SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
- Lionel Perry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 6 Test Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) The number of edges in K12 is 1) 2) The number of Hamilton circuits in K12 is 2) 3) The number of edges in the complete graph with 50 vertices is 3) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 4) n! = A) n (n - 1)! B) n! + (n - 1)! C)n! (n - 1)! D) n + (n - 1)! 4) 5) (n- 1)! = n! A) (n- 1)! B) n! - 1! C) n! n D) n (n - 1)! 5) 6) 101! 100! = A) 101 B) 10,100 C) 1.01 D) 1 6) 7) If 99! 10156, which of the following numbers most closely approximates 100!? A) B) C) D) ) 1
2 8) 26! + 24! 25! A) 50! 25! = B) 25 C) D) 2 9) In a complete graph with 12 vertices (A through L), the total number of Hamilton paths that start at vertex A and end at vertex L is A) 11!. B) 12!. C)10!. D) 13!. 8) 9) 10) In a complete graph with 16 vertices (A through P), the total number of Hamilton paths that start at vertex A, pass through vertex D after traversing exactly three edges, and end at vertex P is A) 13! B) 16! C)3! 12! D) 14! 10) 11) In a complete graph with 720 distinct Hamilton circuits, there is a total of A) 9 vertices. B) 6 vertices. C) 7 vertices. D) 5 vertices. 11) 12) A Hamilton circuit for the following graph 12) A) must contain the edge CD. B) must contain the edge FE. C)must contain the edge AB. D) All of the above 2
3 13) The following graph 13) A) has several Hamilton circuits, none of which contain the edge BD. B) has a single Hamilton circuit (and its mirror-image circuit). C) has no Hamilton circuit. D) has several Hamilton circuits, all of which contain the edge CG. A delivery truck must deliver furniture to 4 different locations (A, B, C, and D). The trip must start and end at A. The graph below shows the distances (in miles) between locations. We want to minimize the total distance traveled. 14) The nearest-neighbor algorithm applied to the graph yields the following solution: A) A, B, D, C, A. B) A, D, B, C, A. C)A, D, C, B, A. D) A, C, B, D, A. 14) A truck must drop off furniture at 4 different homes (A, B, C, and D) as shown in the graph below, starting and ending at A. The numbers on the edges represent distances (in miles) between locations. The truck driver wants to minimize the total length of the trip. 15) The length of the trip of the circuit found using the nearest-neighbor algorithm is: A) 17 miles. B) 16 miles. C)22 miles. D) 19 miles. 15) 3
4 16) The cheapest-link algorithm applied to the graph yields the following solution: A) A, C, D, B, A. B) A, B, D, C, A. C)A, C, B, D, A. D) A, D, C, B, A. 16) 17) The length of the trip of the circuit found using the cheapest-link algorithm is A) 19 miles. B) 22 miles. C)29 miles. D) 17 miles. 17) 18) The repetitive nearest-neighbor algorithm applied to the graph yields the following solution: A) A, B, D, C, A. B) A, C, D, B, A. C)A, D, C, B, A. D) A, C, B, D, A. 18) 19) The length of the trip of the circuit found using the repetitive nearest-neighbor algorithm is: A) 17 miles. B) 16 miles. C)19 miles. D) 22 miles. 19) 20) An optimal solution to this problem is given by A) A, C, D, B, A. B) A, B, D, C, A. C)A, D, B, C, A. D) A, B, C, D, A. 20) 4
5 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. A traveling salesman's territory consists of the 5 cities shown on the following mileage chart. The salesman must organize a round trip that starts and ends at Louisville (his hometown) and will pass through each of the other four cities exactly once. Mileage Chart 21) The nearest-neighbor algorithm applied to this problem yields the following solution: 21) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 22) The cheapest-link algorithm applied to this problem yields the following solution: A) Louisville, Boston, Buffalo, Chicago, Columbus, Louisville. B) Louisville, Columbus, Chicago, Buffalo, Boston, Louisville. C) Louisville, Columbus, Buffalo, Boston, Chicago, Louisville. D) Louisville, Chicago, Buffalo, Boston, Columbus, Louisville. 22) 23) The repetitive nearest-neighbor algorithm applied to this problem yields the following solution: A) Louisville, Columbus, Chicago, Buffalo, Boston, Louisville. B) Louisville, Boston, Buffalo, Chicago, Columbus, Louisville. C) Louisville, Chicago, Buffalo, Boston, Columbus, Louisville. D) Louisville, Columbus, Buffalo, Boston, Chicago, Louisville. 23) 24) At an average cost of 25 cents per mile, the cheapest possible trip that starts at Louisville and passes through each of the other cities exactly once would cost A) $ B) $ C) $ D) $ ) 25) At an average cost of 50 cents per mile, the cheapest possible trip that starts at Louisville and passes through each of the other cities exactly once would cost A) $ B) $ C) $ D) $ ) 5
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 7 & 8 Test Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) Which of the following four graphs is a tree?
Chapter 7 & 8 Test Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) Which of the following four graphs is a tree?
Finite Math A Chapter 6 Notes Hamilton Circuits
 Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring (Hamilton Circuits) and Hamilton Paths 6.1 Traveling Salesman Problems/ 6.2 Hamilton Paths and Circuits A traveling salesman has clients in 5 different cities. He
Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring (Hamilton Circuits) and Hamilton Paths 6.1 Traveling Salesman Problems/ 6.2 Hamilton Paths and Circuits A traveling salesman has clients in 5 different cities. He
Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1
 AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
1. trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) How many different spanning. trees does the network shown in figure (b) have?
 2/28/18, 8:24 M 1. (a) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (b) have? L K M P N O L K M P N
2/28/18, 8:24 M 1. (a) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (b) have? L K M P N O L K M P N
MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak
 MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak 1. On each of three consecutive days the National Weather Service announces that there is a 50-50 chance of rain. Assuming that they are correct, answer the following:
MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak 1. On each of three consecutive days the National Weather Service announces that there is a 50-50 chance of rain. Assuming that they are correct, answer the following:
The Traveling Salesman Problem
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Hamilton path A path that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once. Hamilton circuit A circuit that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once (at the end,
The Traveling Salesman Problem Hamilton path A path that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once. Hamilton circuit A circuit that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once (at the end,
The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm Lecture 31 Sections 6.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 6, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman
The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm Lecture 31 Sections 6.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 6, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman
1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions.
 SSII 2014 1 Instructor: Benjamin Wilson Name: 1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions. 2. No credit will be given for correct answers without supporting work and/ or explanation. 3.
SSII 2014 1 Instructor: Benjamin Wilson Name: 1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions. 2. No credit will be given for correct answers without supporting work and/ or explanation. 3.
6.2 Initial Problem. Section 6.2 Network Problems. 6.2 Initial Problem, cont d. Weighted Graphs. Weighted Graphs, cont d. Weighted Graphs, cont d
 Section 6.2 Network Problems Goals Study weighted graphs Study spanning trees Study minimal spanning trees Use Kruskal s algorithm 6.2 Initial Problem Walkways need to be built between the buildings on
Section 6.2 Network Problems Goals Study weighted graphs Study spanning trees Study minimal spanning trees Use Kruskal s algorithm 6.2 Initial Problem Walkways need to be built between the buildings on
1. The Highway Inspector s Problem
 MATH 100 Survey of Mathematics Fall 2009 1. The Highway Inspector s Problem The Königsberg Bridges over the river Pregel C c d e A g D a B b Figure 1. Bridges f Is there a path that crosses every bridge
MATH 100 Survey of Mathematics Fall 2009 1. The Highway Inspector s Problem The Königsberg Bridges over the river Pregel C c d e A g D a B b Figure 1. Bridges f Is there a path that crosses every bridge
a) Graph 2 and Graph 3 b) Graph 2 and Graph 4 c) Graph 1 and Graph 4 d) Graph 1 and Graph 3 e) Graph 3 and Graph 4 f) None of the above
 Mathematics 105: Math as a Liberal Art. Final Exam. Name Instructor: Ramin Naimi Spring 2008 Close book. Closed notes. No Calculators. NO CELL PHONES! Please turn off your cell phones and put them away.
Mathematics 105: Math as a Liberal Art. Final Exam. Name Instructor: Ramin Naimi Spring 2008 Close book. Closed notes. No Calculators. NO CELL PHONES! Please turn off your cell phones and put them away.
A region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that is divided up by the network.
 Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
The Traveling Salesman Problem Outline/learning Objectives The Traveling Salesman Problem
 Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
14 Graph Theory. Exercise Set 14-1
 14 Graph Theory Exercise Set 14-1 1. A graph in this chapter consists of vertices and edges. In previous chapters the term was used as a visual picture of a set of ordered pairs defined by a relation or
14 Graph Theory Exercise Set 14-1 1. A graph in this chapter consists of vertices and edges. In previous chapters the term was used as a visual picture of a set of ordered pairs defined by a relation or
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION
 SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory 14.1 Graphs, Paths and Circuits Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory 14.1 Graphs, Paths and Circuits Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected
MATH 103: Contemporary Mathematics Study Guide for Chapter 6: Hamilton Circuits and the TSP
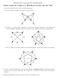 MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
Topics Covered. Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm
 Graph Theory Topics Covered Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm What is a graph? A collection of points, called vertices
Graph Theory Topics Covered Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm What is a graph? A collection of points, called vertices
Note that there are questions printed on both sides of each page!
 Math 1001 Name: Fall 2007 Test 1 Student ID: 10/5/07 Time allowed: 50 minutes Section: 10:10 11:15 12:20 This exam includes 7 pages, including this one and a sheet for scratch work. There are a total of
Math 1001 Name: Fall 2007 Test 1 Student ID: 10/5/07 Time allowed: 50 minutes Section: 10:10 11:15 12:20 This exam includes 7 pages, including this one and a sheet for scratch work. There are a total of
The Traveling Salesman Problem Outline/learning Objectives The Traveling Salesman Problem
 Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Chapter 6. The Traveling-Salesman Problem. Section 1. Hamilton circuits and Hamilton paths.
 Chapter 6. The Traveling-Salesman Problem Section 1. Hamilton circuits and Hamilton paths. Recall: an Euler path is a path that travels through every edge of a graph once and only once; an Euler circuit
Chapter 6. The Traveling-Salesman Problem Section 1. Hamilton circuits and Hamilton paths. Recall: an Euler path is a path that travels through every edge of a graph once and only once; an Euler circuit
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes
 Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes Graph Theory David J. Gisch Networks and Euler Circuits Network Representation Network: A collection of points or objects that are interconnected in some
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes Graph Theory David J. Gisch Networks and Euler Circuits Network Representation Network: A collection of points or objects that are interconnected in some
 Graph Applications, Class Notes, CS 3137 1 Traveling Salesperson Problem Web References: http://www.tsp.gatech.edu/index.html http://www-e.uni-magdeburg.de/mertens/tsp/tsp.html TSP applets A Hamiltonian
Graph Applications, Class Notes, CS 3137 1 Traveling Salesperson Problem Web References: http://www.tsp.gatech.edu/index.html http://www-e.uni-magdeburg.de/mertens/tsp/tsp.html TSP applets A Hamiltonian
Warm -Up. 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices?
 Warm -Up 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices? 1. Is this graph a. traceable? b. Eulerian? 3. Eulerize this graph. Warm-Up Eulerize
Warm -Up 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices? 1. Is this graph a. traceable? b. Eulerian? 3. Eulerize this graph. Warm-Up Eulerize
A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit.
 Math 167 Review of Chapter 2 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 2 BUSINESS EFFICENCY A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian
Math 167 Review of Chapter 2 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 2 BUSINESS EFFICENCY A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian
Street-Routing Problems
 Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
Study Guide Mods: Date:
 Graph Theory Name: Study Guide Mods: Date: Define each of the following. It may be helpful to draw examples that illustrate the vocab word and/or counterexamples to define the word. 1. Graph ~ 2. Vertex
Graph Theory Name: Study Guide Mods: Date: Define each of the following. It may be helpful to draw examples that illustrate the vocab word and/or counterexamples to define the word. 1. Graph ~ 2. Vertex
Section Hamilton Paths, and Hamilton Circuits. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 14.3 Hamilton Paths, and Hamilton Circuits What You Will Learn Hamilton Paths Hamilton Circuits Complete Graphs Traveling Salesman Problems 14.3-2 Hamilton Paths A Hamilton path is a path that
Section 14.3 Hamilton Paths, and Hamilton Circuits What You Will Learn Hamilton Paths Hamilton Circuits Complete Graphs Traveling Salesman Problems 14.3-2 Hamilton Paths A Hamilton path is a path that
Section Hamilton Paths, and Hamilton Circuits. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 14.3 Hamilton Paths, and Hamilton Circuits INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # September 11, 2013 Section 14.3 Examples/Handout 18 September 11, 2013 Section 14.3 Notes 19 2.3-2 What You Will
Section 14.3 Hamilton Paths, and Hamilton Circuits INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # September 11, 2013 Section 14.3 Examples/Handout 18 September 11, 2013 Section 14.3 Notes 19 2.3-2 What You Will
IE 102 Spring Routing Through Networks - 1
 IE 102 Spring 2017 Routing Through Networks - 1 The Bridges of Koenigsberg: Euler 1735 Graph Theory began in 1735 Leonard Eüler Visited Koenigsberg People wondered whether it is possible to take a walk,
IE 102 Spring 2017 Routing Through Networks - 1 The Bridges of Koenigsberg: Euler 1735 Graph Theory began in 1735 Leonard Eüler Visited Koenigsberg People wondered whether it is possible to take a walk,
Mathematical Thinking
 Mathematical Thinking Chapter 2 Hamiltonian Circuits and Spanning Trees It often happens in mathematics that what appears to be a minor detail in the statement of a problem can have a profound effect on
Mathematical Thinking Chapter 2 Hamiltonian Circuits and Spanning Trees It often happens in mathematics that what appears to be a minor detail in the statement of a problem can have a profound effect on
Unit 7 Day 6. Section 5.2 Traveling Salesman Problem & Section 5.3 Finding the Shortest Route
 Unit 7 Day 6 Section 5.2 Traveling Salesman Problem & Section 5.3 Finding the Shortest Route 1 Warm Up Day 7: 1. Draw a planar graph with 6 vertices. 2. Is a K 9,3 graph planar? Explain your reasoning.
Unit 7 Day 6 Section 5.2 Traveling Salesman Problem & Section 5.3 Finding the Shortest Route 1 Warm Up Day 7: 1. Draw a planar graph with 6 vertices. 2. Is a K 9,3 graph planar? Explain your reasoning.
The Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) is where a least cost Hamiltonian circuit is found. CHAPTER 1 URBAN SERVICES
 Math 167 eview 1 (c) Janice Epstein HPE 1 UN SEVIES path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit. Math 167 eview
Math 167 eview 1 (c) Janice Epstein HPE 1 UN SEVIES path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit. Math 167 eview
Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring
 Traveling Salesman Problems Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring 6.1 What Is a Traveling Salesman Problem? The traveling salesman is a convenient metaphor for many different real-life applications. The
Traveling Salesman Problems Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring 6.1 What Is a Traveling Salesman Problem? The traveling salesman is a convenient metaphor for many different real-life applications. The
Math 3012 Combinatorial Optimization Worksheet
 Math 3012 Combinatorial Optimization Worksheet Combinatorial Optimization is the way in which combinatorial thought is applied to real world optimization problems. Optimization entails achieving the sufficient
Math 3012 Combinatorial Optimization Worksheet Combinatorial Optimization is the way in which combinatorial thought is applied to real world optimization problems. Optimization entails achieving the sufficient
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 2: Transportation problems
 Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 2: Transportation problems David Glickenstein September 15, 2014 1 Readings This is based on Chartrand Chapter 3 and Bondy-Murty 18.1, 18.3 (part on Closure of a Graph).
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 2: Transportation problems David Glickenstein September 15, 2014 1 Readings This is based on Chartrand Chapter 3 and Bondy-Murty 18.1, 18.3 (part on Closure of a Graph).
Lesson 5.2. The Traveling Salesperson Problem. Explore This
 Lesson 5.2 The Traveling alesperson Problem In Lesson 4.5, you explored circuits that visited each vertex of your graph exactly once (Hamiltonian circuits). In this lesson, you will extend your thinking
Lesson 5.2 The Traveling alesperson Problem In Lesson 4.5, you explored circuits that visited each vertex of your graph exactly once (Hamiltonian circuits). In this lesson, you will extend your thinking
CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko. Graphs
 CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko Graphs 2014 Definitions Definition: A graph G = (V,E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge
CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko Graphs 2014 Definitions Definition: A graph G = (V,E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics
 Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu P, NP-Problems Class
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu P, NP-Problems Class
Notes for Recitation 9
 6.042/18.062J Mathematics for Computer Science October 8, 2010 Tom Leighton and Marten van Dijk Notes for Recitation 9 1 Traveling Salesperson Problem Now we re going to talk about a famous optimization
6.042/18.062J Mathematics for Computer Science October 8, 2010 Tom Leighton and Marten van Dijk Notes for Recitation 9 1 Traveling Salesperson Problem Now we re going to talk about a famous optimization
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms. Brute-Force Approach
 CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
Hamilton Circuit. Topics in Contemporary Mathematics MA 103 Summer II, 2013
 1 Hamilton Circuit Topics in Contemporary Mathematics MA 103 Summer II, 2013 2 Hamilton Paths and Hamilton Circuits In Euler paths and Euler circuits, the game was to find paths or circuits that include
1 Hamilton Circuit Topics in Contemporary Mathematics MA 103 Summer II, 2013 2 Hamilton Paths and Hamilton Circuits In Euler paths and Euler circuits, the game was to find paths or circuits that include
Sec 2. Euler Circuits, cont.
 Sec 2. uler ircuits, cont. uler ircuits traverse each edge of a connected graph exactly once. Recall that all vertices must have even degree in order for an uler ircuit to exist. leury s lgorithm is a
Sec 2. uler ircuits, cont. uler ircuits traverse each edge of a connected graph exactly once. Recall that all vertices must have even degree in order for an uler ircuit to exist. leury s lgorithm is a
Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs
 Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs Date and Time: May 10 2012 Thursday 11:50AM~1:50PM Location: Eng 120 Start with the Self-Test Exercises (pp.816) in Prichard. 1. Give the adjacency matrix
Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs Date and Time: May 10 2012 Thursday 11:50AM~1:50PM Location: Eng 120 Start with the Self-Test Exercises (pp.816) in Prichard. 1. Give the adjacency matrix
Module 6 P, NP, NP-Complete Problems and Approximation Algorithms
 Module 6 P, NP, NP-Complete Problems and Approximation Algorithms Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Associate Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu
Module 6 P, NP, NP-Complete Problems and Approximation Algorithms Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Associate Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu
The Travelling Salesman Problem
 The Travelling Salesman Problem The travelling salesman problem cannot be solved directly without vast amounts of processing power, since every possible Hamiltonian cycle would need to be measured. For
The Travelling Salesman Problem The travelling salesman problem cannot be solved directly without vast amounts of processing power, since every possible Hamiltonian cycle would need to be measured. For
MULTIMEDIA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING PEM2046 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS IV TUTORIAL
 A. Linear Programming (LP) MULTIMEDIA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING PEM046 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS IV TUTORIAL. Identify the optimal solution and value: (a) Maximize f = 0x + 0 x (b) Minimize f = 45x
A. Linear Programming (LP) MULTIMEDIA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING PEM046 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS IV TUTORIAL. Identify the optimal solution and value: (a) Maximize f = 0x + 0 x (b) Minimize f = 45x
2 Approximation Algorithms for Metric TSP
 Comp260: Advanced Algorithms Tufts University, Spring 2002 Professor Lenore Cowen Scribe: Stephanie Tauber Lecture 3: The Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP) 1 Introduction A salesman wishes to visit every
Comp260: Advanced Algorithms Tufts University, Spring 2002 Professor Lenore Cowen Scribe: Stephanie Tauber Lecture 3: The Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP) 1 Introduction A salesman wishes to visit every
Graphs. Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale Room - Faner 3131
 Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
Euler and Hamilton circuits. Euler paths and circuits
 1 7 16 2013. uler and Hamilton circuits uler paths and circuits o The Seven ridges of Konigsberg In the early 1700 s, Konigsberg was the capital of ast Prussia. Konigsberg was later renamed Kaliningrad
1 7 16 2013. uler and Hamilton circuits uler paths and circuits o The Seven ridges of Konigsberg In the early 1700 s, Konigsberg was the capital of ast Prussia. Konigsberg was later renamed Kaliningrad
TEACHER RESOURCES. Outel Semiconductor s Recruiting Circuit: Teacher Resources 1. Routing Through Networks: Background
 Outel Semiconductor s Recruiting Circuit: Teacher Resources 1 Routing Through Networks: Background TEACHER RESOURCES Graphs and networks are collections of nodes and arcs. The nodes are used to represent
Outel Semiconductor s Recruiting Circuit: Teacher Resources 1 Routing Through Networks: Background TEACHER RESOURCES Graphs and networks are collections of nodes and arcs. The nodes are used to represent
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Test Review Ch 4 Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) According to the 2000 U. S. Census, 6.753% of the U.S. population
Test Review Ch 4 Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) According to the 2000 U. S. Census, 6.753% of the U.S. population
Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4
 MATH 11008: Graph Theory Terminology Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4 Routing problem: A routing problem is concerned with finding ways to route the delivery of good and/or services to an assortment of destinations.
MATH 11008: Graph Theory Terminology Sections 5.2, 5.3. & 5.4 Routing problem: A routing problem is concerned with finding ways to route the delivery of good and/or services to an assortment of destinations.
Simple Graph. General Graph
 Graph Theory A graph is a collection of points (also called vertices) and lines (also called edges), with each edge ending at a vertex In general, it is allowed for more than one edge to have the same
Graph Theory A graph is a collection of points (also called vertices) and lines (also called edges), with each edge ending at a vertex In general, it is allowed for more than one edge to have the same
Brute Force: Selection Sort
 Brute Force: Intro Brute force means straightforward approach Usually based directly on problem s specs Force refers to computational power Usually not as efficient as elegant solutions Advantages: Applicable
Brute Force: Intro Brute force means straightforward approach Usually based directly on problem s specs Force refers to computational power Usually not as efficient as elegant solutions Advantages: Applicable
Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering. Qian Zhu 2/23/2011
 Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering Qian Zhu 2/23/2011 Agenda Assignment: Traveling salesman problem Hierarchical clustering Example Comparisons with K-means TSP TSP: Given the
Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering Qian Zhu 2/23/2011 Agenda Assignment: Traveling salesman problem Hierarchical clustering Example Comparisons with K-means TSP TSP: Given the
Practice Final Exam 1
 Algorithm esign Techniques Practice Final xam Instructions. The exam is hours long and contains 6 questions. Write your answers clearly. You may quote any result/theorem seen in the lectures or in the
Algorithm esign Techniques Practice Final xam Instructions. The exam is hours long and contains 6 questions. Write your answers clearly. You may quote any result/theorem seen in the lectures or in the
Chapter 14. Graphs Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1
 Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
Packet #6: Counting & Graph Theory. Applied Discrete Mathematics
 Packet #6: Counting & Graph Theory Applied Discrete Mathematics Table of Contents Counting Pages 1-8 Graph Theory Pages 9-16 Exam Study Sheet Page 17 Counting Information I. Product Rule: A B C = A * B
Packet #6: Counting & Graph Theory Applied Discrete Mathematics Table of Contents Counting Pages 1-8 Graph Theory Pages 9-16 Exam Study Sheet Page 17 Counting Information I. Product Rule: A B C = A * B
Travel Every Edge 3. Example (Travel Every Edge 3) In the graphs above, can you find a circuit that hits every edge without repeating any edges?
 Travel Every Edge 3 Example (Travel Every Edge 3) In the graphs above, can you find a circuit that hits every edge without repeating any edges? Find the degrees of the vertices of the graphs above! Make
Travel Every Edge 3 Example (Travel Every Edge 3) In the graphs above, can you find a circuit that hits every edge without repeating any edges? Find the degrees of the vertices of the graphs above! Make
Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]
![Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks] Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]](/thumbs/89/97991710.jpg) Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
Vertex-Edge Graphs. Vertex-Edge Graphs In the Georgia Performance Standards. Sarah Holliday Southern Polytechnic State University
 Vertex-Edge Graphs Vertex-Edge Graphs In the Georgia Performance Standards Sarah Holliday Southern Polytechnic State University Math III MM3A7. Students will understand and apply matrix representations
Vertex-Edge Graphs Vertex-Edge Graphs In the Georgia Performance Standards Sarah Holliday Southern Polytechnic State University Math III MM3A7. Students will understand and apply matrix representations
1. Sorting (assuming sorting into ascending order) a) BUBBLE SORT
 DECISION 1 Revision Notes 1. Sorting (assuming sorting into ascending order) a) BUBBLE SORT Make sure you show comparisons clearly and label each pass First Pass 8 4 3 6 1 4 8 3 6 1 4 3 8 6 1 4 3 6 8 1
DECISION 1 Revision Notes 1. Sorting (assuming sorting into ascending order) a) BUBBLE SORT Make sure you show comparisons clearly and label each pass First Pass 8 4 3 6 1 4 8 3 6 1 4 3 8 6 1 4 3 6 8 1
Math 167 Review 1 (c) Janice Epstein
 Math 167 Review 1 (c) Janice Epstein HAPTER 1 URBAN SERVIES A graph is a collection of one or more points (vertices). The vertices may be connected by edges. Two vertices are adjacent if they are connected
Math 167 Review 1 (c) Janice Epstein HAPTER 1 URBAN SERVIES A graph is a collection of one or more points (vertices). The vertices may be connected by edges. Two vertices are adjacent if they are connected
Online Appendix. The Shortest Path Problem and Dijkstra s Algorithm
 Online Appendix The Shortest Path Problem and Dijkstra s Algorithm The purpose of this section is to briefly introduce Dijkstra s algorithm to a reader that has some experience on computer programming,
Online Appendix The Shortest Path Problem and Dijkstra s Algorithm The purpose of this section is to briefly introduce Dijkstra s algorithm to a reader that has some experience on computer programming,
Maximum Flows of Minimum Cost
 Maximum Flows of Minimum Cost Figure 8-24 Two possible maximum flows for the same network Data Structures and Algorithms in Java 1 Maximum Flows of Minimum Cost (continued) Figure 8-25 Finding a maximum
Maximum Flows of Minimum Cost Figure 8-24 Two possible maximum flows for the same network Data Structures and Algorithms in Java 1 Maximum Flows of Minimum Cost (continued) Figure 8-25 Finding a maximum
Chapter 11: Graphs and Trees. March 23, 2008
 Chapter 11: Graphs and Trees March 23, 2008 Outline 1 11.1 Graphs: An Introduction 2 11.2 Paths and Circuits 3 11.3 Matrix Representations of Graphs 4 11.5 Trees Graphs: Basic Definitions Informally, a
Chapter 11: Graphs and Trees March 23, 2008 Outline 1 11.1 Graphs: An Introduction 2 11.2 Paths and Circuits 3 11.3 Matrix Representations of Graphs 4 11.5 Trees Graphs: Basic Definitions Informally, a
Unit graph theory UNIT 4
 Unit graph theory UNIT 4 Concept Characteristics What is a Graph Really? Get in groups of three and discuss what you think a graph really is. Come up with three statements that describe the characteristics
Unit graph theory UNIT 4 Concept Characteristics What is a Graph Really? Get in groups of three and discuss what you think a graph really is. Come up with three statements that describe the characteristics
Eulerian tours. Russell Impagliazzo and Miles Jones Thanks to Janine Tiefenbruck. April 20, 2016
 Eulerian tours Russell Impagliazzo and Miles Jones Thanks to Janine Tiefenbruck http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse21-bd/ April 20, 2016 Seven Bridges of Konigsberg Is there a path that crosses each
Eulerian tours Russell Impagliazzo and Miles Jones Thanks to Janine Tiefenbruck http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse21-bd/ April 20, 2016 Seven Bridges of Konigsberg Is there a path that crosses each
Practice Exam #3, Math 100, Professor Wilson. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Exam #3, Math 100, Professor Wilson MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A tree is A) any graph that is connected and every
Practice Exam #3, Math 100, Professor Wilson MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A tree is A) any graph that is connected and every
CAD Algorithms. Shortest Path
 lgorithms Shortest Path lgorithms Mohammad Tehranipoor epartment September 00 Shortest Path Problem: ind the best way of getting from s to t where s and t are vertices in a graph. est: Min (sum of the
lgorithms Shortest Path lgorithms Mohammad Tehranipoor epartment September 00 Shortest Path Problem: ind the best way of getting from s to t where s and t are vertices in a graph. est: Min (sum of the
Trees Rooted Trees Spanning trees and Shortest Paths. 12. Graphs and Trees 2. Aaron Tan November 2017
 12. Graphs and Trees 2 Aaron Tan 6 10 November 2017 1 10.5 Trees 2 Definition Definition Definition: Tree A graph is said to be circuit-free if, and only if, it has no circuits. A graph is called a tree
12. Graphs and Trees 2 Aaron Tan 6 10 November 2017 1 10.5 Trees 2 Definition Definition Definition: Tree A graph is said to be circuit-free if, and only if, it has no circuits. A graph is called a tree
14.1 and 14.2.notebook. March 07, Module 14 lessons 1: Distance on a coordinate Plane Lesson 2: Polygons in the Coordinate Plane
 Module 14 lessons 1: Distance on a coordinate Plane Lesson 2: Reflection: a transformation of a figure that flips across a line Objectives: solve problems by graphing using coordinates and absolute value
Module 14 lessons 1: Distance on a coordinate Plane Lesson 2: Reflection: a transformation of a figure that flips across a line Objectives: solve problems by graphing using coordinates and absolute value
The Traveling Salesman Problem Brute Force Method
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Brute Force Method Lecture 30 Sections 6.1, 6.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 3, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman Problem
The Traveling Salesman Problem Brute Force Method Lecture 30 Sections 6.1, 6.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 3, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman Problem
Introduction to Graphs
 Graphs Introduction to Graphs Graph Terminology Directed Graphs Special Graphs Graph Coloring Representing Graphs Connected Graphs Connected Component Reading (Epp s textbook) 10.1-10.3 1 Introduction
Graphs Introduction to Graphs Graph Terminology Directed Graphs Special Graphs Graph Coloring Representing Graphs Connected Graphs Connected Component Reading (Epp s textbook) 10.1-10.3 1 Introduction
Use the following preference schedule to answer questions #1 - #4. Number of Voters st choice 2 nd Choice 3 rd choice 4 th choice
 M130 Sample Final Exam Name TA Name Calculators are allowed, but cell phones or palm pilots are NOT acceptable. Mark Version A on your scantron. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
M130 Sample Final Exam Name TA Name Calculators are allowed, but cell phones or palm pilots are NOT acceptable. Mark Version A on your scantron. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
EECS 203 Lecture 20. More Graphs
 EECS 203 Lecture 20 More Graphs Admin stuffs Last homework due today Office hour changes starting Friday (also in Piazza) Friday 6/17: 2-5 Mark in his office. Sunday 6/19: 2-5 Jasmine in the UGLI. Monday
EECS 203 Lecture 20 More Graphs Admin stuffs Last homework due today Office hour changes starting Friday (also in Piazza) Friday 6/17: 2-5 Mark in his office. Sunday 6/19: 2-5 Jasmine in the UGLI. Monday
More NP-complete Problems. CS255 Chris Pollett May 3, 2006.
 More NP-complete Problems CS255 Chris Pollett May 3, 2006. Outline More NP-Complete Problems Hamiltonian Cycle Recall a hamiltonian cycle is a permutation of the vertices v i_1,, v i_n of a graph G so
More NP-complete Problems CS255 Chris Pollett May 3, 2006. Outline More NP-Complete Problems Hamiltonian Cycle Recall a hamiltonian cycle is a permutation of the vertices v i_1,, v i_n of a graph G so
Varying Applications (examples)
 Graph Theory Varying Applications (examples) Computer networks Distinguish between two chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures Solve shortest path problems between cities
Graph Theory Varying Applications (examples) Computer networks Distinguish between two chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures Solve shortest path problems between cities
Problem Set 6 (Due: Wednesday, December 6, 2006)
 Urban OR Fall 2006 Problem Set 6 (Due: Wednesday, December 6, 2006) Problem 1 Problem 6.6 in Larson and Odoni Problem 2 Exercise 6.7 (page 442) in Larson and Odoni. Problem Suppose we have a network G(N,
Urban OR Fall 2006 Problem Set 6 (Due: Wednesday, December 6, 2006) Problem 1 Problem 6.6 in Larson and Odoni Problem 2 Exercise 6.7 (page 442) in Larson and Odoni. Problem Suppose we have a network G(N,
Graph Traversals. CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University. Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 1
 Graph Traversals CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University Villanova CSC 1300 - Dr Papalaskari 1 Graph traversals: Euler circuit/path Major Themes Every edge exactly once Hamilton circuit/path
Graph Traversals CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University Villanova CSC 1300 - Dr Papalaskari 1 Graph traversals: Euler circuit/path Major Themes Every edge exactly once Hamilton circuit/path
II. Functions. 61. Find a way to graph the line from the problem 59 on your calculator. Sketch the calculator graph here, including the window values:
 II Functions Week 4 Functions: graphs, tables and formulas Problem of the Week: The Farmer s Fence A field bounded on one side by a river is to be fenced on three sides so as to form a rectangular enclosure
II Functions Week 4 Functions: graphs, tables and formulas Problem of the Week: The Farmer s Fence A field bounded on one side by a river is to be fenced on three sides so as to form a rectangular enclosure
Discrete Structures CISC 2315 FALL Graphs & Trees
 Discrete Structures CISC 2315 FALL 2010 Graphs & Trees Graphs A graph is a discrete structure, with discrete components Components of a Graph edge vertex (node) Vertices A graph G = (V, E), where V is
Discrete Structures CISC 2315 FALL 2010 Graphs & Trees Graphs A graph is a discrete structure, with discrete components Components of a Graph edge vertex (node) Vertices A graph G = (V, E), where V is
Assignment No 2 (Group B)
 Assignment No 2 (Group B) 1 Problem Statement : Concurrent Implementation of Travelling Salesman Problem. 2 Objective : To develop problem solving abilities using Mathematical Modeling. To apply algorithmic
Assignment No 2 (Group B) 1 Problem Statement : Concurrent Implementation of Travelling Salesman Problem. 2 Objective : To develop problem solving abilities using Mathematical Modeling. To apply algorithmic
Elements of Graph Theory
 Elements of Graph Theory Quick review of Chapters 9.1 9.5, 9.7 (studied in Mt1348/2008) = all basic concepts must be known New topics we will mostly skip shortest paths (Chapter 9.6), as that was covered
Elements of Graph Theory Quick review of Chapters 9.1 9.5, 9.7 (studied in Mt1348/2008) = all basic concepts must be known New topics we will mostly skip shortest paths (Chapter 9.6), as that was covered
Assignment 5: Solutions
 Algorithm Design Techniques Assignment 5: Solutions () Port Authority. [This problem is more commonly called the Bin Packing Problem.] (a) Suppose K = 3 and (w, w, w 3, w 4 ) = (,,, ). The optimal solution
Algorithm Design Techniques Assignment 5: Solutions () Port Authority. [This problem is more commonly called the Bin Packing Problem.] (a) Suppose K = 3 and (w, w, w 3, w 4 ) = (,,, ). The optimal solution
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics
 Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 397 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Optimization vs. Decision
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 397 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Optimization vs. Decision
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Honors Algebra 1 Semester 2 Final Exam Review Packet Name Date Period SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the equation. 1) 27x = 81
Honors Algebra 1 Semester 2 Final Exam Review Packet Name Date Period SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the equation. 1) 27x = 81
Questions... How does one show the first problem is NP-complete? What goes on in a reduction? How hard are NP-complete problems?
 Even More NP Questions... How does one show the first problem is NP-complete? What goes on in a reduction? How hard are NP-complete problems? Reduction We say that problem A reduces to problem B, if there
Even More NP Questions... How does one show the first problem is NP-complete? What goes on in a reduction? How hard are NP-complete problems? Reduction We say that problem A reduces to problem B, if there
Technische Universität München, Zentrum Mathematik Lehrstuhl für Angewandte Geometrie und Diskrete Mathematik. Combinatorial Optimization (MA 4502)
 Technische Universität München, Zentrum Mathematik Lehrstuhl für Angewandte Geometrie und Diskrete Mathematik Combinatorial Optimization (MA 4502) Dr. Michael Ritter Problem Sheet 4 Homework Problems Problem
Technische Universität München, Zentrum Mathematik Lehrstuhl für Angewandte Geometrie und Diskrete Mathematik Combinatorial Optimization (MA 4502) Dr. Michael Ritter Problem Sheet 4 Homework Problems Problem
Fundamental Properties of Graphs
 Chapter three In many real-life situations we need to know how robust a graph that represents a certain network is, how edges or vertices can be removed without completely destroying the overall connectivity,
Chapter three In many real-life situations we need to know how robust a graph that represents a certain network is, how edges or vertices can be removed without completely destroying the overall connectivity,
Discrete Mathematics (2009 Spring) Graphs (Chapter 9, 5 hours)
 Discrete Mathematics (2009 Spring) Graphs (Chapter 9, 5 hours) Chih-Wei Yi Dept. of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University June 1, 2009 9.1 Graphs and Graph Models What are Graphs? General meaning
Discrete Mathematics (2009 Spring) Graphs (Chapter 9, 5 hours) Chih-Wei Yi Dept. of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University June 1, 2009 9.1 Graphs and Graph Models What are Graphs? General meaning
Network Analysis. Links, nodes, trees, graphs, paths and cycles what does it all mean? Minimal spanning tree shortest route maximum flow
 Network Analysis Minimal spanning tree shortest route maximum flow Links, nodes, trees, graphs, paths and cycles what does it all mean? Real OR in action! 1 Network Terminology Graph - set of points (nodes)
Network Analysis Minimal spanning tree shortest route maximum flow Links, nodes, trees, graphs, paths and cycles what does it all mean? Real OR in action! 1 Network Terminology Graph - set of points (nodes)
Introduction to Engineering Systems, ESD.00. Networks. Lecturers: Professor Joseph Sussman Dr. Afreen Siddiqi TA: Regina Clewlow
 Introduction to Engineering Systems, ESD.00 Lecture 7 Networks Lecturers: Professor Joseph Sussman Dr. Afreen Siddiqi TA: Regina Clewlow The Bridges of Königsberg The town of Konigsberg in 18 th century
Introduction to Engineering Systems, ESD.00 Lecture 7 Networks Lecturers: Professor Joseph Sussman Dr. Afreen Siddiqi TA: Regina Clewlow The Bridges of Königsberg The town of Konigsberg in 18 th century
Math 15 - Spring Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so:
 Math 15 - Spring 2017 - Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so: dm = {0: [1,15], 1: [2,16,31], 2: [3,17,32], 3: [4,18,33], 4: [5,19,34],
Math 15 - Spring 2017 - Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so: dm = {0: [1,15], 1: [2,16,31], 2: [3,17,32], 3: [4,18,33], 4: [5,19,34],
10/30/2013. Chapter 7: The Mathematics of Networks. Network. Network. Network. Network. Optimal Network. 7.1 Networks and Trees
 Network Chapter 7: The Mathematics of Networks Our definition of a network is going to be really simple essentially, a network is a graph that is connected. In this context the term is most commonly used
Network Chapter 7: The Mathematics of Networks Our definition of a network is going to be really simple essentially, a network is a graph that is connected. In this context the term is most commonly used
CS1 Lecture 31 Apr. 3, 2019
 CS Lecture 3 Apr. 3, 209 HW6 due Fri. Q3: think carefully about overlaps draw pictures Think dimension by dimension three D problems if they don t overlap in x, they don t overlap» Express this in terms
CS Lecture 3 Apr. 3, 209 HW6 due Fri. Q3: think carefully about overlaps draw pictures Think dimension by dimension three D problems if they don t overlap in x, they don t overlap» Express this in terms
Daily Math Week 10 ( ) Mon. October 21, 2013 Tues. October 22, 2013 Wed. October 23, 2013 Thurs. October 24, 2013 Fri.
 Daily Math Week 10 (2013-2014) Mon. October 21, 2013 Tues. October 22, 2013 Wed. October 23, 2013 Thurs. October 24, 2013 Fri. October 25, 2013 1 Monday, October 21, 2013 1 st Solve 2x + 4x 2 = 26 2 Monday,
Daily Math Week 10 (2013-2014) Mon. October 21, 2013 Tues. October 22, 2013 Wed. October 23, 2013 Thurs. October 24, 2013 Fri. October 25, 2013 1 Monday, October 21, 2013 1 st Solve 2x + 4x 2 = 26 2 Monday,
Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths. April 18, 2010
 Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths April 18, 2010 We have talked about insect worlds which consist of cities connected by tunnels. Here is an example of an insect world (Antland) which we saw last
Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths April 18, 2010 We have talked about insect worlds which consist of cities connected by tunnels. Here is an example of an insect world (Antland) which we saw last
56:272 Integer Programming & Network Flows Final Exam -- December 16, 1997
 56:272 Integer Programming & Network Flows Final Exam -- December 16, 1997 Answer #1 and any five of the remaining six problems! possible score 1. Multiple Choice 25 2. Traveling Salesman Problem 15 3.
56:272 Integer Programming & Network Flows Final Exam -- December 16, 1997 Answer #1 and any five of the remaining six problems! possible score 1. Multiple Choice 25 2. Traveling Salesman Problem 15 3.
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics
 Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 97 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Optimization vs. Decision
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 97 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Optimization vs. Decision
