Cubic Splines and Matlab
|
|
|
- Lynette Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cubic Splines and Matlab October 7, Introduction In this section, we introduce the concept of the cubic spline, and how they are implemented in Matlab. Of particular importance are the new Matlab data structures that we will see. 2 Cubic Splines Defined Definition: Given n data points, (x 1, y 1 ),..., (x n, y n ), a cubic spline is a piecewise-defined function of the form: S 1 (x) = y 1 + b 1 (x x 1 ) + c 1 (x x 1 ) 2 + d 1 (x x 1 ) 3 for x [x 1, x 2 ] S 2 (x) = y 2 + b 2 (x x 2 ) + c 2 (x x 2 ) 2 + d 2 (x x 2 ) 3 for x [x 2, x 3 ].. S n 1 (x) = y n 1 + b n 1 (x x n 1 ) + c n 1 (x x n 1 ) 2 + d n 1 (x x n 1 ) 3 for x [x n 1, x n ] The 3n 3 unknowns (b s, c s, d s) are chosen to satisfy the interpolation constraints and also some smoothness constraints: (Interpolation Conditions) We already have S i (x i ) = y i for i = 1 to n 1. In addition, we want the overall function to be continuous. At the interior points, S i (x i+1 ) = S i+1 (x i+1 ) = y i+1 and at the far right value of x, S n 1 (x n ) = y n Altogether, there are n 1 constraints here. (Smoothness Condition 1) At the interior points, S i (x i+1 ) = S i+1 (x i+1 ) There are n 2 constraints here. 1
2 (Smoothness Condition 2) At the interior points, There are n 2 constraints here. S i (x i+1 ) = S i+1 (x i+1 ) So far, we have (n 1)+(n 2)+(n 2) = 3n 5 constraints, but we have 3(n 1) = 3n 3 coefficients. We need two more constraints to define the cubics uniquely. 2.1 Using the Two Extra Constraints We can have different cubic splines depending on how we want to use our two extra constraints. Here are some common ones: (The Natural Spline) S 1 (x 1 ) = 0 = S n 1 (x n ) (The Clamped Spline) The user defines S 1 (x 1 ) and S n 1 (x n ) Not-A-Knot : The third derivatives match at x 2 and x n 1 - That is, S 1(x 2 ) = S 2(x 2 ) and S n 2(x n 2 ) = S n 1(x n 2 ) Normally, at this step we would include some data. Notice that with cubic splines, you probably would not use them without at least 5 data points. With 4 data points, we could use a single cubic, for example. 2.2 Derivatives and Integrals We just note here the derivative and antiderivative of each piece of the cubic spline, and The antiderivative (note the shift): S i (x) = y i + b i (x x i ) + c i (x x i ) 2 + d i (x x i ) 3 S i (x) = b i + 2c i (x x i ) + 3d i (x x i ) 2 S i (x) = 2c i + 6d i (x x i ) S i (x) dx = y i (x x i ) b i(x x i ) c i(x x i ) d i(x x i ) 4 In particular, if we integrate over the interval [x i, x i+1 ] and the data is evenly spaced with width h, then: xi+1 x i S i (x) dx = y i h b ih c ih d ih 4
3 3 Matlab Data Structures In Matlab, we can collect different types of data together into a single structure. For example, suppose that you have a vector x and a matrix A and several constants, a, b, c that you are going to be using over and over again. To wrap them up into a structure, you could write: Examp.x=x; Examp.A=A; Examp.constants=[a,b,c]; To access, for example, the (1, 3) element you ve stored in the matrix A, you would type: Examp.A(1,3) You can create arrays of structures and structures within structures. For example, suppose we use the data fitting tool in Matlab to create a spline: x=0:10; y=sin(x); plot(x,y, r* ); Choose Tools -> Basic Fitting from the menus at the top of the figure. Click on the Spline Interpolant option, then click on the right arrow at the bottom right corner. We can save the spline structure by selecting Save to Workspace (You can uncheck the residuals boxes, just leave Save fit as a MATLAB struct named box. You can leave it named fit, then press OK. Close down the dialog boxes and plots and return to Matlab. Type in the word for the structure, fit and you ll see a string, type: spline and another structure, coeff. That is, fit.coeff is itself a structure- Type that in, and you ll see the contents: >> fit.coeff ans = form: pp breaks: [ ] coefs: [10x4 double] pieces: 10 order: 4 dim: 1 The actual spline coefficients are stored in the 10 4 array coefs. To see these, we would type: fit.coeff.coefs.
4 3.1 Some Useful Array Commands Suppose I want to delete the second column of the matrix A. In Matlab, I would type: A(:,2)=[]; Note the use of the colon, : to denote all rows. Also, note that delete means to remove that column altogether. Suppose I want to multiply the third column by 5, and put that column back into A: A(:,3)=5*A(:,3); If I want to divide the elements of column 1 by the elements of column 2: A(:,1)./A(:,2); 3.2 Piecewise Polynomials Matlab has built-in commands for dealing with piecewise-defined polynomials, like cubic splines. A piecewise-defined polynomial is defined in Matlab by a vector containing the breaks and a matrix defining the polynomial coefficients. Caution: A vector of coefficients, like [3,2,1], over an interval like [2,3] is interpreted by the piecewise polynomial routines as: 3(x 2) 2 + 2(x 2) + 1 NOT 3x 2 + 2x + 1 Example: Constructing a piecewise polynomial by hand: Suppose we want to define the following: { x P (x) = 2 3x + 1 if x [1, 2) 3x 5 if x [2, 3] (NOTE: In the Matlab documentation, it is unclear which function is used to evaluate the interior breaks. This is the way it is done- The intervals are all assumed to be of the form [a, b) except the last interval.) First we need to rewrite these 1 : and x 2 3x + 1 = (x 1) 2 (x 1) 1 3x 5 = 3(x 2) + 1 In Matlab, make the piecewise polynomial and plot the results: breaks=[1,2,3]; coefs=[1,-1,-1;0,3,1]; pp=mkpp(breaks,coefs); x=linspace(1,3); y=ppval(pp,x); plot(x,y); 1 Is there an easy way to do this? Use a Taylor expansion based at the left endpoint.
5 4 Implementing Splines In Matlab The relevent commands are: spline ppval mkpp (Also see the help page for any of these commands). The spline command takes two forms, depending on what you want out: pp = spline(x,y) Builds the cubic spline using the data in x, y, and outputs the result as a piecewise polynomial, pp. See the previous section for how Matlab defines and works with piecewise defined functions. The second command does not give the piecewise defined polynomial, rather it just evaluates the cubic spline at given values of xin, defined below: yout = spline(x,y,xin) where the cubic spline uses the data in x and y, evaluates the cubic spline at data in the vector xin, and gives the result in yout. 5 Matlab Exercises In these exercises, go ahead and assume that the spline was constructed using Matlab s default algorithm. 1. What flavor of spline does Matlab use as its default? To verify your answer, look at the matrix of spline coefficients. You might use the sine function as a quick example: x=0:10; y=sin(x); pp=spline(x,y); In particular, pay attention to the order of the coefficients- Which column corresponds to constants? 2. How would we manipulate the coefficients to get the first, and second derivatives of a spline? Write functions dspline, d2spline whose input is the original spline structure (we called it pp in the previous exercise), and whose output will give you the derivatives as a piecewise polynomial structure. When you do this, you have a choice as to whether or not you want to change the degree of the polynomial. Below is a sample function that returns the third derivative, and leaves the degree as a cubic.
6 function pp=d3spline(pp) % function p2 = d3spline(pp) % Returns the piecewise polynomial that represents the third % derivative of the cubic spline in the data structure pp. % Example: x=0:10; y=sin(x); pp=spline(x,y); % p2=d3spline(pp); % xx=linspace(0,10); % yy=ppval(p2,xx); % plot(xx,yy); A=zeros(size(pp.coefs)); A(:,4)=6*pp.coefs(:,1); pp.coefs=a; %Initializes a matrix of zeros 3. Do the same thing as before, but implement the antiderivative of the spline. Call the function antispline, and assume the constant of integration is zero. Be sure you also change pp.order. Extra: If you plot the antiderivative, you will get a very choppy curve (because each piece starts at zero). Is it possible to change this so that you get a smooth curve starting at zero? How would this code then be used to numerically estimate a definite integral? 4. We said before that the cubic spline is not well defined at the knots. That is, for the knot x j, Matlab has to make a choice between using S j or S j+1. We know that it doesn t make a difference for the spline, its derivative or second derivative. Can you use the third derivative to determine which function is used at an interior point? Do it! 5. Use cubic splines and its antiderivative to estimate: 3 3 e x2 dx using 20 evenly spaced points. You might check your answer using Maple: evalf(int(exp(-x^2),x=-3..3)); Another way to see how your estimate is doing is to re-do the estimate using more points.
Homework #6 Brief Solutions 2012
 Homework #6 Brief Solutions %page 95 problem 4 data=[-,;-,;,;4,] data = - - 4 xk=data(:,);yk=data(:,);s=csfit(xk,yk,-,) %Using the program to find the coefficients S =.456 -.456 -.. -.5.9 -.5484. -.58.87.
Homework #6 Brief Solutions %page 95 problem 4 data=[-,;-,;,;4,] data = - - 4 xk=data(:,);yk=data(:,);s=csfit(xk,yk,-,) %Using the program to find the coefficients S =.456 -.456 -.. -.5.9 -.5484. -.58.87.
Polynomials tend to oscillate (wiggle) a lot, even when our true function does not.
 AMSC/CMSC 460 Computational Methods, Fall 2007 UNIT 2: Spline Approximations Dianne P O Leary c 2001, 2002, 2007 Piecewise polynomial interpolation Piecewise polynomial interpolation Read: Chapter 3 Skip:
AMSC/CMSC 460 Computational Methods, Fall 2007 UNIT 2: Spline Approximations Dianne P O Leary c 2001, 2002, 2007 Piecewise polynomial interpolation Piecewise polynomial interpolation Read: Chapter 3 Skip:
APPM/MATH Problem Set 4 Solutions
 APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
Handout 4 - Interpolation Examples
 Handout 4 - Interpolation Examples Middle East Technical University Example 1: Obtaining the n th Degree Newton s Interpolating Polynomial Passing through (n+1) Data Points Obtain the 4 th degree Newton
Handout 4 - Interpolation Examples Middle East Technical University Example 1: Obtaining the n th Degree Newton s Interpolating Polynomial Passing through (n+1) Data Points Obtain the 4 th degree Newton
8 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation
 Applied Math Notes by R. J. LeVeque 8 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation 8. Pitfalls of high order interpolation Suppose we know the value of a function at several points on an interval and we wish to
Applied Math Notes by R. J. LeVeque 8 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation 8. Pitfalls of high order interpolation Suppose we know the value of a function at several points on an interval and we wish to
Mar. 20 Math 2335 sec 001 Spring 2014
 Mar. 20 Math 2335 sec 001 Spring 2014 Chebyshev Polynomials Definition: For an integer n 0 define the function ( ) T n (x) = cos n cos 1 (x), 1 x 1. It can be shown that T n is a polynomial of degree n.
Mar. 20 Math 2335 sec 001 Spring 2014 Chebyshev Polynomials Definition: For an integer n 0 define the function ( ) T n (x) = cos n cos 1 (x), 1 x 1. It can be shown that T n is a polynomial of degree n.
An introduction to interpolation and splines
 An introduction to interpolation and splines Kenneth H. Carpenter, EECE KSU November 22, 1999 revised November 20, 2001, April 24, 2002, April 14, 2004 1 Introduction Suppose one wishes to draw a curve
An introduction to interpolation and splines Kenneth H. Carpenter, EECE KSU November 22, 1999 revised November 20, 2001, April 24, 2002, April 14, 2004 1 Introduction Suppose one wishes to draw a curve
Lecture 8. Divided Differences,Least-Squares Approximations. Ceng375 Numerical Computations at December 9, 2010
 Lecture 8, Ceng375 Numerical Computations at December 9, 2010 Computer Engineering Department Çankaya University 8.1 Contents 1 2 3 8.2 : These provide a more efficient way to construct an interpolating
Lecture 8, Ceng375 Numerical Computations at December 9, 2010 Computer Engineering Department Çankaya University 8.1 Contents 1 2 3 8.2 : These provide a more efficient way to construct an interpolating
lecture 10: B-Splines
 9 lecture : -Splines -Splines: a basis for splines Throughout our discussion of standard polynomial interpolation, we viewed P n as a linear space of dimension n +, and then expressed the unique interpolating
9 lecture : -Splines -Splines: a basis for splines Throughout our discussion of standard polynomial interpolation, we viewed P n as a linear space of dimension n +, and then expressed the unique interpolating
Introduction to Matlab
 What is Matlab? Introduction to Matlab Matlab is software written by a company called The Mathworks (mathworks.com), and was first created in 1984 to be a nice front end to the numerical routines created
What is Matlab? Introduction to Matlab Matlab is software written by a company called The Mathworks (mathworks.com), and was first created in 1984 to be a nice front end to the numerical routines created
Rational Bezier Surface
 Rational Bezier Surface The perspective projection of a 4-dimensional polynomial Bezier surface, S w n ( u, v) B i n i 0 m j 0, u ( ) B j m, v ( ) P w ij ME525x NURBS Curve and Surface Modeling Page 97
Rational Bezier Surface The perspective projection of a 4-dimensional polynomial Bezier surface, S w n ( u, v) B i n i 0 m j 0, u ( ) B j m, v ( ) P w ij ME525x NURBS Curve and Surface Modeling Page 97
Engineering Analysis ENG 3420 Fall Dan C. Marinescu Office: HEC 439 B Office hours: Tu-Th 11:00-12:00
 Engineering Analysis ENG 3420 Fall 2009 Dan C. Marinescu Office: HEC 439 B Office hours: Tu-Th 11:00-12:00 1 Lecture 24 Attention: The last homework HW5 and the last project are due on Tuesday November
Engineering Analysis ENG 3420 Fall 2009 Dan C. Marinescu Office: HEC 439 B Office hours: Tu-Th 11:00-12:00 1 Lecture 24 Attention: The last homework HW5 and the last project are due on Tuesday November
Concept of Curve Fitting Difference with Interpolation
 Curve Fitting Content Concept of Curve Fitting Difference with Interpolation Estimation of Linear Parameters by Least Squares Curve Fitting by Polynomial Least Squares Estimation of Non-linear Parameters
Curve Fitting Content Concept of Curve Fitting Difference with Interpolation Estimation of Linear Parameters by Least Squares Curve Fitting by Polynomial Least Squares Estimation of Non-linear Parameters
Curve fitting using linear models
 Curve fitting using linear models Rasmus Waagepetersen Department of Mathematics Aalborg University Denmark September 28, 2012 1 / 12 Outline for today linear models and basis functions polynomial regression
Curve fitting using linear models Rasmus Waagepetersen Department of Mathematics Aalborg University Denmark September 28, 2012 1 / 12 Outline for today linear models and basis functions polynomial regression
Scientific Computing: Interpolation
 Scientific Computing: Interpolation Aleksandar Donev Courant Institute, NYU donev@courant.nyu.edu Course MATH-GA.243 or CSCI-GA.22, Fall 25 October 22nd, 25 A. Donev (Courant Institute) Lecture VIII /22/25
Scientific Computing: Interpolation Aleksandar Donev Courant Institute, NYU donev@courant.nyu.edu Course MATH-GA.243 or CSCI-GA.22, Fall 25 October 22nd, 25 A. Donev (Courant Institute) Lecture VIII /22/25
February 2017 (1/20) 2 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation 2.2 (Natural) Cubic Splines. MA378/531 Numerical Analysis II ( NA2 )
 f f f f f (/2).9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2. S Knots.7.6.5.4.3.2. 5 5.2.8.6.4.2 S Knots.2 5 5.9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2..9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2. S Knots 5 5 S Knots 5 5 5 5.35.3.25.2.5..5 5 5.6.5.4.3.2. 5 5 4 x 3 3.5 3 2.5 2.5.5 5
f f f f f (/2).9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2. S Knots.7.6.5.4.3.2. 5 5.2.8.6.4.2 S Knots.2 5 5.9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2..9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2. S Knots 5 5 S Knots 5 5 5 5.35.3.25.2.5..5 5 5.6.5.4.3.2. 5 5 4 x 3 3.5 3 2.5 2.5.5 5
ME 261: Numerical Analysis Lecture-12: Numerical Interpolation
 1 ME 261: Numerical Analysis Lecture-12: Numerical Interpolation Md. Tanver Hossain Department of Mechanical Engineering, BUET http://tantusher.buet.ac.bd 2 Inverse Interpolation Problem : Given a table
1 ME 261: Numerical Analysis Lecture-12: Numerical Interpolation Md. Tanver Hossain Department of Mechanical Engineering, BUET http://tantusher.buet.ac.bd 2 Inverse Interpolation Problem : Given a table
Cubic spline interpolation
 Cubic spline interpolation In the following, we want to derive the collocation matrix for cubic spline interpolation. Let us assume that we have equidistant knots. To fulfill the Schoenberg-Whitney condition
Cubic spline interpolation In the following, we want to derive the collocation matrix for cubic spline interpolation. Let us assume that we have equidistant knots. To fulfill the Schoenberg-Whitney condition
Evaluating the polynomial at a point
 Evaluating the polynomial at a point Recall that we have a data structure for each piecewise polynomial (linear, quadratic, cubic and cubic Hermite). We have a routine that sets evenly spaced interpolation
Evaluating the polynomial at a point Recall that we have a data structure for each piecewise polynomial (linear, quadratic, cubic and cubic Hermite). We have a routine that sets evenly spaced interpolation
Introduction to Matlab
 Introduction to Matlab November 22, 2013 Contents 1 Introduction to Matlab 1 1.1 What is Matlab.................................. 1 1.2 Matlab versus Maple............................... 2 1.3 Getting
Introduction to Matlab November 22, 2013 Contents 1 Introduction to Matlab 1 1.1 What is Matlab.................................. 1 1.2 Matlab versus Maple............................... 2 1.3 Getting
Getting Started. Chapter 1. How to Get Matlab. 1.1 Before We Begin Matlab to Accompany Lay s Linear Algebra Text
 Chapter 1 Getting Started How to Get Matlab Matlab physically resides on each of the computers in the Olin Hall labs. See your instructor if you need an account on these machines. If you are going to go
Chapter 1 Getting Started How to Get Matlab Matlab physically resides on each of the computers in the Olin Hall labs. See your instructor if you need an account on these machines. If you are going to go
See the course website for important information about collaboration and late policies, as well as where and when to turn in assignments.
 COS Homework # Due Tuesday, February rd See the course website for important information about collaboration and late policies, as well as where and when to turn in assignments. Data files The questions
COS Homework # Due Tuesday, February rd See the course website for important information about collaboration and late policies, as well as where and when to turn in assignments. Data files The questions
Consider functions such that then satisfies these properties: So is represented by the cubic polynomials on on and on.
 1 of 9 3/1/2006 2:28 PM ne previo Next: Trigonometric Interpolation Up: Spline Interpolation Previous: Piecewise Linear Case Cubic Splines A piece-wise technique which is very popular. Recall the philosophy
1 of 9 3/1/2006 2:28 PM ne previo Next: Trigonometric Interpolation Up: Spline Interpolation Previous: Piecewise Linear Case Cubic Splines A piece-wise technique which is very popular. Recall the philosophy
CS 450 Numerical Analysis. Chapter 7: Interpolation
 Lecture slides based on the textbook Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey by Michael T. Heath, copyright c 2018 by the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics. http://www.siam.org/books/cl80
Lecture slides based on the textbook Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey by Michael T. Heath, copyright c 2018 by the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics. http://www.siam.org/books/cl80
The Interpolating Polynomial
 Math 45 Linear Algebra David Arnold David-Arnold@Eureka.redwoods.cc.ca.us Abstract A polynomial that passes through a given set of data points is called an interpolating polynomial. In this exercise you
Math 45 Linear Algebra David Arnold David-Arnold@Eureka.redwoods.cc.ca.us Abstract A polynomial that passes through a given set of data points is called an interpolating polynomial. In this exercise you
Image Zooming using Cubic Spline Interpolation Method
 Image Zooming using Cubic Spline Interpolation Method Poonam Sharma and Mr. Anshuman Kalla Department of ECE, Jaipur National University, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India Abstract: In Linear polynomial phenomenon;
Image Zooming using Cubic Spline Interpolation Method Poonam Sharma and Mr. Anshuman Kalla Department of ECE, Jaipur National University, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India Abstract: In Linear polynomial phenomenon;
Introduction to Matlab to Accompany Linear Algebra. Douglas Hundley Department of Mathematics and Statistics Whitman College
 Introduction to Matlab to Accompany Linear Algebra Douglas Hundley Department of Mathematics and Statistics Whitman College August 27, 2018 2 Contents 1 Getting Started 5 1.1 Before We Begin........................................
Introduction to Matlab to Accompany Linear Algebra Douglas Hundley Department of Mathematics and Statistics Whitman College August 27, 2018 2 Contents 1 Getting Started 5 1.1 Before We Begin........................................
Linear Interpolating Splines
 Jim Lambers MAT 772 Fall Semester 2010-11 Lecture 17 Notes Tese notes correspond to Sections 112, 11, and 114 in te text Linear Interpolating Splines We ave seen tat ig-degree polynomial interpolation
Jim Lambers MAT 772 Fall Semester 2010-11 Lecture 17 Notes Tese notes correspond to Sections 112, 11, and 114 in te text Linear Interpolating Splines We ave seen tat ig-degree polynomial interpolation
Interpolation - 2D mapping Tutorial 1: triangulation
 Tutorial 1: triangulation Measurements (Zk) at irregular points (xk, yk) Ex: CTD stations, mooring, etc... The known Data How to compute some values on the regular spaced grid points (+)? The unknown data
Tutorial 1: triangulation Measurements (Zk) at irregular points (xk, yk) Ex: CTD stations, mooring, etc... The known Data How to compute some values on the regular spaced grid points (+)? The unknown data
Midterm Exam with solutions
 Midterm Exam with solutions CS227-Introduction to Scientific Computation November 8, 2011 1. The following is a transcript of a MATLAB session. >> x=1/62.5 x = 0.016000000000000 >> y=(1+x)-1 y = 0.016000000000000
Midterm Exam with solutions CS227-Introduction to Scientific Computation November 8, 2011 1. The following is a transcript of a MATLAB session. >> x=1/62.5 x = 0.016000000000000 >> y=(1+x)-1 y = 0.016000000000000
Remark. Jacobs University Visualization and Computer Graphics Lab : ESM4A - Numerical Methods 331
 Remark Reconsidering the motivating example, we observe that the derivatives are typically not given by the problem specification. However, they can be estimated in a pre-processing step. A good estimate
Remark Reconsidering the motivating example, we observe that the derivatives are typically not given by the problem specification. However, they can be estimated in a pre-processing step. A good estimate
Fall CSCI 420: Computer Graphics. 4.2 Splines. Hao Li.
 Fall 2014 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 4.2 Splines Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Roller coaster Next programming assignment involves creating a 3D roller coaster animation We must model the 3D curve
Fall 2014 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 4.2 Splines Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Roller coaster Next programming assignment involves creating a 3D roller coaster animation We must model the 3D curve
Introduction to Matlab
 Introduction to Matlab What is Matlab The software program called Matlab (short for MATrix LABoratory) is arguably the world standard for engineering- mainly because of its ability to do very quick prototyping.
Introduction to Matlab What is Matlab The software program called Matlab (short for MATrix LABoratory) is arguably the world standard for engineering- mainly because of its ability to do very quick prototyping.
Math 226A Homework 4 Due Monday, December 11th
 Math 226A Homework 4 Due Monday, December 11th 1. (a) Show that the polynomial 2 n (T n+1 (x) T n 1 (x)), is the unique monic polynomial of degree n + 1 with roots at the Chebyshev points x k = cos ( )
Math 226A Homework 4 Due Monday, December 11th 1. (a) Show that the polynomial 2 n (T n+1 (x) T n 1 (x)), is the unique monic polynomial of degree n + 1 with roots at the Chebyshev points x k = cos ( )
Spline Models. Introduction to CS and NCS. Regression splines. Smoothing splines
 Spline Models Introduction to CS and NCS Regression splines Smoothing splines 3 Cubic Splines a knots: a< 1 < 2 < < m
Spline Models Introduction to CS and NCS Regression splines Smoothing splines 3 Cubic Splines a knots: a< 1 < 2 < < m
Chapter 19 Interpolation
 19.1 One-Dimensional Interpolation Chapter 19 Interpolation Empirical data obtained experimentally often times conforms to a fixed (deterministic) but unkown functional relationship. When estimates of
19.1 One-Dimensional Interpolation Chapter 19 Interpolation Empirical data obtained experimentally often times conforms to a fixed (deterministic) but unkown functional relationship. When estimates of
Four equations are necessary to evaluate these coefficients. Eqn
 1.2 Splines 11 A spline function is a piecewise defined function with certain smoothness conditions [Cheney]. A wide variety of functions is potentially possible; polynomial functions are almost exclusively
1.2 Splines 11 A spline function is a piecewise defined function with certain smoothness conditions [Cheney]. A wide variety of functions is potentially possible; polynomial functions are almost exclusively
Section 5.5 Piecewise Interpolation
 Section 5.5 Piecewise Interpolation Key terms Runge phenomena polynomial wiggle problem Piecewise polynomial interpolation We have considered polynomial interpolation to sets of distinct data like {( )
Section 5.5 Piecewise Interpolation Key terms Runge phenomena polynomial wiggle problem Piecewise polynomial interpolation We have considered polynomial interpolation to sets of distinct data like {( )
A Practical Review of Uniform B-Splines
 A Practical Review of Uniform B-Splines Kristin Branson A B-spline is a convenient form for representing complicated, smooth curves. A uniform B-spline of order k is a piecewise order k Bezier curve, and
A Practical Review of Uniform B-Splines Kristin Branson A B-spline is a convenient form for representing complicated, smooth curves. A uniform B-spline of order k is a piecewise order k Bezier curve, and
1 Introduction to Matlab
 1 Introduction to Matlab 1. What is Matlab? Matlab is a computer program designed to do mathematics. You might think of it as a super-calculator. That is, once Matlab has been started, you can enter computations,
1 Introduction to Matlab 1. What is Matlab? Matlab is a computer program designed to do mathematics. You might think of it as a super-calculator. That is, once Matlab has been started, you can enter computations,
Splines and Piecewise Interpolation. Hsiao-Lung Chan Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan
 Splines and Piecewise Interpolation Hsiao-Lung Chan Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan chanhl@mail.cgu.edu.tw Splines n 1 intervals and n data points 2 Splines (cont.) Go through
Splines and Piecewise Interpolation Hsiao-Lung Chan Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan chanhl@mail.cgu.edu.tw Splines n 1 intervals and n data points 2 Splines (cont.) Go through
An Introduction to Numerical Methods
 An Introduction to Numerical Methods Using MATLAB Khyruddin Akbar Ansari, Ph.D., P.E. Bonni Dichone, Ph.D. SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by
An Introduction to Numerical Methods Using MATLAB Khyruddin Akbar Ansari, Ph.D., P.E. Bonni Dichone, Ph.D. SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by
1 Trajectories. Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733. Figure 1: Robot control system.
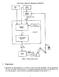 Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
Natural Quartic Spline
 Natural Quartic Spline Rafael E Banchs INTRODUCTION This report describes the natural quartic spline algorithm developed for the enhanced solution of the Time Harmonic Field Electric Logging problem As
Natural Quartic Spline Rafael E Banchs INTRODUCTION This report describes the natural quartic spline algorithm developed for the enhanced solution of the Time Harmonic Field Electric Logging problem As
Video 11.1 Vijay Kumar. Property of University of Pennsylvania, Vijay Kumar
 Video 11.1 Vijay Kumar 1 Smooth three dimensional trajectories START INT. POSITION INT. POSITION GOAL Applications Trajectory generation in robotics Planning trajectories for quad rotors 2 Motion Planning
Video 11.1 Vijay Kumar 1 Smooth three dimensional trajectories START INT. POSITION INT. POSITION GOAL Applications Trajectory generation in robotics Planning trajectories for quad rotors 2 Motion Planning
(Spline, Bezier, B-Spline)
 (Spline, Bezier, B-Spline) Spline Drafting terminology Spline is a flexible strip that is easily flexed to pass through a series of design points (control points) to produce a smooth curve. Spline curve
(Spline, Bezier, B-Spline) Spline Drafting terminology Spline is a flexible strip that is easily flexed to pass through a series of design points (control points) to produce a smooth curve. Spline curve
MAT 275 Laboratory 1 Introduction to MATLAB
 MATLAB sessions: Laboratory 1 1 MAT 275 Laboratory 1 Introduction to MATLAB MATLAB is a computer software commonly used in both education and industry to solve a wide range of problems. This Laboratory
MATLAB sessions: Laboratory 1 1 MAT 275 Laboratory 1 Introduction to MATLAB MATLAB is a computer software commonly used in both education and industry to solve a wide range of problems. This Laboratory
08 - Designing Approximating Curves
 08 - Designing Approximating Curves Acknowledgement: Olga Sorkine-Hornung, Alexander Sorkine-Hornung, Ilya Baran Last time Interpolating curves Monomials Lagrange Hermite Different control types Polynomials
08 - Designing Approximating Curves Acknowledgement: Olga Sorkine-Hornung, Alexander Sorkine-Hornung, Ilya Baran Last time Interpolating curves Monomials Lagrange Hermite Different control types Polynomials
SIMULINK FOR BEGINNERS:
 1 SIMULINK FOR BEGINNERS: To begin your SIMULINK session open first MATLAB ICON by clicking mouse twice and then type»simulink You will now see the Simulink block library. 2 Browse through block libraries.
1 SIMULINK FOR BEGINNERS: To begin your SIMULINK session open first MATLAB ICON by clicking mouse twice and then type»simulink You will now see the Simulink block library. 2 Browse through block libraries.
Important Properties of B-spline Basis Functions
 Important Properties of B-spline Basis Functions P2.1 N i,p (u) = 0 if u is outside the interval [u i, u i+p+1 ) (local support property). For example, note that N 1,3 is a combination of N 1,0, N 2,0,
Important Properties of B-spline Basis Functions P2.1 N i,p (u) = 0 if u is outside the interval [u i, u i+p+1 ) (local support property). For example, note that N 1,3 is a combination of N 1,0, N 2,0,
Interactive Graphics. Lecture 9: Introduction to Spline Curves. Interactive Graphics Lecture 9: Slide 1
 Interactive Graphics Lecture 9: Introduction to Spline Curves Interactive Graphics Lecture 9: Slide 1 Interactive Graphics Lecture 13: Slide 2 Splines The word spline comes from the ship building trade
Interactive Graphics Lecture 9: Introduction to Spline Curves Interactive Graphics Lecture 9: Slide 1 Interactive Graphics Lecture 13: Slide 2 Splines The word spline comes from the ship building trade
Splines. Parameterization of a Curve. Curve Representations. Roller coaster. What Do We Need From Curves in Computer Graphics? Modeling Complex Shapes
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 8 Splines Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Hermite Splines Bezier Splines Catmull-Rom Splines Other Cubic Splines [Angel Ch 12.4-12.12] Roller coaster
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 8 Splines Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Hermite Splines Bezier Splines Catmull-Rom Splines Other Cubic Splines [Angel Ch 12.4-12.12] Roller coaster
Piecewise polynomial interpolation
 Chapter 2 Piecewise polynomial interpolation In ection.6., and in Lab, we learned that it is not a good idea to interpolate unctions by a highorder polynomials at equally spaced points. However, it transpires
Chapter 2 Piecewise polynomial interpolation In ection.6., and in Lab, we learned that it is not a good idea to interpolate unctions by a highorder polynomials at equally spaced points. However, it transpires
Math Homework 3
 Math 0 - Homework 3 Due: Friday Feb. in class. Write on your paper the lab section you have registered for.. Staple the sheets together.. Solve exercise 8. of the textbook : Consider the following data:
Math 0 - Homework 3 Due: Friday Feb. in class. Write on your paper the lab section you have registered for.. Staple the sheets together.. Solve exercise 8. of the textbook : Consider the following data:
Chapter 3. Numerical Differentiation, Interpolation, and Integration. Instructor: Dr. Ming Ye
 Chapter 3 Numerical Differentiation, Interpolation, and Integration Instructor: Dr. Ming Ye Measuring Flow in Natural Channels Mean-Section Method (1) Divide the stream into a number of rectangular elements
Chapter 3 Numerical Differentiation, Interpolation, and Integration Instructor: Dr. Ming Ye Measuring Flow in Natural Channels Mean-Section Method (1) Divide the stream into a number of rectangular elements
Cubic Spline Questions
 Cubic Spline Questions. Find natural cubic splines which interpolate the following dataset of, points:.0,.,.,.0, 7.0,.,.0,0.; estimate the value for. Solution: Step : Use the n- cubic spline equations
Cubic Spline Questions. Find natural cubic splines which interpolate the following dataset of, points:.0,.,.,.0, 7.0,.,.0,0.; estimate the value for. Solution: Step : Use the n- cubic spline equations
EECS 556 Image Processing W 09. Interpolation. Interpolation techniques B splines
 EECS 556 Image Processing W 09 Interpolation Interpolation techniques B splines What is image processing? Image processing is the application of 2D signal processing methods to images Image representation
EECS 556 Image Processing W 09 Interpolation Interpolation techniques B splines What is image processing? Image processing is the application of 2D signal processing methods to images Image representation
Derivative. Bernstein polynomials: Jacobs University Visualization and Computer Graphics Lab : ESM4A - Numerical Methods 313
 Derivative Bernstein polynomials: 120202: ESM4A - Numerical Methods 313 Derivative Bézier curve (over [0,1]): with differences. being the first forward 120202: ESM4A - Numerical Methods 314 Derivative
Derivative Bernstein polynomials: 120202: ESM4A - Numerical Methods 313 Derivative Bézier curve (over [0,1]): with differences. being the first forward 120202: ESM4A - Numerical Methods 314 Derivative
A general matrix representation for non-uniform B-spline subdivision with boundary control
 A general matrix representation for non-uniform B-spline subdivision with boundary control G. Casciola a, L. Romani a a Department of Mathematics, University of Bologna, P.zza di Porta San Donato 5, 40127
A general matrix representation for non-uniform B-spline subdivision with boundary control G. Casciola a, L. Romani a a Department of Mathematics, University of Bologna, P.zza di Porta San Donato 5, 40127
Interpolation & Polynomial Approximation. Cubic Spline Interpolation II
 Interpolation & Polynomial Approximation Cubic Spline Interpolation II Numerical Analysis (9th Edition) R L Burden & J D Faires Beamer Presentation Slides prepared by John Carroll Dublin City University
Interpolation & Polynomial Approximation Cubic Spline Interpolation II Numerical Analysis (9th Edition) R L Burden & J D Faires Beamer Presentation Slides prepared by John Carroll Dublin City University
Objectives. 1 Running, and Interface Layout. 2 Toolboxes, Documentation and Tutorials. 3 Basic Calculations. PS 12a Laboratory 1 Spring 2014
 PS 12a Laboratory 1 Spring 2014 Objectives This session is a tutorial designed to a very quick overview of some of the numerical skills that you ll need to get started. Throughout the tutorial, the instructors
PS 12a Laboratory 1 Spring 2014 Objectives This session is a tutorial designed to a very quick overview of some of the numerical skills that you ll need to get started. Throughout the tutorial, the instructors
Design considerations
 Curves Design considerations local control of shape design each segment independently smoothness and continuity ability to evaluate derivatives stability small change in input leads to small change in
Curves Design considerations local control of shape design each segment independently smoothness and continuity ability to evaluate derivatives stability small change in input leads to small change in
Computational Physics PHYS 420
 Computational Physics PHYS 420 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
Computational Physics PHYS 420 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
Homework #6 Brief Solutions 2011
 Homework #6 Brief Solutions %page 95 problem 4 data=[-,;-,;,;4,] data = - - 4 xk=data(:,);yk=data(:,);s=csfit(xk,yk,-,) %Using the program to find the coefficients S =.456 -.456 -.. -.5.9 -.5484. -.58.87.
Homework #6 Brief Solutions %page 95 problem 4 data=[-,;-,;,;4,] data = - - 4 xk=data(:,);yk=data(:,);s=csfit(xk,yk,-,) %Using the program to find the coefficients S =.456 -.456 -.. -.5.9 -.5484. -.58.87.
Vertical and Horizontal Translations
 SECTION 4.3 Vertical and Horizontal Translations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the vertical translation of a sine or cosine function. Find the horizontal
SECTION 4.3 Vertical and Horizontal Translations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the vertical translation of a sine or cosine function. Find the horizontal
AMS 27L LAB #2 Winter 2009
 AMS 27L LAB #2 Winter 2009 Plots and Matrix Algebra in MATLAB Objectives: 1. To practice basic display methods 2. To learn how to program loops 3. To learn how to write m-files 1 Vectors Matlab handles
AMS 27L LAB #2 Winter 2009 Plots and Matrix Algebra in MATLAB Objectives: 1. To practice basic display methods 2. To learn how to program loops 3. To learn how to write m-files 1 Vectors Matlab handles
Rational Bezier Curves
 Rational Bezier Curves Use of homogeneous coordinates Rational spline curve: define a curve in one higher dimension space, project it down on the homogenizing variable Mathematical formulation: n P(u)
Rational Bezier Curves Use of homogeneous coordinates Rational spline curve: define a curve in one higher dimension space, project it down on the homogenizing variable Mathematical formulation: n P(u)
CS130 : Computer Graphics Curves. Tamar Shinar Computer Science & Engineering UC Riverside
 CS130 : Computer Graphics Curves Tamar Shinar Computer Science & Engineering UC Riverside Design considerations local control of shape design each segment independently smoothness and continuity ability
CS130 : Computer Graphics Curves Tamar Shinar Computer Science & Engineering UC Riverside Design considerations local control of shape design each segment independently smoothness and continuity ability
Lecture 16: High-dimensional regression, non-linear regression
 Lecture 16: High-dimensional regression, non-linear regression Reading: Sections 6.4, 7.1 STATS 202: Data mining and analysis November 3, 2017 1 / 17 High-dimensional regression Most of the methods we
Lecture 16: High-dimensional regression, non-linear regression Reading: Sections 6.4, 7.1 STATS 202: Data mining and analysis November 3, 2017 1 / 17 High-dimensional regression Most of the methods we
Numerical Methods in Physics Lecture 2 Interpolation
 Numerical Methods in Physics Pat Scott Department of Physics, Imperial College November 8, 2016 Slides available from http://astro.ic.ac.uk/pscott/ course-webpage-numerical-methods-201617 Outline The problem
Numerical Methods in Physics Pat Scott Department of Physics, Imperial College November 8, 2016 Slides available from http://astro.ic.ac.uk/pscott/ course-webpage-numerical-methods-201617 Outline The problem
Creating a T-Spline using a Reference Image
 1 / 17 Goals Learn how to create a T-Spline using a Reference Image. 1. Insert an image into the workspace using Attach Canvas. 2. Use Calibrate to set the proper scale for the reference image. 3. Invoke
1 / 17 Goals Learn how to create a T-Spline using a Reference Image. 1. Insert an image into the workspace using Attach Canvas. 2. Use Calibrate to set the proper scale for the reference image. 3. Invoke
Know it. Control points. B Spline surfaces. Implicit surfaces
 Know it 15 B Spline Cur 14 13 12 11 Parametric curves Catmull clark subdivision Parametric surfaces Interpolating curves 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 Control points B Spline surfaces Implicit surfaces Bezier surfaces
Know it 15 B Spline Cur 14 13 12 11 Parametric curves Catmull clark subdivision Parametric surfaces Interpolating curves 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 Control points B Spline surfaces Implicit surfaces Bezier surfaces
Asymptotic Error Analysis
 Asymptotic Error Analysis Brian Wetton Mathematics Department, UBC www.math.ubc.ca/ wetton PIMS YRC, June 3, 2014 Outline Overview Some History Romberg Integration Cubic Splines - Periodic Case More History:
Asymptotic Error Analysis Brian Wetton Mathematics Department, UBC www.math.ubc.ca/ wetton PIMS YRC, June 3, 2014 Outline Overview Some History Romberg Integration Cubic Splines - Periodic Case More History:
Interpolation by Spline Functions
 Interpolation by Spline Functions Com S 477/577 Sep 0 007 High-degree polynomials tend to have large oscillations which are not the characteristics of the original data. To yield smooth interpolating curves
Interpolation by Spline Functions Com S 477/577 Sep 0 007 High-degree polynomials tend to have large oscillations which are not the characteristics of the original data. To yield smooth interpolating curves
MATLAB BASICS. < Any system: Enter quit at Matlab prompt < PC/Windows: Close command window < To interrupt execution: Enter Ctrl-c.
 MATLAB BASICS Starting Matlab < PC: Desktop icon or Start menu item < UNIX: Enter matlab at operating system prompt < Others: Might need to execute from a menu somewhere Entering Matlab commands < Matlab
MATLAB BASICS Starting Matlab < PC: Desktop icon or Start menu item < UNIX: Enter matlab at operating system prompt < Others: Might need to execute from a menu somewhere Entering Matlab commands < Matlab
Lecture 3 Box-partitions and dimension of spline spaces over Box-partition
 Lecture 3 Box-partitions and dimension of spline spaces over Box-partition Definition of LR B-splines some geometric properties Tor Dokken CIME-EMS Summer School June 8 - June, 0 Cetraro, Italy Box-partitions
Lecture 3 Box-partitions and dimension of spline spaces over Box-partition Definition of LR B-splines some geometric properties Tor Dokken CIME-EMS Summer School June 8 - June, 0 Cetraro, Italy Box-partitions
2D Spline Curves. CS 4620 Lecture 13
 2D Spline Curves CS 4620 Lecture 13 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Motivation: smoothness In many applications we need smooth shapes [Boeing] that is, without discontinuities So far we can make things with corners
2D Spline Curves CS 4620 Lecture 13 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Motivation: smoothness In many applications we need smooth shapes [Boeing] that is, without discontinuities So far we can make things with corners
Section Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 Section 5. - Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will graph the basic sine function and the basic cosine function and then graph other sine and cosine functions using transformations.
Section 5. - Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will graph the basic sine function and the basic cosine function and then graph other sine and cosine functions using transformations.
Introduction to Matlab
 Introduction to Matlab Math 339 Fall 2013 First, put the icon in the launcher: Drag and drop Now, open Matlab: * Current Folder * Command Window * Workspace * Command History Operations in Matlab Description:
Introduction to Matlab Math 339 Fall 2013 First, put the icon in the launcher: Drag and drop Now, open Matlab: * Current Folder * Command Window * Workspace * Command History Operations in Matlab Description:
Parametric Curves. University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell
 Parametric Curves University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell Parametric Representations 3 basic representation strategies: Explicit: y = mx + b Implicit: ax + by + c
Parametric Curves University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell Parametric Representations 3 basic representation strategies: Explicit: y = mx + b Implicit: ax + by + c
DATA FITTING IN SCILAB
 powered by DATA FITTING IN SCILAB In this tutorial the reader can learn about data fitting, interpolation and approximation in Scilab. Interpolation is very important in industrial applications for data
powered by DATA FITTING IN SCILAB In this tutorial the reader can learn about data fitting, interpolation and approximation in Scilab. Interpolation is very important in industrial applications for data
Schedule. Matlab Exam. Documentation. Program Building Blocks. Dynamics Makeup Exam. Matlab Exam. Semester Summary and Wrap up.
 Schedule Dynamics Makeup Exam Thursday, May 1, 2:00 p.m., Estabrook 111 3 problems, covers modules 3 & 4 You may bring 1 sheet of notes Matlab Exam See next slide Semester Summary and Wrap up Wednesday,
Schedule Dynamics Makeup Exam Thursday, May 1, 2:00 p.m., Estabrook 111 3 problems, covers modules 3 & 4 You may bring 1 sheet of notes Matlab Exam See next slide Semester Summary and Wrap up Wednesday,
Assignment 2. with (a) (10 pts) naive Gauss elimination, (b) (10 pts) Gauss with partial pivoting
 Assignment (Be sure to observe the rules about handing in homework). Solve: with (a) ( pts) naive Gauss elimination, (b) ( pts) Gauss with partial pivoting *You need to show all of the steps manually.
Assignment (Be sure to observe the rules about handing in homework). Solve: with (a) ( pts) naive Gauss elimination, (b) ( pts) Gauss with partial pivoting *You need to show all of the steps manually.
3D Modeling Parametric Curves & Surfaces
 3D Modeling Parametric Curves & Surfaces Shandong University Spring 2012 3D Object Representations Raw data Point cloud Range image Polygon soup Solids Voxels BSP tree CSG Sweep Surfaces Mesh Subdivision
3D Modeling Parametric Curves & Surfaces Shandong University Spring 2012 3D Object Representations Raw data Point cloud Range image Polygon soup Solids Voxels BSP tree CSG Sweep Surfaces Mesh Subdivision
Introduction to Scientific Computing with Matlab
 Introduction to Scientific Computing with Matlab Matlab is an interactive system for numerical computations. It is widely used in universities and industry, and has many advantages over languages such
Introduction to Scientific Computing with Matlab Matlab is an interactive system for numerical computations. It is widely used in universities and industry, and has many advantages over languages such
Objects 2: Curves & Splines Christian Miller CS Fall 2011
 Objects 2: Curves & Splines Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 Parametric curves Curves that are defined by an equation and a parameter t Usually t [0, 1], and curve is finite Can be discretized at arbitrary
Objects 2: Curves & Splines Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 Parametric curves Curves that are defined by an equation and a parameter t Usually t [0, 1], and curve is finite Can be discretized at arbitrary
Parametric Surfaces. Michael Kazhdan ( /657) HB , FvDFH 11.2
 Parametric Surfaces Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB 10.6 -- 10.9, 10.1 FvDFH 11.2 Announcement OpenGL review session: When: Wednesday (10/1) @ 7:00-9:00 PM Where: Olin 05 Cubic Splines Given a collection
Parametric Surfaces Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB 10.6 -- 10.9, 10.1 FvDFH 11.2 Announcement OpenGL review session: When: Wednesday (10/1) @ 7:00-9:00 PM Where: Olin 05 Cubic Splines Given a collection
CS354 Computer Graphics Surface Representation III. Qixing Huang March 5th 2018
 CS354 Computer Graphics Surface Representation III Qixing Huang March 5th 2018 Today s Topic Bspline curve operations (Brief) Knot Insertion/Deletion Subdivision (Focus) Subdivision curves Subdivision
CS354 Computer Graphics Surface Representation III Qixing Huang March 5th 2018 Today s Topic Bspline curve operations (Brief) Knot Insertion/Deletion Subdivision (Focus) Subdivision curves Subdivision
B(asis) Splines. Ashish Myles CISE, UF
 B(asis) Splines Ashish Myles CISE, UF Splines Piecewise polynomial More flexible than single polynomials can have finite support can be periodic Degree d splines typically C d 1 continuity Some polynomial
B(asis) Splines Ashish Myles CISE, UF Splines Piecewise polynomial More flexible than single polynomials can have finite support can be periodic Degree d splines typically C d 1 continuity Some polynomial
MAT Business Calculus - Quick Notes
 MAT 136 - Business Calculus - Quick Notes Last Updated: 4/3/16 Chapter 2 Applications of Differentiation Section 2.1 Using First Derivatives to Find Maximum and Minimum Values and Sketch Graphs THE FIRST-DERIVATIVE
MAT 136 - Business Calculus - Quick Notes Last Updated: 4/3/16 Chapter 2 Applications of Differentiation Section 2.1 Using First Derivatives to Find Maximum and Minimum Values and Sketch Graphs THE FIRST-DERIVATIVE
Math Numerical Analysis Homework #3 Solutions
 Math 24 - Numerical Analysis Homework #3 Solutions. Write a program for polynomial interpolation of function values. Your program should accept two vectors as input. A vector of x coordinates for interpolation
Math 24 - Numerical Analysis Homework #3 Solutions. Write a program for polynomial interpolation of function values. Your program should accept two vectors as input. A vector of x coordinates for interpolation
Parametric Curves. University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics
 Parametric Curves University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell Parametric Representations 3 basic representation strategies: Explicit: y = mx + b Implicit: ax + by + c
Parametric Curves University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell Parametric Representations 3 basic representation strategies: Explicit: y = mx + b Implicit: ax + by + c
Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 )
 CS480: Computer Graphics Curves and Surfaces Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://jupiter.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg Today s Topics Surface representations Smooth curves Subdivision 2 Smooth Curves and
CS480: Computer Graphics Curves and Surfaces Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://jupiter.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg Today s Topics Surface representations Smooth curves Subdivision 2 Smooth Curves and
B-Spline Polynomials. B-Spline Polynomials. Uniform Cubic B-Spline Curves CS 460. Computer Graphics
 CS 460 B-Spline Polynomials Computer Graphics Professor Richard Eckert March 24, 2004 B-Spline Polynomials Want local control Smoother curves B-spline curves: Segmented approximating curve 4 control points
CS 460 B-Spline Polynomials Computer Graphics Professor Richard Eckert March 24, 2004 B-Spline Polynomials Want local control Smoother curves B-spline curves: Segmented approximating curve 4 control points
Introduction to Scientific Computing with Matlab
 Introduction to Scientific Computing with Matlab In the previous reading, we discussed the basics of vectors and matrices, including matrix addition and multiplication. In this class, we ll explore more
Introduction to Scientific Computing with Matlab In the previous reading, we discussed the basics of vectors and matrices, including matrix addition and multiplication. In this class, we ll explore more
Spline Toolbox. User s Guide Version 3. For Use with MATLAB. Carl de Boor
 Spline Toolbox For Use with MATLAB Carl de Boor User s Guide Version 3 How to Contact The MathWorks: www.mathworks.com comp.soft-sys.matlab support@mathworks.com suggest@mathworks.com bugs@mathworks.com
Spline Toolbox For Use with MATLAB Carl de Boor User s Guide Version 3 How to Contact The MathWorks: www.mathworks.com comp.soft-sys.matlab support@mathworks.com suggest@mathworks.com bugs@mathworks.com
3D Modeling Parametric Curves & Surfaces. Shandong University Spring 2013
 3D Modeling Parametric Curves & Surfaces Shandong University Spring 2013 3D Object Representations Raw data Point cloud Range image Polygon soup Surfaces Mesh Subdivision Parametric Implicit Solids Voxels
3D Modeling Parametric Curves & Surfaces Shandong University Spring 2013 3D Object Representations Raw data Point cloud Range image Polygon soup Surfaces Mesh Subdivision Parametric Implicit Solids Voxels
LECTURE NOTES - SPLINE INTERPOLATION. 1. Introduction. Problems can arise when a single high-degree polynomial is fit to a large number
 LECTURE NOTES - SPLINE INTERPOLATION DR MAZHAR IQBAL 1 Introduction Problems can arise when a single high-degree polynomial is fit to a large number of points High-degree polynomials would obviously pass
LECTURE NOTES - SPLINE INTERPOLATION DR MAZHAR IQBAL 1 Introduction Problems can arise when a single high-degree polynomial is fit to a large number of points High-degree polynomials would obviously pass
Parameterization. Michael S. Floater. November 10, 2011
 Parameterization Michael S. Floater November 10, 2011 Triangular meshes are often used to represent surfaces, at least initially, one reason being that meshes are relatively easy to generate from point
Parameterization Michael S. Floater November 10, 2011 Triangular meshes are often used to represent surfaces, at least initially, one reason being that meshes are relatively easy to generate from point
Curves and Surfaces. Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring Instructor: Brandon Lloyd
 Curves and Surfaces Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 4/11/2007 Final projects Surface representations Smooth curves Subdivision Todays Topics 2 Final Project Requirements
Curves and Surfaces Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 4/11/2007 Final projects Surface representations Smooth curves Subdivision Todays Topics 2 Final Project Requirements
