sum Theorem to find the measures of missing angles. Have students read the Triangle Sum Theorem. Point out that the theorem is
Angle Unit Definitions
 ngle Unit Definitions Name lock Date Term Definition Notes Sketch D djacent ngles Two coplanar angles with a coon side, a coon vertex, and no coon interior points. Must be named with 3 letters OR numbers
ngle Unit Definitions Name lock Date Term Definition Notes Sketch D djacent ngles Two coplanar angles with a coon side, a coon vertex, and no coon interior points. Must be named with 3 letters OR numbers
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Section 1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes
 Section 1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes I CAN. Identify and model points, lines, and planes. Identify collinear and coplanar points and intersecting lines and planes in space. Undefined Term- Words, usually
Section 1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes I CAN. Identify and model points, lines, and planes. Identify collinear and coplanar points and intersecting lines and planes in space. Undefined Term- Words, usually
Math-2. Lesson 7-4 Properties of Parallelograms And Isosceles Triangles
 Math-2 Lesson 7-4 Properties of Parallelograms nd Isosceles Triangles What sequence of angles would you link to prove m4 m9 3 1 4 2 13 14 16 15 lternate Interior Corresponding 8 5 7 6 9 10 12 11 What sequence
Math-2 Lesson 7-4 Properties of Parallelograms nd Isosceles Triangles What sequence of angles would you link to prove m4 m9 3 1 4 2 13 14 16 15 lternate Interior Corresponding 8 5 7 6 9 10 12 11 What sequence
9 3 Rotations 9 4 Symmetry
 h 9: Transformations 9 1 Translations 9 Reflections 9 3 Rotations 9 Smmetr 9 1 Translations: Focused Learning Target: I will be able to Identif Isometries. Find translation images of figures. Vocabular:
h 9: Transformations 9 1 Translations 9 Reflections 9 3 Rotations 9 Smmetr 9 1 Translations: Focused Learning Target: I will be able to Identif Isometries. Find translation images of figures. Vocabular:
Parallel Lines and Triangles. Objectives To use parallel lines to prove a theorem about triangles To find measures of angles of triangles
 -5 Parallel Lines and Triangles ommon ore State Standards G-O..0 Prove theorems about triangles... measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 80. MP, MP, MP 6 Objectives To use parallel lines to
-5 Parallel Lines and Triangles ommon ore State Standards G-O..0 Prove theorems about triangles... measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 80. MP, MP, MP 6 Objectives To use parallel lines to
Grade 6 Math Circles Fall 2010 Tessellations I
 1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics entre for Education in Mathematics and omputing Grade 6 Math ircles Fall 2010 Tessellations I tessellation is a collection of shapes that fit together with
1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics entre for Education in Mathematics and omputing Grade 6 Math ircles Fall 2010 Tessellations I tessellation is a collection of shapes that fit together with
Let s use a more formal definition. An angle is the union of two rays with a common end point.
 hapter 2 ngles What s the secret for doing well in geometry? Knowing all the angles. s we did in the last chapter, we will introduce new terms and new notations, the building blocks for our success. gain,
hapter 2 ngles What s the secret for doing well in geometry? Knowing all the angles. s we did in the last chapter, we will introduce new terms and new notations, the building blocks for our success. gain,
Geometry Definitions, Postulates, and Theorems
 Geometry efinitions, Postulates, and Theorems hapter : Similarity Section.1: Ratios, Proportions, and the Geometric ean Standards: Prepare for 8.0 Students know, derive, and solve problems involving the
Geometry efinitions, Postulates, and Theorems hapter : Similarity Section.1: Ratios, Proportions, and the Geometric ean Standards: Prepare for 8.0 Students know, derive, and solve problems involving the
Section A Types of Angles Grade G / F
 Name: Teacher ssessment Section Types of ngles Grade G / F 1. (a) Measure and write down the size of the angle p. (b) Write down what type of angle it is. p (a) Size of angle (b) Type of angle p =... degrees...
Name: Teacher ssessment Section Types of ngles Grade G / F 1. (a) Measure and write down the size of the angle p. (b) Write down what type of angle it is. p (a) Size of angle (b) Type of angle p =... degrees...
Circles and Polygons Long-Term Memory Review Review 1 (Note: Figures are not drawn to scale.)
 Review 1 (Note: Figures are not drawn to scale.) 1. Fill in the lank: In circle below, the angle shown is a/an angle. 2. The measure of a central angle and the measure of the arc that it intersects are
Review 1 (Note: Figures are not drawn to scale.) 1. Fill in the lank: In circle below, the angle shown is a/an angle. 2. The measure of a central angle and the measure of the arc that it intersects are
Triangle Geometry Isometric Triangles Lesson 1
 Triangle eometry Isometric Triangles Lesson 1 Review of all the TORMS in OMTRY that you know or soon will know!. Triangles 1. The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180º (Triangle
Triangle eometry Isometric Triangles Lesson 1 Review of all the TORMS in OMTRY that you know or soon will know!. Triangles 1. The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180º (Triangle
Review Interior Angle Sum New: Exterior Angle Sum
 Review Interior Angle Sum New: Exterior Angle Sum QUIZ: Prove that the diagonal connecting the vertex angles of a kite cut the kite into two congruent triangles. 1 Interior Angle Sum Formula: Some Problems
Review Interior Angle Sum New: Exterior Angle Sum QUIZ: Prove that the diagonal connecting the vertex angles of a kite cut the kite into two congruent triangles. 1 Interior Angle Sum Formula: Some Problems
Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall October 9/10/11 Angles and Light
 Facult of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall 2018 - October 9/10/11 Angles and Light Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Toda we will be learning about angles.
Facult of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall 2018 - October 9/10/11 Angles and Light Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Toda we will be learning about angles.
Identify parallel lines, skew lines and perpendicular lines.
 Learning Objectives Identify parallel lines, skew lines and perpendicular lines. Parallel Lines and Planes Parallel lines are coplanar (they lie in the same plane) and never intersect. Below is an example
Learning Objectives Identify parallel lines, skew lines and perpendicular lines. Parallel Lines and Planes Parallel lines are coplanar (they lie in the same plane) and never intersect. Below is an example
The side that is opposite the vertex angle is the base of the isosceles triangle.
 Unit 5, Lesson 6. Proving Theorems about Triangles Isosceles triangles can be seen throughout our daily lives in structures, supports, architectural details, and even bicycle frames. Isosceles triangles
Unit 5, Lesson 6. Proving Theorems about Triangles Isosceles triangles can be seen throughout our daily lives in structures, supports, architectural details, and even bicycle frames. Isosceles triangles
Name Class Date 1 C REFLECT. m 1 m 2 m 3 m 4 m 1 + m 2 m 2 + m 3 m 3 + m 4 m 4 + m 1
 Name lass Date 1-4 Pairs of ngles Going Deeper Essential question: How can you use angle pairs to solve problems? Recall that two rays with a common endpoint form an angle. The two rays form the sides
Name lass Date 1-4 Pairs of ngles Going Deeper Essential question: How can you use angle pairs to solve problems? Recall that two rays with a common endpoint form an angle. The two rays form the sides
14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio.
 14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio. Using the space below, draw at least right triangles, each of which has one
14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio. Using the space below, draw at least right triangles, each of which has one
The windows of this building are made up of repeating panes of glass. How many different shapes are in each window?
 MESUEMENT N GEOMETY 7 7 ongruent figures 7 Triangle constructions 7 ongruent triangles 7 uadrilaterals WHT O YOU KNOW? 1 List what ou know aout congruence and transformations. reate a concept map to show
MESUEMENT N GEOMETY 7 7 ongruent figures 7 Triangle constructions 7 ongruent triangles 7 uadrilaterals WHT O YOU KNOW? 1 List what ou know aout congruence and transformations. reate a concept map to show
Angles of Polygons. Essential Question What is the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon?
 7.1 Angles of Polygons Essential Question What is the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon? The Sum of the Angle Measures of a Polygon Work with a partner. Use dynamic geometry software.
7.1 Angles of Polygons Essential Question What is the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon? The Sum of the Angle Measures of a Polygon Work with a partner. Use dynamic geometry software.
Geometry Vocabulary. Name Class
 Geometry Vocabulary Name Class Definition/Description Symbol/Sketch 1 point An exact location in space. In two dimensions, an ordered pair specifies a point in a coordinate plane: (x,y) 2 line 3a line
Geometry Vocabulary Name Class Definition/Description Symbol/Sketch 1 point An exact location in space. In two dimensions, an ordered pair specifies a point in a coordinate plane: (x,y) 2 line 3a line
Properties of Angles and Triangles. Outcomes: G1 Derive proofs that involve the properties of angles and triangles.
 Properties of Angles and Triangles Outcomes: G1 Derive proofs that involve the properties of angles and triangles. Achievement Indicators: Generalize, using inductive reasoning, the relationships between
Properties of Angles and Triangles Outcomes: G1 Derive proofs that involve the properties of angles and triangles. Achievement Indicators: Generalize, using inductive reasoning, the relationships between
Grade 9 Math Terminology
 Unit 1 Basic Skills Review BEDMAS a way of remembering order of operations: Brackets, Exponents, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction Collect like terms gather all like terms and simplify as
Unit 1 Basic Skills Review BEDMAS a way of remembering order of operations: Brackets, Exponents, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction Collect like terms gather all like terms and simplify as
2 and 6 4 and 8 1 and 5 3 and 7
 Geo Ch 3 Angles formed by Lines Parallel lines are two coplanar lines that do not intersect. Skew lines are that are not coplanar and do not intersect. Transversal is a line that two or more lines at different
Geo Ch 3 Angles formed by Lines Parallel lines are two coplanar lines that do not intersect. Skew lines are that are not coplanar and do not intersect. Transversal is a line that two or more lines at different
Integer Operations. Summer Packet 7 th into 8 th grade 1. Name = = = = = 6.
 Summer Packet 7 th into 8 th grade 1 Integer Operations Name Adding Integers If the signs are the same, add the numbers and keep the sign. 7 + 9 = 16-2 + -6 = -8 If the signs are different, find the difference
Summer Packet 7 th into 8 th grade 1 Integer Operations Name Adding Integers If the signs are the same, add the numbers and keep the sign. 7 + 9 = 16-2 + -6 = -8 If the signs are different, find the difference
Angle Unit Definition Packet
 ngle Unit Definition Packet Name lock Date Term Definition Notes Sketch djacent ngles Two angles with a coon, a coon you normay name and, and no coon interior points. 3 4 3 and 4 Vertical ngles Two angles
ngle Unit Definition Packet Name lock Date Term Definition Notes Sketch djacent ngles Two angles with a coon, a coon you normay name and, and no coon interior points. 3 4 3 and 4 Vertical ngles Two angles
CCGPS UNIT 1A Semester 1 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Page 1 of 35. Similarity Congruence and Proofs Name:
 GPS UNIT 1 Semester 1 NLYTI GEOMETRY Page 1 of 35 Similarity ongruence and Proofs Name: Date: Understand similarity in terms of similarity transformations M9-12.G.SRT.1 Verify experimentally the properties
GPS UNIT 1 Semester 1 NLYTI GEOMETRY Page 1 of 35 Similarity ongruence and Proofs Name: Date: Understand similarity in terms of similarity transformations M9-12.G.SRT.1 Verify experimentally the properties
describes a ray whose endpoint is point A. g. A plane has no thickness. h. Symbols XY and YX describe the same line. i. Symbols AB
 RVIW FOR TH GOMTRY MITRM XM. 1. True or False? e prepared to explain your answer. a. efinitions and theorems are very important in mathematics but every mathematical system must contain some undefined
RVIW FOR TH GOMTRY MITRM XM. 1. True or False? e prepared to explain your answer. a. efinitions and theorems are very important in mathematics but every mathematical system must contain some undefined
Points, lines, angles
 Points, lines, angles Point Line Line segment Parallel Lines Perpendicular lines Vertex Angle Full Turn An exact location. A point does not have any parts. A straight length that extends infinitely in
Points, lines, angles Point Line Line segment Parallel Lines Perpendicular lines Vertex Angle Full Turn An exact location. A point does not have any parts. A straight length that extends infinitely in
Shape 2 Assessment Calculator allowed for all questions
 Shape ssessment alculator allowed for all questions Foundation Higher ll questions Time for the test: 60 minutes Use the π button or take π to be. Name: MTHSWTH NSWERS Grade Title of clip Marks Score Percentage
Shape ssessment alculator allowed for all questions Foundation Higher ll questions Time for the test: 60 minutes Use the π button or take π to be. Name: MTHSWTH NSWERS Grade Title of clip Marks Score Percentage
1.6 Classifying Polygons
 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Basics of Geometry 1.6 Classifying Polygons Learning Objectives Define triangle and polygon. Classify triangles by their sides and angles. Understand the difference between convex
www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Basics of Geometry 1.6 Classifying Polygons Learning Objectives Define triangle and polygon. Classify triangles by their sides and angles. Understand the difference between convex
B. Algebraic Properties Reflexive, symmetric, transitive, substitution, addition, subtraction, multiplication, division
 . efinitions 1) cute angle ) cute triangle 3) djacent angles 4) lternate exterior angles 5) lternate interior angles 6) ltitude of a triangle 7) ngle ) ngle bisector of a triangle 9) ngles bisector 10)
. efinitions 1) cute angle ) cute triangle 3) djacent angles 4) lternate exterior angles 5) lternate interior angles 6) ltitude of a triangle 7) ngle ) ngle bisector of a triangle 9) ngles bisector 10)
Chapter 6 REVIEW. 1. Which statement can you use to conclude that quadrilateral XYZW is a parallelogram?
 hapter 6 REVIEW Name: Multiple hoice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement can ou use to conclude that quadrilateral XYZW is a parallelogram?
hapter 6 REVIEW Name: Multiple hoice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement can ou use to conclude that quadrilateral XYZW is a parallelogram?
7 th Grade Accelerated Learning Targets Final 5/5/14
 7 th Grade Accelerated Learning Targets Final 5/5/14 BSD Grade 7 Long Term Learning Targets & Supporting Learning Targets Quarter 1 & 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4 7.02, 7.03, 7.04, 7.05 7.06, 8.04, 8.05 7.08,
7 th Grade Accelerated Learning Targets Final 5/5/14 BSD Grade 7 Long Term Learning Targets & Supporting Learning Targets Quarter 1 & 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4 7.02, 7.03, 7.04, 7.05 7.06, 8.04, 8.05 7.08,
CST Geometry Practice Problems
 ST Geometry Practice Problems. Which of the following best describes deductive reasoning? using logic to draw conclusions based on accepted statements accepting the meaning of a term without definition
ST Geometry Practice Problems. Which of the following best describes deductive reasoning? using logic to draw conclusions based on accepted statements accepting the meaning of a term without definition
describes a ray whose endpoint is point A. TRUE g. A plane has no thickness. TRUE h. Symbols XY and YX describe the same line. TRUE i.
 Geometry Ms. H. Ray, 010 NSWRS TO TH RVIW FOR TH GOMTRY MITRM XM. 1. True or False? e prepared to explain your answer. a. efinitions and theorems are very important in mathematics but every mathematical
Geometry Ms. H. Ray, 010 NSWRS TO TH RVIW FOR TH GOMTRY MITRM XM. 1. True or False? e prepared to explain your answer. a. efinitions and theorems are very important in mathematics but every mathematical
Glossary Common Core Curriculum Maps Math/Grade 6 Grade 8
 Glossary Common Core Curriculum Maps Math/Grade 6 Grade 8 Grade 6 Grade 8 absolute value Distance of a number (x) from zero on a number line. Because absolute value represents distance, the absolute value
Glossary Common Core Curriculum Maps Math/Grade 6 Grade 8 Grade 6 Grade 8 absolute value Distance of a number (x) from zero on a number line. Because absolute value represents distance, the absolute value
Geometry Geometry Grade Grade Grade
 Grade Grade Grade 6.G.1 Find the area of right triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the
Grade Grade Grade 6.G.1 Find the area of right triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the
A VERTICAL LOOK AT KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCEDURES GEOMETRY
 A VERTICAL LOOK AT KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCEDURES GEOMETRY Revised TEKS (2012): Building to Geometry Coordinate and Transformational Geometry A Vertical Look at Key Concepts and Procedures Derive and use
A VERTICAL LOOK AT KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCEDURES GEOMETRY Revised TEKS (2012): Building to Geometry Coordinate and Transformational Geometry A Vertical Look at Key Concepts and Procedures Derive and use
2.4 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals
 Name Class Date.4 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals Essential Question: How can ou use slope and the distance formula in coordinate proofs? Resource Locker Eplore Positioning a Quadrilateral
Name Class Date.4 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals Essential Question: How can ou use slope and the distance formula in coordinate proofs? Resource Locker Eplore Positioning a Quadrilateral
