AP B mirrors and lenses websheet 23.2
|
|
|
- Delphia Arnold
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A AP B mirrors ad leses websheet 232 Multiple Choice Idetify the choice that best completes the statemet or aswers the questio 1 The of light ca chage whe light is refracted because the medium chages a frequecy c wavelegth b medium d trasparecy 2 Whe light passes at a agle to the ormal from oe material ito aother material i which its speed is lower, a it is bet toward the ormal to the surface b it always lies alog the ormal to the surface c it is uaffected d it is bet away from the ormal to the surface 3 Whe a light ray moves from air ito glass, which has a higher idex of refractio, its path is a bet toward the ormal c parallel to the ormal b bet away from the ormal d ot bet 4 Whe a light ray passes from zirco ( = 1923) ito fluorite ( = 1434) at a agle of 60, its path is a bet toward the ormal c parallel to the ormal b bet away from the ormal d ot bet 5 A ray of light i air is icidet o a air-to-glass boudary at a agle of exactly 300 with the ormal If the idex of refractio of the glass is 165, what is the agle of the refracted ray withi the glass with respect to the ormal? a 583 c 344 b 373 d What type of image is formed whe rays of light actually itersect? a real c curved b virtual d projected 7 What type of image does a covergig les produce? a real c real or virtual b virtual d oe of the above 8 I what directio does a parallel ray from a object proceed after passig through a divergig les? a The ray passes through the ceter of curvature, C b The ray cotiues parallel to the pricipal axis c The ray passes through the ceter of the les d The ray is directed away from the focal poit, F 9 All of the followig images ca be formed by a covergig les except which oe? a virtual, upright, ad magified c real, iverted, ad magified b real ad poit d real, upright, ad magified 10 All of the followig images ca be formed by a covergig les except which oe? a image at ifiity c real, iverted, ad same size b virtual, iverted, ad same size d real, iverted, ad reduced 11 How may focal poits ad focal legths do covergig ad divergig leses have? a two, oe c oe, oe b oe, two d two, two 1
2 Name: ID: A 12 The focal legth for a covergig les is a always positive b always egative c depedet o the locatio of the object d depedet o the locatio of the image 13 A virtual image has a image distace (q) ad is located i of the les a positive, frot c egative, frot b positive, back d egative, back 14 The focal legth for a divergig les is a always positive b always egative c depedet o the locatio of the object d depedet o the locatio of the image 15 A object is placed 200 cm from a thi covergig les alog the axis of the les If a real image forms behid the les at a distace of 800 cm from the les, what is the focal legth of the les? a 571 cm c 133 cm b 120 cm d 133 cm 16 A object is placed 140 cm from a divergig les If a virtual image appears 100 cm from the les o the same side as the object, what is the focal legth of the les? a 50 cm c 58 cm b 34 cm d 16 cm 17 A film projector produces a 151 m image of a horse o a scree If the projector les is 400 m from the scree ad the size of the horse o the film is 107 cm, what is the magitude of the magificatio of the image? a 141 c 0708 b 141 d A object that is 18 cm from a covergig les forms a real image 225 cm from the les What is the magificatio of the image? a 125 c 080 b 080 d I the diagram of a compoud microscope show above, where would you place the slide? a at O c at F 0 b at I 2 d at I 1 2
3 Name: ID: A 20 Which is ot correct whe describig the formatio of raibows? a A raibow is really spherical i ature b Sulight is spread ito a spectrum whe it eters a spherical raidrop c Sulight is iterally reflected o the back side of a raidrop d All wavelegths refract at the same agle Short Aswer 21 What is the positio ad kid of image produced by the les show above? Draw a ray diagram to support your aswer 22 A studet burs a hole i a pecil with a magifyig les What is the positio ad kid of image produced by the les? Draw a ray diagram to support your aswer 23 What is the positio ad kid of image produced by the les show above? Draw a ray diagram to support your aswer 3
4 Name: ID: A Problem 24 What is the positio ad kid of image produced by the les show above? Draw a ray diagram to support your aswer 25 Uder what coditios is the thi-les equatio applicable for determiig object distace, image distace, ad focal legth? 26 A real image has a() image distace (p) ad is located i of the les 27 A object is placed 400 cm from a covergig les alog the axis of the les If a virtual image forms at a distace of 500 cm from the les o the same side as the object, what is the focal legth of the les? 28 What does a positive magificatio sigify? 29 What does the perceived color of each water droplet i a raibow deped o? 30 A ray of light passes from air ito carbo disulfide ( = 163) at a agle of 280 to the ormal What is the refracted agle? 31 A ray of light passes from air ito cubic zircoia at a agle of 560 to the ormal The agle of refractio is 220 What is the idex of refractio of cubic zircoia? 32 A ray of light passes from air ito ice ( = 1309) at a agle of 460 to the ormal The refracted ray of light the passes from ice ito glycerie ( = 1473) What is the agle of refractio of the ray of light i glycerie? 33 A ray of light passes from air ito carbo disulfide ( = 1628) at a agle of 550 to the ormal The refracted ray of light the passes from carbo disulfide ito water ( = 1333) What is the refracted agle i the water? 34 A covergig les has a focal legth of 100 cm If a virtual image of a object is formed 250 cm i frot of the les, what is the magificatio of the image? Describe the image 35 A cadle that is 100 cm high is placed 300 cm i frot of a divergig les The les has a focal legth of 200 cm What is the height of the image? 36 A ray of light travels across a liquid-to-glass iterface The idex of refractio is 175 for the liquid ad 152 for the glass If the light meets the iterface at a agle of 59, predict whether the light will refract or whether it will udergo total iteral reflectio 4
5 AP B mirrors ad leses websheet 232 Aswer Sectio MULTIPLE CHOICE 1 C 2 A 3 A 4 B 5 D 6 A 7 C 8 D 9 D 10 B 11 A 12 A 13 C 14 B 15 A 16 B 17 A 18 A 19 A 20 D SHORT ANSWER 21 A real, iverted image that is smaller tha the object will form betwee F ad 2F 1
6 22 A real, poit image will form at F 23 A real, iverted image that is the same size as the object will form at 2F 24 A real, iverted image that is larger tha the object will form outside 2F 25 whe the les thickess is much smaller tha the focal legth 26 positive, back 27 Give p = 400 cm q = 500 cm Áq is egative,sice the image is virtual ad i frot of the lesˆ Use the thi-les equatio to fid f 1 f = 1 p + 1 q = cm cm = cm cm = cm f = cm Ápositive focal legth is cosistet with a covergig lesˆ 2
7 28 The image is upright ad virtual 29 The perceived color depeds o the agle at which that drop is viewed PROBLEM Give θ i = 280 i = 100 r = 163 Rearrage Sell s law, i siθ i = r siθ r, ad solve for θ r θ r = si 1 i 1 siθ Á i ˆ = si 100 si 280 r 163 ( ) = Give θ i = 560 θ r = 220 i = 100 Rearrage Sell s law, i siθ i = r siθ r, ad solve for r Ásiθ i ˆ ( si 560 ) r = i = ( 100) Á siθr ˆ ( si 220 ) = 221 3
8 Give θ i = 460 air = 1000 ice = 1309 glycerie = 1473 First, determie the agle of refractio i ice Rearrage Sell s law, i siθ i = r siθ r, ad solve for θ r θ r(ice) = si 1 i siθ Á i ˆ = si 1 air 1 siθ r Á i ˆ = si 1000 si 460 ice 1309 ( ) = 333 Secod,use θ r(ice) as the agle of icidece for the ice-glycerie boudary ad solve for θ r(glycerie) θ r(glycerie) = si Give θ i = 550 air = 1000 i r carbo disulfide = 1628 water = 1333 Ásiθ i ˆ = si 1 ice glycerie Á siθ r(ice) ˆ 1 = si 1309 si ( ) = 292 First, determie the agle of refractio i carbo disulfide Rearrage Sell s law, i siθ i = r siθ r, ad solve for θ r θ r(carbo disulfide) = si 1 i siθ i Á ˆ = si 1 air siθ i r Á ˆ = si si 550 carbo disulfide 1628 ( ) = 302 Secod, use θ r(carbo disulfide) as the agle of icidece for the carbo disulfide-water boudary ad solve for θ r(water) θ r(water) = si 1 i r Á siθ i ˆ = si 1 carbo disulfide Á water siθ r(carbo disulfide) ˆ = si si ( ) = 387 4
9 The image is three ad a half times larger tha the object Sice M is positive, the image is virtual ad upright Give f = 100 cm (sice this is a covergig les,the focal legth is positive) q = 250 cm (sice the image is located i frot of the les,q is egative) First,rearrage the thi-les equatio, 1 p + 1 q = 1 f,to fid p 1 p = 1 f 1 q = cm cm = cm cm = cm p = 714 cm Use the magificatio of a les equatio,m = q,to fid M p M = q = ( 250 cm ) = 350 p ( 714 cm) The image is three ad a half times larger tha the object Sice M is positive, the image is virtual ad upright cm Give h = 100 cm p = 300 cm f = 200 cm (sice this is a divergig les,the focal legth is egative) First,rearrage the thi-les equatio, 1 p + 1 q = 1 f,to fid q 1 q = 1 f 1 p = cm cm = cm cm = cm q = 120 cm Rearrage the magificatio of a les equatio,m = hʹ h = q,ad solve for hʹ p hʹ = qh p ( 120 cm ) 100 cm = ( ) ( 300 cm) = 400 cm 5
10 36 Sice the agle of icidece, 59, is less tha the critical agle, 603, the light ray will refract Give liquid = 175 glass = 152 θ i = 59 Rearrage the critical agle equatio,si θ c = r i,to fid θ c θ c = si 1 Á r i ˆ 1 = si Á glass liquid ˆ = si ˆ Á 175 = 603 Sice the agle of icidece is less tha the critical agle,the light ray will refract 6
Chapter 18: Ray Optics Questions & Problems
 Chapter 18: Ray Optics Questios & Problems c -1 2 1 1 1 h s θr= θi 1siθ 1 = 2si θ 2 = θ c = si ( ) + = m = = v s s f h s 1 Example 18.1 At high oo, the su is almost directly above (about 2.0 o from the
Chapter 18: Ray Optics Questios & Problems c -1 2 1 1 1 h s θr= θi 1siθ 1 = 2si θ 2 = θ c = si ( ) + = m = = v s s f h s 1 Example 18.1 At high oo, the su is almost directly above (about 2.0 o from the
Final Exam information
 Fial Exam iformatio Wedesday, Jue 6, 2012, 9:30 am - 11:18 am Locatio: i recitatio room Comprehesive (covers all course material) 35 multiple-choice questios --> 175 poits Closed book ad otes Make up your
Fial Exam iformatio Wedesday, Jue 6, 2012, 9:30 am - 11:18 am Locatio: i recitatio room Comprehesive (covers all course material) 35 multiple-choice questios --> 175 poits Closed book ad otes Make up your
The Nature of Light. Chapter 22. Geometric Optics Using a Ray Approximation. Ray Approximation
 The Nature of Light Chapter Reflectio ad Refractio of Light Sectios: 5, 8 Problems: 6, 7, 4, 30, 34, 38 Particles of light are called photos Each photo has a particular eergy E = h ƒ h is Plack s costat
The Nature of Light Chapter Reflectio ad Refractio of Light Sectios: 5, 8 Problems: 6, 7, 4, 30, 34, 38 Particles of light are called photos Each photo has a particular eergy E = h ƒ h is Plack s costat
Spherical Mirrors. Types of spherical mirrors. Lecture convex mirror: the. geometrical center is on the. opposite side of the mirror as
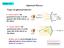 Lecture 14-1 Spherical Mirrors Types of spherical mirrors covex mirror: the geometrical ceter is o the opposite side of the mirror as the object. cocave mirror: the geometrical ceter is o the same side
Lecture 14-1 Spherical Mirrors Types of spherical mirrors covex mirror: the geometrical ceter is o the opposite side of the mirror as the object. cocave mirror: the geometrical ceter is o the same side
27 Refraction, Dispersion, Internal Reflection
 Chapter 7 Refractio, Dispersio, Iteral Reflectio 7 Refractio, Dispersio, Iteral Reflectio Whe we talked about thi film iterferece, we said that whe light ecouters a smooth iterface betwee two trasparet
Chapter 7 Refractio, Dispersio, Iteral Reflectio 7 Refractio, Dispersio, Iteral Reflectio Whe we talked about thi film iterferece, we said that whe light ecouters a smooth iterface betwee two trasparet
Apparent Depth. B' l'
 REFRACTION by PLANE SURFACES Apparet Depth Suppose we have a object B i a medium of idex which is viewed from a medium of idex '. If '
REFRACTION by PLANE SURFACES Apparet Depth Suppose we have a object B i a medium of idex which is viewed from a medium of idex '. If '
Lenses and imaging. MIT 2.71/ /10/01 wk2-a-1
 Leses ad imagig Huyges priciple ad why we eed imagig istrumets A simple imagig istrumet: the pihole camera Priciple of image formatio usig leses Quatifyig leses: paraial approimatio & matri approach Focusig
Leses ad imagig Huyges priciple ad why we eed imagig istrumets A simple imagig istrumet: the pihole camera Priciple of image formatio usig leses Quatifyig leses: paraial approimatio & matri approach Focusig
Lenses and Imaging (Part I) Parabloid mirror: perfect focusing
 Leses ad Imagig (Part I) eview: paraboloid reflector, focusig Why is imagig ecessary: Huyges priciple Spherical & parallel ray budles, poits at ifiity efractio at spherical surfaces (paraial approimatio)
Leses ad Imagig (Part I) eview: paraboloid reflector, focusig Why is imagig ecessary: Huyges priciple Spherical & parallel ray budles, poits at ifiity efractio at spherical surfaces (paraial approimatio)
Lenses and Imaging (Part I)
 Leses ad Imagig (Part I) Why is imagig ecessary: Huyge s priciple Spherical & parallel ray budles, poits at ifiity efractio at spherical surfaces (paraial approimatio) Optical power ad imagig coditio Matri
Leses ad Imagig (Part I) Why is imagig ecessary: Huyge s priciple Spherical & parallel ray budles, poits at ifiity efractio at spherical surfaces (paraial approimatio) Optical power ad imagig coditio Matri
Physics 11b Lecture #19
 Physics b Lecture #9 Geometrical Optics S&J Chapter 34, 35 What We Did Last Time Itesity (power/area) of EM waves is give by the Poytig vector See slide #5 of Lecture #8 for a summary EM waves are produced
Physics b Lecture #9 Geometrical Optics S&J Chapter 34, 35 What We Did Last Time Itesity (power/area) of EM waves is give by the Poytig vector See slide #5 of Lecture #8 for a summary EM waves are produced
Lecture 7 7 Refraction and Snell s Law Reading Assignment: Read Kipnis Chapter 4 Refraction of Light, Section III, IV
 Lecture 7 7 Refractio ad Sell s Law Readig Assigmet: Read Kipis Chapter 4 Refractio of Light, Sectio III, IV 7. History I Eglish-speakig coutries, the law of refractio is kow as Sell s Law, after the Dutch
Lecture 7 7 Refractio ad Sell s Law Readig Assigmet: Read Kipis Chapter 4 Refractio of Light, Sectio III, IV 7. History I Eglish-speakig coutries, the law of refractio is kow as Sell s Law, after the Dutch
. Perform a geometric (ray-optics) construction (i.e., draw in the rays on the diagram) to show where the final image is formed.
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Departmet of Electrical Egieerig ad Computer Sciece 6.161 Moder Optics Project Laboratory 6.637 Optical Sigals, Devices & Systems Problem Set No. 1 Geometric optics
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Departmet of Electrical Egieerig ad Computer Sciece 6.161 Moder Optics Project Laboratory 6.637 Optical Sigals, Devices & Systems Problem Set No. 1 Geometric optics
Propagation of light: rays versus wave fronts; geometrical and physical optics
 Propagatio of light: rays versus wave frots; geometrical ad physical optics A ray is a imagiary lie alog the directio of propagatio of the light wave: this lie is perpedicular to the wave frot If descriptio
Propagatio of light: rays versus wave frots; geometrical ad physical optics A ray is a imagiary lie alog the directio of propagatio of the light wave: this lie is perpedicular to the wave frot If descriptio
Aberrations in Lens & Mirrors (Hecht 6.3)
 Aberratios i Les & Mirrors (Hecht 6.3) Aberratios are failures to focus to a "poit" Both mirrors ad les suffer from these Some are failures of paraxial assumptio 3 5 θ θ si( θ ) = θ + L 3! 5! Paraxial
Aberratios i Les & Mirrors (Hecht 6.3) Aberratios are failures to focus to a "poit" Both mirrors ad les suffer from these Some are failures of paraxial assumptio 3 5 θ θ si( θ ) = θ + L 3! 5! Paraxial
Get Solution of These Packages & Learn by Video Tutorials on GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
 . CONDITION FOR F RECTILINEAR PROP OPAGATION OF LIGHT : (ONLY FORF INFORMA ORMATION NOTE IN JEE SYLLABUS) Some part of the optics ca be uderstood if we assume that light travels i a straight lie ad it
. CONDITION FOR F RECTILINEAR PROP OPAGATION OF LIGHT : (ONLY FORF INFORMA ORMATION NOTE IN JEE SYLLABUS) Some part of the optics ca be uderstood if we assume that light travels i a straight lie ad it
Basic Optics: Index of Refraction
 Basic Optics: Idex of Refractio Deser materials have lower speeds of light Idex of Refractio = where c = speed of light i vacuum v = velocity i medium Eve small chages ca create differece i Higher idex
Basic Optics: Idex of Refractio Deser materials have lower speeds of light Idex of Refractio = where c = speed of light i vacuum v = velocity i medium Eve small chages ca create differece i Higher idex
Section 4. Imaging and Paraxial Optics
 4-1 Sectio 4 Imagig ad Paraxial Optics Optical Sstems A optical sstem is a collectio of optical elemets (leses ad mirrors). While the optical sstem ca cotai multiple optical elemets, the first order properties
4-1 Sectio 4 Imagig ad Paraxial Optics Optical Sstems A optical sstem is a collectio of optical elemets (leses ad mirrors). While the optical sstem ca cotai multiple optical elemets, the first order properties
Section 4. Imaging and Paraxial Optics
 Sectio 4 Imagig ad Paraxial Optics 4- Optical Sstems A optical sstem is a collectio of optical elemets (leses ad mirrors). While the optical sstem ca cotai multiple optical elemets, the first order properties
Sectio 4 Imagig ad Paraxial Optics 4- Optical Sstems A optical sstem is a collectio of optical elemets (leses ad mirrors). While the optical sstem ca cotai multiple optical elemets, the first order properties
EE 584 MACHINE VISION
 METU EE 584 Lecture Notes by A.Aydi ALATAN 0 EE 584 MACHINE VISION Itroductio elatio with other areas Image Formatio & Sesig Projectios Brightess Leses Image Sesig METU EE 584 Lecture Notes by A.Aydi ALATAN
METU EE 584 Lecture Notes by A.Aydi ALATAN 0 EE 584 MACHINE VISION Itroductio elatio with other areas Image Formatio & Sesig Projectios Brightess Leses Image Sesig METU EE 584 Lecture Notes by A.Aydi ALATAN
COMP 558 lecture 6 Sept. 27, 2010
 Radiometry We have discussed how light travels i straight lies through space. We would like to be able to talk about how bright differet light rays are. Imagie a thi cylidrical tube ad cosider the amout
Radiometry We have discussed how light travels i straight lies through space. We would like to be able to talk about how bright differet light rays are. Imagie a thi cylidrical tube ad cosider the amout
RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
 9 AY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTUMENTS Optics is the brach of Physics which deals with the study of light. ay optics is based o the rectiliear propagatio of light ad the laws of reflectio ad refractio. Laws
9 AY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTUMENTS Optics is the brach of Physics which deals with the study of light. ay optics is based o the rectiliear propagatio of light ad the laws of reflectio ad refractio. Laws
Übungsblatt 2 Geometrische und Technische Optik WS 2012/2013
 Übugsblatt 2 Geometrische u Techische Optik WS 202/203 Eie icke Lise besteht aus zwei sphärische Grezfläche mit e beie Krümmugsraie R u R 2, ie eie Absta habe. Die Brechzahle vor er Lise, i er Lise u ach
Übugsblatt 2 Geometrische u Techische Optik WS 202/203 Eie icke Lise besteht aus zwei sphärische Grezfläche mit e beie Krümmugsraie R u R 2, ie eie Absta habe. Die Brechzahle vor er Lise, i er Lise u ach
Physics 30 Lesson 12 Diffraction Gratings
 Physics 30 Lesso 2 Diffractio Gratigs I. Poisso s bright spot Thoas Youg published the results fro his double-slit experiet (Lesso ) i 807 which put the wave theory of light o a fir footig. However, so
Physics 30 Lesso 2 Diffractio Gratigs I. Poisso s bright spot Thoas Youg published the results fro his double-slit experiet (Lesso ) i 807 which put the wave theory of light o a fir footig. However, so
Bezier curves. Figure 2 shows cubic Bezier curves for various control points. In a Bezier curve, only
 Edited: Yeh-Liag Hsu (998--; recommeded: Yeh-Liag Hsu (--9; last updated: Yeh-Liag Hsu (9--7. Note: This is the course material for ME55 Geometric modelig ad computer graphics, Yua Ze Uiversity. art of
Edited: Yeh-Liag Hsu (998--; recommeded: Yeh-Liag Hsu (--9; last updated: Yeh-Liag Hsu (9--7. Note: This is the course material for ME55 Geometric modelig ad computer graphics, Yua Ze Uiversity. art of
EVALUATION OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 EVALUATION OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Whe first exposed to trigoometric fuctios i high school studets are expected to memorize the values of the trigoometric fuctios of sie cosie taget for the special
EVALUATION OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Whe first exposed to trigoometric fuctios i high school studets are expected to memorize the values of the trigoometric fuctios of sie cosie taget for the special
Field Guide to. Geometrical Optics. John E. Greivenkamp. University of Arizona. SPIE Field Guides Volume FG01. John E. Greivenkamp, Series Editor
 Field Guide to Geometrical Optics Joh E. Greivekamp Uiversity of Arizoa SPIE Field Guides Volume FG01 Joh E. Greivekamp, Series Editor Belligham, Washigto USA Library of Cogress Catalogig-i-Publicatio
Field Guide to Geometrical Optics Joh E. Greivekamp Uiversity of Arizoa SPIE Field Guides Volume FG01 Joh E. Greivekamp, Series Editor Belligham, Washigto USA Library of Cogress Catalogig-i-Publicatio
How to Select the Best Refractive Index
 How to Select the Best Refractive Idex Jeffrey Bodycomb, Ph.D. HORIBA Scietific www.horiba.com/us/particle 2013HORIBA, Ltd. All rights reserved. Outlie Laser Diffractio Calculatios Importace of Refractive
How to Select the Best Refractive Idex Jeffrey Bodycomb, Ph.D. HORIBA Scietific www.horiba.com/us/particle 2013HORIBA, Ltd. All rights reserved. Outlie Laser Diffractio Calculatios Importace of Refractive
Algebra Based Physics
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Performance Plus Software Parameter Definitions
 Performace Plus+ Software Parameter Defiitios/ Performace Plus Software Parameter Defiitios Chapma Techical Note-TG-5 paramete.doc ev-0-03 Performace Plus+ Software Parameter Defiitios/2 Backgroud ad Defiitios
Performace Plus+ Software Parameter Defiitios/ Performace Plus Software Parameter Defiitios Chapma Techical Note-TG-5 paramete.doc ev-0-03 Performace Plus+ Software Parameter Defiitios/2 Backgroud ad Defiitios
Mirrors and Lenses - Ch 23 websheet 23.1
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Mirrors and Lenses - Ch 23 websheet 23. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What type of mirror is used whenever
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Mirrors and Lenses - Ch 23 websheet 23. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What type of mirror is used whenever
Lens Design II. Lecture 5: Field flattening Herbert Gross. Winter term
 Les Desig II Lecture 5: Field flatteig 05-8-0 Herbert Gross Witer term 05 www.iap.ui-ea.de Prelimiary Schedule 0.0. Aberratios ad optimizatio Repetitio 7.0. Structural modificatios Zero operads, les splittig,
Les Desig II Lecture 5: Field flatteig 05-8-0 Herbert Gross Witer term 05 www.iap.ui-ea.de Prelimiary Schedule 0.0. Aberratios ad optimizatio Repetitio 7.0. Structural modificatios Zero operads, les splittig,
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Today Last Time Recall from last time. Reflection: q i = q r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Today Last Time Recall from last time. Reflection: q i = q r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
LIGHT. Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses
 LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
The isoperimetric problem on the hypercube
 The isoperimetric problem o the hypercube Prepared by: Steve Butler November 2, 2005 1 The isoperimetric problem We will cosider the -dimesioal hypercube Q Recall that the hypercube Q is a graph whose
The isoperimetric problem o the hypercube Prepared by: Steve Butler November 2, 2005 1 The isoperimetric problem We will cosider the -dimesioal hypercube Q Recall that the hypercube Q is a graph whose
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction
 Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
World Scientific Research Journal (WSRJ) ISSN: Research on Fresnel Lens Optical Receiving Antenna in Indoor Visible
 World Scietific Research Joural (WSRJ) ISSN: 2472-3703 www.wsr-j.org Research o Fresel Les Optical Receivig Atea i Idoor Visible Light Commuicatio Zhihua Du College of Electroics Egieerig, Chogqig Uiversity
World Scietific Research Joural (WSRJ) ISSN: 2472-3703 www.wsr-j.org Research o Fresel Les Optical Receivig Atea i Idoor Visible Light Commuicatio Zhihua Du College of Electroics Egieerig, Chogqig Uiversity
General Physics II. Mirrors & Lenses
 General Physics II Mirrors & Lenses Nothing New! For the next several lectures we will be studying geometrical optics. You already know the fundamentals of what is going on!!! Reflection: θ 1 = θ r incident
General Physics II Mirrors & Lenses Nothing New! For the next several lectures we will be studying geometrical optics. You already know the fundamentals of what is going on!!! Reflection: θ 1 = θ r incident
Area As A Limit & Sigma Notation
 Area As A Limit & Sigma Notatio SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: As you work through the problems listed below, you should referece Chapter 5.4 of the recommeded textbook (or the equivalet chapter i your
Area As A Limit & Sigma Notatio SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: As you work through the problems listed below, you should referece Chapter 5.4 of the recommeded textbook (or the equivalet chapter i your
Normals. In OpenGL the normal vector is part of the state Set by glnormal*()
 Ray Tracig 1 Normals OpeG the ormal vector is part of the state Set by glnormal*() -glnormal3f(x, y, z); -glnormal3fv(p); Usually we wat to set the ormal to have uit legth so cosie calculatios are correct
Ray Tracig 1 Normals OpeG the ormal vector is part of the state Set by glnormal*() -glnormal3f(x, y, z); -glnormal3fv(p); Usually we wat to set the ormal to have uit legth so cosie calculatios are correct
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it?
 What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
Lecture # 09: Flow visualization techniques: schlieren and shadowgraphy
 AerE 344 Lecture Notes Lecture # 9: Flow visualizatio techiques: schliere ad shadowgraph Dr. Hui Hu Dr. Re M Waldma Departmet of Aerospace Egieerig owa State Uiversit Ames, owa 5, U.S.A Sources/ Further
AerE 344 Lecture Notes Lecture # 9: Flow visualizatio techiques: schliere ad shadowgraph Dr. Hui Hu Dr. Re M Waldma Departmet of Aerospace Egieerig owa State Uiversit Ames, owa 5, U.S.A Sources/ Further
Examples and Applications of Binary Search
 Toy Gog ITEE Uiersity of Queeslad I the secod lecture last week we studied the biary search algorithm that soles the problem of determiig if a particular alue appears i a sorted list of iteger or ot. We
Toy Gog ITEE Uiersity of Queeslad I the secod lecture last week we studied the biary search algorithm that soles the problem of determiig if a particular alue appears i a sorted list of iteger or ot. We
AP Physics: Curved Mirrors and Lenses
 The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Recall from last time. Today Last Time Reflection: θ i = θ r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Physics 102: Lecture 17 Reflection and Refraction of Light Physics 102: Lecture 17, Slide 1 Recall from last time. Today Last Time Reflection: θ i = θ r Flat Mirror: image equidistant behind Spherical
Unit 9 Light & Optics
 Unit 9 Light & Optics 1 A quick review of the properties of light. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation Light travels as transverse waves having wavelength and frequency. fλ=c The velocity of EMR
Unit 9 Light & Optics 1 A quick review of the properties of light. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation Light travels as transverse waves having wavelength and frequency. fλ=c The velocity of EMR
CS Polygon Scan Conversion. Slide 1
 CS 112 - Polygo Sca Coversio Slide 1 Polygo Classificatio Covex All iterior agles are less tha 180 degrees Cocave Iterior agles ca be greater tha 180 degrees Degeerate polygos If all vertices are colliear
CS 112 - Polygo Sca Coversio Slide 1 Polygo Classificatio Covex All iterior agles are less tha 180 degrees Cocave Iterior agles ca be greater tha 180 degrees Degeerate polygos If all vertices are colliear
Parametric curves. Reading. Parametric polynomial curves. Mathematical curve representation. Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2015
 Readig Required: Agel 0.-0.3, 0.5., 0.6-0.7, 0.9 Parametric curves Bria Curless CSE 457 Sprig 05 Optioal Bartels, Beatty, ad Barsy. A Itroductio to Splies for use i Computer Graphics ad Geometric Modelig,
Readig Required: Agel 0.-0.3, 0.5., 0.6-0.7, 0.9 Parametric curves Bria Curless CSE 457 Sprig 05 Optioal Bartels, Beatty, ad Barsy. A Itroductio to Splies for use i Computer Graphics ad Geometric Modelig,
Normal Distributions
 Normal Distributios Stacey Hacock Look at these three differet data sets Each histogram is overlaid with a curve : A B C A) Weights (g) of ewly bor lab rat pups B) Mea aual temperatures ( F ) i A Arbor,
Normal Distributios Stacey Hacock Look at these three differet data sets Each histogram is overlaid with a curve : A B C A) Weights (g) of ewly bor lab rat pups B) Mea aual temperatures ( F ) i A Arbor,
OCR Statistics 1. Working with data. Section 3: Measures of spread
 Notes ad Eamples OCR Statistics 1 Workig with data Sectio 3: Measures of spread Just as there are several differet measures of cetral tedec (averages), there are a variet of statistical measures of spread.
Notes ad Eamples OCR Statistics 1 Workig with data Sectio 3: Measures of spread Just as there are several differet measures of cetral tedec (averages), there are a variet of statistical measures of spread.
Intro to Scientific Computing: Solutions
 Itro to Scietific Computig: Solutios Dr. David M. Goulet. How may steps does it take to separate 3 objects ito groups of 4? We start with 5 objects ad apply 3 steps of the algorithm to reduce the pile
Itro to Scietific Computig: Solutios Dr. David M. Goulet. How may steps does it take to separate 3 objects ito groups of 4? We start with 5 objects ad apply 3 steps of the algorithm to reduce the pile
Alpha Individual Solutions MAΘ National Convention 2013
 Alpha Idividual Solutios MAΘ Natioal Covetio 0 Aswers:. D. A. C 4. D 5. C 6. B 7. A 8. C 9. D 0. B. B. A. D 4. C 5. A 6. C 7. B 8. A 9. A 0. C. E. B. D 4. C 5. A 6. D 7. B 8. C 9. D 0. B TB. 570 TB. 5
Alpha Idividual Solutios MAΘ Natioal Covetio 0 Aswers:. D. A. C 4. D 5. C 6. B 7. A 8. C 9. D 0. B. B. A. D 4. C 5. A 6. C 7. B 8. A 9. A 0. C. E. B. D 4. C 5. A 6. D 7. B 8. C 9. D 0. B TB. 570 TB. 5
The Graphs of Polynomial Functions
 Sectio 4.3 The Graphs of Polyomial Fuctios Objective 1: Uderstadig the Defiitio of a Polyomial Fuctio Defiitio Polyomial Fuctio 1 2 The fuctio ax a 1x a 2x a1x a0 is a polyomial fuctio of degree where
Sectio 4.3 The Graphs of Polyomial Fuctios Objective 1: Uderstadig the Defiitio of a Polyomial Fuctio Defiitio Polyomial Fuctio 1 2 The fuctio ax a 1x a 2x a1x a0 is a polyomial fuctio of degree where
Computer Science Foundation Exam. August 12, Computer Science. Section 1A. No Calculators! KEY. Solutions and Grading Criteria.
 Computer Sciece Foudatio Exam August, 005 Computer Sciece Sectio A No Calculators! Name: SSN: KEY Solutios ad Gradig Criteria Score: 50 I this sectio of the exam, there are four (4) problems. You must
Computer Sciece Foudatio Exam August, 005 Computer Sciece Sectio A No Calculators! Name: SSN: KEY Solutios ad Gradig Criteria Score: 50 I this sectio of the exam, there are four (4) problems. You must
Chapter 11. Friends, Overloaded Operators, and Arrays in Classes. Copyright 2014 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 11 Frieds, Overloaded Operators, ad Arrays i Classes Copyright 2014 Pearso Addiso-Wesley. All rights reserved. Overview 11.1 Fried Fuctios 11.2 Overloadig Operators 11.3 Arrays ad Classes 11.4
Chapter 11 Frieds, Overloaded Operators, ad Arrays i Classes Copyright 2014 Pearso Addiso-Wesley. All rights reserved. Overview 11.1 Fried Fuctios 11.2 Overloadig Operators 11.3 Arrays ad Classes 11.4
ENGI 4421 Probability and Statistics Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 1 Descriptive Statistics
 ENGI 44 Probability ad Statistics Faculty of Egieerig ad Applied Sciece Problem Set Descriptive Statistics. If, i the set of values {,, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 } a error causes the value 5 to be replaced by 50,
ENGI 44 Probability ad Statistics Faculty of Egieerig ad Applied Sciece Problem Set Descriptive Statistics. If, i the set of values {,, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 } a error causes the value 5 to be replaced by 50,
Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend...
 SNC 2DI - 10.2 Properties of Light and Reflection Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend... Reflection : Light travels in a straight line as long
SNC 2DI - 10.2 Properties of Light and Reflection Light travels in straight lines, this is referred to as... this means that light does not bend... Reflection : Light travels in a straight line as long
OpenGL Illumination example. 2IV60 Computer graphics set 8: Illumination Models and Surface-Rendering Methods. Introduction 2.
 OpeG Illumiatio example 2I60 Computer graphics set 8: Illumiatio Models ad Surface-ederig Methods Jack va Wijk TU/e Glfloat lightpos[] = {2.0, 0.0, 3.0, 0.0}; Glfloat whitecolor[] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0};
OpeG Illumiatio example 2I60 Computer graphics set 8: Illumiatio Models ad Surface-ederig Methods Jack va Wijk TU/e Glfloat lightpos[] = {2.0, 0.0, 3.0, 0.0}; Glfloat whitecolor[] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0};
PLEASURE TEST SERIES (XI) - 04 By O.P. Gupta (For stuffs on Math, click at theopgupta.com)
 wwwtheopguptacom wwwimathematiciacom For all the Math-Gya Buy books by OP Gupta A Compilatio By : OP Gupta (WhatsApp @ +9-9650 350 0) For more stuffs o Maths, please visit : wwwtheopguptacom Time Allowed
wwwtheopguptacom wwwimathematiciacom For all the Math-Gya Buy books by OP Gupta A Compilatio By : OP Gupta (WhatsApp @ +9-9650 350 0) For more stuffs o Maths, please visit : wwwtheopguptacom Time Allowed
Investigation Monitoring Inventory
 Ivestigatio Moitorig Ivetory Name Period Date Art Smith has bee providig the prits of a egravig to FieArt Gallery. He plas to make just 2000 more prits. FieArt has already received 70 of Art s prits. The
Ivestigatio Moitorig Ivetory Name Period Date Art Smith has bee providig the prits of a egravig to FieArt Gallery. He plas to make just 2000 more prits. FieArt has already received 70 of Art s prits. The
Using the Keyboard. Using the Wireless Keyboard. > Using the Keyboard
 1 A wireless keyboard is supplied with your computer. The wireless keyboard uses a stadard key arragemet with additioal keys that perform specific fuctios. Usig the Wireless Keyboard Two AA alkalie batteries
1 A wireless keyboard is supplied with your computer. The wireless keyboard uses a stadard key arragemet with additioal keys that perform specific fuctios. Usig the Wireless Keyboard Two AA alkalie batteries
The Law of Reflection
 If the surface off which the light is reflected is smooth, then the light undergoes specular reflection (parallel rays will all be reflected in the same directions). If, on the other hand, the surface
If the surface off which the light is reflected is smooth, then the light undergoes specular reflection (parallel rays will all be reflected in the same directions). If, on the other hand, the surface
Pattern Recognition Systems Lab 1 Least Mean Squares
 Patter Recogitio Systems Lab 1 Least Mea Squares 1. Objectives This laboratory work itroduces the OpeCV-based framework used throughout the course. I this assigmet a lie is fitted to a set of poits usig
Patter Recogitio Systems Lab 1 Least Mea Squares 1. Objectives This laboratory work itroduces the OpeCV-based framework used throughout the course. I this assigmet a lie is fitted to a set of poits usig
Lighting and Shading. Outline. Raytracing Example. Global Illumination. Local Illumination. Radiosity Example
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Lightig ad Shadig Light Sources Phog Illumiatio Model Normal Vectors [Agel Ch. 6.1-6.4] February 13, 2013 Jerej Barbic Uiversity of Souther Califoria http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s13/
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Lightig ad Shadig Light Sources Phog Illumiatio Model Normal Vectors [Agel Ch. 6.1-6.4] February 13, 2013 Jerej Barbic Uiversity of Souther Califoria http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s13/
UNIT 4 Section 8 Estimating Population Parameters using Confidence Intervals
 UNIT 4 Sectio 8 Estimatig Populatio Parameters usig Cofidece Itervals To make ifereces about a populatio that caot be surveyed etirely, sample statistics ca be take from a SRS of the populatio ad used
UNIT 4 Sectio 8 Estimatig Populatio Parameters usig Cofidece Itervals To make ifereces about a populatio that caot be surveyed etirely, sample statistics ca be take from a SRS of the populatio ad used
Computational Geometry
 Computatioal Geometry Chapter 4 Liear programmig Duality Smallest eclosig disk O the Ageda Liear Programmig Slides courtesy of Craig Gotsma 4. 4. Liear Programmig - Example Defie: (amout amout cosumed
Computatioal Geometry Chapter 4 Liear programmig Duality Smallest eclosig disk O the Ageda Liear Programmig Slides courtesy of Craig Gotsma 4. 4. Liear Programmig - Example Defie: (amout amout cosumed
Homework 1 Solutions MA 522 Fall 2017
 Homework 1 Solutios MA 5 Fall 017 1. Cosider the searchig problem: Iput A sequece of umbers A = [a 1,..., a ] ad a value v. Output A idex i such that v = A[i] or the special value NIL if v does ot appear
Homework 1 Solutios MA 5 Fall 017 1. Cosider the searchig problem: Iput A sequece of umbers A = [a 1,..., a ] ad a value v. Output A idex i such that v = A[i] or the special value NIL if v does ot appear
Numerical Methods Lecture 6 - Curve Fitting Techniques
 Numerical Methods Lecture 6 - Curve Fittig Techiques Topics motivatio iterpolatio liear regressio higher order polyomial form expoetial form Curve fittig - motivatio For root fidig, we used a give fuctio
Numerical Methods Lecture 6 - Curve Fittig Techiques Topics motivatio iterpolatio liear regressio higher order polyomial form expoetial form Curve fittig - motivatio For root fidig, we used a give fuctio
Using VTR Emulation on Avid Systems
 Usig VTR Emulatio o Avid Systems VTR emulatio allows you to cotrol a sequece loaded i the Record moitor from a edit cotroller for playback i the edit room alog with other sources. I this sceario the edit
Usig VTR Emulatio o Avid Systems VTR emulatio allows you to cotrol a sequece loaded i the Record moitor from a edit cotroller for playback i the edit room alog with other sources. I this sceario the edit
Parabolic Path to a Best Best-Fit Line:
 Studet Activity : Fidig the Least Squares Regressio Lie By Explorig the Relatioship betwee Slope ad Residuals Objective: How does oe determie a best best-fit lie for a set of data? Eyeballig it may be
Studet Activity : Fidig the Least Squares Regressio Lie By Explorig the Relatioship betwee Slope ad Residuals Objective: How does oe determie a best best-fit lie for a set of data? Eyeballig it may be
Light and shading. Source: A. Efros
 Light ad shadig Source: A. Efros Image formatio What determies the brightess of a image piel? Sesor characteristics Light source properties Eposure Surface shape ad orietatio Optics Surface reflectace
Light ad shadig Source: A. Efros Image formatio What determies the brightess of a image piel? Sesor characteristics Light source properties Eposure Surface shape ad orietatio Optics Surface reflectace
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
NTH, GEOMETRIC, AND TELESCOPING TEST
 NTH, GEOMETRIC, AND TELESCOPING TEST Sectio 9. Calculus BC AP/Dual, Revised 08 viet.dag@humbleisd.et /4/08 0:0 PM 9.: th, Geometric, ad Telescopig Test SUMMARY OF TESTS FOR SERIES Lookig at the first few
NTH, GEOMETRIC, AND TELESCOPING TEST Sectio 9. Calculus BC AP/Dual, Revised 08 viet.dag@humbleisd.et /4/08 0:0 PM 9.: th, Geometric, ad Telescopig Test SUMMARY OF TESTS FOR SERIES Lookig at the first few
Optics Course (Phys 311) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses
 Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. Refraction through single spherical refracting surfaces. 2. Lenses:
Optics Course (Phys ) Geometrical Optics Refraction through Lenses Lecturer: Dr Zeina Hashim Slide 1 Objectives covered in this lesson : 1. Refraction through single spherical refracting surfaces. 2. Lenses:
EECS 442 Computer vision. Multiple view geometry Affine structure from Motion
 EECS 442 Computer visio Multiple view geometry Affie structure from Motio - Affie structure from motio problem - Algebraic methods - Factorizatio methods Readig: [HZ] Chapters: 6,4,8 [FP] Chapter: 2 Some
EECS 442 Computer visio Multiple view geometry Affie structure from Motio - Affie structure from motio problem - Algebraic methods - Factorizatio methods Readig: [HZ] Chapters: 6,4,8 [FP] Chapter: 2 Some
The number n of subintervals times the length h of subintervals gives length of interval (b-a).
 Simulator with MadMath Kit: Riema Sums (Teacher s pages) I your kit: 1. GeoGebra file: Ready-to-use projector sized simulator: RiemaSumMM.ggb 2. RiemaSumMM.pdf (this file) ad RiemaSumMMEd.pdf (educator's
Simulator with MadMath Kit: Riema Sums (Teacher s pages) I your kit: 1. GeoGebra file: Ready-to-use projector sized simulator: RiemaSumMM.ggb 2. RiemaSumMM.pdf (this file) ad RiemaSumMMEd.pdf (educator's
Image Segmentation EEE 508
 Image Segmetatio Objective: to determie (etract) object boudaries. It is a process of partitioig a image ito distict regios by groupig together eighborig piels based o some predefied similarity criterio.
Image Segmetatio Objective: to determie (etract) object boudaries. It is a process of partitioig a image ito distict regios by groupig together eighborig piels based o some predefied similarity criterio.
Derivation of perspective stereo projection matrices with depth, shape and magnification consideration
 Derivatio of perspective stereo projectio matrices with depth, shape ad magificatio cosideratio Patrick Oberthür Jauary 2014 This essay will show how to costruct a pair of stereoscopic perspective projectio
Derivatio of perspective stereo projectio matrices with depth, shape ad magificatio cosideratio Patrick Oberthür Jauary 2014 This essay will show how to costruct a pair of stereoscopic perspective projectio
Section 7.2: Direction Fields and Euler s Methods
 Sectio 7.: Directio ields ad Euler s Methods Practice HW from Stewart Tetbook ot to had i p. 5 # -3 9-3 odd or a give differetial equatio we wat to look at was to fid its solutio. I this chapter we will
Sectio 7.: Directio ields ad Euler s Methods Practice HW from Stewart Tetbook ot to had i p. 5 # -3 9-3 odd or a give differetial equatio we wat to look at was to fid its solutio. I this chapter we will
So we find a sample mean but what can we say about the General Education Statistics
 So we fid a ample mea but what ca we ay about the Geeral Educatio Statitic populatio? Cla Note Cofidece Iterval for Populatio Mea (Sectio 9.) We will be doig early the ame tuff a we did i the firt ectio
So we fid a ample mea but what ca we ay about the Geeral Educatio Statitic populatio? Cla Note Cofidece Iterval for Populatio Mea (Sectio 9.) We will be doig early the ame tuff a we did i the firt ectio
Chapter 34. Images. In this chapter we define and classify images, and then classify several basic ways in which they can be produced.
 Chapter 34 Images One of the most important uses of the basic laws governing light is the production of images. Images are critical to a variety of fields and industries ranging from entertainment, security,
Chapter 34 Images One of the most important uses of the basic laws governing light is the production of images. Images are critical to a variety of fields and industries ranging from entertainment, security,
Reading. Parametric curves. Mathematical curve representation. Curves before computers. Required: Angel , , , 11.9.
 Readig Required: Agel.-.3,.5.,.6-.7,.9. Optioal Parametric curves Bartels, Beatty, ad Barsky. A Itroductio to Splies for use i Computer Graphics ad Geometric Modelig, 987. Fari. Curves ad Surfaces for
Readig Required: Agel.-.3,.5.,.6-.7,.9. Optioal Parametric curves Bartels, Beatty, ad Barsky. A Itroductio to Splies for use i Computer Graphics ad Geometric Modelig, 987. Fari. Curves ad Surfaces for
3D Model Retrieval Method Based on Sample Prediction
 20 Iteratioal Coferece o Computer Commuicatio ad Maagemet Proc.of CSIT vol.5 (20) (20) IACSIT Press, Sigapore 3D Model Retrieval Method Based o Sample Predictio Qigche Zhag, Ya Tag* School of Computer
20 Iteratioal Coferece o Computer Commuicatio ad Maagemet Proc.of CSIT vol.5 (20) (20) IACSIT Press, Sigapore 3D Model Retrieval Method Based o Sample Predictio Qigche Zhag, Ya Tag* School of Computer
Coherent effects of flow- and pressure hull of a generic submarine on target scattering in an active sonar performance model
 Coheret effects of flow- ad pressure hull of a geeric submarie o target scatterig i a active soar performace model P. Schippers TNO-D&V-Uderwater Techology, Oude Waalsdorperweg 63, Post Box 96864, 2509
Coheret effects of flow- ad pressure hull of a geeric submarie o target scatterig i a active soar performace model P. Schippers TNO-D&V-Uderwater Techology, Oude Waalsdorperweg 63, Post Box 96864, 2509
Lecture 28: Data Link Layer
 Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) 2. Go ack N ARQ Although the Stop ad Wait ARQ is very simple, you ca easily show that it has very the low efficiecy. The low efficiecy comes from the fact that the trasmittig
Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) 2. Go ack N ARQ Although the Stop ad Wait ARQ is very simple, you ca easily show that it has very the low efficiecy. The low efficiecy comes from the fact that the trasmittig
c) Did doing the transformations in a different order matter? Explain why?
 G.O..5 WORKSHEET #8 geoetrycoocore NME: 1 OMPOSITE TRNSFORMTIONS DOES ORDER MTTER Use the coposite trasforatio to plot ad 1a) T 3,5 r ( ) y axis b) y axis T 3,5 (6,-1) (6,-1) (3,-4) (3,-4) (5,-7) (5,-7)
G.O..5 WORKSHEET #8 geoetrycoocore NME: 1 OMPOSITE TRNSFORMTIONS DOES ORDER MTTER Use the coposite trasforatio to plot ad 1a) T 3,5 r ( ) y axis b) y axis T 3,5 (6,-1) (6,-1) (3,-4) (3,-4) (5,-7) (5,-7)
COMPOSITE TRANSFORMATIONS. DOES ORDER MATTER Use the composite transformation to plot A B C and A B C. 1a)
 U3 L1 HW OMPOSITE TRNSFORMTIONS DOES ORDER MTTER Use the coposite trasforatio to plot ad 1a) T 3,5 ry axis ( ) b) ry axis T 3,5 ( ) c) Did doig the trasforatios i a differet order atter? Explai why? 2a)
U3 L1 HW OMPOSITE TRNSFORMTIONS DOES ORDER MTTER Use the coposite trasforatio to plot ad 1a) T 3,5 ry axis ( ) b) ry axis T 3,5 ( ) c) Did doig the trasforatios i a differet order atter? Explai why? 2a)
Math Section 2.2 Polynomial Functions
 Math 1330 - Sectio. Polyomial Fuctios Our objectives i workig with polyomial fuctios will be, first, to gather iformatio about the graph of the fuctio ad, secod, to use that iformatio to geerate a reasoably
Math 1330 - Sectio. Polyomial Fuctios Our objectives i workig with polyomial fuctios will be, first, to gather iformatio about the graph of the fuctio ad, secod, to use that iformatio to geerate a reasoably
9 x and g(x) = 4. x. Find (x) 3.6. I. Combining Functions. A. From Equations. Example: Let f(x) = and its domain. Example: Let f(x) = and g(x) = x x 4
 1 3.6 I. Combiig Fuctios A. From Equatios Example: Let f(x) = 9 x ad g(x) = 4 f x. Fid (x) g ad its domai. 4 Example: Let f(x) = ad g(x) = x x 4. Fid (f-g)(x) B. From Graphs: Graphical Additio. Example:
1 3.6 I. Combiig Fuctios A. From Equatios Example: Let f(x) = 9 x ad g(x) = 4 f x. Fid (x) g ad its domai. 4 Example: Let f(x) = ad g(x) = x x 4. Fid (f-g)(x) B. From Graphs: Graphical Additio. Example:
The Ray model of Light. Reflection. Class 18
 The Ray model of Light Over distances of a terrestrial scale light travels in a straight line. The path of a laser is now the best way we have of defining a straight line. The model of light which assumes
The Ray model of Light Over distances of a terrestrial scale light travels in a straight line. The path of a laser is now the best way we have of defining a straight line. The model of light which assumes
SD vs. SD + One of the most important uses of sample statistics is to estimate the corresponding population parameters.
 SD vs. SD + Oe of the most importat uses of sample statistics is to estimate the correspodig populatio parameters. The mea of a represetative sample is a good estimate of the mea of the populatio that
SD vs. SD + Oe of the most importat uses of sample statistics is to estimate the correspodig populatio parameters. The mea of a represetative sample is a good estimate of the mea of the populatio that
Exercise 6 (Week 42) For the foreign students only.
 These are the last exercises of the course. Please, remember that to pass exercises, the sum of the poits gathered by solvig the questios ad attedig the exercise groups must be at least 4% ( poits) of
These are the last exercises of the course. Please, remember that to pass exercises, the sum of the poits gathered by solvig the questios ad attedig the exercise groups must be at least 4% ( poits) of
The Closest Line to a Data Set in the Plane. David Gurney Southeastern Louisiana University Hammond, Louisiana
 The Closest Lie to a Data Set i the Plae David Gurey Southeaster Louisiaa Uiversity Hammod, Louisiaa ABSTRACT This paper looks at three differet measures of distace betwee a lie ad a data set i the plae:
The Closest Lie to a Data Set i the Plae David Gurey Southeaster Louisiaa Uiversity Hammod, Louisiaa ABSTRACT This paper looks at three differet measures of distace betwee a lie ad a data set i the plae:
Impact of thin film metrology on the lithographic performance of 193nm bottom antireflective coatings
 Impact of thi film metrology o the lithographic performace of 193m bottom atireflective coatigs Chris A. Mack a, Dale Harriso b, Cristia Rivas b, ad Phillip Walsh b a Lithoguru.com, Austi, TX b MetroSol,
Impact of thi film metrology o the lithographic performace of 193m bottom atireflective coatigs Chris A. Mack a, Dale Harriso b, Cristia Rivas b, ad Phillip Walsh b a Lithoguru.com, Austi, TX b MetroSol,
IMP: Superposer Integrated Morphometrics Package Superposition Tool
 IMP: Superposer Itegrated Morphometrics Package Superpositio Tool Programmig by: David Lieber ( 03) Caisius College 200 Mai St. Buffalo, NY 4208 Cocept by: H. David Sheets, Dept. of Physics, Caisius College
IMP: Superposer Itegrated Morphometrics Package Superpositio Tool Programmig by: David Lieber ( 03) Caisius College 200 Mai St. Buffalo, NY 4208 Cocept by: H. David Sheets, Dept. of Physics, Caisius College
Chapter 9. Pointers and Dynamic Arrays. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 9 Poiters ad Dyamic Arrays Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 9.1 Poiters 9.2 Dyamic Arrays Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Slide 9-3
Chapter 9 Poiters ad Dyamic Arrays Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 9.1 Poiters 9.2 Dyamic Arrays Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Slide 9-3
Test 4 Review. dy du 9 5. sin5 zdz. dt. 5 Ê. x 2 È 1, 3. 2cos( x) dx is less than using Simpson's. ,1 t 5 t 2. ft () t2 4.
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Test Review Short Aswer. Fid the geeral solutio of the differetial equatio below ad check the result by differetiatio. dy du 9 u. Use the error formula to estimate the error i
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Test Review Short Aswer. Fid the geeral solutio of the differetial equatio below ad check the result by differetiatio. dy du 9 u. Use the error formula to estimate the error i
CMPT 125 Assignment 2 Solutions
 CMPT 25 Assigmet 2 Solutios Questio (20 marks total) a) Let s cosider a iteger array of size 0. (0 marks, each part is 2 marks) it a[0]; I. How would you assig a poiter, called pa, to store the address
CMPT 25 Assigmet 2 Solutios Questio (20 marks total) a) Let s cosider a iteger array of size 0. (0 marks, each part is 2 marks) it a[0]; I. How would you assig a poiter, called pa, to store the address
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics. The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light.
 Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
Guide to Applying Online
 Guide to Applyig Olie Itroductio Respodig to requests for additioal iformatio Reportig: submittig your moitorig or ed of grat Pledges: submittig your Itroductio This guide is to help charities submit their
Guide to Applyig Olie Itroductio Respodig to requests for additioal iformatio Reportig: submittig your moitorig or ed of grat Pledges: submittig your Itroductio This guide is to help charities submit their
Chapter 5 Mirrors and Lenses
 Chapter 5 Notes: Mirrors and Lenses Name: Block: The Ray Model of Light The ray model of light represents light as a line, or ray, indicating the path of a beam of light. Light travels in straight lines
Chapter 5 Notes: Mirrors and Lenses Name: Block: The Ray Model of Light The ray model of light represents light as a line, or ray, indicating the path of a beam of light. Light travels in straight lines
