8 Physics Simulations
|
|
|
- Barnard Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8 Physics Simulations 8.1 Billiard-Game Physics 8.2 Game Physics Engines Literature: K. Besley et al.: Flash MX 2004 Games Most Wanted, Apress/Friends of ED 2004 (chapter 3 by Keith Peters) 1
2 Billiard-Game Physics Typical problem: Two round objects moving at different speeds and angles hitting each other How to determine resulting speeds and directions? Classical example: Billiard game 2
3 Speed and Velocity Speed: Magnitude (single number), measured in px/s Suitable for movement along one axis (e.g. x axis) Velocity: Speed plus direction Magnitude (px/s) and angle (degrees) Expressed as a 2D vector: velocity = (horizontal_speed, vertical_speed) v s v s h = cos(α) v s v = sin(α) v α v = s h 2 + s v 2 s h α = atan (s v / s h ) 3
4 Velocity and Acceleration Velocity is added to the position values in each frame cycle Acceleration is a force changing velocity Acceleration is added to velocity in each frame cycle Deceleration is negative acceleration Angular acceleration Acceleration is a 2D vector (or a magnitude plus angle) vx += ax vy += ay x += vx y += vy (ax, ay) acceleration (vx, vy) velocity 4
5 Object Orientation for Animated Graphics Each moving part of the scene is an object (belonging to a class) Class definitions comprise: Reference to graphical representation Properties mirroring physical properties (e.g. position, speed) Properties and methods required for core program logic Two ways of referring to graphics framework: Subclassing: Moving object belongs to a subclass of a framework class» e.g. Sprite class, graphics node in scene graph Delegation: Moving object contains a reference to a framework object Decision criterion: Wanted/needed degree of decoupling between multimedia framework and application logic 5
6 Main program for Moving Balls (1) # Create ball 1 b1 = Ball(20,20,ballsize,red) b1.setbounds(0,sc_w,0,sc_h) b1.setvelocity(10,15) # Create ball 2 b2 = Ball(sc_w-20,sc_h-20,ballsize,blue) b2.setbounds(0,sc_w,0,sc_h) b2.setvelocity(-20,-10) Ball constructor: Position, radius, color Bounds: Walls limiting movement # Set frame rate framerate = 30 # frames per second clock = pygame.time.clock() (contd.) 6
7 Main program for Moving Balls (2) (contd.) running = True while running: for event in pygame.event.get(): if event.type == QUIT: running = False pygame.draw.rect(screen, white, Rect((0, 0), (sc_w, sc_h))) b1.update() b1.draw(screen) b2.update() b2.draw(screen) clock.tick(framerate) pygame.display.update() 7
8 Ball Class (Excerpt) class Ball: def init (self,startx,starty,radius,color): self.posx = startx self.posy = starty self.radius = radius self.color = color def setvelocity(self,vx,vy): self.vx = vx self.vy = vy def update(self): self.posx = self.posx + self.vx self.posy = self.posy + self.vy 8
9 Collision Detection Moving objects may meet other objects and boundaries Collision detection algorithm detecting such situations Simple collision detection: Width and/or height goes beyond some limit» Bounds attributes in current example» Bounds of nodes often available in high-level frameworks Potential problems: Rounding errors may conceal collision event Deep collisions:» Collision is detected several times in sequence» May lead to strange bouncing behaviour 9
10 Repositioning of Object on Collision overshoothr = (self.posx+self.radius) - self.bhr overshoothl = self.bhl - (self.posx-self.radius) overshootvb = (self.posy+self.radius) - self.bvb overshootvt = self.bvt - (self.posy-self.radius) if overshoothr > 0: self.posx = self.posx - overshoothr if overshoothl > 0: self.posx = self.posx + overshoothl if overshootvb > 0: self.posy = self.posy - overshootvb if overshootvt > 0: self.posy = self.posy + overshootvt 10
11 Model and Reality 11
12 Simple Wall-to-Wall Bouncing Bouncing always takes away some part of energy Use bouncing factor 1.0: No loss (unrealistic) In most cases use value smaller than 1, e.g. 0.9 if (overshoothr > 0) or (overshoothl > 0): self.vx = - self.vx*bounce_loss if (overshootvb > 0) or (overshootvt > 0): self.vy = - self.vy*bounce_loss 12
13 Bounce and Friction Surface absorbs some part of the energy and slows down the ball Reduce velocity by some factor each frame Use friction factor 1.0: No friction (unrealistic) In most cases use value smaller than 1, e.g self.vx = self.vx*frict_loss self.vy = self.vy*frict_loss 13
14 Minimum Speed if self.getspeed() < MIN_SPEED: self.vx = 0 self.vy = 0 Needed for this: Effective speed out of x and y velocities v eff vy v eff = vx 2 + vy 2 vx def getspeed(self): return math.sqrt(self.vx*self.vx+self.vy*self.vy) 14
15 Collision Detection Between Balls (1) Two moving balls may collide. Collision detection needs access to data of both balls Main program, or sprite manager class calling collision detection regularly Actual collision handling depends on geometry of objects Bounding box is often not adequate for detection (e.g. for balls) Main program loop: b1.update() b1.draw(screen) b2.update() b2.draw(screen) b1.handlecollision(b2) Ball class: def handlecollision(self,other): 15
16 Collision Detection Between Balls (2) def handlecollision(self,other): dx = self.posx - other.getposx() dy = self.posy - other.getposy() dist = math.sqrt(dx*dx+dy*dy) overlap = self.radius + other.getradius() - dist if overlap > 0: # Collision detected angle = math.atan2(dy,dx) cosa = math.cos(angle) sina = math.sin(angle)
17 Collision Angle Velocity of red ball dy dx Velocity of white ball angle = math.atan2(dy,dx) 17
18 Repositioning Balls At Collision Time overlapx = overlap*cosa overlapy = overlap*sina posxnew = self.posx + overlapx/2 posynew = self.posy + overlapy/2 otherposxnew = other.getposx() - overlapx/2 otherposynew = other.getposy() - overlapy/2 self.setpos(posxnew,posynew) other.setpos(otherposxnew,otherposynew) This is a simplification compared to the actual physical laws. 18
19 A Simple Case of Collision Two balls collide head on Balls have same size and same mass v1 v2 v2 v1 19
20 Physics of Collision, Step 1 Velocity of red ball Line of collision Velocity of white ball We need to determine those parts of the forces which actually contribute to the reaction, i.e. the projections on the collision line 20
21 Physics of Collision, Step 2 vx1 vy1 vy1 vx2 (old vx1) vy2 vy2 vx2 vx1 (old vx2) 21
22 Physics of Collision, Step 3 22
23 Computation Part 1 vx1 vy1 Counterclockwise rotation of vector (x, y): x1 = cos(α) x + sin(α) y y1 = cos(α) y sin(α) x vy2 vx1 = self.vx vy1 = self.vy vx2 = other.getvelocityx() vy2 = other.getvelocityy() px1 = cosa*vx1 + sina*vy1 py1 = cosa*vx1 - sina*vy1 px2 = cosa*vx2 + sina*vy2 py2 = cosa*vx2 - sina*vy2 vx2 23
24 Computation Part 2 pnewx1 = px2 pnewy1 = py2 pnewx2 = px1 pnewy2 = py1 24
25 Computation Part 3 Clockwise rotation of vector (x, y): x1 = cos(α) x sin(α) y y1 = cos(α) y + sin(α) x vxnew = cosa*pnewx1 - sina*pnewy1 vynew = cosa*pnewx1 + sina*pnewy1 othervxnew = cosa*pnewx2 - sina*pnewy2 othervynew = cosa*pnewx2 + sina*pnewy2 25
26 Final Step: Readjusting Velocities Taking into account energy loss through collision! self.setvelocity(vxnew*bounce_loss,vynew*bounce_loss) other.setvelocity(othervxnew*bounce_loss,othervynew*bounce_loss) 26
27 Physics: Speed, Velocity, Mass, Momentum Speed: How fast is something moving (length/time) Velocity: Vector describing movement: speed + direction Mass: Basic property of object, depending on its material, leads under gravity to its weight Momentum (dt. Impuls): Mass x Velocity Principle of Conservation of Momentum (dt. Impulserhaltung): Total momentum of the two objects before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision. 27
5 Programming with Animations
 5 Programming with Animations 5.1 Animated Graphics: Principles and History 5.2 Types of Animation 5.3 Programming Animations 5.4 Design of Animations Principles of Animation Optimizing Vector Graphics
5 Programming with Animations 5.1 Animated Graphics: Principles and History 5.2 Types of Animation 5.3 Programming Animations 5.4 Design of Animations Principles of Animation Optimizing Vector Graphics
4! Programming with Animations
 4! Programming with Animations 4.1! Animated Graphics: Principles and History 4.2! Types of Animation 4.3! Programming Animations 4.4! Design of Animations 4.5! Game Physics Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität
4! Programming with Animations 4.1! Animated Graphics: Principles and History 4.2! Types of Animation 4.3! Programming Animations 4.4! Design of Animations 4.5! Game Physics Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität
4! Programming with Animations
 4! Programming with Animations 4.1! Animated Graphics: Principles and History 4.2! Types of Animation 4.3! Programming Animations 4.4! Design of Animations!!Principles of Animation!! Optimizing Vector
4! Programming with Animations 4.1! Animated Graphics: Principles and History 4.2! Types of Animation 4.3! Programming Animations 4.4! Design of Animations!!Principles of Animation!! Optimizing Vector
Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 7
 Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 7 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Sommersemester 2017 Today Particles Sound Illustrated with + Physics Users have specific expectations For example, if something
Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 7 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Sommersemester 2017 Today Particles Sound Illustrated with + Physics Users have specific expectations For example, if something
Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 5
 Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 5 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Sommersemester 2009 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Multimedia-Programmierung 5-1 Today Sprite animations in Advanced collision
Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 5 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Sommersemester 2009 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Multimedia-Programmierung 5-1 Today Sprite animations in Advanced collision
7 Programming with Animations
 7 Programming with Animations 7.1 Animated Graphics: Principles and History 7.2 Types of Animation 7.3 Programming Animations: Interpolation 7.4 Design of Animations 1 Reminder: Frame-by-Frame Animations
7 Programming with Animations 7.1 Animated Graphics: Principles and History 7.2 Types of Animation 7.3 Programming Animations: Interpolation 7.4 Design of Animations 1 Reminder: Frame-by-Frame Animations
Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 7
 Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 7 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Sommersemester 2013 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Multimedia-Programmierung 7-1 Today Sprite animations in Advanced collision
Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 7 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Sommersemester 2013 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Multimedia-Programmierung 7-1 Today Sprite animations in Advanced collision
A simple OpenGL animation Due: Wednesday, January 27 at 4pm
 CMSC 23700 Winter 2010 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 1 January 12 A simple OpenGL animation Due: Wednesday, January 27 at 4pm 1 Summary This project is the first part of a three-part project.
CMSC 23700 Winter 2010 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 1 January 12 A simple OpenGL animation Due: Wednesday, January 27 at 4pm 1 Summary This project is the first part of a three-part project.
pygame Lecture #2 (Examples: movingellipse, bouncingball, planets, bouncingballgravity)
 pygame Lecture #2 (Examples: movingellipse, bouncingball, planets, bouncingballgravity) MOVEMENT IN PYGAME I. Realizing the screen is getting redrawn many times. Let's take a look at the key portion of
pygame Lecture #2 (Examples: movingellipse, bouncingball, planets, bouncingballgravity) MOVEMENT IN PYGAME I. Realizing the screen is getting redrawn many times. Let's take a look at the key portion of
Collisions/Reflection
 Collisions/Reflection General Collisions The calculating whether or not two 2D objects collide is equivalent to calculating if the two shapes share a common area (intersect). For general polygons this
Collisions/Reflection General Collisions The calculating whether or not two 2D objects collide is equivalent to calculating if the two shapes share a common area (intersect). For general polygons this
A simple example. Assume we want to find the change in the rotation angles to get the end effector to G. Effect of changing s
 CENG 732 Computer Animation This week Inverse Kinematics (continued) Rigid Body Simulation Bodies in free fall Bodies in contact Spring 2006-2007 Week 5 Inverse Kinematics Physically Based Rigid Body Simulation
CENG 732 Computer Animation This week Inverse Kinematics (continued) Rigid Body Simulation Bodies in free fall Bodies in contact Spring 2006-2007 Week 5 Inverse Kinematics Physically Based Rigid Body Simulation
Lesson 18: Animation. Computer Programming is Fun!
 Lesson 18: Animation So how do you make your drawings move and change? That's what this section is about. I'd like to introduce you to your new friend, Mr. Timer. A timer gives you the ability to tell
Lesson 18: Animation So how do you make your drawings move and change? That's what this section is about. I'd like to introduce you to your new friend, Mr. Timer. A timer gives you the ability to tell
Game Board: Enabling Simple Games in TouchDevelop
 Game Board: Enabling Simple Games in TouchDevelop Manuel Fähndrich Microsoft Research One Microsoft Way, Redmond WA 98052, USA maf@microsoft.com February 23, 2012 Abstract TouchDevelop is a novel application
Game Board: Enabling Simple Games in TouchDevelop Manuel Fähndrich Microsoft Research One Microsoft Way, Redmond WA 98052, USA maf@microsoft.com February 23, 2012 Abstract TouchDevelop is a novel application
Useful Formulas. Appendix. Chapter 3. Calculate basic trigonometric functions. Convert radians to degrees and degrees to radians
 Appendix Useful Formulas Throughout the book, there are various formulas related to the different motions and effects you ve created. These have been distilled down to the most useful and most commonly
Appendix Useful Formulas Throughout the book, there are various formulas related to the different motions and effects you ve created. These have been distilled down to the most useful and most commonly
7! Programming with Animations
 7! Programming with Animations 7.1! Animated Graphics: Principles and History! 7.2! Types of Animation! 7.3! Programming Animations: Interpolation! 7.4! Design of Animations! 7.5! Game Physics 1 Eadweard
7! Programming with Animations 7.1! Animated Graphics: Principles and History! 7.2! Types of Animation! 7.3! Programming Animations: Interpolation! 7.4! Design of Animations! 7.5! Game Physics 1 Eadweard
Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 6
 Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 6 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Sommersemester 2018 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Multimedia-Programmierung 6-1 Today Sprites, Sprite Groups and Sprite
Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 6 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Sommersemester 2018 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Multimedia-Programmierung 6-1 Today Sprites, Sprite Groups and Sprite
Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 5
 Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 5 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Sommersemester 2018 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Multimedia-Programmierung 5-1 Today Animations Illustrated with + Literature:
Multimedia-Programmierung Übung 5 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Sommersemester 2018 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Multimedia-Programmierung 5-1 Today Animations Illustrated with + Literature:
The use of the UML within the modelling process of Modelica-models
 The use of the UML within the modelling process of Modelica-models Christoph Nytsch-Geusen 1 1 Fraunhofer Institute for Computer Architecture and Software Technology, Kekuléstr. 7, 12489 Berlin, Germany
The use of the UML within the modelling process of Modelica-models Christoph Nytsch-Geusen 1 1 Fraunhofer Institute for Computer Architecture and Software Technology, Kekuléstr. 7, 12489 Berlin, Germany
PSE Game Physics. Session (3) Springs, Ropes, Linear Momentum and Rotations. Oliver Meister, Roland Wittmann
 PSE Game Physics Session (3) Springs, Ropes, Linear Momentum and Rotations Oliver Meister, Roland Wittmann 08.05.2015 Session (3) Springs, Ropes, Linear Momentum and Rotations, 08.05.2015 1 Outline Springs
PSE Game Physics Session (3) Springs, Ropes, Linear Momentum and Rotations Oliver Meister, Roland Wittmann 08.05.2015 Session (3) Springs, Ropes, Linear Momentum and Rotations, 08.05.2015 1 Outline Springs
The Jello Cube Assignment 1, CSCI 520. Jernej Barbic, USC
 The Jello Cube Assignment 1, CSCI 520 Jernej Barbic, USC 1 The jello cube Undeformed cube Deformed cube The jello cube is elastic, Can be bent, stretched, squeezed,, Without external forces, it eventually
The Jello Cube Assignment 1, CSCI 520 Jernej Barbic, USC 1 The jello cube Undeformed cube Deformed cube The jello cube is elastic, Can be bent, stretched, squeezed,, Without external forces, it eventually
slide 1 gaius Python Classes you can use theclass keyword to create your own classes here is a tiny example of a class
 Python Classes slide 1 you can use theclass keyword to create your own classes here is a tiny example of a class Python Classes slide 2 tinyclass.py #!/usr/bin/python import math class vector: def init
Python Classes slide 1 you can use theclass keyword to create your own classes here is a tiny example of a class Python Classes slide 2 tinyclass.py #!/usr/bin/python import math class vector: def init
Platform Games Drawing Sprites & Detecting Collisions
 Platform Games Drawing Sprites & Detecting Collisions Computer Games Development David Cairns Contents Drawing Sprites Collision Detection Animation Loop Introduction 1 Background Image - Parallax Scrolling
Platform Games Drawing Sprites & Detecting Collisions Computer Games Development David Cairns Contents Drawing Sprites Collision Detection Animation Loop Introduction 1 Background Image - Parallax Scrolling
Pong in Unity a basic Intro
 This tutorial recreates the classic game Pong, for those unfamiliar with the game, shame on you what have you been doing, living under a rock?! Go google it. Go on. For those that now know the game, this
This tutorial recreates the classic game Pong, for those unfamiliar with the game, shame on you what have you been doing, living under a rock?! Go google it. Go on. For those that now know the game, this
Class Design (Section 9 of 17)
 the architects themselves came in to explain the advantages of both designs Class Design (Section 9 of 17) In the previous sections we have used existing classes that enable us to be able to write functions
the architects themselves came in to explain the advantages of both designs Class Design (Section 9 of 17) In the previous sections we have used existing classes that enable us to be able to write functions
(C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Omer Boyaci
 Omer Boyaci A sprite must monitor the game environment, for example, reacting to collisions with different sprites or stopping when it encounters an obstacle. Collision processing can be split into two
Omer Boyaci A sprite must monitor the game environment, for example, reacting to collisions with different sprites or stopping when it encounters an obstacle. Collision processing can be split into two
EEN118 LAB FOUR. h = v t - ½ g t 2
 EEN118 LAB FOUR In this lab you will be performing a simulation of a physical system, shooting a projectile from a cannon and working out where it will land. Although this is not a very complicated physical
EEN118 LAB FOUR In this lab you will be performing a simulation of a physical system, shooting a projectile from a cannon and working out where it will land. Although this is not a very complicated physical
Figure 2.1: High level diagram of system.
 Basile and Choudhury 6.111 Final Project: La PC-na Project Proposal 1 Introduction The luxury of purchasing separate pool tables, foosball tables, and air hockey tables is beyond the budget of many, particularly
Basile and Choudhury 6.111 Final Project: La PC-na Project Proposal 1 Introduction The luxury of purchasing separate pool tables, foosball tables, and air hockey tables is beyond the budget of many, particularly
8 Physics Simulations
 8 Physics Simulations 8.1 Billiard-Game Physics 8.2 Game Physics Engines Literature: cocos2d-x.org R. Engelbert: Cocos2d-x Beginner's Guide, 2nd ed., Packt Publishing 2015 1 Particle Animations Animation
8 Physics Simulations 8.1 Billiard-Game Physics 8.2 Game Physics Engines Literature: cocos2d-x.org R. Engelbert: Cocos2d-x Beginner's Guide, 2nd ed., Packt Publishing 2015 1 Particle Animations Animation
Principles of Computer Game Design and Implementation. Lecture 6
 Principles of Computer Game Design and Implementation Lecture 6 We already knew Game history game design information Game engine 2 What s Next Mathematical concepts (lecture 6-10) Collision detection and
Principles of Computer Game Design and Implementation Lecture 6 We already knew Game history game design information Game engine 2 What s Next Mathematical concepts (lecture 6-10) Collision detection and
ROSE-HULMAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 Introduction to Working Model Welcome to Working Model! What is Working Model? It's an advanced 2-dimensional motion simulation package with sophisticated editing capabilities. It allows you to build and
Introduction to Working Model Welcome to Working Model! What is Working Model? It's an advanced 2-dimensional motion simulation package with sophisticated editing capabilities. It allows you to build and
Virtual Environments
 ELG 524 Virtual Environments Jean-Christian Delannoy viewing in 3D world coordinates / geometric modeling culling lighting virtualized reality collision detection collision response interactive forces
ELG 524 Virtual Environments Jean-Christian Delannoy viewing in 3D world coordinates / geometric modeling culling lighting virtualized reality collision detection collision response interactive forces
CSE 131 Computer Science 1 Module 10a: Hierarchies
 CSE 131 Computer Science 1 Module 10a: Hierarchies introduction to BrickBreaker game extending classes and class hierarchies abstract methods and classes Introduction to BrickBreaker Game consists of bricks,
CSE 131 Computer Science 1 Module 10a: Hierarchies introduction to BrickBreaker game extending classes and class hierarchies abstract methods and classes Introduction to BrickBreaker Game consists of bricks,
Erasmus+ Project: Yestermorrow Year 1 Maths: Pythagorean Theorem
 Erasmus+ Project: Yestermorrow Year 1 Maths: Pythagorean Theorem Workshop (Coding Android Mobile Apps): Collision Detection and the Pythagorean Theorem (Based on the code.org worksheet) WORKSHOP OVERVIEW
Erasmus+ Project: Yestermorrow Year 1 Maths: Pythagorean Theorem Workshop (Coding Android Mobile Apps): Collision Detection and the Pythagorean Theorem (Based on the code.org worksheet) WORKSHOP OVERVIEW
Today s examples online at.
 Physics 9 Wednesday, November 21, 2018 HW10 due Friday, November 30. For Monday, read Giancoli chapter 19 (DC circuits). Today: a tutorial of the Processing.py computer programming language whose purpose
Physics 9 Wednesday, November 21, 2018 HW10 due Friday, November 30. For Monday, read Giancoli chapter 19 (DC circuits). Today: a tutorial of the Processing.py computer programming language whose purpose
Elements of 2d Computational Geometry. AI for Gaming Santa Clara, 2016
 Elements of 2d Computational Geometry AI for Gaming Santa Clara, 2016 3d Determinants Absolute value is the volume of the parallelepiped Sign is the orientation 2d Orientation A+B+C A+C B+C C A+B A B Sign
Elements of 2d Computational Geometry AI for Gaming Santa Clara, 2016 3d Determinants Absolute value is the volume of the parallelepiped Sign is the orientation 2d Orientation A+B+C A+C B+C C A+B A B Sign
KINEMATIC ANALYSIS OF A THREE-MEMBER END CAM MECHANISM
 Tome V (year 2007), Fascicole 2, (ISSN 1584 2665) KINEMATIC ANALYSIS OF A THREE-MEMBER END CAM MECHANISM Milcho DIMITROV TASHEV Department of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering TC John Atanasoff TU
Tome V (year 2007), Fascicole 2, (ISSN 1584 2665) KINEMATIC ANALYSIS OF A THREE-MEMBER END CAM MECHANISM Milcho DIMITROV TASHEV Department of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering TC John Atanasoff TU
Simulation (last lecture and this one)
 Simulation (last lecture and this one) How used in games? Dynamics Collisions simple ------------------------------- Collisions harder detection bounding boxes response Controllers Mocap + simulation User
Simulation (last lecture and this one) How used in games? Dynamics Collisions simple ------------------------------- Collisions harder detection bounding boxes response Controllers Mocap + simulation User
Projectile Motion. A.1. Finding the flight time from the vertical motion. The five variables for the vertical motion are:
 Projectile Motion A. Finding the muzzle speed v0 The speed of the projectile as it leaves the gun can be found by firing it horizontally from a table, and measuring the horizontal range R0. On the diagram,
Projectile Motion A. Finding the muzzle speed v0 The speed of the projectile as it leaves the gun can be found by firing it horizontally from a table, and measuring the horizontal range R0. On the diagram,
pygame Lecture #5 (Examples: fruitgame)
 pygame Lecture #5 (Examples: fruitgame) MOUSE INPUT IN PYGAME I. Detecting Mouse Input in pygame In addition to waiting for a keyboard event to precipitate some action, pygame allows us to wait for a mouse
pygame Lecture #5 (Examples: fruitgame) MOUSE INPUT IN PYGAME I. Detecting Mouse Input in pygame In addition to waiting for a keyboard event to precipitate some action, pygame allows us to wait for a mouse
Ragdoll Physics. Abstract. 2 Background. 1 Introduction. Gabe Mulley, Matt Bittarelli. April 25th, Previous Work
 Ragdoll Physics Gabe Mulley, Matt Bittarelli April 25th, 2007 Abstract The goal of this project was to create a real-time, interactive, and above all, stable, ragdoll physics simulation. This simulation
Ragdoll Physics Gabe Mulley, Matt Bittarelli April 25th, 2007 Abstract The goal of this project was to create a real-time, interactive, and above all, stable, ragdoll physics simulation. This simulation
Steering 1. from Millington, "Artificial Intelligence for Games", MKP 2006.
 Steering 1 from Millington, "Artificial Intelligence for Games", MKP 2006. Movement Algorithms kinematic movement computes a velocity for the object based on current position no acceleration dynamic movement
Steering 1 from Millington, "Artificial Intelligence for Games", MKP 2006. Movement Algorithms kinematic movement computes a velocity for the object based on current position no acceleration dynamic movement
Robotics Project. Final Report. Computer Science University of Minnesota. December 17, 2007
 Robotics Project Final Report Computer Science 5551 University of Minnesota December 17, 2007 Peter Bailey, Matt Beckler, Thomas Bishop, and John Saxton Abstract: A solution of the parallel-parking problem
Robotics Project Final Report Computer Science 5551 University of Minnesota December 17, 2007 Peter Bailey, Matt Beckler, Thomas Bishop, and John Saxton Abstract: A solution of the parallel-parking problem
To Measure a Constant Velocity. Enter.
 To Measure a Constant Velocity Apparatus calculator, black lead, calculator based ranger (cbr, shown), Physics application this text, the use of the program becomes second nature. At the Vernier Software
To Measure a Constant Velocity Apparatus calculator, black lead, calculator based ranger (cbr, shown), Physics application this text, the use of the program becomes second nature. At the Vernier Software
Animation. Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 4/23/07 1
 Animation Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 4/23/07 1 Today s Topics Interpolation Forward and inverse kinematics Rigid body simulation Fluids Particle systems Behavioral
Animation Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 4/23/07 1 Today s Topics Interpolation Forward and inverse kinematics Rigid body simulation Fluids Particle systems Behavioral
Motion Control (wheeled robots)
 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground Definition of required motion -> speed control,
Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground Definition of required motion -> speed control,
Design of a dynamic simulation system for VR applications
 Design of a dynamic simulation system for VR applications Jan Bender Abstract A dynamic simulation system for VR applications consists of multiple parts. The first task that must be accomplished is the
Design of a dynamic simulation system for VR applications Jan Bender Abstract A dynamic simulation system for VR applications consists of multiple parts. The first task that must be accomplished is the
Graphs, Search, Pathfinding (behavior involving where to go) Steering, Flocking, Formations (behavior involving how to go)
 Graphs, Search, Pathfinding (behavior involving where to go) Steering, Flocking, Formations (behavior involving how to go) Class N-2 1. What are some benefits of path networks? 2. Cons of path networks?
Graphs, Search, Pathfinding (behavior involving where to go) Steering, Flocking, Formations (behavior involving how to go) Class N-2 1. What are some benefits of path networks? 2. Cons of path networks?
Path Objects. Introduction. Methods. Data Types. Create, Delete, Validate Methods. Configuration and Information Methods. Relational Methods
 Path Objects Path Objects Introduction A Path object manages coordinated multi-axis motion profiles. It is used when the motion profiles in an N-Dimensional space are required to follow a specific coordinated
Path Objects Path Objects Introduction A Path object manages coordinated multi-axis motion profiles. It is used when the motion profiles in an N-Dimensional space are required to follow a specific coordinated
CISC 1600, Lab 2.3: Processing animation, objects, and arrays
 CISC 1600, Lab 2.3: Processing animation, objects, and arrays Prof Michael Mandel 1 Getting set up For this lab, we will again be using Sketchpad. sketchpad.cc in your browser and log in. Go to http://cisc1600.
CISC 1600, Lab 2.3: Processing animation, objects, and arrays Prof Michael Mandel 1 Getting set up For this lab, we will again be using Sketchpad. sketchpad.cc in your browser and log in. Go to http://cisc1600.
Use Parametric notation. Interpret the effect that T has on the graph as motion.
 Learning Objectives Parametric Functions Lesson 3: Go Speed Racer! Level: Algebra 2 Time required: 90 minutes One of the main ideas of the previous lesson is that the control variable t does not appear
Learning Objectives Parametric Functions Lesson 3: Go Speed Racer! Level: Algebra 2 Time required: 90 minutes One of the main ideas of the previous lesson is that the control variable t does not appear
An actor-critic reinforcement learning controller for a 2-DOF ball-balancer
 An actor-critic reinforcement learning controller for a 2-DOF ball-balancer Andreas Stückl Michael Meyer Sebastian Schelle Projektpraktikum: Computational Neuro Engineering 2 Empty side for praktikums
An actor-critic reinforcement learning controller for a 2-DOF ball-balancer Andreas Stückl Michael Meyer Sebastian Schelle Projektpraktikum: Computational Neuro Engineering 2 Empty side for praktikums
Anatomy of a Physics Engine. Erwin Coumans
 Anatomy of a Physics Engine Erwin Coumans erwin_coumans@playstation.sony.com How it fits together» Terminology» Rigid Body Dynamics» Collision Detection» Software Design Decisions» Trip through the Physics
Anatomy of a Physics Engine Erwin Coumans erwin_coumans@playstation.sony.com How it fits together» Terminology» Rigid Body Dynamics» Collision Detection» Software Design Decisions» Trip through the Physics
Lec 10 MEL for Dynamics
 Lec 10 MEL for Dynamics Create user windows Create customize shelf command icon Create and use of expression within MEL script Create and use of particle and rigid body dynamics panelbreakup exercise (The
Lec 10 MEL for Dynamics Create user windows Create customize shelf command icon Create and use of expression within MEL script Create and use of particle and rigid body dynamics panelbreakup exercise (The
Art 486: Introduction to Interactive Media.
 Art 486: Introduction to Interactive Media mcdo@umbc.edu Schedule Chapter 3! Comments and stuff 3: Puzzles Attributes of Good Puzzle Design Intuitive controls Readily-Identifiable patterns Allows skill
Art 486: Introduction to Interactive Media mcdo@umbc.edu Schedule Chapter 3! Comments and stuff 3: Puzzles Attributes of Good Puzzle Design Intuitive controls Readily-Identifiable patterns Allows skill
Review: Rough Structure
 Break Out Canvas Tutorial con/nue Simple Game: Break Out Animate, Game Elements ª Breakout ª Bill Mill Modified Tutorial So?ware developer in Maryland Elements: ª Color ª Collision Detec/on ª Interac/on
Break Out Canvas Tutorial con/nue Simple Game: Break Out Animate, Game Elements ª Breakout ª Bill Mill Modified Tutorial So?ware developer in Maryland Elements: ª Color ª Collision Detec/on ª Interac/on
CS 387/680: GAME AI MOVEMENT
 CS 387/680: GAME AI MOVEMENT 4/5/2016 Instructor: Santiago Ontañón santi@cs.drexel.edu Class website: https://www.cs.drexel.edu/~santi/teaching/2016/cs387/intro.html Reminders Check Blackboard site for
CS 387/680: GAME AI MOVEMENT 4/5/2016 Instructor: Santiago Ontañón santi@cs.drexel.edu Class website: https://www.cs.drexel.edu/~santi/teaching/2016/cs387/intro.html Reminders Check Blackboard site for
Multimedia Technology CHAPTER 4. Video and Animation
 CHAPTER 4 Video and Animation - Both video and animation give us a sense of motion. They exploit some properties of human eye s ability of viewing pictures. - Motion video is the element of multimedia
CHAPTER 4 Video and Animation - Both video and animation give us a sense of motion. They exploit some properties of human eye s ability of viewing pictures. - Motion video is the element of multimedia
Centroid Principles. Object s center of gravity or center of mass. Graphically labeled as
 Centroids Centroid Principles Object s center of gravity or center of mass. Graphically labeled as Centroid Principles Point of applied force caused by acceleration due to gravity. Object is in state of
Centroids Centroid Principles Object s center of gravity or center of mass. Graphically labeled as Centroid Principles Point of applied force caused by acceleration due to gravity. Object is in state of
[ the academy_of_code] Senior Beginners
![[ the academy_of_code] Senior Beginners [ the academy_of_code] Senior Beginners](/thumbs/73/69558996.jpg) [ the academy_of_code] Senior Beginners 1 Drawing Circles First step open Processing Open Processing by clicking on the Processing icon (that s the white P on the blue background your teacher will tell
[ the academy_of_code] Senior Beginners 1 Drawing Circles First step open Processing Open Processing by clicking on the Processing icon (that s the white P on the blue background your teacher will tell
4.5 Conservative Forces
 4 CONSERVATION LAWS 4.5 Conservative Forces Name: 4.5 Conservative Forces In the last activity, you looked at the case of a block sliding down a curved plane, and determined the work done by gravity as
4 CONSERVATION LAWS 4.5 Conservative Forces Name: 4.5 Conservative Forces In the last activity, you looked at the case of a block sliding down a curved plane, and determined the work done by gravity as
Creating Breakout - Part 2
 Creating Breakout - Part 2 Adapted from Basic Projects: Game Maker by David Waller So the game works, it is a functioning game. It s not very challenging though, and it could use some more work to make
Creating Breakout - Part 2 Adapted from Basic Projects: Game Maker by David Waller So the game works, it is a functioning game. It s not very challenging though, and it could use some more work to make
OPTI 421/521 Introductory Optomechanical Engineering. 6. Mirror matrices. Matrix formalism is used to model reflection from plane mirrors.
 OPTI 42/52 Introductory Optomechanical Engineering 6. irror matrices atrix formalism is used to model reflection from plane mirrors. Start with the vector law of reflection: kˆ kˆ 2(ˆ k 2 nˆ) nˆ 2(ˆ k
OPTI 42/52 Introductory Optomechanical Engineering 6. irror matrices atrix formalism is used to model reflection from plane mirrors. Start with the vector law of reflection: kˆ kˆ 2(ˆ k 2 nˆ) nˆ 2(ˆ k
BCC 3D Extruded Image Shatter Filter
 BCC 3D Extruded Image Shatter Filter 3D Extruded Image Shatter shatters the image in 3D space and disperses the image fragments. Unlike the 3D Image Shatter filter, this filter allows you to create threedimensional
BCC 3D Extruded Image Shatter Filter 3D Extruded Image Shatter shatters the image in 3D space and disperses the image fragments. Unlike the 3D Image Shatter filter, this filter allows you to create threedimensional
CHAPTER- 10 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
 CHAPTER- 10 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION LIGHT Light is a form of energy, which enable us to see the object. Its speed is 3 10 8 m/s in vacuum. Light always travel in straight line. Reflection: The
CHAPTER- 10 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION LIGHT Light is a form of energy, which enable us to see the object. Its speed is 3 10 8 m/s in vacuum. Light always travel in straight line. Reflection: The
Experimental Competition
 Please read this first: Experimental Competition Saturday, June 30 th, 001 1. The time available is 5 hours for the experimental competition.. Use only the pen provided. 3. Use only the front side of the
Please read this first: Experimental Competition Saturday, June 30 th, 001 1. The time available is 5 hours for the experimental competition.. Use only the pen provided. 3. Use only the front side of the
ECE-161C Cameras. Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD
 ECE-161C Cameras Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD Image formation all image understanding starts with understanding of image formation: projection of a scene from 3D world into image on 2D plane 2
ECE-161C Cameras Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD Image formation all image understanding starts with understanding of image formation: projection of a scene from 3D world into image on 2D plane 2
CS770/870 Spring 2017 Animation Basics
 Preview CS770/870 Spring 2017 Animation Basics Related material Angel 6e: 1.1.3, 8.6 Thalman, N and D. Thalman, Computer Animation, Encyclopedia of Computer Science, CRC Press. Lasseter, J. Principles
Preview CS770/870 Spring 2017 Animation Basics Related material Angel 6e: 1.1.3, 8.6 Thalman, N and D. Thalman, Computer Animation, Encyclopedia of Computer Science, CRC Press. Lasseter, J. Principles
CS770/870 Spring 2017 Animation Basics
 CS770/870 Spring 2017 Animation Basics Related material Angel 6e: 1.1.3, 8.6 Thalman, N and D. Thalman, Computer Animation, Encyclopedia of Computer Science, CRC Press. Lasseter, J. Principles of traditional
CS770/870 Spring 2017 Animation Basics Related material Angel 6e: 1.1.3, 8.6 Thalman, N and D. Thalman, Computer Animation, Encyclopedia of Computer Science, CRC Press. Lasseter, J. Principles of traditional
Kinematics Review. Physics 2012
 Kinematics Review Physics 2012 Question 1 Mom and Junior are driving north in a car. They pass Spike who is standing on the side of the road. Which of these statements are correct? 1. Spike sees mom and
Kinematics Review Physics 2012 Question 1 Mom and Junior are driving north in a car. They pass Spike who is standing on the side of the road. Which of these statements are correct? 1. Spike sees mom and
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it?
 What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
9 Dynamics. Getting Started with Maya 491
 9 Dynamics Dynamics is a branch of physics that describes how objects move using physical rules to simulate the natural forces that act upon them. Dynamic simulations are difficult to achieve with traditional
9 Dynamics Dynamics is a branch of physics that describes how objects move using physical rules to simulate the natural forces that act upon them. Dynamic simulations are difficult to achieve with traditional
Worksheet 5. 3 Less trigonometry and more dishonesty/linear algebra knowledge Less trigonometry, less dishonesty... 4
 Worksheet 5 Contents 1 Just look at the book, on page 74 1 2 Trigonometry and honesty 1 3 Less trigonometry and more dishonesty/linear algebra knowledge 3 3.1 Less trigonometry, less dishonesty...............................
Worksheet 5 Contents 1 Just look at the book, on page 74 1 2 Trigonometry and honesty 1 3 Less trigonometry and more dishonesty/linear algebra knowledge 3 3.1 Less trigonometry, less dishonesty...............................
Learning Objectives. Math Prerequisites. Technology Prerequisites. Materials. Math Objectives. Technology Objectives
 Learning Objectives Parametric Functions Lesson 2: Dude, Where s My Football? Level: Algebra 2 Time required: 60 minutes Many students expect a falling object graph to look just like the path of the falling
Learning Objectives Parametric Functions Lesson 2: Dude, Where s My Football? Level: Algebra 2 Time required: 60 minutes Many students expect a falling object graph to look just like the path of the falling
Billiard Paths on Arbitrary Tables
 Billiard Paths on Arbitrary Tables Note: The first time you evaluate a cell in this notebook you will get a popup asking you if you want to evaluate all initialization cells in the notebook - say Yes to
Billiard Paths on Arbitrary Tables Note: The first time you evaluate a cell in this notebook you will get a popup asking you if you want to evaluate all initialization cells in the notebook - say Yes to
Goals: - to be able to recognize the position-time, velocity-time and acceleration-time graphs of each of these main types of motion:
 Unit: One-Dimensional Kinematics Level: 1 Prerequisites: None Points to: Goals: - to be able to recognize the position-time, velocity-time and acceleration-time graphs of each of these main types of motion:
Unit: One-Dimensional Kinematics Level: 1 Prerequisites: None Points to: Goals: - to be able to recognize the position-time, velocity-time and acceleration-time graphs of each of these main types of motion:
EEN118 LAB FOUR. h = v t ½ g t 2
 EEN118 LAB FOUR In this lab you will be performing a simulation of a physical system, shooting a projectile from a cannon and working out where it will land. Although this is not a very complicated physical
EEN118 LAB FOUR In this lab you will be performing a simulation of a physical system, shooting a projectile from a cannon and working out where it will land. Although this is not a very complicated physical
Working with the BCC 2D Particles Filter
 Working with the BCC 2D Particles Filter 2D Particles breaks the source image into particles and disperses them in 2D space. This Þlter also provides a variety of explosion, velocity, and gravity controls
Working with the BCC 2D Particles Filter 2D Particles breaks the source image into particles and disperses them in 2D space. This Þlter also provides a variety of explosion, velocity, and gravity controls
Content Standards G.CO.4 Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel
 Content Standards G.CO.4 Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. G.CO.5 Given a geometric figure
Content Standards G.CO.4 Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. G.CO.5 Given a geometric figure
Making things move. Time and Space
 Making things move Time and Space Animation Persistance of Vision/ Illusion of Motion showing a human a sequence of still images in rapid succession is perceived as motion. screen refresh rate: how often
Making things move Time and Space Animation Persistance of Vision/ Illusion of Motion showing a human a sequence of still images in rapid succession is perceived as motion. screen refresh rate: how often
Notes 3: Actionscript to control symbol locations
 Notes 3: Actionscript to control symbol locations Okay, you now know enough actionscript to shoot yourself in the foot, especially if you don t use types. REMEMBER to always declare vars and specify data
Notes 3: Actionscript to control symbol locations Okay, you now know enough actionscript to shoot yourself in the foot, especially if you don t use types. REMEMBER to always declare vars and specify data
A NON-TRIGONOMETRIC, PSEUDO AREA PRESERVING, POLYLINE SMOOTHING ALGORITHM
 A NON-TRIGONOMETRIC, PSEUDO AREA PRESERVING, POLYLINE SMOOTHING ALGORITHM Wayne Brown and Leemon Baird Department of Computer Science The United States Air Force Academy 2354 Fairchild Dr., Suite 6G- USAF
A NON-TRIGONOMETRIC, PSEUDO AREA PRESERVING, POLYLINE SMOOTHING ALGORITHM Wayne Brown and Leemon Baird Department of Computer Science The United States Air Force Academy 2354 Fairchild Dr., Suite 6G- USAF
SimTenero Particle Physics
 SimTenero Particle Physics Getting Started The heart of the particle system is the Emitter. This represents the point in space where particles will be created and contains all of the parameters that define
SimTenero Particle Physics Getting Started The heart of the particle system is the Emitter. This represents the point in space where particles will be created and contains all of the parameters that define
Sphero Lightning Lab Cheat Sheet
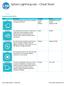 Actions Tool Description Variables Ranges Roll Combines heading, speed and time variables to make the robot roll. Duration Speed Heading (0 to 999999 seconds) (degrees 0-359) Set Speed Sets the speed of
Actions Tool Description Variables Ranges Roll Combines heading, speed and time variables to make the robot roll. Duration Speed Heading (0 to 999999 seconds) (degrees 0-359) Set Speed Sets the speed of
Fruit Snake SECTION 1
 Fruit Snake SECTION 1 For the first full Construct 2 game you're going to create a snake game. In this game, you'll have a snake that will "eat" fruit, and grow longer with each object or piece of fruit
Fruit Snake SECTION 1 For the first full Construct 2 game you're going to create a snake game. In this game, you'll have a snake that will "eat" fruit, and grow longer with each object or piece of fruit
C:\Users\weaver\Justin\Workspace\UAA_2011_A_Spring\CS470\Project\OrbitClash\OrbitClash\SolidEntity.cs
 1 #region Header Comments 2 3 /* $Id: SolidEntity.cs 1355 2011-03-25 22:53:42Z weaver $ 4 * 5 * Author: Justin Weaver 6 * Date: Mar 2011 7 * Description: Extendable abstract class to facilitate collision
1 #region Header Comments 2 3 /* $Id: SolidEntity.cs 1355 2011-03-25 22:53:42Z weaver $ 4 * 5 * Author: Justin Weaver 6 * Date: Mar 2011 7 * Description: Extendable abstract class to facilitate collision
WP5 - Computational Mechanics Acceleration transducers on Finite Element vehicle models for crash simulations with Ls-Dyna
 ROBUST PROJECT Department of Aerospace engineering* - Politecnico di Milano Volume 1 of 1 (*)via La Masa, 34 Milan-ITALY tel: +39 2 23998316 - fax: +39 2 23998334 Jan 25 Doc. No.: ROBUST-5-7 - Rev. Pagei
ROBUST PROJECT Department of Aerospace engineering* - Politecnico di Milano Volume 1 of 1 (*)via La Masa, 34 Milan-ITALY tel: +39 2 23998316 - fax: +39 2 23998334 Jan 25 Doc. No.: ROBUST-5-7 - Rev. Pagei
Animation Essentially a question of flipping between many still images, fast enough
 33(70) Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH Animation Essentially a question of flipping between many still images, fast enough 33(70) Animation as a topic Page flipping, double-buffering
33(70) Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH Animation Essentially a question of flipping between many still images, fast enough 33(70) Animation as a topic Page flipping, double-buffering
EEN118 LAB FOUR. h = v t ½ g t 2
 EEN118 LAB FOUR In this lab you will be performing a simulation of a physical system, shooting a projectile from a cannon and working out where it will land. Although this is not a very complicated physical
EEN118 LAB FOUR In this lab you will be performing a simulation of a physical system, shooting a projectile from a cannon and working out where it will land. Although this is not a very complicated physical
SVSM 2008 Mathematical Modeling MODELING MOTION IN VPYTHON
 SVSM 2008 Mathematical Modeling MODELING MOTION IN VPYTHON VPYTHON = VISUAL PYTHON Easy to learn 3D Interactive modeling Python background language Main site http://vpython.org/ Download http://vpython.org/win_download25.html
SVSM 2008 Mathematical Modeling MODELING MOTION IN VPYTHON VPYTHON = VISUAL PYTHON Easy to learn 3D Interactive modeling Python background language Main site http://vpython.org/ Download http://vpython.org/win_download25.html
Particle Systems. Lecture 8 Taku Komura
 Particle Systems Computer Animation and Visualisation Lecture 8 Taku Komura Overview Particle System Modelling fuzzy objects (fire, smoke) Modelling liquid Modelling cloth Integration : implicit integration,
Particle Systems Computer Animation and Visualisation Lecture 8 Taku Komura Overview Particle System Modelling fuzzy objects (fire, smoke) Modelling liquid Modelling cloth Integration : implicit integration,
PyGame Sprites. an excellent turorial exists for PyGame sprites here kai.vm.bytemark.co.uk/ piman/writing/spritetutorial.shtml.
 PyGame Sprites slide 1 an excellent turorial exists for PyGame sprites here http:// kai.vm.bytemark.co.uk/ piman/writing/spritetutorial.shtml. these notes are derived from this tutorial and the examples
PyGame Sprites slide 1 an excellent turorial exists for PyGame sprites here http:// kai.vm.bytemark.co.uk/ piman/writing/spritetutorial.shtml. these notes are derived from this tutorial and the examples
Area and Volume. where x right and x left are written in terms of y.
 Area and Volume Area between two curves Sketch the region and determine the points of intersection. Draw a small strip either as dx or dy slicing. Use the following templates to set up a definite integral:
Area and Volume Area between two curves Sketch the region and determine the points of intersection. Draw a small strip either as dx or dy slicing. Use the following templates to set up a definite integral:
Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe
 Tutorial 4. Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D turbulent fluid flow in a pipe. The pipe networks are common
Tutorial 4. Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D turbulent fluid flow in a pipe. The pipe networks are common
Game Starter Kit Cheat Sheet
 Game Starter Kit Cheat Sheet In this cheat sheet, I am going to show you how you can create your own custom Flappy Bird Game in a matter of minutes, using FREE Software. The same style of game that was
Game Starter Kit Cheat Sheet In this cheat sheet, I am going to show you how you can create your own custom Flappy Bird Game in a matter of minutes, using FREE Software. The same style of game that was
1. Defining Procedures and Reusing Blocks
 1. Defining Procedures and Reusing Blocks 1.1 Eliminating Redundancy By creating a procedure, move a copy of the redundant blocks into it, and then call the procedure from the places containing the redundant
1. Defining Procedures and Reusing Blocks 1.1 Eliminating Redundancy By creating a procedure, move a copy of the redundant blocks into it, and then call the procedure from the places containing the redundant
To graph the point (r, θ), simply go out r units along the initial ray, then rotate through the angle θ. The point (1, 5π 6. ) is graphed below:
 Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
ROSE-HULMAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 More Working Model Today we are going to look at even more features of Working Model. Specifically, we are going to 1) Learn how to add ropes and rods. 2) Learn how to connect object using joints and slots.
More Working Model Today we are going to look at even more features of Working Model. Specifically, we are going to 1) Learn how to add ropes and rods. 2) Learn how to connect object using joints and slots.
Lesson 1: Introduction to Pro/MECHANICA Motion
 Lesson 1: Introduction to Pro/MECHANICA Motion 1.1 Overview of the Lesson The purpose of this lesson is to provide you with a brief overview of Pro/MECHANICA Motion, also called Motion in this book. Motion
Lesson 1: Introduction to Pro/MECHANICA Motion 1.1 Overview of the Lesson The purpose of this lesson is to provide you with a brief overview of Pro/MECHANICA Motion, also called Motion in this book. Motion
INSRUCTION SHEET. Flash Lab #1
 Advanced Web Page Design STANDARD 5 The student will use commercial animation software (for example: Flash, Alice, Anim8, Ulead) to create graphics/web page. Student Learning Objectives: Objective 1: Draw,
Advanced Web Page Design STANDARD 5 The student will use commercial animation software (for example: Flash, Alice, Anim8, Ulead) to create graphics/web page. Student Learning Objectives: Objective 1: Draw,
EEN118 LAB FOUR. h = v t ½ g t 2
 EEN118 LAB FOUR In this lab you will be performing a simulation of a physical system, shooting a projectile from a cannon and working out where it will land. Although this is not a very complicated physical
EEN118 LAB FOUR In this lab you will be performing a simulation of a physical system, shooting a projectile from a cannon and working out where it will land. Although this is not a very complicated physical
