Ecological modelling with Simile
|
|
|
- Dwight Green
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Ecological modelling with Simile Lecture 4 Part A: Conditional submodels Part B: Association submodels Robert Muetzelfeldt Jasper Taylor Jonathan Massheder Feb 2006
2 2 Part A Conditional submodels
3 3 What are conditional submodels used for? A particular subsystem that may or may not be present e.g.: In different instances (forest on land) at different times (seasonal plants) for different conditions (plankton in ocean)
4 4 How do we set one up? A submodel with a condition component Square box with? on Equation is boolean, like what comes after if Submodel can have dimensions, but must not be a population Diagram has notation
5 5 Using variable-membership models Influence coming out gets 'list' dimensions, so: cannot be used directly use a cumulative function, such as sum(...) don't take it out of lots of nested submodels at once
6 6 Part B Association submodels
7 7 What are association submodels used for? Interactions that depend on proximity, similarity, reference Move values between instances in variablemembership submodels Speed up calculations of fixed interactions
8 8 Examples of associations Neighbourhood, land use change Proximity: shading, seeding, grazing Fixed association: parenthood Social constructs: tenure, territory, mating
9 More examples of associations 9
10 10 Example 1: Field ownership We want to model a collection of farmers owning a collection of fields. Each field is owned by one farmer; one farmer can own several fields. Information is to be transferred from a field to the farner that owns it: e.g. the area of the field, the yield obtained from it, etc.
11 11 Field ownership: step 1 Create the submodels representing the farmers and fields ID = index(1) ownerid = int(rand_const(0,10))+1 area = 1
12 12 Field ownership: step 2 Add the ownership submodel.
13 13 Field ownership: step 3 Create the association between farmers and fields cond1 = ID == ownerid
14 14 Field ownership: step 4 Work out the total area per farmer Farmer/total area = sum({area}) (to farmer in owner) Ownership/area = Field/area (from Field in owned)
15 Example 2: Water flow between soil layers rain Layer 1 interflow 1 Layer 2 interflow 2 Layer 3 interflow 3 Layer 4 drainage 15 Problem: to simulate soil water dynamics Illustrates the use of Simile for 1-D spatial modelling Implements the concept of the above association between Layers
16 Water flow between soil layers: step 1 1) Create the compartments layer_number = index(1) water = 0 Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 Layer 4 16
17 Water flow between soil layers: step 2 Add in the flows outflow = 0.2*water Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 Layer 4 17
18 Water flow between soil layers: step 3 Create the 'above' association between layers above? = layer_number-layer_number_0 Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 Layer 4 18
19 Water flow between soil layers: step 4 Create a variable to link the flows Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 Layer 4 19
20 Water flow between soil layers: step 5 20 Link the variable to the outflow of the upper level interflow = outflow (from Layer in upper) Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 Layer 4
21 Water flow between soil layers: step 6 Link the variable to the inflow of the lower level inflow = interflow_0 (to Layer in lower) Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 Layer 4 21
22 Water flow between soil layers: step 7 Add in the rain flow to the top layer rain Layer 1 rain = if layer_number==1 and time(1)<10 then 10 else 0 interflow 1 Layer 2 interflow 2 Layer 3 interflow 3 Layer 4 drainage 22
23 23 Example 3: Land-use change Problem: to simulate land-use change at the forest margin Illustrates the use of conditional submodels: the forest and crop submodels may or may not exist in a patch Implements the concept of the next-to association between patches Illustrates the use of Simile for spatial modelling
24 24 Land-use change: step 1 Create a multiple instance submodel so as each plot can have a different position column = floor((index(1)-1)/10)+1 row = fmod(index(1)-1,10)+1
25 25 Land-use change: step 2 Specify the types of land that will be used
26 26 Land-use change: step 3 Add an existence condition to the 2 land types
27 27 Land-use change: step 4 Create a compartment that defines the state of a particular plot state = if row < 3 then 2 else 1 exists/forest = state == 1 exists/crop = state == 2
28 28 Land-use change: step 5 Set the conditions for a change of state change_to_crop = if state==1 and sum({volume})>rand_var(250,400) and n_crop_neighbour > 1.9 then 1 else 0 change to forest = if state==2 and sum({time_under_crop})>100 then 1 else 0
29 29 Land-use change: step 6 Make a way of changing the state of a plot change_state = if change_to_crop == 1 then 1/dt(1) elseif change_to_forest == 1 then -1/dt(1) else 0
30 30 Land-use change: step 7 Add an association submodel that exists if any 2 plots of land are next to each other condition = not(column == column_0 and row == row_0) and abs(column - column_0) <1.5 and abs(row - row_0) <1.5
31 31 Land-use change: step 8 Complete the model by working out how many crop neighbours a particular plot has. crop_neighbour = if state == 2 then 1 else 0 n_crop_neighbour = sum({crop neighbour_0})
32 32 Land-use change: results crop forest
Ecological modelling with Simile
 1 Ecological modelling with Simile Lecture 1 Part A: Introduction to ecological modelling Part B: Introduction to Simile Part C: System Dynamics in Simile Robert Muetzelfeldt Jasper Taylor Jonathan Massheder
1 Ecological modelling with Simile Lecture 1 Part A: Introduction to ecological modelling Part B: Introduction to Simile Part C: System Dynamics in Simile Robert Muetzelfeldt Jasper Taylor Jonathan Massheder
Environmental modelling in Simile Declarative modelling MultiGuise Model transformation. Robert Muetzelfeldt
 Environmental modelling in Simile Declarative modelling MultiGuise Model transformation Robert Muetzelfeldt robertm@ed.ac.uk 1 Ecosystem energy flow 2 Population dynamics: simple population 3 Population
Environmental modelling in Simile Declarative modelling MultiGuise Model transformation Robert Muetzelfeldt robertm@ed.ac.uk 1 Ecosystem energy flow 2 Population dynamics: simple population 3 Population
The Simile visual modelling environment
 Europ. J. Agronomy 18 (2003) 345/358 www.elsevier.com/locate/eja The Simile visual modelling environment Robert Muetzelfeldt, Jon Massheder The University of Edinburgh, Institute of Ecology and Resource
Europ. J. Agronomy 18 (2003) 345/358 www.elsevier.com/locate/eja The Simile visual modelling environment Robert Muetzelfeldt, Jon Massheder The University of Edinburgh, Institute of Ecology and Resource
This document will cover some of the key features available only in SMS Advanced, including:
 Key Differences between SMS Basic and SMS Advanced SMS Advanced includes all of the same functionality as the SMS Basic Software as well as adding numerous tools that provide management solutions for multiple
Key Differences between SMS Basic and SMS Advanced SMS Advanced includes all of the same functionality as the SMS Basic Software as well as adding numerous tools that provide management solutions for multiple
Introduction to Modeling with Simile
 Introduction to Modeling with Simile This is an introduction to using Simile for building and analysing a model. Simile is a visual modeling tool. It allows you to draw a conceptual model diagram, and
Introduction to Modeling with Simile This is an introduction to using Simile for building and analysing a model. Simile is a visual modeling tool. It allows you to draw a conceptual model diagram, and
Attribute Accuracy. Quantitative accuracy refers to the level of bias in estimating the values assigned such as estimated values of ph in a soil map.
 Attribute Accuracy Objectives (Entry) This basic concept of attribute accuracy has been introduced in the unit of quality and coverage. This unit will teach a basic technique to quantify the attribute
Attribute Accuracy Objectives (Entry) This basic concept of attribute accuracy has been introduced in the unit of quality and coverage. This unit will teach a basic technique to quantify the attribute
1) As a logical statement, is 1 considered true or false in MATLAB? Explain your answer.
 ENGR 1181 Midterm 2+ Review Note: This practice material does not contain actual test questions or represent the format of the final. The first 20 questions should be completed WITHOUT using MATLAB. This
ENGR 1181 Midterm 2+ Review Note: This practice material does not contain actual test questions or represent the format of the final. The first 20 questions should be completed WITHOUT using MATLAB. This
The Future Evolution of APEX & SWAT Robin Taylor, Jaehak Jeong, Michael White & Jeff Arnold
 The Future Evolution of APEX & SWAT Robin Taylor, Jaehak Jeong, Michael White & Jeff Arnold Texas A&M University, Blackland Research Center & Grassland Soil & Water Laboratory, Temple, Texas Why Rebuild
The Future Evolution of APEX & SWAT Robin Taylor, Jaehak Jeong, Michael White & Jeff Arnold Texas A&M University, Blackland Research Center & Grassland Soil & Water Laboratory, Temple, Texas Why Rebuild
ANNEX IX. Technical guidance on LPIS population for LPIS QA inspection (TG population)
 DS/CDP/2015/07-REV2 part A LPIS Quality Assurance Framework Based on IES/H04/2016/21736 ANNEX IX Technical guidance on LPIS population for LPIS QA inspection (TG population) LPIS executable test suite,
DS/CDP/2015/07-REV2 part A LPIS Quality Assurance Framework Based on IES/H04/2016/21736 ANNEX IX Technical guidance on LPIS population for LPIS QA inspection (TG population) LPIS executable test suite,
METAPOPULATION DYNAMICS
 16 METAPOPULATION DYNAMICS Objectives Determine how extinction and colonization parameters influence metapopulation dynamics. Determine how the number of patches in a system affects the probability of
16 METAPOPULATION DYNAMICS Objectives Determine how extinction and colonization parameters influence metapopulation dynamics. Determine how the number of patches in a system affects the probability of
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling
 Spatial Analysis in GIS (cont d) GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling - the basic types of analysis that can be accomplished with a GIS are outlined in The Esri Guide to GIS Analysis
Spatial Analysis in GIS (cont d) GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling - the basic types of analysis that can be accomplished with a GIS are outlined in The Esri Guide to GIS Analysis
GIS: Raster Analysis
 GIS: Raster Analysis Ts (K) High : 311 Low : 299 500 Meters Albedo G / Rn High : 0.35 High : 0.50 Low : 0.03 Low : 0.10 1 Raster analysis: Outline Raster analysis applications Map algebra Local functions
GIS: Raster Analysis Ts (K) High : 311 Low : 299 500 Meters Albedo G / Rn High : 0.35 High : 0.50 Low : 0.03 Low : 0.10 1 Raster analysis: Outline Raster analysis applications Map algebra Local functions
ANNEX IX. Technical guidance on LPIS population for LPIS QA inspection (TG population)
 DS/CDP/2015/07-REV3 part A LPIS Quality Assurance Framework Based on IES/H04/2016/21736 ANNEX IX Technical guidance on LPIS population for LPIS QA inspection (TG population) LPIS executable test suite,
DS/CDP/2015/07-REV3 part A LPIS Quality Assurance Framework Based on IES/H04/2016/21736 ANNEX IX Technical guidance on LPIS population for LPIS QA inspection (TG population) LPIS executable test suite,
Epidemic spreading on networks
 Epidemic spreading on networks Due date: Sunday October 25th, 2015, at 23:59. Always show all the steps which you made to arrive at your solution. Make sure you answer all parts of each question. Always
Epidemic spreading on networks Due date: Sunday October 25th, 2015, at 23:59. Always show all the steps which you made to arrive at your solution. Make sure you answer all parts of each question. Always
Measure the Perimeter of Polygons Over a Surface. Operations. What Do I Need?
 Measure the Perimeter of Polygons Over a Surface Operations What Do I Need? Incremental Frontage Score To measure the perimeter of polygons over a surface you need to have two input map layers. The first
Measure the Perimeter of Polygons Over a Surface Operations What Do I Need? Incremental Frontage Score To measure the perimeter of polygons over a surface you need to have two input map layers. The first
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
NCAR SUMMER COLLOQUIUM: July 24-Aug.6, 2011 Boulder, Colorado, USA. General Large Area Crop Model (GLAM) TUTORIAL
 NCAR SUMMER COLLOQUIUM: July 24-Aug.6, 2011 Boulder, Colorado, USA General Large Area Crop Model (GLAM) TUTORIAL Gizaw Mengistu, Dept. of Physics, Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia This document provides
NCAR SUMMER COLLOQUIUM: July 24-Aug.6, 2011 Boulder, Colorado, USA General Large Area Crop Model (GLAM) TUTORIAL Gizaw Mengistu, Dept. of Physics, Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia This document provides
Lecture 8. Vector Data Analyses. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lecture 8 Vector Data Analyses Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Vector Data Analysis Vector data analysis involves one or a combination of: Measuring
Lecture 8 Vector Data Analyses Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Vector Data Analysis Vector data analysis involves one or a combination of: Measuring
Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS
 Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS CE 412/512 Spring 2017 Introduction The intent of this exercise is to introduce you to the structure and some of the functions of the HEC-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS),
Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS CE 412/512 Spring 2017 Introduction The intent of this exercise is to introduce you to the structure and some of the functions of the HEC-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS),
Introduction to GIS. Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 9/24/2015. R. Khosla Fall Semester The real world. What in the world is GIS?
 Introduction to GIS Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 What in the world is GIS? GIS is simultaneously the telescope, the microscope, the computer and the Xerox machine of regional analysis and synthesis
Introduction to GIS Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 What in the world is GIS? GIS is simultaneously the telescope, the microscope, the computer and the Xerox machine of regional analysis and synthesis
GIS Data Models. 4/9/ GIS Data Models
 GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
Lecture 3 (02/06, 02/08): Condition Statements Decision, Operations & Information Technologies Robert H. Smith School of Business Spring, 2017
 Lecture 3 (02/06, 02/08): Condition Statements Decision, Operations & Information Technologies Robert H. Smith School of Business Spring, 2017 K. Zhang BMGT 404 The modulus operator It works on integers
Lecture 3 (02/06, 02/08): Condition Statements Decision, Operations & Information Technologies Robert H. Smith School of Business Spring, 2017 K. Zhang BMGT 404 The modulus operator It works on integers
IP SWITCHES. 1. Receive INFLOWS DATA IN
 IP SWITCHES 1. Receive INFLOWS IP SWITCHES 1. Receive INFLOWS 2. BUFFER & Route IP SWITCHES 1. Receive INFLOWS 2. BUFFER & Route 3. Transmit OUTFLOWS IP SWITCHES 1. Receive INFLOWS 2. BUFFER & Route 3.
IP SWITCHES 1. Receive INFLOWS IP SWITCHES 1. Receive INFLOWS 2. BUFFER & Route IP SWITCHES 1. Receive INFLOWS 2. BUFFER & Route 3. Transmit OUTFLOWS IP SWITCHES 1. Receive INFLOWS 2. BUFFER & Route 3.
Watershed Modeling HEC-HMS Interface
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to set up a basic HEC-HMS model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-HMS model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to set up a basic HEC-HMS model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-HMS model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic
Landscape Ecology. Lab 2: Indices of Landscape Pattern
 Introduction In this lab exercise we explore some metrics commonly used to summarize landscape pattern. You will begin with a presettlement landscape entirely covered in forest. You will then develop this
Introduction In this lab exercise we explore some metrics commonly used to summarize landscape pattern. You will begin with a presettlement landscape entirely covered in forest. You will then develop this
Drainage Design Exercise. Computer-based Subsurface Design
 Drainage Design Exercise Computer-based Subsurface Design OBJECTIVES Introduction of the LANDRAIN software: a program for subsurface drainage design. During last year's cropping season, a farmer, Mr. Igro
Drainage Design Exercise Computer-based Subsurface Design OBJECTIVES Introduction of the LANDRAIN software: a program for subsurface drainage design. During last year's cropping season, a farmer, Mr. Igro
Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3
 Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3 Practical: Creating and Editing Shapefiles Using Straight, AutoComplete and Cut Polygon Tools Use ArcCatalog to copy data files from:
Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3 Practical: Creating and Editing Shapefiles Using Straight, AutoComplete and Cut Polygon Tools Use ArcCatalog to copy data files from:
Data Mining on Agriculture Data using Neural Networks
 Data Mining on Agriculture Data using Neural Networks June 26th, 28 Outline Data Details Data Overview precision farming cheap data collection GPS-based technology divide field into small-scale parts treat
Data Mining on Agriculture Data using Neural Networks June 26th, 28 Outline Data Details Data Overview precision farming cheap data collection GPS-based technology divide field into small-scale parts treat
Finding Perimeter and Area with Coordinates
 Finding Perimeter and Area with Coordinates When a figure is on a coordinate plane and no measurements are given, the distance formula can be used to determine the measurements necessary to find the area
Finding Perimeter and Area with Coordinates When a figure is on a coordinate plane and no measurements are given, the distance formula can be used to determine the measurements necessary to find the area
GateKeeper Mapping Creating Zone Layers & Utilising the Grid Generator GateKeeper Version 3.5 February 2015
 GateKeeper Mapping Creating Zone Layers & Utilising the Grid Generator GateKeeper Version 3.5 February 2015 Contents Introduction... 2 Grid Generator Requirements... 2 Creating a Zone Layer... 3 Drawing
GateKeeper Mapping Creating Zone Layers & Utilising the Grid Generator GateKeeper Version 3.5 February 2015 Contents Introduction... 2 Grid Generator Requirements... 2 Creating a Zone Layer... 3 Drawing
Simplification of Boolean Functions
 COM111 Introduction to Computer Engineering (Fall 2006-2007) NOTES 5 -- page 1 of 5 Introduction Simplification of Boolean Functions You already know one method for simplifying Boolean expressions: Boolean
COM111 Introduction to Computer Engineering (Fall 2006-2007) NOTES 5 -- page 1 of 5 Introduction Simplification of Boolean Functions You already know one method for simplifying Boolean expressions: Boolean
Points Addressed in this Lecture. Standard form of Boolean Expressions. Lecture 4: Logic Simplication & Karnaugh Map
 Points Addressed in this Lecture Lecture 4: Logic Simplication & Karnaugh Map Professor Peter Cheung Department of EEE, Imperial College London Standard form of Boolean Expressions Sum-of-Products (SOP),
Points Addressed in this Lecture Lecture 4: Logic Simplication & Karnaugh Map Professor Peter Cheung Department of EEE, Imperial College London Standard form of Boolean Expressions Sum-of-Products (SOP),
Computational Finance
 Computational Finance Introduction to Matlab Marek Kolman Matlab program/programming language for technical computing particularly for numerical issues works on matrix/vector basis usually used for functional
Computational Finance Introduction to Matlab Marek Kolman Matlab program/programming language for technical computing particularly for numerical issues works on matrix/vector basis usually used for functional
(Refer Slide Time: 0:51)
 Introduction to Remote Sensing Dr. Arun K Saraf Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee Lecture 16 Image Classification Techniques Hello everyone welcome to 16th lecture in
Introduction to Remote Sensing Dr. Arun K Saraf Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee Lecture 16 Image Classification Techniques Hello everyone welcome to 16th lecture in
Connecting 1D and 2D Domains
 Connecting 1D and 2D Domains XP Solutions has a long history of Providing original, high-performing software solutions Leading the industry in customer service and support Educating our customers to be
Connecting 1D and 2D Domains XP Solutions has a long history of Providing original, high-performing software solutions Leading the industry in customer service and support Educating our customers to be
GIS and Forest Engineering Applications
 FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 3 This week s topics Clip and erase processes Chapter 6 Selecting landscape features in a GIS Chapter 5 GIS Lab3: Determining land use and ownership
FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 3 This week s topics Clip and erase processes Chapter 6 Selecting landscape features in a GIS Chapter 5 GIS Lab3: Determining land use and ownership
Member Online Data Management Tool. Instruction Handbook
 Subwatershed Program P.O. Box 1205, Willows, California 95988 - Phone (530) 934-8036 - Email info@cgsubwatershed.com Member Online Data Management Tool Instruction Handbook V3-Condensed (2018 Reporting
Subwatershed Program P.O. Box 1205, Willows, California 95988 - Phone (530) 934-8036 - Email info@cgsubwatershed.com Member Online Data Management Tool Instruction Handbook V3-Condensed (2018 Reporting
Dynamic Programming. Other Topics
 Dynamic Programming Other Topics 1 Objectives To explain the difference between discrete and continuous dynamic programming To discuss about multiple state variables To discuss the curse of dimensionality
Dynamic Programming Other Topics 1 Objectives To explain the difference between discrete and continuous dynamic programming To discuss about multiple state variables To discuss the curse of dimensionality
GTS. midas GTS Advanced Webinar. Date: June 5, 2012 Topic: General Use of midas GTS (Part II) Presenter: Vipul Kumar
 midas GTS Advanced Webinar Date: June 5, 2012 Topic: General Use of midas GTS (Part II) Presenter: Vipul Kumar Bridging Your Innovations to Realities GTS MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd. [1/30] Contents:
midas GTS Advanced Webinar Date: June 5, 2012 Topic: General Use of midas GTS (Part II) Presenter: Vipul Kumar Bridging Your Innovations to Realities GTS MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd. [1/30] Contents:
New Features in the Software
 New Features in the Software Eland Afuang Client Service Manager Innovyze s Melbourne User Group 24 th November 2016 Marriott Hotel InfoWorks ICM Version 6.5 November 2015 36 new features Version 7.0 May
New Features in the Software Eland Afuang Client Service Manager Innovyze s Melbourne User Group 24 th November 2016 Marriott Hotel InfoWorks ICM Version 6.5 November 2015 36 new features Version 7.0 May
Arithmetic expressions can be typed into Maple using the regular operators:
 Basic arithmetic Arithmetic expressions can be typed into Maple using the regular operators: (type "3 + 4" and then press "[Enter]" to start the evaluation of the expression) 7 (1.1) 5 (1.2) 21 (1.3) (type
Basic arithmetic Arithmetic expressions can be typed into Maple using the regular operators: (type "3 + 4" and then press "[Enter]" to start the evaluation of the expression) 7 (1.1) 5 (1.2) 21 (1.3) (type
Classification of Soil and Vegetation by Fuzzy K-means Classification and Particle Swarm Optimization
 Classification of Soil and Vegetation by Fuzzy K-means Classification and Particle Swarm Optimization M. Chapron ETIS, ENSEA, UCP, CNRS, 6 avenue du ponceau 95014 Cergy-Pontoise, France chapron@ensea.fr
Classification of Soil and Vegetation by Fuzzy K-means Classification and Particle Swarm Optimization M. Chapron ETIS, ENSEA, UCP, CNRS, 6 avenue du ponceau 95014 Cergy-Pontoise, France chapron@ensea.fr
GIS in the Social and Natural Sciences. Last Lecture. Today s Outline 5/14/2017. GEOG 4110/5100 Special Topics in Geography
 GEOG 4110/5100 Special Topics in Geography GIS in the Social and Natural Sciences Working with Vector Data in a GIS Last Lecture We talked about the main types of vector data models (CDS, TDS, TIN, Networks)
GEOG 4110/5100 Special Topics in Geography GIS in the Social and Natural Sciences Working with Vector Data in a GIS Last Lecture We talked about the main types of vector data models (CDS, TDS, TIN, Networks)
Exercise 2-1 Cartographic Modeling
 Exercise 2-1 Cartographic Modeling A cartographic model is a graphic representation of the data and analytical procedures used in a study. Its purpose is to help the analyst organize and structure the
Exercise 2-1 Cartographic Modeling A cartographic model is a graphic representation of the data and analytical procedures used in a study. Its purpose is to help the analyst organize and structure the
EE 301 Signals & Systems I MATLAB Tutorial with Questions
 EE 301 Signals & Systems I MATLAB Tutorial with Questions Under the content of the course EE-301, this semester, some MATLAB questions will be assigned in addition to the usual theoretical questions. This
EE 301 Signals & Systems I MATLAB Tutorial with Questions Under the content of the course EE-301, this semester, some MATLAB questions will be assigned in addition to the usual theoretical questions. This
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY
 EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 2015 MODULE 4 : Modelling experimental data Time allowed: Three hours Candidates should answer FIVE questions. All questions carry equal
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 2015 MODULE 4 : Modelling experimental data Time allowed: Three hours Candidates should answer FIVE questions. All questions carry equal
RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O
 RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O TOPICS COVERED Spatial Analyst basics Raster / Vector conversion Raster data
RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O TOPICS COVERED Spatial Analyst basics Raster / Vector conversion Raster data
LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS
 LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Computers and GIS cannot directly be applied to the real world: a data gathering step comes first. Digital computers operate in numbers and characters held internally as binary
LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Computers and GIS cannot directly be applied to the real world: a data gathering step comes first. Digital computers operate in numbers and characters held internally as binary
ÇANKAYA UNIVERSITY Department of Industrial Engineering SPRING SEMESTER
 TECHNIQUES FOR CONTINOUS SPACE LOCATION PROBLEMS Continuous space location models determine the optimal location of one or more facilities on a two-dimensional plane. The obvious disadvantage is that the
TECHNIQUES FOR CONTINOUS SPACE LOCATION PROBLEMS Continuous space location models determine the optimal location of one or more facilities on a two-dimensional plane. The obvious disadvantage is that the
Multivariate Normal Random Numbers
 Multivariate Normal Random Numbers Revised: 10/11/2017 Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Analysis Options... 4 Analysis Summary... 5 Matrix Plot... 6 Save Results... 8 Calculations... 9 Summary This procedure
Multivariate Normal Random Numbers Revised: 10/11/2017 Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Analysis Options... 4 Analysis Summary... 5 Matrix Plot... 6 Save Results... 8 Calculations... 9 Summary This procedure
Loops and Files. Chapter 04 MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz
 Loops and Files Chapter 04 MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Chapter Topics o The Increment and Decrement Operators o The while Loop o Shorthand Assignment Operators o The do-while
Loops and Files Chapter 04 MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Chapter Topics o The Increment and Decrement Operators o The while Loop o Shorthand Assignment Operators o The do-while
More About Factoring Trinomials
 Section 6.3 More About Factoring Trinomials 239 83. x 2 17x 70 x 7 x 10 Width of rectangle: Length of rectangle: x 7 x 10 Width of shaded region: 7 Length of shaded region: x 10 x 10 Area of shaded region:
Section 6.3 More About Factoring Trinomials 239 83. x 2 17x 70 x 7 x 10 Width of rectangle: Length of rectangle: x 7 x 10 Width of shaded region: 7 Length of shaded region: x 10 x 10 Area of shaded region:
Computational Photonics, Summer Term 2012, Abbe School of Photonics, FSU Jena, Prof. Thomas Pertsch
 Computational Photonics Seminar 02, 30 April 2012 Programming in MATLAB controlling of a program s flow of execution branching loops loop control several programming tasks 1 Programming task 1 Plot the
Computational Photonics Seminar 02, 30 April 2012 Programming in MATLAB controlling of a program s flow of execution branching loops loop control several programming tasks 1 Programming task 1 Plot the
AGRICULTURE CORRECTION SERVICES
 AGRICULTURE CORRECTION SERVICES NEW! CENterPoint RTX The new Trimble CenterPoint RTX Correction Service delivers GNSS enabled, repeatable 1.5-inch (4 cm) corrections to your receiver anywhere in the world.
AGRICULTURE CORRECTION SERVICES NEW! CENterPoint RTX The new Trimble CenterPoint RTX Correction Service delivers GNSS enabled, repeatable 1.5-inch (4 cm) corrections to your receiver anywhere in the world.
Available Map Views & Dash View Screen
 Singulation: Displays meter performance. Identifies the percentage of seeds properly singulated by your meters. Contributing factors to this value include: Speed, Good Ride, Seed Size, Seed Shape, Meter
Singulation: Displays meter performance. Identifies the percentage of seeds properly singulated by your meters. Contributing factors to this value include: Speed, Good Ride, Seed Size, Seed Shape, Meter
Chapter 4: Programming with MATLAB
 Chapter 4: Programming with MATLAB Topics Covered: Programming Overview Relational Operators and Logical Variables Logical Operators and Functions Conditional Statements For Loops While Loops Debugging
Chapter 4: Programming with MATLAB Topics Covered: Programming Overview Relational Operators and Logical Variables Logical Operators and Functions Conditional Statements For Loops While Loops Debugging
TIPS AND HINTS FOR SHARING DATA
 TIPS AND HINTS FOR SHARING DATA Summary Salesforce provides many flexible options for you to control how records are shared within your organization. To specify the objects and tabs that a user can access,
TIPS AND HINTS FOR SHARING DATA Summary Salesforce provides many flexible options for you to control how records are shared within your organization. To specify the objects and tabs that a user can access,
MA30SA Applied Math Unit D - Linear Programming Revd:
 1 Introduction to Linear Programming MA30SA Applied Math Unit D - Linear Programming Revd: 120051212 1. Linear programming is a very important skill. It is a brilliant method for establishing optimum solutions
1 Introduction to Linear Programming MA30SA Applied Math Unit D - Linear Programming Revd: 120051212 1. Linear programming is a very important skill. It is a brilliant method for establishing optimum solutions
The Use and Applications of Unmanned- Aerial Systems (UAS) In Agriculture
 The Use and Applications of Unmanned- Aerial Systems (UAS) In Agriculture R O B E R T A U S T I N, D E P A R T M E N T O F S O I L S C I E N C E N C S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y DJI Inspire Photo Credit:
The Use and Applications of Unmanned- Aerial Systems (UAS) In Agriculture R O B E R T A U S T I N, D E P A R T M E N T O F S O I L S C I E N C E N C S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y DJI Inspire Photo Credit:
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Dr. Arun K Saraf Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee
 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Dr. Arun K Saraf Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture 04 Raster data model and comparisons with vector Hello friends,
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Dr. Arun K Saraf Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture 04 Raster data model and comparisons with vector Hello friends,
DS504/CS586: Big Data Analytics Big Data Clustering II
 Welcome to DS504/CS586: Big Data Analytics Big Data Clustering II Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 6pm 8:50pm Thu Location: AK 232 Fall 2016 More Discussions, Limitations v Center based clustering K-means BFR algorithm
Welcome to DS504/CS586: Big Data Analytics Big Data Clustering II Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 6pm 8:50pm Thu Location: AK 232 Fall 2016 More Discussions, Limitations v Center based clustering K-means BFR algorithm
MATH ALGEBRA AND FUNCTIONS 5 Performance Objective Task Analysis Benchmarks/Assessment Students:
 Students: 1. Use information taken from a graph or Which table, a or b, matches the linear equation to answer questions about a graph? problem situation. y 1. Students use variables in simple expressions,
Students: 1. Use information taken from a graph or Which table, a or b, matches the linear equation to answer questions about a graph? problem situation. y 1. Students use variables in simple expressions,
Note Set 4: Finite Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm
 Note Set 4: Finite Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm Padhraic Smyth, Department of Computer Science University of California, Irvine Finite Mixture Models A finite mixture model with K components, for
Note Set 4: Finite Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm Padhraic Smyth, Department of Computer Science University of California, Irvine Finite Mixture Models A finite mixture model with K components, for
Name Date Period. Multiple Choice
 Name Date Period Worksheet 3.6 Optimization Show all work. Calculator permitted. Show all set-ups and analysis. Report all answers to 3 decimals and avoid intermediate rounding error. Multiple Choice 1.
Name Date Period Worksheet 3.6 Optimization Show all work. Calculator permitted. Show all set-ups and analysis. Report all answers to 3 decimals and avoid intermediate rounding error. Multiple Choice 1.
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Intensity Transformations (Histogram Processing) Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr University of Ioannina - Department of Computer Science and Engineering 2 Contents Over the
Digital Image Processing Intensity Transformations (Histogram Processing) Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr University of Ioannina - Department of Computer Science and Engineering 2 Contents Over the
COMPUTER EXERCISE: POPULATION DYNAMICS IN SPACE September 3, 2013
 COMPUTER EXERCISE: POPULATION DYNAMICS IN SPACE September 3, 2013 Objectives: Introduction to coupled maps lattice as a basis for spatial modeling Solve a spatial Ricker model to investigate how wave speed
COMPUTER EXERCISE: POPULATION DYNAMICS IN SPACE September 3, 2013 Objectives: Introduction to coupled maps lattice as a basis for spatial modeling Solve a spatial Ricker model to investigate how wave speed
Industrialising Small Area Estimation at the Australian Bureau of Statistics
 Industrialising Small Area Estimation at the Australian Bureau of Statistics Peter Radisich Australian Bureau of Statistics Workshop on Methods in Official Statistics - March 14 2014 Outline Background
Industrialising Small Area Estimation at the Australian Bureau of Statistics Peter Radisich Australian Bureau of Statistics Workshop on Methods in Official Statistics - March 14 2014 Outline Background
Uncertainty analysis in spatial environmental modelling. Kasia Sawicka Athens, 29 Mar 2017
 Uncertainty analysis in spatial environmental modelling Kasia Sawicka Athens, 29 Mar 2017 Uncertainty propagation overview Input ± U Model (± U) Output ± U Input data Model parameters Model structure Solution
Uncertainty analysis in spatial environmental modelling Kasia Sawicka Athens, 29 Mar 2017 Uncertainty propagation overview Input ± U Model (± U) Output ± U Input data Model parameters Model structure Solution
Spread Map Tab - Soil Zones
 Spread Map Tab - Soil Zones The Spread Map page provides functions for creating spread maps. To activate the options, select the Spread Map tab. 1. The Rx Export tab will display immediately. Select the
Spread Map Tab - Soil Zones The Spread Map page provides functions for creating spread maps. To activate the options, select the Spread Map tab. 1. The Rx Export tab will display immediately. Select the
v TUFLOW FV SMS 13.0 Tutorial Requirements Time Prerequisites Objectives
 v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates creating a simple model of a short section of river using the SMS TUFLOW FV interface. A mesh for an inbank area of a river will be built,
v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates creating a simple model of a short section of river using the SMS TUFLOW FV interface. A mesh for an inbank area of a river will be built,
CS130 Software Tools. Fall 2010 Getting More from Office
 Software Tools Getting More from Office 1 Microsoft Office Additional Tools Most of you are skilled in using Word and Excel to do the basics, but as an university student, there are a few more advanced
Software Tools Getting More from Office 1 Microsoft Office Additional Tools Most of you are skilled in using Word and Excel to do the basics, but as an university student, there are a few more advanced
Computer Programming ECIV 2303 Chapter 6 Programming in MATLAB Instructor: Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering
 Computer Programming ECIV 2303 Chapter 6 Programming in MATLAB Instructor: Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering 1 Introduction A computer program is a sequence of computer
Computer Programming ECIV 2303 Chapter 6 Programming in MATLAB Instructor: Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering 1 Introduction A computer program is a sequence of computer
CREATING & RUNNING A VERY SIMPLE MODEL
 CREATING & RUNNING A VERY SIMPLE MODEL Goal: This activity introduces a simple analog model of population change using dynamic systems modeling terminology and diagrams. It will serve as a launching point
CREATING & RUNNING A VERY SIMPLE MODEL Goal: This activity introduces a simple analog model of population change using dynamic systems modeling terminology and diagrams. It will serve as a launching point
Causes of spatial variation
 Field Trials Plant breeding trials Laid out in a grid (rows and columns) From few entries (3-5) to many entries (100s) Plots close together are more similar than those far away. Causes of spatial variation
Field Trials Plant breeding trials Laid out in a grid (rows and columns) From few entries (3-5) to many entries (100s) Plots close together are more similar than those far away. Causes of spatial variation
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations,
 Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Spirits Version 1.5.1
 Spirits Version 1.5.1 Dominique Haesen - VITO Contents Summary of changes between version 1.5.1 and 1.4.1... 2 Major changes... 2 Minor changes... 2 Description of the main new features of SPIRITS 1.5.1...
Spirits Version 1.5.1 Dominique Haesen - VITO Contents Summary of changes between version 1.5.1 and 1.4.1... 2 Major changes... 2 Minor changes... 2 Description of the main new features of SPIRITS 1.5.1...
Properties. Comparing and Ordering Rational Numbers Using a Number Line
 Chapter 5 Summary Key Terms natural numbers (counting numbers) (5.1) whole numbers (5.1) integers (5.1) closed (5.1) rational numbers (5.1) irrational number (5.2) terminating decimal (5.2) repeating decimal
Chapter 5 Summary Key Terms natural numbers (counting numbers) (5.1) whole numbers (5.1) integers (5.1) closed (5.1) rational numbers (5.1) irrational number (5.2) terminating decimal (5.2) repeating decimal
Farming alfalfa and corn in Nebraska
 Farming alfalfa and corn in Nebraska Geospatial technologies provide farmers with tools to help them decide which crops to plant and how to get the most from every acre. Agriculture data taken at specific
Farming alfalfa and corn in Nebraska Geospatial technologies provide farmers with tools to help them decide which crops to plant and how to get the most from every acre. Agriculture data taken at specific
EL2310 Scientific Programming
 (pronobis@kth.se) Overview Overview Wrap Up More on Scripts and Functions Basic Programming Lecture 2 Lecture 3 Lecture 4 Wrap Up Last time Loading data from file: load( filename ) Graphical input and
(pronobis@kth.se) Overview Overview Wrap Up More on Scripts and Functions Basic Programming Lecture 2 Lecture 3 Lecture 4 Wrap Up Last time Loading data from file: load( filename ) Graphical input and
Section Graphing Systems of Linear Inequalities
 Section 3.1 - Graphing Systems of Linear Inequalities Example 1: Find the graphical solution of the inequality y x 0. Example 2: Find the graphical solution of the inequality 5x 3y < 15. 1 How to find
Section 3.1 - Graphing Systems of Linear Inequalities Example 1: Find the graphical solution of the inequality y x 0. Example 2: Find the graphical solution of the inequality 5x 3y < 15. 1 How to find
Lab 1: Exploring ArcMap and ArcCatalog In this lab, you will explore the ArcGIS applications ArcCatalog and ArcMap. You will learn how to use
 Lab 1: Exploring ArcMap and ArcCatalog In this lab, you will explore the ArcGIS applications ArcCatalog and ArcMap. You will learn how to use ArcCatalog to find maps and data and how to display maps in
Lab 1: Exploring ArcMap and ArcCatalog In this lab, you will explore the ArcGIS applications ArcCatalog and ArcMap. You will learn how to use ArcCatalog to find maps and data and how to display maps in
layers in a raster model
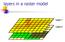 layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
Introduction to Functional Programming. Slides by Koen Claessen and Emil Axelsson
 Introduction to Functional Programming Slides by Koen Claessen and Emil Axelsson Goal of the Course Start from the basics Learn to write small-to-medium sized programs in Haskell Introduce basic concepts
Introduction to Functional Programming Slides by Koen Claessen and Emil Axelsson Goal of the Course Start from the basics Learn to write small-to-medium sized programs in Haskell Introduce basic concepts
Solve, RootOf, fsolve, isolve
 Solve, RootOf, fsolve, isolve Maple is capable of solving a huge class of equations: (the solution tells us that can be arbitrary). One may extract the solutions using the "[ ]" notation (we will learn
Solve, RootOf, fsolve, isolve Maple is capable of solving a huge class of equations: (the solution tells us that can be arbitrary). One may extract the solutions using the "[ ]" notation (we will learn
Hydrologic modelling at a continuous permafrost site using MESH. S. Pohl, P. Marsh, and S. Endrizzi
 Hydrologic modelling at a continuous permafrost site using MESH S. Pohl, P. Marsh, and S. Endrizzi Purpose of Study Test the latest version of MESH at a continuous permafrost site Model performance will
Hydrologic modelling at a continuous permafrost site using MESH S. Pohl, P. Marsh, and S. Endrizzi Purpose of Study Test the latest version of MESH at a continuous permafrost site Model performance will
Introduction to Matlab. By: Hossein Hamooni Fall 2014
 Introduction to Matlab By: Hossein Hamooni Fall 2014 Why Matlab? Data analytics task Large data processing Multi-platform, Multi Format data importing Graphing Modeling Lots of built-in functions for rapid
Introduction to Matlab By: Hossein Hamooni Fall 2014 Why Matlab? Data analytics task Large data processing Multi-platform, Multi Format data importing Graphing Modeling Lots of built-in functions for rapid
Measures of Dispersion
 Lesson 7.6 Objectives Find the variance of a set of data. Calculate standard deviation for a set of data. Read data from a normal curve. Estimate the area under a curve. Variance Measures of Dispersion
Lesson 7.6 Objectives Find the variance of a set of data. Calculate standard deviation for a set of data. Read data from a normal curve. Estimate the area under a curve. Variance Measures of Dispersion
Unit 4: Vector Overlay Analysis. Lecture Outline. Possible background reading material: McHarg, Ian 1992 Design with Nature. Wiley and Sons, New York.
 Unit 4: Vector Overlay Analysis Lecture Outline Possible background reading material: McHarg, Ian 1992 Design with Nature. Wiley and Sons, New York. Introduction: The idea of overlay originated when maps
Unit 4: Vector Overlay Analysis Lecture Outline Possible background reading material: McHarg, Ian 1992 Design with Nature. Wiley and Sons, New York. Introduction: The idea of overlay originated when maps
AGVITA NU-test REPORTING TEMPLATE INSTRUCTIONS:
 AGVITA NU-test REPORTING TEMPLATE INSTRUCTIONS: AgVita are implementing a new LIMS at our Laboratory from May 2014. This is due to the increasing strain on our old system which has simply been unable to
AGVITA NU-test REPORTING TEMPLATE INSTRUCTIONS: AgVita are implementing a new LIMS at our Laboratory from May 2014. This is due to the increasing strain on our old system which has simply been unable to
Practical 4: The Integrate & Fire neuron
 Practical 4: The Integrate & Fire neuron 2014 version by Mark van Rossum 2018 version by Matthias Hennig and Theoklitos Amvrosiadis 16th October 2018 1 Introduction to MATLAB basics You can start MATLAB
Practical 4: The Integrate & Fire neuron 2014 version by Mark van Rossum 2018 version by Matthias Hennig and Theoklitos Amvrosiadis 16th October 2018 1 Introduction to MATLAB basics You can start MATLAB
*Optimized Coverage Path Planning and Headland Turning Trajectory Optimization for Auto-Steer Agricultural Field Equipment
 *Optimized Coverage Path Planning and Headland Turning Trajectory Optimization for Auto-Steer Agricultural Field Equipment Lie Tang, PhD Associate Professor Agricultural Automation and Robotics Laboratory
*Optimized Coverage Path Planning and Headland Turning Trajectory Optimization for Auto-Steer Agricultural Field Equipment Lie Tang, PhD Associate Professor Agricultural Automation and Robotics Laboratory
CS-465 Computer Vision
 CS-465 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT 9. Optic Flow Optic Flow Nazar Khan Computer Vision 2 / 25 Optic Flow Nazar Khan Computer Vision 3 / 25 Optic Flow Where does pixel (x, y) in frame z move to in
CS-465 Computer Vision Nazar Khan PUCIT 9. Optic Flow Optic Flow Nazar Khan Computer Vision 2 / 25 Optic Flow Nazar Khan Computer Vision 3 / 25 Optic Flow Where does pixel (x, y) in frame z move to in
Procedures for Farm & Field Setup within AgroDoc.NET
 P a g e 1 Procedures for Farm & Field Setup within AgroDoc.NET AgWorks Structure follows this hierarchy: Growers Farms Fields Management Zones Soil Tests Management Zone: Portions of fields that growers
P a g e 1 Procedures for Farm & Field Setup within AgroDoc.NET AgWorks Structure follows this hierarchy: Growers Farms Fields Management Zones Soil Tests Management Zone: Portions of fields that growers
VCell Tutorial. FRAP: Fluorescence Redistribution After Photo bleaching
 VCell Tutorial FRAP: Fluorescence Redistribution After Photo bleaching Create a simple biomodel and spatial (PDE) application to simulate a photobleaching experiment and view the results. In this tutorial
VCell Tutorial FRAP: Fluorescence Redistribution After Photo bleaching Create a simple biomodel and spatial (PDE) application to simulate a photobleaching experiment and view the results. In this tutorial
DS504/CS586: Big Data Analytics Big Data Clustering II
 Welcome to DS504/CS586: Big Data Analytics Big Data Clustering II Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 6pm 8:50pm Thu Location: KH 116 Fall 2017 Updates: v Progress Presentation: Week 15: 11/30 v Next Week Office hours
Welcome to DS504/CS586: Big Data Analytics Big Data Clustering II Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 6pm 8:50pm Thu Location: KH 116 Fall 2017 Updates: v Progress Presentation: Week 15: 11/30 v Next Week Office hours
CropWalker. Field Information
 CropWalker Field Information Contents FIELDS AND CROPS... 2 ADD, EDIT OR DELETE FIELDS... 2 ADD CROPS... 4 MULTIPLE FIELD CROPPING... 5 CROP ESTABLISHMENT... 6 SOIL ANALYSIS... 9 FIELD WORK... 13 FURTHER
CropWalker Field Information Contents FIELDS AND CROPS... 2 ADD, EDIT OR DELETE FIELDS... 2 ADD CROPS... 4 MULTIPLE FIELD CROPPING... 5 CROP ESTABLISHMENT... 6 SOIL ANALYSIS... 9 FIELD WORK... 13 FURTHER
Functions 3.6. Fall Math (Math 1010) M / 13
 Functions 3.6 Fall 2013 - Math 1010 (Math 1010) M 1010 3.6 1 / 13 Roadmap 3.6 - Functions: Relations, Functions 3.6 - Evaluating Functions, Finding Domains and Ranges (Math 1010) M 1010 3.6 2 / 13 3.6
Functions 3.6 Fall 2013 - Math 1010 (Math 1010) M 1010 3.6 1 / 13 Roadmap 3.6 - Functions: Relations, Functions 3.6 - Evaluating Functions, Finding Domains and Ranges (Math 1010) M 1010 3.6 2 / 13 3.6
Standardizing the Geospatial Farm
 Standardizing the Geospatial Farm ESRI User Conference 2016 06-27-2016 / Jim Koob and Gavin Rehkemper / Version 1 Agenda Bayer Crop Science The End Motivation Standardizing the Experiment Sort of Standardizing
Standardizing the Geospatial Farm ESRI User Conference 2016 06-27-2016 / Jim Koob and Gavin Rehkemper / Version 1 Agenda Bayer Crop Science The End Motivation Standardizing the Experiment Sort of Standardizing
APPLICATION OF SOFTMAX REGRESSION AND ITS VALIDATION FOR SPECTRAL-BASED LAND COVER MAPPING
 APPLICATION OF SOFTMAX REGRESSION AND ITS VALIDATION FOR SPECTRAL-BASED LAND COVER MAPPING J. Wolfe a, X. Jin a, T. Bahr b, N. Holzer b, * a Harris Corporation, Broomfield, Colorado, U.S.A. (jwolfe05,
APPLICATION OF SOFTMAX REGRESSION AND ITS VALIDATION FOR SPECTRAL-BASED LAND COVER MAPPING J. Wolfe a, X. Jin a, T. Bahr b, N. Holzer b, * a Harris Corporation, Broomfield, Colorado, U.S.A. (jwolfe05,
What can we represent as a Surface?
 Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
