Cabriolet for RISC OS
|
|
|
- Douglas O’Neal’
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 abriolet for RIS OS a dynamic geometry program Version 2.5 i
2 opyright opyright Murklesoft Murklesoft can be contacted care of: Icon Technology hurch House hurch Street arlby Stamford Lincs PE9 4N +44 (0) Upgrades to abriolet (as a zip d archive) and the latest version of this guide (in TechWriter and PF format) are available from: redits This guide was written and typeset on RIS OS using TechWriter Professional. ll the diagrams were drawn in abriolet and exported to TechWriter in raw format. abriolet was written by Michael orcherds. First Published October 1997 by Murklesoft Manual Issue October 2002 ii abriolet for RIS OS:
3 ontents opyright ii redits ii bout this Guide v onventions used v hapter one Using abriolet The Toolbar The uttons Tool Menus The Panes Menus The Mouse uttons The Mouse Pointer Reconfiguring the Menus hapter two Tutorial Introduction ircumcircle of a Triangle Incircle of a Triangle Tracing a Point hapter three Reference Point and Label Tool Intersection Tool Midpoint Tool Perpendicular Point Tool Mirror Point Tool Rotate Point Tool Vector Point Tool Line Segment Tool Line Tool ircle Tool ircle Given Radius Tool Ellipse Tool Perpendicular Line Tool Parallel Line Tool Perpendicular isector Tool ngle isector Tool ngle Trisector Tool Measurement Tool Measure rea Tool Mark ngle Tool Hide Object Tool Thicken Line Tool olour Red Tool olour Grey Tool olour lack Tool olour Purple Tool olour lue Tool iii
4 elete Object Tool Set Ratio Tool Link Objects Tool nimate Tool Static Locus Tool Vector Tool Vector Sum Tool opy Vector Tool ddition Tool Subtraction Tool Multiplication Tool Square Tool Square Root Tool X oordinate Tool Y oordinate Tool iv abriolet for RIS OS:
5 bout this Guide This guide is about abriolet a dynamic geometry package for that has been designed both to be easy to use and to run at a good speed even on low specification machines. The manual is divided into three chapters: hapter one describes how abriolet works. hapter two is a tutorial. hapter three is a reference section detailing all the Tools that abriolet has. onventions used ragging the mouse between two points means to press the appropriate mouse button, moving the mouse and then finally releasing the button again.where click is used on its own it refers to the left hand mouse button. Geometrical objects that abriolet uses are referred to in italic, for example Perpendicular isector. Tools are referred to in bold, for example, Perpendicular isector Tool. v
6 vi abriolet for RIS OS:
7 hapter one Using abriolet hapter one Using abriolet 1
8 abriolet The Toolbar To load abriolet, double-click on it from a filer window. abriolet s icon will then appear on the icon bar. lick on this icon each time you wish to open a new abriolet document. The toolbar is at the top of every abriolet window. It consists of two parts: the buttons on the bottom left are for selecting different tools and on the top and right are two panes which display helpful information. The uttons Tool Menus s you move the mouse over the buttons, the top pane tells you what each Tool is. licking with Select (the left mouse button) will then activate that tool (see hapter three for a thorough description of each Tool). Each button can be used to select more than one Tool. To select a different Tool to the one displayed in the pane, press the middle mouse button Menu as instructed in the lower pane. This brings up a menu of other available Tools which can be chosen. This will then be the default Tool for that button, until another Tool is chosen from its menu. The Panes The two panes display different information depending upon where the mouse pointer is. When the mouse pointer is over the buttons on the Tool ar, the top pane gives you the name of each Tool. When the mouse pointer is over the main window, the top pane tells you how to use the current Tool. The bottom pane will usually give some information about the object that the mouse pointer is over. Menus part from the menus used to select different Tools, there are two other menus available. The first is obtained by pressing Menu (the middle mouse button) over abriolet s icon on the icon bar. This allows you to either quit abriolet or view some information about abriolet, including the version number and who is licensed to use it. The second is obtained by pressing Menu over abriolet s main window. This allows you to: Save a file, so that it can be reloaded on a future occasion (also F3). Export a file in raw format so that it can be used in other programs. Save a locus out as a SV file. Show any objects that may have been hidden. Undelete any objects that may have been deleted. Turn the grid on or off, and set its size. Undo or Redo the last action (also F8). 2 abriolet for RIS OS: hapter one Using abriolet
9 The Mouse uttons Select, the left button, is generally used for selecting an object, or the position for an object (depending on the Tool selected). For example when using the Line Segment Tool, you click and drag from where you want the line to start. If you click near a point, the Line Segment will start at this point. However if you click nowhere near a point then a starting point will be automatically created. Similarly if you place the mouse near a Point when the left hand mouse button is pressed, the Line Segment will snap onto that Point. If you release the mouse button here, the Line Segment will have this Point as its endpoint. The right button can always be used for dragging points and labels around (although not all points and labels can be moved). The Mouse Pointer Reconfiguring the Menus The mouse pointer will change depending on what object it is near. This is useful when two objects are close together and you need to know which one you are clicking on. If you press and hold lt when dragging the mouse, it will confine the point being dragged to a grid. You can also turn the grid on permanently (see Menu section, above). ll the the Tool menus obtained by pressing Menu over the Tool buttons can be reconfigured, as can the buttons themselves. To change them, load the file!abriolet.efault.menus into a text editor such as Edit or Zap. Each line of the file defines the menu for a button. It consists of names of Tools as they appear in the menus, separated by commas. Up to fifteen buttons can be defined. When the file has been altered it should be saved in the appropriate directory for your configured country (e.g.!abriolet.efault.uk) which you can find out by pressing F12 and typing: Show abriolet$ountry If the menus are reconfigured then they will obviously not be as described in the manual! hapter one Using abriolet 3
10 4 abriolet for RIS OS: hapter one Using abriolet
11 hapter two Tutorial hapter two Tutorial 5
12 Introduction This chapter is a short tutorial that shows you, step by step, how to create the following examples: ircumcircle of a Triangle Incircle of a Triangle Tracing a Point 6 abriolet for RIS OS: hapter two Tutorial
13 ircumcircle of a Triangle The circumcircle of a triangle always passes through all its corners. 1 Open a new document (after loading abriolet) by clicking on its icon on the icon bar. 2 Now construct Line Segment. Press the right hand mouse button over the second button on the Toolbar, which will bring up a menu. hoose Line Segment from this. Then, over the main window, hold down the left mouse button and move the mouse before releasing it. 3 Then construct a triangle. Move the mouse to the Point (the mouse pointer changes to say This Point ). Then hold down the left hand mouse button and move the mouse to where you wish the Point to be, before releasing the mouse button. 4 Now complete the triangle. Move the mouse to Point, press the left hand mouse button, move the mouse to Point and release the mouse button. efore proceeding, check that the Line Segments join up. Hold down the right hand mouse button over any of, or and then move the mouse around: the Point that you have clicked on should follow the mouse around, as should the Line Segments joined to that Point. 1 Now construct two Perpendicular isectors. lick the right hand mouse button over the fourth button from the left on the Toolbar. hoose Perpendicular isector from the menu. Then simply click on Line Segment and then on Line Segment. 2 Now construct the Intersection of the Perpendicular isectors. lick the right hand mouse button over the leftmost button and choose Intersection. Then click on both the Perpendicular isectors in turn. 3 Now construct the circumcircle itself. hoose ircle from the Toolbar (it is the default tool for the third button, so simply click on it, or you can choose it from the menu obtained by clicking the right hand mouse button). Then move the mouse pointer to Point, hold down the left hand mouse button, move the mouse to Point and then release the mouse button. hapter two Tutorial 7
14 4 If you wish you can now hide the construction lines. hoose Hide Object (seventh button) and then click on any lines, points or labels that you don t want to be shown. 5 Now check that the circumcircle always goes through Points, and by dragging these three points round with the right hand mouse button. 8 abriolet for RIS OS: hapter two Tutorial
15 Incircle of a Triangle The incircle of a triangle always touches the edges of the triangle. 1 Start off by opening up a new document. 2 s before, start off by constructing a triangle from three Line Segments. 3 Next construct the ngle isector of angle. hoose ngle isector (from the menu on the fourth button) then click on the three Points,, in that order. 4 Then construct the ngle isector of angle. Still using the ngle isector Tool click on the three Points,, in that order. 5 Then choose Intersection (from the first button) to construct the Intersection of the ngle isectors by clicking on each one in turn. 6 Now to construct a Point on the Line Segment that is on the radius of the incircle, we use the Perpendicular Point Tool (from the menu of the first button). lick on Point and then on Line Segment. E 7 Finally we can construct the incircle using the ircle Tool (third button). lick over Point (the centre of the ircle), move the mouse pointer to Point E (the radius point) and then release the mouse button. E hapter two Tutorial 9
16 8 heck that the incircle always touches all three sides of the triangle by dragging the corners around with the right hand mouse button. E 10 abriolet for RIS OS: hapter two Tutorial
17 Tracing a Point Here we will construct a Point whose locus is an ellipse (i.e. it will trace out an ellipse when we move another point). 1 First use the Line Segment Tool (second button s menu) to make Line Segment. 2 Next use the Point and Label Tool (first button) to construct Point on Line. heck by dragging it with the right hand mouse button that it cannot move off Line Segment. 3 To construct the ircle centre we use the ircle Given Radius Tool (third button s menu). To use it, first click where you wish Point to be, then click on Point, then on Point. Now the ircle s radius will always be the same length as the line joining and. heck this by dragging Point with the right hand mouse button: the ircle should change size as Point moves. 4 Similarly, still using the ircle Given Radius Tool, construct the second ircle by clicking where you wish Point E to be, then on Point and then on Point. E F G 5 Now use the Intersection Tool (first button s menu) to construct Points F and G. Simply click on the first ircle, and then the second. E hapter two Tutorial 11
18 6 Now as Point is moved along Line Segment (with the right hand mouse button) Points F and G will both trace out half an ellipse. F E G To see this, choose Static Locus (seventh button s menu). Then click on, say, Point F. Then drag Point with the right hand mouse button. The trail left will be traced out in Green. To see the path traced out by Point G, click on Point G with the left hand mouse button and drag Point with the right hand mouse button. nother way to check this (as shown) is to actually construct the Ellipse. To do this, choose Ellipse (third button s menu) and then click on Points, E and F in that order (so that and E are the foci of the Ellipse and F is a Point on its edge). Then Points F and G will stay on the Ellipse as Point is moved. 12 abriolet for RIS OS: hapter two Tutorial
19 hapter three Reference hapter three Reference 13
20 Tools The tools can be choosen from the utton bar. Pressing the right hand mouse button over a button will reveal additional tools. This brings up a menu of other available Tools which can be chosen. This will then be the default Tool for that button, until another Tool is chosen from its menu. Point and Label Tool To create a asic Point, click anywhere away from other objects. The Point can then be dragged to where it is required with the right hand mouse button. Label is automatically created next to the Point. It can also be moved with the right hand mouse button. To create a Point on ircle or a Point on Line, move the mouse until the pointer changes to indicate that you are near enough to a ircle or any sort of line (Line, Line Segment, ngle isector, Parallel Line, Perpendicular Line or Perpendicular isector) and click with the left hand mouse button. When you then try to move one of these with the right hand mouse button, it will be constrained to move only along the circle or line. is a Point on Line on Line Segment Mathematical efinition point is a geometrical object with zero dimension. Intersection Tool To create the Point(s) at the intersection of two objects, simply click on them. Suitable such objects are ircles and any sort of Line, for example Line Segments, ngle isectors, Perpendicular isectors. E and F are the intersections of Line Segment and the ircle centre, E F Mathematical efinition Midpoint Tool The intersections of two objects are the points which satisfy the conditions for both objects simultaneously. To create the Midpoint of two Points either click on both Points or, if it exists, click on a Line Segment joining them. is the Midpoint of Line Segment Mathematical efinition The midpoint of two points is exactly half way in between them. 14 abriolet for RIS OS: hapter three Reference
21 Perpendicular Point Tool To create the nearest Point on a line to a given Point, click on both the Point and the line. E is the Perpendicular Point obtained by clicking on Point and Line Segment. It has been used to construct the incircle of triangle. ( is the Intersection of the ngle isectors of the triangle) E Mathematical efinition Mirror Point Tool The perpendicular point is such that the line joining the two points is at right angles to the original line. To create a Mirror Point that is the reflection of another point in a line click on both the point and the line. is the Mirror Point of in the line. Hence will always be a kite. Rotate Point Tool The Rotate Point Tool can be used to rotate a Point through a fixed angle. To rotate a whole shape each Point that determines the shape can be rotated and then the shape redrawn. It can also be used to create an angle of a fixed size. To rotate a Point by a fixed angle, first click on the Point to be rotated then click on the Point that is to be the centre of the rotation. window will then appear, into which you should type an angle in degrees. This will be the size of the rotation (anti-clockwise). negative angle can be entered for a clockwise rotation. Point has been rotated through 72 about Point to make Point. Point has been rotated through 72 about Point to make Point. Point has been rotated through 72 about Point to make Point E. Point E has been rotated through 72 about Point to make Point F E F Hence shape EF is a regular pentagon. hapter three Reference 15
22 Vector Point Tool To create a Vector Point, click on a Point and, while still holding the mouse button, move the mouse to where you want the Vector Point and then release the mouse button. The Vector Point will then always remain the same distance and direction from the original Point. is a Vector Point depending upon Point. The ircle has centre and radius point. When Point is moved, Vector Point will also move and so the ircle will stay the same size, rather than growing or shrinking. Note: This tool was called the Vector Tool with a different icon in some previous releases of abriolet. The Vector Tool is similar but can automatically create the initial point and draw a Line Segment. Line Segment Tool To create a Line Segment, drag the mouse with the left hand mouse button pressed from the start point to the end point. If you wish it to start and/or end on a Point, simply start and/or end your drag on the appropriate Point(s). Line Segment Mathematical efinition Related Tools line segment is a finite section of a line, as opposed to an infinite (unending) line which is normally just referred to as a line. Line Tool, Point and Label Tool Line Tool To create a Line, drag the mouse, with the left hand button pressed, from one point you wish to be on the line to another point on the line. If you wish it to go through one or two existing Points, simply start and/or end your drag on the appropriate Point(s). Line produced. 16 abriolet for RIS OS: hapter three Reference
23 ircle Tool To draw a ircle, drag the mouse from where you want the centre to be to where you want the edge of the ircle to be. While you drag the mouse, the ircle will be shown in the position according to the current mouse position. If you want the ircle either to have a particular Point at its centre or to have a particular Point on its radius, simply start or finish the mouse drag on the appropriate Point(s). ircle with radius and radius point. Mathematical efinition ircle Given Radius Tool circle is the set of points equidistant from the centre point. To create a ircle whose radius is the same length as a Line Segment, firstly click on the Point you wish to be the centre then click on the two endpoints of the Line Segment. s with the ircle Tool, if you click where there is no point, one will be automatically created. is a Point on Line Segment. ircle centre has its radius set to Line Segment. ircle centre E has its radius set to Line Segment. F and G are the Intersections of the two ircles. s Point is moved along Line Segment, each of F and G trace out half an ellipse (whose foci are and E). G E F This is because the length G + GE is always the same (and is equal to length + = ), and it is equivalent to the mechanical construction of an ellipse by putting two pins in a piece of paper (at and E), tying a piece of string to them (length ) and moving a pencil round (at Point F or G) keeping the string taught. hapter three Reference 17
24 Ellipse Tool To create an Ellipse, click on three points: two foci and a point that is to be on the circumference. s with the ircle Tool, if you click where there is no point, one will be automatically created. and are the foci of the ellipse, defines where the circumference of the ellipse is. Mathematical efinition n ellipse is a stretched circle. Ellipses have the property that if and are the foci and is any point on the edge then the angle bisector of is perpendicular to the tangent to the ellipse at. Hence if a snooker ball is hit in any direction from one focus, it will always go through the other focus, where a pocket can be cunningly placed! Perpendicular Line Tool To create a line that is perpendicular (at right angles to) another line, click (in either order) on the line you wish to be at right angles to and a Point which you want your new Perpendicular Line to go through. The Perpendicular Line through will always go through and will always remain at right angles to Line. Parallel Line Tool To create a line that is parallel to another line, click (in either order) on the line you wish to be a parallel to and a Point which you want your new Parallel Line to go through. The Parallel Line through will always go through and will always remain parallel to Line. 18 abriolet for RIS OS: hapter three Reference
25 Perpendicular isector Tool To create the perpendicular bisector of two Points, click on the first Point (which will turn red) then click on the second Point. To create the Perpendicular isector of a Line Segment, just click on the Line Segment. The Perpendicular isector of. Mathematical efinition perpendicular bisector of two points is a line, each point of which is the same distance (equidistant) from the two original points. In practice this is a line that cuts the Line Segment at right angles exactly half way in between the two points. ngle isector Tool To create an ngle isector, either click on an ngle that has already been marked with the Mark ngle Tool, or click on three Points that define the angle to be bisected. The ngle isector of ngle. ngle Trisector Tool To create an ngle Trisector, either click on an ngle that has already been marked with the Mark ngle Tool, or click on three Points that define the angle to be trisected. The ngle Trisector of angle. hapter three Reference 19
26 Measurement Tool To measure the distance between two Points, click on them or, if it exists, click on a Line Segment joining them. To Measure an angle, it must first have been marked with the Mark ngle tool. Then simply click on the angle. To Measure an area, use the Measure rea tool. alculations can be performed on Measurements using various other Tools (see ddition Tool). Length = 3.79cm, angle = Measure rea Tool To measure the area of a triangle, click on all three corners. The area of triangle is cm Mark ngle Tool To mark an acute angle click on three Points that specify the angle with the second Point being the Point at the angle. ngle has been marked. Uses Hide Object Tool This is necessary for specifying an angle to measure and also allows you to specify an angle more quickly for the ngle isector Tool. It also makes clear which angle is being bisected or measured. To hide an object, simply click on it. Unlike eleting an object, hiding it does not affect any objects that it depends upon (for example if you hide a Line, any Points on that Line will not disappear). To unhide objects, choose Show Hidden from the main menu. Point is a Point on Line on Line Segment, but Line Segment has been hidden. 20 abriolet for RIS OS: hapter three Reference
27 Thicken Line Tool The Thicken Line Tool can be used to draw Lines and ircles with a thicker (bolder) line. To thicken a Line or a ircle, simply click on it. To revert to normal, simply click again. olour Red Tool To colour an object red, simply click on it. olour Grey Tool To colour an object grey, simply click on it. olour lack Tool To colour an object black, simply click on it. olour Purple Tool To colour an object purple, simply click on it. olour lue Tool To colour an object blue, simply click on it. elete Object Tool Set Ratio Tool To delete an object, simply click on it. This will also delete all the objects that depend upon the deleted object. The Hide Object Tool can be used if you simply want an object not to be displayed. ll the objects that have been deleted previously can be recreated by choosing Undelete from the main menu. This works even after a file has been saved and reloaded. lso note that if an object is inadvertently deleted, the Undo/Redo menu option (or pressing F8) can be used to bring back only the just-deleted objects. The Set Ratio Tool can be used to set precisely how far along a Line Segment a Point on Line is. To set this, click on a Point on Line. window will appear into which you should type a decimal value between 0 and 1. This ratio is always preserved, unless the Point on Line is dragged by the mouse. Point on Line has been set to be 0.33 along Line Segment. hapter three Reference 21
28 Link Objects Tool This Tool can be used to change any point into a Point on Line or a Point on ircle. It can even be used to move a Point On ircle/line to a different circle/line. To achieve this, simply click on the desired point to change, and then click on the line or circle that you wish it to lie on. Note that if the Point originally depended upon some other objects, these dependencies will be lost when the Point is redefined. nimate Tool The nimate Tool can be used to create simple animations. To use it, either click on a Point on Line or a Point on ircle. The Point clicked upon will then move smoothly around the ircle or back and forth along the Line. Simpler but more general animations can be created by pressing or holding down F8 to repeatedly undo and then redo the last action taken. Static Locus Tool To create the Locus of a Point (i.e. to trace its path), click on a Point (which will turn red). Then simply drag any other Points about with the right hand mouse button. If the original Point moves, its path will be traced out by green dots. If the mouse is moved slowly and carefully (press Shift before dragging to facilitate this) then the green dots will be closer together so that the Locus will look like a curve. Only one Locus is allowed (including in different windows) at a time. To clear a Locus, select a different Tool and then reselect the Locus Tool. It is possible to save out the coordinates of all the points in the Locus as a omma Separated Variable (SV) file from the menu which is obtained by pressing the middle mouse button over the main window. Peaucellier s ell is a mechanical construction that will draw a line without a straight edge. ll the Line Segments in the diagram have been arranged to have a fixed length (representing rods). s Point moves around the ircle, Point K traces out a line (i.e. the locus of K is a line). K Mathematical efinition The locus of a point is the path traced out by it as it moves under certain constraints. 22 abriolet for RIS OS: hapter three Reference
29 Vector Tool The Vector Tool lets you create a Vector! In abriolet, this consists of a Vector Point (see separate Vector Point Tool) joined to any other sort of Point with a Line Segment. Such a construction has the property that the Vector Point end of the Vector will always stay in exactly the same position relative to the other end (in both distance and direction). In operation, the Vector Point Tool is similar in operation to the Line Segment Tool: press the left hand mouse button, move the mouse and then release. If you click near to a Point, then this will become one end of the Vector, otherwise another Point will be created automatically. However, unlike the Line Segment Tool, if you release the mouse near a Point, the Vector will not attach itself to it. Lines,, and E are all Vectors. Line E is a Line Segment. Mathematical efinition Vector Sum Tool Mathematical efinition E If Point is moved, the whole shape is preserved and moves with. If any other Point is moved the shape is altered accordingly. Geometrically, a vector is something with both distance and direction. So, for instance, a vector is a measure of the relative position of two points. See Vector Sum Tool for some more detail. The Vector Sum Tool can be used to create the Vector that is the sum (also known as the resultant) of two other Vectors. To use this tool, first select two Vectors. This can be done either by clicking on a Vector or by clicking on a Vector Point (the endpoint of a Vector). Then click on a Point that you wish the new Vector to start at. If you do not click on a Point then one will be created automatically. vector can be thought of as an instruction to move a certain distance in a certain direction. The resultant (or sum) of two vectors is defined to be a single distance and direction instruction that will move you to the same place as if you had carried out the instructions relating to the two original vectors one after the other. i.e. the route taken does not matter; vectors are added as the crow flies. hapter three Reference 23
30 opy Vector Tool The opy Vector Tool can be used in two related ways. Firstly it can be used to simply make a copy of a Vector but with a different starting point. Secondly it can be used to make a Vector that can be defined by any two Points. To use this Tool, first click either on a Line Segment (which may be a Vector) or on any two Points (these can be the start and end Points of a Vector). Then click on a Point that you wish the new Vector to start at (if you do not click on a Point, a new one will be created automatically). is a Vector. is a Vector opy of. Hence is a parallelogram. 2 If Point is moved, Point also moves. If Point is moved, Point also moves. If Point is moved, Point also moves. is a Line Segment. is a Vector opy of. Hence is a parallelogram. If Point is moved, Point also moves. If Point is moved, Point also moves. If Point is moved, Point also moves. ddition Tool This Tool can be used to add up any two Measurements and then display the result. This can then be treated like any other Measurement; it can be moved around and it can have other calculations performed upon it. The same is true of the other Tools on this page. To use it, simply click on any two Measurements. Subtraction Tool This Tool can be used to find the difference between any two Measurements. To use it, simply click on any two Measurements. Multiplication Tool This Tool can be used to find the product of any two Measurements. To use it, simply click on any two Measurements. Square Tool This Tool can be used to find the square of any Measurement. To use it, simply click on any Measurement. Square Root Tool This Tool can be used to find the square root of any Measurement. To use it, simply click on any Measurement. 24 abriolet for RIS OS: hapter three Reference
31 X oordinate Tool This Tool can be used to display the ordinate of any Point. To use it, simply click on a Point. Y oordinate Tool This Tool can be used to display the abscissa of any Point. To use it, simply click on a Point. hapter three Reference 25
G12 Centers of Triangles
 Summer 2006 I2T2 Geometry Page 45 6. Turn this page over and complete the activity with a different original shape. Scale actor 1 6 0.5 3 3.1 Perimeter of Original shape Measuring Perimeter Perimeter of
Summer 2006 I2T2 Geometry Page 45 6. Turn this page over and complete the activity with a different original shape. Scale actor 1 6 0.5 3 3.1 Perimeter of Original shape Measuring Perimeter Perimeter of
Tutorial 3: Constructive Editing (2D-CAD)
 (2D-CAD) The editing done up to now is not much different from the normal drawing board techniques. This section deals with commands to copy items we have already drawn, to move them and to make multiple
(2D-CAD) The editing done up to now is not much different from the normal drawing board techniques. This section deals with commands to copy items we have already drawn, to move them and to make multiple
5 km. 1. Open the sketch home.gsp provided by your teacher that shows the map above. * Construct a point P anywhere to represent James s home.
 uilding a Home Name James owns a small trout farm near the Drakensberg mountains, South frica, in the shape of a quadrilateral as shown. He wants to build his house so that it takes him the same time to
uilding a Home Name James owns a small trout farm near the Drakensberg mountains, South frica, in the shape of a quadrilateral as shown. He wants to build his house so that it takes him the same time to
An Introduction to GeoGebra
 An Introduction to GeoGebra Downloading and Installing Acquiring GeoGebra GeoGebra is an application for exploring and demonstrating Geometry and Algebra. It is an open source application and is freely
An Introduction to GeoGebra Downloading and Installing Acquiring GeoGebra GeoGebra is an application for exploring and demonstrating Geometry and Algebra. It is an open source application and is freely
G15 Developing Conic Sections with GSP
 Summer 2006 I2T2 Geometry Page 63 G15 Developing Conic Sections with GSP Conics using Locus Definitions Exploration #1 Parabola as a locus Objective: The definition of a parabola is the set of points that
Summer 2006 I2T2 Geometry Page 63 G15 Developing Conic Sections with GSP Conics using Locus Definitions Exploration #1 Parabola as a locus Objective: The definition of a parabola is the set of points that
Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop
 Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop Don Spickler Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Salisbury University Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop Outline 1. asic Construction, Measurement and Transformation
Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop Don Spickler Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Salisbury University Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop Outline 1. asic Construction, Measurement and Transformation
8.3 Technology: Loci and Conics
 8.3 Technology: Loci and Conics The diagram shows a double cone. The two cones have one point in common. The intersection of a double cone and a plane is called a conic section or a conic. The circle,
8.3 Technology: Loci and Conics The diagram shows a double cone. The two cones have one point in common. The intersection of a double cone and a plane is called a conic section or a conic. The circle,
Day 5: Inscribing and Circumscribing Getting Closer to π: Inscribing and Circumscribing Polygons - Archimedes Method. Goals:
 Day 5: Inscribing and Circumscribing Getting Closer to π: Inscribing and Circumscribing Polygons - Archimedes Method Goals: Construct an inscribed hexagon and dodecagon. Construct a circumscribed hexagon
Day 5: Inscribing and Circumscribing Getting Closer to π: Inscribing and Circumscribing Polygons - Archimedes Method Goals: Construct an inscribed hexagon and dodecagon. Construct a circumscribed hexagon
Name: Tutor s
 Name: Tutor s Email: Bring a couple, just in case! Necessary Equipment: Black Pen Pencil Rubber Pencil Sharpener Scientific Calculator Ruler Protractor (Pair of) Compasses 018 AQA Exam Dates Paper 1 4
Name: Tutor s Email: Bring a couple, just in case! Necessary Equipment: Black Pen Pencil Rubber Pencil Sharpener Scientific Calculator Ruler Protractor (Pair of) Compasses 018 AQA Exam Dates Paper 1 4
Unit 8 Plane Geometry
 Unit 8 Plane Geometry Grade 9 pplied Lesson Outline *Note: This unit could stand alone and be placed anywhere in the course. IG PITURE Students will: investigate properties of geometric objects using dynamic
Unit 8 Plane Geometry Grade 9 pplied Lesson Outline *Note: This unit could stand alone and be placed anywhere in the course. IG PITURE Students will: investigate properties of geometric objects using dynamic
G7-3 Measuring and Drawing Angles and Triangles
 G7-3 Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles right angle acute angles obtuse angles 90 less than 90 more than 90 and less than 180 1. Without using a protractor, identify each angle as acute or obtuse.
G7-3 Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles right angle acute angles obtuse angles 90 less than 90 more than 90 and less than 180 1. Without using a protractor, identify each angle as acute or obtuse.
Modeling a Gear Standard Tools, Surface Tools Solid Tool View, Trackball, Show-Hide Snaps Window 1-1
 Modeling a Gear This tutorial describes how to create a toothed gear. It combines using wireframe, solid, and surface modeling together to create a part. The model was created in standard units. To begin,
Modeling a Gear This tutorial describes how to create a toothed gear. It combines using wireframe, solid, and surface modeling together to create a part. The model was created in standard units. To begin,
Lesson 5: Definition of Rotation and Basic Properties
 Student Outcomes Students know how to rotate a figure a given degree around a given center. Students know that rotations move lines to lines, rays to rays, segments to segments, and angles to angles. Students
Student Outcomes Students know how to rotate a figure a given degree around a given center. Students know that rotations move lines to lines, rays to rays, segments to segments, and angles to angles. Students
Use Geometry Expressions to create an envelope curve Use Geometry Expressions as an aide to creating geometric proof.
 Learning Objectives Loci and onics Lesson 4: onics and Envelope urves Level: Precalculus Time required: 90 minutes Students begin by looking at an envelope curve that generates an ellipse. The curve is
Learning Objectives Loci and onics Lesson 4: onics and Envelope urves Level: Precalculus Time required: 90 minutes Students begin by looking at an envelope curve that generates an ellipse. The curve is
The Geometry of Piles of Salt Thinking Deeply About Simple Things
 The Geometry of Piles of Salt Thinking eeply bout Simple Things University of Utah Teacher s Math ircle Monday, February 4 th, 2008 y Troy Jones Waterford School Important Terms (the word line may be
The Geometry of Piles of Salt Thinking eeply bout Simple Things University of Utah Teacher s Math ircle Monday, February 4 th, 2008 y Troy Jones Waterford School Important Terms (the word line may be
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source:
 Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
3.2 A Three-Bar Linkage 51
 3.2 A Three-Bar Linkage 51 It may happen that the drawing in Euclidean view is too big or too small. You can use the zooming tools to change this. There is a Zoom-In and a Zoom-Out tool below the Euclidean
3.2 A Three-Bar Linkage 51 It may happen that the drawing in Euclidean view is too big or too small. You can use the zooming tools to change this. There is a Zoom-In and a Zoom-Out tool below the Euclidean
Generating Vectors Overview
 Generating Vectors Overview Vectors are mathematically defined shapes consisting of a series of points (nodes), which are connected by lines, arcs or curves (spans) to form the overall shape. Vectors can
Generating Vectors Overview Vectors are mathematically defined shapes consisting of a series of points (nodes), which are connected by lines, arcs or curves (spans) to form the overall shape. Vectors can
VERIFYING PROPERTIES OF GEOMETRIC FIGURES. Ad is a median
 UNIT NLYTI GEOMETRY VERIFYING PROPERTIES OF GEOMETRI FIGURES Parallelogram Rhombus Quadrilateral E H D F G = D and = D EF FG GH EH I L J Right Triangle Median of a Triangle K b a c d is a median D ltitude
UNIT NLYTI GEOMETRY VERIFYING PROPERTIES OF GEOMETRI FIGURES Parallelogram Rhombus Quadrilateral E H D F G = D and = D EF FG GH EH I L J Right Triangle Median of a Triangle K b a c d is a median D ltitude
Day 1: Geometry Terms & Diagrams CC Geometry Module 1
 Name ate ay 1: Geometry Terms & iagrams Geometry Module 1 For #1-3: Identify each of the following diagrams with the correct geometry term. #1-3 Vocab. ank Line Segment Line Ray 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain why
Name ate ay 1: Geometry Terms & iagrams Geometry Module 1 For #1-3: Identify each of the following diagrams with the correct geometry term. #1-3 Vocab. ank Line Segment Line Ray 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain why
Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes
 Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My
Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My
Mid-point & Perpendicular Bisector of a line segment AB
 Mid-point & Perpendicular isector of a line segment Starting point: Line Segment Midpoint of 1. Open compasses so the points are approximately ¾ of the length of apart point 3. y eye - estimate the midpoint
Mid-point & Perpendicular isector of a line segment Starting point: Line Segment Midpoint of 1. Open compasses so the points are approximately ¾ of the length of apart point 3. y eye - estimate the midpoint
Math Dr. Miller - Constructing in Sketchpad (tm) - Due via by Friday, Mar. 18, 2016
 Math 304 - Dr. Miller - Constructing in Sketchpad (tm) - Due via email by Friday, Mar. 18, 2016 As with our second GSP activity for this course, you will email the assignment at the end of this tutorial
Math 304 - Dr. Miller - Constructing in Sketchpad (tm) - Due via email by Friday, Mar. 18, 2016 As with our second GSP activity for this course, you will email the assignment at the end of this tutorial
Geometry. Points, Lines, Planes & Angles. Part 2. Slide 1 / 185. Slide 2 / 185. Slide 3 / 185. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 185 Slide 2 / 185 Geometry Points, Lines, Planes & ngles Part 2 2014-09-20 www.njctl.org Part 1 Introduction to Geometry Table of ontents Points and Lines Planes ongruence, istance and Length
Slide 1 / 185 Slide 2 / 185 Geometry Points, Lines, Planes & ngles Part 2 2014-09-20 www.njctl.org Part 1 Introduction to Geometry Table of ontents Points and Lines Planes ongruence, istance and Length
StickFont Editor v1.01 User Manual. Copyright 2012 NCPlot Software LLC
 StickFont Editor v1.01 User Manual Copyright 2012 NCPlot Software LLC StickFont Editor Manual Table of Contents Welcome... 1 Registering StickFont Editor... 3 Getting Started... 5 Getting Started...
StickFont Editor v1.01 User Manual Copyright 2012 NCPlot Software LLC StickFont Editor Manual Table of Contents Welcome... 1 Registering StickFont Editor... 3 Getting Started... 5 Getting Started...
GeoGebra Workshop. (Short Version)
 GeoGebra Workshop (Short Version) Contents Introduction... 2 What is GeoGebra?... 2 Get GeoGebra... 2 Workshop Format... 2 GeoGebra Layout... 3 Examples... 5 The Incenter and Incircle... 5 The Sine Function
GeoGebra Workshop (Short Version) Contents Introduction... 2 What is GeoGebra?... 2 Get GeoGebra... 2 Workshop Format... 2 GeoGebra Layout... 3 Examples... 5 The Incenter and Incircle... 5 The Sine Function
1. Use the Trapezium Rule with five ordinates to find an approximate value for the integral
 1. Use the Trapezium Rule with five ordinates to find an approximate value for the integral Show your working and give your answer correct to three decimal places. 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 When When When When When
1. Use the Trapezium Rule with five ordinates to find an approximate value for the integral Show your working and give your answer correct to three decimal places. 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 When When When When When
Curriki Geometry Glossary
 Curriki Geometry Glossary The following terms are used throughout the Curriki Geometry projects and represent the core vocabulary and concepts that students should know to meet Common Core State Standards.
Curriki Geometry Glossary The following terms are used throughout the Curriki Geometry projects and represent the core vocabulary and concepts that students should know to meet Common Core State Standards.
DISCOVERING CONICS WITH. Dr Toh Pee Choon NIE 2 June 2016
 DISCOVERING CONICS WITH Dr Toh Pee Choon MTC @ NIE 2 June 2016 Introduction GeoGebra is a dynamic mathematics software that integrates both geometry and algebra Open source and free to download www.geogebra.org
DISCOVERING CONICS WITH Dr Toh Pee Choon MTC @ NIE 2 June 2016 Introduction GeoGebra is a dynamic mathematics software that integrates both geometry and algebra Open source and free to download www.geogebra.org
GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders
 GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders Paddy Johnson and Tim Brophy www.ul.ie/cemtl/ Table of Contents 1. Square Construction and Measurement 2 2. Circumscribed Circle of a Triangle
GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders Paddy Johnson and Tim Brophy www.ul.ie/cemtl/ Table of Contents 1. Square Construction and Measurement 2 2. Circumscribed Circle of a Triangle
edunepal_info
 facebook.com/edunepal.info @ edunepal_info Tangent Constructions Session 1 Drawing and designing logos Many symbols are constructed using geometric shapes. The following section explains common geometrical
facebook.com/edunepal.info @ edunepal_info Tangent Constructions Session 1 Drawing and designing logos Many symbols are constructed using geometric shapes. The following section explains common geometrical
Geometry Basics * Rory Adams Free High School Science Texts Project Mark Horner Heather Williams. 1 Introduction. 2 Points and Lines
 OpenStax-NX module: m31494 1 Geometry asics * Rory dams Free High School Science Texts Project Mark Horner Heather Williams This work is produced by OpenStax-NX and licensed under the reative ommons ttribution
OpenStax-NX module: m31494 1 Geometry asics * Rory dams Free High School Science Texts Project Mark Horner Heather Williams This work is produced by OpenStax-NX and licensed under the reative ommons ttribution
Press the Plus + key to zoom in. Press the Minus - key to zoom out. Scroll the mouse wheel away from you to zoom in; towards you to zoom out.
 Navigate Around the Map Interactive maps provide many choices for displaying information, searching for more details, and moving around the map. Most navigation uses the mouse, but at times you may also
Navigate Around the Map Interactive maps provide many choices for displaying information, searching for more details, and moving around the map. Most navigation uses the mouse, but at times you may also
Activity 1. Simple Constructions. Introduction. Construction. Objective. Cabri Jr. Tools. Part I: Construct a parallelogram.
 Objective To use Cabri Jr. tools to perform simple constructions Activity 1 Cabri Jr. Tools Introduction Construction Simple Constructions The Constructions Tools Menu in Cabri Jr. contains tools for operating
Objective To use Cabri Jr. tools to perform simple constructions Activity 1 Cabri Jr. Tools Introduction Construction Simple Constructions The Constructions Tools Menu in Cabri Jr. contains tools for operating
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 Patterns are pleasing to the eye. They are used by designers, architects, and engineers to make their products more attractive. Look at the quilt pattern. Which figures are used as quilt blocks? Which
Patterns are pleasing to the eye. They are used by designers, architects, and engineers to make their products more attractive. Look at the quilt pattern. Which figures are used as quilt blocks? Which
Getting Started. Moving Around in 3D
 Getting Started 1 Double-click the SketchUp icon or click: Start All Programs SketchUp 2018 SketchUp 2018 The start screen should look something like this: This person is about 5 5 tall this sets the scale
Getting Started 1 Double-click the SketchUp icon or click: Start All Programs SketchUp 2018 SketchUp 2018 The start screen should look something like this: This person is about 5 5 tall this sets the scale
Getting Started. Double-click the SketchUp icon or click: Start All Programs SketchUp 2018 SketchUp 2018
 Getting Started 1 Double-click the SketchUp icon or click: Start All Programs SketchUp 2018 SketchUp 2018 The start screen should look something like this: This person is about 5 5 tall this sets the scale
Getting Started 1 Double-click the SketchUp icon or click: Start All Programs SketchUp 2018 SketchUp 2018 The start screen should look something like this: This person is about 5 5 tall this sets the scale
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric Activities
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
A "Quick and Dirty" Introduction to THE GEOMETER'S SKETCHPAD
 A "Quick and Dirty" Introduction to the GEOMETER'S SKETCHPAD v. 4.0 Dynamic Geometry in the Mathematics Classroom _/_/_/ _/_/_/ _/_/ _/_/ Dr. _/ _/ _/ _/ Distinguished Teaching Professor _/_/_/ _/_/ _/
A "Quick and Dirty" Introduction to the GEOMETER'S SKETCHPAD v. 4.0 Dynamic Geometry in the Mathematics Classroom _/_/_/ _/_/_/ _/_/ _/_/ Dr. _/ _/ _/ _/ Distinguished Teaching Professor _/_/_/ _/_/ _/
The Cabri Jr. Create and Construction menus contain a plethora. Constructing Geometric Figures. Bonus Chapter 2. Constructing Points.
 Bonus Chapter 2 Constructing Geometric Figures In This Chapter Constructing geometric figures Finding midpoints, points of intersection, and angle bisectors Moving and reshaping figures Hiding and deleting
Bonus Chapter 2 Constructing Geometric Figures In This Chapter Constructing geometric figures Finding midpoints, points of intersection, and angle bisectors Moving and reshaping figures Hiding and deleting
Ancient Cell Phone Tracing an Object and Drawing with Layers
 Ancient Cell Phone Tracing an Object and Drawing with Layers 1) Open Corel Draw. Create a blank 8.5 x 11 Document. 2) Go to the Import option and browse to the Graphics 1 > Lessons folder 3) Find the Cell
Ancient Cell Phone Tracing an Object and Drawing with Layers 1) Open Corel Draw. Create a blank 8.5 x 11 Document. 2) Go to the Import option and browse to the Graphics 1 > Lessons folder 3) Find the Cell
GEOMETER SKETCHPAD INTRODUCTION
 GEOMETER SKETHPD INTRODUTION ctivity 1: onstruct, Don t Draw onstruct a right triangle Use the line segment tool, and draw a right angled triangle. When finished, use the select tool to drag point to the
GEOMETER SKETHPD INTRODUTION ctivity 1: onstruct, Don t Draw onstruct a right triangle Use the line segment tool, and draw a right angled triangle. When finished, use the select tool to drag point to the
Google SketchUp. and SketchUp Pro 7. The book you need to succeed! CD-ROM Included! Kelly L. Murdock. Master SketchUp Pro 7 s tools and features
 CD-ROM Included! Free version of Google SketchUp 7 Trial version of Google SketchUp Pro 7 Chapter example files from the book Kelly L. Murdock Google SketchUp and SketchUp Pro 7 Master SketchUp Pro 7 s
CD-ROM Included! Free version of Google SketchUp 7 Trial version of Google SketchUp Pro 7 Chapter example files from the book Kelly L. Murdock Google SketchUp and SketchUp Pro 7 Master SketchUp Pro 7 s
Geo - CH1 Practice Test
 Geo - H1 Practice Test Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the length of. a. = 7 c. = 7 b. = 9 d. = 8 2. Find the best sketch, drawing,
Geo - H1 Practice Test Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the length of. a. = 7 c. = 7 b. = 9 d. = 8 2. Find the best sketch, drawing,
For more info and downloads go to: Gerrit Stols
 For more info and downloads go to: http://school-maths.com Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source (free) software for learning and teaching mathematics in schools. It
For more info and downloads go to: http://school-maths.com Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source (free) software for learning and teaching mathematics in schools. It
If three points A (h, 0), P (a, b) and B (0, k) lie on a line, show that: a b 1.
 ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
I can solve simultaneous equations algebraically and graphically. I can solve inequalities algebraically and graphically.
 B I can factorise and expand complex expressions. I can factorise Quadratics I can recognise the Difference of Two Squares (D.O.T.S) simultaneous equations algebraically and graphically. inequalities algebraically
B I can factorise and expand complex expressions. I can factorise Quadratics I can recognise the Difference of Two Squares (D.O.T.S) simultaneous equations algebraically and graphically. inequalities algebraically
A GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTION OF AN ELLIPSE USING A TI-92 Stuart Moskowitz Humboldt State University
 A GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTION OF AN ELLIPSE USING A TI-92 Stuart Moskowitz Humboldt State University sml4@axe.humboldt.edu The following exploration builds an ellipse based on the geometric definition: An ellipse
A GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTION OF AN ELLIPSE USING A TI-92 Stuart Moskowitz Humboldt State University sml4@axe.humboldt.edu The following exploration builds an ellipse based on the geometric definition: An ellipse
change divided by original times 100 divide by the bottom, times by the top Divide both the top and bottom of a fraction by the same number
 Averages and Range How do you work out the mean? How do you get the mode? How do you work out the median? How do you work out the range? How do you work out the mean for a frequency table? Add up all the
Averages and Range How do you work out the mean? How do you get the mode? How do you work out the median? How do you work out the range? How do you work out the mean for a frequency table? Add up all the
Angle, symmetry and transformation
 Terms Illustrations Definition Acute angle An angle greater than 0 and less than 90. Alternate angles Where two straight lines are cut by a third, as in the diagrams, the angles d and f (also c and e)
Terms Illustrations Definition Acute angle An angle greater than 0 and less than 90. Alternate angles Where two straight lines are cut by a third, as in the diagrams, the angles d and f (also c and e)
Use the Move tool to drag A around and see how the automatically constructed objects (like G or the perpendicular and parallel lines) are updated.
 Math 5335 Fall 2015 Lab #0: Installing and using GeoGebra This semester you will have a number of lab assignments which require you to use GeoGebra, a dynamic geometry program. GeoGebra lets you explore
Math 5335 Fall 2015 Lab #0: Installing and using GeoGebra This semester you will have a number of lab assignments which require you to use GeoGebra, a dynamic geometry program. GeoGebra lets you explore
Plane Geometry. Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2011
 lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
Adobe InDesign CS6 Tutorial
 Adobe InDesign CS6 Tutorial Adobe InDesign CS6 is a page-layout software that takes print publishing and page design beyond current boundaries. InDesign is a desktop publishing program that incorporates
Adobe InDesign CS6 Tutorial Adobe InDesign CS6 is a page-layout software that takes print publishing and page design beyond current boundaries. InDesign is a desktop publishing program that incorporates
form are graphed in Cartesian coordinates, and are graphed in Cartesian coordinates.
 Plot 3D Introduction Plot 3D graphs objects in three dimensions. It has five basic modes: 1. Cartesian mode, where surfaces defined by equations of the form are graphed in Cartesian coordinates, 2. cylindrical
Plot 3D Introduction Plot 3D graphs objects in three dimensions. It has five basic modes: 1. Cartesian mode, where surfaces defined by equations of the form are graphed in Cartesian coordinates, 2. cylindrical
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Tutorial 7: Adding Features and Editing Line and Polygon Layers
 Tutorial 7: Adding Features and Editing Line and Polygon Layers Tutorial Content 7.1. When should I use a line layer to represent data? 7.2. How do I add line features? 7.3. How to use the snapping tool?
Tutorial 7: Adding Features and Editing Line and Polygon Layers Tutorial Content 7.1. When should I use a line layer to represent data? 7.2. How do I add line features? 7.3. How to use the snapping tool?
by person construction. who weighs 100 pounds on Earth would weigh only about 40 pounds on
 Treasure Trip to Hunt the Moon Using Midpoints Tables and to Bisectors Represent Equivalent Ratios 1.1 1.3 Learning Goals Key TermS Key Term Constructions In this lesson, you will: midpoint ratio bisecting
Treasure Trip to Hunt the Moon Using Midpoints Tables and to Bisectors Represent Equivalent Ratios 1.1 1.3 Learning Goals Key TermS Key Term Constructions In this lesson, you will: midpoint ratio bisecting
Quick Crash Scene Tutorial
 Quick Crash Scene Tutorial With Crash Zone or Crime Zone, even new users can create a quick crash scene diagram in less than 10 minutes! In this tutorial we ll show how to use Crash Zone s unique features
Quick Crash Scene Tutorial With Crash Zone or Crime Zone, even new users can create a quick crash scene diagram in less than 10 minutes! In this tutorial we ll show how to use Crash Zone s unique features
Geometry. Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 G.CO.2. Common Core Institute
 Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Designing Simple Buildings
 Designing Simple Buildings Contents Introduction 2 1. Pitched-roof Buildings 5 2. Flat-roof Buildings 25 3. Adding Doors and Windows 27 9. Windmill Sequence 45 10. Drawing Round Towers 49 11. Drawing Polygonal
Designing Simple Buildings Contents Introduction 2 1. Pitched-roof Buildings 5 2. Flat-roof Buildings 25 3. Adding Doors and Windows 27 9. Windmill Sequence 45 10. Drawing Round Towers 49 11. Drawing Polygonal
Photocopiable/digital resources may only be copied by the purchasing institution on a single site and for their own use ZigZag Education, 2013
 SketchUp Level of Difficulty Time Approximately 15 20 minutes Photocopiable/digital resources may only be copied by the purchasing institution on a single site and for their own use ZigZag Education, 2013
SketchUp Level of Difficulty Time Approximately 15 20 minutes Photocopiable/digital resources may only be copied by the purchasing institution on a single site and for their own use ZigZag Education, 2013
Exercise Guide. Published: August MecSoft Corpotation
 VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
Basic Euclidean Geometry
 hapter 1 asic Euclidean Geometry This chapter is not intended to be a complete survey of basic Euclidean Geometry, but rather a review for those who have previously taken a geometry course For a definitive
hapter 1 asic Euclidean Geometry This chapter is not intended to be a complete survey of basic Euclidean Geometry, but rather a review for those who have previously taken a geometry course For a definitive
Selective Space Structures Manual
 Selective Space Structures Manual February 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Overview and Concept 4 1.1 General Concept........................... 4 1.2 Modules................................ 6 2 The 3S Generator
Selective Space Structures Manual February 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Overview and Concept 4 1.1 General Concept........................... 4 1.2 Modules................................ 6 2 The 3S Generator
Honors Geometry Pacing Guide Honors Geometry Pacing First Nine Weeks
 Unit Topic To recognize points, lines and planes. To be able to recognize and measure segments and angles. To classify angles and name the parts of a degree To recognize collinearity and betweenness of
Unit Topic To recognize points, lines and planes. To be able to recognize and measure segments and angles. To classify angles and name the parts of a degree To recognize collinearity and betweenness of
Geometry Vocabulary. acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees
 Geometry Vocabulary acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees angle-the turn or bend between two intersecting lines, line segments, rays, or planes angle bisector-an angle bisector is a ray that
Geometry Vocabulary acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees angle-the turn or bend between two intersecting lines, line segments, rays, or planes angle bisector-an angle bisector is a ray that
LIGHT: Two-slit Interference
 LIGHT: Two-slit Interference Objective: To study interference of light waves and verify the wave nature of light. Apparatus: Two red lasers (wavelength, λ = 633 nm); two orange lasers (λ = 612 nm); two
LIGHT: Two-slit Interference Objective: To study interference of light waves and verify the wave nature of light. Apparatus: Two red lasers (wavelength, λ = 633 nm); two orange lasers (λ = 612 nm); two
The National Strategies Secondary Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9
 Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9 183 As outcomes, Year 8 pupils should, for example: Understand a proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 and of a quadrilateral is 360, and that the exterior
Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9 183 As outcomes, Year 8 pupils should, for example: Understand a proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 and of a quadrilateral is 360, and that the exterior
pine cone Ratio = 13:8 or 8:5
 Chapter 10: Introducing Geometry 10.1 Basic Ideas of Geometry Geometry is everywhere o Road signs o Carpentry o Architecture o Interior design o Advertising o Art o Science Understanding and appreciating
Chapter 10: Introducing Geometry 10.1 Basic Ideas of Geometry Geometry is everywhere o Road signs o Carpentry o Architecture o Interior design o Advertising o Art o Science Understanding and appreciating
Summer Dear Geometry Students and Parents:
 Summer 2018 Dear Geometry Students and Parents: Welcome to Geometry! For the 2018-2019 school year, we would like to focus your attention to the prerequisite skills and concepts for Geometry. In order
Summer 2018 Dear Geometry Students and Parents: Welcome to Geometry! For the 2018-2019 school year, we would like to focus your attention to the prerequisite skills and concepts for Geometry. In order
Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes
 Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess
Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess
EDITING SHAPES. Lesson overview
 3 CREATING AND EDITING SHAPES Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Create a document with multiple artboards. Use tools and commands to create basic shapes. Work with drawing
3 CREATING AND EDITING SHAPES Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Create a document with multiple artboards. Use tools and commands to create basic shapes. Work with drawing
CCGPS UNIT 5 Semester 2 COORDINATE ALGEBRA Page 1 of 38. Transformations in the Coordinate Plane
 CCGPS UNIT 5 Semester 2 COORDINATE ALGEBRA Page 1 of 38 Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Name: Date: MCC9-12.G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line,
CCGPS UNIT 5 Semester 2 COORDINATE ALGEBRA Page 1 of 38 Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Name: Date: MCC9-12.G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line,
SketchUp. SketchUp. Google SketchUp. Using SketchUp. The Tool Set
 Google Google is a 3D Modelling program which specialises in making computer generated representations of real-world objects, especially architectural, mechanical and building components, such as windows,
Google Google is a 3D Modelling program which specialises in making computer generated representations of real-world objects, especially architectural, mechanical and building components, such as windows,
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
How to draw and create shapes
 Adobe Flash Professional Guide How to draw and create shapes You can add artwork to your Adobe Flash Professional documents in two ways: You can import images or draw original artwork in Flash by using
Adobe Flash Professional Guide How to draw and create shapes You can add artwork to your Adobe Flash Professional documents in two ways: You can import images or draw original artwork in Flash by using
Geometric Constructions
 HISTORY OF MATHEMATICS Spring 2005 Geometric Constructions Notes, activities, assignment; #3 in a series. Note: I m not giving a specific due date for this somewhat vague assignment. The idea is that it
HISTORY OF MATHEMATICS Spring 2005 Geometric Constructions Notes, activities, assignment; #3 in a series. Note: I m not giving a specific due date for this somewhat vague assignment. The idea is that it
Randy H. Shih. Jack Zecher PUBLICATIONS
 Randy H. Shih Jack Zecher PUBLICATIONS WWW.SDCACAD.COM AutoCAD LT 2000 MultiMedia Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric Construction Basics! " # 1-2 AutoCAD LT 2000 MultiMedia Tutorial Introduction Learning
Randy H. Shih Jack Zecher PUBLICATIONS WWW.SDCACAD.COM AutoCAD LT 2000 MultiMedia Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric Construction Basics! " # 1-2 AutoCAD LT 2000 MultiMedia Tutorial Introduction Learning
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
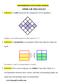 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
PASS. 5.2.b Use transformations (reflection, rotation, translation) on geometric figures to solve problems within coordinate geometry.
 Geometry Name Oklahoma cademic tandards for Oklahoma P PRCC odel Content Frameworks Current ajor Curriculum Topics G.CO.01 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle,
Geometry Name Oklahoma cademic tandards for Oklahoma P PRCC odel Content Frameworks Current ajor Curriculum Topics G.CO.01 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle,
2. A straightedge can create straight line, but can't measure. A ruler can create straight lines and measure distances.
 5.1 Copies of Line Segments and Angles Answers 1. A drawing is a rough sketch and a construction is a process to create an exact and accurate geometric figure. 2. A straightedge can create straight line,
5.1 Copies of Line Segments and Angles Answers 1. A drawing is a rough sketch and a construction is a process to create an exact and accurate geometric figure. 2. A straightedge can create straight line,
UNIT 1 SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE, AND PROOFS Lesson 4: Exploring Congruence Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: constructing perpendicular bisectors copying a segment copying an angle Introduction Think about trying to move a drop of water
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: constructing perpendicular bisectors copying a segment copying an angle Introduction Think about trying to move a drop of water
1 General Principles. General Principles. In this chapter 1-1
 1 General Principles In this chapter 1 General Principles 1.1 User Interface 1.2 Title bar 1.3 Menu bar 1.4 Standard Toolbar 1.5 The drawing area 1.6 Component tabs 1.7 Status Bar 1.8 Manipulating Components
1 General Principles In this chapter 1 General Principles 1.1 User Interface 1.2 Title bar 1.3 Menu bar 1.4 Standard Toolbar 1.5 The drawing area 1.6 Component tabs 1.7 Status Bar 1.8 Manipulating Components
What's New in Cut2D Desktop 8.5
 What's New in Cut2D Desktop 8.5 A quick start guide for Cut2D Desktop upgraders Copyright Vectric Ltd. Document V.1.0 Contents CONTENTS... 2 OVERVIEW... 3 ENHANCED & EXTENDED DRAWING TOOLS... 4 ENHANCED
What's New in Cut2D Desktop 8.5 A quick start guide for Cut2D Desktop upgraders Copyright Vectric Ltd. Document V.1.0 Contents CONTENTS... 2 OVERVIEW... 3 ENHANCED & EXTENDED DRAWING TOOLS... 4 ENHANCED
MATH 30 GEOMETRY UNIT OUTLINE AND DEFINITIONS Prepared by: Mr. F.
 1 MTH 30 GEMETRY UNIT UTLINE ND DEFINITINS Prepared by: Mr. F. Some f The Typical Geometric Properties We Will Investigate: The converse holds in many cases too! The Measure f The entral ngle Tangent To
1 MTH 30 GEMETRY UNIT UTLINE ND DEFINITINS Prepared by: Mr. F. Some f The Typical Geometric Properties We Will Investigate: The converse holds in many cases too! The Measure f The entral ngle Tangent To
Drawing Tools. Drawing a Rectangle
 Chapter Microsoft Word provides extensive DRAWING TOOLS that allow you to enhance the appearance of your documents. You can use these tools to assist in the creation of detailed publications, newsletters,
Chapter Microsoft Word provides extensive DRAWING TOOLS that allow you to enhance the appearance of your documents. You can use these tools to assist in the creation of detailed publications, newsletters,
Full Search Map Tab. This map is the result of selecting the Map tab within Full Search.
 Full Search Map Tab This map is the result of selecting the Map tab within Full Search. This map can be used when defining your parameters starting from a Full Search. Once you have entered your desired
Full Search Map Tab This map is the result of selecting the Map tab within Full Search. This map can be used when defining your parameters starting from a Full Search. Once you have entered your desired
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Name ate hapter 6 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Write an equation of the line passing through point P that is perpendicular to the given line. 1. P(5, ), y = x + 6. P(4, ), y = 6x 3 3. P( 1, ),
Name ate hapter 6 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Write an equation of the line passing through point P that is perpendicular to the given line. 1. P(5, ), y = x + 6. P(4, ), y = 6x 3 3. P( 1, ),
Designer Reference 1
 Designer Reference 1 Table of Contents USE OF THE DESIGNER...4 KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS...5 Shortcuts...5 Keyboard Hints...5 MENUS...7 File Menu...7 Edit Menu...8 Favorites Menu...9 Document Menu...10 Item Menu...12
Designer Reference 1 Table of Contents USE OF THE DESIGNER...4 KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS...5 Shortcuts...5 Keyboard Hints...5 MENUS...7 File Menu...7 Edit Menu...8 Favorites Menu...9 Document Menu...10 Item Menu...12
KeY TeRM. perpendicular bisector
 .6 Making opies Just as Perfect as the Original! onstructing Perpendicular Lines, Parallel Lines, and Polygons LeARnInG GOALS In this lesson, you will: KeY TeRM perpendicular bisector OnSTRUTIOnS a perpendicular
.6 Making opies Just as Perfect as the Original! onstructing Perpendicular Lines, Parallel Lines, and Polygons LeARnInG GOALS In this lesson, you will: KeY TeRM perpendicular bisector OnSTRUTIOnS a perpendicular
Preliminary: First you must understand the relationship between inscribed and circumscribed, for example:
 10.7 Inscribed and Circumscribed Polygons Lesson Objective: After studying this section, you will be able to: Recognize inscribed and circumscribed polygons Apply the relationship between opposite angles
10.7 Inscribed and Circumscribed Polygons Lesson Objective: After studying this section, you will be able to: Recognize inscribed and circumscribed polygons Apply the relationship between opposite angles
Compass and Straight Edge. Compass/Straight Edge. Constructions with some proofs.
 Compass and Straight Edge Compass/Straight Edge Constructions with some proofs. To Construct the Perpendicular isector of a line. 1. Place compass at, set over halfway and draw 2 arcs. 2. Place compass
Compass and Straight Edge Compass/Straight Edge Constructions with some proofs. To Construct the Perpendicular isector of a line. 1. Place compass at, set over halfway and draw 2 arcs. 2. Place compass
On the Web sun.com/aboutsun/comm_invest STAROFFICE 8 DRAW
 STAROFFICE 8 DRAW Graphics They say a picture is worth a thousand words. Pictures are often used along with our words for good reason. They help communicate our thoughts. They give extra information that
STAROFFICE 8 DRAW Graphics They say a picture is worth a thousand words. Pictures are often used along with our words for good reason. They help communicate our thoughts. They give extra information that
Geometry Foundations Planning Document
 Geometry Foundations Planning Document Unit 1: Chromatic Numbers Unit Overview A variety of topics allows students to begin the year successfully, review basic fundamentals, develop cooperative learning
Geometry Foundations Planning Document Unit 1: Chromatic Numbers Unit Overview A variety of topics allows students to begin the year successfully, review basic fundamentals, develop cooperative learning
User Guide. for. JewelCAD Professional Version 2.0
 User Guide Page 1 of 121 User Guide for JewelCAD Professional Version 2.0-1 - User Guide Page 2 of 121 Table of Content 1. Introduction... 7 1.1. Purpose of this document... 7 2. Launch JewelCAD Professional
User Guide Page 1 of 121 User Guide for JewelCAD Professional Version 2.0-1 - User Guide Page 2 of 121 Table of Content 1. Introduction... 7 1.1. Purpose of this document... 7 2. Launch JewelCAD Professional
Geometry. Quadrilaterals. Slide 1 / 189. Slide 2 / 189. Slide 3 / 189. Table of Contents. New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning
 New Jersey enter for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 189 Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
New Jersey enter for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 189 Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
How to create shapes. Drawing basic shapes. Adobe Photoshop Elements 8 guide
 How to create shapes With the shape tools in Adobe Photoshop Elements, you can draw perfect geometric shapes, regardless of your artistic ability or illustration experience. The first step to drawing shapes
How to create shapes With the shape tools in Adobe Photoshop Elements, you can draw perfect geometric shapes, regardless of your artistic ability or illustration experience. The first step to drawing shapes
Beginning Paint 3D A Step by Step Tutorial. By Len Nasman
 A Step by Step Tutorial By Len Nasman Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Paint 3D User Interface...4 Creating 2D Shapes...5 Drawing Lines with Paint 3D...6 Straight Lines...6 Multi-Point Curves...6
A Step by Step Tutorial By Len Nasman Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Paint 3D User Interface...4 Creating 2D Shapes...5 Drawing Lines with Paint 3D...6 Straight Lines...6 Multi-Point Curves...6
Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units
 Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units affine linear equation: an equation in which both sides are sums of terms that are either a number times y or a number times x or just a number [SlL2-D5]
Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units affine linear equation: an equation in which both sides are sums of terms that are either a number times y or a number times x or just a number [SlL2-D5]
Let s Make a Front Panel using FrontCAD
 Let s Make a Front Panel using FrontCAD By Jim Patchell FrontCad is meant to be a simple, easy to use CAD program for creating front panel designs and artwork. It is a free, open source program, with the
Let s Make a Front Panel using FrontCAD By Jim Patchell FrontCad is meant to be a simple, easy to use CAD program for creating front panel designs and artwork. It is a free, open source program, with the
