Fast-Lipschitz Optimization
|
|
|
- Rudolf Bishop
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fast-Lipschitz Optimization DREAM Seminar Series University of California at Berkeley September 11, 2012 Carlo Fischione ACCESS Linnaeus Center, Electrical Engineering KTH Royal Institute of Technology Stockholm, Sweden web:
2 Optimization is pervasive over networks Parallel computing Smart grids Environmental monitoring Smart buildings Intelligent transportation systems Industrial control
3 Optimization over networks Optimization needs fast solver algorithms of low complexity Ø Time-varying networks, little time to compute solution Ø Distributed computations Ø E.g., networks of parallel processors, cross layer networking, distributed detection, estimation, content distribution,... Parallel and distributed computation Ø Fundamental theory for optimization over networks Ø Drawback over energy-constrained wireless networks: the cost for communication not considered An alternative theory is needed Ø In a number of cases, Fast-Lipschitz optimization
4 Outline Motivating example: distributed detection Definition of Fast-Lipschitz optimization Computation of the optimal solution Problems in canonical form Examples Conclusions
5 Distributed binary detection measurements at node i hypothesis testing with S measurements and threshold x i probability of false alarm probability of misdetection A threshold minimizing the prob. of false alarm maximizes the prob. of misdetection. How to choose optimally the thresholds when nodes exchange opinions?
6 Threshold optimization in distributed detection How to solve the problem by distributed operations among the nodes? The problem is convex Ø Lagrangian methods (interior point) can be applied Ø Drawback: too many message passing (Lagrangian multipliers) among nodes to compute iteratively the optimal solution An alternative method: Fast-Lipschitz optimization C. Fischione, Fast-Lipschitz Optimization with Wireless Sensor Networks Applications, IEEE TAC, 2011
7 Outline Motivating example: distributed detection Definition of Fast-Lipschitz optimization Computation of the optimal solution Problems in canonical form Examples Conclusions
8 The Fast-Lipschitz optimization nonempty compact set containing the vertexes of the constraints
9 Computation of the solution Centralized optimization Ø Problem solved by a central processor Network of n nodes Distributed optimization Ø Decision variables and constraints are associated to nodes that cooperate to compute the solution in parallel
10 Pareto Optimal Solution
11 Notation Gradient Norm infinity: sum along a row Norm 1: sum along a column
12 Qualifying conditions Now that we have introduced basic notation and concepts, we give some conditions for which a problem is Fast-Lipschitz
13 Qualifying conditions Functions may be non-convex
14 Outline Motivating example: distributed detection Definition of Fast-Lipschitz optimization Computation of the optimal solution Problems in canonical form Examples Conclusions
15 Optimal Solution The Pareto optimal solution is just given by a set of (in general nonlinear) equations. Solving a set of equations is much easier than solving an optimization problem by traditional Lagrangian methods!
16 Lagrangian methods Let s have a closer look at the Lagrangian methods, which are normally used to solve optimization problems Lagrangian methods are the essential to solve, for example, convex problems
17 Lagrangian methods G. L. Lagrange, The methods I set forth require neither constructions nor geometric or mechanical considerations. They require only algebraic operations subject to a systematic and uniform course
18 Lagrangian methods Theorem: Consider a feasible F-Lipschitz problem. Then, the KKT conditions are necessary and sufficient. Ø KKT conditions: Lagrangian Lagrangian methods to compute the solution
19 Lagrangian methods Lagrangian Lagragian methods need 1. a central computation of the Lagrangian function 2. an endless collect-and-broadcast iterative message passing of primal and dual variables Fast-Lipschitz methods avoid the central computation and substantially reduce the collect-and-broadcast procedure
20 The Fast-Lipschitz optimization Non-Convex Optimization Convex Optimization Fast-Lipschitz Optimization Interference Function Optimization Geometric Optimization Fast-Lipschitz optimization problems can be convex, geometric, quadratic, interference-function,...
21 Fast-Lipschitz methods Let us see how a Fast-Lipschitz problem is solved without Lagrangian methods
22 Centralized optimization The optimal solution is given by iterative methods to solve systems of non-linear equations (e.g., Newton methods) is a matrix to ensure and maximize convergence speed Many other methods are available, e.g., second-order methods
23 Distributed optimization
24 Outline Motivating example: distributed detection Definition of Fast-Lipschitz optimization Computation of the optimal solution Problems in canonical form Examples Conclusions
25 Problems in canonical form Canonical form Bertsekas, Non Linear Programming, 2004 Fast-Lipschitz form
26 Problems in canonical form
27 Fast-Lipschitz Matlab Toolbox M. Leithe, Introducing a Matlab Toolbox for Fast-Lipschitz optimization, Master Thesis KTH, 2011
28 Outline Motivating example: distributed detection Definition of Fast-Lipschitz optimization Computation of the optimal solution Problems in canonical form Examples Conclusions
29 Example 1: from canonical to Fast-Lipschitz The problem is both convex and Fast-Lipschitz: Off-diagonal monotonicity Diagonal dominance The optimal solution is given by the constraints at the equality, trivially
30 Example 2: hidden Fast-Lipschitz Non Fast-Lipschitz Simple variable transformation,, gives a Fast-Lipschitz form
31 Threshold optimization in distributed detection How to solve the problem by parallel and distributed operations among the nodes? The problem is convex Ø Lagrangian methods (interior point methods) could be applied Ø Drowback: too many message passing (Lagrangian multipliers) among nodes to compute iteratively the optimal solution An alternative method: F-Lipschitz optimization
32 Distributed detection: Fast-Lipschitz vs Lagrangian methods nodes network Fast-Lipschitz Lagrangian methods (interior point) Number of iterations Number of function evaluations
33 Summary yes Inequality constraints satisfy the equality at the optimum? no Compute the solution by Fast- Lipschitz methods Compute the solution by Lagrangian methods Fast-Lipschitz optimization: a class of problems for which all the constraints are active at the optimum Optimum: the solution to the set of equations given by the constraints No Lagrangian methods, which are computationally expensive, particularly on wireless networks
34 Conclusions Existing methods for optimization over networks are too expensive Proposed the Fast-Lipschitz optimization Ø Application to distributed detection, many other cases Fast-Lipschitz optimization is a panacea for many cases, but still there is a lack of a theory for fast parallel and distributed computations How to generalize it for Ø static optimization? Ø dynamic optimization? Ø stochastic optimization? Ø game theoretical extensions?
35 Selected bibliography M. Jacobsson, C. Fischione, A Comparative Analysis of the Fast-Lipschitz Convergence Speed, To Appear, IEEE CDC 2012 M. Jacobsson, C. Fischione, On Some Extensions of Fast-Lipschitz Optimization for Convex and Non-convex Problems, To Appear, IFAC NecSys 2012 C. Fischione, F-Lipschitz Optimization with Wireless Sensor Networks Applications, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, A. Speranzon, C. Fischione, K. H. Johansson, A. Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, A Distributed Minimum Variance Estimator for Sensor Networks, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, special issue on Control and Communications, Vol. 26, N. 4, pp , May 2008.
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks. Fast-Lipschitz Optimization
 http://www.ee.kth.se/~carlofi/teaching/pwsn-2011/wsn_course.shtml Lecture 5 Stockholm, October 14, 2011 Fast-Lipschitz Optimization Royal Institute of Technology - KTH Stockholm, Sweden e-mail: carlofi@kth.se
http://www.ee.kth.se/~carlofi/teaching/pwsn-2011/wsn_course.shtml Lecture 5 Stockholm, October 14, 2011 Fast-Lipschitz Optimization Royal Institute of Technology - KTH Stockholm, Sweden e-mail: carlofi@kth.se
Lecture 4 Duality and Decomposition Techniques
 Lecture 4 Duality and Decomposition Techniques Jie Lu (jielu@kth.se) Richard Combes Alexandre Proutiere Automatic Control, KTH September 19, 2013 Consider the primal problem Lagrange Duality Lagrangian
Lecture 4 Duality and Decomposition Techniques Jie Lu (jielu@kth.se) Richard Combes Alexandre Proutiere Automatic Control, KTH September 19, 2013 Consider the primal problem Lagrange Duality Lagrangian
David G. Luenberger Yinyu Ye. Linear and Nonlinear. Programming. Fourth Edition. ö Springer
 David G. Luenberger Yinyu Ye Linear and Nonlinear Programming Fourth Edition ö Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Optimization 1 1.2 Types of Problems 2 1.3 Size of Problems 5 1.4 Iterative Algorithms
David G. Luenberger Yinyu Ye Linear and Nonlinear Programming Fourth Edition ö Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Optimization 1 1.2 Types of Problems 2 1.3 Size of Problems 5 1.4 Iterative Algorithms
Programming, numerics and optimization
 Programming, numerics and optimization Lecture C-4: Constrained optimization Łukasz Jankowski ljank@ippt.pan.pl Institute of Fundamental Technological Research Room 4.32, Phone +22.8261281 ext. 428 June
Programming, numerics and optimization Lecture C-4: Constrained optimization Łukasz Jankowski ljank@ippt.pan.pl Institute of Fundamental Technological Research Room 4.32, Phone +22.8261281 ext. 428 June
Contents. I Basics 1. Copyright by SIAM. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited.
 page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
LECTURE 13: SOLUTION METHODS FOR CONSTRAINED OPTIMIZATION. 1. Primal approach 2. Penalty and barrier methods 3. Dual approach 4. Primal-dual approach
 LECTURE 13: SOLUTION METHODS FOR CONSTRAINED OPTIMIZATION 1. Primal approach 2. Penalty and barrier methods 3. Dual approach 4. Primal-dual approach Basic approaches I. Primal Approach - Feasible Direction
LECTURE 13: SOLUTION METHODS FOR CONSTRAINED OPTIMIZATION 1. Primal approach 2. Penalty and barrier methods 3. Dual approach 4. Primal-dual approach Basic approaches I. Primal Approach - Feasible Direction
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks
 Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks www.kth.se/student/program-kurser/kurshemsidor/kurshemsidor/control/el2745 Lecture 6 Stockholm, February 6, 2012 Carlo Fischione Royal Institute of Technology - KTH
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks www.kth.se/student/program-kurser/kurshemsidor/kurshemsidor/control/el2745 Lecture 6 Stockholm, February 6, 2012 Carlo Fischione Royal Institute of Technology - KTH
PRIMAL-DUAL INTERIOR POINT METHOD FOR LINEAR PROGRAMMING. 1. Introduction
 PRIMAL-DUAL INTERIOR POINT METHOD FOR LINEAR PROGRAMMING KELLER VANDEBOGERT AND CHARLES LANNING 1. Introduction Interior point methods are, put simply, a technique of optimization where, given a problem
PRIMAL-DUAL INTERIOR POINT METHOD FOR LINEAR PROGRAMMING KELLER VANDEBOGERT AND CHARLES LANNING 1. Introduction Interior point methods are, put simply, a technique of optimization where, given a problem
Computational Methods. Constrained Optimization
 Computational Methods Constrained Optimization Manfred Huber 2010 1 Constrained Optimization Unconstrained Optimization finds a minimum of a function under the assumption that the parameters can take on
Computational Methods Constrained Optimization Manfred Huber 2010 1 Constrained Optimization Unconstrained Optimization finds a minimum of a function under the assumption that the parameters can take on
INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING
 INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING DAVID G. LUENBERGER Stanford University TT ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California London Don Mills, Ontario CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING DAVID G. LUENBERGER Stanford University TT ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California London Don Mills, Ontario CONTENTS
Theoretical Concepts of Machine Learning
 Theoretical Concepts of Machine Learning Part 2 Institute of Bioinformatics Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria Outline 1 Introduction 2 Generalization Error 3 Maximum Likelihood 4 Noise Models 5
Theoretical Concepts of Machine Learning Part 2 Institute of Bioinformatics Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria Outline 1 Introduction 2 Generalization Error 3 Maximum Likelihood 4 Noise Models 5
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks
 Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks https://www.kth.se/social/course/el2745/ Lecture 6 Routing Carlo Fischione Associate Professor of Sensor Networks e-mail:carlofi@kth.se http://www.ee.kth.se/ carlofi/
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks https://www.kth.se/social/course/el2745/ Lecture 6 Routing Carlo Fischione Associate Professor of Sensor Networks e-mail:carlofi@kth.se http://www.ee.kth.se/ carlofi/
CONLIN & MMA solvers. Pierre DUYSINX LTAS Automotive Engineering Academic year
 CONLIN & MMA solvers Pierre DUYSINX LTAS Automotive Engineering Academic year 2018-2019 1 CONLIN METHOD 2 LAY-OUT CONLIN SUBPROBLEMS DUAL METHOD APPROACH FOR CONLIN SUBPROBLEMS SEQUENTIAL QUADRATIC PROGRAMMING
CONLIN & MMA solvers Pierre DUYSINX LTAS Automotive Engineering Academic year 2018-2019 1 CONLIN METHOD 2 LAY-OUT CONLIN SUBPROBLEMS DUAL METHOD APPROACH FOR CONLIN SUBPROBLEMS SEQUENTIAL QUADRATIC PROGRAMMING
Convex Optimization and Machine Learning
 Convex Optimization and Machine Learning Mengliu Zhao Machine Learning Reading Group School of Computing Science Simon Fraser University March 12, 2014 Mengliu Zhao SFU-MLRG March 12, 2014 1 / 25 Introduction
Convex Optimization and Machine Learning Mengliu Zhao Machine Learning Reading Group School of Computing Science Simon Fraser University March 12, 2014 Mengliu Zhao SFU-MLRG March 12, 2014 1 / 25 Introduction
Convex Optimization. Lijun Zhang Modification of
 Convex Optimization Lijun Zhang zlj@nju.edu.cn http://cs.nju.edu.cn/zlj Modification of http://stanford.edu/~boyd/cvxbook/bv_cvxslides.pdf Outline Introduction Convex Sets & Functions Convex Optimization
Convex Optimization Lijun Zhang zlj@nju.edu.cn http://cs.nju.edu.cn/zlj Modification of http://stanford.edu/~boyd/cvxbook/bv_cvxslides.pdf Outline Introduction Convex Sets & Functions Convex Optimization
Constrained Optimization COS 323
 Constrained Optimization COS 323 Last time Introduction to optimization objective function, variables, [constraints] 1-dimensional methods Golden section, discussion of error Newton s method Multi-dimensional
Constrained Optimization COS 323 Last time Introduction to optimization objective function, variables, [constraints] 1-dimensional methods Golden section, discussion of error Newton s method Multi-dimensional
PARALLEL OPTIMIZATION
 PARALLEL OPTIMIZATION Theory, Algorithms, and Applications YAIR CENSOR Department of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Haifa STAVROS A. ZENIOS Department of Public and Business Administration
PARALLEL OPTIMIZATION Theory, Algorithms, and Applications YAIR CENSOR Department of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Haifa STAVROS A. ZENIOS Department of Public and Business Administration
Programs. Introduction
 16 Interior Point I: Linear Programs Lab Objective: For decades after its invention, the Simplex algorithm was the only competitive method for linear programming. The past 30 years, however, have seen
16 Interior Point I: Linear Programs Lab Objective: For decades after its invention, the Simplex algorithm was the only competitive method for linear programming. The past 30 years, however, have seen
ME 555: Distributed Optimization
 ME 555: Distributed Optimization Duke University Spring 2015 1 Administrative Course: ME 555: Distributed Optimization (Spring 2015) Instructor: Time: Location: Office hours: Website: Soomin Lee (email:
ME 555: Distributed Optimization Duke University Spring 2015 1 Administrative Course: ME 555: Distributed Optimization (Spring 2015) Instructor: Time: Location: Office hours: Website: Soomin Lee (email:
Lecture 18: March 23
 0-725/36-725: Convex Optimization Spring 205 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Lecture 8: March 23 Scribes: James Duyck Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes have not
0-725/36-725: Convex Optimization Spring 205 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Lecture 8: March 23 Scribes: James Duyck Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes have not
Nonlinear Programming
 Nonlinear Programming SECOND EDITION Dimitri P. Bertsekas Massachusetts Institute of Technology WWW site for book Information and Orders http://world.std.com/~athenasc/index.html Athena Scientific, Belmont,
Nonlinear Programming SECOND EDITION Dimitri P. Bertsekas Massachusetts Institute of Technology WWW site for book Information and Orders http://world.std.com/~athenasc/index.html Athena Scientific, Belmont,
Part 4. Decomposition Algorithms Dantzig-Wolf Decomposition Algorithm
 In the name of God Part 4. 4.1. Dantzig-Wolf Decomposition Algorithm Spring 2010 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Introduction Introduction Real world linear programs having thousands of rows and columns.
In the name of God Part 4. 4.1. Dantzig-Wolf Decomposition Algorithm Spring 2010 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Introduction Introduction Real world linear programs having thousands of rows and columns.
Module 1 Lecture Notes 2. Optimization Problem and Model Formulation
 Optimization Methods: Introduction and Basic concepts 1 Module 1 Lecture Notes 2 Optimization Problem and Model Formulation Introduction In the previous lecture we studied the evolution of optimization
Optimization Methods: Introduction and Basic concepts 1 Module 1 Lecture Notes 2 Optimization Problem and Model Formulation Introduction In the previous lecture we studied the evolution of optimization
Linear Programming Problems
 Linear Programming Problems Two common formulations of linear programming (LP) problems are: min Subject to: 1,,, 1,2,,;, max Subject to: 1,,, 1,2,,;, Linear Programming Problems The standard LP problem
Linear Programming Problems Two common formulations of linear programming (LP) problems are: min Subject to: 1,,, 1,2,,;, max Subject to: 1,,, 1,2,,;, Linear Programming Problems The standard LP problem
Data Mining Chapter 8: Search and Optimization Methods Fall 2011 Ming Li Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University
 Data Mining Chapter 8: Search and Optimization Methods Fall 2011 Ming Li Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Search & Optimization Search and Optimization method deals with
Data Mining Chapter 8: Search and Optimization Methods Fall 2011 Ming Li Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Search & Optimization Search and Optimization method deals with
Interior Point I. Lab 21. Introduction
 Lab 21 Interior Point I Lab Objective: For decades after its invention, the Simplex algorithm was the only competitive method for linear programming. The past 30 years, however, have seen the discovery
Lab 21 Interior Point I Lab Objective: For decades after its invention, the Simplex algorithm was the only competitive method for linear programming. The past 30 years, however, have seen the discovery
Unconstrained Optimization Principles of Unconstrained Optimization Search Methods
 1 Nonlinear Programming Types of Nonlinear Programs (NLP) Convexity and Convex Programs NLP Solutions Unconstrained Optimization Principles of Unconstrained Optimization Search Methods Constrained Optimization
1 Nonlinear Programming Types of Nonlinear Programs (NLP) Convexity and Convex Programs NLP Solutions Unconstrained Optimization Principles of Unconstrained Optimization Search Methods Constrained Optimization
Lecture 7: Support Vector Machine
 Lecture 7: Support Vector Machine Hien Van Nguyen University of Houston 9/28/2017 Separating hyperplane Red and green dots can be separated by a separating hyperplane Two classes are separable, i.e., each
Lecture 7: Support Vector Machine Hien Van Nguyen University of Houston 9/28/2017 Separating hyperplane Red and green dots can be separated by a separating hyperplane Two classes are separable, i.e., each
CS 473: Algorithms. Ruta Mehta. Spring University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign. Ruta (UIUC) CS473 1 Spring / 36
 CS 473: Algorithms Ruta Mehta University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign Spring 2018 Ruta (UIUC) CS473 1 Spring 2018 1 / 36 CS 473: Algorithms, Spring 2018 LP Duality Lecture 20 April 3, 2018 Some of the
CS 473: Algorithms Ruta Mehta University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign Spring 2018 Ruta (UIUC) CS473 1 Spring 2018 1 / 36 CS 473: Algorithms, Spring 2018 LP Duality Lecture 20 April 3, 2018 Some of the
DETERMINISTIC OPERATIONS RESEARCH
 DETERMINISTIC OPERATIONS RESEARCH Models and Methods in Optimization Linear DAVID J. RADER, JR. Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Department of Mathematics Terre Haute, IN WILEY A JOHN WILEY & SONS,
DETERMINISTIC OPERATIONS RESEARCH Models and Methods in Optimization Linear DAVID J. RADER, JR. Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Department of Mathematics Terre Haute, IN WILEY A JOHN WILEY & SONS,
Introduction to Optimization
 Introduction to Optimization Second Order Optimization Methods Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart Planned Outline Gradient-based optimization (1st order methods) plain grad., steepest descent, conjugate grad.,
Introduction to Optimization Second Order Optimization Methods Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart Planned Outline Gradient-based optimization (1st order methods) plain grad., steepest descent, conjugate grad.,
Perceptron Learning Algorithm (PLA)
 Review: Lecture 4 Perceptron Learning Algorithm (PLA) Learning algorithm for linear threshold functions (LTF) (iterative) Energy function: PLA implements a stochastic gradient algorithm Novikoff s theorem
Review: Lecture 4 Perceptron Learning Algorithm (PLA) Learning algorithm for linear threshold functions (LTF) (iterative) Energy function: PLA implements a stochastic gradient algorithm Novikoff s theorem
Simulation. Lecture O1 Optimization: Linear Programming. Saeed Bastani April 2016
 Simulation Lecture O Optimization: Linear Programming Saeed Bastani April 06 Outline of the course Linear Programming ( lecture) Integer Programming ( lecture) Heuristics and Metaheursitics (3 lectures)
Simulation Lecture O Optimization: Linear Programming Saeed Bastani April 06 Outline of the course Linear Programming ( lecture) Integer Programming ( lecture) Heuristics and Metaheursitics (3 lectures)
Convex Analysis and Minimization Algorithms I
 Jean-Baptiste Hiriart-Urruty Claude Lemarechal Convex Analysis and Minimization Algorithms I Fundamentals With 113 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona
Jean-Baptiste Hiriart-Urruty Claude Lemarechal Convex Analysis and Minimization Algorithms I Fundamentals With 113 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona
A Short SVM (Support Vector Machine) Tutorial
 A Short SVM (Support Vector Machine) Tutorial j.p.lewis CGIT Lab / IMSC U. Southern California version 0.zz dec 004 This tutorial assumes you are familiar with linear algebra and equality-constrained optimization/lagrange
A Short SVM (Support Vector Machine) Tutorial j.p.lewis CGIT Lab / IMSC U. Southern California version 0.zz dec 004 This tutorial assumes you are familiar with linear algebra and equality-constrained optimization/lagrange
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks. Routing, Zigbee, and RPL
 http://www.ee.kth.se/~carlofi/teaching/pwsn-2011/wsn_course.shtml Lecture 8 Stockholm, November 11, 2011 Routing, Zigbee, and RPL Royal Institute of Technology - KTH Stockholm, Sweden e-mail: carlofi@kth.se
http://www.ee.kth.se/~carlofi/teaching/pwsn-2011/wsn_course.shtml Lecture 8 Stockholm, November 11, 2011 Routing, Zigbee, and RPL Royal Institute of Technology - KTH Stockholm, Sweden e-mail: carlofi@kth.se
Gate Sizing by Lagrangian Relaxation Revisited
 Gate Sizing by Lagrangian Relaxation Revisited Jia Wang, Debasish Das, and Hai Zhou Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Northwestern University Evanston, Illinois, United States October 17, 2007
Gate Sizing by Lagrangian Relaxation Revisited Jia Wang, Debasish Das, and Hai Zhou Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Northwestern University Evanston, Illinois, United States October 17, 2007
Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Chapter 9 Classification: Support Vector Machines. Support Vector Machines (SVMs)
 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques Chapter 9 Classification: Support Vector Machines 1 Support Vector Machines (SVMs) SVMs are a set of related supervised learning methods used for classification Based
Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques Chapter 9 Classification: Support Vector Machines 1 Support Vector Machines (SVMs) SVMs are a set of related supervised learning methods used for classification Based
New Methods for Solving Large Scale Linear Programming Problems in the Windows and Linux computer operating systems
 arxiv:1209.4308v1 [math.oc] 19 Sep 2012 New Methods for Solving Large Scale Linear Programming Problems in the Windows and Linux computer operating systems Saeed Ketabchi, Hossein Moosaei, Hossein Sahleh
arxiv:1209.4308v1 [math.oc] 19 Sep 2012 New Methods for Solving Large Scale Linear Programming Problems in the Windows and Linux computer operating systems Saeed Ketabchi, Hossein Moosaei, Hossein Sahleh
Chapter II. Linear Programming
 1 Chapter II Linear Programming 1. Introduction 2. Simplex Method 3. Duality Theory 4. Optimality Conditions 5. Applications (QP & SLP) 6. Sensitivity Analysis 7. Interior Point Methods 1 INTRODUCTION
1 Chapter II Linear Programming 1. Introduction 2. Simplex Method 3. Duality Theory 4. Optimality Conditions 5. Applications (QP & SLP) 6. Sensitivity Analysis 7. Interior Point Methods 1 INTRODUCTION
DM6 Support Vector Machines
 DM6 Support Vector Machines Outline Large margin linear classifier Linear separable Nonlinear separable Creating nonlinear classifiers: kernel trick Discussion on SVM Conclusion SVM: LARGE MARGIN LINEAR
DM6 Support Vector Machines Outline Large margin linear classifier Linear separable Nonlinear separable Creating nonlinear classifiers: kernel trick Discussion on SVM Conclusion SVM: LARGE MARGIN LINEAR
Lecture 2. Topology of Sets in R n. August 27, 2008
 Lecture 2 Topology of Sets in R n August 27, 2008 Outline Vectors, Matrices, Norms, Convergence Open and Closed Sets Special Sets: Subspace, Affine Set, Cone, Convex Set Special Convex Sets: Hyperplane,
Lecture 2 Topology of Sets in R n August 27, 2008 Outline Vectors, Matrices, Norms, Convergence Open and Closed Sets Special Sets: Subspace, Affine Set, Cone, Convex Set Special Convex Sets: Hyperplane,
Support Vector Machines. James McInerney Adapted from slides by Nakul Verma
 Support Vector Machines James McInerney Adapted from slides by Nakul Verma Last time Decision boundaries for classification Linear decision boundary (linear classification) The Perceptron algorithm Mistake
Support Vector Machines James McInerney Adapted from slides by Nakul Verma Last time Decision boundaries for classification Linear decision boundary (linear classification) The Perceptron algorithm Mistake
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks
 Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks https://kth.instructure.com/courses/293 Lecture 1 Introduction to WSNs Carlo Fischione Associate Professor of Sensor Networks e-mail:carlofi@kth.se http://www.ee.kth.se/
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks https://kth.instructure.com/courses/293 Lecture 1 Introduction to WSNs Carlo Fischione Associate Professor of Sensor Networks e-mail:carlofi@kth.se http://www.ee.kth.se/
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Maximum Margin Methods Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB CSE 474/574
Introduction to Machine Learning Maximum Margin Methods Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB CSE 474/574
An Introduction to Bilevel Programming
 An Introduction to Bilevel Programming Chris Fricke Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Melbourne Outline What is Bilevel Programming? Origins of Bilevel Programming. Some Properties
An Introduction to Bilevel Programming Chris Fricke Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Melbourne Outline What is Bilevel Programming? Origins of Bilevel Programming. Some Properties
Objectives and Homework List
 MAC 1140 Objectives and Homework List Each objective covered in MAC1140 is listed below. Along with each objective is the homework list used with MyMathLab (MML) and a list to use with the text (if you
MAC 1140 Objectives and Homework List Each objective covered in MAC1140 is listed below. Along with each objective is the homework list used with MyMathLab (MML) and a list to use with the text (if you
of Convex Analysis Fundamentals Jean-Baptiste Hiriart-Urruty Claude Lemarechal Springer With 66 Figures
 2008 AGI-Information Management Consultants May be used for personal purporses only or by libraries associated to dandelon.com network. Jean-Baptiste Hiriart-Urruty Claude Lemarechal Fundamentals of Convex
2008 AGI-Information Management Consultants May be used for personal purporses only or by libraries associated to dandelon.com network. Jean-Baptiste Hiriart-Urruty Claude Lemarechal Fundamentals of Convex
The Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers
 The Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers With Adaptive Step Size Selection Peter Sutor, Jr. Project Advisor: Professor Tom Goldstein October 8, 2015 1 / 30 Introduction Presentation Outline 1 Convex
The Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers With Adaptive Step Size Selection Peter Sutor, Jr. Project Advisor: Professor Tom Goldstein October 8, 2015 1 / 30 Introduction Presentation Outline 1 Convex
Kernel Methods & Support Vector Machines
 & Support Vector Machines & Support Vector Machines Arvind Visvanathan CSCE 970 Pattern Recognition 1 & Support Vector Machines Question? Draw a single line to separate two classes? 2 & Support Vector
& Support Vector Machines & Support Vector Machines Arvind Visvanathan CSCE 970 Pattern Recognition 1 & Support Vector Machines Question? Draw a single line to separate two classes? 2 & Support Vector
5 Machine Learning Abstractions and Numerical Optimization
 Machine Learning Abstractions and Numerical Optimization 25 5 Machine Learning Abstractions and Numerical Optimization ML ABSTRACTIONS [some meta comments on machine learning] [When you write a large computer
Machine Learning Abstractions and Numerical Optimization 25 5 Machine Learning Abstractions and Numerical Optimization ML ABSTRACTIONS [some meta comments on machine learning] [When you write a large computer
Sequential Coordinate-wise Algorithm for Non-negative Least Squares Problem
 CENTER FOR MACHINE PERCEPTION CZECH TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY Sequential Coordinate-wise Algorithm for Non-negative Least Squares Problem Woring document of the EU project COSPAL IST-004176 Vojtěch Franc, Miro
CENTER FOR MACHINE PERCEPTION CZECH TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY Sequential Coordinate-wise Algorithm for Non-negative Least Squares Problem Woring document of the EU project COSPAL IST-004176 Vojtěch Franc, Miro
Composite Self-concordant Minimization
 Composite Self-concordant Minimization Volkan Cevher Laboratory for Information and Inference Systems-LIONS Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL) volkan.cevher@epfl.ch Paris 6 Dec 11, 2013 joint
Composite Self-concordant Minimization Volkan Cevher Laboratory for Information and Inference Systems-LIONS Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL) volkan.cevher@epfl.ch Paris 6 Dec 11, 2013 joint
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks
 Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks https://www.kth.se/social/course/el2745/ Lecture 1 Introduction to WSNs Carlo Fischione Associate Professor of Sensor Networks e-mail:carlofi@kth.se http://www.ee.kth.se/
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks https://www.kth.se/social/course/el2745/ Lecture 1 Introduction to WSNs Carlo Fischione Associate Professor of Sensor Networks e-mail:carlofi@kth.se http://www.ee.kth.se/
A Tutorial on Decomposition Methods for Network Utility Maximization Daniel P. Palomar, Member, IEEE, and Mung Chiang, Member, IEEE.
 IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 24, NO. 8, AUGUST 2006 1439 A Tutorial on Decomposition Methods for Network Utility Maximization Daniel P. Palomar, Member, IEEE, and Mung Chiang,
IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 24, NO. 8, AUGUST 2006 1439 A Tutorial on Decomposition Methods for Network Utility Maximization Daniel P. Palomar, Member, IEEE, and Mung Chiang,
A Feasible Region Contraction Algorithm (Frca) for Solving Linear Programming Problems
 A Feasible Region Contraction Algorithm (Frca) for Solving Linear Programming Problems E. O. Effanga Department of Mathematics/Statistics and Comp. Science University of Calabar P.M.B. 1115, Calabar, Cross
A Feasible Region Contraction Algorithm (Frca) for Solving Linear Programming Problems E. O. Effanga Department of Mathematics/Statistics and Comp. Science University of Calabar P.M.B. 1115, Calabar, Cross
Local and Global Minimum
 Local and Global Minimum Stationary Point. From elementary calculus, a single variable function has a stationary point at if the derivative vanishes at, i.e., 0. Graphically, the slope of the function
Local and Global Minimum Stationary Point. From elementary calculus, a single variable function has a stationary point at if the derivative vanishes at, i.e., 0. Graphically, the slope of the function
Chapter 3 Numerical Methods
 Chapter 3 Numerical Methods Part 1 3.1 Linearization and Optimization of Functions of Vectors 1 Problem Notation 2 Outline 3.1.1 Linearization 3.1.2 Optimization of Objective Functions 3.1.3 Constrained
Chapter 3 Numerical Methods Part 1 3.1 Linearization and Optimization of Functions of Vectors 1 Problem Notation 2 Outline 3.1.1 Linearization 3.1.2 Optimization of Objective Functions 3.1.3 Constrained
Lecture 19: November 5
 0-725/36-725: Convex Optimization Fall 205 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Lecture 9: November 5 Scribes: Hyun Ah Song Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes have not
0-725/36-725: Convex Optimization Fall 205 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Lecture 9: November 5 Scribes: Hyun Ah Song Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Disclaimer: These notes have not
COMS 4771 Support Vector Machines. Nakul Verma
 COMS 4771 Support Vector Machines Nakul Verma Last time Decision boundaries for classification Linear decision boundary (linear classification) The Perceptron algorithm Mistake bound for the perceptron
COMS 4771 Support Vector Machines Nakul Verma Last time Decision boundaries for classification Linear decision boundary (linear classification) The Perceptron algorithm Mistake bound for the perceptron
Submodularity Reading Group. Matroid Polytopes, Polymatroid. M. Pawan Kumar
 Submodularity Reading Group Matroid Polytopes, Polymatroid M. Pawan Kumar http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~oval/ Outline Linear Programming Matroid Polytopes Polymatroid Polyhedron Ax b A : m x n matrix b:
Submodularity Reading Group Matroid Polytopes, Polymatroid M. Pawan Kumar http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~oval/ Outline Linear Programming Matroid Polytopes Polymatroid Polyhedron Ax b A : m x n matrix b:
Optimization. Industrial AI Lab.
 Optimization Industrial AI Lab. Optimization An important tool in 1) Engineering problem solving and 2) Decision science People optimize Nature optimizes 2 Optimization People optimize (source: http://nautil.us/blog/to-save-drowning-people-ask-yourself-what-would-light-do)
Optimization Industrial AI Lab. Optimization An important tool in 1) Engineering problem solving and 2) Decision science People optimize Nature optimizes 2 Optimization People optimize (source: http://nautil.us/blog/to-save-drowning-people-ask-yourself-what-would-light-do)
OPTIMIZATION METHODS
 D. Nagesh Kumar Associate Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore - 50 0 Email : nagesh@civil.iisc.ernet.in URL: http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Brief Contents
D. Nagesh Kumar Associate Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore - 50 0 Email : nagesh@civil.iisc.ernet.in URL: http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Brief Contents
Computational Optimization. Constrained Optimization Algorithms
 Computational Optimization Constrained Optimization Algorithms Same basic algorithms Repeat Determine descent direction Determine step size Take a step Until Optimal But now must consider feasibility,
Computational Optimization Constrained Optimization Algorithms Same basic algorithms Repeat Determine descent direction Determine step size Take a step Until Optimal But now must consider feasibility,
minimize ½(x 1 + 2x 2 + x 32 ) subject to x 1 + x 2 + x 3 = 5
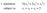 minimize ½(x 1 2 + 2x 2 2 + x 32 ) subject to x 1 + x 2 + x 3 = 5 In this Chapter We will study a new theory for constrained optimization Local optimality condition Easier to implement Deeper insights
minimize ½(x 1 2 + 2x 2 2 + x 32 ) subject to x 1 + x 2 + x 3 = 5 In this Chapter We will study a new theory for constrained optimization Local optimality condition Easier to implement Deeper insights
A Comparative Study of Frequency-domain Finite Element Updating Approaches Using Different Optimization Procedures
 A Comparative Study of Frequency-domain Finite Element Updating Approaches Using Different Optimization Procedures Xinjun DONG 1, Yang WANG 1* 1 School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Georgia Institute
A Comparative Study of Frequency-domain Finite Element Updating Approaches Using Different Optimization Procedures Xinjun DONG 1, Yang WANG 1* 1 School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Georgia Institute
Multidimensional scaling
 Multidimensional scaling Lecture 5 Alexander & Michael Bronstein tosca.cs.technion.ac.il/book Numerical geometry of non-rigid shapes Stanford University, Winter 2009 Cinderella 2.0 2 If it doesn t fit,
Multidimensional scaling Lecture 5 Alexander & Michael Bronstein tosca.cs.technion.ac.il/book Numerical geometry of non-rigid shapes Stanford University, Winter 2009 Cinderella 2.0 2 If it doesn t fit,
Lecture 15: Log Barrier Method
 10-725/36-725: Convex Optimization Spring 2015 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Lecture 15: Log Barrier Method Scribes: Pradeep Dasigi, Mohammad Gowayyed Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept.
10-725/36-725: Convex Optimization Spring 2015 Lecturer: Ryan Tibshirani Lecture 15: Log Barrier Method Scribes: Pradeep Dasigi, Mohammad Gowayyed Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept.
SDLS: a Matlab package for solving conic least-squares problems
 SDLS: a Matlab package for solving conic least-squares problems Didier Henrion 1,2 Jérôme Malick 3 June 28, 2007 Abstract This document is an introduction to the Matlab package SDLS (Semi-Definite Least-Squares)
SDLS: a Matlab package for solving conic least-squares problems Didier Henrion 1,2 Jérôme Malick 3 June 28, 2007 Abstract This document is an introduction to the Matlab package SDLS (Semi-Definite Least-Squares)
Lecture 10: SVM Lecture Overview Support Vector Machines The binary classification problem
 Computational Learning Theory Fall Semester, 2012/13 Lecture 10: SVM Lecturer: Yishay Mansour Scribe: Gitit Kehat, Yogev Vaknin and Ezra Levin 1 10.1 Lecture Overview In this lecture we present in detail
Computational Learning Theory Fall Semester, 2012/13 Lecture 10: SVM Lecturer: Yishay Mansour Scribe: Gitit Kehat, Yogev Vaknin and Ezra Levin 1 10.1 Lecture Overview In this lecture we present in detail
Lecture 2 September 3
 EE 381V: Large Scale Optimization Fall 2012 Lecture 2 September 3 Lecturer: Caramanis & Sanghavi Scribe: Hongbo Si, Qiaoyang Ye 2.1 Overview of the last Lecture The focus of the last lecture was to give
EE 381V: Large Scale Optimization Fall 2012 Lecture 2 September 3 Lecturer: Caramanis & Sanghavi Scribe: Hongbo Si, Qiaoyang Ye 2.1 Overview of the last Lecture The focus of the last lecture was to give
Linear programming and duality theory
 Linear programming and duality theory Complements of Operations Research Giovanni Righini Linear Programming (LP) A linear program is defined by linear constraints, a linear objective function. Its variables
Linear programming and duality theory Complements of Operations Research Giovanni Righini Linear Programming (LP) A linear program is defined by linear constraints, a linear objective function. Its variables
Rules for Identifying the Initial Design Points for Use in the Quick Convergent Inflow Algorithm
 International Journal of Statistics and Probability; Vol. 5, No. 1; 2016 ISSN 1927-7032 E-ISSN 1927-7040 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Rules for Identifying the Initial Design for
International Journal of Statistics and Probability; Vol. 5, No. 1; 2016 ISSN 1927-7032 E-ISSN 1927-7040 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Rules for Identifying the Initial Design for
DM545 Linear and Integer Programming. Lecture 2. The Simplex Method. Marco Chiarandini
 DM545 Linear and Integer Programming Lecture 2 The Marco Chiarandini Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Southern Denmark Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Standard Form Basic Feasible Solutions
DM545 Linear and Integer Programming Lecture 2 The Marco Chiarandini Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Southern Denmark Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Standard Form Basic Feasible Solutions
Linear Optimization and Extensions: Theory and Algorithms
 AT&T Linear Optimization and Extensions: Theory and Algorithms Shu-Cherng Fang North Carolina State University Sarai Puthenpura AT&T Bell Labs Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 Contents
AT&T Linear Optimization and Extensions: Theory and Algorithms Shu-Cherng Fang North Carolina State University Sarai Puthenpura AT&T Bell Labs Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 Contents
Surrogate Gradient Algorithm for Lagrangian Relaxation 1,2
 Surrogate Gradient Algorithm for Lagrangian Relaxation 1,2 X. Zhao 3, P. B. Luh 4, and J. Wang 5 Communicated by W.B. Gong and D. D. Yao 1 This paper is dedicated to Professor Yu-Chi Ho for his 65th birthday.
Surrogate Gradient Algorithm for Lagrangian Relaxation 1,2 X. Zhao 3, P. B. Luh 4, and J. Wang 5 Communicated by W.B. Gong and D. D. Yao 1 This paper is dedicated to Professor Yu-Chi Ho for his 65th birthday.
Simplicial Global Optimization
 Simplicial Global Optimization Julius Žilinskas Vilnius University, Lithuania September, 7 http://web.vu.lt/mii/j.zilinskas Global optimization Find f = min x A f (x) and x A, f (x ) = f, where A R n.
Simplicial Global Optimization Julius Žilinskas Vilnius University, Lithuania September, 7 http://web.vu.lt/mii/j.zilinskas Global optimization Find f = min x A f (x) and x A, f (x ) = f, where A R n.
Mathematical Programming and Research Methods (Part II)
 Mathematical Programming and Research Methods (Part II) 4. Convexity and Optimization Massimiliano Pontil (based on previous lecture by Andreas Argyriou) 1 Today s Plan Convex sets and functions Types
Mathematical Programming and Research Methods (Part II) 4. Convexity and Optimization Massimiliano Pontil (based on previous lecture by Andreas Argyriou) 1 Today s Plan Convex sets and functions Types
Constrained optimization
 Constrained optimization A general constrained optimization problem has the form where The Lagrangian function is given by Primal and dual optimization problems Primal: Dual: Weak duality: Strong duality:
Constrained optimization A general constrained optimization problem has the form where The Lagrangian function is given by Primal and dual optimization problems Primal: Dual: Weak duality: Strong duality:
Delay-minimal Transmission for Energy Constrained Wireless Communications
 Delay-minimal Transmission for Energy Constrained Wireless Communications Jing Yang Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland, College Park, M0742 yangjing@umd.edu
Delay-minimal Transmission for Energy Constrained Wireless Communications Jing Yang Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland, College Park, M0742 yangjing@umd.edu
Computational study of the step size parameter of the subgradient optimization method
 1 Computational study of the step size parameter of the subgradient optimization method Mengjie Han 1 Abstract The subgradient optimization method is a simple and flexible linear programming iterative
1 Computational study of the step size parameter of the subgradient optimization method Mengjie Han 1 Abstract The subgradient optimization method is a simple and flexible linear programming iterative
Characterizing Improving Directions Unconstrained Optimization
 Final Review IE417 In the Beginning... In the beginning, Weierstrass's theorem said that a continuous function achieves a minimum on a compact set. Using this, we showed that for a convex set S and y not
Final Review IE417 In the Beginning... In the beginning, Weierstrass's theorem said that a continuous function achieves a minimum on a compact set. Using this, we showed that for a convex set S and y not
Lecture 12: Feasible direction methods
 Lecture 12 Lecture 12: Feasible direction methods Kin Cheong Sou December 2, 2013 TMA947 Lecture 12 Lecture 12: Feasible direction methods 1 / 1 Feasible-direction methods, I Intro Consider the problem
Lecture 12 Lecture 12: Feasible direction methods Kin Cheong Sou December 2, 2013 TMA947 Lecture 12 Lecture 12: Feasible direction methods 1 / 1 Feasible-direction methods, I Intro Consider the problem
Chapter 15 Introduction to Linear Programming
 Chapter 15 Introduction to Linear Programming An Introduction to Optimization Spring, 2015 Wei-Ta Chu 1 Brief History of Linear Programming The goal of linear programming is to determine the values of
Chapter 15 Introduction to Linear Programming An Introduction to Optimization Spring, 2015 Wei-Ta Chu 1 Brief History of Linear Programming The goal of linear programming is to determine the values of
Solution Methods Numerical Algorithms
 Solution Methods Numerical Algorithms Evelien van der Hurk DTU Managment Engineering Class Exercises From Last Time 2 DTU Management Engineering 42111: Static and Dynamic Optimization (6) 09/10/2017 Class
Solution Methods Numerical Algorithms Evelien van der Hurk DTU Managment Engineering Class Exercises From Last Time 2 DTU Management Engineering 42111: Static and Dynamic Optimization (6) 09/10/2017 Class
Projection onto the probability simplex: An efficient algorithm with a simple proof, and an application
 Proection onto the probability simplex: An efficient algorithm with a simple proof, and an application Weiran Wang Miguel Á. Carreira-Perpiñán Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of
Proection onto the probability simplex: An efficient algorithm with a simple proof, and an application Weiran Wang Miguel Á. Carreira-Perpiñán Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of
Linear methods for supervised learning
 Linear methods for supervised learning LDA Logistic regression Naïve Bayes PLA Maximum margin hyperplanes Soft-margin hyperplanes Least squares resgression Ridge regression Nonlinear feature maps Sometimes
Linear methods for supervised learning LDA Logistic regression Naïve Bayes PLA Maximum margin hyperplanes Soft-margin hyperplanes Least squares resgression Ridge regression Nonlinear feature maps Sometimes
Primal and Dual Methods for Optimisation over the Non-dominated Set of a Multi-objective Programme and Computing the Nadir Point
 Primal and Dual Methods for Optimisation over the Non-dominated Set of a Multi-objective Programme and Computing the Nadir Point Ethan Liu Supervisor: Professor Matthias Ehrgott Lancaster University Outline
Primal and Dual Methods for Optimisation over the Non-dominated Set of a Multi-objective Programme and Computing the Nadir Point Ethan Liu Supervisor: Professor Matthias Ehrgott Lancaster University Outline
STRUCTURAL & MULTIDISCIPLINARY OPTIMIZATION
 STRUCTURAL & MULTIDISCIPLINARY OPTIMIZATION Pierre DUYSINX Patricia TOSSINGS Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering Academic year 2018-2019 1 Course objectives To become familiar with the introduction
STRUCTURAL & MULTIDISCIPLINARY OPTIMIZATION Pierre DUYSINX Patricia TOSSINGS Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering Academic year 2018-2019 1 Course objectives To become familiar with the introduction
Convex Optimization. Erick Delage, and Ashutosh Saxena. October 20, (a) (b) (c)
 Convex Optimization (for CS229) Erick Delage, and Ashutosh Saxena October 20, 2006 1 Convex Sets Definition: A set G R n is convex if every pair of point (x, y) G, the segment beteen x and y is in A. More
Convex Optimization (for CS229) Erick Delage, and Ashutosh Saxena October 20, 2006 1 Convex Sets Definition: A set G R n is convex if every pair of point (x, y) G, the segment beteen x and y is in A. More
Optimization for Machine Learning
 Optimization for Machine Learning (Problems; Algorithms - C) SUVRIT SRA Massachusetts Institute of Technology PKU Summer School on Data Science (July 2017) Course materials http://suvrit.de/teaching.html
Optimization for Machine Learning (Problems; Algorithms - C) SUVRIT SRA Massachusetts Institute of Technology PKU Summer School on Data Science (July 2017) Course materials http://suvrit.de/teaching.html
Fundamentals of Integer Programming
 Fundamentals of Integer Programming Di Yuan Department of Information Technology, Uppsala University January 2018 Outline Definition of integer programming Formulating some classical problems with integer
Fundamentals of Integer Programming Di Yuan Department of Information Technology, Uppsala University January 2018 Outline Definition of integer programming Formulating some classical problems with integer
Support Vector Machines.
 Support Vector Machines srihari@buffalo.edu SVM Discussion Overview 1. Overview of SVMs 2. Margin Geometry 3. SVM Optimization 4. Overlapping Distributions 5. Relationship to Logistic Regression 6. Dealing
Support Vector Machines srihari@buffalo.edu SVM Discussion Overview 1. Overview of SVMs 2. Margin Geometry 3. SVM Optimization 4. Overlapping Distributions 5. Relationship to Logistic Regression 6. Dealing
Discrete Geometry Processing
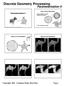 Non Convex Boundary Convex boundary creates significant distortion Free boundary is better Some slides from the Mesh Parameterization Course (Siggraph Asia 008) 1 Fixed vs Free Boundary Fixed vs Free Boundary
Non Convex Boundary Convex boundary creates significant distortion Free boundary is better Some slides from the Mesh Parameterization Course (Siggraph Asia 008) 1 Fixed vs Free Boundary Fixed vs Free Boundary
Distributed Optimization of Continuoustime Multi-agent Networks
 University of Maryland, Dec 2016 Distributed Optimization of Continuoustime Multi-agent Networks Yiguang Hong Academy of Mathematics & Systems Science Chinese Academy of Sciences Outline 1. Background
University of Maryland, Dec 2016 Distributed Optimization of Continuoustime Multi-agent Networks Yiguang Hong Academy of Mathematics & Systems Science Chinese Academy of Sciences Outline 1. Background
Preface. and Its Applications 81, ISBN , doi: / , Springer Science+Business Media New York, 2013.
 Preface This book is for all those interested in using the GAMS technology for modeling and solving complex, large-scale, continuous nonlinear optimization problems or applications. Mainly, it is a continuation
Preface This book is for all those interested in using the GAMS technology for modeling and solving complex, large-scale, continuous nonlinear optimization problems or applications. Mainly, it is a continuation
Research Interests Optimization:
 Mitchell: Research interests 1 Research Interests Optimization: looking for the best solution from among a number of candidates. Prototypical optimization problem: min f(x) subject to g(x) 0 x X IR n Here,
Mitchell: Research interests 1 Research Interests Optimization: looking for the best solution from among a number of candidates. Prototypical optimization problem: min f(x) subject to g(x) 0 x X IR n Here,
Ellipsoid Algorithm :Algorithms in the Real World. Ellipsoid Algorithm. Reduction from general case
 Ellipsoid Algorithm 15-853:Algorithms in the Real World Linear and Integer Programming II Ellipsoid algorithm Interior point methods First polynomial-time algorithm for linear programming (Khachian 79)
Ellipsoid Algorithm 15-853:Algorithms in the Real World Linear and Integer Programming II Ellipsoid algorithm Interior point methods First polynomial-time algorithm for linear programming (Khachian 79)
Simplex Algorithm in 1 Slide
 Administrivia 1 Canonical form: Simplex Algorithm in 1 Slide If we do pivot in A r,s >0, where c s
Administrivia 1 Canonical form: Simplex Algorithm in 1 Slide If we do pivot in A r,s >0, where c s
A Truncated Newton Method in an Augmented Lagrangian Framework for Nonlinear Programming
 A Truncated Newton Method in an Augmented Lagrangian Framework for Nonlinear Programming Gianni Di Pillo (dipillo@dis.uniroma1.it) Giampaolo Liuzzi (liuzzi@iasi.cnr.it) Stefano Lucidi (lucidi@dis.uniroma1.it)
A Truncated Newton Method in an Augmented Lagrangian Framework for Nonlinear Programming Gianni Di Pillo (dipillo@dis.uniroma1.it) Giampaolo Liuzzi (liuzzi@iasi.cnr.it) Stefano Lucidi (lucidi@dis.uniroma1.it)
