Network Based Models For Analysis of SNPs Yalta Opt
|
|
|
- Phebe O’Neal’
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Outline Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Optimization Conference 2010 Network Science Zeynep Ertem*, Sergiy Butenko*, Clare Gill** *Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, **Department of Animal Science, Texas A& M University College Station, TX July 29, /25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
2 Outline Outline 1 Introduction to Graph Theory /25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
3 Introduction to Graph Theory G = (V, E) is a simple undirected graph V = {1, 2,..., n} - set of vertices E V V - set of edges (arcs, lines) A subset C V is called a clique if G(C) is complete, i.e. it has all possible edges. 3/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
4 Introduction to Graph Theory A graph without cycles is acyclic A graph is connected if there is a path between any pair of vertices A tree is a simple, undirected, connected, acyclic graph 4/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
5 Introduction to Graph Theory G = (V, E), is the complement graph of G = (V, E) where E = {(i, j) i, j V, i j and (i, j) / E}. For S V, G(S) = (S, E S S) the subgraph induced by S. 5/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
6 Introduction to Graph Theory A subset C V is called a clique if G(C) is complete, i.e. it has all possible edges. A subset I V is called an independent set (stable set, vertex packing) if G(I ) has no edges. A clique (independent set) is said to be maximal, if it is not a subset of any larger clique (independent set); maximum, if there is no larger clique (independent set) in the graph. 6/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
7 k-plex Given a positive integer k, a k-plex is a subset of vertices C such that each vertex v C is adjacent to all but at most k vertices in C. 1-plex is a clique. 7/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
8 Graph Theory Basics α(g) the independence (stability) number of G. ω(g) the clique number of G. VC V is a vertex cover if every edge has at least one endpoint in VC. 8/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
9 Graph Theory Basics I is a maximum independent set of G I is a maximum clique of Ḡ V \ I is a minimum vertex cover of G. 9/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
10 Graph Theory Problems Maximum Clique Problem (MCP) To find largest k-plex in a given graph G Maximum independent set problem(misp) Minimum vertex cover problem (MVC) MC, MIS and MVC problems are NP-hard 10/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
11 Graph Theory Problems and Constructing a complete map of all occurring in human genome is one of the most important goal. WHAT ARE THOSE? 11/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
12 SNP Single - Nucleotide Polymorphism DNA sequence variation Disease development, response to pathogens, drugs... They do not cause diseases, however they determine susceptibility to them Between members of species or pairs of chromosomes in an individual 12/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
13 Difference is in single nucleotide ATTCGA ATTTGA In human DNA, more than 10 million. However only a few million discovered so far. Substitution Deletion Insertion 13/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
14 Occur in every 100 to 300 nucleotides in the genome Two of every three SNP are C and T substitutions 90% of genetic variation is attributed to SNP 14/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
15 SNP in Genomic Sequences 15/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
16 Tag A representative SNP in a region of the genome with high linkage disequilibrium With the help of tag it is possible to identify genetic variation without genotyping every SNP in a chromosomal region Reduction in experimental cost 16/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
17 Linkage Disequilibrium Nonrandom association of alleles between 2 or more loci Can be calculated as difference between observed and expected allelic frequencies Alleles There may be two or more bases can occur in, these bases 17/25 are called alleles. Like A and C Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
18 Linkage Disequilibrium Generally LD is high when the distance between 2 is low Influenced by a number of factors Genetic linkage, selection the rate of recombination rate of mutation non-random mating population structure 18/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
19 Linkage Disequilibrium 19/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
20 Data With the help of HapMap Project= Haploid Mapping Project able to map genomic data Cattle Chromosome 1 20/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
21 Data Different threshold values ranging from 0.1 to 0.5 are used for the r 2 values Largest k-plexes found. BUT HOW? 21/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
22 How to find k-plexes? k-plexes in social network analysis introduced by Seidman and Foster (1978). ideal for cohesive subgroup not practical due to its restrictive nature Ostergard s algorithm(1999) Branch-and-bound algorithm for maximum-weight clique problem Balasundram et al.(2009) Branch-and-cut algorithm k-plex detection 22/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
23 Results Threshold # of in 2-plex # of in 3-plex # of in 4-plex /25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
24 Results Largest clusters are very stable and well defined in terms of cliques. If we increase k, clusters are not changing drastically. There is high correlation in between the associated in the cattle s chromosome 1. 24/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
25 Thank You. 25/25 Network Based Models For Analysis of Yalta Opt
Computing Largest Correcting Codes and Their Estimates Using Optimization on Specially Constructed Graphs p.1/30
 Computing Largest Correcting Codes and Their Estimates Using Optimization on Specially Constructed Graphs Sergiy Butenko Department of Industrial Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843
Computing Largest Correcting Codes and Their Estimates Using Optimization on Specially Constructed Graphs Sergiy Butenko Department of Industrial Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843
Introduction to Graph Theory
 Introduction to Graph Theory Tandy Warnow January 20, 2017 Graphs Tandy Warnow Graphs A graph G = (V, E) is an object that contains a vertex set V and an edge set E. We also write V (G) to denote the vertex
Introduction to Graph Theory Tandy Warnow January 20, 2017 Graphs Tandy Warnow Graphs A graph G = (V, E) is an object that contains a vertex set V and an edge set E. We also write V (G) to denote the vertex
On the Complexity of Broadcast Scheduling. Problem
 On the Complexity of Broadcast Scheduling Problem Sergiy Butenko, Clayton Commander and Panos Pardalos Abstract In this paper, a broadcast scheduling problem (BSP) in a time division multiple access (TDMA)
On the Complexity of Broadcast Scheduling Problem Sergiy Butenko, Clayton Commander and Panos Pardalos Abstract In this paper, a broadcast scheduling problem (BSP) in a time division multiple access (TDMA)
The Maximum Clique Problem
 November, 2012 Motivation How to put as much left-over stuff as possible in a tasty meal before everything will go off? Motivation Find the largest collection of food where everything goes together! Here,
November, 2012 Motivation How to put as much left-over stuff as possible in a tasty meal before everything will go off? Motivation Find the largest collection of food where everything goes together! Here,
ON THE COMPLEXITY OF THE BROADCAST SCHEDULING PROBLEM
 ON THE COMPLEXITY OF THE BROADCAST SCHEDULING PROBLEM SERGIY I. BUTENKO, CLAYTON W. COMMANDER, AND PANOS M. PARDALOS Abstract. In this paper, a Broadcast Scheduling Problem (bsp) in a time division multiple
ON THE COMPLEXITY OF THE BROADCAST SCHEDULING PROBLEM SERGIY I. BUTENKO, CLAYTON W. COMMANDER, AND PANOS M. PARDALOS Abstract. In this paper, a Broadcast Scheduling Problem (bsp) in a time division multiple
Introduction to Combinatorial Algorithms
 Fall 2009 Intro Introduction to the course What are : Combinatorial Structures? Combinatorial Algorithms? Combinatorial Problems? Combinatorial Structures Combinatorial Structures Combinatorial structures
Fall 2009 Intro Introduction to the course What are : Combinatorial Structures? Combinatorial Algorithms? Combinatorial Problems? Combinatorial Structures Combinatorial Structures Combinatorial structures
Iterative Learning of Single Individual Haplotypes from High-Throughput DNA Sequencing Data
 Iterative Learning of Single Individual Haplotypes from High-Throughput DNA Sequencing Data Zrinka Puljiz and Haris Vikalo Electrical and Computer Engineering Department The University of Texas at Austin
Iterative Learning of Single Individual Haplotypes from High-Throughput DNA Sequencing Data Zrinka Puljiz and Haris Vikalo Electrical and Computer Engineering Department The University of Texas at Austin
Graph Theory. Probabilistic Graphical Models. L. Enrique Sucar, INAOE. Definitions. Types of Graphs. Trajectories and Circuits.
 Theory Probabilistic ical Models L. Enrique Sucar, INAOE and (INAOE) 1 / 32 Outline and 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 and 9 (INAOE) 2 / 32 A graph provides a compact way to represent binary relations between a set of
Theory Probabilistic ical Models L. Enrique Sucar, INAOE and (INAOE) 1 / 32 Outline and 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 and 9 (INAOE) 2 / 32 A graph provides a compact way to represent binary relations between a set of
Let G = (V, E) be a graph. If u, v V, then u is adjacent to v if {u, v} E. We also use the notation u v to denote that u is adjacent to v.
 Graph Adjacent Endpoint of an edge Incident Neighbors of a vertex Degree of a vertex Theorem Graph relation Order of a graph Size of a graph Maximum and minimum degree Let G = (V, E) be a graph. If u,
Graph Adjacent Endpoint of an edge Incident Neighbors of a vertex Degree of a vertex Theorem Graph relation Order of a graph Size of a graph Maximum and minimum degree Let G = (V, E) be a graph. If u,
On Clique Relaxation Models in Network Analysis
 On Clique Relaxation Models in Network Analysis Jeffrey Pattillo Department of Mathematics, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77843-3131, jeff.pattillo@gmail.com Nataly Youssef Operations Research
On Clique Relaxation Models in Network Analysis Jeffrey Pattillo Department of Mathematics, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77843-3131, jeff.pattillo@gmail.com Nataly Youssef Operations Research
Xiao, M. (Mingyu); Lin, W. (Weibo); Dai, Y. (Yuanshun); Zeng, Y. (Yifeng)
 TeesRep - Teesside's Research Repository A Fast Algorithm to Compute Maximum k-plexes in Social Network Analysis Item type Authors Citation Eprint Version Publisher Additional Link Rights Meetings and
TeesRep - Teesside's Research Repository A Fast Algorithm to Compute Maximum k-plexes in Social Network Analysis Item type Authors Citation Eprint Version Publisher Additional Link Rights Meetings and
Minimum Recombinant Haplotype Configuration on Tree Pedigrees (Extended Abstract)
 Minimum Recombinant Haplotype Configuration on Tree Pedigrees (Extended Abstract) Koichiro Doi 1, Jing Li 2, and Tao Jiang 2 1 Department of Computer Science Graduate School of Information Science and
Minimum Recombinant Haplotype Configuration on Tree Pedigrees (Extended Abstract) Koichiro Doi 1, Jing Li 2, and Tao Jiang 2 1 Department of Computer Science Graduate School of Information Science and
Network Clustering. Balabhaskar Balasundaram, Sergiy Butenko
 Network Clustering Balabhaskar Balasundaram, Sergiy Butenko Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, Texas 77843, USA. Introduction Clustering can be loosely
Network Clustering Balabhaskar Balasundaram, Sergiy Butenko Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, Texas 77843, USA. Introduction Clustering can be loosely
COMP 355 Advanced Algorithms Approximation Algorithms: VC and TSP Chapter 11 (KT) Section (CLRS)
 COMP 355 Advanced Algorithms Approximation Algorithms: VC and TSP Chapter 11 (KT) Section 35.1-35.2(CLRS) 1 Coping with NP-Completeness Brute-force search: This is usually only a viable option for small
COMP 355 Advanced Algorithms Approximation Algorithms: VC and TSP Chapter 11 (KT) Section 35.1-35.2(CLRS) 1 Coping with NP-Completeness Brute-force search: This is usually only a viable option for small
Small Survey on Perfect Graphs
 Small Survey on Perfect Graphs Michele Alberti ENS Lyon December 8, 2010 Abstract This is a small survey on the exciting world of Perfect Graphs. We will see when a graph is perfect and which are families
Small Survey on Perfect Graphs Michele Alberti ENS Lyon December 8, 2010 Abstract This is a small survey on the exciting world of Perfect Graphs. We will see when a graph is perfect and which are families
Genetic Programming. Charles Chilaka. Department of Computational Science Memorial University of Newfoundland
 Genetic Programming Charles Chilaka Department of Computational Science Memorial University of Newfoundland Class Project for Bio 4241 March 27, 2014 Charles Chilaka (MUN) Genetic algorithms and programming
Genetic Programming Charles Chilaka Department of Computational Science Memorial University of Newfoundland Class Project for Bio 4241 March 27, 2014 Charles Chilaka (MUN) Genetic algorithms and programming
Web Structure Mining Community Detection and Evaluation
 Web Structure Mining Community Detection and Evaluation 1 Community Community. It is formed by individuals such that those within a group interact with each other more frequently than with those outside
Web Structure Mining Community Detection and Evaluation 1 Community Community. It is formed by individuals such that those within a group interact with each other more frequently than with those outside
NP Completeness. Andreas Klappenecker [partially based on slides by Jennifer Welch]
![NP Completeness. Andreas Klappenecker [partially based on slides by Jennifer Welch] NP Completeness. Andreas Klappenecker [partially based on slides by Jennifer Welch]](/thumbs/76/73396698.jpg) NP Completeness Andreas Klappenecker [partially based on slides by Jennifer Welch] Overview We already know the following examples of NPC problems: SAT 3SAT We are going to show that the following are
NP Completeness Andreas Klappenecker [partially based on slides by Jennifer Welch] Overview We already know the following examples of NPC problems: SAT 3SAT We are going to show that the following are
On the Approximability of Modularity Clustering
 On the Approximability of Modularity Clustering Newman s Community Finding Approach for Social Nets Bhaskar DasGupta Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Chicago Chicago, IL 60607,
On the Approximability of Modularity Clustering Newman s Community Finding Approach for Social Nets Bhaskar DasGupta Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Chicago Chicago, IL 60607,
Decision Problems. Observation: Many polynomial algorithms. Questions: Can we solve all problems in polynomial time? Answer: No, absolutely not.
 Decision Problems Observation: Many polynomial algorithms. Questions: Can we solve all problems in polynomial time? Answer: No, absolutely not. Definition: The class of problems that can be solved by polynomial-time
Decision Problems Observation: Many polynomial algorithms. Questions: Can we solve all problems in polynomial time? Answer: No, absolutely not. Definition: The class of problems that can be solved by polynomial-time
Paths. Path is a sequence of edges that begins at a vertex of a graph and travels from vertex to vertex along edges of the graph.
 Paths Path is a sequence of edges that begins at a vertex of a graph and travels from vertex to vertex along edges of the graph. Formal Definition of a Path (Undirected) Let n be a nonnegative integer
Paths Path is a sequence of edges that begins at a vertex of a graph and travels from vertex to vertex along edges of the graph. Formal Definition of a Path (Undirected) Let n be a nonnegative integer
Algorithms for the maximum k-club problem in graphs
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Algorithms for the maximum k-club problem in graphs Shahram Shahinpour Sergiy Butenko Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract Given a simple undirected
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Algorithms for the maximum k-club problem in graphs Shahram Shahinpour Sergiy Butenko Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract Given a simple undirected
Isolation Concepts for Enumerating Dense Subgraphs
 Isolation Concepts for Enumerating Dense Subgraphs Christian Komusiewicz, Falk Hüffner, Hannes Moser, and Rolf Niedermeier Institut für Informatik, Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, Ernst-Abbe-Platz
Isolation Concepts for Enumerating Dense Subgraphs Christian Komusiewicz, Falk Hüffner, Hannes Moser, and Rolf Niedermeier Institut für Informatik, Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, Ernst-Abbe-Platz
Genetic Algorithms Based Solution To Maximum Clique Problem
 Genetic Algorithms Based Solution To Maximum Clique Problem Harsh Bhasin computergrad.com Faridabad, India i_harsh_bhasin@yahoo.com Rohan Mahajan Lingaya s University Faridabad, India mahajanr28@gmail.com
Genetic Algorithms Based Solution To Maximum Clique Problem Harsh Bhasin computergrad.com Faridabad, India i_harsh_bhasin@yahoo.com Rohan Mahajan Lingaya s University Faridabad, India mahajanr28@gmail.com
Graphs: Introduction. Ali Shokoufandeh, Department of Computer Science, Drexel University
 Graphs: Introduction Ali Shokoufandeh, Department of Computer Science, Drexel University Overview of this talk Introduction: Notations and Definitions Graphs and Modeling Algorithmic Graph Theory and Combinatorial
Graphs: Introduction Ali Shokoufandeh, Department of Computer Science, Drexel University Overview of this talk Introduction: Notations and Definitions Graphs and Modeling Algorithmic Graph Theory and Combinatorial
Estimating. Local Ancestry in admixed Populations (LAMP)
 Estimating Local Ancestry in admixed Populations (LAMP) QIAN ZHANG 572 6/05/2014 Outline 1) Sketch Method 2) Algorithm 3) Simulated Data: Accuracy Varying Pop1-Pop2 Ancestries r 2 pruning threshold Number
Estimating Local Ancestry in admixed Populations (LAMP) QIAN ZHANG 572 6/05/2014 Outline 1) Sketch Method 2) Algorithm 3) Simulated Data: Accuracy Varying Pop1-Pop2 Ancestries r 2 pruning threshold Number
Colouring graphs with no odd holes
 Colouring graphs with no odd holes Paul Seymour (Princeton) joint with Alex Scott (Oxford) 1 / 17 Chromatic number χ(g): minimum number of colours needed to colour G. 2 / 17 Chromatic number χ(g): minimum
Colouring graphs with no odd holes Paul Seymour (Princeton) joint with Alex Scott (Oxford) 1 / 17 Chromatic number χ(g): minimum number of colours needed to colour G. 2 / 17 Chromatic number χ(g): minimum
Spotter Documentation Version 0.5, Released 4/12/2010
 Spotter Documentation Version 0.5, Released 4/12/2010 Purpose Spotter is a program for delineating an association signal from a genome wide association study using features such as recombination rates,
Spotter Documentation Version 0.5, Released 4/12/2010 Purpose Spotter is a program for delineating an association signal from a genome wide association study using features such as recombination rates,
31.6 Powers of an element
 31.6 Powers of an element Just as we often consider the multiples of a given element, modulo, we consider the sequence of powers of, modulo, where :,,,,. modulo Indexing from 0, the 0th value in this sequence
31.6 Powers of an element Just as we often consider the multiples of a given element, modulo, we consider the sequence of powers of, modulo, where :,,,,. modulo Indexing from 0, the 0th value in this sequence
Kernelization Through Tidying A Case-Study Based on s-plex Cluster Vertex Deletion
 1/18 Kernelization Through Tidying A Case-Study Based on s-plex Cluster Vertex Deletion René van Bevern Hannes Moser Rolf Niedermeier Institut für Informatik Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, Germany
1/18 Kernelization Through Tidying A Case-Study Based on s-plex Cluster Vertex Deletion René van Bevern Hannes Moser Rolf Niedermeier Institut für Informatik Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, Germany
Genetic Analysis. Page 1
 Genetic Analysis Page 1 Genetic Analysis Objectives: 1) Set up Case-Control Association analysis and the Basic Genetics Workflow 2) Use JMP tools to interact with and explore results 3) Learn advanced
Genetic Analysis Page 1 Genetic Analysis Objectives: 1) Set up Case-Control Association analysis and the Basic Genetics Workflow 2) Use JMP tools to interact with and explore results 3) Learn advanced
LD vignette Measures of linkage disequilibrium
 LD vignette Measures of linkage disequilibrium David Clayton June 13, 2018 Calculating linkage disequilibrium statistics We shall first load some illustrative data. > data(ld.example) The data are drawn
LD vignette Measures of linkage disequilibrium David Clayton June 13, 2018 Calculating linkage disequilibrium statistics We shall first load some illustrative data. > data(ld.example) The data are drawn
Community Detection. Community
 Community Detection Community In social sciences: Community is formed by individuals such that those within a group interact with each other more frequently than with those outside the group a.k.a. group,
Community Detection Community In social sciences: Community is formed by individuals such that those within a group interact with each other more frequently than with those outside the group a.k.a. group,
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms
 W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 11/23/99 NP-completeness of 3SAT, Minimum Vertex Cover, Maximum Independent Set, Boolean Formulae A Boolean formula is an expression that we can build starting from Boolean
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 11/23/99 NP-completeness of 3SAT, Minimum Vertex Cover, Maximum Independent Set, Boolean Formulae A Boolean formula is an expression that we can build starting from Boolean
P = NP; P NP. Intuition of the reduction idea:
 1 Polynomial Time Reducibility The question of whether P = NP is one of the greatest unsolved problems in the theoretical computer science. Two possibilities of relationship between P and N P P = NP; P
1 Polynomial Time Reducibility The question of whether P = NP is one of the greatest unsolved problems in the theoretical computer science. Two possibilities of relationship between P and N P P = NP; P
Kyle Gettig. Mentor Benjamin Iriarte Fourth Annual MIT PRIMES Conference May 17, 2014
 Linear Extensions of Directed Acyclic Graphs Kyle Gettig Mentor Benjamin Iriarte Fourth Annual MIT PRIMES Conference May 17, 2014 Motivation Individuals can be modeled as vertices of a graph, with edges
Linear Extensions of Directed Acyclic Graphs Kyle Gettig Mentor Benjamin Iriarte Fourth Annual MIT PRIMES Conference May 17, 2014 Motivation Individuals can be modeled as vertices of a graph, with edges
Statistical relationship discovery in SNP data using Bayesian networks
 Statistical relationship discovery in SNP data using Bayesian networks Pawe l Szlendak and Robert M. Nowak Institute of Electronic Systems, Warsaw University of Technology, Nowowiejska 5/9, -665 Warsaw,
Statistical relationship discovery in SNP data using Bayesian networks Pawe l Szlendak and Robert M. Nowak Institute of Electronic Systems, Warsaw University of Technology, Nowowiejska 5/9, -665 Warsaw,
Bipartite Roots of Graphs
 Bipartite Roots of Graphs Lap Chi Lau Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Graph H is a root of graph G if there exists a positive integer k such that x and y are adjacent in G if and only
Bipartite Roots of Graphs Lap Chi Lau Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Graph H is a root of graph G if there exists a positive integer k such that x and y are adjacent in G if and only
Clustering of SNP Data with Application to Genomics
 Clustering of SNP Data with Application to Genomics Michael K Ng, Mark J Li, Sio I Ao Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong Email: mng@mathhkbueduhk Yiu-ming Cheung
Clustering of SNP Data with Application to Genomics Michael K Ng, Mark J Li, Sio I Ao Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong Email: mng@mathhkbueduhk Yiu-ming Cheung
Graph Theory. Connectivity, Coloring, Matching. Arjun Suresh 1. 1 GATE Overflow
 Graph Theory Connectivity, Coloring, Matching Arjun Suresh 1 1 GATE Overflow GO Classroom, August 2018 Thanks to Subarna/Sukanya Das for wonderful figures Arjun, Suresh (GO) Graph Theory GATE 2019 1 /
Graph Theory Connectivity, Coloring, Matching Arjun Suresh 1 1 GATE Overflow GO Classroom, August 2018 Thanks to Subarna/Sukanya Das for wonderful figures Arjun, Suresh (GO) Graph Theory GATE 2019 1 /
Critical Node Detection Problem. Panos Pardalos Distinguished Professor CAO, Dept. of Industrial and Systems Engineering, University of Florida
 Critical Node Detection Problem ITALY May, 2008 Panos Pardalos Distinguished Professor CAO, Dept. of Industrial and Systems Engineering, University of Florida Outline of Talk Introduction Problem Definition
Critical Node Detection Problem ITALY May, 2008 Panos Pardalos Distinguished Professor CAO, Dept. of Industrial and Systems Engineering, University of Florida Outline of Talk Introduction Problem Definition
Step-by-Step Guide to Basic Genetic Analysis
 Step-by-Step Guide to Basic Genetic Analysis Page 1 Introduction This document shows you how to clean up your genetic data, assess its statistical properties and perform simple analyses such as case-control
Step-by-Step Guide to Basic Genetic Analysis Page 1 Introduction This document shows you how to clean up your genetic data, assess its statistical properties and perform simple analyses such as case-control
arxiv: v1 [cs.dm] 21 Dec 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cs.dm] 21 Dec 2015 arxiv: v1 [cs.dm] 21 Dec 2015](/thumbs/84/90806310.jpg) The Maximum Cardinality Cut Problem is Polynomial in Proper Interval Graphs Arman Boyacı 1, Tinaz Ekim 1, and Mordechai Shalom 1 Department of Industrial Engineering, Boğaziçi University, Istanbul, Turkey
The Maximum Cardinality Cut Problem is Polynomial in Proper Interval Graphs Arman Boyacı 1, Tinaz Ekim 1, and Mordechai Shalom 1 Department of Industrial Engineering, Boğaziçi University, Istanbul, Turkey
PROJECT PROPOSALS: COMMUNITY DETECTION AND ENTITY RESOLUTION. Donatella Firmani
 PROJECT PROPOSALS: COMMUNITY DETECTION AND ENTITY RESOLUTION Donatella Firmani donatella.firmani@uniroma3.it PROJECT 1: COMMUNITY DETECTION What is Community Detection? What Social Network Analysis is?
PROJECT PROPOSALS: COMMUNITY DETECTION AND ENTITY RESOLUTION Donatella Firmani donatella.firmani@uniroma3.it PROJECT 1: COMMUNITY DETECTION What is Community Detection? What Social Network Analysis is?
Effective Recombination in Plant Breeding and Linkage Mapping Populations: Testing Models and Mating Schemes
 Effective Recombination in Plant Breeding and Linkage Mapping Populations: Testing Models and Mating Schemes Raven et al., 1999 Seth C. Murray Assistant Professor of Quantitative Genetics and Maize Breeding
Effective Recombination in Plant Breeding and Linkage Mapping Populations: Testing Models and Mating Schemes Raven et al., 1999 Seth C. Murray Assistant Professor of Quantitative Genetics and Maize Breeding
Package SimGbyE. July 20, 2009
 Package SimGbyE July 20, 2009 Type Package Title Simulated case/control or survival data sets with genetic and environmental interactions. Author Melanie Wilson Maintainer Melanie
Package SimGbyE July 20, 2009 Type Package Title Simulated case/control or survival data sets with genetic and environmental interactions. Author Melanie Wilson Maintainer Melanie
Extremal Graph Theory: Turán s Theorem
 Bridgewater State University Virtual Commons - Bridgewater State University Honors Program Theses and Projects Undergraduate Honors Program 5-9-07 Extremal Graph Theory: Turán s Theorem Vincent Vascimini
Bridgewater State University Virtual Commons - Bridgewater State University Honors Program Theses and Projects Undergraduate Honors Program 5-9-07 Extremal Graph Theory: Turán s Theorem Vincent Vascimini
HPC methods for hidden Markov models (HMMs) in population genetics
 HPC methods for hidden Markov models (HMMs) in population genetics Peter Kecskemethy supervised by: Chris Holmes Department of Statistics and, University of Oxford February 20, 2013 Outline Background
HPC methods for hidden Markov models (HMMs) in population genetics Peter Kecskemethy supervised by: Chris Holmes Department of Statistics and, University of Oxford February 20, 2013 Outline Background
The k-center problem Approximation Algorithms 2009 Petros Potikas
 Approximation Algorithms 2009 Petros Potikas 1 Definition: Let G=(V,E) be a complete undirected graph with edge costs satisfying the triangle inequality and k be an integer, 0 < k V. For any S V and vertex
Approximation Algorithms 2009 Petros Potikas 1 Definition: Let G=(V,E) be a complete undirected graph with edge costs satisfying the triangle inequality and k be an integer, 0 < k V. For any S V and vertex
Matchings and Covers in bipartite graphs
 Matchings and Covers in bipartite graphs A bipartite graph, also called a bigraph, is a set of graph vertices decomposed into two disjoint sets such that no two graph vertices within the same set are adjacent.
Matchings and Covers in bipartite graphs A bipartite graph, also called a bigraph, is a set of graph vertices decomposed into two disjoint sets such that no two graph vertices within the same set are adjacent.
The complement of PATH is in NL
 340 The complement of PATH is in NL Let c be the number of nodes in graph G that are reachable from s We assume that c is provided as an input to M Given G, s, t, and c the machine M operates as follows:
340 The complement of PATH is in NL Let c be the number of nodes in graph G that are reachable from s We assume that c is provided as an input to M Given G, s, t, and c the machine M operates as follows:
Step-by-Step Guide to Advanced Genetic Analysis
 Step-by-Step Guide to Advanced Genetic Analysis Page 1 Introduction In the previous document, 1 we covered the standard genetic analyses available in JMP Genomics. Here, we cover the more advanced options
Step-by-Step Guide to Advanced Genetic Analysis Page 1 Introduction In the previous document, 1 we covered the standard genetic analyses available in JMP Genomics. Here, we cover the more advanced options
Partha Sarathi Mandal
 MA 515: Introduction to Algorithms & MA353 : Design and Analysis of Algorithms [3-0-0-6] Lecture 39 http://www.iitg.ernet.in/psm/indexing_ma353/y09/index.html Partha Sarathi Mandal psm@iitg.ernet.in Dept.
MA 515: Introduction to Algorithms & MA353 : Design and Analysis of Algorithms [3-0-0-6] Lecture 39 http://www.iitg.ernet.in/psm/indexing_ma353/y09/index.html Partha Sarathi Mandal psm@iitg.ernet.in Dept.
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
GWAsimulator: A rapid whole-genome simulation program
 GWAsimulator: A rapid whole-genome simulation program Version 1.1 Chun Li and Mingyao Li September 21, 2007 (revised October 9, 2007) 1. Introduction...1 2. Download and compile the program...2 3. Input
GWAsimulator: A rapid whole-genome simulation program Version 1.1 Chun Li and Mingyao Li September 21, 2007 (revised October 9, 2007) 1. Introduction...1 2. Download and compile the program...2 3. Input
Genetic type 1 Error Calculator (GEC)
 Genetic type 1 Error Calculator (GEC) (Version 0.2) User Manual Miao-Xin Li Department of Psychiatry and State Key Laboratory for Cognitive and Brain Sciences; the Centre for Reproduction, Development
Genetic type 1 Error Calculator (GEC) (Version 0.2) User Manual Miao-Xin Li Department of Psychiatry and State Key Laboratory for Cognitive and Brain Sciences; the Centre for Reproduction, Development
HapBlock A Suite of Dynamic Programming Algorithms for Haplotype Block Partitioning and Tag SNP Selection Based on Haplotype and Genotype Data
 HapBlock A Suite of Dynamic Programming Algorithms for Haplotype Block Partitioning and Tag SNP Selection Based on Haplotype and Genotype Data Introduction The suite of programs, HapBlock, is developed
HapBlock A Suite of Dynamic Programming Algorithms for Haplotype Block Partitioning and Tag SNP Selection Based on Haplotype and Genotype Data Introduction The suite of programs, HapBlock, is developed
Approximation Algorithms for Geometric Intersection Graphs
 Approximation Algorithms for Geometric Intersection Graphs Subhas C. Nandy (nandysc@isical.ac.in) Advanced Computing and Microelectronics Unit Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata 700108, India. Outline
Approximation Algorithms for Geometric Intersection Graphs Subhas C. Nandy (nandysc@isical.ac.in) Advanced Computing and Microelectronics Unit Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata 700108, India. Outline
11/22/2016. Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms. Introduction. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions
 Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Computability Theory
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Other NP-Complete Problems Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 7 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Sections 7.4 and 7.5. The 3SAT
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Other NP-Complete Problems Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 7 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Sections 7.4 and 7.5. The 3SAT
Linkage Disequilibrium Map by Unidimensional Nonnegative Scaling
 The First International Symposium on Optimization and Systems Biology (OSB 07) Beijing, China, August 8 10, 2007 Copyright 2007 ORSC & APORC pp. 302 308 Linkage Disequilibrium Map by Unidimensional Nonnegative
The First International Symposium on Optimization and Systems Biology (OSB 07) Beijing, China, August 8 10, 2007 Copyright 2007 ORSC & APORC pp. 302 308 Linkage Disequilibrium Map by Unidimensional Nonnegative
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
Graph Theory: Introduction
 Graph Theory: Introduction Pallab Dasgupta, Professor, Dept. of Computer Sc. and Engineering, IIT Kharagpur pallab@cse.iitkgp.ernet.in Resources Copies of slides available at: http://www.facweb.iitkgp.ernet.in/~pallab
Graph Theory: Introduction Pallab Dasgupta, Professor, Dept. of Computer Sc. and Engineering, IIT Kharagpur pallab@cse.iitkgp.ernet.in Resources Copies of slides available at: http://www.facweb.iitkgp.ernet.in/~pallab
CS388C: Combinatorics and Graph Theory
 CS388C: Combinatorics and Graph Theory David Zuckerman Review Sheet 2003 TA: Ned Dimitrov updated: September 19, 2007 These are some of the concepts we assume in the class. If you have never learned them
CS388C: Combinatorics and Graph Theory David Zuckerman Review Sheet 2003 TA: Ned Dimitrov updated: September 19, 2007 These are some of the concepts we assume in the class. If you have never learned them
Class Six: Coloring Planar Graphs
 Class Six: Coloring Planar Graphs A coloring of a graph is obtained by assigning every vertex a color such that if two vertices are adjacent, then they receive different colors. Drawn below are three different
Class Six: Coloring Planar Graphs A coloring of a graph is obtained by assigning every vertex a color such that if two vertices are adjacent, then they receive different colors. Drawn below are three different
Minimum Multicolored Subgraph Problem in Multiplex PCR Primer Set Selection and Population Haplotyping
 Minimum Multicolored Subgraph Problem in Multiplex PCR Primer Set Selection and Population Haplotyping M.T. Hajiaghayi 1,K.Jain 2,L.C.Lau 3,I.I.Măndoiu 4,A.Russell 4,and V.V. Vazirani 5 1 Laboratory for
Minimum Multicolored Subgraph Problem in Multiplex PCR Primer Set Selection and Population Haplotyping M.T. Hajiaghayi 1,K.Jain 2,L.C.Lau 3,I.I.Măndoiu 4,A.Russell 4,and V.V. Vazirani 5 1 Laboratory for
How many colors are needed to color a map?
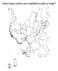 How many colors are needed to color a map? Is 4 always enough? Two relevant concepts How many colors do we need to color a map so neighboring countries get different colors? Simplifying assumption (not
How many colors are needed to color a map? Is 4 always enough? Two relevant concepts How many colors do we need to color a map so neighboring countries get different colors? Simplifying assumption (not
Introduction to Algorithms. Lecture 24. Prof. Patrick Jaillet
 6.006- Introduction to Algorithms Lecture 24 Prof. Patrick Jaillet Outline Decision vs optimization problems P, NP, co-np Reductions between problems NP-complete problems Beyond NP-completeness Readings
6.006- Introduction to Algorithms Lecture 24 Prof. Patrick Jaillet Outline Decision vs optimization problems P, NP, co-np Reductions between problems NP-complete problems Beyond NP-completeness Readings
GBS Bioinformatics Pipeline(s) Overview
 GBS Bioinformatics Pipeline(s) Overview Getting from sequence files to genotypes. Pipeline Coding: Ed Buckler Jeff Glaubitz James Harriman Presentation: Terry Casstevens With supporting information from
GBS Bioinformatics Pipeline(s) Overview Getting from sequence files to genotypes. Pipeline Coding: Ed Buckler Jeff Glaubitz James Harriman Presentation: Terry Casstevens With supporting information from
Practice Final Exam 1
 Algorithm esign Techniques Practice Final xam Instructions. The exam is hours long and contains 6 questions. Write your answers clearly. You may quote any result/theorem seen in the lectures or in the
Algorithm esign Techniques Practice Final xam Instructions. The exam is hours long and contains 6 questions. Write your answers clearly. You may quote any result/theorem seen in the lectures or in the
REU Problems of the Czech Group
 REU Problems of the Czech Group Adam Juraszek, Tomáš Masařík, Jitka Novotná, Martin Töpfer, Tomáš Toufar, Jan Voborník, Peter Zeman Mentor: Dr. James Abello DIMACS REU 2015, Piscataway Dominating Sets
REU Problems of the Czech Group Adam Juraszek, Tomáš Masařík, Jitka Novotná, Martin Töpfer, Tomáš Toufar, Jan Voborník, Peter Zeman Mentor: Dr. James Abello DIMACS REU 2015, Piscataway Dominating Sets
A GENETIC ALGORITHM FOR CLUSTERING ON VERY LARGE DATA SETS
 A GENETIC ALGORITHM FOR CLUSTERING ON VERY LARGE DATA SETS Jim Gasvoda and Qin Ding Department of Computer Science, Pennsylvania State University at Harrisburg, Middletown, PA 17057, USA {jmg289, qding}@psu.edu
A GENETIC ALGORITHM FOR CLUSTERING ON VERY LARGE DATA SETS Jim Gasvoda and Qin Ding Department of Computer Science, Pennsylvania State University at Harrisburg, Middletown, PA 17057, USA {jmg289, qding}@psu.edu
freebayes in depth: model, filtering, and walkthrough Erik Garrison Wellcome Trust Sanger of Iowa May 19, 2015
 freebayes in depth: model, filtering, and walkthrough Erik Garrison Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute @University of Iowa May 19, 2015 Overview 1. Primary filtering: Bayesian callers 2. Post-call filtering:
freebayes in depth: model, filtering, and walkthrough Erik Garrison Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute @University of Iowa May 19, 2015 Overview 1. Primary filtering: Bayesian callers 2. Post-call filtering:
The Structure of Bull-Free Perfect Graphs
 The Structure of Bull-Free Perfect Graphs Maria Chudnovsky and Irena Penev Columbia University, New York, NY 10027 USA May 18, 2012 Abstract The bull is a graph consisting of a triangle and two vertex-disjoint
The Structure of Bull-Free Perfect Graphs Maria Chudnovsky and Irena Penev Columbia University, New York, NY 10027 USA May 18, 2012 Abstract The bull is a graph consisting of a triangle and two vertex-disjoint
Lecture 4: Walks, Trails, Paths and Connectivity
 Lecture 4: Walks, Trails, Paths and Connectivity Rosa Orellana Math 38 April 6, 2015 Graph Decompositions Def: A decomposition of a graph is a list of subgraphs such that each edge appears in exactly one
Lecture 4: Walks, Trails, Paths and Connectivity Rosa Orellana Math 38 April 6, 2015 Graph Decompositions Def: A decomposition of a graph is a list of subgraphs such that each edge appears in exactly one
4. (a) Draw the Petersen graph. (b) Use Kuratowski s teorem to prove that the Petersen graph is non-planar.
 UPPSALA UNIVERSITET Matematiska institutionen Anders Johansson Graph Theory Frist, KandMa, IT 010 10 1 Problem sheet 4 Exam questions Solve a subset of, say, four questions to the problem session on friday.
UPPSALA UNIVERSITET Matematiska institutionen Anders Johansson Graph Theory Frist, KandMa, IT 010 10 1 Problem sheet 4 Exam questions Solve a subset of, say, four questions to the problem session on friday.
4.1. Access the internet and log on to the UCSC Genome Bioinformatics Web Page (Figure 1-
 1. PURPOSE To provide instructions for finding rs Numbers (SNP database ID numbers) and increasing sequence length by utilizing the UCSC Genome Bioinformatics Database. 2. MATERIALS 2.1. Sequence Information
1. PURPOSE To provide instructions for finding rs Numbers (SNP database ID numbers) and increasing sequence length by utilizing the UCSC Genome Bioinformatics Database. 2. MATERIALS 2.1. Sequence Information
Preventing Unraveling in Social Networks: The Anchored k-core Problem
 Preventing Unraveling in Social Networks: Kshipra Bhawalkar 1 Jon Kleinberg 2 1 Tim Roughgarden 1 Aneesh Sharma 3 1 Stanford University 2 Cornell University 3 Twitter, Inc. ICALP 2012 Outline 1 The Problem
Preventing Unraveling in Social Networks: Kshipra Bhawalkar 1 Jon Kleinberg 2 1 Tim Roughgarden 1 Aneesh Sharma 3 1 Stanford University 2 Cornell University 3 Twitter, Inc. ICALP 2012 Outline 1 The Problem
Lecture Note: Computation problems in social. network analysis
 Lecture Note: Computation problems in social network analysis Bang Ye Wu CSIE, Chung Cheng University, Taiwan September 29, 2008 In this lecture note, several computational problems are listed, including
Lecture Note: Computation problems in social network analysis Bang Ye Wu CSIE, Chung Cheng University, Taiwan September 29, 2008 In this lecture note, several computational problems are listed, including
On Approximating Minimum Vertex Cover for Graphs with Perfect Matching
 On Approximating Minimum Vertex Cover for Graphs with Perfect Matching Jianer Chen and Iyad A. Kanj Abstract It has been a challenging open problem whether there is a polynomial time approximation algorithm
On Approximating Minimum Vertex Cover for Graphs with Perfect Matching Jianer Chen and Iyad A. Kanj Abstract It has been a challenging open problem whether there is a polynomial time approximation algorithm
Paths, Flowers and Vertex Cover
 Paths, Flowers and Vertex Cover Venkatesh Raman, M.S. Ramanujan, and Saket Saurabh Presenting: Hen Sender 1 Introduction 2 Abstract. It is well known that in a bipartite (and more generally in a Konig)
Paths, Flowers and Vertex Cover Venkatesh Raman, M.S. Ramanujan, and Saket Saurabh Presenting: Hen Sender 1 Introduction 2 Abstract. It is well known that in a bipartite (and more generally in a Konig)
DNA Sequencing. Overview
 BINF 3350, Genomics and Bioinformatics DNA Sequencing Young-Rae Cho Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University Overview Backgrounds Eulerian Cycles Problem Hamiltonian Cycles
BINF 3350, Genomics and Bioinformatics DNA Sequencing Young-Rae Cho Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University Overview Backgrounds Eulerian Cycles Problem Hamiltonian Cycles
P and NP (Millenium problem)
 CMPS 2200 Fall 2017 P and NP (Millenium problem) Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Piotr Indyk with additions by Carola Wenk CMPS 2200 Introduction to Algorithms 1 We have seen so far Algorithms for various
CMPS 2200 Fall 2017 P and NP (Millenium problem) Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Piotr Indyk with additions by Carola Wenk CMPS 2200 Introduction to Algorithms 1 We have seen so far Algorithms for various
Dominating Set. Stephen Grady, Jeremy Poff
 Dominating Set Stephen Grady, Jeremy Poff Outline Questions About us Overview Problem Similarities History Bounds Complexity Algorithms Applications Implementation Open Questions Discussion Questions To
Dominating Set Stephen Grady, Jeremy Poff Outline Questions About us Overview Problem Similarities History Bounds Complexity Algorithms Applications Implementation Open Questions Discussion Questions To
Graphs and Network Flows IE411. Lecture 21. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Graphs and Network Flows IE411 Lecture 21 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE411 Lecture 21 1 Combinatorial Optimization and Network Flows In general, most combinatorial optimization and integer programming problems are
Graphs and Network Flows IE411 Lecture 21 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE411 Lecture 21 1 Combinatorial Optimization and Network Flows In general, most combinatorial optimization and integer programming problems are
COMP260 Spring 2014 Notes: February 4th
 COMP260 Spring 2014 Notes: February 4th Andrew Winslow In these notes, all graphs are undirected. We consider matching, covering, and packing in bipartite graphs, general graphs, and hypergraphs. We also
COMP260 Spring 2014 Notes: February 4th Andrew Winslow In these notes, all graphs are undirected. We consider matching, covering, and packing in bipartite graphs, general graphs, and hypergraphs. We also
Multiplexing Schemes for Generic SNP Genotyping Assays 1 ABSTRACT
 JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY Volume 12, Number 5, 2005 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 514 533 Multiplexing Schemes for Generic SNP Genotyping Assays 1 RODED SHARAN, 2,3 JENS GRAMM, 2,4 ZOHAR YAKHINI, 5
JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY Volume 12, Number 5, 2005 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 514 533 Multiplexing Schemes for Generic SNP Genotyping Assays 1 RODED SHARAN, 2,3 JENS GRAMM, 2,4 ZOHAR YAKHINI, 5
The Structure and Properties of Clique Graphs of Regular Graphs
 The University of Southern Mississippi The Aquila Digital Community Master's Theses 1-014 The Structure and Properties of Clique Graphs of Regular Graphs Jan Burmeister University of Southern Mississippi
The University of Southern Mississippi The Aquila Digital Community Master's Theses 1-014 The Structure and Properties of Clique Graphs of Regular Graphs Jan Burmeister University of Southern Mississippi
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
Accelerating the Prediction of Protein Interactions
 Accelerating the Prediction of Protein Interactions Alex Rodionov, Jonathan Rose, Elisabeth R.M. Tillier, Alexandr Bezginov October 21 21 Motivation The human genome is sequenced, but we don't know what
Accelerating the Prediction of Protein Interactions Alex Rodionov, Jonathan Rose, Elisabeth R.M. Tillier, Alexandr Bezginov October 21 21 Motivation The human genome is sequenced, but we don't know what
Stanford University CS261: Optimization Handout 1 Luca Trevisan January 4, 2011
 Stanford University CS261: Optimization Handout 1 Luca Trevisan January 4, 2011 Lecture 1 In which we describe what this course is about and give two simple examples of approximation algorithms 1 Overview
Stanford University CS261: Optimization Handout 1 Luca Trevisan January 4, 2011 Lecture 1 In which we describe what this course is about and give two simple examples of approximation algorithms 1 Overview
Graph Theory S 1 I 2 I 1 S 2 I 1 I 2
 Graph Theory S I I S S I I S Graphs Definition A graph G is a pair consisting of a vertex set V (G), and an edge set E(G) ( ) V (G). x and y are the endpoints of edge e = {x, y}. They are called adjacent
Graph Theory S I I S S I I S Graphs Definition A graph G is a pair consisting of a vertex set V (G), and an edge set E(G) ( ) V (G). x and y are the endpoints of edge e = {x, y}. They are called adjacent
XLVI Pesquisa Operacional na Gestão da Segurança Pública
 Setembro de 014 Approximation algorithms for simple maxcut of split graphs Rubens Sucupira 1 Luerbio Faria 1 Sulamita Klein 1- IME/UERJ UERJ, Rio de JaneiroRJ, Brasil rasucupira@oi.com.br, luerbio@cos.ufrj.br
Setembro de 014 Approximation algorithms for simple maxcut of split graphs Rubens Sucupira 1 Luerbio Faria 1 Sulamita Klein 1- IME/UERJ UERJ, Rio de JaneiroRJ, Brasil rasucupira@oi.com.br, luerbio@cos.ufrj.br
SNP HiTLink Manual. Yoko Fukuda 1, Hiroki Adachi 2, Eiji Nakamura 2, and Shoji Tsuji 1
 SNP HiTLink Manual Yoko Fukuda 1, Hiroki Adachi 2, Eiji Nakamura 2, and Shoji Tsuji 1 1 Department of Neurology, Graduate School of Medicine, the University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan 2 Dynacom Co., Ltd, Kanagawa,
SNP HiTLink Manual Yoko Fukuda 1, Hiroki Adachi 2, Eiji Nakamura 2, and Shoji Tsuji 1 1 Department of Neurology, Graduate School of Medicine, the University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan 2 Dynacom Co., Ltd, Kanagawa,
OmegaPlus Pavlos Pavlidis & Nikolaos Alachiotis
 1 OmegaPlus 2.0.0 Pavlos Pavlidis & Nikolaos Alachiotis Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 The linkage disequilibrium (LD) pattern of selective sweeps 3 3 Features 7 3.1 Command line options.................................
1 OmegaPlus 2.0.0 Pavlos Pavlidis & Nikolaos Alachiotis Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 The linkage disequilibrium (LD) pattern of selective sweeps 3 3 Features 7 3.1 Command line options.................................
THE INDEPENDENCE NUMBER PROJECT:
 THE INDEPENDENCE NUMBER PROJECT: α-properties AND α-reductions C. E. LARSON DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIVERSITY 1. Introduction A graph property P is an α-property
THE INDEPENDENCE NUMBER PROJECT: α-properties AND α-reductions C. E. LARSON DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIVERSITY 1. Introduction A graph property P is an α-property
Complementary Acyclic Weak Domination Preserving Sets
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 30-9364, ISSN (Print): 30-9356 ijresorg Volume 4 Issue 7 ǁ July 016 ǁ PP 44-48 Complementary Acyclic Weak Domination
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 30-9364, ISSN (Print): 30-9356 ijresorg Volume 4 Issue 7 ǁ July 016 ǁ PP 44-48 Complementary Acyclic Weak Domination
Genetic Algorithm for Dynamic Capacitated Minimum Spanning Tree
 28 Genetic Algorithm for Dynamic Capacitated Minimum Spanning Tree 1 Tanu Gupta, 2 Anil Kumar 1 Research Scholar, IFTM, University, Moradabad, India. 2 Sr. Lecturer, KIMT, Moradabad, India. Abstract Many
28 Genetic Algorithm for Dynamic Capacitated Minimum Spanning Tree 1 Tanu Gupta, 2 Anil Kumar 1 Research Scholar, IFTM, University, Moradabad, India. 2 Sr. Lecturer, KIMT, Moradabad, India. Abstract Many
A taste of perfect graphs (continued)
 A taste of perfect graphs (continued) Recall two theorems from last class characterizing perfect graphs (and that we observed that the α ω theorem implied the Perfect Graph Theorem). Perfect Graph Theorem.
A taste of perfect graphs (continued) Recall two theorems from last class characterizing perfect graphs (and that we observed that the α ω theorem implied the Perfect Graph Theorem). Perfect Graph Theorem.
A Genetic Algorithm Applied to Graph Problems Involving Subsets of Vertices
 A Genetic Algorithm Applied to Graph Problems Involving Subsets of Vertices Yaser Alkhalifah Roger L. Wainwright Department of Mathematical Department of Mathematical and Computer Sciences and Computer
A Genetic Algorithm Applied to Graph Problems Involving Subsets of Vertices Yaser Alkhalifah Roger L. Wainwright Department of Mathematical Department of Mathematical and Computer Sciences and Computer
