Math 407 Solutions to Exam 3 April 24, Let f = u + iv, and let Γ be parmetrized by Γ = (x (t),y(t)) = x (t) +iy (t) for a t b.
|
|
|
- Evan Douglas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 7 Solutions to Exam 3 April, 3 1. (1 Define the following: (a f (z dz, where Γ is a smooth curve with finite length. Γ Let f u + iv, and let Γ be parmetrized by Γ (x (t,y(t x (t +iy (t for a t b. Then Γ f (z dz b a ( u dx dt v dy b ( dt + i u dy dt dt + v dx dt dt a The parametrization of Γ is assumed to be smooth and the functions u and v are assumed to be continuous functions of x and y. (b The function f is analytic at z. f is analytic at z if there is a neighborhood of z such that f is differentiable at every point in this neighborhood. (c The function f has a pole of order at z. The statement means that z is an isolated singular point of f, and that the Laurent expansion of f about the point z has the form f (z b (z z + b 3 (z z 3 b (z z + b 1 (z z 1 + a n (z z n n with the coefficienct b. (d The residue of f at z. The residue of f at z is the coefficient of (z z 1 in the Laurent expansion of f.. (8 If f (z u+iv has a derivative at z x + iy, then the real valued functions u and v satisfy a pair of partial differential equations at z. These equations are called the Cauchy-Riemann equations. (a State the Cauchy-Riemann equations. x v y v y x
2 (b Prove that u and v must satisfy these equations. The Cauchy Riemann equations follow from the fact that if f (z exists, then its value must be the same regardless of how z appoaches zero. The lines below calculate the derivative of f by first letting z appoaches zero through real values and then through imaginary values. Set f u + iv, and z h, with h a real number, then df dz h u (x + h, y+iv (x + h, y u (x, y iv (x, y h u (x + h, y u (x, y iv (x + h, y iv (x, y + lim h h h h x + i v x Now set z ih, with h a real number, then df dz u (x, y + h+iv (x, y + h u (x, y iv (x, y h ih u (x, y + h u (x, y iv (x, y + h iv (x, y + lim h ih h ih 1 i y + v y v y i y Two complex numbers are equal if and only if they have the same real and imaginary parts. Thus, x v y v y x
3 3. (15 (a State the Cauchy-Goursat theorem. Be sure to include any needed hypotheses. Suppose f (z is analytic inside and on a simple closed contour Γ. Then f (z dz Γ (b Suppose f has singular points z 1 and z inside a closed contour C. Why does C f (z dz πi (Res zz1 f + Res zz f Let C 1 and C denote positively oriented circles centered at z 1 and z respectively, such that both circles and their interiors are disjoint from each other, and both are completely contained inside the original contour C. Then the Cauchy-Goursat theorem is used to show that f (z dz f (z dz + f (z dz C C 1 C The value of the contour integral of f over these positively oriented circles is then computed by looking at the Laurent series expansion of f around each of these points. We parametrize the circle C i by z (t z i +ρe iθ, θ π. Then we have ( f (z dz c n (z z i n dz C i C i n n n c n C i (z z i n dz π c n i ρ n+1 e i(n+1θ dθ The only one of the integrals that is not equal to zero is the one in which the exponent in e i(n+1θ is zero. That is, n +1 orn 1. Thus, π f (z dz (c 1 i dθ C i πi (c 1 πires zzi f 3
4 . ( Let f (z z (z 1 (z. (a Locate all of the isolated singular points of f and determine their type. The isolated singular points of f are z, 1, and. Since is zero at z, and not equal to zero at the other two singular points, is a removable singularity, z 1 is a simple pole, that is a pole of order 1, and z is a pole of order. (b Calculate the residue of f at each of its isolated singular points. At z the residue of f is zero. At z 1 the residue equals At z the residue equals Res z1 f (z 1 z 1 z (z 1 (z d Res z f z dz z 1 z (z sin [ (z [ d z dz z (z 1 z (z 1 (z ] z (cos z z (z 1 (z 1 z (z 1 cos 3 sin.89 ]
5 5. ( Let f (z z ( e 1/z 1. (a Find the Laurent series expansion of f about z. What type of singular point is? ( f (z z 1 z n n! 1 n1 n 1 z n n! z z (3! + 1 z (! z n (n+! + Since the number of terms in which z appears to a negative exponent is not finite, is an essential singular point for f. (b Let C denote the positively oriented circle of radius centered at the origin. Calculate C f (z dz. f (z dz πi (Res z f C πi ( 1 6 πi 3 6. (15 Let f (z z 1+z and let C R denote the upper half of the positively oriented circle of radius R centered at the origin. (a Show lim C R f(z dz. If z R then z 1+z R 1+z f (z dz C R R R 1. Thus, R R 1 (πr πr3 R 1 Thus, as R gets arbitrarily large the absolute value of the integral approaches zero. That is, C R f(z dz. lim 5
6 (b Using residue theory calculate 1+xdx. Hint: the integrand is an even function of x. Let Γ R denote the closed contour that consists of that part of the real line between R and R, and the half circle C R. Then we have 1+x dx 1 1 lim 1+x dx ( R R 1 lim z (ΓR 1+z dz 1+x CR dx + z 1+z dz For R>1 the only singular points of the integrand are at z 1 e πi/ and z e 3πi /. These are simple poles of the integrand. Thus, 1+x dx 1 [ [ ] z z (Res πi zz1 ]+ 1+z Res zz 1+z ( z πi 1 z1 3 + z z 3 πi ( z 1 z πi ( e πi/ + e 3πi πi ( ( π i sin π 6
7 7. (1 Let C ρ denote the top half of the circle of radius ρ centered at the origin. Suppose that C ρ is traced out from right to left. Calculate lim ρ + C ρ z dz. The upper half circle is parametrized by z ρe iθ, θ π. The Laurent series expansion of /z about z is Thus, the contour integral equals C ρ z dz z 1 z n n ( 1 n z n+1 (n +1! ( 1 n z n 1 (n +1! 1 z + ( 1 n z n 1 (n +1! π π πi [ n1 1 ρe iθ + idθ+i n 1 n1 ( ρe ( 1 n iθ ] n 1 iρe iθ dθ (n +1! ( 1 n ρ n (n + 1! π e niθ dθ Note: for this particular function there is no need to actually take the limit as ρ tends to zero from above as each of the integrals π eniθ dθ. Thus, lim ρ + C ρ z dz. πi 7
MATH 417 Homework 8 Instructor: D. Cabrera Due August 4. e i(2z) (z 2 +1) 2 C R. z 1 C 1. 2 (z 2 + 1) dz 2. φ(z) = ei(2z) (z i) 2
 MATH 47 Homework 8 Instructor: D. abrera Due August 4. ompute the improper integral cos x (x + ) dx Solution: To evaluate the integral consider the complex integral e i(z) (z + ) dz where is the union
MATH 47 Homework 8 Instructor: D. abrera Due August 4. ompute the improper integral cos x (x + ) dx Solution: To evaluate the integral consider the complex integral e i(z) (z + ) dz where is the union
Complex Integration (2A) Young Won Lim 1/29/13
 omplex Integration (2A) opyright (c) 2012 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free ocumentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
omplex Integration (2A) opyright (c) 2012 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free ocumentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
Math 814 HW 2. September 29, p. 43: 1,4,6,13,15, p. 54 1, 3 (cos z only). u(x, y) = x 3 3xy 2, u(x, y) = x/(x 2 + y 2 ),
 Math 814 HW 2 September 29, 2007 p. 43: 1,4,6,13,15, p. 54 1, 3 (cos z only). u(x, y) = x 3 3xy 2, u(x, y) = x/(x 2 + y 2 ), p.43, Exercise 1. Show that the function f(z) = z 2 = x 2 + y 2 has a derivative
Math 814 HW 2 September 29, 2007 p. 43: 1,4,6,13,15, p. 54 1, 3 (cos z only). u(x, y) = x 3 3xy 2, u(x, y) = x/(x 2 + y 2 ), p.43, Exercise 1. Show that the function f(z) = z 2 = x 2 + y 2 has a derivative
1. Suppose that the equation F (x, y, z) = 0 implicitly defines each of the three variables x, y, and z as functions of the other two:
 Final Solutions. Suppose that the equation F (x, y, z) implicitly defines each of the three variables x, y, and z as functions of the other two: z f(x, y), y g(x, z), x h(y, z). If F is differentiable
Final Solutions. Suppose that the equation F (x, y, z) implicitly defines each of the three variables x, y, and z as functions of the other two: z f(x, y), y g(x, z), x h(y, z). If F is differentiable
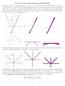
The Differential df, the Gradient f, & the Directional Derivative Dû f sec 14.4 (cont), Goals. Warm-up: Differentiability. Notes. Notes.
 The Differential df, the Gradient f, & the Directional Derivative Dû f sec 14.4 (cont), 14.5 10 March 2014 Goals. We will: Define the differential df and use it to approximate changes in a function s value.
The Differential df, the Gradient f, & the Directional Derivative Dû f sec 14.4 (cont), 14.5 10 March 2014 Goals. We will: Define the differential df and use it to approximate changes in a function s value.
MATH 104 First Midterm Exam - Fall (d) A solid has as its base the region in the xy-plane the region between the curve y = 1 x2
 MATH 14 First Midterm Exam - Fall 214 1. Find the area between the graphs of y = x 2 + x + 5 and y = 2x 2 x. 1. Find the area between the graphs of y = x 2 + 4x + 6 and y = 2x 2 x. 1. Find the area between
MATH 14 First Midterm Exam - Fall 214 1. Find the area between the graphs of y = x 2 + x + 5 and y = 2x 2 x. 1. Find the area between the graphs of y = x 2 + 4x + 6 and y = 2x 2 x. 1. Find the area between
Calculus III. Math 233 Spring In-term exam April 11th. Suggested solutions
 Calculus III Math Spring 7 In-term exam April th. Suggested solutions This exam contains sixteen problems numbered through 6. Problems 5 are multiple choice problems, which each count 5% of your total
Calculus III Math Spring 7 In-term exam April th. Suggested solutions This exam contains sixteen problems numbered through 6. Problems 5 are multiple choice problems, which each count 5% of your total
3. The three points (2, 4, 1), (1, 2, 2) and (5, 2, 2) determine a plane. Which of the following points is in that plane?
 Math 4 Practice Problems for Midterm. A unit vector that is perpendicular to both V =, 3, and W = 4,, is (a) V W (b) V W (c) 5 6 V W (d) 3 6 V W (e) 7 6 V W. In three dimensions, the graph of the equation
Math 4 Practice Problems for Midterm. A unit vector that is perpendicular to both V =, 3, and W = 4,, is (a) V W (b) V W (c) 5 6 V W (d) 3 6 V W (e) 7 6 V W. In three dimensions, the graph of the equation
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV. Exam I (Friday, April 29) will cover sections
 REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
Math 265 Exam 3 Solutions
 C Roettger, Fall 16 Math 265 Exam 3 Solutions Problem 1 Let D be the region inside the circle r 5 sin θ but outside the cardioid r 2 + sin θ. Find the area of D. Note that r and θ denote polar coordinates.
C Roettger, Fall 16 Math 265 Exam 3 Solutions Problem 1 Let D be the region inside the circle r 5 sin θ but outside the cardioid r 2 + sin θ. Find the area of D. Note that r and θ denote polar coordinates.
Cauchy's Integral Formula
 Cauchy's Integral Formula Thursday, October 24, 2013 1:57 PM Last time we discussed functions defined by integration over complex contours, and let's look at a particularly important example: Where C is
Cauchy's Integral Formula Thursday, October 24, 2013 1:57 PM Last time we discussed functions defined by integration over complex contours, and let's look at a particularly important example: Where C is
Lecture 15. Lecturer: Prof. Sergei Fedotov Calculus and Vectors. Length of a Curve and Parametric Equations
 Lecture 15 Lecturer: Prof. Sergei Fedotov 10131 - Calculus and Vectors Length of a Curve and Parametric Equations Sergei Fedotov (University of Manchester) MATH10131 2011 1 / 5 Lecture 15 1 Length of a
Lecture 15 Lecturer: Prof. Sergei Fedotov 10131 - Calculus and Vectors Length of a Curve and Parametric Equations Sergei Fedotov (University of Manchester) MATH10131 2011 1 / 5 Lecture 15 1 Length of a
Polar Coordinates. Chapter 10: Parametric Equations and Polar coordinates, Section 10.3: Polar coordinates 28 / 46
 Polar Coordinates Polar Coordinates: Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ)
Polar Coordinates Polar Coordinates: Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ)
We can conclude that if f is differentiable in an interval containing a, then. f(x) L(x) = f(a) + f (a)(x a).
 = sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
= sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
Introduction to Complex Analysis
 Introduction to Complex Analysis George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 413 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Complex Analysis October 2014 1 / 50 Outline
Introduction to Complex Analysis George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 413 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Complex Analysis October 2014 1 / 50 Outline
Chapter 10 Homework: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
 Chapter 1 Homework: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Name Homework 1.2 1. Consider the parametric equations x = t and y = 3 t. a. Construct a table of values for t =, 1, 2, 3, and 4 b. Plot the
Chapter 1 Homework: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Name Homework 1.2 1. Consider the parametric equations x = t and y = 3 t. a. Construct a table of values for t =, 1, 2, 3, and 4 b. Plot the
38. Triple Integration over Rectangular Regions
 8. Triple Integration over Rectangular Regions A rectangular solid region S in R can be defined by three compound inequalities, a 1 x a, b 1 y b, c 1 z c, where a 1, a, b 1, b, c 1 and c are constants.
8. Triple Integration over Rectangular Regions A rectangular solid region S in R can be defined by three compound inequalities, a 1 x a, b 1 y b, c 1 z c, where a 1, a, b 1, b, c 1 and c are constants.
MATH 261 EXAM III PRACTICE PROBLEMS
 MATH 6 EXAM III PRACTICE PROBLEMS These practice problems are pulled from actual midterms in previous semesters. Exam 3 typically has 5 (not 6!) problems on it, with no more than one problem of any given
MATH 6 EXAM III PRACTICE PROBLEMS These practice problems are pulled from actual midterms in previous semesters. Exam 3 typically has 5 (not 6!) problems on it, with no more than one problem of any given
Polar Coordinates. Chapter 10: Parametric Equations and Polar coordinates, Section 10.3: Polar coordinates 27 / 45
 : Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ) Chapter 10: Parametric Equations
: Given any point P = (x, y) on the plane r stands for the distance from the origin (0, 0). θ stands for the angle from positive x-axis to OP. Polar coordinate: (r, θ) Chapter 10: Parametric Equations
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 2003
 Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Math Exam III Review
 Math 213 - Exam III Review Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 10, 2019 Homework Exam III is tonight at 5 PM Exam III will cover 15.1 15.3, 15.6 15.9, 16.1 16.2, and identifying conservative vector
Math 213 - Exam III Review Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 10, 2019 Homework Exam III is tonight at 5 PM Exam III will cover 15.1 15.3, 15.6 15.9, 16.1 16.2, and identifying conservative vector
Math 241, Final Exam. 12/11/12.
 Math, Final Exam. //. No notes, calculator, or text. There are points total. Partial credit may be given. ircle or otherwise clearly identify your final answer. Name:. (5 points): Equation of a line. Find
Math, Final Exam. //. No notes, calculator, or text. There are points total. Partial credit may be given. ircle or otherwise clearly identify your final answer. Name:. (5 points): Equation of a line. Find
Worksheet 3.2: Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates
 Boise State Math 75 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.: ouble Integrals in Polar Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Trig/Calc II: Convert equations in x and y into r and θ, using the
Boise State Math 75 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.: ouble Integrals in Polar Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Trig/Calc II: Convert equations in x and y into r and θ, using the
Math 11 Fall 2016 Section 1 Monday, October 17, 2016
 Math 11 Fall 16 Section 1 Monday, October 17, 16 First, some important points from the last class: f(x, y, z) dv, the integral (with respect to volume) of f over the three-dimensional region, is a triple
Math 11 Fall 16 Section 1 Monday, October 17, 16 First, some important points from the last class: f(x, y, z) dv, the integral (with respect to volume) of f over the three-dimensional region, is a triple
Topic 5.1: Line Elements and Scalar Line Integrals. Textbook: Section 16.2
 Topic 5.1: Line Elements and Scalar Line Integrals Textbook: Section 16.2 Warm-Up: Derivatives of Vector Functions Suppose r(t) = x(t) î + y(t) ĵ + z(t) ˆk parameterizes a curve C. The vector: is: r (t)
Topic 5.1: Line Elements and Scalar Line Integrals Textbook: Section 16.2 Warm-Up: Derivatives of Vector Functions Suppose r(t) = x(t) î + y(t) ĵ + z(t) ˆk parameterizes a curve C. The vector: is: r (t)
Worksheet 3.4: Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates. Warm-Up: Cylindrical Volume Element d V
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.4: Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know what the volume element dv represents. Be able to find
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.4: Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know what the volume element dv represents. Be able to find
f xx (x, y) = 6 + 6x f xy (x, y) = 0 f yy (x, y) = y In general, the quantity that we re interested in is
 1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
1. Let f(x, y) = 5 + 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 2y 3 + x 3. (a) Final all critical points of f. (b) Use the second derivatives test to classify the critical points you found in (a) as a local maximum, local minimum,
MIDTERM. Section: Signature:
 MIDTERM Math 32B 8/8/2 Name: Section: Signature: Read all of the following information before starting the exam: Check your exam to make sure all pages are present. NO CALCULATORS! Show all work, clearly
MIDTERM Math 32B 8/8/2 Name: Section: Signature: Read all of the following information before starting the exam: Check your exam to make sure all pages are present. NO CALCULATORS! Show all work, clearly
Functions of Two variables.
 Functions of Two variables. Ferdinánd Filip filip.ferdinand@bgk.uni-obuda.hu siva.banki.hu/jegyzetek 27 February 217 Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 1 / 36 Table of contents
Functions of Two variables. Ferdinánd Filip filip.ferdinand@bgk.uni-obuda.hu siva.banki.hu/jegyzetek 27 February 217 Ferdinánd Filip 27 February 217 Functions of Two variables. 1 / 36 Table of contents
Triple Integrals. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Triple Integrals
 Triple Integrals MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 211 Riemann Sum Approach Suppose we wish to integrate w f (x, y, z), a continuous function, on the box-shaped region
Triple Integrals MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 211 Riemann Sum Approach Suppose we wish to integrate w f (x, y, z), a continuous function, on the box-shaped region
Section Parametrized Surfaces and Surface Integrals. (I) Parametrizing Surfaces (II) Surface Area (III) Scalar Surface Integrals
 Section 16.4 Parametrized Surfaces and Surface Integrals (I) Parametrizing Surfaces (II) Surface Area (III) Scalar Surface Integrals MATH 127 (Section 16.4) Parametrized Surfaces and Surface Integrals
Section 16.4 Parametrized Surfaces and Surface Integrals (I) Parametrizing Surfaces (II) Surface Area (III) Scalar Surface Integrals MATH 127 (Section 16.4) Parametrized Surfaces and Surface Integrals
Math 52 - Fall Final Exam PART 1
 Math 52 - Fall 2013 - Final Exam PART 1 Name: Student ID: Signature: Instructions: Print your name and student ID number and write your signature to indicate that you accept the Honor Code. This exam consists
Math 52 - Fall 2013 - Final Exam PART 1 Name: Student ID: Signature: Instructions: Print your name and student ID number and write your signature to indicate that you accept the Honor Code. This exam consists
Examples from Section 7.1: Integration by Parts Page 1
 Examples from Section 7.: Integration by Parts Page Questions Example Determine x cos x dx. Example e θ cos θ dθ Example You may wonder why we do not add a constant at the point where we integrate for
Examples from Section 7.: Integration by Parts Page Questions Example Determine x cos x dx. Example e θ cos θ dθ Example You may wonder why we do not add a constant at the point where we integrate for
MATH 2400, Analytic Geometry and Calculus 3
 MATH 2400, Analytic Geometry and Calculus 3 List of important Definitions and Theorems 1 Foundations Definition 1. By a function f one understands a mathematical object consisting of (i) a set X, called
MATH 2400, Analytic Geometry and Calculus 3 List of important Definitions and Theorems 1 Foundations Definition 1. By a function f one understands a mathematical object consisting of (i) a set X, called
Calculus IV. Exam 2 November 13, 2003
 Name: Section: Calculus IV Math 1 Fall Professor Ben Richert Exam November 1, Please do all your work in this booklet and show all the steps. Calculators and note-cards are not allowed. Problem Possible
Name: Section: Calculus IV Math 1 Fall Professor Ben Richert Exam November 1, Please do all your work in this booklet and show all the steps. Calculators and note-cards are not allowed. Problem Possible
The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations
 1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
MAC2313 Final A. a. The vector r u r v lies in the tangent plane of S at a given point. b. S f(x, y, z) ds = R f(r(u, v)) r u r v du dv.
 MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. Let f(x, y, z) be a function continuous in R 3 and let S be a surface parameterized by r(u, v) with the domain of the parameterization given by R; how many of the following are
MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. Let f(x, y, z) be a function continuous in R 3 and let S be a surface parameterized by r(u, v) with the domain of the parameterization given by R; how many of the following are
University of California, Berkeley
 University of California, Berkeley FINAL EXAMINATION, Fall 2012 DURATION: 3 hours Department of Mathematics MATH 53 Multivariable Calculus Examiner: Sean Fitzpatrick Total: 100 points Family Name: Given
University of California, Berkeley FINAL EXAMINATION, Fall 2012 DURATION: 3 hours Department of Mathematics MATH 53 Multivariable Calculus Examiner: Sean Fitzpatrick Total: 100 points Family Name: Given
Homework 8. Due: Tuesday, March 31st, 2009
 MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 9 Homework 8 Due: Tuesday, March 3st, 9 Section 6.5, pg. 54: 7, 3. Section 6.6, pg. 58:, 3. Section 6.7, pg. 66: 3, 5, 47. Section 6.8, pg. 73: 33, 38. Section
MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 9 Homework 8 Due: Tuesday, March 3st, 9 Section 6.5, pg. 54: 7, 3. Section 6.6, pg. 58:, 3. Section 6.7, pg. 66: 3, 5, 47. Section 6.8, pg. 73: 33, 38. Section
Calculus on the complex plane C
 Calculus on the complex plane C Let z = x + iy be the complex variable on the complex plane C == R ir where i = 1. Definition A function f : C C is holomorphic if it is complex differentiable, i.e., for
Calculus on the complex plane C Let z = x + iy be the complex variable on the complex plane C == R ir where i = 1. Definition A function f : C C is holomorphic if it is complex differentiable, i.e., for
Math 5320, 3/28/18 Worksheet 26: Ruler and compass constructions. 1. Use your ruler and compass to construct a line perpendicular to the line below:
 Math 5320, 3/28/18 Worksheet 26: Ruler and compass constructions Name: 1. Use your ruler and compass to construct a line perpendicular to the line below: 2. Suppose the following two points are spaced
Math 5320, 3/28/18 Worksheet 26: Ruler and compass constructions Name: 1. Use your ruler and compass to construct a line perpendicular to the line below: 2. Suppose the following two points are spaced
Chapter 15 Vector Calculus
 Chapter 15 Vector Calculus 151 Vector Fields 152 Line Integrals 153 Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path 153 Conservative Fields and Potential Functions 154 Green s Theorem 155 urface Integrals
Chapter 15 Vector Calculus 151 Vector Fields 152 Line Integrals 153 Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path 153 Conservative Fields and Potential Functions 154 Green s Theorem 155 urface Integrals
Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( ) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent
 Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
Lecture 9. Partial Derivatives: Signs on Level Curves, Tangent Planes, and Differentials ( 11.3-11.4) Feb. 26, 2012 (Sun) Signs of Partial Derivatives on Level Curves Level curves are shown for a function
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today Tangent Planes and Linear Approximation and the Gradient Vector Vector Functions 1/21 Recall in one-variable calculus, as we zoom in toward a point on a curve, the graph becomes
What you will learn today Tangent Planes and Linear Approximation and the Gradient Vector Vector Functions 1/21 Recall in one-variable calculus, as we zoom in toward a point on a curve, the graph becomes
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester Lecture 33 Notes
 Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 33 Notes These notes correspond to Section 9.3 in the text. Polar Coordinates Throughout this course, we have denoted a point in the plane by an ordered
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 33 Notes These notes correspond to Section 9.3 in the text. Polar Coordinates Throughout this course, we have denoted a point in the plane by an ordered
Gradient and Directional Derivatives
 Gradient and Directional Derivatives MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Given z = f (x, y) we understand that f : gives the rate of change of z in
Gradient and Directional Derivatives MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Given z = f (x, y) we understand that f : gives the rate of change of z in
Math 241, Exam 3 Information.
 Math 241, xam 3 Information. 11/28/12, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. xam 3 will be based on: Sections 15.2-15.4, 15.6-15.8. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241fa12/241.html)
Math 241, xam 3 Information. 11/28/12, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. xam 3 will be based on: Sections 15.2-15.4, 15.6-15.8. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241fa12/241.html)
2.4 Quadratic differentials and their horizontal and vertical foliations
 2 MEASURED FOLIATIONS 37 in P[0, ) C is a closed ball of dimension 6g 6+2p whose interior is P L(T ). The boundary points of this ball are usually described in one of two ways: using measured geodesic
2 MEASURED FOLIATIONS 37 in P[0, ) C is a closed ball of dimension 6g 6+2p whose interior is P L(T ). The boundary points of this ball are usually described in one of two ways: using measured geodesic
302 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES. 4. Function of several variables, their domain. 6. Limit of a function of several variables
 302 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES 3.8 Chapter Review 3.8.1 Concepts to Know You should have an understanding of, and be able to explain the concepts listed below. 1. Boundary and interior points
302 CHAPTER 3. FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES 3.8 Chapter Review 3.8.1 Concepts to Know You should have an understanding of, and be able to explain the concepts listed below. 1. Boundary and interior points
MATH. 2153, Spring 16, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 January 25, 2016 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points.
 MATH. 2153, Spring 16, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 January 25, 2016 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points. 1. Evaluate the area A of the triangle with the vertices
MATH. 2153, Spring 16, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 January 25, 2016 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points. 1. Evaluate the area A of the triangle with the vertices
MH2800/MAS183 - Linear Algebra and Multivariable Calculus
 MH28/MAS83 - Linear Algebra and Multivariable Calculus SEMESTER II EXAMINATION 2-22 Solved by Tao Biaoshuai Email: taob@e.ntu.edu.sg QESTION Let A 2 2 2. Solve the homogeneous linear system Ax and write
MH28/MAS83 - Linear Algebra and Multivariable Calculus SEMESTER II EXAMINATION 2-22 Solved by Tao Biaoshuai Email: taob@e.ntu.edu.sg QESTION Let A 2 2 2. Solve the homogeneous linear system Ax and write
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS. Page. 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary Assignments...2
 PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary...1 3. Assignments...2 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2010 Assignment Date to be Posted
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary...1 3. Assignments...2 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2010 Assignment Date to be Posted
Math 52 Final Exam March 16, 2009
 Math 52 Final Exam March 16, 2009 Name : Section Leader: Josh Lan Xiannan (Circle one) Genauer Huang Li Section Time: 10:00 11:00 1:15 2:15 (Circle one) This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. No calculators
Math 52 Final Exam March 16, 2009 Name : Section Leader: Josh Lan Xiannan (Circle one) Genauer Huang Li Section Time: 10:00 11:00 1:15 2:15 (Circle one) This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. No calculators
Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two
 Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Thursday, February 28, class time. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration: sections 13.3,
Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Thursday, February 28, class time. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration: sections 13.3,
Math 213 Calculus III Practice Exam 2 Solutions Fall 2002
 Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
18.02 Final Exam. y = 0
 No books, notes or calculators. 5 problems, 50 points. 8.0 Final Exam Useful formula: cos (θ) = ( + cos(θ)) Problem. (0 points) a) (5 pts.) Find the equation in the form Ax + By + z = D of the plane P
No books, notes or calculators. 5 problems, 50 points. 8.0 Final Exam Useful formula: cos (θ) = ( + cos(θ)) Problem. (0 points) a) (5 pts.) Find the equation in the form Ax + By + z = D of the plane P
Worksheet 3.5: Triple Integrals in Spherical Coordinates. Warm-Up: Spherical Coordinates (ρ, φ, θ)
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.5: Triple Integrals in Spherical Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know what the volume element dv represents. Be able to find
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.5: Triple Integrals in Spherical Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know what the volume element dv represents. Be able to find
Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two
 Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Tuesday, August 16. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration. You should review the double
Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Tuesday, August 16. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration. You should review the double
MAC2313 Test 3 A E g(x, y, z) dy dx dz
 MAC2313 Test 3 A (5 pts) 1. If the function g(x, y, z) is integrated over the cylindrical solid bounded by x 2 + y 2 = 3, z = 1, and z = 7, the correct integral in Cartesian coordinates is given by: A.
MAC2313 Test 3 A (5 pts) 1. If the function g(x, y, z) is integrated over the cylindrical solid bounded by x 2 + y 2 = 3, z = 1, and z = 7, the correct integral in Cartesian coordinates is given by: A.
8(x 2) + 21(y 1) + 6(z 3) = 0 8x + 21y + 6z = 55.
 MATH 24 -Review for Final Exam. Let f(x, y, z) x 2 yz + y 3 z x 2 + z, and a (2,, 3). Note: f (2xyz 2x, x 2 z + 3y 2 z, x 2 y + y 3 + ) f(a) (8, 2, 6) (a) Find all stationary points (if any) of f. et f.
MATH 24 -Review for Final Exam. Let f(x, y, z) x 2 yz + y 3 z x 2 + z, and a (2,, 3). Note: f (2xyz 2x, x 2 z + 3y 2 z, x 2 y + y 3 + ) f(a) (8, 2, 6) (a) Find all stationary points (if any) of f. et f.
Line Integration in the Complex Plane
 න f z dz C Engineering Math EECE 3640 1 A Review of Integration of Functions of Real Numbers: a b f x dx is the area under the curve in the figure below: The interval of integration is the path along the
න f z dz C Engineering Math EECE 3640 1 A Review of Integration of Functions of Real Numbers: a b f x dx is the area under the curve in the figure below: The interval of integration is the path along the
MAT1B01: Curves defined by parametric equations
 MAT1B01: Curves defined by parametric equations Dr Craig 24 October 2016 My details: acraig@uj.ac.za Consulting hours: Thursday 11h20 12h55 Friday 11h30 13h00 Office C-Ring 508 https://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com/
MAT1B01: Curves defined by parametric equations Dr Craig 24 October 2016 My details: acraig@uj.ac.za Consulting hours: Thursday 11h20 12h55 Friday 11h30 13h00 Office C-Ring 508 https://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com/
MATH 1020 WORKSHEET 10.1 Parametric Equations
 MATH WORKSHEET. Parametric Equations If f and g are continuous functions on an interval I, then the equations x ft) and y gt) are called parametric equations. The parametric equations along with the graph
MATH WORKSHEET. Parametric Equations If f and g are continuous functions on an interval I, then the equations x ft) and y gt) are called parametric equations. The parametric equations along with the graph
Chapter 11. Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates
 Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ayman H. Sakka Chapter 11 Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates In this chapter we study new ways to define curves in the plane, give geometric definitions of parabolas, ellipses,
Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ayman H. Sakka Chapter 11 Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates In this chapter we study new ways to define curves in the plane, give geometric definitions of parabolas, ellipses,
Multiple Integrals. max x i 0
 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals Definite integrals appear when one solves Area problem. Find the area A of the region bounded above by the curve y = f(x), below by the x-axis, and on the sides by
Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals Definite integrals appear when one solves Area problem. Find the area A of the region bounded above by the curve y = f(x), below by the x-axis, and on the sides by
Directional Derivatives as Vectors
 Directional Derivatives as Vectors John Ganci 1 Al Lehnen 2 1 Richland College Dallas, TX jganci@dcccd.edu 2 Madison Area Technical College Madison, WI alehnen@matcmadison.edu Statement of problem We are
Directional Derivatives as Vectors John Ganci 1 Al Lehnen 2 1 Richland College Dallas, TX jganci@dcccd.edu 2 Madison Area Technical College Madison, WI alehnen@matcmadison.edu Statement of problem We are
= f (a, b) + (hf x + kf y ) (a,b) +
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
MAT203 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS
 MAT203 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT203 covers essentially the same material as MAT201, but is more in depth and theoretical. Exam problems are often more sophisticated in scope and difficulty
MAT203 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT203 covers essentially the same material as MAT201, but is more in depth and theoretical. Exam problems are often more sophisticated in scope and difficulty
Background for Surface Integration
 Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
Coordinate Transformations in Advanced Calculus
 Coordinate Transformations in Advanced Calculus by Sacha Nandlall T.A. for MATH 264, McGill University Email: sacha.nandlall@mail.mcgill.ca Website: http://www.resanova.com/teaching/calculus/ Fall 2006,
Coordinate Transformations in Advanced Calculus by Sacha Nandlall T.A. for MATH 264, McGill University Email: sacha.nandlall@mail.mcgill.ca Website: http://www.resanova.com/teaching/calculus/ Fall 2006,
Applications of Triple Integrals
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
Tutorial 4. Differential Geometry I - Curves
 23686 Numerical Geometry of Images Tutorial 4 Differential Geometry I - Curves Anastasia Dubrovina c 22 / 2 Anastasia Dubrovina CS 23686 - Tutorial 4 - Differential Geometry I - Curves Differential Geometry
23686 Numerical Geometry of Images Tutorial 4 Differential Geometry I - Curves Anastasia Dubrovina c 22 / 2 Anastasia Dubrovina CS 23686 - Tutorial 4 - Differential Geometry I - Curves Differential Geometry
Study Guide for Test 2
 Study Guide for Test Math 6: Calculus October, 7. Overview Non-graphing calculators will be allowed. You will need to know the following:. Set Pieces 9 4.. Trigonometric Substitutions (Section 7.).. Partial
Study Guide for Test Math 6: Calculus October, 7. Overview Non-graphing calculators will be allowed. You will need to know the following:. Set Pieces 9 4.. Trigonometric Substitutions (Section 7.).. Partial
7. The Gauss-Bonnet theorem
 7. The Gauss-Bonnet theorem 7.1 Hyperbolic polygons In Euclidean geometry, an n-sided polygon is a subset of the Euclidean plane bounded by n straight lines. Thus the edges of a Euclidean polygon are formed
7. The Gauss-Bonnet theorem 7.1 Hyperbolic polygons In Euclidean geometry, an n-sided polygon is a subset of the Euclidean plane bounded by n straight lines. Thus the edges of a Euclidean polygon are formed
F dr = f dx + g dy + h dz. Using that dz = q x dx + q y dy we get. (g + hq y ) x (f + hq x ) y da.
 Math 55 - Vector alculus II Notes 14.7 tokes Theorem tokes Theorem is the three-dimensional version of the circulation form of Green s Theorem. Let s quickly recall that theorem: Green s Theorem: Let be
Math 55 - Vector alculus II Notes 14.7 tokes Theorem tokes Theorem is the three-dimensional version of the circulation form of Green s Theorem. Let s quickly recall that theorem: Green s Theorem: Let be
27. Tangent Planes & Approximations
 27. Tangent Planes & Approximations If z = f(x, y) is a differentiable surface in R 3 and (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is a point on this surface, then it is possible to construct a plane passing through this point,
27. Tangent Planes & Approximations If z = f(x, y) is a differentiable surface in R 3 and (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is a point on this surface, then it is possible to construct a plane passing through this point,
) in the k-th subbox. The mass of the k-th subbox is M k δ(x k, y k, z k ) V k. Thus,
 1 Triple Integrals Mass problem. Find the mass M of a solid whose density (the mass per unit volume) is a continuous nonnegative function δ(x, y, z). 1. Divide the box enclosing into subboxes, and exclude
1 Triple Integrals Mass problem. Find the mass M of a solid whose density (the mass per unit volume) is a continuous nonnegative function δ(x, y, z). 1. Divide the box enclosing into subboxes, and exclude
Solution 2. ((3)(1) (2)(1), (4 3), (4)(2) (3)(3)) = (1, 1, 1) D u (f) = (6x + 2yz, 2y + 2xz, 2xy) (0,1,1) = = 4 14
 Vector and Multivariable Calculus L Marizza A Bailey Practice Trimester Final Exam Name: Problem 1. To prepare for true/false and multiple choice: Compute the following (a) (4, 3) ( 3, 2) Solution 1. (4)(
Vector and Multivariable Calculus L Marizza A Bailey Practice Trimester Final Exam Name: Problem 1. To prepare for true/false and multiple choice: Compute the following (a) (4, 3) ( 3, 2) Solution 1. (4)(
Review 1. Richard Koch. April 23, 2005
 Review Richard Koch April 3, 5 Curves From the chapter on curves, you should know. the formula for arc length in section.;. the definition of T (s), κ(s), N(s), B(s) in section.4. 3. the fact that κ =
Review Richard Koch April 3, 5 Curves From the chapter on curves, you should know. the formula for arc length in section.;. the definition of T (s), κ(s), N(s), B(s) in section.4. 3. the fact that κ =
NAME: Section # SSN: X X X X
 Math 155 FINAL EXAM A May 5, 2003 NAME: Section # SSN: X X X X Question Grade 1 5 (out of 25) 6 10 (out of 25) 11 (out of 20) 12 (out of 20) 13 (out of 10) 14 (out of 10) 15 (out of 16) 16 (out of 24)
Math 155 FINAL EXAM A May 5, 2003 NAME: Section # SSN: X X X X Question Grade 1 5 (out of 25) 6 10 (out of 25) 11 (out of 20) 12 (out of 20) 13 (out of 10) 14 (out of 10) 15 (out of 16) 16 (out of 24)
Math 2374 Spring 2007 Midterm 3 Solutions - Page 1 of 6 April 25, 2007
 Math 374 Spring 7 Midterm 3 Solutions - Page of 6 April 5, 7. (3 points) Consider the surface parametrized by (x, y, z) Φ(x, y) (x, y,4 (x +y )) between the planes z and z 3. (i) (5 points) Set up the
Math 374 Spring 7 Midterm 3 Solutions - Page of 6 April 5, 7. (3 points) Consider the surface parametrized by (x, y, z) Φ(x, y) (x, y,4 (x +y )) between the planes z and z 3. (i) (5 points) Set up the
(c) 0 (d) (a) 27 (b) (e) x 2 3x2
 1. Sarah the architect is designing a modern building. The base of the building is the region in the xy-plane bounded by x =, y =, and y = 3 x. The building itself has a height bounded between z = and
1. Sarah the architect is designing a modern building. The base of the building is the region in the xy-plane bounded by x =, y =, and y = 3 x. The building itself has a height bounded between z = and
Math 209, Fall 2009 Homework 3
 Math 209, Fall 2009 Homework 3 () Find equations of the tangent plane and the normal line to the given surface at the specified point: x 2 + 2y 2 3z 2 = 3, P (2,, ). Solution Using implicit differentiation
Math 209, Fall 2009 Homework 3 () Find equations of the tangent plane and the normal line to the given surface at the specified point: x 2 + 2y 2 3z 2 = 3, P (2,, ). Solution Using implicit differentiation
PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES
 10 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS & POLAR COORDINATES A coordinate system represents a point in the plane by an ordered pair of numbers called coordinates. PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS
10 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS & POLAR COORDINATES A coordinate system represents a point in the plane by an ordered pair of numbers called coordinates. PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS
MAT01B1: Surface Area of Solids of Revolution
 MAT01B1: Surface Area of Solids of Revolution Dr Craig 02 October 2018 My details: acraig@uj.ac.za Consulting hours: Monday 14h40 15h25 Thursday 11h20 12h55 Friday 11h20 12h55 Office C-Ring 508 https://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com/
MAT01B1: Surface Area of Solids of Revolution Dr Craig 02 October 2018 My details: acraig@uj.ac.za Consulting hours: Monday 14h40 15h25 Thursday 11h20 12h55 Friday 11h20 12h55 Office C-Ring 508 https://andrewcraigmaths.wordpress.com/
First of all, we need to know what it means for a parameterize curve to be differentiable. FACT:
 CALCULUS WITH PARAMETERIZED CURVES In calculus I we learned how to differentiate and integrate functions. In the chapter covering the applications of the integral, we learned how to find the length of
CALCULUS WITH PARAMETERIZED CURVES In calculus I we learned how to differentiate and integrate functions. In the chapter covering the applications of the integral, we learned how to find the length of
Polar (BC Only) They are necessary to find the derivative of a polar curve in x- and y-coordinates. The derivative
 Polar (BC Only) Polar coordinates are another way of expressing points in a plane. Instead of being centered at an origin and moving horizontally or vertically, polar coordinates are centered at the pole
Polar (BC Only) Polar coordinates are another way of expressing points in a plane. Instead of being centered at an origin and moving horizontally or vertically, polar coordinates are centered at the pole
1.(6pts) Which integral computes the area of the quarter-disc of radius a centered at the origin in the first quadrant? rdr d
 .(6pts) Which integral computes the area of the quarter-disc of radius a centered at the origin in the first quadrant? (a) / Z a rdr d (b) / Z a rdr d (c) Z a dr d (d) / Z a dr d (e) / Z a a rdr d.(6pts)
.(6pts) Which integral computes the area of the quarter-disc of radius a centered at the origin in the first quadrant? (a) / Z a rdr d (b) / Z a rdr d (c) Z a dr d (d) / Z a dr d (e) / Z a a rdr d.(6pts)
MATH 104 Sample problems for first exam - Fall MATH 104 First Midterm Exam - Fall (d) 256 3
 MATH 14 Sample problems for first exam - Fall 1 MATH 14 First Midterm Exam - Fall 1. Find the area between the graphs of y = 9 x and y = x + 1. (a) 4 (b) (c) (d) 5 (e) 4 (f) 81. A solid has as its base
MATH 14 Sample problems for first exam - Fall 1 MATH 14 First Midterm Exam - Fall 1. Find the area between the graphs of y = 9 x and y = x + 1. (a) 4 (b) (c) (d) 5 (e) 4 (f) 81. A solid has as its base
f (Pijk ) V. may form the Riemann sum: . Definition. The triple integral of f over the rectangular box B is defined to f (x, y, z) dv = lim
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals..1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections.2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals.3
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals..1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections.2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals.3
Math 5BI: Problem Set 2 The Chain Rule
 Math 5BI: Problem Set 2 The Chain Rule April 5, 2010 A Functions of two variables Suppose that γ(t) = (x(t), y(t), z(t)) is a differentiable parametrized curve in R 3 which lies on the surface S defined
Math 5BI: Problem Set 2 The Chain Rule April 5, 2010 A Functions of two variables Suppose that γ(t) = (x(t), y(t), z(t)) is a differentiable parametrized curve in R 3 which lies on the surface S defined
Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 11.
 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 11. Show all your work on the standard
Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 11. Show all your work on the standard
Grad operator, triple and line integrals. Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures
 Grad operator, triple and line integrals Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures 1 .1 The grad operator Let f(x 1, x,..., x n ) be a function of the n variables
Grad operator, triple and line integrals Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures 1 .1 The grad operator Let f(x 1, x,..., x n ) be a function of the n variables
A1:Orthogonal Coordinate Systems
 A1:Orthogonal Coordinate Systems A1.1 General Change of Variables Suppose that we express x and y as a function of two other variables u and by the equations We say that these equations are defining a
A1:Orthogonal Coordinate Systems A1.1 General Change of Variables Suppose that we express x and y as a function of two other variables u and by the equations We say that these equations are defining a
Exam 2 Preparation Math 2080 (Spring 2011) Exam 2: Thursday, May 12.
 Multivariable Calculus Exam 2 Preparation Math 28 (Spring 2) Exam 2: Thursday, May 2. Friday May, is a day off! Instructions: () There are points on the exam and an extra credit problem worth an additional
Multivariable Calculus Exam 2 Preparation Math 28 (Spring 2) Exam 2: Thursday, May 2. Friday May, is a day off! Instructions: () There are points on the exam and an extra credit problem worth an additional
Name: Final Exam Review. (b) Reparameterize r(t) with respect to arc length measured for the point (1, 0, 1) in the direction of increasing t.
 MATH 127 ALULU III Name: 1. Let r(t) = e t i + e t sin t j + e t cos t k (a) Find r (t) Final Exam Review (b) Reparameterize r(t) with respect to arc length measured for the point (1,, 1) in the direction
MATH 127 ALULU III Name: 1. Let r(t) = e t i + e t sin t j + e t cos t k (a) Find r (t) Final Exam Review (b) Reparameterize r(t) with respect to arc length measured for the point (1,, 1) in the direction
Taylor and Laurent Series
 hapter Nine Taylor and Laurent Series 9.. Taylor series. Suppose f is analytic on the open disk z z 0 r. Let z be any point in this disk and choose to be the positively oriented circle of radius, where
hapter Nine Taylor and Laurent Series 9.. Taylor series. Suppose f is analytic on the open disk z z 0 r. Let z be any point in this disk and choose to be the positively oriented circle of radius, where
MATH 122 FINAL EXAM WINTER March 15, 2011
 MATH 1 FINAL EXAM WINTER 010-011 March 15, 011 NAME: SECTION: ONLY THE CORRECT ANSWER AND ALL WORK USED TO REACH IT WILL EARN FULL CREDIT. Simplify all answers as much as possible unless explicitly stated
MATH 1 FINAL EXAM WINTER 010-011 March 15, 011 NAME: SECTION: ONLY THE CORRECT ANSWER AND ALL WORK USED TO REACH IT WILL EARN FULL CREDIT. Simplify all answers as much as possible unless explicitly stated
4. LINE AND PATH INTEGRALS
 Universidad arlos III de Madrid alculus II 4. LINE AN PATH INTEGRALS Marina elgado Téllez de epeda Parametrizations of important curves: ircumference: (x a) 2 + (y b) 2 = r 2 1 (t) = (a + cos t,b + sin
Universidad arlos III de Madrid alculus II 4. LINE AN PATH INTEGRALS Marina elgado Téllez de epeda Parametrizations of important curves: ircumference: (x a) 2 + (y b) 2 = r 2 1 (t) = (a + cos t,b + sin
Surfaces and Integral Curves
 MODULE 1: MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES 16 Lecture 3 Surfaces and Integral Curves In Lecture 3, we recall some geometrical concepts that are essential for understanding the nature of solutions of partial
MODULE 1: MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES 16 Lecture 3 Surfaces and Integral Curves In Lecture 3, we recall some geometrical concepts that are essential for understanding the nature of solutions of partial
