COMPARATIVE ASSESSMENT OF MULTI-TEMPORAL INSAR TECHNIQUES FOR GENERATION OF DISPLACEMENT MAPS: A CASE STUDY FOR BUCHAREST AREA
|
|
|
- Vernon Harris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series C, Vol. 78, Iss. 2, 2016 ISSN COMPARATIVE ASSESSMENT OF MULTI-TEMPORAL INSAR TECHNIQUES FOR GENERATION OF DISPLACEMENT MAPS: A CASE STUDY FOR BUCHAREST AREA Carmen PATRASCU 1, Anca Andreea POPESCU 2, Mihai DATCU 3 This paper presents a comparative assessment of Synthetic Aperture Radar interferometric techniques (InSAR) that allow the detection of deformation models along the line-of-sight of the radar. Given the susceptibility of these methods to several limitations that act as noise effects in the interferograms, known as decorrelation phenomena, multi-temporal InSAR techniques have been used for the exploiting of phase information acquired over long time intervals. Keywords: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), SAR Interferometry (InSAR), Permanent Scatterers (PS), Small BAseline Subsets (SBAS) 1. Introduction Differential InSAR (DInSAR) is a special processing technique that enables the combination of the phase information of at least two complex images acquired over the same area at simultaneous or different times for several applications. An important feature of DInSAR is the fact that topographic contributions to the resulting phase have been removed from the final results, thus allowing the extraction of linear deformations along the system s line of sight with millimetric accuracy [1][2]. These techniques are mainly used for extracting earth deformation patterns, with one of the most important application being the computation of digital elevation models (DEM) corresponding to the imaged scene [3]. Other applications include measuring the effects of a large series of ground deformation phenomena, such as: deformation induced by volcanic activity [4], co-seismic and post-seismic motions [5], mining and groundwater induced deformation [6][1], or measurement of the soil moisture [2]. However, the number of usable interferometric pairs, which has to range in the tens domain, 1 PhD Student, Research Centre for Spatial Information CEOSpaceTech, University POLITEHNICA of Bucharest, cpatrascu@ceospacetech.pub.ro 2 Associate Professor, Research Centre for Spatial Information CEOSpaceTech, University POLITEHNICA of Bucharest, apopescu@ceospacetech.pub.ro 3 Professor, Research Centre for Spatial Information CEOSpaceTech, University POLITEHNICA of Bucharest, German Aerospace Center (DLR Oberpfaffenhofen), mihai.datcu@dlr.de
2 136 Carmen Patrascu, Anca Andreea Popescu, Mihai Datcu is limited by noise like effects noticeable in the computed interferograms, known as decorrelation phenomena [7]. Apart from these, other limitations are mainly due to cycle ambiguity problems caused by the necessity of both SBAS and PS techniques for phase unwrapping [8] and extraction of atmospheric induced artifacts. Multi-temporal InSAR techniques are extensions of conventional InSAR methods that aim at addressing problems caused by decorrelation effects and atmospheric delay. These techniques involve the simultaneous processing of multiple SAR acquisitions of the same area extended over large periods of time to allow for the correction of the uncorrelated phase noise terms, reducing errors associated with deformation elements. At this moment, these techniques fall into two main categories: permanent scatterer techniques (PSInSAR) [11-13] and small baseline subset algorithms (SBAS) [14][15]. These methods try to overcome limitations induced by large baseline values by using points characterized by long-term phase coherence, known as persistent (PS) or distributed (DS) scatterers. In non-urban areas the incidence of such points is low, due to the reduced number of scatterers with sufficiently high coherence levels. For this reason, a method to improve the coherence estimates must be found. A straightforward solution is given by multi-looking techniques, which perform filtering of the interferometric phase by computing a weighted average of pixels located in a neighborhood [9]. An adaptive approach is proposed, which selects statistically homogeneous pixels by analyzing the temporal distribution of the amplitude levels in a goodness-of-fit approach. The resulting phase estimates are filtered for non-uniform contributions (APS), allowing for the extraction of deformation profiles for the analyzed area. This article aims at performing a complete analysis of the millimetric deformations which affect the area of Bucharest using both PSInSAR and SBAS techniques. A comparison of the results will be performed. The proposed methodology has been applied on a set of 32 TerraSAR-X images, acquired over the South-Eastern area of Romania. The image stack covers a period of 16 months, from July 2011, to December The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the methods used by the authors to extract point-wise deformation histories using the PSInSAR and SBAS approaches. The adaptive phase filtering algorithm will be described. Experimental results (Section 3) and the conclusions (Section 4) will contribute to the assessment of both methods performances.
3 Comparative assessment of multi-temporal InSAR techniques for generation of ( ) Methodology for extraction of deformation maps In order to obtain an estimate of the displacement rates in the test area, we employ a processing workflow based on the functionality of the GAMMA interferometric processor [10]. Starting from a set of N available SLC images, M differential interferograms are generated using either a single reference (PSInSAR) or a SB constraint (SBAS). The results of this step are adaptively filtered and used to extract deformation histories for targets located in the analyzed area. The main processing steps are detailed in the following sections Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSInSAR) In the case of differential interferometry, the resulting phase represents the phase difference between two considered acquisitions, from which the influence of the topography has been removed. However, if multiple acquisitions are considered, the phase of each pixel does not only change to the difference in the relative position between the target and the satellite, but also due to a temporal evolution of the target, as well as influence in the atmospheric term, especially for long observation intervals. Hence, the final estimate of the phase ( ) will comprise information about the acquisition geometry ( R, ), terrain motion (, ), scattering properties of the imaged target ( A, ) and the atmospheric influence ( APS, ), as seen in Eq. (1).,,,, (1) The persistent scatterer technique was first described in [11], [12]. The main goal of this approach is to overcome limitations imposed by the decorrelation phenomena and atmospheric induced limitations affecting conventional DInSAR systems, to compute deformation time series in the form of displacement maps [13]. The motivation behind this approach is that, in the case of methods based on the identification of stable targets, it is considered that only one scatterer in the resolution cell dominates the backscattered signal. Hence, a network of such scatterer-dominant pixels may be used to extract information signatures from interferograms that have been severely compromised by decorrelation effects. Despite several terms influencing the phase of the final phase value corresponding to each interferometric acquisition, the amplitude values of the complex data are virtually insensitive to those variations, rendering amplitude statistics analysis a robust method for the extraction of stable targets. In the case of PS, we are interested in finding pixels characterized by high values of the SNR. Hence, the phase dispersion can be analyzed based on the dispersion of the amplitude values, as seen in Eq. (2). (2)
4 138 Carmen Patrascu, Anca Andreea Popescu, Mihai Datcu where m A and σ A are the first and second moments of the amplitude computed in a neighborhood. The amplitude dispersion index offers information with respect to phase stability, and PS candidates are selected by thresholding (D A 0.25). Important advantages of this processing method are the short time required for the analysis, as well as no resolution loss. However, its accuracy depends on the size of the image stack, used to estimate the statistical properties of the amplitude Small BAseline Subset Algorithm (SBAS) If all scatterers have comparable strengths, then the interferometric phase is randomly distributed in the ; interval and the interferometric signal can be improved by averaging the signal from adjacent resolution cells. Under this assumption, the random contribution due to the movement of the scatterers cancel out and the results only account for the average motion of the resolution elements. This was originally the basis of the SBAS method [14]. Considering a series of 1 images acquired over the same area at consecutive times,,, a number of M unwrapped interferograms can be computed. Moreover, we assume that each image can interfere with at least another image under the baseline restriction considered, which implies that each small baseline (SB) subset has a minimum of two acquisitions. If we assume that the images are chronologically ordered (i.e. the master image was acquired before the slave), the deformation values associated with the considered pixel can be obtained using the matrix representation in Eq. (3)., for 1, (3) where A is an incidence-like matrix directly related to the interferograms generated from the available data and is the interferometric phase of the master (IE) and slave (IS) images. In order to invert the system in Eq. (3), the Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) algorithm is employed [15]. This algorithm links the independent SAR acquisition data sets generated under the SB constraint. A direct advantage of this approach is the ability to include in the processing interferometric pairs which would otherwise be separated by large baselines and therefore not suitable for other processing methodologies. Following this step, the phase estimate associated with the unknown deformation values can be extracted in an LS sense, as seen in Eq. (4). (4) where we define L as the number of generated subsets, and u i and v i are the column vectors of the U and V matrices resulting from the SVD decomposition. At this point, we can manipulate Eq. (4) and replace the unknowns with the mean velocity between time acquisitions, generating a physically sound solution.
5 Comparative assessment of multi-temporal InSAR techniques for generation of ( ) 139 The main purpose of the SBAS algorithm is to minimize the effects of spatial de-correlation and DEM errors. An important advantage of this method is the increase in the temporal sampling rate, due to the usage of all acquisitions in the subsets Adaptive Phase Improvement based on Amplitude Statistics Long term monitoring of critical infrastructure is usually performed using coherent multi-temporal InSAR techniques, such as PSInSAR and SBAS. These methods use points that exhibit long term phase coherence, known as persistent and distributed scatterers, to overcome limitations induced by long time intervals between acquisitions. Given the relatively low incidence of such elements, especially in non-urban areas, a good estimation of the phase values and, consequently, complex correlation, is mandatory to achieve accurate results [16]. Authors in [10] have proved that using the backscattered amplitude statistics represents an efficient method to adaptively extract regions of homogeneous pixels, leading to the preservation of phase signatures in the analyzed region. Traditional multi-looking methods use sliding windows with rectangular form and perform a weighted averaging of the neighboring complex pixels, under the hypothesis of statistical homogeneity [17]. However, in the case of high resolution data, this hypothesis is extremely short lived when increasing the size of the neighborhood given the different scattering phenomenology of the analyzed targets. Due to different shapes and properties of objects in high resolution images, elements with similar statistical properties can be several pixels away. The concept behind the proposed approach is to average each considered element only with such pixels that are adaptively selected based on the similarities of their scattering properties. We employ the Anderson-Darling (AD) test to perform a statistical analysis of the complex data in a goodness-of-fit approach, by temporally sampling the image stack using stationary time intervals. The AD method gives more weight to the tail of the distribution [18], leading to a better performance in the case of radar applications, where the information in the tail plays an important rose due to the influence it has on higher statistic order moments. The test statistic is defined in Eq. (5).,, (4) where,, represents the empirical cumulative distribution function (ECDF) of the analyzed pixel and all neighboring pixels from the patch (p), while is the ECDF of the new population obtained by merging and ordering independent data sets corresponding to the current and tested pixels (q) into one set. The threshold used for processing was selecting empirically. Processing was
6 140 Carmen Patrascu, Anca Andreea Popescu, Mihai Datcu carried out with a number of L=200 looks. An example of statistically homogeneous pixels selected based on the AD approach is presented in Fig. 1. Fig.1. (a) Google Earth ( Google Inc.) image of the Palace of Parliament; (b) Amplitude image of a TerraSAR-X acquisition corresponding to the same area; (c) Goodness-of-fit for homogeneous area identification: the statistically homogeneous pixels selected based on the AD test are shown in green for the analyzed pixel (marked in red). The influence of the image stack size is minimized by the dynamic expansion of the population associated to each identified homogeneous area. This way, the statistical test will be performed between the temporal PDF of each considered pixel and the PDF of the entire population included in one region, leading to increased confidence levels in the analysis, given the size of the population. Furthermore, the optimal size of the sliding windows included in the processing has been computed by employing the rate distortion theory and analyzing the level of variability in the neighborhood. Fig.2. Coherence histograms for the initial (left) and adaptively filtered (right) differential interferograms. The result corresponds to the ( ) image pair. The histogram before the adaptive filtering is superimposed in red. An increase of 3.53% in the total number of pixels selected for further processing ( 0.4) is observed.
7 Comparative assessment of multi-temporal InSAR techniques for generation of ( ) 141 The effects of the adaptive filtering method are presented using the estimated coherence of the interferometric phase. Figure 2 shows the histogram of coherence estimates before and after the ML operation. The results correspond to the ( ) image pair. To measure the improvement effected by the usage of this algorithm, we compute the number of pixels included in the following processing steps ( 0.4). An increase of 3.6% in the overall number of unwrapped pixels has been observed. 3. Experimental Setup and Results The proposed methodology has been tested on a dataset consisting of 32 SLC StripMap TerraSAR-X images, acquired over the area of Bucharest, Romania. The data spans a 16 months temporal interval, between July 2011 and December All acquisitions are characterized by a descending orbit and HH polarization. In the case of the PSInSAR technique, the image stack was processed based on a single acquisition, namely the image on Two criteria were employed in this selection: minimization of the perpendicular baseline values and acquisition date near the center of the studied temporal interval. For the SBAS method, a number of M=134 differential interferograms are generated under the imposed SB constraint ( 200m). (a) (b) Fig.3. Distribution of the spatial and temporal baselines computed using the PSInSAR (a) and SBAS (b) methods. As can be observed, the values of the perpendicular baselines are kept small, the absolute maximal value being of 250m for PSInSAR and 89.5m for the SBAS algorithm The baseline distributions graphs are presented in Fig. 3. As can be observed, both methods lead to the generation of small baseline values. In the case of PSInSAR method, the absolute maximal value is of 250m, with a medium
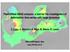
8 142 Carmen Patrascu, Anca Andreea Popescu, Mihai Datcu value of 46.7m. For the SBAS algorithm, the average value of the perpendicular component is 89.5m, while the temporal value is 99 days. Following this step, the PSInSAR method is used to extract an initial set of persistent scatterer candidates, using the intensity variation of image targets. Following this process, a mask corresponding to the PSC locations is created and used to generate the differential interferograms. At this point, a multi-looking algorithm with L=200 looks is applied for the adaptive filtering of the interferometric phase computed for both algorithms. In the case of PSInSAR method, the final displacement rates are computed after an iterative process which improves the baseline estimates and extracts the influence of the APS. For the SBAS method, an SVD inversion is applied to information extracted from the data itself, to link the independent image subsets generated under the SB subsets. Following an additional integration step, displacement histories can be extracted for all points included in the processing. Fig.4. Average displacement rates [meters/year] for the TerraSAR-X image stack, corresponding to the Bucharest area. A preliminary analysis of the average displacement rates [meters/year] for the TerraSAR-X image stack, allows us to identify three interest regions characterized by significant deformation phenomena (A1-A3 in Fig.4), with respect to a reference point (marked Ref in Fig.4). We present for comparison deformation histories for the A2 and A4 areas. The following conclusions were drawn with respect to the presented points: A1: historical building (built in 1906) corresponding to the former Bucharest City Hall premises (until 2010). It can be observed that an accentuated
9 Comparative assessment of multi-temporal InSAR techniques for generation of ( ) 143 deformation phenomenon is present in the results. Currently, the building is closed for consolidation work; A2: office building with 19 floors, completed in This building is located in the proximity of a historic monument. It is important to note that at the moment of the construction there was a strong controversy about its stability; A3: small area in the Northern part of the Morii Lake. A constant small deformation rate corresponding to the subsidence motion has been observed in the area in two more datasets (ASAR, ERS). The area consist of apartment buildings and is located in the vicinity of the Granmetal Industrial platform; A4: Esplanada Commercial Center. Strong subsidence was observed in the area following the processing of the TerraSAR-X dataset. This region is situated in the Eastern part of Bucharest and houses a new retail space comprising of a supermarket and shopping center. (a) (b) (d) (c) Fig.5. Deformation histories for points in the A1 and A4 interest regions extracted with the PSInSAR (a,b) and SBAS (c,d) methods; (a) A1 region, (σ 0.8 rad); (b) A4 region, 0.76rad); (c) A1 region, (σ m); (d) A4 region, (σ m). (σ
10 144 Carmen Patrascu, Anca Andreea Popescu, Mihai Datcu Displacement rates for the points extracted using the PS approach from the interest region are presented in Fig.5. Using the small baseline technique, we have extracted several areas affected by this phenomenon. The upper graphs show the displacement rate measured using the PSInSAR method, and the linear regression model superimposed in red. The second line depicts the results from the SBAS method, with the graphics representing deformation profiles. In the absence of an external validation method in the form of ground truth measurements (GPS, leveling), the quality of the displacement estimates was assessed by means of the estimate variance, computed using equally sized sets defined by the coordinates of the identified PS. In this case, a significant narrowing of 3% is observed. Moreover, average displacement rates computed by the PSInSAR and SBAS algorithms show a very high correlation coefficient (ρ = ). This result proves similar displacement trends and values in both methods. 4. Conclusions This paper presents a complete multi-temporal analysis methodology for the monitoring of small coherent displacements in the area of Bucharest, Romania, based on TerraSAR-X data acquired over a period of 16 months. We extract point-wise displacement trends using a persistent scatterer methodology and imposing a SB constraint on the perpendicular values of the baselines. The processing workflow incorporates an improvement of the coherence estimates performed by employing an adaptive phase filtering algorithm which selects statistically homogeneous areas based on the amplitude temporal statistics of the SLC data, leading to the conservation of interferometric phase information of the analyzed targets. In general, the quality of multi-temporal InSAR techniques is very difficult to assess without the existence of a priori knowledge about the deformation in the area. Given the absence of ground truth information, we propose the assessment of the displacement estimates by means of the estimate variance. This result shows a significant narrowing for equally sized sample sets. The estimated displacement rates for both methods are highly correlated, proving the similarity of displacement trends and values. A small deformation trend in the W-E direction was detected and extracted. The displacement histories are in accordance with results published following independent studies on ENVISAT and TerraSAR-X data for the area [19].
11 Comparative assessment of multi-temporal InSAR techniques for generation of ( ) 145 Acknowledgement This work was supported by the Romanian Sectoral Operational Programme Human Resources Development of the Ministry of European Funds through the Financial Agreements POSDRU/107/1.5/S/76903 and POSDRU/159/1.5/S/ This work was supported by a grant of the Romanian National Authority for Scientific Research, CNCS UEFISCDI, project number PN-II-ID-PCE The work has been funded by: Sectoral Operational Programme Human Resources Development of the Romanian Ministry of Labour, Family and Social Protection through the Financial Agreement POSDRU/159/1.5/S/ R E F E R E N C E S [1] L. Gong, J. Zhang, Z. Chang, Z. Li, and Q. Guo, M. Ivan, Measuring Mining Induced Subsidence with, Proceedings of IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, pp , Jul [2] M. Nolan, D. R. Fatland, and L. Hinzman, DInSAR Measurement of Soil Moisture,'' IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 41, No. 12, pp , Dec [3] O. Mora, R. Arbiol, V. Palà, A. Adell, and M. Torre, Generation of Accurate DEMs Using DInSAR Methodology (TopoDInSAR), IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, Vol. 3, No. 4, Oct [4] J.-L. Froger, F. Yukushima, P. Tinard, V. Cayol, T. Souriot, O. Mora, T. Staudacher, P. Durand, B. Fruneau, and N. Villeneuve, Multi Sensors InSAR Monitoring of Volcanic Activity: the February and April 2007 Eruptions at Piton de la Fournaise, Reunion Island, Imaged with ENVISAT-ASAR and ALOS-PALSAR Data, Fringe Workshop, Frascati, Italy, Nov [5] M. Chini, S. Atzori, E. Trasatti, C. Bignami, C. Kyriakopoulos, C. Tolomei, and S. Stramondo, The May 12, 2008 (Mw 7.9) Sichuan Earthquake (China): Multiframe ALOS-PALSAR DInSAR Analysis of Coseismic Deformation, IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, Vol. 7, No. 2, pp , [6] Y. Luo, J. Zhang, Q. Zeng, J. Wu, L. Gong, W. Jiang, Y. Dai, PS InSAR Monitoring of Land Subsidence in Suzhou, Beijing, ESA SP-655, [7] H. A. Zebker, and J. Villasenor, Decorrelation in Interferometric Radar Echoes'', IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 30, No. 5, pp , Sept [8] L. Zhang, X. Ding, and Z. Lu, Modeling PSInSAR Time Series Without Phase Unwrapping'', IEEE Trans. on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 49, No. 1, pp , Jan [9] F. Argenti, A. Lapini, T. Bianchi, L. Alparone, A tutorial on speckle reduction in synthetic aperture radar images, IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, Vol. 1, No. 3, pp. 6 35, Sept [10] A. Ferretti, A. Fumagalli, F. Novali, C. Prati, F. Rocca, A. Rucci, A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 49, Nr. 9, pp , Sept 2011.
12 146 Carmen Patrascu, Anca Andreea Popescu, Mihai Datcu [11] A. Ferretti, C. Prati, F. Rocca, Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 38, Nr. 5, pp , Sept [12] A. Ferretti, C. Prati, F. Rocca, Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 39, Nr. 1, pp. 8-20, Jan [13] L C. Colesanti, A. Ferretti, F. Novali, C. Prati, and F. Rocca, SAR Monitoring of Progressive and Seasonal Ground Deformation using the Permanent Scatterer Technique, IEEE Trans. on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 41, No. 7, pp , Sept [14] R. Lanari, F. Casu, M. Manzo, G. Zeni, P. Bernardino, M. Manunta, A. Pepe, An overview of the small baseline subset algorithm: A DInSAR technique for surface deformation analysis, Pure and Applied Geophysics, Vol. 164, Nr. 4, pp , 2007 [15] G.H. Golub, and C.F. Van Loan, A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms'', IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 40, No. 11, pp , Nov [16] J.S. Lee, K. Papathanassiou, T. Ainsworth, M. Grunes, A. Reigber, A new technique for noise filtering of SAR interferometric phase images, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 36, Nr. 5, pp , Sep 1998 [17] R. Touzi, A. Lopes, J. Bruniquel, P. Vachon, Coherence estimation for SAR imagery, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 37, No. 1, pp , Jan 1999 [18] A.N. Pettitt, A two-sample Anderson-Darling rank statistic, Biometrika, Vol. 63, No. 1, 1976 [19] Advanced Studies and Research Center,
MULTI-TEMPORAL INTERFEROMETRIC POINT TARGET ANALYSIS
 MULTI-TEMPORAL INTERFEROMETRIC POINT TARGET ANALYSIS U. WEGMÜLLER, C. WERNER, T. STROZZI, AND A. WIESMANN Gamma Remote Sensing AG. Thunstrasse 130, CH-3074 Muri (BE), Switzerland wegmuller@gamma-rs.ch,
MULTI-TEMPORAL INTERFEROMETRIC POINT TARGET ANALYSIS U. WEGMÜLLER, C. WERNER, T. STROZZI, AND A. WIESMANN Gamma Remote Sensing AG. Thunstrasse 130, CH-3074 Muri (BE), Switzerland wegmuller@gamma-rs.ch,
LINEAR AND NON-LINEAR LONG-TERM TERRAIN DEFORMATION WITH DINSAR (CPT: COHERENT PIXELS TECHNIQUE)
 LINEAR AND NON-LINEAR LONG-TERM TERRAIN DEFORMATION WITH DINSAR (CPT: COHERENT PIXELS TECHNIQUE) Jordi J. Mallorquí (1), Oscar Mora (1,2), Pablo Blanco (1), Antoni Broquetas (1) (1) Universitat Politècnica
LINEAR AND NON-LINEAR LONG-TERM TERRAIN DEFORMATION WITH DINSAR (CPT: COHERENT PIXELS TECHNIQUE) Jordi J. Mallorquí (1), Oscar Mora (1,2), Pablo Blanco (1), Antoni Broquetas (1) (1) Universitat Politècnica
ALOS-PALSAR performances on a multiple sensor DInSAR scenario for deformation monitoring
 ALOS-PALSAR performances on a multiple sensor DInSAR scenario for deformation monitoring Pablo Blanco, Roman Arbiol and Vicenç Palà Remote Sensing Department Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC) Parc
ALOS-PALSAR performances on a multiple sensor DInSAR scenario for deformation monitoring Pablo Blanco, Roman Arbiol and Vicenç Palà Remote Sensing Department Institut Cartogràfic de Catalunya (ICC) Parc
A STATISTICAL-COST APPROACH TO UNWRAPPING THE PHASE OF INSAR TIME SERIES
 A STATISTICAL-COST APPROACH TO UNWRAPPING THE PHASE OF INSAR TIME SERIES Andrew Hooper Delft Institute of Earth Observation and Space Systems, Delft University of Technology, Delft, Netherlands, Email:
A STATISTICAL-COST APPROACH TO UNWRAPPING THE PHASE OF INSAR TIME SERIES Andrew Hooper Delft Institute of Earth Observation and Space Systems, Delft University of Technology, Delft, Netherlands, Email:
Coherence Based Polarimetric SAR Tomography
 I J C T A, 9(3), 2016, pp. 133-141 International Science Press Coherence Based Polarimetric SAR Tomography P. Saranya*, and K. Vani** Abstract: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) three dimensional image provides
I J C T A, 9(3), 2016, pp. 133-141 International Science Press Coherence Based Polarimetric SAR Tomography P. Saranya*, and K. Vani** Abstract: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) three dimensional image provides
SAR Interferogram Phase Filtering Using Wavelet Transform
 Formatted: Font: 16 pt, Nazanin, 16 pt, (Complex) Farsi, 12 pt SAR Interferogram Phase Filtering Using Wavelet Transform V. Akbari, M. Motagh and M. A. Rajabi 1 Dept. o Surveying Eng., University College
Formatted: Font: 16 pt, Nazanin, 16 pt, (Complex) Farsi, 12 pt SAR Interferogram Phase Filtering Using Wavelet Transform V. Akbari, M. Motagh and M. A. Rajabi 1 Dept. o Surveying Eng., University College
DINSAR: Differential SAR Interferometry
 DINSAR: Differential SAR Interferometry Fabio Rocca 1 SAR interferometric phase: ground motion contribution If a scatterer on the ground slightly changes its relative position in the time interval between
DINSAR: Differential SAR Interferometry Fabio Rocca 1 SAR interferometric phase: ground motion contribution If a scatterer on the ground slightly changes its relative position in the time interval between
Sentinel-1 Toolbox. TOPS Interferometry Tutorial Issued May 2014
 Sentinel-1 Toolbox TOPS Interferometry Tutorial Issued May 2014 Copyright 2015 Array Systems Computing Inc. http://www.array.ca/ https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/toolboxes Interferometry Tutorial
Sentinel-1 Toolbox TOPS Interferometry Tutorial Issued May 2014 Copyright 2015 Array Systems Computing Inc. http://www.array.ca/ https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/toolboxes Interferometry Tutorial
COREGISTRATION BETWEEN SAR IMAGE SUBSETS USING POINTWISE TARGETS
 COREGISTRATION BETWEEN SAR IMAGE SUBSETS USING POINTWISE TARGETS Teng Wang (1), Sigurjón Jónsson (1), Ramon Hanssen (2) (1) Division of Physical Sciences and Engineering, King Abdullah University of Science
COREGISTRATION BETWEEN SAR IMAGE SUBSETS USING POINTWISE TARGETS Teng Wang (1), Sigurjón Jónsson (1), Ramon Hanssen (2) (1) Division of Physical Sciences and Engineering, King Abdullah University of Science
InSAR Operational and Processing Steps for DEM Generation
 InSAR Operational and Processing Steps for DEM Generation By F. I. Okeke Department of Geoinformatics and Surveying, University of Nigeria, Enugu Campus Tel: 2-80-5627286 Email:francisokeke@yahoo.com Promoting
InSAR Operational and Processing Steps for DEM Generation By F. I. Okeke Department of Geoinformatics and Surveying, University of Nigeria, Enugu Campus Tel: 2-80-5627286 Email:francisokeke@yahoo.com Promoting
AMBIGUOUS PSI MEASUREMENTS
 AMBIGUOUS PSI MEASUREMENTS J. Duro (1), N. Miranda (1), G. Cooksley (1), E. Biescas (1), A. Arnaud (1) (1). Altamira Information, C/ Còrcega 381 387, 2n 3a, E 8037 Barcelona, Spain, Email: javier.duro@altamira
AMBIGUOUS PSI MEASUREMENTS J. Duro (1), N. Miranda (1), G. Cooksley (1), E. Biescas (1), A. Arnaud (1) (1). Altamira Information, C/ Còrcega 381 387, 2n 3a, E 8037 Barcelona, Spain, Email: javier.duro@altamira
Sentinel-1 Toolbox. Interferometry Tutorial Issued March 2015 Updated August Luis Veci
 Sentinel-1 Toolbox Interferometry Tutorial Issued March 2015 Updated August 2016 Luis Veci Copyright 2015 Array Systems Computing Inc. http://www.array.ca/ http://step.esa.int Interferometry Tutorial The
Sentinel-1 Toolbox Interferometry Tutorial Issued March 2015 Updated August 2016 Luis Veci Copyright 2015 Array Systems Computing Inc. http://www.array.ca/ http://step.esa.int Interferometry Tutorial The
Repeat-pass SAR Interferometry Experiments with Gaofen-3: A Case Study of Ningbo Area
 Repeat-pass SAR Interferometry Experiments with Gaofen-3: A Case Study of Ningbo Area Tao Zhang, Xiaolei Lv, Bing Han, Bin Lei and Jun Hong Key Laboratory of Technology in Geo-spatial Information Processing
Repeat-pass SAR Interferometry Experiments with Gaofen-3: A Case Study of Ningbo Area Tao Zhang, Xiaolei Lv, Bing Han, Bin Lei and Jun Hong Key Laboratory of Technology in Geo-spatial Information Processing
In addition, the image registration and geocoding functionality is also available as a separate GEO package.
 GAMMA Software information: GAMMA Software supports the entire processing from SAR raw data to products such as digital elevation models, displacement maps and landuse maps. The software is grouped into
GAMMA Software information: GAMMA Software supports the entire processing from SAR raw data to products such as digital elevation models, displacement maps and landuse maps. The software is grouped into
Lateral Ground Movement Estimation from Space borne Radar by Differential Interferometry.
 Lateral Ground Movement Estimation from Space borne Radar by Differential Interferometry. Abstract S.Sircar 1, 2, C.Randell 1, D.Power 1, J.Youden 1, E.Gill 2 and P.Han 1 Remote Sensing Group C-CORE 1
Lateral Ground Movement Estimation from Space borne Radar by Differential Interferometry. Abstract S.Sircar 1, 2, C.Randell 1, D.Power 1, J.Youden 1, E.Gill 2 and P.Han 1 Remote Sensing Group C-CORE 1
Airborne Differential SAR Interferometry: First Results at L-Band
 1516 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 41, NO. 6, JUNE 2003 Airborne Differential SAR Interferometry: First Results at L-Band Andreas Reigber, Member, IEEE, and Rolf Scheiber Abstract
1516 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 41, NO. 6, JUNE 2003 Airborne Differential SAR Interferometry: First Results at L-Band Andreas Reigber, Member, IEEE, and Rolf Scheiber Abstract
Pixel-Offset SBAS analysis: a tool for the investigation of deformation time-series with large dynamics
 Pixel-Offset SBAS analysis: a tool for the investigation of deformation time-series with large dynamics F. Casu, A. Manconi, A. Pepe, M. Manzo, R. Lanari IREA-CNR Napoli, Italy casu.f@irea.cnr.it Summary
Pixel-Offset SBAS analysis: a tool for the investigation of deformation time-series with large dynamics F. Casu, A. Manconi, A. Pepe, M. Manzo, R. Lanari IREA-CNR Napoli, Italy casu.f@irea.cnr.it Summary
DEM RETRIEVAL AND GROUND MOTION MONITORING IN CHINA
 DEM RETRIEVAL AND GROUND MOTION MONITORING IN CHINA Guido Gatti ¹, Daniele Perissin ², Teng Wang ¹ ³ and Fabio Rocca ¹ (1) Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione, Politecnico di Milano, via Ponzio
DEM RETRIEVAL AND GROUND MOTION MONITORING IN CHINA Guido Gatti ¹, Daniele Perissin ², Teng Wang ¹ ³ and Fabio Rocca ¹ (1) Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione, Politecnico di Milano, via Ponzio
The 2017 InSAR package also provides support for the generation of interferograms for: PALSAR-2, TanDEM-X
 Technical Specifications InSAR The Interferometric SAR (InSAR) package can be used to generate topographic products to characterize digital surface models (DSMs) or deformation products which identify
Technical Specifications InSAR The Interferometric SAR (InSAR) package can be used to generate topographic products to characterize digital surface models (DSMs) or deformation products which identify
THREE DIMENSIONAL SAR TOMOGRAPHY IN SHANGHAI USING HIGH RESOLU- TION SPACE-BORNE SAR DATA
 THREE DIMENSIONAL SAR TOMOGRAPHY IN SHANGHAI USING HIGH RESOLU- TION SPACE-BORNE SAR DATA Lianhuan Wei, Timo Balz, Kang Liu, Mingsheng Liao LIESMARS, Wuhan University, 129 Luoyu Road, 430079 Wuhan, China,
THREE DIMENSIONAL SAR TOMOGRAPHY IN SHANGHAI USING HIGH RESOLU- TION SPACE-BORNE SAR DATA Lianhuan Wei, Timo Balz, Kang Liu, Mingsheng Liao LIESMARS, Wuhan University, 129 Luoyu Road, 430079 Wuhan, China,
2-PASS DIFFERENTIAL INTERFEROMETRY IN THE AREA OF THE SLATINICE ABOVE- LEVEL DUMP. Milan BOŘÍK 1
 2-PASS DIFFERENTIAL INTERFEROMETRY IN THE AREA OF THE SLATINICE ABOVE- LEVEL DUMP Milan BOŘÍK 1 1 Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, Thákurova
2-PASS DIFFERENTIAL INTERFEROMETRY IN THE AREA OF THE SLATINICE ABOVE- LEVEL DUMP Milan BOŘÍK 1 1 Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, Thákurova
INTEGRATED USE OF INTERFEROMETRIC SAR DATA AND LEVELLING MEASUREMENTS FOR MONITORING LAND SUBSIDENCE
 INTEGRATED USE OF INTERFEROMETRIC SAR DATA AND LEVELLING MEASUREMENTS FOR MONITORING LAND SUBSIDENCE Yueqin Zhou *, Martien Molenaar *, Deren Li ** * International Institute for Aerospace Survey and Earth
INTEGRATED USE OF INTERFEROMETRIC SAR DATA AND LEVELLING MEASUREMENTS FOR MONITORING LAND SUBSIDENCE Yueqin Zhou *, Martien Molenaar *, Deren Li ** * International Institute for Aerospace Survey and Earth
SBAS- InSAR SERVICE WITHIN THE G- POD PLATFORM
 SBAS- InSAR SERVICE WITHIN THE G- POD PLATFORM USER MANUAL Prepared by: Reference: Issue: 2 Revision: 0 Claudio De Luca (CNR- IREA) Francesco Casu (CNR- IREA) IREA- GPOD- UM- 14-003 Date of Issue: November
SBAS- InSAR SERVICE WITHIN THE G- POD PLATFORM USER MANUAL Prepared by: Reference: Issue: 2 Revision: 0 Claudio De Luca (CNR- IREA) Francesco Casu (CNR- IREA) IREA- GPOD- UM- 14-003 Date of Issue: November
NEW IMPROVEMENTS OF THE EMCF PHASE UNWRAPPING ALGORITHM FOR SURFACE DEFORMATION ANALYSIS AT FULL SPATIAL RESOLUTION SCALE
 NEW IMPROVEMENTS OF THE EMCF PHASE UNWRAPPING ALGORITHM FOR SURFACE DEFORMATION ANALYSIS AT FULL SPATIAL RESOLUTION SCALE Pepe A 1, Manunta M 1, Euillades L 2, Paglia L 1, Yang Y 1,3, and Lanari R 1 (1).
NEW IMPROVEMENTS OF THE EMCF PHASE UNWRAPPING ALGORITHM FOR SURFACE DEFORMATION ANALYSIS AT FULL SPATIAL RESOLUTION SCALE Pepe A 1, Manunta M 1, Euillades L 2, Paglia L 1, Yang Y 1,3, and Lanari R 1 (1).
WIDE AREA DEFORMATION MAP GENERATION WITH TERRASAR-X DATA: THE TOHOKU-OKI EARTHQUAKE 2011 CASE
 WIDE AREA DEFORMATION MAP GENERATION WITH TERRASAR-X DATA: THE TOHOKU-OKI EARTHQUAKE 2011 CASE Nestor Yague-Martinez (1), Michael Eineder (2), Christian Minet (2), Birgitt Schättler (2) (1) Starlab Barcelona
WIDE AREA DEFORMATION MAP GENERATION WITH TERRASAR-X DATA: THE TOHOKU-OKI EARTHQUAKE 2011 CASE Nestor Yague-Martinez (1), Michael Eineder (2), Christian Minet (2), Birgitt Schättler (2) (1) Starlab Barcelona
GAMMA Interferometric Point Target Analysis Software (IPTA): Users Guide
 GAMMA Interferometric Point Target Analysis Software (IPTA): Users Guide Contents User Handbook Introduction IPTA overview Input data Point list generation SLC point data Differential interferogram point
GAMMA Interferometric Point Target Analysis Software (IPTA): Users Guide Contents User Handbook Introduction IPTA overview Input data Point list generation SLC point data Differential interferogram point
APPLICATION OF SAR INTERFEROMETRIC TECHNIQUES FOR SURFACE DEFORMATION MONITORING
 APPLICATION OF SAR INTERFEROMETRIC TECHNIQUES FOR SURFACE DEFORMATION MONITORING Urs Wegmüller, Charles Werner, Tazio Strozzi, and Andreas Wiesmann Gamma Remote Sensing, Worbstrasse 225, 3073 Gümligen,
APPLICATION OF SAR INTERFEROMETRIC TECHNIQUES FOR SURFACE DEFORMATION MONITORING Urs Wegmüller, Charles Werner, Tazio Strozzi, and Andreas Wiesmann Gamma Remote Sensing, Worbstrasse 225, 3073 Gümligen,
Interferometry Tutorial with RADARSAT-2 Issued March 2014 Last Update November 2017
 Sentinel-1 Toolbox with RADARSAT-2 Issued March 2014 Last Update November 2017 Luis Veci Copyright 2015 Array Systems Computing Inc. http://www.array.ca/ http://step.esa.int with RADARSAT-2 The goal of
Sentinel-1 Toolbox with RADARSAT-2 Issued March 2014 Last Update November 2017 Luis Veci Copyright 2015 Array Systems Computing Inc. http://www.array.ca/ http://step.esa.int with RADARSAT-2 The goal of
PSI Precision, accuracy and validation aspects
 PSI Precision, accuracy and validation aspects Urs Wegmüller Charles Werner Gamma Remote Sensing AG, Gümligen, Switzerland, wegmuller@gamma-rs.ch Contents Aim is to obtain a deeper understanding of what
PSI Precision, accuracy and validation aspects Urs Wegmüller Charles Werner Gamma Remote Sensing AG, Gümligen, Switzerland, wegmuller@gamma-rs.ch Contents Aim is to obtain a deeper understanding of what
SAR time series. JM Nicolas F. Tupin
 SAR time series JM Nicolas F. Tupin Context Golden age of SAR sensors: improved spatial, polarimetric and temporal resolutions CSK TerraSAR-X Sentinel I RadarSAT-2 page 1 SAR sensors resolutions Polarimetric
SAR time series JM Nicolas F. Tupin Context Golden age of SAR sensors: improved spatial, polarimetric and temporal resolutions CSK TerraSAR-X Sentinel I RadarSAT-2 page 1 SAR sensors resolutions Polarimetric
MULTI-TEMPORAL SAR DATA FILTERING FOR LAND APPLICATIONS. I i is the estimate of the local mean backscattering
 MULTI-TEMPORAL SAR DATA FILTERING FOR LAND APPLICATIONS Urs Wegmüller (1), Maurizio Santoro (1), and Charles Werner (1) (1) Gamma Remote Sensing AG, Worbstrasse 225, CH-3073 Gümligen, Switzerland http://www.gamma-rs.ch,
MULTI-TEMPORAL SAR DATA FILTERING FOR LAND APPLICATIONS Urs Wegmüller (1), Maurizio Santoro (1), and Charles Werner (1) (1) Gamma Remote Sensing AG, Worbstrasse 225, CH-3073 Gümligen, Switzerland http://www.gamma-rs.ch,
2003 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes
 2003 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or
2003 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or
Letter. Wide Band SAR Sub-Band Splitting and Inter-Band Coherence Measurements
 International Journal of Remote Sensing Vol. 00, No. 00, DD Month 200x, 1 8 Letter Wide Band SAR Sub-Band Splitting and Inter-Band Coherence Measurements D. DERAUW, A. ORBAN and Ch. BARBIER Centre Spatial
International Journal of Remote Sensing Vol. 00, No. 00, DD Month 200x, 1 8 Letter Wide Band SAR Sub-Band Splitting and Inter-Band Coherence Measurements D. DERAUW, A. ORBAN and Ch. BARBIER Centre Spatial
SAR Interferometry. Dr. Rudi Gens. Alaska SAR Facility
 SAR Interferometry Dr. Rudi Gens Alaska SAR Facility 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Geometry! What does InSAR do?! Why does InSAR work?! Processing chain " Data sets " Coregistration " Interferogram generation
SAR Interferometry Dr. Rudi Gens Alaska SAR Facility 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Geometry! What does InSAR do?! Why does InSAR work?! Processing chain " Data sets " Coregistration " Interferogram generation
LONG-TERM SUBSIDENCE MONITORING OF CITY AREAS AT NORDIC LATITUDES USING ERS SAR DATA
 LONG-TERM SUBSIDENCE MONITORING OF CITY AREAS AT NORDIC LATITUDES USING ERS SAR DATA Tom R. Lauknes (1,2), Geir Engen (1), Kjell A. Høgda (1), Inge Lauknes (1), Torbjørn Eltoft (2), Dan J. Weydahl (3)
LONG-TERM SUBSIDENCE MONITORING OF CITY AREAS AT NORDIC LATITUDES USING ERS SAR DATA Tom R. Lauknes (1,2), Geir Engen (1), Kjell A. Høgda (1), Inge Lauknes (1), Torbjørn Eltoft (2), Dan J. Weydahl (3)
Inversion Algorithms and PS Detection in SAR Tomography, Case Study of Bucharest City
 20 Telfor Journal, Vol. 8, o., 206. Inversion Algorithms and PS Detection in SAR Tomography, Case Study of Bucharest City Cosmin Dănişor, Student Member, IEEE, Gianfranco Fornaro, Senior Member, IEEE,
20 Telfor Journal, Vol. 8, o., 206. Inversion Algorithms and PS Detection in SAR Tomography, Case Study of Bucharest City Cosmin Dănişor, Student Member, IEEE, Gianfranco Fornaro, Senior Member, IEEE,
SUBSIDENCE MONITORING USING CONTIGUOUS AND PS-INSAR: QUALITY ASSESSMENT BASED ON PRECISION AND RELIABILITY
 Proceedings, 11 th FIG Symposium on Deformation Measurements, Santorini, Greece, 2003. SUBSIDENCE MONITORING USING CONTIGUOUS AND PS-INSAR: QUALITY ASSESSMENT BASED ON PRECISION AND RELIABILITY Ramon F.
Proceedings, 11 th FIG Symposium on Deformation Measurements, Santorini, Greece, 2003. SUBSIDENCE MONITORING USING CONTIGUOUS AND PS-INSAR: QUALITY ASSESSMENT BASED ON PRECISION AND RELIABILITY Ramon F.
Operational process interferometric for the generation of a digital model of ground Applied to the couple of images ERS-1 ERS-2 to the area of Algiers
 Operational process interferometric for the generation of a digital model of ground Applied to the couple of images ERS-1 ERS-2 to the area of Algiers F. Hocine, M.Ouarzeddine, A. elhadj-aissa,, M. elhadj-aissa,,
Operational process interferometric for the generation of a digital model of ground Applied to the couple of images ERS-1 ERS-2 to the area of Algiers F. Hocine, M.Ouarzeddine, A. elhadj-aissa,, M. elhadj-aissa,,
Ground deformation monitoring at the Phlegrean Fields (Naples, Italy) from the exploitation of SAR data in the framework of CAT-1 and DUP activities
 S. Borgström, I. Aquino, C. Del Gaudio, C. Ricco, V. Siniscalchi, G. Solaro, P. Tizzani & G.P. Ricciardi I.N.G.V. Osservatorio Vesuviano - Via Diocleziano 328, 80124 Naples, Italy INTRODUCTION CAT-1 1065
S. Borgström, I. Aquino, C. Del Gaudio, C. Ricco, V. Siniscalchi, G. Solaro, P. Tizzani & G.P. Ricciardi I.N.G.V. Osservatorio Vesuviano - Via Diocleziano 328, 80124 Naples, Italy INTRODUCTION CAT-1 1065
DEFORMATION MEASUREMENT USING INTERFEROMETRIC SAR DATA
 DEFORMATION MEASUREMENT USING INTERFEROMETRIC SAR DATA M. Crosetto Institute of Geomatics, Campus de Castelldefels, 08860 Castelldefels (Barcelona), Spain - michele.crosetto@ideg.es Commission II, WG II/2
DEFORMATION MEASUREMENT USING INTERFEROMETRIC SAR DATA M. Crosetto Institute of Geomatics, Campus de Castelldefels, 08860 Castelldefels (Barcelona), Spain - michele.crosetto@ideg.es Commission II, WG II/2
WIDE BASELINE INTERFEROMETRY WITH VERY LOW RESOLUTION SAR SYSTEMS
 1 of 25 26/03/2008 22.35 ne previo WIDE BASELINE INTERFEROMETRY WITH VERY LOW RESOLUTION SAR SYSTEMS Abstract: A. Monti Guarnieri, C. Prati, F. Rocca and Y-L. Desnos (*) Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione
1 of 25 26/03/2008 22.35 ne previo WIDE BASELINE INTERFEROMETRY WITH VERY LOW RESOLUTION SAR SYSTEMS Abstract: A. Monti Guarnieri, C. Prati, F. Rocca and Y-L. Desnos (*) Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione
A simple solution to mitigate noise effects in timeredundant sequences of small baseline multi-look DInSAR interferograms
 Remote Sensing Letters ISSN: 2150-704X (Print) 2150-7058 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/trsl20 A simple solution to mitigate noise effects in timeredundant sequences of small
Remote Sensing Letters ISSN: 2150-704X (Print) 2150-7058 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/trsl20 A simple solution to mitigate noise effects in timeredundant sequences of small
ALOS PALSAR SCANSAR INTERFEROMETRY AND ITS APPLICATION IN WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE
 ALOS PALSAR SCANSAR INTERFEROMETRY AND ITS APPLICATION IN WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE Cunren Liang (1) (2), Qiming Zeng (1) (2), Jianying Jia (1) (2), Jian Jiao (1) (2), Xiai Cui (1) (2) (1) (2), Xiao Zhou (1)
ALOS PALSAR SCANSAR INTERFEROMETRY AND ITS APPLICATION IN WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE Cunren Liang (1) (2), Qiming Zeng (1) (2), Jianying Jia (1) (2), Jian Jiao (1) (2), Xiai Cui (1) (2) (1) (2), Xiao Zhou (1)
DEFORMATION MONITORING USING REMOTELY SENSED RADAR INTERFEROMETRIC DATA
 Proceedings, 11 th FIG Symposium on Deformation Measurements, Santorini, Greece, 2003. DEFORMATION MONITORING USING REMOTELY SENSED RADAR INTERFEROMETRIC DATA Michele Crosetto 1, Alain Arnaud 2, Javier
Proceedings, 11 th FIG Symposium on Deformation Measurements, Santorini, Greece, 2003. DEFORMATION MONITORING USING REMOTELY SENSED RADAR INTERFEROMETRIC DATA Michele Crosetto 1, Alain Arnaud 2, Javier
SAR Interferometry on a Very Long Time Scale: A Study of the Interferometric Characteristics of Man-Made Features
 2118 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 37, NO. 4, JULY 1999 training set size reflects the true priors. The classification maps for LOOC+DAFE+ECHO and blooc+dafe+echo are shown in
2118 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 37, NO. 4, JULY 1999 training set size reflects the true priors. The classification maps for LOOC+DAFE+ECHO and blooc+dafe+echo are shown in
The STUN algorithm for Persistent Scatterer Interferometry
 [1/27] The STUN algorithm for Persistent Scatterer Interferometry Bert Kampes, Nico Adam 1. Theory 2. PSIC4 Processing 3. Conclusions [2/27] STUN Algorithm Spatio-Temporal Unwrapping Network (STUN) 4 1D
[1/27] The STUN algorithm for Persistent Scatterer Interferometry Bert Kampes, Nico Adam 1. Theory 2. PSIC4 Processing 3. Conclusions [2/27] STUN Algorithm Spatio-Temporal Unwrapping Network (STUN) 4 1D
Interferometric Synthetic-Aperture Radar (InSAR) Basics
 Interferometric Synthetic-Aperture Radar (InSAR) Basics 1 Outline SAR limitations Interferometry SAR interferometry (InSAR) Single-pass InSAR Multipass InSAR InSAR geometry InSAR processing steps Phase
Interferometric Synthetic-Aperture Radar (InSAR) Basics 1 Outline SAR limitations Interferometry SAR interferometry (InSAR) Single-pass InSAR Multipass InSAR InSAR geometry InSAR processing steps Phase
Target recognition by means of spaceborne C-band SAR data
 Target recognition by means of spaceborne C-band SAR data Daniele Perissin, Claudio Prati Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione POLIMI - Politecnico di Milano Milano, Italy daniele.perissin@polimi.it
Target recognition by means of spaceborne C-band SAR data Daniele Perissin, Claudio Prati Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione POLIMI - Politecnico di Milano Milano, Italy daniele.perissin@polimi.it
Multi Baseline Interferometric Techniques and
 Pagina 1 di 11 FRINGE 96 Multi Baseline Interferometric Techniques and Applications A.Ferretti, A. Monti Guarnieri, C.Prati and F.Rocca Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione (DEI) Politecnico di Milano
Pagina 1 di 11 FRINGE 96 Multi Baseline Interferometric Techniques and Applications A.Ferretti, A. Monti Guarnieri, C.Prati and F.Rocca Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione (DEI) Politecnico di Milano
RESOLUTION enhancement is achieved by combining two
 IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 1, JANUARY 2006 135 Range Resolution Improvement of Airborne SAR Images Stéphane Guillaso, Member, IEEE, Andreas Reigber, Member, IEEE, Laurent Ferro-Famil,
IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 1, JANUARY 2006 135 Range Resolution Improvement of Airborne SAR Images Stéphane Guillaso, Member, IEEE, Andreas Reigber, Member, IEEE, Laurent Ferro-Famil,
DETECTION AND QUANTIFICATION OF ROCK GLACIER. DEFORMATION USING ERS D-InSAR DATA
 DETECTION AND QUANTIFICATION OF ROCK GLACIER DEFORMATION USING ERS D-InSAR DATA Lado W. Kenyi 1 and Viktor Kaufmann 2 1 Institute of Digital Image Processing, Joanneum Research Wastiangasse 6, A-8010 Graz,
DETECTION AND QUANTIFICATION OF ROCK GLACIER DEFORMATION USING ERS D-InSAR DATA Lado W. Kenyi 1 and Viktor Kaufmann 2 1 Institute of Digital Image Processing, Joanneum Research Wastiangasse 6, A-8010 Graz,
InSAR DEM; why it is better?
 InSAR DEM; why it is better? What is a DEM? Digital Elevation Model (DEM) refers to the process of demonstrating terrain elevation characteristics in 3-D space, but very often it specifically means the
InSAR DEM; why it is better? What is a DEM? Digital Elevation Model (DEM) refers to the process of demonstrating terrain elevation characteristics in 3-D space, but very often it specifically means the
SAOCOM 1A INTERFEROMETRIC ERROR MODEL AND ANALYSIS
 SAOCOM A INTERFEROMETRIC ERROR MODEL AND ANALYSIS Pablo Andrés Euillades (), Leonardo Daniel Euillades (), Mario Azcueta (), Gustavo Sosa () () Instituto CEDIAC FI UNCuyo & CONICET, Centro Universitario,
SAOCOM A INTERFEROMETRIC ERROR MODEL AND ANALYSIS Pablo Andrés Euillades (), Leonardo Daniel Euillades (), Mario Azcueta (), Gustavo Sosa () () Instituto CEDIAC FI UNCuyo & CONICET, Centro Universitario,
Individual Interferograms to Stacks!
 Individual Interferograms to Stacks! Piyush Agram! Jet Propulsion Laboratory!! Jun 29, 2015! @UNAVCO! Thanks to my colleagues from JPL, Caltech, Stanford University and from all over the world for providing
Individual Interferograms to Stacks! Piyush Agram! Jet Propulsion Laboratory!! Jun 29, 2015! @UNAVCO! Thanks to my colleagues from JPL, Caltech, Stanford University and from all over the world for providing
GABOR AND WEBER FEATURE EXTRACTION PERFORMANCE BASED ON URBAN ATLAS GROUND TRUTH
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series C, Vol. 78, Iss. 3, 2016 ISSN 2286-3540 GABOR AND WEBER FEATURE EXTRACTION PERFORMANCE BASED ON URBAN ATLAS GROUND TRUTH Mihaela STAN 1, Anca POPESCU 2, Dan Alexandru STOICHESCU
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series C, Vol. 78, Iss. 3, 2016 ISSN 2286-3540 GABOR AND WEBER FEATURE EXTRACTION PERFORMANCE BASED ON URBAN ATLAS GROUND TRUTH Mihaela STAN 1, Anca POPESCU 2, Dan Alexandru STOICHESCU
ON THE PHYSICAL NATURE OF URBAN SAR PERMANENT SCATTERERS
 ON THE PHYSICAL NATURE OF URBAN SAR PERMANENT SCATTERERS Daniele Perissin (1), Claudio Prati (1) (1) Politecnico di Milano, Piazza L. da Vinci 32, 20133 Milano, Italy, Email: perissin@elet.polimi.it KEY
ON THE PHYSICAL NATURE OF URBAN SAR PERMANENT SCATTERERS Daniele Perissin (1), Claudio Prati (1) (1) Politecnico di Milano, Piazza L. da Vinci 32, 20133 Milano, Italy, Email: perissin@elet.polimi.it KEY
Playa del Rey, California InSAR Ground Deformation Monitoring
 Playa del Rey, California InSAR Ground Deformation Monitoring Master Document Ref.: RV-14524 July 13, 2009 SUBMITTED TO: ATTN: Mr. Rick Gailing Southern California Gas Company 555 W. Fifth Street (Mail
Playa del Rey, California InSAR Ground Deformation Monitoring Master Document Ref.: RV-14524 July 13, 2009 SUBMITTED TO: ATTN: Mr. Rick Gailing Southern California Gas Company 555 W. Fifth Street (Mail
RADARGRAMMETRY AND INTERFEROMETRY SAR FOR DEM GENERATION
 RADARGRAMMETRY AND INTERFEROMETRY SAR FOR DEM GENERATION Jung Hum Yu 1, Xiaojing Li, Linlin Ge, and Hsing-Chung Chang School of Surveying and Spatial Information Systems University of New South Wales,
RADARGRAMMETRY AND INTERFEROMETRY SAR FOR DEM GENERATION Jung Hum Yu 1, Xiaojing Li, Linlin Ge, and Hsing-Chung Chang School of Surveying and Spatial Information Systems University of New South Wales,
Ground Subsidence Monitored by L-band Satellite Radar. Interferometry
 Ground Subsidence Monitored by L-band Satellite Radar Interferometry Hsing-Chung Chang, Ming-han Chen, Lijiong Qin, Linlin Ge and Chris Rizos Satellite Navigation And Positioning Group School of Surveying
Ground Subsidence Monitored by L-band Satellite Radar Interferometry Hsing-Chung Chang, Ming-han Chen, Lijiong Qin, Linlin Ge and Chris Rizos Satellite Navigation And Positioning Group School of Surveying
Improved SAR Image Coregistration Using Pixel-Offset Series
 Improved SAR Image Coregistration Using Pixel-Offset Series Item Type Article Authors Wang, Teng; Jonsson, Sigurjon; Hanssen, Ramon F. Citation Improved SAR Image Coregistration Using Pixel-Offset Series
Improved SAR Image Coregistration Using Pixel-Offset Series Item Type Article Authors Wang, Teng; Jonsson, Sigurjon; Hanssen, Ramon F. Citation Improved SAR Image Coregistration Using Pixel-Offset Series
INTERFEROMETRIC MULTI-CHROMATIC ANALYSIS OF HIGH RESOLUTION X-BAND DATA
 INTERFEROMETRIC MULTI-CHROMATIC ANALYSIS OF HIGH RESOLUTION X-BAND DATA F. Bovenga (1), V. M. Giacovazzo (1), A. Refice (1), D.O. Nitti (2), N. Veneziani (1) (1) CNR-ISSIA, via Amendola 122 D, 70126 Bari,
INTERFEROMETRIC MULTI-CHROMATIC ANALYSIS OF HIGH RESOLUTION X-BAND DATA F. Bovenga (1), V. M. Giacovazzo (1), A. Refice (1), D.O. Nitti (2), N. Veneziani (1) (1) CNR-ISSIA, via Amendola 122 D, 70126 Bari,
MULTID FOCUSING FOR ACCURATE TARGET LOCATION AND TRACKING OF SLOW MOVEMENTS: RESULTS AND VALIDATION
 MULTID FOCUSING FOR ACCURATE TARGET LOCATION AND TRACKING OF SLOW MOVEMENTS: RESULTS AND VALIDATION F. Serafino 1, G. Fornaro 1, A. Pauciullo 1, F. Lombardini 2, M. Costantini 3 1 IREA-CNR via Diocleziano
MULTID FOCUSING FOR ACCURATE TARGET LOCATION AND TRACKING OF SLOW MOVEMENTS: RESULTS AND VALIDATION F. Serafino 1, G. Fornaro 1, A. Pauciullo 1, F. Lombardini 2, M. Costantini 3 1 IREA-CNR via Diocleziano
Individual Interferograms to Stacks
 Individual Interferograms to Stacks Piyush Agram Jet Propulsion Laboratory Aug 1, 2016 @UNAVCO Thanks to my colleagues from JPL, Caltech, Stanford University and from all over the world for providing images
Individual Interferograms to Stacks Piyush Agram Jet Propulsion Laboratory Aug 1, 2016 @UNAVCO Thanks to my colleagues from JPL, Caltech, Stanford University and from all over the world for providing images
Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (InSAR)
 CEE 6100 / CSS 6600 Remote Sensing Fundamentals 1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (InSAR) Adapted from and the ESA Interferometric SAR overview by Rocca et al. http://earth.esa.int/workshops/ers97/program-details/speeches/rocca-et-al/
CEE 6100 / CSS 6600 Remote Sensing Fundamentals 1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (InSAR) Adapted from and the ESA Interferometric SAR overview by Rocca et al. http://earth.esa.int/workshops/ers97/program-details/speeches/rocca-et-al/
DIFFERENTIAL synthetic aperture radar (SAR) interferometry
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 5, NO. 7, JULY 03 449 DEM Error Correction in InSAR Time Series Heresh Fattahi, Student Member, IEEE, and Falk Amelung Abstract We present a mathematical
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 5, NO. 7, JULY 03 449 DEM Error Correction in InSAR Time Series Heresh Fattahi, Student Member, IEEE, and Falk Amelung Abstract We present a mathematical
Playa del Rey, California InSAR Ground Deformation Monitoring
 Document Title Playa del Rey, California InSAR Ground Deformation Monitoring Prepared By: (signature / date) Ref.: RV-14524 Project Manager: xxxxxx July 13, 2009 SUBMITTED TO: ATTN: Mr. Rick Gailing Southern
Document Title Playa del Rey, California InSAR Ground Deformation Monitoring Prepared By: (signature / date) Ref.: RV-14524 Project Manager: xxxxxx July 13, 2009 SUBMITTED TO: ATTN: Mr. Rick Gailing Southern
INSAR DEMS; ACHIEVEMENTS AND BENEFITS
 INSAR DEMS; ACHIEVEMENTS AND BENEFITS Parviz TARIKHI, Iran Key words: remote sensing, InSAR, DEM, deformation measurement, Iran SUMMARY InSAR is a radar technique for combining synthetic aperture radar
INSAR DEMS; ACHIEVEMENTS AND BENEFITS Parviz TARIKHI, Iran Key words: remote sensing, InSAR, DEM, deformation measurement, Iran SUMMARY InSAR is a radar technique for combining synthetic aperture radar
SENTINEL-1 SUPPORT IN THE GAMMA SOFTWARE
 SENTINEL-1 SUPPORT IN THE GAMMA SOFTWARE Urs Wegmüller, Charles Werner, Tazio Strozzi, Andreas Wiesmann, Othmar Frey, and Maurizio Santoro Gamma Remote Sensing, Worbstrasse 225, 3073 Gümligen BE, Switzerland
SENTINEL-1 SUPPORT IN THE GAMMA SOFTWARE Urs Wegmüller, Charles Werner, Tazio Strozzi, Andreas Wiesmann, Othmar Frey, and Maurizio Santoro Gamma Remote Sensing, Worbstrasse 225, 3073 Gümligen BE, Switzerland
Ice surface velocities using SAR
 Ice surface velocities using SAR Thomas Schellenberger, PhD ESA Cryosphere Remote Sensing Training Course 2018 UNIS Longyearbyen, Svalbard 12 th June 2018 thomas.schellenberger@geo.uio.no Outline Synthetic
Ice surface velocities using SAR Thomas Schellenberger, PhD ESA Cryosphere Remote Sensing Training Course 2018 UNIS Longyearbyen, Svalbard 12 th June 2018 thomas.schellenberger@geo.uio.no Outline Synthetic
AIRBORNE synthetic aperture radar (SAR) systems
 IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL 3, NO 1, JANUARY 2006 145 Refined Estimation of Time-Varying Baseline Errors in Airborne SAR Interferometry Andreas Reigber, Member, IEEE, Pau Prats, Student
IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL 3, NO 1, JANUARY 2006 145 Refined Estimation of Time-Varying Baseline Errors in Airborne SAR Interferometry Andreas Reigber, Member, IEEE, Pau Prats, Student
Interferometry Module for Digital Elevation Model Generation
 Interferometry Module for Digital Elevation Model Generation In order to fully exploit processes of the Interferometry Module for Digital Elevation Model generation, the European Space Agency (ESA) has
Interferometry Module for Digital Elevation Model Generation In order to fully exploit processes of the Interferometry Module for Digital Elevation Model generation, the European Space Agency (ESA) has
ON THE USE OF POINT TARGET CHARACTERISTICS IN THE ESTIMATION OF LOW SUBSIDENCE RATES DUE TO GAS EXTRACTION IN GRONINGEN, THE NETHERLANDS
 ON THE USE OF POINT TARGET CHARACTERISTICS IN THE ESTIMATION OF LOW SUBSIDENCE RATES DUE TO GAS EXTRACTION IN GRONINGEN, THE NETHERLANDS ABSTRACT Gini Ketelaar (1), Freek van Leijen (1), Petar Marinkovic
ON THE USE OF POINT TARGET CHARACTERISTICS IN THE ESTIMATION OF LOW SUBSIDENCE RATES DUE TO GAS EXTRACTION IN GRONINGEN, THE NETHERLANDS ABSTRACT Gini Ketelaar (1), Freek van Leijen (1), Petar Marinkovic
IDENTIFICATION OF THE LOCATION PHASE SCREEN OF ERS-ENVISAT PERMANENT SCATTERERS
 IDENTIFICATION OF THE LOCATION PHASE SCREEN OF ERS-ENVISAT PERMANENT SCATTERERS M. Arrigoni (1), C. Colesanti (1), A. Ferretti (2), D. Perissin (1), C. Prati (1), F. Rocca (1) (1) Dipartimento di Elettronica
IDENTIFICATION OF THE LOCATION PHASE SCREEN OF ERS-ENVISAT PERMANENT SCATTERERS M. Arrigoni (1), C. Colesanti (1), A. Ferretti (2), D. Perissin (1), C. Prati (1), F. Rocca (1) (1) Dipartimento di Elettronica
Concept and methodology of SAR Interferometry technique
 Concept and methodology of SAR Interferometry technique March 2016 Differen;al SAR Interferometry Young s double slit experiment - Construc;ve interference (bright) - Destruc;ve interference (dark) http://media-2.web.britannica.com/eb-media/96/96596-004-1d8e9f0f.jpg
Concept and methodology of SAR Interferometry technique March 2016 Differen;al SAR Interferometry Young s double slit experiment - Construc;ve interference (bright) - Destruc;ve interference (dark) http://media-2.web.britannica.com/eb-media/96/96596-004-1d8e9f0f.jpg
ENVI 5 & E3De. The Next Generation of Image Analysis
 ENVI 5 & E3De The Next Generation of Image Analysis The information contained in this document pertains to software products and services that are subject to the controls of the Export Administration Regulations
ENVI 5 & E3De The Next Generation of Image Analysis The information contained in this document pertains to software products and services that are subject to the controls of the Export Administration Regulations
SentiNel Application Platform as InSAR processor for PSI processing with StaMPS
 SentiNel Application Platform as InSAR processor for PSI processing with StaMPS Authors: José Manuel Delgado Blasco Michael Foumelis Date: June 2018 1 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Installation... 3
SentiNel Application Platform as InSAR processor for PSI processing with StaMPS Authors: José Manuel Delgado Blasco Michael Foumelis Date: June 2018 1 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Installation... 3
ERS AND ENVISAT DIFFERENTIAL SAR INTERFEROMETRY FOR SUBSIDENCE MONITORING
 ERS AND ENVISAT DIFFERENTIAL SAR INTERFEROMETRY FOR SUBSIDENCE MONITORING Urs Wegmüller 1, Tazio Strozzi 1, and Luigi Tosi 2 1 Gamma Remote Sensing, Thunstrasse 130, CH-3074 Muri b. Bern, Switzerland Tel:
ERS AND ENVISAT DIFFERENTIAL SAR INTERFEROMETRY FOR SUBSIDENCE MONITORING Urs Wegmüller 1, Tazio Strozzi 1, and Luigi Tosi 2 1 Gamma Remote Sensing, Thunstrasse 130, CH-3074 Muri b. Bern, Switzerland Tel:
A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L23611, doi:10.1029/2004gl021737, 2004 A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers Andrew Hooper,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L23611, doi:10.1029/2004gl021737, 2004 A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers Andrew Hooper,
SMALL SCALE SURFACE DEFORMATION MONITORING IN MINING REGIONS USING DIFFERENTIAL RADAR INTERFEROMETRY.
 Proceedings, 11 th FIG Symposium on Deformation Measurements, Santorini, Greece, 003. SMALL SCALE SURFACE DEFORMATION MONITORING IN MINING REGIONS USING DIFFERENTIAL RADAR INTERFEROMETRY. Ireneusz Baran
Proceedings, 11 th FIG Symposium on Deformation Measurements, Santorini, Greece, 003. SMALL SCALE SURFACE DEFORMATION MONITORING IN MINING REGIONS USING DIFFERENTIAL RADAR INTERFEROMETRY. Ireneusz Baran
DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL GENERATION FROM INTERFEROMETRIC SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADAR USING MULTI-SCALE METHOD
 DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL GENERATION FROM INTERFEROMETRIC SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADAR USING MULTI-SCALE METHOD Jung Hum Yu 1, Linlin Ge, Chris Rizos School of Surveying and Spatial Information Systems University
DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL GENERATION FROM INTERFEROMETRIC SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADAR USING MULTI-SCALE METHOD Jung Hum Yu 1, Linlin Ge, Chris Rizos School of Surveying and Spatial Information Systems University
GMES TERRAFIRMA: VALIDATION OF PSI FOR USERS RESULTS OF THE PROVENCE INTER-COMPARISON
 GMES TERRAFIRMA: VALIDATION OF PSI FOR USERS RESULTS OF THE PROVENCE INTER-COMPARISON Crosetto, M. (1), Agudo, M. (1), Capes, R. (2), Marsh, S. (3) (1) Institute of Geomatics, Parc Mediterrani de la Tecnologia,
GMES TERRAFIRMA: VALIDATION OF PSI FOR USERS RESULTS OF THE PROVENCE INTER-COMPARISON Crosetto, M. (1), Agudo, M. (1), Capes, R. (2), Marsh, S. (3) (1) Institute of Geomatics, Parc Mediterrani de la Tecnologia,
An empirical model for interferometric coherence
 An empirical model for interferometric coherence Chaabane F. a, Tupin F. b and Maître H. b a URISA-SUP COM, 3.5 route de Raoued, 283 Ariana, Tunisie b GET-Télécom-Paris - CNRS URA 82, 46 rue Barrault,
An empirical model for interferometric coherence Chaabane F. a, Tupin F. b and Maître H. b a URISA-SUP COM, 3.5 route de Raoued, 283 Ariana, Tunisie b GET-Télécom-Paris - CNRS URA 82, 46 rue Barrault,
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
SENTINEL-1 PRECISE ORBIT CALIBRATION AND VALIDATION
 SENTINEL-1 PRECISE ORBIT CALIBRATION AND VALIDATION Andrea Monti Guarnieri, Simone Mancon, and Stefano Tebaldini Politecnico di Milano, Italy ABSTRACT In this paper, we propose a model-based procedure
SENTINEL-1 PRECISE ORBIT CALIBRATION AND VALIDATION Andrea Monti Guarnieri, Simone Mancon, and Stefano Tebaldini Politecnico di Milano, Italy ABSTRACT In this paper, we propose a model-based procedure
SEA SURFACE SPEED FROM TERRASAR-X ATI DATA
 SEA SURFACE SPEED FROM TERRASAR-X ATI DATA Matteo Soccorsi (1) and Susanne Lehner (1) (1) German Aerospace Center, Remote Sensing Technology Institute, 82234 Weßling, Germany, Email: matteo.soccorsi@dlr.de
SEA SURFACE SPEED FROM TERRASAR-X ATI DATA Matteo Soccorsi (1) and Susanne Lehner (1) (1) German Aerospace Center, Remote Sensing Technology Institute, 82234 Weßling, Germany, Email: matteo.soccorsi@dlr.de
Dual-Platform GMTI: First Results With The TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X Constellation
 Dual-Platform GMTI: First Results With The TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X Constellation Stefan V. Baumgartner, Gerhard Krieger Microwaves and Radar Institute, German Aerospace Center (DLR) Muenchner Strasse 20, 82234
Dual-Platform GMTI: First Results With The TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X Constellation Stefan V. Baumgartner, Gerhard Krieger Microwaves and Radar Institute, German Aerospace Center (DLR) Muenchner Strasse 20, 82234
PolSARpro v4.03 Forest Applications
 PolSARpro v4.03 Forest Applications Laurent Ferro-Famil Lecture on polarimetric SAR Theory and applications to agriculture & vegetation Thursday 19 April, morning Pol-InSAR Tutorial Forest Application
PolSARpro v4.03 Forest Applications Laurent Ferro-Famil Lecture on polarimetric SAR Theory and applications to agriculture & vegetation Thursday 19 April, morning Pol-InSAR Tutorial Forest Application
DETECTING REGULAR PATTERNS IN URBAN PS SETS
 DETECTING REGULAR PATTERNS IN URBAN PS SETS Alexander Schunert, Uwe Soergel Institute of Photogrammetry and GeoInformation, Leibniz Universität Hannover, Germany ABSTRACT The analysis of SAR data stacks
DETECTING REGULAR PATTERNS IN URBAN PS SETS Alexander Schunert, Uwe Soergel Institute of Photogrammetry and GeoInformation, Leibniz Universität Hannover, Germany ABSTRACT The analysis of SAR data stacks
Mission Status and Data Availability: TanDEM-X
 Mission Status and Data Availability: TanDEM-X Irena Hajnsek, Thomas Busche, Alberto Moreira & TanDEM-X Team Microwaves and Radar Institute, German Aerospace Center irena.hajnsek@dlr.de 26-Jan-2009 Outline
Mission Status and Data Availability: TanDEM-X Irena Hajnsek, Thomas Busche, Alberto Moreira & TanDEM-X Team Microwaves and Radar Institute, German Aerospace Center irena.hajnsek@dlr.de 26-Jan-2009 Outline
Sentinel-1 InSAR AP workshop
 Sentinel-1 InSAR AP workshop Sentinel-1 InSAR progress and experience at GAMMA U. Wegmüller, C. Werner, A. Wiesmann, T. Strozzi Gamma Remote Sensing AG - Progress made since S1A Expert Users meeting at
Sentinel-1 InSAR AP workshop Sentinel-1 InSAR progress and experience at GAMMA U. Wegmüller, C. Werner, A. Wiesmann, T. Strozzi Gamma Remote Sensing AG - Progress made since S1A Expert Users meeting at
Multipass/Multiview Interferometric SAR
 Gianfranco Fornaro National Research Council (CNR) Institute for Electromagnetic Sensing of the Environment (IREA) Via Diocleziano, 328 I-80124 Napoli ITALY fornaro.g@irea.cnr.it ABSTRACT Synthetic Aperture
Gianfranco Fornaro National Research Council (CNR) Institute for Electromagnetic Sensing of the Environment (IREA) Via Diocleziano, 328 I-80124 Napoli ITALY fornaro.g@irea.cnr.it ABSTRACT Synthetic Aperture
Interferometric processing. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens Why InSAR processing? extracting three-dimensional information out of a radar image pair covering the same area digital elevation model change detection 2 Processing chain 3 Processing chain
Rüdiger Gens Why InSAR processing? extracting three-dimensional information out of a radar image pair covering the same area digital elevation model change detection 2 Processing chain 3 Processing chain
ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 The PSIG procedure to Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) using X-band and C-band Sentinel-1 data María Cuevas-González* a, Núria Devanthéry a, Michele Crosetto a, Oriol Monserrat a, Bruno Crippa
The PSIG procedure to Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) using X-band and C-band Sentinel-1 data María Cuevas-González* a, Núria Devanthéry a, Michele Crosetto a, Oriol Monserrat a, Bruno Crippa
DEFORMATION MONITORING USING INSAR AND ARTIFICIAL REFLECTORS
 DEFORMATION MONITORING USING INSAR AND ARTIFICIAL REFLECTORS Ivana, HLAVÁČOVÁ 1, Lena, HALOUNOVÁ 1, Květoslava, SVOBODOVÁ 1 1 Department of Mapping and Cartography, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Czech
DEFORMATION MONITORING USING INSAR AND ARTIFICIAL REFLECTORS Ivana, HLAVÁČOVÁ 1, Lena, HALOUNOVÁ 1, Květoslava, SVOBODOVÁ 1 1 Department of Mapping and Cartography, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Czech
Do It Yourself 8. Polarization Coherence Tomography (P.C.T) Training Course
 Do It Yourself 8 Polarization Coherence Tomography (P.C.T) Training Course 1 Objectives To provide a self taught introduction to Polarization Coherence Tomography (PCT) processing techniques to enable
Do It Yourself 8 Polarization Coherence Tomography (P.C.T) Training Course 1 Objectives To provide a self taught introduction to Polarization Coherence Tomography (PCT) processing techniques to enable
BY VIRTUE of its high precision and wide coverage,
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 55, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2017 1053 On the Accuracy of Topographic Residuals Retrieved by MTInSAR Yanan Du, Lei Zhang, Guangcai Feng, Zhong Lu, and Qian
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 55, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2017 1053 On the Accuracy of Topographic Residuals Retrieved by MTInSAR Yanan Du, Lei Zhang, Guangcai Feng, Zhong Lu, and Qian
FIRST RESULTS OF THE ALOS PALSAR VERIFICATION PROCESSOR
 FIRST RESULTS OF THE ALOS PALSAR VERIFICATION PROCESSOR P. Pasquali (1), A. Monti Guarnieri (2), D. D Aria (3), L. Costa (3), D. Small (4), M. Jehle (4) and B. Rosich (5) (1) sarmap s.a., Cascine di Barico,
FIRST RESULTS OF THE ALOS PALSAR VERIFICATION PROCESSOR P. Pasquali (1), A. Monti Guarnieri (2), D. D Aria (3), L. Costa (3), D. Small (4), M. Jehle (4) and B. Rosich (5) (1) sarmap s.a., Cascine di Barico,
SAR IMAGE PROCESSING FOR CROP MONITORING
 SAR IMAGE PROCESSING FOR CROP MONITORING Anne Orban, Dominique Derauw, and Christian Barbier Centre Spatial de Liège Université de Liège cbarbier@ulg.ac.be Agriculture and Vegetation at a Local Scale Habay-La-Neuve,
SAR IMAGE PROCESSING FOR CROP MONITORING Anne Orban, Dominique Derauw, and Christian Barbier Centre Spatial de Liège Université de Liège cbarbier@ulg.ac.be Agriculture and Vegetation at a Local Scale Habay-La-Neuve,
ARTIFICIAL SCATTERERS FOR S.A.R. INTERFEROMETRY
 ARTIFICIAL SCATTERERS FOR S.A.R. INTERFEROMETRY Parizzi A. (1), Perissin D. (1), Prati C. (1), Rocca F. (1) (1) Politecnico di Milano, Via Ponzio 34/5, 20133 Milano, Italy ABSTRACT. The evaluation of land
ARTIFICIAL SCATTERERS FOR S.A.R. INTERFEROMETRY Parizzi A. (1), Perissin D. (1), Prati C. (1), Rocca F. (1) (1) Politecnico di Milano, Via Ponzio 34/5, 20133 Milano, Italy ABSTRACT. The evaluation of land
ALOS PALSAR VERIFICATION PROCESSOR
 ALOS PALSAR VERIFICATION PROCESSOR P. Pasquali (1), A. Monti Guarnieri (2), D. D Aria (3), L. Costa (3), D. Small (4), M. Jehle (4) and B. Rosich (5) (1) sarmap s.a., Cascine di Barico, 6989 Purasca, Switzerland,
ALOS PALSAR VERIFICATION PROCESSOR P. Pasquali (1), A. Monti Guarnieri (2), D. D Aria (3), L. Costa (3), D. Small (4), M. Jehle (4) and B. Rosich (5) (1) sarmap s.a., Cascine di Barico, 6989 Purasca, Switzerland,
