5.5 Alternating Series
|
|
|
- Malcolm Casey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5.5 Alternating Series Most of the tests we ve dealt with used a series with positive terms. Now we ll focus on the type of series where the sequence a n alternates between positive and negative terms. Definition 5.0 (Alternating Series). A series whose terms are alternately positive and negative. For example, = ( ) n n=0 ( ) n 2 = n Theorem 5.4 (Alternating Series Test). If the alternating series ( ) n b n = b b 2 + b b 4 + b 5... satisfies the following requirements. b n > 0 2. b n+ b n (terms are decreasing). lim n b n = 0 then the alternating series is convergent. Additionally, we also have the following conclusion If ( ) n b n = S, then 0 < S < a and S 2N < S < S 2N+ 260
2 This conclusion states that if the altnerating series converges, then its sum will always be between consectuve partial sums. Let s take a look at an example. Example Consider the following alternating series ( ) n 2. Note, this is a geometric serires with r = 2, so we know it will converge. It will converge to ( ) n 2 = 2. Let s look at it now as an alternating series ( 2 ) = 5 = 0.6 where b n = test. ( 2 ( ) n ) n ( ) n 2. Note that b n satisfies the requirements for the alternating series (a) b n > 0 (b) b n is decreasing (c) b n 0 as n By the alternating series test, that. ( ) n ( 2 ) n converges. But we already knew. The last part of the alternating series test states a way to estimate the sum by looking at two consecutive partial sums. It states that the true sum of the series will always be 26
3 between two consecutive partial sums. Let s check that. Recall the true sum is S = 0.6. (a) S = Note that we satisfy 0 < S < (b) S 2 = 2 = and < S < (c) S = = and < S < 7 9 (d) S 4 = = 27 = and 8 27 < S < If we keep this process up, we will eventually trap the true sum between two very close numbers. For example, S S or 262
4 S S Example Recall that the harmonic series n diverges (p-series test). What about ( ) n This series is an alternating series. Let b n = n. n. b n = n > 0 2. b n = n is decreasing. b n 0 as n Since it satisfies the altnerating series test, we conclude that Example Determine if n=2 ( ) n converges n ( ) n (n ) 2n + converges. It s clear it altnernates because of the ( ) n. So now let s consider b n = n 2n + if it satisfies the rest of the alternating series test. and see. b n = n 2n + > 0 2. If we want to check to see if b n is decreasing, we need to find the derivative and show it s negative. The problem is the derivative is 26
5 So b n is not decreasing.. Also, b n > 0 for all n (2n + ) 2 The fact that the series is not decreasing to 0 means this series diverges. Recall from a few sections ago that if the sequence a n doesn t converge to 0 means the series a n automatically diverges. Let s return to estimating an alternating series. Theorem 5.5. Let S = ( ) n b n, where b n > 0, decreases, and b n 0. Then R n = S S N < b N+ This theorem states that you can add up the first N terms. The remainder (the stuff that we haven t added yet) must be less than the next term in the sequence b N+. Example: Recall the series ( ) n ( 2 ) n, which converges to S = 0.6. R 0 = S S 0 < b = ( ) 2 = Recall from a couple of examples ago that S 0 = So did our theorem work? so R 0 = =
6 R 0 = < b = Yes, our theorem worked. Let s check another one. so R 20 = = b 2 = R 20 = < b 2 = So what can we get from this method? If we want to estimate to within say, 0.000, we need to find out when R N < or instead b N+ < Example: Consider the following series n=0 ( ) n 0 n n! Estimate the series so it has an error less than In order to use our theorem, it needs to satisfiy the altnerating series test. Let b n = 0 n n!. 265
7 (a) b n = 0 n n! > 0 (b) b n is decreasing. We don t have a derivative to check, but c mon! I think we can agree this decreases. (c) b n 0 as n 2. Now that we know it converges by the Alternating Series Test, let s work on estimating. Initially we want to find N such that R N < But since R N < b N+, it s much easier to find N where b N+ < So let s get started. 0 N+ (N + )! < < 0 N+ (N + )! 266
8 . We just need to check a few values for N (a) If N =, 0 4 4! = < (b) If N = 4, 0 5 5! = > We conclude we need N 4 to get our series within Since n starts at n =, we need the first N = 4 terms to get our required accuracy. Let s verify that we did in fact get our required accuracy. Assume the true sum is S = (a) S 2 = S 2 S = > (b) S = S S = >
9 (c) S 4 = S 4 S = < So it s confirmed. We reach our required accuracy at N =
Calculus II. Step 1 First, here is a quick sketch of the graph of the region we are interested in.
 Preface Here are the solutions to the practice problems for my Calculus II notes. Some solutions will have more or less detail than other solutions. As the difficulty level of the problems increases less
Preface Here are the solutions to the practice problems for my Calculus II notes. Some solutions will have more or less detail than other solutions. As the difficulty level of the problems increases less
Sequences and Series. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Sequences and Series Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 12.3 Geometric Sequences Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives Geometric Sequences Partial Sums of Geometric
Sequences and Series Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 12.3 Geometric Sequences Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives Geometric Sequences Partial Sums of Geometric
Table of Laplace Transforms
 Table of Laplace Transforms 1 1 2 3 4, p > -1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Heaviside Function 27 28. Dirac Delta Function 29 30. 31 32. 1 33 34. 35 36. 37 Laplace Transforms
Table of Laplace Transforms 1 1 2 3 4, p > -1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Heaviside Function 27 28. Dirac Delta Function 29 30. 31 32. 1 33 34. 35 36. 37 Laplace Transforms
Math 126 Number Theory
 Math 16 Number Theory Prof. D. Joyce, Clark University 8 Mar 006 Due Friday. Page 155: exercises 1,, 7. Choose one of the three and write it up completely. Whichever one you choose, find all those solutions
Math 16 Number Theory Prof. D. Joyce, Clark University 8 Mar 006 Due Friday. Page 155: exercises 1,, 7. Choose one of the three and write it up completely. Whichever one you choose, find all those solutions
A. Incorrect! This would be the negative of the range. B. Correct! The range is the maximum data value minus the minimum data value.
 AP Statistics - Problem Drill 05: Measures of Variation No. 1 of 10 1. The range is calculated as. (A) The minimum data value minus the maximum data value. (B) The maximum data value minus the minimum
AP Statistics - Problem Drill 05: Measures of Variation No. 1 of 10 1. The range is calculated as. (A) The minimum data value minus the maximum data value. (B) The maximum data value minus the minimum
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Using the Rule of Three
 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Using the Rule of Three A. Approimations with Riemann sums. The area under a curve can be approimated through the use of Riemann (or rectangular) sums: n Area f ( k
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Using the Rule of Three A. Approimations with Riemann sums. The area under a curve can be approimated through the use of Riemann (or rectangular) sums: n Area f ( k
1.2 Adding Integers. Contents: Numbers on the Number Lines Adding Signed Numbers on the Number Line
 1.2 Adding Integers Contents: Numbers on the Number Lines Adding Signed Numbers on the Number Line Finding Sums Mentally The Commutative Property Finding Sums using And Patterns and Rules of Adding Signed
1.2 Adding Integers Contents: Numbers on the Number Lines Adding Signed Numbers on the Number Line Finding Sums Mentally The Commutative Property Finding Sums using And Patterns and Rules of Adding Signed
Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Applications of Partial Derivatives / Lagrange Multipliers Problems][Assignment Problems]
![Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Applications of Partial Derivatives / Lagrange Multipliers Problems][Assignment Problems] Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Applications of Partial Derivatives / Lagrange Multipliers Problems][Assignment Problems]](/thumbs/77/75726948.jpg) 1 of 9 25/04/2016 13:15 Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Applications of Partial Derivatives / Lagrange Multipliers Problems][Assignment Problems] [Notes] [Practice Calculus III - Notes
1 of 9 25/04/2016 13:15 Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Applications of Partial Derivatives / Lagrange Multipliers Problems][Assignment Problems] [Notes] [Practice Calculus III - Notes
Math 5320, 3/28/18 Worksheet 26: Ruler and compass constructions. 1. Use your ruler and compass to construct a line perpendicular to the line below:
 Math 5320, 3/28/18 Worksheet 26: Ruler and compass constructions Name: 1. Use your ruler and compass to construct a line perpendicular to the line below: 2. Suppose the following two points are spaced
Math 5320, 3/28/18 Worksheet 26: Ruler and compass constructions Name: 1. Use your ruler and compass to construct a line perpendicular to the line below: 2. Suppose the following two points are spaced
SPRITES Moving Two At the Same Using Game State
 If you recall our collision detection lesson, you ll likely remember that you couldn t move both sprites at the same time unless you hit a movement key for each at exactly the same time. Why was that?
If you recall our collision detection lesson, you ll likely remember that you couldn t move both sprites at the same time unless you hit a movement key for each at exactly the same time. Why was that?
Lesson 20: Every Line is a Graph of a Linear Equation
 Student Outcomes Students know that any non vertical line is the graph of a linear equation in the form of, where is a constant. Students write the equation that represents the graph of a line. Lesson
Student Outcomes Students know that any non vertical line is the graph of a linear equation in the form of, where is a constant. Students write the equation that represents the graph of a line. Lesson
Typing Control. Chapter Conditionals
 Chapter 26 Typing Control 26.1 Conditionals Let s expand our language with a conditional construct. We can use if0 like before, but for generality it s going to be more convenient to have a proper conditional
Chapter 26 Typing Control 26.1 Conditionals Let s expand our language with a conditional construct. We can use if0 like before, but for generality it s going to be more convenient to have a proper conditional
Is the statement sufficient? If both x and y are odd, is xy odd? 1) xy 2 < 0. Odds & Evens. Positives & Negatives. Answer: Yes, xy is odd
 Is the statement sufficient? If both x and y are odd, is xy odd? Is x < 0? 1) xy 2 < 0 Positives & Negatives Answer: Yes, xy is odd Odd numbers can be represented as 2m + 1 or 2n + 1, where m and n are
Is the statement sufficient? If both x and y are odd, is xy odd? Is x < 0? 1) xy 2 < 0 Positives & Negatives Answer: Yes, xy is odd Odd numbers can be represented as 2m + 1 or 2n + 1, where m and n are
Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions
 Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Variable is a letter or symbol that represents a number. Variable (algebraic)
Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Variable is a letter or symbol that represents a number. Variable (algebraic)
CS140 Lecture 03: The Machinery of Computation: Combinational Logic
 CS140 Lecture 03: The Machinery of Computation: Combinational Logic John Magee 25 January 2017 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett Some slides credit Aaron Stevens 1 Overview/Questions What did
CS140 Lecture 03: The Machinery of Computation: Combinational Logic John Magee 25 January 2017 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett Some slides credit Aaron Stevens 1 Overview/Questions What did
Differentiability and Tangent Planes October 2013
 Differentiability and Tangent Planes 14.4 04 October 2013 Differentiability in one variable. Recall for a function of one variable, f is differentiable at a f (a + h) f (a) lim exists and = f (a) h 0 h
Differentiability and Tangent Planes 14.4 04 October 2013 Differentiability in one variable. Recall for a function of one variable, f is differentiable at a f (a + h) f (a) lim exists and = f (a) h 0 h
RACKET BASICS, ORDER OF EVALUATION, RECURSION 1
 RACKET BASICS, ORDER OF EVALUATION, RECURSION 1 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61AS 1. What is functional programming? Give an example of a function below: Functional Programming In functional programming, you do not
RACKET BASICS, ORDER OF EVALUATION, RECURSION 1 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61AS 1. What is functional programming? Give an example of a function below: Functional Programming In functional programming, you do not
Chapter 3: Mirrors and Lenses
 Chapter 3: Mirrors and Lenses Chapter 3: Mirrors and Lenses Lenses Refraction Converging rays Diverging rays Converging Lens Ray tracing rules Image formation Diverging Lens Ray tracing Image formation
Chapter 3: Mirrors and Lenses Chapter 3: Mirrors and Lenses Lenses Refraction Converging rays Diverging rays Converging Lens Ray tracing rules Image formation Diverging Lens Ray tracing Image formation
Paperless Terms and Conditions. Customer information
 Paperless Terms and Conditions Customer information Terms and Conditions These terms apply when you choose to: Receive online statements for Personal Loans, Accounts and s Receive online statements and
Paperless Terms and Conditions Customer information Terms and Conditions These terms apply when you choose to: Receive online statements for Personal Loans, Accounts and s Receive online statements and
Signed umbers. Sign/Magnitude otation
 Signed umbers So far we have discussed unsigned number representations. In particular, we have looked at the binary number system and shorthand methods in representing binary codes. With m binary digits,
Signed umbers So far we have discussed unsigned number representations. In particular, we have looked at the binary number system and shorthand methods in representing binary codes. With m binary digits,
Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross Product
 University of Babylon College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. Subject : Mathematics III Class : 2 nd year - first semester Date: / 10 / 2016 2016 \ 2017 Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross
University of Babylon College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. Subject : Mathematics III Class : 2 nd year - first semester Date: / 10 / 2016 2016 \ 2017 Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross
Project Report Number Plate Recognition
 Project Report Number Plate Recognition Ribemont Francois Supervisor: Nigel Whyte April 17, 2012 Contents 1 Introduction............................... 2 2 Description of Submitted Project...................
Project Report Number Plate Recognition Ribemont Francois Supervisor: Nigel Whyte April 17, 2012 Contents 1 Introduction............................... 2 2 Description of Submitted Project...................
Divisibility Rules and Their Explanations
 Divisibility Rules and Their Explanations Increase Your Number Sense These divisibility rules apply to determining the divisibility of a positive integer (1, 2, 3, ) by another positive integer or 0 (although
Divisibility Rules and Their Explanations Increase Your Number Sense These divisibility rules apply to determining the divisibility of a positive integer (1, 2, 3, ) by another positive integer or 0 (although
Lab 6 Vectors and functions
 CMSC160 Intro to Algorithmic Design Blaheta Lab 6 Vectors and functions 11 October 2016 The drill for this lab is another part of the Chapter 4 drill. Come to lab on Tuesday either with it completed or
CMSC160 Intro to Algorithmic Design Blaheta Lab 6 Vectors and functions 11 October 2016 The drill for this lab is another part of the Chapter 4 drill. Come to lab on Tuesday either with it completed or
What is version control? (discuss) Who has used version control? Favorite VCS? Uses of version control (read)
 1 For the remainder of the class today, I want to introduce you to a topic we will spend one or two more classes discussing and that is source code control or version control. What is version control?
1 For the remainder of the class today, I want to introduce you to a topic we will spend one or two more classes discussing and that is source code control or version control. What is version control?
Problem Solving for Intro to Computer Science
 Problem Solving for Intro to Computer Science The purpose of this document is to review some principles for problem solving that are relevant to Intro to Computer Science course. Introduction: A Sample
Problem Solving for Intro to Computer Science The purpose of this document is to review some principles for problem solving that are relevant to Intro to Computer Science course. Introduction: A Sample
Legal Notice: COPYRIGHT: Copyright 2012 Hitman Advertising, all rights reserved. LIMITS OF LIABILITY / DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTY:
 Legal Notice: COPYRIGHT: Copyright 2012 Hitman Advertising, all rights reserved. LIMITS OF LIABILITY / DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTY: This report is NOT legal or accounting advice. You need to do your own due
Legal Notice: COPYRIGHT: Copyright 2012 Hitman Advertising, all rights reserved. LIMITS OF LIABILITY / DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTY: This report is NOT legal or accounting advice. You need to do your own due
Solving for dynamic user equilibrium
 Solving for dynamic user equilibrium CE 392D Overall DTA problem 1. Calculate route travel times 2. Find shortest paths 3. Adjust route choices toward equilibrium We can envision each of these steps as
Solving for dynamic user equilibrium CE 392D Overall DTA problem 1. Calculate route travel times 2. Find shortest paths 3. Adjust route choices toward equilibrium We can envision each of these steps as
Lecture 4: examples of topological spaces, coarser and finer topologies, bases and closed sets
 Lecture 4: examples of topological spaces, coarser and finer topologies, bases and closed sets Saul Glasman 14 September 2016 Let s give the definition of an open subset of R. Definition 1. Let U R. We
Lecture 4: examples of topological spaces, coarser and finer topologies, bases and closed sets Saul Glasman 14 September 2016 Let s give the definition of an open subset of R. Definition 1. Let U R. We
Introduction to Programming
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Programming Begin at the beginning, and go on till you come to the end: then stop. This method of telling a story is as good today as it was when the King of Hearts prescribed
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Programming Begin at the beginning, and go on till you come to the end: then stop. This method of telling a story is as good today as it was when the King of Hearts prescribed
DropSend Getting Started Guide
 DropSend Getting Started Guide DropSend. 2016 Step 1: How to send a file without registration If you want to quickly send a large file, you can do it from the homepage in just a couple of clicks. Here
DropSend Getting Started Guide DropSend. 2016 Step 1: How to send a file without registration If you want to quickly send a large file, you can do it from the homepage in just a couple of clicks. Here
Section 1.3 Adding Integers
 Section 1.3 Adding Integers Objectives In this section, you will learn to: To successfully complete this section, you need to understand: Represent integers as vectors. The integer number line (1.2) Add
Section 1.3 Adding Integers Objectives In this section, you will learn to: To successfully complete this section, you need to understand: Represent integers as vectors. The integer number line (1.2) Add
Lesson 17 MA Nick Egbert
 Overview There is no new major information in this lesson; instead we wish to apply our knowledge of geometric series to various types of word problems These types of word problems can be difficult to
Overview There is no new major information in this lesson; instead we wish to apply our knowledge of geometric series to various types of word problems These types of word problems can be difficult to
Limits and Derivatives (Review of Math 249 or 251)
 Chapter 3 Limits and Derivatives (Review of Math 249 or 251) 3.1 Overview This is the first of two chapters reviewing material from calculus; its and derivatives are discussed in this chapter, and integrals
Chapter 3 Limits and Derivatives (Review of Math 249 or 251) 3.1 Overview This is the first of two chapters reviewing material from calculus; its and derivatives are discussed in this chapter, and integrals
, etc. Let s work with the last one. We can graph a few points determined by this equation.
 1. Lines By a line, we simply mean a straight curve. We will always think of lines relative to the cartesian plane. Consider the equation 2x 3y 4 = 0. We can rewrite it in many different ways : 2x 3y =
1. Lines By a line, we simply mean a straight curve. We will always think of lines relative to the cartesian plane. Consider the equation 2x 3y 4 = 0. We can rewrite it in many different ways : 2x 3y =
15-780: Graduate AI Homework Assignment #2 Solutions
 15-780: Graduate AI Homework Assignment #2 Solutions Out: February 12, 2015 Due: February 25, 2015 Collaboration Policy: You may discuss the problems with others, but you must write all code and your writeup
15-780: Graduate AI Homework Assignment #2 Solutions Out: February 12, 2015 Due: February 25, 2015 Collaboration Policy: You may discuss the problems with others, but you must write all code and your writeup
SCHEME 8. 1 Introduction. 2 Primitives COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A. March 23, 2017
 SCHEME 8 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A March 2, 2017 1 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
SCHEME 8 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A March 2, 2017 1 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
4.7 Approximate Integration
 4.7 Approximate Integration Some anti-derivatives are difficult to impossible to find. For example, 1 0 e x2 dx or 1 1 1 + x3 dx We came across this situation back in calculus I when we introduced the
4.7 Approximate Integration Some anti-derivatives are difficult to impossible to find. For example, 1 0 e x2 dx or 1 1 1 + x3 dx We came across this situation back in calculus I when we introduced the
Joining Flickr. Each of the above steps is detailed below: Step 1: Sign up for a Yahoo! account (skip this step if you already have one)
 Joining Flickr Flickr is a photo sharing website. The photography group at the Library has organized a group for members to post and share their photos. Here s how to join: 1. Sign up for a Yahoo! account
Joining Flickr Flickr is a photo sharing website. The photography group at the Library has organized a group for members to post and share their photos. Here s how to join: 1. Sign up for a Yahoo! account
Paul's Online Math Notes. Online Notes / Algebra (Notes) / Systems of Equations / Augmented Matricies
 1 of 8 5/17/2011 5:58 PM Paul's Online Math Notes Home Class Notes Extras/Reviews Cheat Sheets & Tables Downloads Algebra Home Preliminaries Chapters Solving Equations and Inequalities Graphing and Functions
1 of 8 5/17/2011 5:58 PM Paul's Online Math Notes Home Class Notes Extras/Reviews Cheat Sheets & Tables Downloads Algebra Home Preliminaries Chapters Solving Equations and Inequalities Graphing and Functions
A Solidify Understanding Task
 17 A Solidify Understanding Task We know that two triangles are congruent if all pairs of corresponding sides are congruent and all pairs of corresponding angles are congruent. We may wonder if knowing
17 A Solidify Understanding Task We know that two triangles are congruent if all pairs of corresponding sides are congruent and all pairs of corresponding angles are congruent. We may wonder if knowing
Circulation density and an argument for Stokes Theorem
 MATH 221A Multivariate Calculus pring 2004 Circulation density and an argument for tokes Theorem Version 1 (May 13, 2004) There are three sections in these notes. The goal for the first section is to see
MATH 221A Multivariate Calculus pring 2004 Circulation density and an argument for tokes Theorem Version 1 (May 13, 2004) There are three sections in these notes. The goal for the first section is to see
CS 468 (Spring 2013) Discrete Differential Geometry
 CS 468 (Spring 2013) Discrete Differential Geometry 1 Math Review Lecture 14 15 May 2013 Discrete Exterior Calculus Lecturer: Justin Solomon Scribe: Cassidy Saenz Before we dive into Discrete Exterior
CS 468 (Spring 2013) Discrete Differential Geometry 1 Math Review Lecture 14 15 May 2013 Discrete Exterior Calculus Lecturer: Justin Solomon Scribe: Cassidy Saenz Before we dive into Discrete Exterior
NQF ONLINE MEASURE SUBMISSION FORM USERS GUIDE
 NQF ONLINE MEASURE SUBMISSION FORM USERS GUIDE VERSION 1.1 Guide Version 1.0 01/11 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1: TECHNICAL SUPPORT FOR SUBMISSION FORM TABLE OF CONTENTS... CREATING AN INDIVIDUAL ACCOUNT...
NQF ONLINE MEASURE SUBMISSION FORM USERS GUIDE VERSION 1.1 Guide Version 1.0 01/11 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1: TECHNICAL SUPPORT FOR SUBMISSION FORM TABLE OF CONTENTS... CREATING AN INDIVIDUAL ACCOUNT...
COP Programming Assignment #7
 1 of 5 03/13/07 12:36 COP 3330 - Programming Assignment #7 Due: Mon, Nov 21 (revised) Objective: Upon completion of this program, you should gain experience with operator overloading, as well as further
1 of 5 03/13/07 12:36 COP 3330 - Programming Assignment #7 Due: Mon, Nov 21 (revised) Objective: Upon completion of this program, you should gain experience with operator overloading, as well as further
Unit 5: Division. By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys
 Math Fundamentals for Statistics I (Math ) Unit : Division By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Math Fundamentals for Statistics I (Math ) Unit : Division By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Here are some of the more basic curves that we ll need to know how to do as well as limits on the parameter if they are required.
 1 of 10 23/07/2016 05:15 Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Line Integrals / Line Integrals - Part I Problems] [Notes] [Practice Problems] [Assignment Calculus III - Notes Line Integrals Part
1 of 10 23/07/2016 05:15 Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Line Integrals / Line Integrals - Part I Problems] [Notes] [Practice Problems] [Assignment Calculus III - Notes Line Integrals Part
How to Register your Institution with proposalcentral
 How to Register your Institution with proposalcentral CUSTOMER SUPPORT: The Institution Profile is created once by the appropriate institution official. The institution information is then available to
How to Register your Institution with proposalcentral CUSTOMER SUPPORT: The Institution Profile is created once by the appropriate institution official. The institution information is then available to
Accelerated Pre-Calculus Unit 1 Task 1: Our Only Focus: Circles & Parabolas Review
 Accelerated Pre-Calculus Unit 1 Task 1: Our Only Focus: Circles & Parabolas Review Name: Date: Period: For most students, you last learned about conic sections in Analytic Geometry, which was a while ago.
Accelerated Pre-Calculus Unit 1 Task 1: Our Only Focus: Circles & Parabolas Review Name: Date: Period: For most students, you last learned about conic sections in Analytic Geometry, which was a while ago.
MA 1128: Lecture 02 1/22/2018
 MA 1128: Lecture 02 1/22/2018 Exponents Scientific Notation 1 Exponents Exponents are used to indicate how many copies of a number are to be multiplied together. For example, I like to deal with the signs
MA 1128: Lecture 02 1/22/2018 Exponents Scientific Notation 1 Exponents Exponents are used to indicate how many copies of a number are to be multiplied together. For example, I like to deal with the signs
Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ x + 5y + 7z 9x + 3y + 11z
 Basic Linear Algebra Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ 1 5 ] 7 9 3 11 Often matrices are used to describe in a simpler way a series of linear equations.
Basic Linear Algebra Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ 1 5 ] 7 9 3 11 Often matrices are used to describe in a simpler way a series of linear equations.
INTRODUCTION TO ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY, CLASS 10
 INTRODUCTION TO ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY, CLASS 10 RAVI VAKIL Contents 1. Schemes 1 1.1. Affine schemes 2 1.2. Schemes 3 1.3. Morphisms of affine schemes 3 1.4. Morphisms of general schemes 4 1.5. Scheme-theoretic
INTRODUCTION TO ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY, CLASS 10 RAVI VAKIL Contents 1. Schemes 1 1.1. Affine schemes 2 1.2. Schemes 3 1.3. Morphisms of affine schemes 3 1.4. Morphisms of general schemes 4 1.5. Scheme-theoretic
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 6 ArrayLists
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 6 ArrayLists 1 A programming problem Consider the following task: Double values representing grades are read until the user enters a negative
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 6 ArrayLists 1 A programming problem Consider the following task: Double values representing grades are read until the user enters a negative
Repetition Through Recursion
 Fundamentals of Computer Science I (CS151.02 2007S) Repetition Through Recursion Summary: In many algorithms, you want to do things again and again and again. For example, you might want to do something
Fundamentals of Computer Science I (CS151.02 2007S) Repetition Through Recursion Summary: In many algorithms, you want to do things again and again and again. For example, you might want to do something
How to Downline/Delete Contact Groups
 Bill Good Marketing How to Downline/Delete Contact Groups Questions that apply to this topic Answer How do I delete a Contact Group? Multiple Contact Groups? How do I remove a Contact Group or multiple
Bill Good Marketing How to Downline/Delete Contact Groups Questions that apply to this topic Answer How do I delete a Contact Group? Multiple Contact Groups? How do I remove a Contact Group or multiple
Logistic Regression and Gradient Ascent
 Logistic Regression and Gradient Ascent CS 349-02 (Machine Learning) April 0, 207 The perceptron algorithm has a couple of issues: () the predictions have no probabilistic interpretation or confidence
Logistic Regression and Gradient Ascent CS 349-02 (Machine Learning) April 0, 207 The perceptron algorithm has a couple of issues: () the predictions have no probabilistic interpretation or confidence
Increasing/Decreasing Behavior
 Derivatives and the Shapes of Graphs In this section, we will specifically discuss the information that f (x) and f (x) give us about the graph of f(x); it turns out understanding the first and second
Derivatives and the Shapes of Graphs In this section, we will specifically discuss the information that f (x) and f (x) give us about the graph of f(x); it turns out understanding the first and second
Add a multiple of a row to another row, replacing the row which was not multiplied.
 Determinants Properties involving elementary row operations There are a few sections on properties. Rirst, we ll simply state collections of properties, provide some examples, and talk about why they are
Determinants Properties involving elementary row operations There are a few sections on properties. Rirst, we ll simply state collections of properties, provide some examples, and talk about why they are
CS103 Handout 29 Winter 2018 February 9, 2018 Inductive Proofwriting Checklist
 CS103 Handout 29 Winter 2018 February 9, 2018 Inductive Proofwriting Checklist In Handout 28, the Guide to Inductive Proofs, we outlined a number of specifc issues and concepts to be mindful about when
CS103 Handout 29 Winter 2018 February 9, 2018 Inductive Proofwriting Checklist In Handout 28, the Guide to Inductive Proofs, we outlined a number of specifc issues and concepts to be mindful about when
Post Experiment Interview Questions
 Post Experiment Interview Questions Questions about the Maximum Problem 1. What is this problem statement asking? 2. What is meant by positive integers? 3. What does it mean by the user entering valid
Post Experiment Interview Questions Questions about the Maximum Problem 1. What is this problem statement asking? 2. What is meant by positive integers? 3. What does it mean by the user entering valid
ATMS ACTION TRACKING MANAGEMENT SYSTEM. Quick Start Guide. The ATMS dev team
 ATMS ACTION TRACKING MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Quick Start Guide The ATMS dev team Contents What is ATMS?... 2 How does ATMS work?... 2 I get it, now where can I find more info?... 2 What s next?... 2 Welcome
ATMS ACTION TRACKING MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Quick Start Guide The ATMS dev team Contents What is ATMS?... 2 How does ATMS work?... 2 I get it, now where can I find more info?... 2 What s next?... 2 Welcome
Hot X: Algebra Exposed
 Hot X: Algebra Exposed Solution Guide for Chapter 11 Here are the solutions for the Doing the Math exercises in Hot X: Algebra Exposed! DTM from p.149 2. Since m = 2, our equation will look like this:
Hot X: Algebra Exposed Solution Guide for Chapter 11 Here are the solutions for the Doing the Math exercises in Hot X: Algebra Exposed! DTM from p.149 2. Since m = 2, our equation will look like this:
Excerpt from "Art of Problem Solving Volume 1: the Basics" 2014 AoPS Inc.
 Chapter 5 Using the Integers In spite of their being a rather restricted class of numbers, the integers have a lot of interesting properties and uses. Math which involves the properties of integers is
Chapter 5 Using the Integers In spite of their being a rather restricted class of numbers, the integers have a lot of interesting properties and uses. Math which involves the properties of integers is
CH 87 FUNCTIONS: TABLES AND MAPPINGS
 CH 87 FUNCTIONS: TABLES AND MAPPINGS INTRODUCTION T he notion of a function is much more abstract than most of the algebra concepts you ve seen so far, so we ll start with three specific non-math examples.
CH 87 FUNCTIONS: TABLES AND MAPPINGS INTRODUCTION T he notion of a function is much more abstract than most of the algebra concepts you ve seen so far, so we ll start with three specific non-math examples.
In math, the rate of change is called the slope and is often described by the ratio rise
 Chapter 3 Equations of Lines Sec. Slope The idea of slope is used quite often in our lives, however outside of school, it goes by different names. People involved in home construction might talk about
Chapter 3 Equations of Lines Sec. Slope The idea of slope is used quite often in our lives, however outside of school, it goes by different names. People involved in home construction might talk about
AXIOMS FOR THE INTEGERS
 AXIOMS FOR THE INTEGERS BRIAN OSSERMAN We describe the set of axioms for the integers which we will use in the class. The axioms are almost the same as what is presented in Appendix A of the textbook,
AXIOMS FOR THE INTEGERS BRIAN OSSERMAN We describe the set of axioms for the integers which we will use in the class. The axioms are almost the same as what is presented in Appendix A of the textbook,
Induction and Semantics in Dafny
 15-414 Lecture 11 1 Instructor: Matt Fredrikson Induction and Semantics in Dafny TA: Ryan Wagner Encoding the syntax of Imp Recall the abstract syntax of Imp: a AExp ::= n Z x Var a 1 + a 2 b BExp ::=
15-414 Lecture 11 1 Instructor: Matt Fredrikson Induction and Semantics in Dafny TA: Ryan Wagner Encoding the syntax of Imp Recall the abstract syntax of Imp: a AExp ::= n Z x Var a 1 + a 2 b BExp ::=
Homework 3: Recursion Due: 11:59 PM, Sep 25, 2018
 CS17 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Klein Homework 3: Recursion Due: 11:59 PM, Sep 25, 2018 Contents 1 Factorial 3 2 Fibonacci 4 3 Odds Only 5 4 Increment All 6 5 Frequency 6 6 Sublist 7 6.1
CS17 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Klein Homework 3: Recursion Due: 11:59 PM, Sep 25, 2018 Contents 1 Factorial 3 2 Fibonacci 4 3 Odds Only 5 4 Increment All 6 5 Frequency 6 6 Sublist 7 6.1
DLD VIDYA SAGAR P. potharajuvidyasagar.wordpress.com. Vignana Bharathi Institute of Technology UNIT 1 DLD P VIDYA SAGAR
 UNIT I Digital Systems: Binary Numbers, Octal, Hexa Decimal and other base numbers, Number base conversions, complements, signed binary numbers, Floating point number representation, binary codes, error
UNIT I Digital Systems: Binary Numbers, Octal, Hexa Decimal and other base numbers, Number base conversions, complements, signed binary numbers, Floating point number representation, binary codes, error
Lesson 12: Order and Compare with Benchmarks
 Lesson 12: Order and Compare with Benchmarks Objective By the end of the lesson, students will be able to order and compare fractions with like and unlike denominators, using the definition for equivalent
Lesson 12: Order and Compare with Benchmarks Objective By the end of the lesson, students will be able to order and compare fractions with like and unlike denominators, using the definition for equivalent
The transition: Each student passes half his store of candies to the right. students with an odd number of candies eat one.
 Kate s problem: The students are distributed around a circular table The teacher distributes candies to all the students, so that each student has an even number of candies The transition: Each student
Kate s problem: The students are distributed around a circular table The teacher distributes candies to all the students, so that each student has an even number of candies The transition: Each student
Recursively Enumerable Languages, Turing Machines, and Decidability
 Recursively Enumerable Languages, Turing Machines, and Decidability 1 Problem Reduction: Basic Concepts and Analogies The concept of problem reduction is simple at a high level. You simply take an algorithm
Recursively Enumerable Languages, Turing Machines, and Decidability 1 Problem Reduction: Basic Concepts and Analogies The concept of problem reduction is simple at a high level. You simply take an algorithm
Beginning Course Lecture 3
 Beginning Course Lecture 3 Joan E. Licata May 17, 2012 1 Introduction Last time we defined the classical invariants of oriented Legendrian knots, the Thurston- Bennequin and rotation numbers. Our definitions
Beginning Course Lecture 3 Joan E. Licata May 17, 2012 1 Introduction Last time we defined the classical invariants of oriented Legendrian knots, the Thurston- Bennequin and rotation numbers. Our definitions
CSC-140 Assignment 4
 CSC-140 Assignment 4 Please do not Google a solution to these problem, cause that won t teach you anything about programming - the only way to get good at it, and understand it, is to do it! 1 Introduction
CSC-140 Assignment 4 Please do not Google a solution to these problem, cause that won t teach you anything about programming - the only way to get good at it, and understand it, is to do it! 1 Introduction
In this project, you ll learn how to create your own webpage to tell a story, joke or poem. Think about the story you want to tell.
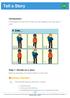 Tell a Story Introduction In this project, you ll learn how to create your own webpage to tell a story, joke or poem. Step 1: Decide on a story Before you get coding, you ll need to decide on a story to
Tell a Story Introduction In this project, you ll learn how to create your own webpage to tell a story, joke or poem. Step 1: Decide on a story Before you get coding, you ll need to decide on a story to
Creating Custom Financial Statements Using
 Creating Custom Financial Statements Using Steve Collins Sage 50 Solution Provider scollins@iqacct.com 918-851-9713 www.iqaccountingsolutions.com Financial Statement Design Sage 50 Accounting s built in
Creating Custom Financial Statements Using Steve Collins Sage 50 Solution Provider scollins@iqacct.com 918-851-9713 www.iqaccountingsolutions.com Financial Statement Design Sage 50 Accounting s built in
11.3 Analyzing a Conclusion
 KEY TAKEAWAYS An effective conclusion contains three basic parts: a restatement of the speech s thesis; a review of the main points discussed within the speech; and a concluding device that helps create
KEY TAKEAWAYS An effective conclusion contains three basic parts: a restatement of the speech s thesis; a review of the main points discussed within the speech; and a concluding device that helps create
CHAPTER 2. Graphs. 1. Introduction to Graphs and Graph Isomorphism
 CHAPTER 2 Graphs 1. Introduction to Graphs and Graph Isomorphism 1.1. The Graph Menagerie. Definition 1.1.1. A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of a set V of vertices and a set E of edges, represented
CHAPTER 2 Graphs 1. Introduction to Graphs and Graph Isomorphism 1.1. The Graph Menagerie. Definition 1.1.1. A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of a set V of vertices and a set E of edges, represented
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science. Lecture Notes #38 and #39 Quicksort. c 2005, 2003, 2002, 2000 Jason Zych
 CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #38 and #39 Quicksort c 2005, 2003, 2002, 2000 Jason Zych 1 Lectures 38 and 39 : Quicksort Quicksort is the best sorting algorithm known which is
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #38 and #39 Quicksort c 2005, 2003, 2002, 2000 Jason Zych 1 Lectures 38 and 39 : Quicksort Quicksort is the best sorting algorithm known which is
Rec 8 Notes. 1 Divide-and-Conquer Convex Hull. 1.1 Algorithm Idea. 1.2 Algorithm. Here s another random Divide-And-Conquer algorithm.
 Divide-and-Conquer Convex Hull Here s another random Divide-And-Conquer algorithm. Recall, possibly from CS 2, that the convex hull H(Q) of a set of points Q is the smallest convex set containing Q (that
Divide-and-Conquer Convex Hull Here s another random Divide-And-Conquer algorithm. Recall, possibly from CS 2, that the convex hull H(Q) of a set of points Q is the smallest convex set containing Q (that
Creating a Box-and-Whisker Graph in Excel: Step One: Step Two:
 Creating a Box-and-Whisker Graph in Excel: It s not as simple as selecting Box and Whisker from the Chart Wizard. But if you ve made a few graphs in Excel before, it s not that complicated to convince
Creating a Box-and-Whisker Graph in Excel: It s not as simple as selecting Box and Whisker from the Chart Wizard. But if you ve made a few graphs in Excel before, it s not that complicated to convince
Unit 3 Notes: Parallel Lines, Perpendicular Lines, and Angles 3-1 Transversal
 Unit 3 Notes: Parallel Lines, Perpendicular Lines, and Angles 3-1 Transversal REVIEW: *Postulates are Fundamentals of Geometry (Basic Rules) To mark line segments as congruent draw the same amount of tic
Unit 3 Notes: Parallel Lines, Perpendicular Lines, and Angles 3-1 Transversal REVIEW: *Postulates are Fundamentals of Geometry (Basic Rules) To mark line segments as congruent draw the same amount of tic
Chapter01.fm Page 1 Monday, August 23, :52 PM. Part I of Change. The Mechanics. of Change
 Chapter01.fm Page 1 Monday, August 23, 2004 1:52 PM Part I The Mechanics of Change The Mechanics of Change Chapter01.fm Page 2 Monday, August 23, 2004 1:52 PM Chapter01.fm Page 3 Monday, August 23, 2004
Chapter01.fm Page 1 Monday, August 23, 2004 1:52 PM Part I The Mechanics of Change The Mechanics of Change Chapter01.fm Page 2 Monday, August 23, 2004 1:52 PM Chapter01.fm Page 3 Monday, August 23, 2004
The method of rationalizing
 Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Chapter : Resolving indeterminate forms Section The method of rationalizing What you need to know already: The concept of it and the factor-and-cancel method of
Roberto s Notes on Differential Calculus Chapter : Resolving indeterminate forms Section The method of rationalizing What you need to know already: The concept of it and the factor-and-cancel method of
Spring 2018 Discussion 7: March 21, Introduction. 2 Primitives
 CS 61A Scheme Spring 2018 Discussion 7: March 21, 2018 1 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme
CS 61A Scheme Spring 2018 Discussion 7: March 21, 2018 1 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme
8 1 Sequences. Defining a Sequence. A sequence {a n } is a list of numbers written in explicit order. e.g.
 8 1 Sequences Defining a Sequence A sequence {a n } is a list of numbers written in explicit order. e.g. If the domain is finite, then the sequence is a Ex.1 Explicit Sequence Find the first six terms
8 1 Sequences Defining a Sequence A sequence {a n } is a list of numbers written in explicit order. e.g. If the domain is finite, then the sequence is a Ex.1 Explicit Sequence Find the first six terms
Recursion. CSCI 112: Programming in C
 Recursion CSCI 112: Programming in C 1 What is recursion? Recursion looks at a large problem as a bunch of smaller versions of the same problem. 2 2 What is recursion? Recursion looks at a large problem
Recursion CSCI 112: Programming in C 1 What is recursion? Recursion looks at a large problem as a bunch of smaller versions of the same problem. 2 2 What is recursion? Recursion looks at a large problem
User Defined Functions
 User Defined Functions 120 90 1 0.8 60 Chapter 6 150 0.6 0.4 30 0.2 180 0 210 330 240 270 300 Objectives Create and use MATLAB functions with both single and multiple inputs and outputs Learn how to store
User Defined Functions 120 90 1 0.8 60 Chapter 6 150 0.6 0.4 30 0.2 180 0 210 330 240 270 300 Objectives Create and use MATLAB functions with both single and multiple inputs and outputs Learn how to store
Heuristic Evaluation of igetyou
 Heuristic Evaluation of igetyou 1. Problem i get you is a social platform for people to share their own, or read and respond to others stories, with the goal of creating more understanding about living
Heuristic Evaluation of igetyou 1. Problem i get you is a social platform for people to share their own, or read and respond to others stories, with the goal of creating more understanding about living
Lesson 2-5: Proving Angles Congruent
 Lesson -5: Proving Angles Congruent Geometric Proofs Yesterday we discovered that solving an algebraic expression is essentially doing a proof, provided you justify each step you take. Today we are going
Lesson -5: Proving Angles Congruent Geometric Proofs Yesterday we discovered that solving an algebraic expression is essentially doing a proof, provided you justify each step you take. Today we are going
1 Linear programming relaxation
 Cornell University, Fall 2010 CS 6820: Algorithms Lecture notes: Primal-dual min-cost bipartite matching August 27 30 1 Linear programming relaxation Recall that in the bipartite minimum-cost perfect matching
Cornell University, Fall 2010 CS 6820: Algorithms Lecture notes: Primal-dual min-cost bipartite matching August 27 30 1 Linear programming relaxation Recall that in the bipartite minimum-cost perfect matching
Outputs. Inputs. the point where the graph starts, as we ll see on Example 1.
 We ve seen how to work with functions algebraically, by finding domains as well as function values. In this set of notes we ll be working with functions graphically, and we ll see how to find the domain
We ve seen how to work with functions algebraically, by finding domains as well as function values. In this set of notes we ll be working with functions graphically, and we ll see how to find the domain
Cardinality of Sets MAT231. Fall Transition to Higher Mathematics. MAT231 (Transition to Higher Math) Cardinality of Sets Fall / 15
 Cardinality of Sets MAT Transition to Higher Mathematics Fall 0 MAT (Transition to Higher Math) Cardinality of Sets Fall 0 / Outline Sets with Equal Cardinality Countable and Uncountable Sets MAT (Transition
Cardinality of Sets MAT Transition to Higher Mathematics Fall 0 MAT (Transition to Higher Math) Cardinality of Sets Fall 0 / Outline Sets with Equal Cardinality Countable and Uncountable Sets MAT (Transition
Many people find group theory pretty difficult because the logic behind it seems
 VISUAL GOUP THEOY Many people find group theory pretty difficult because the logic behind it seems algebraic to the extreme and geometric not at all. However, there are a few ways to visualize groups that
VISUAL GOUP THEOY Many people find group theory pretty difficult because the logic behind it seems algebraic to the extreme and geometric not at all. However, there are a few ways to visualize groups that
DealerNet 2.0 Guide. Full Version: February 2015
 DealerNet 2.0 Guide Full Version: February 2015 This is the full version of the reference guide with an in depth overview of each section. For a brief overview download our Quick Guide. 1 Table of Contents
DealerNet 2.0 Guide Full Version: February 2015 This is the full version of the reference guide with an in depth overview of each section. For a brief overview download our Quick Guide. 1 Table of Contents
Math 221 Final Exam Review
 Math 221 Final Exam Review Preliminary comment: Some of these problems a formulated using language and structures from graph theory. However they are generally self contained; no theorems from graph theory
Math 221 Final Exam Review Preliminary comment: Some of these problems a formulated using language and structures from graph theory. However they are generally self contained; no theorems from graph theory
An aside. Lecture 14: Last time
 An aside Lecture 14: Recall from last time that aggregate() allowed us to combine data that referred to the same building; it is possible to implement this with lower-level tools in R Similarly, our dance
An aside Lecture 14: Recall from last time that aggregate() allowed us to combine data that referred to the same building; it is possible to implement this with lower-level tools in R Similarly, our dance
CH 21 CONSECUTIVE INTEGERS
 201 CH 21 CONSECUTIVE INTEGERS Introduction An integer is either a positive whole number, or zero, or a negative whole number; in other words it s the collection of numbers:... 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,
201 CH 21 CONSECUTIVE INTEGERS Introduction An integer is either a positive whole number, or zero, or a negative whole number; in other words it s the collection of numbers:... 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,
Encoding functions in FOL. Where we re at. Ideally, would like an IF stmt. Another example. Solution 1: write your own IF. No built-in IF in Simplify
 Where we re at We explored the three standard logics, and compared them along three dimensions expressiveness automation human-friendliness Next we ll look in more detail at FOL we will explore how to
Where we re at We explored the three standard logics, and compared them along three dimensions expressiveness automation human-friendliness Next we ll look in more detail at FOL we will explore how to
Points are not transferable. Aon employees are not eligible to receive Points.
 Q: What are Points? A: Talk to Aon uses a Points system to reward members for completing certain surveys. When you receive emails that invite you to participate in surveys, you ll be told whether the survey
Q: What are Points? A: Talk to Aon uses a Points system to reward members for completing certain surveys. When you receive emails that invite you to participate in surveys, you ll be told whether the survey
