ForestClaw : Mapped, multiblock adaptive quadtrees
|
|
|
- Juliana Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ForestClaw : Mapped, multiblock adaptive quadtrees Donna Calhoun (Boise State University) Carsten Burstedde (Univ. of Bonn) HPC 3 November 9-13, 2014 KAUST - Saudi Arabia
2 The ForestClaw Project Project to develop highly scalable adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) code that combines quadtree data structures with patch based refinement Uses the p4est (Carsten Burstedde, Univ. of Bonn) dynamic grid management library Explicit solver algorithms are those described by Berger- Oliger in Implicit solvers to be added. Design goal : Develop an easily accessible, highly scalable AMR framework to spur development of novel numerical methods and applications for AMR.
3 AMR using ForestClaw
4 AMR using ForestClaw Fine level grids Each grid has a layer of ghost cells (not shown) to facilitate communication Coarse level grids Quadtree based refinement
5 Progress on ForestClaw ForestClaw started at [HPC] ! Progress to date Multi-rate time stepping (Fall, 2012) General mappings available (Fall, 2012) MPI parallel capabilities implemented (Summer, 2013) Build system using GNU Autotools (Summer, 2014) Mapped, multiblock capabilities for several useful domains, including cubed disk and sphere (Summer, 2014) Periodic domains (Fall 2014)
6 Gridding strategies Compare patch-based vs. quad tree on this solution
7 Filament example Solve q t +urq = 0, u = r, (x, y) =(4/3)r 3. Domain :[0, 2] [0, 2] Fixed t = for x = 1/16 (CFL approx. 0.74). Run to T =8.0 Refine to an e ective resolution of and Use multirate time stepping Regrid at least every coarse grid time step Use MC limiter
8 Filament example (ForestClaw) 512x512 grid (mx=64)
9 Filament example (AMRClaw) mx = 512 (max1d=80)
10 Gridding strategies (uniform) 512x512 effective resolution Levels 0 (max1d=80) 1751s Levels 3 (mx=64) 1671s
11 Gridding strategies (512) 256x256 effective resolution Levels 0-3 (max1d=80) 617s Levels 2-3 (mx=64) 1178s
12 Gridding strategies (512) 256x256 effective resolution Levels 0-3 (max1d=80) 617s Levels 3-4 (mx=32) 904s
13 Gridding strategies (512) 128x128 effective resolution Levels 0-3 (max1d=80) 617s Levels 3-5 (mx=16) 777s
14 Gridding strategies (512) 64x64 effective resolution Levels 0-3 (max1d=80) 617s Levels 3-6 (mx=8) 811s
15 Gridding strategies (512) 64x64 effective resolution Levels 0-3 (max1d=40) 720s Levels 3-6 (mx=8) 811s
16 Gridding strategies (512) 32x32 coarsest level grid Levels 0-2 (max1d=40; factor 4) 636s Levels 3-6 (mx=8) 811s
17 Gridding strategies (1024) 64x64 effective resolution Levels 0-2 (R Factor : 4,4) 3212s Levels 3-7 (mx=8) 3567s
18 Gridding strategies 32x32 coarsest level grid Levels 0-3 (R Factor : 4,4,2) 3891s Levels 3-7 (mx=8) 3567s
19 Gridding strategies 64x64 effective resolution Levels 0-5 (R Factor : 2) 4060s Levels 3-7 (mx=8) 3567s
20 Summary AMRClaw ForestClaw Total Regrid Total Advance Exchange Regrid 512x512.grid.:.Uniform.refinement.(ForestClaw.5%.faster) Example max1d= mx = x512.effective.resolution.(AMRClaw.about.12%.faster) Example % max1d= % 1.5% 1.7% mx = 64 Example % 3.8% 5.6% mx = 32 Example % 8.6% 7.6% mx = 16 Example % 17.5% 11.9% mx = 8 Example % max1d=40 Example % max1d=40; RF=4 1024x1024.effective.resolution.(ForestClaw.and.AMRClaw.are.within.about.15%.of.each.other) Example % max1d=40; RF= % 18.7% 3.6% mx=8 Example % max1d=40; RF=4,4,2 Example % max1d=40; RF=2 AMRClaw prefers larger refinement ratio; ForestClaw prefers smaller grids Timings all done on a desktop
21 Why use quadtrees? Refinement patches and parallel units are the same Tree-based grid layout makes communication between patches and blocks much simpler, especially in 3d. Has the aesthetic appeal of a quad/octree refinement Make use of existing literature on make quad/octrees efficient and scalable.
22 What next? Grid exchanges and communication Grid mappings and multiblock Multi-rate time stepping
23 Multi-block disk Multiblock capabilities are inherited from p4est.
24 Sphere domains
25 Periodic brick domains
26 Multiblock disk
27 Mixing diagnostic Preservation of functional relationship between tracers. Lauritzen, P. H., Skamarock, W. C., Prather, M. J., and and, M. A. T. A standard test case suite for two-dimensional linear transport on the sphere. Geoscientific Model Development 5 (2012),
28 Mixing diagnostics (256 x 256) No AMR with AMR Diagnostic Fraction Diagnostic Fraction Real mixing (r) 5.45E E Range preserving mixing (g) 1.49E E Under and over shoots (b) 2.63E E
29 Flow on a torus Cool! Periodic boundary conditions!
30 Handling multiblock boundaries c c c & # Exchange at left neighbor! if (idir.eq. 0) then! do j = 1,my! do ibc = 1,mbc! do mq = 1,meqn! if (iface.eq. 0) then! # Left face! i1 = 1-ibc! j1 = j! elseif (iface.eq. 1) then! # Right face! i1 = mx+ibc! j1 = j! endif! enddo! enddo! enddo Loop over all ghost cells at left edge call fclaw2d_transform_face(i1,j1,i2,j2,! transform_ptr)! qthis(mq,i1,j1) = qneighbor(mq,i2,j2)! This is the code used for every exchange at a left edge even if it is not a block boundary. transform_face maps (i1,j1) ghost cell values to neighbor values, using information about block boundary orientations encoded in transform_ptr. HPC 3 November 9-13, 2014
31 Mapping contexts fclaw2d_map_context_t* fclaw2d_map_new_squareddisk(const double alpha)! {!! } fclaw2d_map_context_t *cont;! cont = FCLAW_ALLOC_ZERO (fclaw2d_map_context_t, 1);! cont->query = fclaw2d_map_query_squareddisk;! cont->mapc2m = fclaw2d_map_c2m_squareddisk;! cont->user_double[0] = alpha;! No need to rely on a fixed argument list; arguments specific to the mapping can be passed into the mapping routine. c call mapc2m(xc,yc,xd1,yd1,zd1)! call fclaw2d_map_c2m(map_context,blockno,xc,yc,xd1,yd1,zd1) static void! fclaw2d_map_c2m_squareddisk(fclaw2d_map_context_t *cont, int blockno,! double xc, double yc,! double *xp, double *yp, double *zp)! {! double alpha = cont->user_double[0];! mapc2m_squareddisk(&blockno,&xc,&yc,xp,yp,zp,&alpha);! }!
32 Current practical limitations Multiblock limitations Users cannot yet design their own block connectivity - p4est needs to first set up the connectivity - Need a file format for specifying general connectivities At most four blocks can meet at a corner Solver limitations Metric terms limit solutions to second order (most likely) Solution errors at mapping seams not properly handled. Software Visualization done in Matlab (no VisClaw, Visit, etc support yet) Regridding done only at coarse time step, not at intermediate time steps.
33 Future? Extend code to 3d Parallel performance testing Better treatment of metric terms Documentation Recent NSF funding to Develop multistage methods in an AMR Framework (D. Ketcheson) Extend existing Ash3d code to AMR (USGS, D. George)
34 Alpha testers needed! Let me know if you d like to out ForestClaw - Test installation procedure - Run existing examples - Port Clawpack examples - Get some VisClaw graphics support? No prior experience needed!
35 Thanks! Thanks to David Ketcheson, Heba, Ting and KAUST for organizing hosting this event!
36 Work-Precision
Parallel, adaptive framework for mapped, multi-block domains
 Parallel, adaptive framework for mapped, multi-block domains Donna Calhoun (Boise State University) Carsten Burstedde (University of Bonn) Randall J. LeVeque (Univ. of WA), Marsha Berger (NYU), David George
Parallel, adaptive framework for mapped, multi-block domains Donna Calhoun (Boise State University) Carsten Burstedde (University of Bonn) Randall J. LeVeque (Univ. of WA), Marsha Berger (NYU), David George
Donna Calhoun. Boise State University
 Wave propagation algorithms in two dimensions, adaptive refinement and wellbalancing Donna Calhoun Boise State University PASI 2013 Valparaiso, Chile January 2-13 Plan How do these Riemann solvers make
Wave propagation algorithms in two dimensions, adaptive refinement and wellbalancing Donna Calhoun Boise State University PASI 2013 Valparaiso, Chile January 2-13 Plan How do these Riemann solvers make
Forest-of-octrees AMR: algorithms and interfaces
 Forest-of-octrees AMR: algorithms and interfaces Carsten Burstedde joint work with Omar Ghattas, Tobin Isaac, Georg Stadler, Lucas C. Wilcox Institut für Numerische Simulation (INS) Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität
Forest-of-octrees AMR: algorithms and interfaces Carsten Burstedde joint work with Omar Ghattas, Tobin Isaac, Georg Stadler, Lucas C. Wilcox Institut für Numerische Simulation (INS) Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität
Python, Clawpack, PyClaw, and PetClaw (using PETSc)
 Python, Clawpack, PyClaw, and PetClaw (using PETSc) Randall J. LeVeque Kyle Mandli Applied Mathematics University of Washington Conservation Laws Package www.clawpack.org Supported in part by NSF, ONR,
Python, Clawpack, PyClaw, and PetClaw (using PETSc) Randall J. LeVeque Kyle Mandli Applied Mathematics University of Washington Conservation Laws Package www.clawpack.org Supported in part by NSF, ONR,
Generic finite element capabilities for forest-of-octrees AMR
 Generic finite element capabilities for forest-of-octrees AMR Carsten Burstedde joint work with Omar Ghattas, Tobin Isaac Institut für Numerische Simulation (INS) Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität
Generic finite element capabilities for forest-of-octrees AMR Carsten Burstedde joint work with Omar Ghattas, Tobin Isaac Institut für Numerische Simulation (INS) Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität
Parallel adaptive mesh refinement using multiple octrees and the p4est software
 Parallel adaptive mesh refinement using multiple octrees and the p4est software Carsten Burstedde Institut für Numerische Simulation (INS) Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn, Germany August
Parallel adaptive mesh refinement using multiple octrees and the p4est software Carsten Burstedde Institut für Numerische Simulation (INS) Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn, Germany August
Parallel Algorithms: Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) method and its implementation
 Parallel Algorithms: Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) method and its implementation Massimiliano Guarrasi m.guarrasi@cineca.it Super Computing Applications and Innovation Department AMR - Introduction Solving
Parallel Algorithms: Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) method and its implementation Massimiliano Guarrasi m.guarrasi@cineca.it Super Computing Applications and Innovation Department AMR - Introduction Solving
Adaptive Mesh Refinement in Titanium
 Adaptive Mesh Refinement in Titanium http://seesar.lbl.gov/anag Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory April 7, 2005 19 th IPDPS, April 7, 2005 1 Overview Motivations: Build the infrastructure in Titanium
Adaptive Mesh Refinement in Titanium http://seesar.lbl.gov/anag Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory April 7, 2005 19 th IPDPS, April 7, 2005 1 Overview Motivations: Build the infrastructure in Titanium
AMR Multi-Moment FVM Scheme
 Chapter 4 AMR Multi-Moment FVM Scheme 4.1 Berger s AMR scheme An AMR grid with the hierarchy of Berger s AMR scheme proposed in [13] for CFD simulations is given in Fig.4.1 as a simple example for following
Chapter 4 AMR Multi-Moment FVM Scheme 4.1 Berger s AMR scheme An AMR grid with the hierarchy of Berger s AMR scheme proposed in [13] for CFD simulations is given in Fig.4.1 as a simple example for following
Scalability of Uintah Past Present and Future
 DOE for funding the CSAFE project (97-10), DOE NETL, DOE NNSA NSF for funding via SDCI and PetaApps, INCITE, XSEDE Scalability of Uintah Past Present and Future Martin Berzins Qingyu Meng John Schmidt,
DOE for funding the CSAFE project (97-10), DOE NETL, DOE NNSA NSF for funding via SDCI and PetaApps, INCITE, XSEDE Scalability of Uintah Past Present and Future Martin Berzins Qingyu Meng John Schmidt,
CLAWPACK Version 4.1 User s Guide
 CLAWPACK Version 4.1 User s Guide Randall J. LeVeque University of Washington September 15, 2002 http://www.amath.washington.edu/~claw/ c R. J. LeVeque, 2002 2 Authors. Most of the one-dimensional and
CLAWPACK Version 4.1 User s Guide Randall J. LeVeque University of Washington September 15, 2002 http://www.amath.washington.edu/~claw/ c R. J. LeVeque, 2002 2 Authors. Most of the one-dimensional and
HPC Computer Aided CINECA
 HPC Computer Aided Engineering @ CINECA Raffaele Ponzini Ph.D. CINECA SuperComputing Applications and Innovation Department SCAI 16-18 June 2014 Segrate (MI), Italy Outline Open-source CAD and Meshing
HPC Computer Aided Engineering @ CINECA Raffaele Ponzini Ph.D. CINECA SuperComputing Applications and Innovation Department SCAI 16-18 June 2014 Segrate (MI), Italy Outline Open-source CAD and Meshing
Performance Optimization of a Massively Parallel Phase-Field Method Using the HPC Framework walberla
 Performance Optimization of a Massively Parallel Phase-Field Method Using the HPC Framework walberla SIAM PP 2016, April 13 th 2016 Martin Bauer, Florian Schornbaum, Christian Godenschwager, Johannes Hötzer,
Performance Optimization of a Massively Parallel Phase-Field Method Using the HPC Framework walberla SIAM PP 2016, April 13 th 2016 Martin Bauer, Florian Schornbaum, Christian Godenschwager, Johannes Hötzer,
CLAWPACK Version 4.3 User s Guide
 CLAWPACK Version 4.3 User s Guide Randall J. LeVeque University of Washington April 8, 2006 http://www.amath.washington.edu/~claw/ c R. J. LeVeque, 2006 2 3 Authors. Most of the one-dimensional and two-dimensional
CLAWPACK Version 4.3 User s Guide Randall J. LeVeque University of Washington April 8, 2006 http://www.amath.washington.edu/~claw/ c R. J. LeVeque, 2006 2 3 Authors. Most of the one-dimensional and two-dimensional
Dynamic Load Partitioning Strategies for Managing Data of Space and Time Heterogeneity in Parallel SAMR Applications
 Dynamic Load Partitioning Strategies for Managing Data of Space and Time Heterogeneity in Parallel SAMR Applications Xiaolin Li and Manish Parashar The Applied Software Systems Laboratory Department of
Dynamic Load Partitioning Strategies for Managing Data of Space and Time Heterogeneity in Parallel SAMR Applications Xiaolin Li and Manish Parashar The Applied Software Systems Laboratory Department of
ALE and AMR Mesh Refinement Techniques for Multi-material Hydrodynamics Problems
 ALE and AMR Mesh Refinement Techniques for Multi-material Hydrodynamics Problems A. J. Barlow, AWE. ICFD Workshop on Mesh Refinement Techniques 7th December 2005 Acknowledgements Thanks to Chris Powell,
ALE and AMR Mesh Refinement Techniques for Multi-material Hydrodynamics Problems A. J. Barlow, AWE. ICFD Workshop on Mesh Refinement Techniques 7th December 2005 Acknowledgements Thanks to Chris Powell,
arxiv: v1 [cs.ms] 8 Aug 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cs.ms] 8 Aug 2018 arxiv: v1 [cs.ms] 8 Aug 2018](/thumbs/83/87599411.jpg) ACCELERATING WAVE-PROPAGATION ALGORITHMS WITH ADAPTIVE MESH REFINEMENT USING THE GRAPHICS PROCESSING UNIT (GPU) XINSHENG QIN, RANDALL LEVEQUE, AND MICHAEL MOTLEY arxiv:1808.02638v1 [cs.ms] 8 Aug 2018 Abstract.
ACCELERATING WAVE-PROPAGATION ALGORITHMS WITH ADAPTIVE MESH REFINEMENT USING THE GRAPHICS PROCESSING UNIT (GPU) XINSHENG QIN, RANDALL LEVEQUE, AND MICHAEL MOTLEY arxiv:1808.02638v1 [cs.ms] 8 Aug 2018 Abstract.
CAF versus MPI Applicability of Coarray Fortran to a Flow Solver
 CAF versus MPI Applicability of Coarray Fortran to a Flow Solver Manuel Hasert, Harald Klimach, Sabine Roller m.hasert@grs-sim.de Applied Supercomputing in Engineering Motivation We develop several CFD
CAF versus MPI Applicability of Coarray Fortran to a Flow Solver Manuel Hasert, Harald Klimach, Sabine Roller m.hasert@grs-sim.de Applied Supercomputing in Engineering Motivation We develop several CFD
Massively Parallel Finite Element Simulations with deal.ii
 Massively Parallel Finite Element Simulations with deal.ii Timo Heister, Texas A&M University 2012-02-16 SIAM PP2012 joint work with: Wolfgang Bangerth, Carsten Burstedde, Thomas Geenen, Martin Kronbichler
Massively Parallel Finite Element Simulations with deal.ii Timo Heister, Texas A&M University 2012-02-16 SIAM PP2012 joint work with: Wolfgang Bangerth, Carsten Burstedde, Thomas Geenen, Martin Kronbichler
Enabling In Situ Viz and Data Analysis with Provenance in libmesh
 Enabling In Situ Viz and Data Analysis with Provenance in libmesh Vítor Silva Jose J. Camata Marta Mattoso Alvaro L. G. A. Coutinho (Federal university Of Rio de Janeiro/Brazil) Patrick Valduriez (INRIA/France)
Enabling In Situ Viz and Data Analysis with Provenance in libmesh Vítor Silva Jose J. Camata Marta Mattoso Alvaro L. G. A. Coutinho (Federal university Of Rio de Janeiro/Brazil) Patrick Valduriez (INRIA/France)
Skåne University Hospital Lund, Lund, Sweden 2 Deparment of Numerical Analysis, Centre for Mathematical Sciences, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
 Volume Tracking: A New Method for Visualization of Intracardiac Blood Flow from Three-Dimensional, Time-Resolved, Three-Component Magnetic Resonance Velocity Mapping Appendix: Theory and Numerical Implementation
Volume Tracking: A New Method for Visualization of Intracardiac Blood Flow from Three-Dimensional, Time-Resolved, Three-Component Magnetic Resonance Velocity Mapping Appendix: Theory and Numerical Implementation
Evaluating the Performance of the Community Atmosphere Model at High Resolutions
 Evaluating the Performance of the Community Atmosphere Model at High Resolutions Soumi Manna MS candidate, University of Wyoming Mentor: Dr. Ben Jamroz National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder,
Evaluating the Performance of the Community Atmosphere Model at High Resolutions Soumi Manna MS candidate, University of Wyoming Mentor: Dr. Ben Jamroz National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder,
Spatial Data Models. Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities
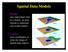 Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Development of a Computational Framework for Block-Based AMR Simulations
 Procedia Computer Science Volume 29, 2014, Pages 2351 2359 ICCS 2014. 14th International Conference on Computational Science Development of a Computational Framework for Block-Based AMR Simulations Hideyuki
Procedia Computer Science Volume 29, 2014, Pages 2351 2359 ICCS 2014. 14th International Conference on Computational Science Development of a Computational Framework for Block-Based AMR Simulations Hideyuki
Efficiency of adaptive mesh algorithms
 Efficiency of adaptive mesh algorithms 23.11.2012 Jörn Behrens KlimaCampus, Universität Hamburg http://www.katrina.noaa.gov/satellite/images/katrina-08-28-2005-1545z.jpg Model for adaptive efficiency 10
Efficiency of adaptive mesh algorithms 23.11.2012 Jörn Behrens KlimaCampus, Universität Hamburg http://www.katrina.noaa.gov/satellite/images/katrina-08-28-2005-1545z.jpg Model for adaptive efficiency 10
Topological Issues in Hexahedral Meshing
 Topological Issues in Hexahedral Meshing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine Dept. of Information and Computer Science Outline I. What is meshing? Problem statement Types of mesh Quality issues
Topological Issues in Hexahedral Meshing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine Dept. of Information and Computer Science Outline I. What is meshing? Problem statement Types of mesh Quality issues
Predictive Engineering and Computational Sciences. Data Structures and Methods for Unstructured Distributed Meshes. Roy H. Stogner
 PECOS Predictive Engineering and Computational Sciences Data Structures and Methods for Unstructured Distributed Meshes Roy H. Stogner The University of Texas at Austin May 23, 2012 Roy H. Stogner Distributed
PECOS Predictive Engineering and Computational Sciences Data Structures and Methods for Unstructured Distributed Meshes Roy H. Stogner The University of Texas at Austin May 23, 2012 Roy H. Stogner Distributed
PAMR Reference Manual
 PAMR Reference Manual Frans Pretorius Department of Physics P-412, Avadh Bhatia Physics Laboratory University of Alberta Edmonton, AB, T6G 2J1 Contents I. Introduction 1 II. Initialization and clean-up
PAMR Reference Manual Frans Pretorius Department of Physics P-412, Avadh Bhatia Physics Laboratory University of Alberta Edmonton, AB, T6G 2J1 Contents I. Introduction 1 II. Initialization and clean-up
Multilevel Methods for Forward and Inverse Ice Sheet Modeling
 Multilevel Methods for Forward and Inverse Ice Sheet Modeling Tobin Isaac Institute for Computational Engineering & Sciences The University of Texas at Austin SIAM CSE 2015 Salt Lake City, Utah τ 2 T.
Multilevel Methods for Forward and Inverse Ice Sheet Modeling Tobin Isaac Institute for Computational Engineering & Sciences The University of Texas at Austin SIAM CSE 2015 Salt Lake City, Utah τ 2 T.
HPC Algorithms and Applications
 HPC Algorithms and Applications Dwarf #5 Structured Grids Michael Bader Winter 2012/2013 Dwarf #5 Structured Grids, Winter 2012/2013 1 Dwarf #5 Structured Grids 1. dense linear algebra 2. sparse linear
HPC Algorithms and Applications Dwarf #5 Structured Grids Michael Bader Winter 2012/2013 Dwarf #5 Structured Grids, Winter 2012/2013 1 Dwarf #5 Structured Grids 1. dense linear algebra 2. sparse linear
Interconnection Network. Jinkyu Jeong Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Interconnection Network Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Topics Taxonomy Metric Topologies Characteristics Cost Performance 2 Interconnection
Interconnection Network Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Topics Taxonomy Metric Topologies Characteristics Cost Performance 2 Interconnection
Enzo-P / Cello. Formation of the First Galaxies. San Diego Supercomputer Center. Department of Physics and Astronomy
 Enzo-P / Cello Formation of the First Galaxies James Bordner 1 Michael L. Norman 1 Brian O Shea 2 1 University of California, San Diego San Diego Supercomputer Center 2 Michigan State University Department
Enzo-P / Cello Formation of the First Galaxies James Bordner 1 Michael L. Norman 1 Brian O Shea 2 1 University of California, San Diego San Diego Supercomputer Center 2 Michigan State University Department
Principles of Computer Game Design and Implementation. Lecture 13
 Principles of Computer Game Design and Implementation Lecture 13 We already knew Collision detection overlap test and intersection test Detailed view Mid-level view 2 Outline for today High-level view
Principles of Computer Game Design and Implementation Lecture 13 We already knew Collision detection overlap test and intersection test Detailed view Mid-level view 2 Outline for today High-level view
Subdivision Surfaces
 Subdivision Surfaces 1 Geometric Modeling Sometimes need more than polygon meshes Smooth surfaces Traditional geometric modeling used NURBS Non uniform rational B-Spline Demo 2 Problems with NURBS A single
Subdivision Surfaces 1 Geometric Modeling Sometimes need more than polygon meshes Smooth surfaces Traditional geometric modeling used NURBS Non uniform rational B-Spline Demo 2 Problems with NURBS A single
Advective and conservative semi-lagrangian schemes on uniform and non-uniform grids
 Advective and conservative semi-lagrangian schemes on uniform and non-uniform grids M. Mehrenberger Université de Strasbourg and Max-Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik 5 September 2013 M. Mehrenberger (UDS
Advective and conservative semi-lagrangian schemes on uniform and non-uniform grids M. Mehrenberger Université de Strasbourg and Max-Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik 5 September 2013 M. Mehrenberger (UDS
Hierarchical Grid Conversion
 Hierarchical Grid Conversion Ali Mahdavi-Amiri, Erika Harrison, Faramarz Samavati Abstract Hierarchical grids appear in various applications in computer graphics such as subdivision and multiresolution
Hierarchical Grid Conversion Ali Mahdavi-Amiri, Erika Harrison, Faramarz Samavati Abstract Hierarchical grids appear in various applications in computer graphics such as subdivision and multiresolution
Interconnection Network
 Interconnection Network Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu SSE3054: Multicore Systems, Spring 2017, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Topics
Interconnection Network Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu SSE3054: Multicore Systems, Spring 2017, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Topics
Efficient Global Element Indexing for Parallel Adaptive Flow Solvers
 Procedia Computer Science Volume 29, 2014, Pages 246 255 ICCS 2014. 14th International Conference on Computational Science Efficient Global Element Indexing for Parallel Adaptive Flow Solvers Michael Lieb,
Procedia Computer Science Volume 29, 2014, Pages 246 255 ICCS 2014. 14th International Conference on Computational Science Efficient Global Element Indexing for Parallel Adaptive Flow Solvers Michael Lieb,
Block-Structured Adaptive Mesh Refinement Algorithms and Software Phillip Colella Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 Block-Structured Adaptive Mesh Refinement Algorithms and Software Phillip Colella Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) Modified equation analysis: finite difference solutions
Block-Structured Adaptive Mesh Refinement Algorithms and Software Phillip Colella Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) Modified equation analysis: finite difference solutions
A Local-View Array Library for Partitioned Global Address Space C++ Programs
 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory A Local-View Array Library for Partitioned Global Address Space C++ Programs Amir Kamil, Yili Zheng, and Katherine Yelick Lawrence Berkeley Lab Berkeley, CA, USA June
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory A Local-View Array Library for Partitioned Global Address Space C++ Programs Amir Kamil, Yili Zheng, and Katherine Yelick Lawrence Berkeley Lab Berkeley, CA, USA June
p4est: SCALABLE ALGORITHMS FOR PARALLEL ADAPTIVE MESH REFINEMENT ON FORESTS OF OCTREES
 p4est: SCALABLE ALGORITHMS FOR PARALLEL ADAPTIVE MESH REFINEMENT ON FORESTS OF OCTREES CARSTEN BURSTEDDE, LUCAS C. WILCOX, AND OMAR GHATTAS Abstract. We present scalable algorithms for parallel adaptive
p4est: SCALABLE ALGORITHMS FOR PARALLEL ADAPTIVE MESH REFINEMENT ON FORESTS OF OCTREES CARSTEN BURSTEDDE, LUCAS C. WILCOX, AND OMAR GHATTAS Abstract. We present scalable algorithms for parallel adaptive
Structured Grid Generation for Turbo Machinery Applications using Topology Templates
 Structured Grid Generation for Turbo Machinery Applications using Topology Templates January 13th 2011 Martin Spel martin.spel@rtech.fr page 1 Agenda: R.Tech activities Grid Generation Techniques Structured
Structured Grid Generation for Turbo Machinery Applications using Topology Templates January 13th 2011 Martin Spel martin.spel@rtech.fr page 1 Agenda: R.Tech activities Grid Generation Techniques Structured
Towards a Reconfigurable HPC Component Model
 C2S@EXA Meeting July 10, 2014 Towards a Reconfigurable HPC Component Model Vincent Lanore1, Christian Pérez2 1 ENS de Lyon, LIP 2 Inria, LIP Avalon team 1 Context 1/4 Adaptive Mesh Refinement 2 Context
C2S@EXA Meeting July 10, 2014 Towards a Reconfigurable HPC Component Model Vincent Lanore1, Christian Pérez2 1 ENS de Lyon, LIP 2 Inria, LIP Avalon team 1 Context 1/4 Adaptive Mesh Refinement 2 Context
Investigation of cross flow over a circular cylinder at low Re using the Immersed Boundary Method (IBM)
 Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XVII 235 Investigation of cross flow over a circular cylinder at low Re using the Immersed Boundary Method (IBM) K. Rehman Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XVII 235 Investigation of cross flow over a circular cylinder at low Re using the Immersed Boundary Method (IBM) K. Rehman Department of Mechanical Engineering,
STREAM and RA HPC Challenge Benchmarks
 STREAM and RA HPC Challenge Benchmarks simple, regular 1D computations results from SC 09 competition AMR Computations hierarchical, regular computation SSCA #2 unstructured graph computation 2 Two classes
STREAM and RA HPC Challenge Benchmarks simple, regular 1D computations results from SC 09 competition AMR Computations hierarchical, regular computation SSCA #2 unstructured graph computation 2 Two classes
A Semi-Lagrangian Discontinuous Galerkin (SLDG) Conservative Transport Scheme on the Cubed-Sphere
 A Semi-Lagrangian Discontinuous Galerkin (SLDG) Conservative Transport Scheme on the Cubed-Sphere Ram Nair Computational and Information Systems Laboratory (CISL) National Center for Atmospheric Research
A Semi-Lagrangian Discontinuous Galerkin (SLDG) Conservative Transport Scheme on the Cubed-Sphere Ram Nair Computational and Information Systems Laboratory (CISL) National Center for Atmospheric Research
A Zooming Technique for Wind Transport of Air Pollution
 A Zooming Technique for Wind Transport of Air Pollution P.J.F. Berkvens, M.A. Botchev, W.M. Lioen and J.G. Verwer CWI P.O. Box 94079, 1090 GB Amsterdam, The Netherlands www.cwi.nl [berkvens, botchev, walter,
A Zooming Technique for Wind Transport of Air Pollution P.J.F. Berkvens, M.A. Botchev, W.M. Lioen and J.G. Verwer CWI P.O. Box 94079, 1090 GB Amsterdam, The Netherlands www.cwi.nl [berkvens, botchev, walter,
Introduction to 3D Scientific Visualization. Training in Visualization for PRACE Summer of HPC 2013 Leon Kos, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Introduction to 3D Scientific Visualization Training in Visualization for PRACE Summer of HPC 2013 Leon Kos, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia Motto Few correctly put words is worth hundreds of images.
Introduction to 3D Scientific Visualization Training in Visualization for PRACE Summer of HPC 2013 Leon Kos, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia Motto Few correctly put words is worth hundreds of images.
simulation framework for piecewise regular grids
 WALBERLA, an ultra-scalable multiphysics simulation framework for piecewise regular grids ParCo 2015, Edinburgh September 3rd, 2015 Christian Godenschwager, Florian Schornbaum, Martin Bauer, Harald Köstler
WALBERLA, an ultra-scalable multiphysics simulation framework for piecewise regular grids ParCo 2015, Edinburgh September 3rd, 2015 Christian Godenschwager, Florian Schornbaum, Martin Bauer, Harald Köstler
Recent developments for the multigrid scheme of the DLR TAU-Code
 www.dlr.de Chart 1 > 21st NIA CFD Seminar > Axel Schwöppe Recent development s for the multigrid scheme of the DLR TAU-Code > Apr 11, 2013 Recent developments for the multigrid scheme of the DLR TAU-Code
www.dlr.de Chart 1 > 21st NIA CFD Seminar > Axel Schwöppe Recent development s for the multigrid scheme of the DLR TAU-Code > Apr 11, 2013 Recent developments for the multigrid scheme of the DLR TAU-Code
Fluent User Services Center
 Solver Settings 5-1 Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring Stability Accelerating Convergence Accuracy Grid Independence Adaption Appendix: Background Finite Volume
Solver Settings 5-1 Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring Stability Accelerating Convergence Accuracy Grid Independence Adaption Appendix: Background Finite Volume
The CSLaM transport scheme & new numerical mixing diagnostics
 The CSLaM transport scheme & new numerical mixing diagnostics CESM Ocean Model Working Group Meeting 14 15 December, 2011 Peter Hjort Lauritzen Outline: Two parts Briefly introduce the CSLaM scheme (Conservative
The CSLaM transport scheme & new numerical mixing diagnostics CESM Ocean Model Working Group Meeting 14 15 December, 2011 Peter Hjort Lauritzen Outline: Two parts Briefly introduce the CSLaM scheme (Conservative
SPE Distinguished Lecturer Program
 SPE Distinguished Lecturer Program Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow
SPE Distinguished Lecturer Program Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow
On Partitioning Dynamic Adaptive Grid Hierarchies*
 On Partitioning Dynamic Adaptive Grid Hierarchies* Manish Parashar and James C. Browne Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin {parashar, browne}@cs.utexas.edu Abstract This paper
On Partitioning Dynamic Adaptive Grid Hierarchies* Manish Parashar and James C. Browne Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin {parashar, browne}@cs.utexas.edu Abstract This paper
Workloads Programmierung Paralleler und Verteilter Systeme (PPV)
 Workloads Programmierung Paralleler und Verteilter Systeme (PPV) Sommer 2015 Frank Feinbube, M.Sc., Felix Eberhardt, M.Sc., Prof. Dr. Andreas Polze Workloads 2 Hardware / software execution environment
Workloads Programmierung Paralleler und Verteilter Systeme (PPV) Sommer 2015 Frank Feinbube, M.Sc., Felix Eberhardt, M.Sc., Prof. Dr. Andreas Polze Workloads 2 Hardware / software execution environment
Workshop 10-1: HPC for Finite Arrays
 Workshop 10-1: HPC for Finite Arrays 2015.0 Release ANSYS HFSS for Antenna Design 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. Getting Started Launching ANSYS Electronics Desktop 2015 Select Programs > ANSYS Electromagnetics >
Workshop 10-1: HPC for Finite Arrays 2015.0 Release ANSYS HFSS for Antenna Design 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. Getting Started Launching ANSYS Electronics Desktop 2015 Select Programs > ANSYS Electromagnetics >
CPU Isosurface Ray Tracing of Adaptive Mesh Refinement Data
 1142 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VISUALIZATION AND COMPUTER GRAPHICS, VOL. 25, NO. 1, JANUARY 2019 CPU Isosurface Ray Tracing of Adaptive Mesh Refinement Data Feng Wang, Ingo Wald, Qi Wu, Will Usher and Chris
1142 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VISUALIZATION AND COMPUTER GRAPHICS, VOL. 25, NO. 1, JANUARY 2019 CPU Isosurface Ray Tracing of Adaptive Mesh Refinement Data Feng Wang, Ingo Wald, Qi Wu, Will Usher and Chris
Scalable Parallel AMR for the Uintah Multiphysics Code
 Chapter 4 Scalable Parallel AMR for the Uintah Multiphysics Code Justin Luitjens SCI Institute, University of Utah Bryan Worthen SCI Institute, University of Utah Martin Berzins SCI Institute, University
Chapter 4 Scalable Parallel AMR for the Uintah Multiphysics Code Justin Luitjens SCI Institute, University of Utah Bryan Worthen SCI Institute, University of Utah Martin Berzins SCI Institute, University
Shared Memory programming paradigm: openmp
 IPM School of Physics Workshop on High Performance Computing - HPC08 Shared Memory programming paradigm: openmp Luca Heltai Stefano Cozzini SISSA - Democritos/INFM
IPM School of Physics Workshop on High Performance Computing - HPC08 Shared Memory programming paradigm: openmp Luca Heltai Stefano Cozzini SISSA - Democritos/INFM
Physically-Based Modeling and Animation. University of Missouri at Columbia
 Overview of Geometric Modeling Overview 3D Shape Primitives: Points Vertices. Curves Lines, polylines, curves. Surfaces Triangle meshes, splines, subdivision surfaces, implicit surfaces, particles. Solids
Overview of Geometric Modeling Overview 3D Shape Primitives: Points Vertices. Curves Lines, polylines, curves. Surfaces Triangle meshes, splines, subdivision surfaces, implicit surfaces, particles. Solids
Special Topics in Visualization
 Special Topics in Visualization Final Project Report Dual contouring of Hermite Data Submitted By S M Shahed Nejhum 8589-1199 May 19, 2008 Introduction Iso-surface extraction from 3D volumetric data is
Special Topics in Visualization Final Project Report Dual contouring of Hermite Data Submitted By S M Shahed Nejhum 8589-1199 May 19, 2008 Introduction Iso-surface extraction from 3D volumetric data is
RAMSES on the GPU: An OpenACC-Based Approach
 RAMSES on the GPU: An OpenACC-Based Approach Claudio Gheller (ETHZ-CSCS) Giacomo Rosilho de Souza (EPFL Lausanne) Romain Teyssier (University of Zurich) Markus Wetzstein (ETHZ-CSCS) PRACE-2IP project EU
RAMSES on the GPU: An OpenACC-Based Approach Claudio Gheller (ETHZ-CSCS) Giacomo Rosilho de Souza (EPFL Lausanne) Romain Teyssier (University of Zurich) Markus Wetzstein (ETHZ-CSCS) PRACE-2IP project EU
An Embedded Boundary Method with Adaptive Mesh Refinements
 An Embedded Boundary Method with Adaptive Mesh Refinements Marcos Vanella and Elias Balaras 8 th World Congress on Computational Mechanics, WCCM8 5 th European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied
An Embedded Boundary Method with Adaptive Mesh Refinements Marcos Vanella and Elias Balaras 8 th World Congress on Computational Mechanics, WCCM8 5 th European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied
Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR)
 Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) Carsten Burstedde Omar Ghattas, Georg Stadler, Lucas C. Wilcox Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences (ICES) The University of Texas at Austin Collaboration
Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) Carsten Burstedde Omar Ghattas, Georg Stadler, Lucas C. Wilcox Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences (ICES) The University of Texas at Austin Collaboration
arxiv: v2 [cs.ms] 2 Oct 2017
![arxiv: v2 [cs.ms] 2 Oct 2017 arxiv: v2 [cs.ms] 2 Oct 2017](/thumbs/95/124123515.jpg) Enhancing speed and scalability of the ParFlow simulation code Carsten Burstedde, Jose A. Fonseca, Stefan Kollet arxiv:1702.06898v2 [cs.ms] 2 Oct 2017 Abstract Regional hydrology studies are often supported
Enhancing speed and scalability of the ParFlow simulation code Carsten Burstedde, Jose A. Fonseca, Stefan Kollet arxiv:1702.06898v2 [cs.ms] 2 Oct 2017 Abstract Regional hydrology studies are often supported
GEOMETRY MODELING & GRID GENERATION
 GEOMETRY MODELING & GRID GENERATION Dr.D.Prakash Senior Assistant Professor School of Mechanical Engineering SASTRA University, Thanjavur OBJECTIVE The objectives of this discussion are to relate experiences
GEOMETRY MODELING & GRID GENERATION Dr.D.Prakash Senior Assistant Professor School of Mechanical Engineering SASTRA University, Thanjavur OBJECTIVE The objectives of this discussion are to relate experiences
Solving Partial Differential Equations Using The Chombo Framework for Block-Structured Adaptive Mesh Refinement Algorithms
 Solving Partial Differential Equations Using The Chombo Framework for Block-Structured Adaptive Mesh Refinement Algorithms Dan Martin Applied Numerical Algorithms Group (ANAG) Lawrence Berkeley National
Solving Partial Differential Equations Using The Chombo Framework for Block-Structured Adaptive Mesh Refinement Algorithms Dan Martin Applied Numerical Algorithms Group (ANAG) Lawrence Berkeley National
The Shallow Water Equations and CUDA
 The Shallow Water Equations and CUDA HPC - Algorithms and Applications Alexander Pöppl Technical University of Munich Chair of Scientific Computing January 11 th 2017 Last Tutorial Discretized Heat Equation
The Shallow Water Equations and CUDA HPC - Algorithms and Applications Alexander Pöppl Technical University of Munich Chair of Scientific Computing January 11 th 2017 Last Tutorial Discretized Heat Equation
Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow
 Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Objectives The main objectives of the project are to learn (i) how to set up and perform flow simulations with heat transfer and mixing, (ii) post-processing and
Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Objectives The main objectives of the project are to learn (i) how to set up and perform flow simulations with heat transfer and mixing, (ii) post-processing and
Optimising MPI Applications for Heterogeneous Coupled Clusters with MetaMPICH
 Optimising MPI Applications for Heterogeneous Coupled Clusters with MetaMPICH Carsten Clauss, Martin Pöppe, Thomas Bemmerl carsten@lfbs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.mp-mpich.de Lehrstuhl für Betriebssysteme
Optimising MPI Applications for Heterogeneous Coupled Clusters with MetaMPICH Carsten Clauss, Martin Pöppe, Thomas Bemmerl carsten@lfbs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.mp-mpich.de Lehrstuhl für Betriebssysteme
The Cactus Framework. Erik Schnetter September 2006
 The Cactus Framework Erik Schnetter September 2006 Outline History The Cactus User Community Cactus Usage Patterns Bird s eye view Cactus is a freely available, portable, and manageable environment for
The Cactus Framework Erik Schnetter September 2006 Outline History The Cactus User Community Cactus Usage Patterns Bird s eye view Cactus is a freely available, portable, and manageable environment for
Construction and Application of an AMR Algorithm for Distributed Memory Computers
 Construction and Application of an AMR Algorithm for Distributed Memory Computers Ralf Deiterding California Institute of Technology,1200 East California Blvd., Mail-Code 158-79, Pasadena, CA 91125, ralf@cacr.caltech.edu
Construction and Application of an AMR Algorithm for Distributed Memory Computers Ralf Deiterding California Institute of Technology,1200 East California Blvd., Mail-Code 158-79, Pasadena, CA 91125, ralf@cacr.caltech.edu
Adaptive Mesh Refinement Based on a Posteriori Error Estimation. Martin Juhas
 Adaptive Mesh Refinement Based on a Posteriori Error Estimation by Martin Juhas A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Applied Science Graduate Department of
Adaptive Mesh Refinement Based on a Posteriori Error Estimation by Martin Juhas A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Applied Science Graduate Department of
Polygonal Mesh. Geometric object made of vertices, edges and faces. Faces are polygons. Polyhedron. Triangular mesh Quad mesh. Pyramid Cube Sphere (?
 1 Mesh Modeling Polygonal Mesh Geometric object made of vertices, edges and faces Polyhedron Pyramid Cube Sphere (?) Can also be 2D (although much less interesting) Faces are polygons Triangular mesh Quad
1 Mesh Modeling Polygonal Mesh Geometric object made of vertices, edges and faces Polyhedron Pyramid Cube Sphere (?) Can also be 2D (although much less interesting) Faces are polygons Triangular mesh Quad
Memory Hierarchy Management for Iterative Graph Structures
 Memory Hierarchy Management for Iterative Graph Structures Ibraheem Al-Furaih y Syracuse University Sanjay Ranka University of Florida Abstract The increasing gap in processor and memory speeds has forced
Memory Hierarchy Management for Iterative Graph Structures Ibraheem Al-Furaih y Syracuse University Sanjay Ranka University of Florida Abstract The increasing gap in processor and memory speeds has forced
HPC parallelization of oceanographic models via high-level techniques
 HPC parallelization of oceanographic models via high-level techniques Piero Lanucara, Vittorio Ruggiero CASPUR Vincenzo Artale, Andrea Bargagli, Adriana Carillo, Gianmaria Sannino ENEA Casaccia Roma, Italy
HPC parallelization of oceanographic models via high-level techniques Piero Lanucara, Vittorio Ruggiero CASPUR Vincenzo Artale, Andrea Bargagli, Adriana Carillo, Gianmaria Sannino ENEA Casaccia Roma, Italy
Logically Rectangular Grids and Finite Volume Methods for PDEs in Circular and Spherical Domains
 SIAM REVIEW Vol. 5, No. 4, pp. 723 752 c 28 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics Logically Rectangular Grids and Finite Volume Methods for PDEs in Circular and Spherical Domains Donna A. Calhoun
SIAM REVIEW Vol. 5, No. 4, pp. 723 752 c 28 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics Logically Rectangular Grids and Finite Volume Methods for PDEs in Circular and Spherical Domains Donna A. Calhoun
Highly efficient «on-the-fly» data processing using the open-source library CPPPO
 Highly efficient «on-the-fly» data processing using the open-source library CPPPO Graz University of Technology, DCS Computing GmbH Federico Municchi, Stefan Radl, Christoph Goniva April 7 2016, Workshop
Highly efficient «on-the-fly» data processing using the open-source library CPPPO Graz University of Technology, DCS Computing GmbH Federico Municchi, Stefan Radl, Christoph Goniva April 7 2016, Workshop
Subdivision Surfaces
 Subdivision Surfaces 1 Geometric Modeling Sometimes need more than polygon meshes Smooth surfaces Traditional geometric modeling used NURBS Non uniform rational B-Spline Demo 2 Problems with NURBS A single
Subdivision Surfaces 1 Geometric Modeling Sometimes need more than polygon meshes Smooth surfaces Traditional geometric modeling used NURBS Non uniform rational B-Spline Demo 2 Problems with NURBS A single
Progress on Advanced Dynamical Cores for the Community Atmosphere Model. June 2010
 Progress on Advanced Dynamical Cores for the Community Atmosphere Model June 2010 Art Mirin, P. O. Box 808, Livermore, CA 94551 This work performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by
Progress on Advanced Dynamical Cores for the Community Atmosphere Model June 2010 Art Mirin, P. O. Box 808, Livermore, CA 94551 This work performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by
Cubed Sphere Dynamics on the Intel Xeon Phi
 Cubed Sphere Dynamics on the Intel Xeon Phi Early Experience and Progress Collaborators: Chris Kerr (GFDL) Craig Pelissier (NASA) Bill Putman (NASA) Chuck Yount (Intel) Hoang Vu Nguyen (KAUST) Kareem Sorathia
Cubed Sphere Dynamics on the Intel Xeon Phi Early Experience and Progress Collaborators: Chris Kerr (GFDL) Craig Pelissier (NASA) Bill Putman (NASA) Chuck Yount (Intel) Hoang Vu Nguyen (KAUST) Kareem Sorathia
Introduction to Computer Graphics. Modeling (3) April 27, 2017 Kenshi Takayama
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Modeling (3) April 27, 2017 Kenshi Takayama Solid modeling 2 Solid models Thin shapes represented by single polygons Unorientable Clear definition of inside & outside
Introduction to Computer Graphics Modeling (3) April 27, 2017 Kenshi Takayama Solid modeling 2 Solid models Thin shapes represented by single polygons Unorientable Clear definition of inside & outside
PEANOCLAWâ A FUNCTIONALLY-DECOMPOSED APPROACH TO ADAPTIVE MESH REFINEMENT WITH LOCAL TIME
 TUM TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITÄT MÜNCHEN INSTITUT FÜR INFORMATIK PEANOCLAWâ A FUNCTIONALLY-DECOMPOSED APPROACH TO ADAPTIVE MESH REFINEMENT WITH LOCAL TIME Kristof Unterweger, Tobias Weinzierl, David I. Ketcheson,
TUM TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITÄT MÜNCHEN INSTITUT FÜR INFORMATIK PEANOCLAWâ A FUNCTIONALLY-DECOMPOSED APPROACH TO ADAPTIVE MESH REFINEMENT WITH LOCAL TIME Kristof Unterweger, Tobias Weinzierl, David I. Ketcheson,
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
On Partitioning Dynamic Adaptive Grid Hierarchies. Manish Parashar and James C. Browne. University of Texas at Austin
 On Partitioning Dynamic Adaptive Grid Hierarchies Manish Parashar and James C. Browne Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin fparashar, browneg@cs.utexas.edu (To be presented at
On Partitioning Dynamic Adaptive Grid Hierarchies Manish Parashar and James C. Browne Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin fparashar, browneg@cs.utexas.edu (To be presented at
Computational Astrophysics 5 Higher-order and AMR schemes
 Computational Astrophysics 5 Higher-order and AMR schemes Oscar Agertz Outline - The Godunov Method - Second-order scheme with MUSCL - Slope limiters and TVD schemes - Characteristics tracing and 2D slopes.
Computational Astrophysics 5 Higher-order and AMR schemes Oscar Agertz Outline - The Godunov Method - Second-order scheme with MUSCL - Slope limiters and TVD schemes - Characteristics tracing and 2D slopes.
Advanced Computer Graphics
 G22.2274 001, Fall 2009 Advanced Computer Graphics Project details and tools 1 Project Topics Computer Animation Geometric Modeling Computational Photography Image processing 2 Optimization All projects
G22.2274 001, Fall 2009 Advanced Computer Graphics Project details and tools 1 Project Topics Computer Animation Geometric Modeling Computational Photography Image processing 2 Optimization All projects
Getting Started with GCHP v11-02c
 Getting Started with GCHP v11-02c Lizzie Lundgren GEOS-Chem Support Team geos-chem-support@as.harvard.edu September 2017 Overview 1) What is GCHP and why use it? 2) Common Misconceptions 3) Useful Tips
Getting Started with GCHP v11-02c Lizzie Lundgren GEOS-Chem Support Team geos-chem-support@as.harvard.edu September 2017 Overview 1) What is GCHP and why use it? 2) Common Misconceptions 3) Useful Tips
SHARCNET Workshop on Parallel Computing. Hugh Merz Laurentian University May 2008
 SHARCNET Workshop on Parallel Computing Hugh Merz Laurentian University May 2008 What is Parallel Computing? A computational method that utilizes multiple processing elements to solve a problem in tandem
SHARCNET Workshop on Parallel Computing Hugh Merz Laurentian University May 2008 What is Parallel Computing? A computational method that utilizes multiple processing elements to solve a problem in tandem
Fast unstructured quadrilateral mesh generation
 Fast unstructured quadrilateral mesh generation Andrew Giuliani a, Lilia Krivodonova a, a Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Waterloo Abstract We present a novel approach for the indirect
Fast unstructured quadrilateral mesh generation Andrew Giuliani a, Lilia Krivodonova a, a Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Waterloo Abstract We present a novel approach for the indirect
Parallel Adaptive Tsunami Modelling with Triangular Discontinuous Galerkin Schemes
 Parallel Adaptive Tsunami Modelling with Triangular Discontinuous Galerkin Schemes Stefan Vater 1 Kaveh Rahnema 2 Jörn Behrens 1 Michael Bader 2 1 Universität Hamburg 2014 PDES Workshop 2 TU München Partial
Parallel Adaptive Tsunami Modelling with Triangular Discontinuous Galerkin Schemes Stefan Vater 1 Kaveh Rahnema 2 Jörn Behrens 1 Michael Bader 2 1 Universität Hamburg 2014 PDES Workshop 2 TU München Partial
Future of Enzo. Michael L. Norman James Bordner LCA/SDSC/UCSD
 Future of Enzo Michael L. Norman James Bordner LCA/SDSC/UCSD SDSC Resources Data to Discovery Host SDNAP San Diego network access point for multiple 10 Gbs WANs ESNet, NSF TeraGrid, CENIC, Internet2, StarTap
Future of Enzo Michael L. Norman James Bordner LCA/SDSC/UCSD SDSC Resources Data to Discovery Host SDNAP San Diego network access point for multiple 10 Gbs WANs ESNet, NSF TeraGrid, CENIC, Internet2, StarTap
4. Networks. in parallel computers. Advances in Computer Architecture
 4. Networks in parallel computers Advances in Computer Architecture System architectures for parallel computers Control organization Single Instruction stream Multiple Data stream (SIMD) All processors
4. Networks in parallel computers Advances in Computer Architecture System architectures for parallel computers Control organization Single Instruction stream Multiple Data stream (SIMD) All processors
Massively Parallel Phase Field Simulations using HPC Framework walberla
 Massively Parallel Phase Field Simulations using HPC Framework walberla SIAM CSE 2015, March 15 th 2015 Martin Bauer, Florian Schornbaum, Christian Godenschwager, Johannes Hötzer, Harald Köstler and Ulrich
Massively Parallel Phase Field Simulations using HPC Framework walberla SIAM CSE 2015, March 15 th 2015 Martin Bauer, Florian Schornbaum, Christian Godenschwager, Johannes Hötzer, Harald Köstler and Ulrich
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING
 CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
EN2910A: Advanced Computer Architecture Topic 06: Supercomputers & Data Centers Prof. Sherief Reda School of Engineering Brown University
 EN2910A: Advanced Computer Architecture Topic 06: Supercomputers & Data Centers Prof. Sherief Reda School of Engineering Brown University Material from: The Datacenter as a Computer: An Introduction to
EN2910A: Advanced Computer Architecture Topic 06: Supercomputers & Data Centers Prof. Sherief Reda School of Engineering Brown University Material from: The Datacenter as a Computer: An Introduction to
CMSC 714 Lecture 6 MPI vs. OpenMP and OpenACC. Guest Lecturer: Sukhyun Song (original slides by Alan Sussman)
 CMSC 714 Lecture 6 MPI vs. OpenMP and OpenACC Guest Lecturer: Sukhyun Song (original slides by Alan Sussman) Parallel Programming with Message Passing and Directives 2 MPI + OpenMP Some applications can
CMSC 714 Lecture 6 MPI vs. OpenMP and OpenACC Guest Lecturer: Sukhyun Song (original slides by Alan Sussman) Parallel Programming with Message Passing and Directives 2 MPI + OpenMP Some applications can
A mass-conservative version of the semi- Lagrangian semi-implicit HIRLAM using Lagrangian vertical coordinates
 A mass-conservative version of the semi- Lagrangian semi-implicit HIRLAM using Lagrangian vertical coordinates Peter Hjort Lauritzen Atmospheric Modeling & Predictability Section National Center for Atmospheric
A mass-conservative version of the semi- Lagrangian semi-implicit HIRLAM using Lagrangian vertical coordinates Peter Hjort Lauritzen Atmospheric Modeling & Predictability Section National Center for Atmospheric
The Icosahedral Nonhydrostatic (ICON) Model
 The Icosahedral Nonhydrostatic (ICON) Model Scalability on Massively Parallel Computer Architectures Florian Prill, DWD + the ICON team 15th ECMWF Workshop on HPC in Meteorology October 2, 2012 ICON =
The Icosahedral Nonhydrostatic (ICON) Model Scalability on Massively Parallel Computer Architectures Florian Prill, DWD + the ICON team 15th ECMWF Workshop on HPC in Meteorology October 2, 2012 ICON =
Advanced Computer Graphics
 G22.2274 001, Fall 2010 Advanced Computer Graphics Project details and tools 1 Projects Details of each project are on the website under Projects Please review all the projects and come see me if you would
G22.2274 001, Fall 2010 Advanced Computer Graphics Project details and tools 1 Projects Details of each project are on the website under Projects Please review all the projects and come see me if you would
