Verification of Behavior-Based Control Systems in their Physical Environment
|
|
|
- Bennett Shelton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Verification of Behavior-Based Control Systems in their Physical Environment Thorsten Ropertz, Prof. Dr. Karsten Berns Robotics Research Lab Department of Computer Science University of Kaiserslautern, Germany Xian Li, Prof. Dr. Klaus Schneider Embedded System Group Department of Computer Science University of Kaiserslautern, Germany
2 Outline Behavior-Based Control Systems 2-Step Verification Approach Network Reduction Verification using Hybrid Quartz Application Example Conclusion and Future Work
3 Behavior-Based Control System Global system behavior emerges from rather simple interacting local behaviors (behavior network) Robust due to partially overlapping functionality Modular structure fosters reuse Distributed design, implementation, and testing Network size and complexity can lead to difficulties to locate errors Safety critical application scenarios require correct control
4 Integrated Behavior-Based Control (ib2c) Fundamental unit in ib2c More information: [Proetzsch10]
5 2-Step Verification Direct verification not feasible due to network size and complexity Network structure (fusion+stimulation+inhibition) allows high level reduction Formal verification of reduced control network using synchronous programming language Quartz with hybrid system extension
6 Reduction Behaviors which have no connection to the realizing behaviors can be discarded Competing behaviors can be reduced if they are suppressed by behaviors on signal path Requirements: Mapping of properties to behaviors from design phase available Activity functions designed such that behavior is active if it requires full control to keep the intended property valid
7 Reduction 1. Identification of property-realizing behaviors 2. Separation of network into connected subnets 3. Removing networks that do not contain emphasized behaviors 4. For each emphasized behavior check competing behaviors on signal path If behaviors cannot be active at the same time then remove corresponding branch
8 Reduction Based on requirements the control networks always maintain properties realized by behavior A direct suppression: indirect suppression:
9 Reduction Problem: check whether two behaviors can be active at the same time Modelling the network structure using finite state automata 5 synchronizing FSMs per behavior Limiting behavior signals to {0,1} Using Uppaal verifier to check for concurrent activity
10 Verification Reduced behavior network modeled using the Quartz language VCG procedure for Quartz programs based on induction proofs on the strongly connected components (SCCs) of the underlying state transition diagram Validity of VCs is proven by standard SMT solvers like CVC4, isat, or Z3
11 Averest Toolkit Model-based design of software and hardware Based on the synchronous programming language Quartz Allows simple analysis and verification
12 Application Example Collision avoidance system Safety behavior limits velocity High level behaviors process velocity given by Joystick Trajectory following Target point tracking Others Question: Does the robot always keep a minimum distance to obstacles in front of it?
13 Reduction Uppaal model contains 408 locations and 927 edges Signal path from SlowDown to sink examined Tested against HighLevel Forward Cannot be active at the same time -> reduction of HighLevel Forward branch two behaviors remaining
14 Hybrid System Verification Hybrid Quartz Program macro delta=?, max_velocity_v =?, protect_distance =?; module SlowDown(real? obstacle_x,? vehicle_xi) { real max_velocity_a, slow_down_a, distance_front, vehicle_v ; hybrid real vehicle_x; vehicle_x = vehicle_xi ; // the movement of the vehicle towards the obstacle loop { // detect the distance betwee the vehicle and the obstacle distance_front = obstacle_x - vehicle_x ; // decide the velocity for the movement if( distance_front < protect_distance ) slow_down_a = 1; else slow_down_a = 0; max_velocity_a = 1.0- slow_down_a; vehicle_v = max_velocity_v*max_velocity_a; // the vehicle moves forward for delta unit time w0,w1: flow{ drv(vehicle_x) <- vehicle_v ; }until(cont(time)-time>=delta); } } Properties satisfies{ assume ((protect_distance >= 0) and (delta > 0)) ; // for bounded initial distance assume (abs(vehicle_xi-obstacle_x) > protect_distance ) ; // for fixed initial distance assume ((vehicle_xi = 0.0 ) and (obstacle_x = 15.0) ) ; // the vehicle keeps a certain distance to the obstacle assume (abs(max_velocity_v * delta) < protect_distance ) ; assert A G (abs(obstacle_x-vehicle_x) > protect_distance - vehicle_v* delta ) ;}
15 EFSM Generation
16 Verification Condition Generation Experiment with fixed and bounded initial distance VCG procedure generates 7 VCs All ODEs solved by Mathematica Application of SMT solver Z3 and isat
17 Experimental Results Application of 2 different solvers due to different handling of non-linear equations In bounded initial distance case isat returned CANDIDATE SOLUTION due to Zeno behaviors
18 Conclusion and Future Work Direct hybrid verification of behavior-based control systems not feasible due to complexity/size Exploiting arbitration mechanism allows efficient high level control system reduction Modelling the resulting system using the Quartz language and applying the VCG procedure to decompose the verification goal allows for further verification effort reduction and makes the hybrid system verification feasible Reduction procedure shall be extended and the correctness formally shown VCG procedure shall be extended to allow induction over program loops
Verification of Behavior-Based Control Systems in their Physical Environment
 Verification of Behavior-Based Control Systems in their Physical Environment Thorsten Ropertz 1, Karsten Berns 1, Xian Li 2, and Klaus Schneider 2 1 The Robotics Research Lab 2 Embedded System Group 1,2
Verification of Behavior-Based Control Systems in their Physical Environment Thorsten Ropertz 1, Karsten Berns 1, Xian Li 2, and Klaus Schneider 2 1 The Robotics Research Lab 2 Embedded System Group 1,2
Verification Condition Generation for Hybrid Systems described by Synchronous Languages
 UNIVERSITY OF KAISERSLAUTERN Verification Condition Generation for Hybrid Systems described by Synchronous Languages by Marcel Heer A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment for the degree of Master of
UNIVERSITY OF KAISERSLAUTERN Verification Condition Generation for Hybrid Systems described by Synchronous Languages by Marcel Heer A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment for the degree of Master of
Towards an Integrated System Model for Testing and Verification
 Towards an Integrated System Model for Testing and Verification Benjamin Hummel and Peter Braun MiSE 2008 Domain Development of controller software for production machines Special case of mechatronic system
Towards an Integrated System Model for Testing and Verification Benjamin Hummel and Peter Braun MiSE 2008 Domain Development of controller software for production machines Special case of mechatronic system
Parametric Real Time System Feasibility Analysis Using Parametric Timed Automata
 Parametric Real Time System Feasibility Analysis Using Parametric Timed Automata PhD Dissertation Yusi Ramadian Advisor : Luigi Palopoli Co advisor : Alessandro Cimatti 1 Real Time System Applications
Parametric Real Time System Feasibility Analysis Using Parametric Timed Automata PhD Dissertation Yusi Ramadian Advisor : Luigi Palopoli Co advisor : Alessandro Cimatti 1 Real Time System Applications
This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No
 This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 643921. TOOLS INTEGRATION UnCoVerCPS toolchain Goran Frehse, UGA Xavier
This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 643921. TOOLS INTEGRATION UnCoVerCPS toolchain Goran Frehse, UGA Xavier
Xuandong Li. BACH: Path-oriented Reachability Checker of Linear Hybrid Automata
 BACH: Path-oriented Reachability Checker of Linear Hybrid Automata Xuandong Li Department of Computer Science and Technology, Nanjing University, P.R.China Outline Preliminary Knowledge Path-oriented Reachability
BACH: Path-oriented Reachability Checker of Linear Hybrid Automata Xuandong Li Department of Computer Science and Technology, Nanjing University, P.R.China Outline Preliminary Knowledge Path-oriented Reachability
Safety for an Autonomous Bucket Excavator During Typical Landscaping Tasks
 Safety for an Autonomous Bucket Excavator During Typical Landscaping Tasks Gregor Zolynski, Daniel Schmidt and Karsten Berns Abstract The Robotics Research Lab in Kaiserserlautern, Germany, pursues the
Safety for an Autonomous Bucket Excavator During Typical Landscaping Tasks Gregor Zolynski, Daniel Schmidt and Karsten Berns Abstract The Robotics Research Lab in Kaiserserlautern, Germany, pursues the
CIS 1.5 Course Objectives. a. Understand the concept of a program (i.e., a computer following a series of instructions)
 By the end of this course, students should CIS 1.5 Course Objectives a. Understand the concept of a program (i.e., a computer following a series of instructions) b. Understand the concept of a variable
By the end of this course, students should CIS 1.5 Course Objectives a. Understand the concept of a program (i.e., a computer following a series of instructions) b. Understand the concept of a variable
Lecture 9: Reachability
 Lecture 9: Reachability Outline of Lecture Reachability General Transition Systems Algorithms for Reachability Safety through Reachability Backward Reachability Algorithm Given hybrid automaton H : set
Lecture 9: Reachability Outline of Lecture Reachability General Transition Systems Algorithms for Reachability Safety through Reachability Backward Reachability Algorithm Given hybrid automaton H : set
1 Mission Level Design. of Autonomous Underwater Vehicles
 Mission Level Design of Autonomous Underwater Vehicles Thomas Liebezeit, Volker Zerbe Department of Automatic Control and System Engineering, TU Ilmenau, Germany e-mail: thomas.liebezeit@tu-ilmenau.de
Mission Level Design of Autonomous Underwater Vehicles Thomas Liebezeit, Volker Zerbe Department of Automatic Control and System Engineering, TU Ilmenau, Germany e-mail: thomas.liebezeit@tu-ilmenau.de
Formal Modeling and Verification of Interlocking Systems Featuring Sequential Release
 Formal Modeling and Verification of Interlocking Systems Featuring Sequential Release Linh H. Vu (lvho@dtu.dk) Anne E. Haxthausen (aeha@dtu.dk) Jan Peleska (jp@informatik.uni-bremen.de) Technical Univesity
Formal Modeling and Verification of Interlocking Systems Featuring Sequential Release Linh H. Vu (lvho@dtu.dk) Anne E. Haxthausen (aeha@dtu.dk) Jan Peleska (jp@informatik.uni-bremen.de) Technical Univesity
M. De Wulf, L. Doyen,J.-F. Raskin Université Libre de Bruxelles Centre Fédéré en Vérification
 Systematic Implementation of Real-Time Models M. De Wulf, L. Doyen,J.-F. Raskin Université Libre de Bruxelles Centre Fédéré en Vérification Model-based Development for Controllers Make a model of the environment
Systematic Implementation of Real-Time Models M. De Wulf, L. Doyen,J.-F. Raskin Université Libre de Bruxelles Centre Fédéré en Vérification Model-based Development for Controllers Make a model of the environment
Applications of Program analysis in Model-Based Design
 Applications of Program analysis in Model-Based Design Prahlad Sampath (Prahlad.Sampath@mathworks.com) 2018 by The MathWorks, Inc., MATLAB, Simulink, Stateflow, are registered trademarks of The MathWorks,
Applications of Program analysis in Model-Based Design Prahlad Sampath (Prahlad.Sampath@mathworks.com) 2018 by The MathWorks, Inc., MATLAB, Simulink, Stateflow, are registered trademarks of The MathWorks,
LabVIEW Based Embedded Design [First Report]
![LabVIEW Based Embedded Design [First Report] LabVIEW Based Embedded Design [First Report]](/thumbs/89/97853595.jpg) LabVIEW Based Embedded Design [First Report] Sadia Malik Ram Rajagopal Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Texas at Austin Austin, TX 78712 malik@ece.utexas.edu ram.rajagopal@ni.com
LabVIEW Based Embedded Design [First Report] Sadia Malik Ram Rajagopal Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Texas at Austin Austin, TX 78712 malik@ece.utexas.edu ram.rajagopal@ni.com
Robotic Behaviors. Potential Field Methods
 Robotic Behaviors Potential field techniques - trajectory generation - closed feedback-loop control Design of variety of behaviors - motivated by potential field based approach steering behaviors Closed
Robotic Behaviors Potential field techniques - trajectory generation - closed feedback-loop control Design of variety of behaviors - motivated by potential field based approach steering behaviors Closed
Lecture 2. Decidability and Verification
 Lecture 2. Decidability and Verification model temporal property Model Checker yes error-trace Advantages Automated formal verification, Effective debugging tool Moderate industrial success In-house groups:
Lecture 2. Decidability and Verification model temporal property Model Checker yes error-trace Advantages Automated formal verification, Effective debugging tool Moderate industrial success In-house groups:
Lecture 05 ( ) High-Level Design with SysML. Systeme hoher Qualität und Sicherheit Universität Bremen WS 2015/2016
 Systeme hoher Qualität und Sicherheit Universität Bremen WS 2015/2016 Lecture 05 (09-11-2015) High-Level Design with SysML Christoph Lüth Jan Peleska Dieter Hutter Where are we? 01: Concepts of Quality
Systeme hoher Qualität und Sicherheit Universität Bremen WS 2015/2016 Lecture 05 (09-11-2015) High-Level Design with SysML Christoph Lüth Jan Peleska Dieter Hutter Where are we? 01: Concepts of Quality
Self-Collision Detection and Prevention for Humanoid Robots. Talk Overview
 Self-Collision Detection and Prevention for Humanoid Robots James Kuffner, Jr. Carnegie Mellon University Koichi Nishiwaki The University of Tokyo Satoshi Kagami Digital Human Lab (AIST) Masayuki Inaba
Self-Collision Detection and Prevention for Humanoid Robots James Kuffner, Jr. Carnegie Mellon University Koichi Nishiwaki The University of Tokyo Satoshi Kagami Digital Human Lab (AIST) Masayuki Inaba
Timed Automata Based Scheduling for a Miniature Pipeless Plant with Mobile Robots *
 Timed Automata Based Scheduling for a Miniature Pipeless Plant with Mobile Robots * Christian Schoppmeyer, Martin Hüfner, Subanatarajan Subbiah, and Sebastian Engell Abstract In this contribution we present
Timed Automata Based Scheduling for a Miniature Pipeless Plant with Mobile Robots * Christian Schoppmeyer, Martin Hüfner, Subanatarajan Subbiah, and Sebastian Engell Abstract In this contribution we present
Module 10. Network Simplex Method:
 Module 10 1 Network Simplex Method: In this lecture we shall study a specialized simplex method specifically designed to solve network structured linear programming problems. This specialized algorithm
Module 10 1 Network Simplex Method: In this lecture we shall study a specialized simplex method specifically designed to solve network structured linear programming problems. This specialized algorithm
Integer Programming ISE 418. Lecture 7. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Integer Programming ISE 418 Lecture 7 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 418 Lecture 7 1 Reading for This Lecture Nemhauser and Wolsey Sections II.3.1, II.3.6, II.4.1, II.4.2, II.5.4 Wolsey Chapter 7 CCZ Chapter 1 Constraint
Integer Programming ISE 418 Lecture 7 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 418 Lecture 7 1 Reading for This Lecture Nemhauser and Wolsey Sections II.3.1, II.3.6, II.4.1, II.4.2, II.5.4 Wolsey Chapter 7 CCZ Chapter 1 Constraint
Feed Forward Parameter Identification for Precise Periodic Quadrocopter Motions
 Feed Forward Parameter Identification for Precise Periodic Quadrocopter Motions Angela P. Schoellig, Clemens Wiltsche, Raffaello D Andrea Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control ETH Zürich, Switzerland
Feed Forward Parameter Identification for Precise Periodic Quadrocopter Motions Angela P. Schoellig, Clemens Wiltsche, Raffaello D Andrea Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control ETH Zürich, Switzerland
Fundamental Graph Algorithms Part Four
 Fundamental Graph Algorithms Part Four Announcements Problem Set One due right now. Due Friday at 2:15PM using one late period. Problem Set Two out, due next Friday, July 12 at 2:15PM. Play around with
Fundamental Graph Algorithms Part Four Announcements Problem Set One due right now. Due Friday at 2:15PM using one late period. Problem Set Two out, due next Friday, July 12 at 2:15PM. Play around with
Building Reliable 2D Maps from 3D Features
 Building Reliable 2D Maps from 3D Features Dipl. Technoinform. Jens Wettach, Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Karsten Berns TU Kaiserslautern; Robotics Research Lab 1, Geb. 48; Gottlieb-Daimler- Str.1; 67663 Kaiserslautern;
Building Reliable 2D Maps from 3D Features Dipl. Technoinform. Jens Wettach, Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Karsten Berns TU Kaiserslautern; Robotics Research Lab 1, Geb. 48; Gottlieb-Daimler- Str.1; 67663 Kaiserslautern;
VHDL Essentials Simulation & Synthesis
 VHDL Essentials Simulation & Synthesis Course Description This course provides all necessary theoretical and practical know-how to design programmable logic devices using VHDL standard language. The course
VHDL Essentials Simulation & Synthesis Course Description This course provides all necessary theoretical and practical know-how to design programmable logic devices using VHDL standard language. The course
Hybrid Agent-Landscape Model Composition
 Hybrid Agent-Landscape Model Composition Gary Mayer, Hessam Sarjoughian, Eowyn Allen Presented at the 1 st CSE Student Research Expo Hybrid Agent-Landscape Models Hybrid : both the human and environmental
Hybrid Agent-Landscape Model Composition Gary Mayer, Hessam Sarjoughian, Eowyn Allen Presented at the 1 st CSE Student Research Expo Hybrid Agent-Landscape Models Hybrid : both the human and environmental
A CSP Search Algorithm with Reduced Branching Factor
 A CSP Search Algorithm with Reduced Branching Factor Igor Razgon and Amnon Meisels Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105, Israel {irazgon,am}@cs.bgu.ac.il
A CSP Search Algorithm with Reduced Branching Factor Igor Razgon and Amnon Meisels Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84-105, Israel {irazgon,am}@cs.bgu.ac.il
Behavior-based Arm Control for an Autonomous Bucket Excavator
 Behavior-based Arm Control for an Autonomous Bucket Excavator Sergey Pluzhnikov, Daniel Schmidt, Jochen Hirth, and Karsten Berns Robotics Research Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Kaiserslautern,
Behavior-based Arm Control for an Autonomous Bucket Excavator Sergey Pluzhnikov, Daniel Schmidt, Jochen Hirth, and Karsten Berns Robotics Research Lab, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Kaiserslautern,
ECE 4750 Computer Architecture, Fall 2017 Lab 1: Iterative Integer Multiplier
 School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University revision: 2017-08-31-12-21 The first lab assignment is a warmup lab where you will design two implementations of an integer iterative multiplier:
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University revision: 2017-08-31-12-21 The first lab assignment is a warmup lab where you will design two implementations of an integer iterative multiplier:
Cuts from Proofs: A Complete and Practical Technique for Solving Linear Inequalities over Integers
 Cuts from Proofs: A Complete and Practical Technique for Solving Linear Inequalities over Integers Isil Dillig, Thomas Dillig, and Alex Aiken Computer Science Department Stanford University Linear Arithmetic
Cuts from Proofs: A Complete and Practical Technique for Solving Linear Inequalities over Integers Isil Dillig, Thomas Dillig, and Alex Aiken Computer Science Department Stanford University Linear Arithmetic
Abstract Interpretation
 Abstract Interpretation Ranjit Jhala, UC San Diego April 22, 2013 Fundamental Challenge of Program Analysis How to infer (loop) invariants? Fundamental Challenge of Program Analysis Key issue for any analysis
Abstract Interpretation Ranjit Jhala, UC San Diego April 22, 2013 Fundamental Challenge of Program Analysis How to infer (loop) invariants? Fundamental Challenge of Program Analysis Key issue for any analysis
Distributed Systems Programming (F21DS1) Formal Verification
 Distributed Systems Programming (F21DS1) Formal Verification Andrew Ireland Department of Computer Science School of Mathematical and Computer Sciences Heriot-Watt University Edinburgh Overview Focus on
Distributed Systems Programming (F21DS1) Formal Verification Andrew Ireland Department of Computer Science School of Mathematical and Computer Sciences Heriot-Watt University Edinburgh Overview Focus on
SOFTWARE DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF MUTIMODAL INTERACTION
 SOFTWARE DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF MUTIMODAL INTERACTION Marie-Luce Bourguet Queen Mary University of London Abstract: Key words: The multimodal dimension of a user interface raises numerous problems that
SOFTWARE DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF MUTIMODAL INTERACTION Marie-Luce Bourguet Queen Mary University of London Abstract: Key words: The multimodal dimension of a user interface raises numerous problems that
Component-Based Software Engineering TIP
 Component-Based Software Engineering TIP X LIU, School of Computing, Napier University This chapter will present a complete picture of how to develop software systems with components and system integration.
Component-Based Software Engineering TIP X LIU, School of Computing, Napier University This chapter will present a complete picture of how to develop software systems with components and system integration.
DSVerifier: A Bounded Model Checking Tool for Digital Systems
 DSVerifier: A Bounded Model Checking Tool for Digital Systems Hussama I. Ismail, Iury V. Bessa, Lucas C. Cordeiro, Eddie B. de Lima Filho and João E. Chaves Filho Electronic and Information Research Center
DSVerifier: A Bounded Model Checking Tool for Digital Systems Hussama I. Ismail, Iury V. Bessa, Lucas C. Cordeiro, Eddie B. de Lima Filho and João E. Chaves Filho Electronic and Information Research Center
Cyber Physical System Verification with SAL
 Cyber Physical System Verification with July 22, 2013 Cyber Physical System Verification with Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Cyber Physical System Verification with Table of Contents 1 2 3 4 5 Cyber Physical System
Cyber Physical System Verification with July 22, 2013 Cyber Physical System Verification with Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Cyber Physical System Verification with Table of Contents 1 2 3 4 5 Cyber Physical System
Model Checking and Its Applications
 Model Checking and Its Applications Orna Grumberg Technion, Israel Verification and Deduction Mentoring Workshop July 13, 2018 1 Personal data Ph.d. in (non-automated) verification Postdoc in Model Checking
Model Checking and Its Applications Orna Grumberg Technion, Israel Verification and Deduction Mentoring Workshop July 13, 2018 1 Personal data Ph.d. in (non-automated) verification Postdoc in Model Checking
A Pattern-supported Parallelization Approach
 A Pattern-supported Parallelization Approach Ralf Jahr, Mike Gerdes, Theo Ungerer University of Augsburg, Germany The 2013 International Workshop on Programming Models and Applications for Multicores and
A Pattern-supported Parallelization Approach Ralf Jahr, Mike Gerdes, Theo Ungerer University of Augsburg, Germany The 2013 International Workshop on Programming Models and Applications for Multicores and
Limitations of Algorithmic Solvability In this Chapter we investigate the power of algorithms to solve problems Some can be solved algorithmically and
 Computer Language Theory Chapter 4: Decidability 1 Limitations of Algorithmic Solvability In this Chapter we investigate the power of algorithms to solve problems Some can be solved algorithmically and
Computer Language Theory Chapter 4: Decidability 1 Limitations of Algorithmic Solvability In this Chapter we investigate the power of algorithms to solve problems Some can be solved algorithmically and
Strategies for simulating pedestrian navigation with multiple reinforcement learning agents
 Strategies for simulating pedestrian navigation with multiple reinforcement learning agents Francisco Martinez-Gil, Miguel Lozano, Fernando Ferna ndez Presented by: Daniel Geschwender 9/29/2016 1 Overview
Strategies for simulating pedestrian navigation with multiple reinforcement learning agents Francisco Martinez-Gil, Miguel Lozano, Fernando Ferna ndez Presented by: Daniel Geschwender 9/29/2016 1 Overview
Cyber Physical System Verification Seminar: Event-B
 Cyber Physical System Verification Seminar: Event-B Sebastian Schumb University of Kaiserslautern Embedded Systems Group s schumb10@cs.uni-kl.de 1 Introduction A Cyber-physical systems is a system of computer
Cyber Physical System Verification Seminar: Event-B Sebastian Schumb University of Kaiserslautern Embedded Systems Group s schumb10@cs.uni-kl.de 1 Introduction A Cyber-physical systems is a system of computer
Automated Software Synthesis for Complex Robotic Systems
 Automated Software Synthesis for Complex Robotic Systems Indranil Saha Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Indranil Saha Automated Software Synthesis for
Automated Software Synthesis for Complex Robotic Systems Indranil Saha Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Indranil Saha Automated Software Synthesis for
Static Analysis! Prof. Leon J. Osterweil! CS 520/620! Fall 2012! Characteristics of! System to be! built must! match required! characteristics!
 Static Analysis! Prof. Leon J. Osterweil! CS 520/620! Fall 2012! Requirements Spec.! Design! Test Results must! match required behavior! Characteristics of! System to be! built must! match required! characteristics!
Static Analysis! Prof. Leon J. Osterweil! CS 520/620! Fall 2012! Requirements Spec.! Design! Test Results must! match required behavior! Characteristics of! System to be! built must! match required! characteristics!
Extended Finite-State Machine Induction using SAT-Solver
 Extended Finite-State Machine Induction using SAT-Solver Vladimir Ulyantsev, Fedor Tsarev ulyantsev@rain.ifmo.ru, tsarev@rain.ifmo.ru St. Petersburg National Research University of IT, Mechanics and Optics
Extended Finite-State Machine Induction using SAT-Solver Vladimir Ulyantsev, Fedor Tsarev ulyantsev@rain.ifmo.ru, tsarev@rain.ifmo.ru St. Petersburg National Research University of IT, Mechanics and Optics
Semantic Subtyping. Alain Frisch (ENS Paris) Giuseppe Castagna (ENS Paris) Véronique Benzaken (LRI U Paris Sud)
 Semantic Subtyping Alain Frisch (ENS Paris) Giuseppe Castagna (ENS Paris) Véronique Benzaken (LRI U Paris Sud) http://www.cduce.org/ Semantic Subtyping - Groupe de travail BD LRI p.1/28 CDuce A functional
Semantic Subtyping Alain Frisch (ENS Paris) Giuseppe Castagna (ENS Paris) Véronique Benzaken (LRI U Paris Sud) http://www.cduce.org/ Semantic Subtyping - Groupe de travail BD LRI p.1/28 CDuce A functional
Supervisory Control Synthesis the Focus in Model-Based Systems Engineering
 Supervisory Control Synthesis the Focus in Model-Based Systems Engineering Jos Baeten and Asia van de Mortel-Fronczak Systems Engineering Group Department of Mechanical Engineering November 23, 2011 What
Supervisory Control Synthesis the Focus in Model-Based Systems Engineering Jos Baeten and Asia van de Mortel-Fronczak Systems Engineering Group Department of Mechanical Engineering November 23, 2011 What
Flight Systems are Cyber-Physical Systems
 Flight Systems are Cyber-Physical Systems Dr. Christopher Landauer Software Systems Analysis Department The Aerospace Corporation Computer Science Division / Software Engineering Subdivision 08 November
Flight Systems are Cyber-Physical Systems Dr. Christopher Landauer Software Systems Analysis Department The Aerospace Corporation Computer Science Division / Software Engineering Subdivision 08 November
A Framework for the Formal Verification of Time-Triggered Systems
 A Framework for the Formal Verification of Time-Triggered Systems Lee Pike leepike@galois.com Indiana University, Bloomington Department of Computer Science Advisor: Prof. Steven D. Johnson December 12,
A Framework for the Formal Verification of Time-Triggered Systems Lee Pike leepike@galois.com Indiana University, Bloomington Department of Computer Science Advisor: Prof. Steven D. Johnson December 12,
Simulation and Verification of Timed and Hybrid Systems
 Simulation and Verification of Timed and Hybrid Systems Bert van Beek and Koos Rooda Systems Engineering Group Eindhoven University of Technology ISC 2007 Delft 11 June 2007 Bert van Beek and Koos Rooda
Simulation and Verification of Timed and Hybrid Systems Bert van Beek and Koos Rooda Systems Engineering Group Eindhoven University of Technology ISC 2007 Delft 11 June 2007 Bert van Beek and Koos Rooda
Formal Verification of Business Continuity Solutions
 Formal Verification of Business Continuity Solutions Emmanuel Zarpas, Sivan Tal IBM Research Lab in Haifa, May 2006 IBM Labs in Haifa Agenda Rationale What is Formal Verification / Model Checking How can
Formal Verification of Business Continuity Solutions Emmanuel Zarpas, Sivan Tal IBM Research Lab in Haifa, May 2006 IBM Labs in Haifa Agenda Rationale What is Formal Verification / Model Checking How can
VS 3 : SMT Solvers for Program Verification
 VS 3 : SMT Solvers for Program Verification Saurabh Srivastava 1,, Sumit Gulwani 2, and Jeffrey S. Foster 1 1 University of Maryland, College Park, {saurabhs,jfoster}@cs.umd.edu 2 Microsoft Research, Redmond,
VS 3 : SMT Solvers for Program Verification Saurabh Srivastava 1,, Sumit Gulwani 2, and Jeffrey S. Foster 1 1 University of Maryland, College Park, {saurabhs,jfoster}@cs.umd.edu 2 Microsoft Research, Redmond,
Planning & Decision-making in Robotics Case Study: Planning for Autonomous Driving
 16-782 Planning & Decision-making in Robotics Case Study: Planning for Autonomous Driving Maxim Likhachev Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University Typical Planning Architecture for Autonomous Vehicle
16-782 Planning & Decision-making in Robotics Case Study: Planning for Autonomous Driving Maxim Likhachev Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University Typical Planning Architecture for Autonomous Vehicle
LIMoSim: A Lightweight and Integrated Approach for Simulating Vehicular Mobility with OMNeT++
 OMNeT++ Community Summit 2017 LIMoSim: A Lightweight and Integrated Approach for Simulating Vehicular Mobility with OMNeT++ Benjamin Sliwa, Johannes Pillmann, Fabian Eckermann and Christian Wietfeld Bremen,
OMNeT++ Community Summit 2017 LIMoSim: A Lightweight and Integrated Approach for Simulating Vehicular Mobility with OMNeT++ Benjamin Sliwa, Johannes Pillmann, Fabian Eckermann and Christian Wietfeld Bremen,
Sciduction: Combining Induction, Deduction and Structure for Verification and Synthesis
 Sciduction: Combining Induction, Deduction and Structure for Verification and Synthesis (abridged version of DAC slides) Sanjit A. Seshia Associate Professor EECS Department UC Berkeley Design Automation
Sciduction: Combining Induction, Deduction and Structure for Verification and Synthesis (abridged version of DAC slides) Sanjit A. Seshia Associate Professor EECS Department UC Berkeley Design Automation
Software Engineering of Robots
 Software Engineering of Robots Ana Cavalcanti Jon Timmis, Jim Woodcock Wei Li, Alvaro Miyazawa, Pedro Ribeiro University of York December 2015 Overview One of UK eight great technologies: robotics and
Software Engineering of Robots Ana Cavalcanti Jon Timmis, Jim Woodcock Wei Li, Alvaro Miyazawa, Pedro Ribeiro University of York December 2015 Overview One of UK eight great technologies: robotics and
Marrying Formal Methods With Simulation-Based Verification Function Verification Research at UCSB. Tim Cheng & Li-C. Wang UC-Santa Barbara
 Marrying Formal Methods With Simulation-Based Verification Function Verification Research at UCSB Tim Cheng & Li-C. Wang UC-Santa Barbara 1 Outline Current Issues in Functional Verification Functional
Marrying Formal Methods With Simulation-Based Verification Function Verification Research at UCSB Tim Cheng & Li-C. Wang UC-Santa Barbara 1 Outline Current Issues in Functional Verification Functional
Jane Li. Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute
 Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) Compare the testing methods for testing path segment and finding first
Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) Compare the testing methods for testing path segment and finding first
Range Sensing Based Autonomous Canal Following Using a Simulated Multi-copter. Ali Ahmad
 Range Sensing Based Autonomous Canal Following Using a Simulated Multi-copter Ali Ahmad MS Student of Electrical Engineering Laboratory for Cyber Physical Networks and Systems LUMS School of Science &
Range Sensing Based Autonomous Canal Following Using a Simulated Multi-copter Ali Ahmad MS Student of Electrical Engineering Laboratory for Cyber Physical Networks and Systems LUMS School of Science &
Graphical Tool For SC Automata.
 Graphical Tool For SC Automata. Honours Project: 2000 Dr. Padmanabhan Krishnan 1 Luke Haslett 1 Supervisor Abstract SC automata are a variation of timed automata which are closed under complementation.
Graphical Tool For SC Automata. Honours Project: 2000 Dr. Padmanabhan Krishnan 1 Luke Haslett 1 Supervisor Abstract SC automata are a variation of timed automata which are closed under complementation.
Software Testing IV. Prof. Dr. Holger Schlingloff. Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
 Software Testing IV Prof. Dr. Holger Schlingloff Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Fraunhofer Institute of Computer Architecture and Software Technology FIRST Outline of this Lecture Series 2006/11/24:
Software Testing IV Prof. Dr. Holger Schlingloff Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Fraunhofer Institute of Computer Architecture and Software Technology FIRST Outline of this Lecture Series 2006/11/24:
Detection and Tracking of Moving Objects Using 2.5D Motion Grids
 Detection and Tracking of Moving Objects Using 2.5D Motion Grids Alireza Asvadi, Paulo Peixoto and Urbano Nunes Institute of Systems and Robotics, University of Coimbra September 2015 1 Outline: Introduction
Detection and Tracking of Moving Objects Using 2.5D Motion Grids Alireza Asvadi, Paulo Peixoto and Urbano Nunes Institute of Systems and Robotics, University of Coimbra September 2015 1 Outline: Introduction
By: Chaitanya Settaluri Devendra Kalia
 By: Chaitanya Settaluri Devendra Kalia What is an embedded system? An embedded system Uses a controller to perform some function Is not perceived as a computer Software is used for features and flexibility
By: Chaitanya Settaluri Devendra Kalia What is an embedded system? An embedded system Uses a controller to perform some function Is not perceived as a computer Software is used for features and flexibility
Slicing for Model Reduction in Adaptive Embedded Systems Development
 Slicing for Model Reduction in Adaptive Embedded Systems Development Ina Schaefer and Arnd Poetzsch-Heffter Software Technology Group, TU Kaiserslautern, Germany Software Engineering for Adaptive and Self-Managing
Slicing for Model Reduction in Adaptive Embedded Systems Development Ina Schaefer and Arnd Poetzsch-Heffter Software Technology Group, TU Kaiserslautern, Germany Software Engineering for Adaptive and Self-Managing
Emerging Connected Vehicle based
 Exposing Congestion Attack on Emerging Connected Vehicle based Traffic Signal Control Qi Alfred Chen, Yucheng Yin, Yiheng Feng, Z. Morley Mao, Henry X. Liu Presented by Sezana Fahmida Outline Introduction
Exposing Congestion Attack on Emerging Connected Vehicle based Traffic Signal Control Qi Alfred Chen, Yucheng Yin, Yiheng Feng, Z. Morley Mao, Henry X. Liu Presented by Sezana Fahmida Outline Introduction
A Real-Time Animator for Hybrid Systems
 A Real-Time Animator for Hybrid Systems Tobias Amnell, Alexandre David Wang Yi Department of Computer Systems, Uppsala University {adavid, tobiasa, yi} @docsuuse Abstract In this paper, we present a real
A Real-Time Animator for Hybrid Systems Tobias Amnell, Alexandre David Wang Yi Department of Computer Systems, Uppsala University {adavid, tobiasa, yi} @docsuuse Abstract In this paper, we present a real
SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR
 SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & APPLICATIONS QUESTION BANK (2017-2018) Course / Branch : M.Sc-CST Semester / Year : Even / II Subject Name
SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & APPLICATIONS QUESTION BANK (2017-2018) Course / Branch : M.Sc-CST Semester / Year : Even / II Subject Name
ACCELERATION TECHNIQUES FOR BUSY BEAVER CANDIDATES
 ACCELERATION TECHNIQUES FOR BUSY BEAVER CANDIDATES Alex Holkner 1 1 School of Computer Science and Information Technology, RMIT University ABSTRACT: A busy beaver is a Turing machine of N states which,
ACCELERATION TECHNIQUES FOR BUSY BEAVER CANDIDATES Alex Holkner 1 1 School of Computer Science and Information Technology, RMIT University ABSTRACT: A busy beaver is a Turing machine of N states which,
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 8: Automata Theory VI (PDA, PDA = CFG)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 8: Automata Theory VI (PDA, PDA = CFG) Objectives Introduce Pushdown Automaton (PDA) Show that PDA = CFG In terms of descriptive power Pushdown Automaton (PDA) Roughly
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 8: Automata Theory VI (PDA, PDA = CFG) Objectives Introduce Pushdown Automaton (PDA) Show that PDA = CFG In terms of descriptive power Pushdown Automaton (PDA) Roughly
DO-254 Implementation of CAN for Mil-Aero/ Safety Critical Applications
 DO-254 Implementation of CAN for Mil-Aero/ Safety Critical Applications Reshma N 1, Dr. Srividya P 2, Kumaraswamy K V 3 P.G. Student (VLSI Design and Embedded Systems), Dept. of E.C.E, SJBIT, Bengaluru,
DO-254 Implementation of CAN for Mil-Aero/ Safety Critical Applications Reshma N 1, Dr. Srividya P 2, Kumaraswamy K V 3 P.G. Student (VLSI Design and Embedded Systems), Dept. of E.C.E, SJBIT, Bengaluru,
Overview of SRI s. Lee Pike. June 3, 2005 Overview of SRI s. Symbolic Analysis Laboratory (SAL) Lee Pike
 June 3, 2005 lee.s.pike@nasa.gov Model-Checking 101 Model-checking is a way automatically to verify hardware or software. For a property P, A Model-checking program checks to ensure that every state on
June 3, 2005 lee.s.pike@nasa.gov Model-Checking 101 Model-checking is a way automatically to verify hardware or software. For a property P, A Model-checking program checks to ensure that every state on
A Framework for Asynchronous Circuit Modeling and Verification in ACL2
 A Framework for Asynchronous Circuit Modeling and Verification in ACL2 Cuong Chau 1, Warren A. Hunt, Jr. 1, Marly Roncken 2, and Ivan Sutherland 2 {ckcuong,hunt}@cs.utexas.edu, marly.roncken@gmail.com,
A Framework for Asynchronous Circuit Modeling and Verification in ACL2 Cuong Chau 1, Warren A. Hunt, Jr. 1, Marly Roncken 2, and Ivan Sutherland 2 {ckcuong,hunt}@cs.utexas.edu, marly.roncken@gmail.com,
Part II. Hoare Logic and Program Verification. Why specify programs? Specification and Verification. Code Verification. Why verify programs?
 Part II. Hoare Logic and Program Verification Part II. Hoare Logic and Program Verification Dilian Gurov Props: Models: Specs: Method: Tool: safety of data manipulation source code logic assertions Hoare
Part II. Hoare Logic and Program Verification Part II. Hoare Logic and Program Verification Dilian Gurov Props: Models: Specs: Method: Tool: safety of data manipulation source code logic assertions Hoare
Automatic Software Verification
 Automatic Software Verification Instructor: Mooly Sagiv TA: Oded Padon Slides from Eran Yahav and the Noun Project, Wikipedia Course Requirements Summarize one lecture 10% one lecture notes 45% homework
Automatic Software Verification Instructor: Mooly Sagiv TA: Oded Padon Slides from Eran Yahav and the Noun Project, Wikipedia Course Requirements Summarize one lecture 10% one lecture notes 45% homework
Word-Level Equivalence Checking in Bit-Level Accuracy by Synthesizing Designs onto Identical Datapath
 972 PAPER Special Section on Formal Approach Word-Level Equivalence Checking in Bit-Level Accuracy by Synthesizing Designs onto Identical Datapath Tasuku NISHIHARA a), Member, Takeshi MATSUMOTO, and Masahiro
972 PAPER Special Section on Formal Approach Word-Level Equivalence Checking in Bit-Level Accuracy by Synthesizing Designs onto Identical Datapath Tasuku NISHIHARA a), Member, Takeshi MATSUMOTO, and Masahiro
Everything You Always Wanted To Know About Programming Behaviors But Were Afraid To Ask
 Everything You Always Wanted To Know About Programming Behaviors But Were Afraid To Ask By Kevin Harrelson Machine Intelligence Lab University of Florida Spring, 1995 Overview Programming multiple behaviors
Everything You Always Wanted To Know About Programming Behaviors But Were Afraid To Ask By Kevin Harrelson Machine Intelligence Lab University of Florida Spring, 1995 Overview Programming multiple behaviors
Enhancement of Feedback Congestion Control Mechanisms by Deploying Active Congestion Control
 Enhancement of Feedback Congestion Control Mechanisms by Deploying Active Congestion Control Yoganandhini Janarthanan Aug 30,2001 Committee : Dr.Gary Minden Dr. Joseph Evans Dr.Perry Alexander Introduction
Enhancement of Feedback Congestion Control Mechanisms by Deploying Active Congestion Control Yoganandhini Janarthanan Aug 30,2001 Committee : Dr.Gary Minden Dr. Joseph Evans Dr.Perry Alexander Introduction
Volvo Car Group Jonn Lantz Agile by Models
 Volvo Car Group Jonn Lantz Agile by Models Challenge Scaling agile model driven development of AUTOSAR embedded software. Lift the abstraction level of in-house development. Create reliable, automated
Volvo Car Group Jonn Lantz Agile by Models Challenge Scaling agile model driven development of AUTOSAR embedded software. Lift the abstraction level of in-house development. Create reliable, automated
PLDI 2016 Tutorial Automata-Based String Analysis
 PLDI 2016 Tutorial Automata-Based String Analysis Tevfik Bultan, Abdulbaki Aydin, Lucas Bang Verification Laboratory http://vlab.cs.ucsb.edu Department of Computer Science Common Usages of Strings } Input
PLDI 2016 Tutorial Automata-Based String Analysis Tevfik Bultan, Abdulbaki Aydin, Lucas Bang Verification Laboratory http://vlab.cs.ucsb.edu Department of Computer Science Common Usages of Strings } Input
16-811: Math Fundamentals for Robotics, Fall 2014 Finding minimum energy trajectories of a two linked pendulum
 16-811: Math Fundamentals for Robotics, Fall 014 Finding minimum energy trajectories of a two linked pendulum Lerrel Pinto < lerrelp > December 1th 014 Problem Statement: Find a zero energy end effector
16-811: Math Fundamentals for Robotics, Fall 014 Finding minimum energy trajectories of a two linked pendulum Lerrel Pinto < lerrelp > December 1th 014 Problem Statement: Find a zero energy end effector
Inverse KKT Motion Optimization: A Newton Method to Efficiently Extract Task Spaces and Cost Parameters from Demonstrations
 Inverse KKT Motion Optimization: A Newton Method to Efficiently Extract Task Spaces and Cost Parameters from Demonstrations Peter Englert Machine Learning and Robotics Lab Universität Stuttgart Germany
Inverse KKT Motion Optimization: A Newton Method to Efficiently Extract Task Spaces and Cost Parameters from Demonstrations Peter Englert Machine Learning and Robotics Lab Universität Stuttgart Germany
Future Directions. Edward A. Lee. Berkeley, CA May 12, A New Computational Platform: Ubiquitous Networked Embedded Systems. actuate.
 Future Directions Edward A. Lee 6th Biennial Ptolemy Miniconference Berkeley, CA May 12, 2005 A New Computational Platform: Ubiquitous Networked Embedded Systems sense actuate control Ptolemy II support
Future Directions Edward A. Lee 6th Biennial Ptolemy Miniconference Berkeley, CA May 12, 2005 A New Computational Platform: Ubiquitous Networked Embedded Systems sense actuate control Ptolemy II support
Chapter Outline. Chapter 2 Distributed Information Systems Architecture. Distributed transactions (quick refresh) Layers of an information system
 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Deßloch AG Heterogene Informationssysteme Geb. 36, Raum 329 Tel. 0631/205 3275 dessloch@informatik.uni-kl.de Chapter 2 Distributed Information Systems Architecture Chapter Outline
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Deßloch AG Heterogene Informationssysteme Geb. 36, Raum 329 Tel. 0631/205 3275 dessloch@informatik.uni-kl.de Chapter 2 Distributed Information Systems Architecture Chapter Outline
Recitation Session 6
 Recitation Session 6 CSE341 Computer Organization University at Buffalo radhakri@buffalo.edu March 11, 2016 CSE341 Computer Organization Recitation Session 6 1/26 Recitation Session Outline 1 Overview
Recitation Session 6 CSE341 Computer Organization University at Buffalo radhakri@buffalo.edu March 11, 2016 CSE341 Computer Organization Recitation Session 6 1/26 Recitation Session Outline 1 Overview
Autonomous and Mobile Robotics. Whole-body motion planning for humanoid robots (Slides prepared by Marco Cognetti) Prof.
 Autonomous and Mobile Robotics Whole-body motion planning for humanoid robots (Slides prepared by Marco Cognetti) Prof. Giuseppe Oriolo Motivations task-constrained motion planning: find collision-free
Autonomous and Mobile Robotics Whole-body motion planning for humanoid robots (Slides prepared by Marco Cognetti) Prof. Giuseppe Oriolo Motivations task-constrained motion planning: find collision-free
Petri Nets ee249 Fall 2000
 Petri Nets ee249 Fall 2000 Marco Sgroi Most slides borrowed from Luciano Lavagno s lecture ee249 (1998) 1 Models Of Computation for reactive systems Main MOCs: Communicating Finite State Machines Dataflow
Petri Nets ee249 Fall 2000 Marco Sgroi Most slides borrowed from Luciano Lavagno s lecture ee249 (1998) 1 Models Of Computation for reactive systems Main MOCs: Communicating Finite State Machines Dataflow
Chapter 8 Fault Tolerance
 DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Principles and Paradigms Second Edition ANDREW S. TANENBAUM MAARTEN VAN STEEN Chapter 8 Fault Tolerance Fault Tolerance Basic Concepts Being fault tolerant is strongly related to what
DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS Principles and Paradigms Second Edition ANDREW S. TANENBAUM MAARTEN VAN STEEN Chapter 8 Fault Tolerance Fault Tolerance Basic Concepts Being fault tolerant is strongly related to what
Advanced Driver Assistance: Modular Image Sensor Concept
 Vision Advanced Driver Assistance: Modular Image Sensor Concept Supplying value. Integrated Passive and Active Safety Systems Active Safety Passive Safety Scope Reduction of accident probability Get ready
Vision Advanced Driver Assistance: Modular Image Sensor Concept Supplying value. Integrated Passive and Active Safety Systems Active Safety Passive Safety Scope Reduction of accident probability Get ready
Some Applications of Graph Bandwidth to Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Some Applications of Graph Bandwidth to Constraint Satisfaction Problems Ramin Zabih Computer Science Department Stanford University Stanford, California 94305 Abstract Bandwidth is a fundamental concept
Some Applications of Graph Bandwidth to Constraint Satisfaction Problems Ramin Zabih Computer Science Department Stanford University Stanford, California 94305 Abstract Bandwidth is a fundamental concept
Indistinguishability: Friend and Foe of Concurrent Data Structures. Hagit Attiya CS, Technion
 Indistinguishability: Friend and Foe of Concurrent Data Structures Hagit Attiya CS, Technion Uncertainty is a main obstacle for designing correct applications in concurrent systems Formally captured by
Indistinguishability: Friend and Foe of Concurrent Data Structures Hagit Attiya CS, Technion Uncertainty is a main obstacle for designing correct applications in concurrent systems Formally captured by
A Modular Sensor Fusion Approach for Agricultural Machines
 A Modular Sensor Fusion Approach for Agricultural Machines Sebastian Blank (1), Georg Kormann (2), Karsten Berns (1) (1) Robotics Research Lab University of Kaiserslautern, Germany (2) John Deere European
A Modular Sensor Fusion Approach for Agricultural Machines Sebastian Blank (1), Georg Kormann (2), Karsten Berns (1) (1) Robotics Research Lab University of Kaiserslautern, Germany (2) John Deere European
College of Sciences. College of Sciences. Master s of Science in Computer Sciences Master s of Science in Biotechnology
 Master s of Science in Computer Sciences Master s of Science in Biotechnology Department of Computer Sciences 1. Introduction\Program Mission The Program mission is to prepare students to be fully abreast
Master s of Science in Computer Sciences Master s of Science in Biotechnology Department of Computer Sciences 1. Introduction\Program Mission The Program mission is to prepare students to be fully abreast
Complex behavior emergent from simpler ones
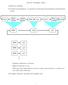 Reactive Paradigm: Basics Based on ethology Vertical decomposition, as opposed to horizontal decomposition of hierarchical model Primitive behaviors at bottom Higher behaviors at top Each layer has independent
Reactive Paradigm: Basics Based on ethology Vertical decomposition, as opposed to horizontal decomposition of hierarchical model Primitive behaviors at bottom Higher behaviors at top Each layer has independent
Quantitative Timing Analysis of UML Activity Digrams using Statistical Model Checking
 Quantitative Timing Analysis of UML Activity Digrams using Statistical Model Checking Fan Gu 1, Xinqian Zhang 1, Mingsong Chen 1, Daniel Grosse 2 and Rolf Drechsler 2 1 Institute of CS & SE, East China
Quantitative Timing Analysis of UML Activity Digrams using Statistical Model Checking Fan Gu 1, Xinqian Zhang 1, Mingsong Chen 1, Daniel Grosse 2 and Rolf Drechsler 2 1 Institute of CS & SE, East China
System Correctness. EEC 421/521: Software Engineering. System Correctness. The Problem at Hand. A system is correct when it meets its requirements
 System Correctness EEC 421/521: Software Engineering A Whirlwind Intro to Software Model Checking A system is correct when it meets its requirements a design without requirements cannot be right or wrong,
System Correctness EEC 421/521: Software Engineering A Whirlwind Intro to Software Model Checking A system is correct when it meets its requirements a design without requirements cannot be right or wrong,
724. Simulation of the radiation therapy system for respiratory movement compensation
 724. Simulation of the radiation therapy system for respiratory movement compensation Tomas Krilavičius 1, Daiva Vitkutė-Adžgauskienė 2, Kęstutis Šidlauskas 3 Vytautas Magnus University, Kaunas, Lithuania
724. Simulation of the radiation therapy system for respiratory movement compensation Tomas Krilavičius 1, Daiva Vitkutė-Adžgauskienė 2, Kęstutis Šidlauskas 3 Vytautas Magnus University, Kaunas, Lithuania
Symbolic Evaluation/Execution
 Symbolic Evaluation/Execution Reading Assignment *R.W. Floyd, "Assigning Meaning to Programs, Symposium on Applied Mathematics, 1967, pp. 19-32 (Appeared as volume 19 of Mathematical Aspects of Computer
Symbolic Evaluation/Execution Reading Assignment *R.W. Floyd, "Assigning Meaning to Programs, Symposium on Applied Mathematics, 1967, pp. 19-32 (Appeared as volume 19 of Mathematical Aspects of Computer
Automata-based Model Counting for String Constraints. Abdulbaki Aydin, Lucas Bang, Tevfik Bultan
 Automata-based Model Counting for String Constraints Abdulbaki Aydin, Lucas Bang, Tevfik Bultan https://vlab.cs.ucsb.edu Model Counting for String Constraints Automata-Based model Counter (ABC) 2 Can you
Automata-based Model Counting for String Constraints Abdulbaki Aydin, Lucas Bang, Tevfik Bultan https://vlab.cs.ucsb.edu Model Counting for String Constraints Automata-Based model Counter (ABC) 2 Can you
Combining Induction, Deduction and Structure for Synthesis
 Combining Induction, Deduction and Structure for Synthesis Sanjit A. Seshia Associate Professor EECS Department UC Berkeley Students: S. Jha, B. Brady, J. Kotker, W.Li Collaborators: R. Bryant, S. Gulwani,
Combining Induction, Deduction and Structure for Synthesis Sanjit A. Seshia Associate Professor EECS Department UC Berkeley Students: S. Jha, B. Brady, J. Kotker, W.Li Collaborators: R. Bryant, S. Gulwani,
Safe Prediction-Based Local Path Planning using Obstacle Probability Sections
 Slide 1 Safe Prediction-Based Local Path Planning using Obstacle Probability Sections Tanja Hebecker and Frank Ortmeier Chair of Software Engineering, Otto-von-Guericke University of Magdeburg, Germany
Slide 1 Safe Prediction-Based Local Path Planning using Obstacle Probability Sections Tanja Hebecker and Frank Ortmeier Chair of Software Engineering, Otto-von-Guericke University of Magdeburg, Germany
Verifying Recursive Programs using Intra-procedural Analyzers
 Verifying Recursive Programs using Intra-procedural Analyzers Yu-Fang Chen, Academia Sinica, Taiwan joint work with Chiao Hsieh, Ming-Hsien Tsai, Bow-Yaw Wang and Farn Wang First of all Thanks for the
Verifying Recursive Programs using Intra-procedural Analyzers Yu-Fang Chen, Academia Sinica, Taiwan joint work with Chiao Hsieh, Ming-Hsien Tsai, Bow-Yaw Wang and Farn Wang First of all Thanks for the
