CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms
|
|
|
- Noreen Jennings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 15: Graph Data Structures, Topological Sort, and Traversals (DFS, BFS) Instructor: Lilian de Greef Quarter: Summer 2017
2 Today: Announcements Graph data structures Topological Sort Graph Traversals Depth First Search (DFS) Breadth First Search (BFS)
3 Announcement: Received Course Feedback What s working well: Walking through in-class examples Posted, printed, and annotated slides Interactive questions & in-class partner discussion Things to address: Amount to write on printed slides Why using polling system for in-class exercises Concern about not getting through entire slide deck
4 25 Year in Program this Fall Freshman Sophomore Junior Senior 5th year Graduate student other
5 Last Time Programmed / Taken CS Course
6 Represented Majors Engineering Math Science Informatics Geology Spanish Asian Language Pre-major And more!
7 Graph Data Structures A couple of different ways to store adjacencies
8 What is the Data Structure? So graphs are really useful for lots of data and questions For example, what s the lowest-cost path from x to y But we need a data structure that represents graphs The best one can depend on: Properties of the graph (e.g., dense versus sparse) The common queries (e.g., is (u,v) an edge? versus what are the neighbors of node u? ) So we ll discuss the two standard graph representations Adjacency Matrix and Adjacency List Different trade-offs, particularly time versus space
9 Adjacency Matrix Assign each node a number from 0 to V -1 A V x V matrix (i.e., 2-D array) of Booleans (or 1 vs. 0) If M is the matrix, then M[u][v] == true means there is an edge from u to v B (0) S (1) M (3) E (2)
10 Adjacency Matrix Properties Running time to: Get a vertex s out-edges: Get a vertex s in-edges: Decide if some edge exists: Insert an edge: Delete an edge: F F F F T F T T F F T T F T T F Space requirements: Best for sparse or dense graphs? B (0) S (1) E M (3) (2)
11 Adjacency Matrix Properties How will the adjacency matrix vary for an undirected graph? Undirected will be symmetric around the diagonal How can we adapt the representation for weighted graphs? Instead of a Boolean, store a number in each cell Need some value to represent not an edge In some situations, 0 or -1 works
12 Adjacency List Assign each node a number from 0 to V -1 An array of length V in which each entry stores a list of all adjacent vertices (e.g., linked list) B (0) S (1) M (3) E (2)
13 Adjacency List Properties 0 1 / / Running time to: Get all of a vertex s out-edges: where d is out-degree of vertex Get all of a vertex s in-edges: (but could keep a second adjacency list for this!) Decide if some edge exists: where d is out-degree of source Insert an edge: (unless you need to check if it s there) Delete an edge: where d is out-degree of source Space requirements: / 1 2 / Best for sparse or dense graphs? B (0) S (1) E M (3) (2)
14 Algorithms Okay, we can represent graphs Now we ll implement some useful and non-trivial algorithms! Topological Sort Shortest Paths Related: Determining if such a path exists Depth First Search Breadth First Search
15 Graphs: Topological Sort Ordering vertices in a DAG
16 Topological Sort Topological sort: Given a DAG, order all the vertices so that every vertex comes before all of its neighbors One example output: CSE 142 CSE 143 MATH 126 CSE 374 CSE 373 CSE 410 CSE 413 CSE 415 CSE 417 XYZ
17 Questions and comments Why do we perform topological sorts only on DAGs? 2 Is there always a unique answer? Do some DAGs have exactly 1 answer? Terminology: A DAG represents a partial order and a topological sort produces a total order that is consistent with it
18 A few of its uses Figuring out how to graduate Computing an order in which to recompute cells in a spreadsheet Determining an order to compile files using a Makefile In general, taking a dependency graph and finding an order of execution
19 A First Algorithm for Topological Sort 1. Label ( mark ) each vertex with its in-degree Could write in a field in the vertex Could also do this via a data structure (e.g., array) on the side 2. While there are vertices not yet output: a) Choose a vertex v with in-degree of 0 b) Output v and conceptually remove it from the graph c) For each vertex u adjacent to v (i.e. u such that (v,u) in E), decrement the in-degree of u
20 Example Output: CSE 374 XYZ CSE 142 CSE 143 MATH 126 CSE 373 CSE 410 CSE 413 CSE 415 CSE 417 Node: XYZ Removed? In-degree:
21 Notice Needed a vertex with in-degree 0 to start Will always have at least 1 because Ties among vertices with in-degrees of 0 can be broken arbitrarily Can be more than one correct answer, by definition, depending on the graph
22 Running time? labeleachvertexwithitsindegree(); for(i = 0; i < numvertices; i++){ v = findnewvertexofdegreezero(); put v next in output for each u adjacent to v u.indegree--; } What is the worst-case running time? Initialization (assuming adjacency list) Sum of all find-new-vertex (because each O( V )) Sum of all decrements (assuming adjacency list) So total is not good for a sparse graph!
23 Doing better The trick is to avoid searching for a zero-degree node every time! Keep the pending zero-degree nodes in a list, stack, queue, bag, table, or something Order we process them affects output but not correctness or efficiency, provided that add/remove are both O(1) Using a queue: 1. Label each vertex with its in-degree, enqueue 0-degree nodes 2. While queue is not empty a) v = dequeue() b) Output v and remove it from the graph c) For each vertex u adjacent to v (i.e. u such that (v,u) in E), decrement the in-degree of u, if new degree is 0, enqueue it
24 Example: Topological Sort Using Queues A B D C Node A B C D Removed? In-degree Queue: Output: The trick is to avoid searching for a zero-degree node every time! 1. Label each vertex with its in-degree, enqueue 0-degree nodes 2. While queue is not empty a) v = dequeue() b) Output v and remove it from the graph c) For each vertex u adjacent to v (i.e. u such that (v,u) in E), decrement the in-degree of u, if new degree is 0, enqueue it
25 Running time? labelallandenqueuezeros(); for(i=0; ctr < numvertices; ctr++){ v = dequeue(); put v next in output for each u adjacent to v { u.indegree--; if(u.indegree==0) enqueue(u); } } What is the worst-case running time? Initialization: (assuming adjacency list) Sum of all enqueues and dequeues: Sum of all decrements: (assuming adjacency list) Total: much better for sparse graph!
26 Graph Traversals Depth- and Breadth- First Searches!
27 Introductory Example: Graph Traversals How would a computer systematically find a path through the maze? Source A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O Destination
28 Note: under the hood, we re using a graph to represent the maze In graph terminology: find a path (if any) from one vertex to another. Source Source A B C D E A B C D E F G H I J F G H I J K L M N O K L M N O Destination Destination
29 Find a path (if any) from one vertex to another. Idea: Repeatedly explore and keep track of adjacent vertices. Mark each vertex we visit, so we don t process each more than once. Source A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O Destination
30 Depth First Search (DFS) Depth First Search (DFS): Explore as far as possible along each branch before backtracking Repeatedly explore adjacent vertices using or Mark each vertex we visit, so we don t process each more than once. Example pseudocode: DFS(Node start) { mark and process start for each node u adjacent to start if u is not marked DFS(u) }
31 Find a path (if any) from one vertex to another. Idea: Repeatedly explore and keep track of adjacent vertices. Mark each vertex we visit, so we don t process each more than once. Source A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O Destination
32 Breadth First Search (BFS) Breadth First Search (BFS): Explore neighbors first, before moving to the next level of neighbors. Repeatedly explore adjacent vertices using Mark each vertex we visit, so we don t process each more than once. Example pseudocode: BFS(Node start) { initialize queue q and enqueue start mark start as visited while(q is not empty) { next = q.dequeue() // and process for each node u adjacent to next if(u is not marked) mark u and enqueue onto q } }
33 Practice time! What is one possible order of visiting the nodes of the following graph when using Breadth First Search (BFS)? M N O R Q P A) MNOPQR B) NQMPOR C) QMNPRO D) QMNPOR
34
CSE 332: Data Abstractions Lecture 15: Topological Sort / Graph Traversals. Ruth Anderson Winter 2013
 CSE 332: Data Abstractions Lecture 15: Topological Sort / Graph Traversals Ruth Anderson Winter 2013 Announcements Homework 4 due Friday Feb 15 th at the BEGINNING of lecture Project 2 Phase B due Tues
CSE 332: Data Abstractions Lecture 15: Topological Sort / Graph Traversals Ruth Anderson Winter 2013 Announcements Homework 4 due Friday Feb 15 th at the BEGINNING of lecture Project 2 Phase B due Tues
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT
 CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT PROJECT 3 500 Internal Error problems Hopefully all resolved (or close to) P3P1 grades are up (but muted) Leave canvas comment Emails tomorrow End of quarter GRAPHS
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT PROJECT 3 500 Internal Error problems Hopefully all resolved (or close to) P3P1 grades are up (but muted) Leave canvas comment Emails tomorrow End of quarter GRAPHS
Graphs: Topological Sort / Graph Traversals (Chapter 9)
 Today s Outline raphs: Topological Sort / raph Traversals (hapter 9) S 373 ata Structures and lgorithms dmin: omework #4 - due Thurs, Nov 8 th at pm Midterm 2, ri Nov 6 raphs Representations Topological
Today s Outline raphs: Topological Sort / raph Traversals (hapter 9) S 373 ata Structures and lgorithms dmin: omework #4 - due Thurs, Nov 8 th at pm Midterm 2, ri Nov 6 raphs Representations Topological
CSE 332 Data Abstractions: Graphs and Graph Traversals
 CSE 332 Data Abstractions: Graphs and Graph Traversals Kate Deibel Summer 2012 July 23, 2012 CSE 332 Data Abstractions, Summer 2012 1 Some course stuff and a humorous story GRADES, MIDTERMS, AND IT SEEMED
CSE 332 Data Abstractions: Graphs and Graph Traversals Kate Deibel Summer 2012 July 23, 2012 CSE 332 Data Abstractions, Summer 2012 1 Some course stuff and a humorous story GRADES, MIDTERMS, AND IT SEEMED
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms
 CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 6: Dijkstra s Algorithm (Graphs) Instructor: Lilian de Greef Quarter: Summer 207 Today Announcements Graph Traversals Continued Remarks on DFS & BFS Shortest
CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 6: Dijkstra s Algorithm (Graphs) Instructor: Lilian de Greef Quarter: Summer 207 Today Announcements Graph Traversals Continued Remarks on DFS & BFS Shortest
Introduction to Graphs. CS2110, Spring 2011 Cornell University
 Introduction to Graphs CS2110, Spring 2011 Cornell University A graph is a data structure for representing relationships. Each graph is a set of nodes connected by edges. Synonym Graph Hostile Slick Icy
Introduction to Graphs CS2110, Spring 2011 Cornell University A graph is a data structure for representing relationships. Each graph is a set of nodes connected by edges. Synonym Graph Hostile Slick Icy
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
Lecture 26: Graphs: Traversal (Part 1)
 CS8 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Fisler, Nelson Lecture 6: Graphs: Traversal (Part ) 0:00 AM, Apr, 08 Contents Introduction. Definitions........................................... Representations.......................................
CS8 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Fisler, Nelson Lecture 6: Graphs: Traversal (Part ) 0:00 AM, Apr, 08 Contents Introduction. Definitions........................................... Representations.......................................
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12. Questions? Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first Search. (Introduce permutation and subset generation)
 MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
Graph Theory. Many problems are mapped to graphs. Problems. traffic VLSI circuits social network communication networks web pages relationship
 Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal
 Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Announcements Problem Set 4 is out!
 CSC263 Week 8 Announcements Problem Set 4 is out! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Other Announcements Drop date Nov 8 Final exam schedule is posted CSC263 exam Dec 11, 2-5pm This week s outline Graphs BFS Graph A
CSC263 Week 8 Announcements Problem Set 4 is out! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Other Announcements Drop date Nov 8 Final exam schedule is posted CSC263 exam Dec 11, 2-5pm This week s outline Graphs BFS Graph A
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007
 Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Outline. Graphs. Divide and Conquer.
 GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
Graph: representation and traversal
 Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications. graphs zybooks chapter 10
 CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications graphs zybooks chapter 10 directed graphs A collection of vertices and directed edges What can this represent? undirected graphs A collection of vertices
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications graphs zybooks chapter 10 directed graphs A collection of vertices and directed edges What can this represent? undirected graphs A collection of vertices
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms
 W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
CSC263 Week 8. Larry Zhang.
 CSC263 Week 8 Larry Zhang http://goo.gl/forms/s9yie3597b Announcements (strike related) Lectures go as normal Tutorial this week everyone go to BA32 (T8, F2, F2, F3) Problem sets / Assignments are submitted
CSC263 Week 8 Larry Zhang http://goo.gl/forms/s9yie3597b Announcements (strike related) Lectures go as normal Tutorial this week everyone go to BA32 (T8, F2, F2, F3) Problem sets / Assignments are submitted
Plan. CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms. Recall. Adjacency List Representation. DFS Descriptions. BFS Description
 Plan CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms Akshay Krishnamurthy and Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Review: Breadth First Search Depth First Search Traversal Implementation and Running Time
Plan CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms Akshay Krishnamurthy and Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Review: Breadth First Search Depth First Search Traversal Implementation and Running Time
Today s Outline. CSE 326: Data Structures. Topic #15: Cool Graphs n Pretty Pictures. A Great Mathematician. The Bridges of Königsberg
 CSE 326: Data Structures Topic #15: Cool Graphs n Pretty Pictures Ashish Sabharwal Autumn, 2003 Today s Outline Admin Project 3 in-progress checkin due tonight! Graph Algorithms Representation Applications
CSE 326: Data Structures Topic #15: Cool Graphs n Pretty Pictures Ashish Sabharwal Autumn, 2003 Today s Outline Admin Project 3 in-progress checkin due tonight! Graph Algorithms Representation Applications
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs
 CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
Graphs - II. Announcements. Where did I leave that book? Where did I leave that book? Where did I leave that book? CS 2110, Fall 2016
 Graphs - II CS, Fall Announcements A will be available tonight or tomorrow. Gries lunch canceled today Gries office hours today from to only Q. Why do programmers confuse Halloween and Christmas? Answer.
Graphs - II CS, Fall Announcements A will be available tonight or tomorrow. Gries lunch canceled today Gries office hours today from to only Q. Why do programmers confuse Halloween and Christmas? Answer.
Today s Outline. Graph ADT? Graph Definitions. Trees as Graphs. Graphs Chapter 9 in Weiss. More Definitions: Simple Paths and Cycles.
 Today s Outline Graphs Chapter 9 in Weiss CSE 6 Data Structures Ruth Anderson /6/00 Announcements Written Homework #6 due NOW Project Code due Mon March by pm Project Benchmarking & Written due Thurs March
Today s Outline Graphs Chapter 9 in Weiss CSE 6 Data Structures Ruth Anderson /6/00 Announcements Written Homework #6 due NOW Project Code due Mon March by pm Project Benchmarking & Written due Thurs March
Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs. CMSC 420: Lecture 3
 Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs CMSC 420: Lecture 3 Mini-Review Abstract Data Types: List Stack Queue Deque Dictionary Set Implementations: Linked Lists Circularly linked lists Doubly linked lists XOR
Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs CMSC 420: Lecture 3 Mini-Review Abstract Data Types: List Stack Queue Deque Dictionary Set Implementations: Linked Lists Circularly linked lists Doubly linked lists XOR
(Refer Slide Time: 05:25)
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering IIT Delhi Lecture 30 Applications of DFS in Directed Graphs Today we are going to look at more applications
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering IIT Delhi Lecture 30 Applications of DFS in Directed Graphs Today we are going to look at more applications
Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS
 Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Directed and Undirected Graphs I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Directed and Undirected Graphs I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of. I Formally: G =(V, E), where V is a set and E V V.
 Directed and Undirected Graphs Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
Directed and Undirected Graphs Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
Graphs. CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington
 Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
CSE 332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 19: Introduction to Graphs. Ruth Anderson Autumn 2018
 SE 332: ata Structures & Parallelism Lecture 19: Introduction to Graphs Ruth nderson utumn 2018 Today Graphs Intro & efinitions 11/19/2018 2 Graphs graph is a formalism for representing relationships among
SE 332: ata Structures & Parallelism Lecture 19: Introduction to Graphs Ruth nderson utumn 2018 Today Graphs Intro & efinitions 11/19/2018 2 Graphs graph is a formalism for representing relationships among
More Graph Algorithms
 More Graph Algorithms Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 1 Announcements Calendar on the webpage has updated office hours for this week. Last Time: Dijkstra s Algorithm to find
More Graph Algorithms Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 1 Announcements Calendar on the webpage has updated office hours for this week. Last Time: Dijkstra s Algorithm to find
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Exploring graphs Adam Smith 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne Puzzles Suppose an undirected graph G is connected.
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Exploring graphs Adam Smith 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne Puzzles Suppose an undirected graph G is connected.
CS 491 CAP Introduction to Graphs and Search
 CS 491 CAP Introduction to Graphs and Search Jingbo Shang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Sep 9, 2016 Outline Graphs Adjacency Matrix vs. Adjacency List Special Graphs Depth-first and Breadth-first
CS 491 CAP Introduction to Graphs and Search Jingbo Shang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Sep 9, 2016 Outline Graphs Adjacency Matrix vs. Adjacency List Special Graphs Depth-first and Breadth-first
Dijkstra s Algorithm and Priority Queue Implementations. CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 5
 Dijkstra s Algorithm and Priority Queue Implementations CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 5 CSE 101: Design and analysis of algorithms Dijkstra s algorithm and priority queue implementations
Dijkstra s Algorithm and Priority Queue Implementations CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 5 CSE 101: Design and analysis of algorithms Dijkstra s algorithm and priority queue implementations
CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 28: Final review and class wrap-up. Nicki Dell Spring 2014
 CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 28: Final review and class wrap-up Nicki Dell Spring 2014 Final Exam As also indicated on the web page: Next Tuesday, 2:30-4:20 in this room Cumulative but
CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 28: Final review and class wrap-up Nicki Dell Spring 2014 Final Exam As also indicated on the web page: Next Tuesday, 2:30-4:20 in this room Cumulative but
CS 106X, Lecture 23 Dijkstra and A* Search
 CS 106X, Lecture 23 Dijkstra and A* Search reading: Programming Abstractions in C++, Chapter 18 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Nick Troccoli, licensed under Creative Commons
CS 106X, Lecture 23 Dijkstra and A* Search reading: Programming Abstractions in C++, Chapter 18 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Nick Troccoli, licensed under Creative Commons
Undirected Graphs. V = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 } E = { 1-2, 1-3, 2-3, 2-4, 2-5, 3-5, 3-7, 3-8, 4-5, 5-6 } n = 8 m = 11
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms
 COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms Topic 14. Graph Algorithms 11/7/2016 1 Elementary Graph Algorithms How to represent a graph? Adjacency lists Adjacency matrix How to search a graph? Breadth-first
COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms Topic 14. Graph Algorithms 11/7/2016 1 Elementary Graph Algorithms How to represent a graph? Adjacency lists Adjacency matrix How to search a graph? Breadth-first
Copyright 2000, Kevin Wayne 1
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
Homework Assignment #3 Graph
 CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
Breadth First Search. Graph Traversal. CSE 2011 Winter Application examples. Two common graph traversal algorithms
 Breadth irst Search CSE Winter Graph raversal Application examples Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph ind all paths from s to the other vertices wo common graph traversal algorithms
Breadth irst Search CSE Winter Graph raversal Application examples Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph ind all paths from s to the other vertices wo common graph traversal algorithms
CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity. 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications. Goals. Chapter 3. Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 3 CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity Graphs Reading: 3.1-3.6 Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
Chapter 3 CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity Graphs Reading: 3.1-3.6 Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
Goals! CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity!
 Goals! CSE : Algorithms and Computational Complexity! Graphs: defns, examples, utility, terminology! Representation: input, internal! Traversal: Breadth- & Depth-first search! Three Algorithms:!!Connected
Goals! CSE : Algorithms and Computational Complexity! Graphs: defns, examples, utility, terminology! Representation: input, internal! Traversal: Breadth- & Depth-first search! Three Algorithms:!!Connected
Lecture 25 Spanning Trees
 Lecture 25 Spanning Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning, Iliano Cervesato The following is a simple example of a connected, undirected graph with 5 vertices (A,
Lecture 25 Spanning Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning, Iliano Cervesato The following is a simple example of a connected, undirected graph with 5 vertices (A,
Chapter 14. Graphs Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1
 Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
Elementary Graph Algorithms. Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph:
 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Graph Algorithms. Chapter 22. CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms 1
 Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms. Brute-Force Approach
 CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
Trees. Arash Rafiey. 20 October, 2015
 20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
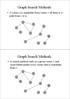 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Introduction to Graphs. common/notes/ppt/
 Introduction to Graphs http://people.cs.clemson.edu/~pargas/courses/cs212/ common/notes/ppt/ Introduction Graphs are a generalization of trees Nodes or verticies Edges or arcs Two kinds of graphs irected
Introduction to Graphs http://people.cs.clemson.edu/~pargas/courses/cs212/ common/notes/ppt/ Introduction Graphs are a generalization of trees Nodes or verticies Edges or arcs Two kinds of graphs irected
CSE 100: GRAPH SEARCH
 CSE 100: GRAPH SEARCH Announcements PA3 released Checkpoint due Tuesday, May 5 @10:00pm Final submission due Thursday, May 14 @10:00PM Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! I
CSE 100: GRAPH SEARCH Announcements PA3 released Checkpoint due Tuesday, May 5 @10:00pm Final submission due Thursday, May 14 @10:00PM Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! I
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms
 (Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
Lesson 1 Introduction to Path Planning Graph Searches: BFS and DFS
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Path Planning Graph Searches: BFS and DFS DASL Summer Program Path Planning References: http://robotics.mem.drexel.edu/mhsieh/courses/mem380i/index.html http://dasl.mem.drexel.edu/hing/bfsdfstutorial.htm
Lesson 1 Introduction to Path Planning Graph Searches: BFS and DFS DASL Summer Program Path Planning References: http://robotics.mem.drexel.edu/mhsieh/courses/mem380i/index.html http://dasl.mem.drexel.edu/hing/bfsdfstutorial.htm
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II. Shortest Paths
 CMSC 13: Object-Oriented Programming II Shortest Paths 1 Quiz 1 One advantage of adjacency list representation over adjacency matrix representation of a graph is that in adjacency list representation,
CMSC 13: Object-Oriented Programming II Shortest Paths 1 Quiz 1 One advantage of adjacency list representation over adjacency matrix representation of a graph is that in adjacency list representation,
CS/COE
 CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
Graphs. Graph G = (V, E) Types of graphs E = O( V 2 ) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V)
 Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms
 CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
Dynamic-Programming algorithms for shortest path problems: Bellman-Ford (for singlesource) and Floyd-Warshall (for all-pairs).
 Lecture 13 Graph Algorithms I 13.1 Overview This is the first of several lectures on graph algorithms. We will see how simple algorithms like depth-first-search can be used in clever ways (for a problem
Lecture 13 Graph Algorithms I 13.1 Overview This is the first of several lectures on graph algorithms. We will see how simple algorithms like depth-first-search can be used in clever ways (for a problem
An undirected graph G can be represented by G = (V, E), where
 CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2017 Note Spring/2017 1 What is graph? A graph is a set of vertices (or nodes) V, and a set of edges E between pairs of vertices. Graph represents some kind of binary
CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2017 Note Spring/2017 1 What is graph? A graph is a set of vertices (or nodes) V, and a set of edges E between pairs of vertices. Graph represents some kind of binary
Graph Algorithms. Definition
 Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
Basic Graph Algorithms (CLRS B.4-B.5, )
 Basic Graph Algorithms (CLRS B.-B.,.-.) Basic Graph Definitions A graph G = (V,E) consists of a finite set of vertices V and a finite set of edges E. Directed graphs: E is a set of ordered pairs of vertices
Basic Graph Algorithms (CLRS B.-B.,.-.) Basic Graph Definitions A graph G = (V,E) consists of a finite set of vertices V and a finite set of edges E. Directed graphs: E is a set of ordered pairs of vertices
Graph Representations and Traversal
 COMPSCI 330: Design and Analysis of Algorithms 02/08/2017-02/20/2017 Graph Representations and Traversal Lecturer: Debmalya Panigrahi Scribe: Tianqi Song, Fred Zhang, Tianyu Wang 1 Overview This lecture
COMPSCI 330: Design and Analysis of Algorithms 02/08/2017-02/20/2017 Graph Representations and Traversal Lecturer: Debmalya Panigrahi Scribe: Tianqi Song, Fred Zhang, Tianyu Wang 1 Overview This lecture
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CS6301 PROGRAMMING DATA STRUCTURES II
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI Department of Computer Science and Engineering CS6301 PROGRAMMING DATA STRUCTURES II Anna University 2 & 16 Mark Questions & Answers Year / Semester: II / III
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI Department of Computer Science and Engineering CS6301 PROGRAMMING DATA STRUCTURES II Anna University 2 & 16 Mark Questions & Answers Year / Semester: II / III
Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications
 Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications Topics: Introduction to Graph Theory Representing (undirected) graphs Basic graph algorithms 1 Consider the following: Traveling Salesman Problem
Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications Topics: Introduction to Graph Theory Representing (undirected) graphs Basic graph algorithms 1 Consider the following: Traveling Salesman Problem
Graphs and Graph Algorithms. Slides by Larry Ruzzo
 Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Larry Ruzzo Goals Graphs: defns, examples, utility, terminology Representation: input, internal Traversal: Breadth- & Depth-first search Three Algorithms: Connected
Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Larry Ruzzo Goals Graphs: defns, examples, utility, terminology Representation: input, internal Traversal: Breadth- & Depth-first search Three Algorithms: Connected
Algorithms: Lecture 10. Chalmers University of Technology
 Algorithms: Lecture 10 Chalmers University of Technology Today s Topics Basic Definitions Path, Cycle, Tree, Connectivity, etc. Graph Traversal Depth First Search Breadth First Search Testing Bipartatiness
Algorithms: Lecture 10 Chalmers University of Technology Today s Topics Basic Definitions Path, Cycle, Tree, Connectivity, etc. Graph Traversal Depth First Search Breadth First Search Testing Bipartatiness
CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 9
 CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 9 Graphs The remaining three lectures of the Algorithms and Data Structures thread will be devoted to graph algorithms. 9.1 Directed and Undirected Graphs A graph
CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 9 Graphs The remaining three lectures of the Algorithms and Data Structures thread will be devoted to graph algorithms. 9.1 Directed and Undirected Graphs A graph
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CSE 101, Winter 2018 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 6: BFS, SPs, Dijkstra Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ Distance in a Graph The distance between two nodes is the length
CSE 101, Winter 2018 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 6: BFS, SPs, Dijkstra Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ Distance in a Graph The distance between two nodes is the length
Some major graph problems
 CS : Graphs and Blobs! Prof. Graeme Bailey http://cs.cs.cornell.edu (notes modified from Noah Snavely, Spring 009) Some major graph problems! Graph colouring Ensuring that radio stations don t clash! Graph
CS : Graphs and Blobs! Prof. Graeme Bailey http://cs.cs.cornell.edu (notes modified from Noah Snavely, Spring 009) Some major graph problems! Graph colouring Ensuring that radio stations don t clash! Graph
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CSE 101, Winter 2018 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 6: BFS, SPs, Dijkstra Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ Distance in a Graph The distance between two nodes is the length
CSE 101, Winter 2018 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 6: BFS, SPs, Dijkstra Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ Distance in a Graph The distance between two nodes is the length
UNIT Name the different ways of representing a graph? a.adjacencymatrix b. Adjacency list
 UNIT-4 Graph: Terminology, Representation, Traversals Applications - spanning trees, shortest path and Transitive closure, Topological sort. Sets: Representation - Operations on sets Applications. 1. Name
UNIT-4 Graph: Terminology, Representation, Traversals Applications - spanning trees, shortest path and Transitive closure, Topological sort. Sets: Representation - Operations on sets Applications. 1. Name
Representations of Graphs
 ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS -- CS-5321 Presentation -- I am Nishit Kapadia Representations of Graphs There are two standard ways: A collection of adjacency lists - they provide a compact way to represent
ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS -- CS-5321 Presentation -- I am Nishit Kapadia Representations of Graphs There are two standard ways: A collection of adjacency lists - they provide a compact way to represent
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 13 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Depth First Search (DFS) Shortest path Shortest weight path (Dijkstra's
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 13 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Depth First Search (DFS) Shortest path Shortest weight path (Dijkstra's
Chapter 5. Decrease-and-Conquer. Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Decrease-and-Conquer Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Decrease-and-Conquer 1. Reduce problem instance to smaller instance of the same problem 2. Solve smaller instance
Chapter 5 Decrease-and-Conquer Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Decrease-and-Conquer 1. Reduce problem instance to smaller instance of the same problem 2. Solve smaller instance
Graphs. Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale Room - Faner 3131
 Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
Discrete Motion Planning
 RBE MOTION PLANNING Discrete Motion Planning Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Announcement Homework 1 is out Due Date - Feb 1 Updated
RBE MOTION PLANNING Discrete Motion Planning Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Announcement Homework 1 is out Due Date - Feb 1 Updated
Spanning Trees 4/19/17. Prelim 2, assignments. Undirected trees
 /9/7 Prelim, assignments Prelim is Tuesday. See the course webpage for details. Scope: up to but not including today s lecture. See the review guide for details. Deadline for submitting conflicts has passed.
/9/7 Prelim, assignments Prelim is Tuesday. See the course webpage for details. Scope: up to but not including today s lecture. See the review guide for details. Deadline for submitting conflicts has passed.
Spanning Trees. Lecture 22 CS2110 Spring 2017
 1 Spanning Trees Lecture 22 CS2110 Spring 2017 1 Prelim 2, assignments Prelim 2 is Tuesday. See the course webpage for details. Scope: up to but not including today s lecture. See the review guide for
1 Spanning Trees Lecture 22 CS2110 Spring 2017 1 Prelim 2, assignments Prelim 2 is Tuesday. See the course webpage for details. Scope: up to but not including today s lecture. See the review guide for
Data Structures and Algorithms. Chapter 7. Graphs
 1 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 7 Werner Nutt 2 Acknowledgments The course follows the book Introduction to Algorithms, by Cormen, Leiserson, Rivest and Stein, MIT Press [CLRST]. Many examples
1 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 7 Werner Nutt 2 Acknowledgments The course follows the book Introduction to Algorithms, by Cormen, Leiserson, Rivest and Stein, MIT Press [CLRST]. Many examples
CSE 101. Algorithm Design and Analysis Miles Jones Office 4208 CSE Building Lecture 5: SCC/BFS
 CSE 101 Algorithm Design and Analysis Miles Jones mej016@eng.ucsd.edu Office 4208 CSE Building Lecture 5: SCC/BFS DECOMPOSITION There is a linear time algorithm that decomposes a directed graph into its
CSE 101 Algorithm Design and Analysis Miles Jones mej016@eng.ucsd.edu Office 4208 CSE Building Lecture 5: SCC/BFS DECOMPOSITION There is a linear time algorithm that decomposes a directed graph into its
Data Structure Lecture#23: Graphs (Chapter 11) U Kang Seoul National University
 Data Structure Lecture#23: Graphs (Chapter 11) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang 1 In This Lecture Basic terms and definitions of graphs How to represent graphs Graph traversal methods U Kang 2 Graphs
Data Structure Lecture#23: Graphs (Chapter 11) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang 1 In This Lecture Basic terms and definitions of graphs How to represent graphs Graph traversal methods U Kang 2 Graphs
22.3 Depth First Search
 22.3 Depth First Search Depth-First Search(DFS) always visits a neighbour of the most recently visited vertex with an unvisited neighbour. This means the search moves forward when possible, and only backtracks
22.3 Depth First Search Depth-First Search(DFS) always visits a neighbour of the most recently visited vertex with an unvisited neighbour. This means the search moves forward when possible, and only backtracks
IS 709/809: Computational Methods in IS Research. Graph Algorithms: Introduction
 IS 709/809: Computational Methods in IS Research Graph Algorithms: Introduction Nirmalya Roy Department of Information Systems University of Maryland Baltimore County www.umbc.edu Motivation Several real-life
IS 709/809: Computational Methods in IS Research Graph Algorithms: Introduction Nirmalya Roy Department of Information Systems University of Maryland Baltimore County www.umbc.edu Motivation Several real-life
CS302 - Data Structures using C++
 CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms CSE 5311 Lecture 18 Graph Algorithm Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE5311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 1 Graphs Graph G = (V,
Design and Analysis of Algorithms CSE 5311 Lecture 18 Graph Algorithm Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE5311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 1 Graphs Graph G = (V,
Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms. Lecture 22 CS2110 Fall 2017
 1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 22 CS2110 Fall 2017 1 We demo A8 Your space ship is on earth, and you hear a distress signal from a distance Planet X. Your job: 1. Rescue stage: Fly your ship
1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 22 CS2110 Fall 2017 1 We demo A8 Your space ship is on earth, and you hear a distress signal from a distance Planet X. Your job: 1. Rescue stage: Fly your ship
Theory of Computing. Lecture 4/5 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck
 Theory of Computing Lecture 4/5 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck How fast can we sort? There are deterministic algorithms that sort in worst case time O(n log n) Do better algorithms exist? Example [Andersson et
Theory of Computing Lecture 4/5 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck How fast can we sort? There are deterministic algorithms that sort in worst case time O(n log n) Do better algorithms exist? Example [Andersson et
The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value
 The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value 1 Possible implementations Sorted linear implementations o Appropriate if
The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value 1 Possible implementations Sorted linear implementations o Appropriate if
Graph. Vertex. edge. Directed Graph. Undirected Graph
 Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
CS 1114: Implementing Search. Last time. ! Graph traversal. ! Two types of todo lists: ! Prof. Graeme Bailey.
 CS 1114: Implementing Search! Prof. Graeme Bailey http://cs1114.cs.cornell.edu (notes modified from Noah Snavely, Spring 2009) Last time! Graph traversal 1 1 2 10 9 2 3 6 3 5 6 8 5 4 7 9 4 7 8 10! Two
CS 1114: Implementing Search! Prof. Graeme Bailey http://cs1114.cs.cornell.edu (notes modified from Noah Snavely, Spring 2009) Last time! Graph traversal 1 1 2 10 9 2 3 6 3 5 6 8 5 4 7 9 4 7 8 10! Two
FINAL EXAM REVIEW CS 200 RECITATIOIN 14
 FINAL EXAM REVIEW CS 200 RECITATIOIN 14 I don t *think* the final is cumulative. Sangmi will say for sure during her review sessions. Either way, keep in mind that this course s material is naturally cumulative
FINAL EXAM REVIEW CS 200 RECITATIOIN 14 I don t *think* the final is cumulative. Sangmi will say for sure during her review sessions. Either way, keep in mind that this course s material is naturally cumulative
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 7 Greedy Graph Algorithms Topological sort Shortest paths Adam Smith The (Algorithm) Design Process 1. Work out the answer for some examples. Look for a general principle
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 7 Greedy Graph Algorithms Topological sort Shortest paths Adam Smith The (Algorithm) Design Process 1. Work out the answer for some examples. Look for a general principle
(Dijkstra s Algorithm) Consider the following positively weighted undirected graph for the problems below: 8 7 b c d h g f
 CS6: Algorithm Design and Analysis Recitation Section 8 Stanford University Week of 5 March, 08 Problem 8-. (Graph Representation) (a) Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using an adjacency matrix
CS6: Algorithm Design and Analysis Recitation Section 8 Stanford University Week of 5 March, 08 Problem 8-. (Graph Representation) (a) Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using an adjacency matrix
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 3 Data Structures Graphs Traversals Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova L3.1 Measuring Running Time Focus on scalability: parameterize the running time
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 3 Data Structures Graphs Traversals Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova L3.1 Measuring Running Time Focus on scalability: parameterize the running time
CS 561, Lecture 10. Jared Saia University of New Mexico
 CS 561, Lecture 10 Jared Saia University of New Mexico Today s Outline The path that can be trodden is not the enduring and unchanging Path. The name that can be named is not the enduring and unchanging
CS 561, Lecture 10 Jared Saia University of New Mexico Today s Outline The path that can be trodden is not the enduring and unchanging Path. The name that can be named is not the enduring and unchanging
Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]
![Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch] Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]](/thumbs/81/84350835.jpg) Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Directed Graphs Let V be a finite set and E a binary relation on V, that is, E VxV. Then the pair G=(V,E) is called a directed graph.
Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Directed Graphs Let V be a finite set and E a binary relation on V, that is, E VxV. Then the pair G=(V,E) is called a directed graph.
SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES. Chapter 11
 SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES Chapter 11 Tree Balance and Rotation Section 11.1 Algorithm for Rotation BTNode root = left right = data = 10 BTNode = left right = data = 20 BTNode NULL = left right = NULL
SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES Chapter 11 Tree Balance and Rotation Section 11.1 Algorithm for Rotation BTNode root = left right = data = 10 BTNode = left right = data = 20 BTNode NULL = left right = NULL
