Introduction to Modeling with Simile
|
|
|
- Felix Nichols
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Modeling with Simile This is an introduction to using Simile for building and analysing a model. Simile is a visual modeling tool. It allows you to draw a conceptual model diagram, and if you have quantitative information you can then add this into the conceptual model to produce a quantitative model. Simile also allows the dynamics of a quantitative model to be simulated and the results displayed in graphs and tables. Extra documentation on Simile can be found in the Simile's help files and on the Simile web site Links to the relevant web help pages can be found throughout this guide. The best way to learn about modelling is by practice. So we will look at a simple model which is the Hunter-Gather example from the book "Ecological Modelling: A Common-Sense Approach to Theory and Practice" (Grant and Swannack 2007). We will see how to build and analyse the model with Simile, and then there are some problems which you should try and answer using Simile. At the end I present some additional functionalities of Simile which may be useful for other modelling problems. Starting Simile You start Simile by double-clicking on the desktop icon created during installation, or by clicking on the Simile icon in the Start Menu. Within a few seconds, the main window will be displayed. The Main Window When Simile starts, you see a single window. If you see a welcome page (shown opposite), click on the "New" button 1
2 You should now see the Main Simile window, like this Menu bar Tool bar Equation bar Component bar Desktop canvas The main window contains: The Menu Bar, containing a standard File menu, some menus specific to Simile, and a Help menu. Hold the mouse over the title for each menu to see the options it contains. The Toolbar, with standard tools (e.g. for opening and closing files), plus some specific to Simile. The Component Bar, containing buttons corresponding to each type of model-diagram element: you will use these for building up your model diagram. The right-hand part contains buttons for editing the model diagram. Hold the mouse over each button to get a brief description of its function. The Equation Bar, for entering equations into the model. At the right-hand end of the equation bar are the tools to accept or reject changes to equations, and to help build equations. The Desktop Canvas, where you will draw your model diagram. The grid can help you arrange your diagram neatly. 2
3 The ecological system: The question and the data The ecological system we are going to consider is the first example in the book by Grant and Swannack (Grant and Swannack 2007). It is called the Hunter-Gatherer Model. The Question Will deforestation have a serious impact on the winter food reserves of a hunter-gather group? The group usually hunts in the savannah until the end of October and then moves to the forest to spend the winter. Can the group collect enough food for the winter despite deforestation? The Data Severe winter weather, which prevents all food gathering activities, typically arrives by the end of November. Thus the group has the month of November to harvest the food items they need for the winter. There are usually 100 food items in the forest at the beginning of November. For practical purposes, food items are a non-renewable resource during November since plants no longer produce fruits and both birth and death rates of animal populations are essentially zero. Historically, the group has had no trouble harvesting the 75 food items they need for the winter, although the group has told us the rate at which they can harvest food items decreases noticeably as abundance of food items decreases. The group estimates they can harvest about 10% of the available food items per day. As a result of the recent deforestation, we estimate only about 80 food items will remain in the forest when the group arrives this autumn. Although there still appears to be enough food available, we wonder if the group will have enough time to harvest all they need before the severe weather arrives. The steps taken to model the problem Two important steps have already been completed. 1. We have a good idea of the question we want to ask. 2. We have a good idea of the data available to us. We will continue by 3. Developing a conceptual model of the system which is suited to the data and the question 4. Developing a quantitative model from the conceptual model by explicitly including the data 5. Evaluating and analyzing the model s simulation results 6. Some problems for you to answer about the model system 7. Looking at some additional Simile skills 3
4 Conceptual Model Drawing a conceptual model in Simile Begin by drawing a conceptual model diagram for the Hunter-Gatherer model. We are interested in the Total Harvest across one season, and this harvest comes from the Food in the forest. The Food and the Total Harvest are linked by the daily harvest that removes food from the forest and increases the total harvest. A sketch of the system is shown below. There are two state variables: Food and Total Harvest. The solid arrows show the "flow" from forest food into total harvest. A note on colours in Simile When you select a compartment it will turn blue (a new compartment will automatically be selected). When you select a flow it will turn green (a new flow will automatically be selected). A compartment or flow will be red if it is not selected and it needs some extra information (like a value or equation). When a compartment or flow is complete it will turn black. When a model diagram is all black the model can be run. The dashed arrow shows that the daily harvest is influenced by the amount of food in the forest. Now draw this conceptual model in Simile. Adding a compartment to a model Click on the compartment symbol in the toolbar. Move the mouse to the middle of the desktop window, and click again. You should see a blue box labelled comp1. 4
5 Conceptual Model Type in the label Food. This box will be the food available in the forest. Now repeat this step to create another compartment and label it Total Harvest. Adding a flow to a model Add in the flow from the Food into the Total Harvest. Click on the flow symbol in the toolbar. Move the mouse to the compartment labelled Food. Hold the mouse button down and drag the mouse into the centre of the compartment labelled Total Harvest. Release the mouse button. Type in the label Daily Harvest. Adding in an influence to a model The food in the forest influences the daily harvest (the dashed arrow in our sketch). In Simile this is represented by an influence arrow. Click on the influence arrow button in the toolbar. Move the mouse to the middle of the compartment labelled Food, and drag an influence arrow to the flow labelled Daily Harvest. Release the mouse button when the flow has turned green. Re-arrange the model diagram Click on the pointer button in the toolbar. Move the mouse to the middle of the compartment labelled Food. Drag the mouse, and watch the compartment and its associated arrows re-arrange themselves. You can move many of the components in Simile, including the flows, the influence arrows, etc. The labels of a component can also be moved. 5
6 Conceptual Model Re-sizing the model diagram You can zoom the model diagram to fit the current window by clicking on the button You can zoom in to a diagram by clicking on the button You can zoom out of a diagram by clicking on the button Removing model components Click on the pointer button in the toolbar. Click on the model component you want to remove (it will turn blue). Select the Edit/Delete option in the menu bar and the selected component will be deleted. We now have the conceptual model drawn in Simile, which looks something like this... Save the model by selecting File/Save in the menu bar. Call the model gatherer.sml Copying a picture of the conceptual model The diagram of the model can be copied and pasted into another document by selecting Edit/Select All in the menu bar, followed by Edit/Copy. Additional model components Simile has many other models components, which are described in the help pages. Some other components will be discussed later on. 6
7 Quantitative Model Making a quantitative model in Simile The conceptual model contains no numerical data. But we are given values for the initial amount of food in the forest and the rate at which it can be harvested. So the next step is to include information into our model, and make the model quantitative. We are told that the daily harvest is 10% of the food in the forest, so on Day 1 the harvest is The daily harvest is calculated from the food available at the start of day (hence the influence arrow in the conceptual model from Food to DailyHarvest). Every day the food in the forest is reduced due to harvesting, and the Total Harvest is increased The value of DailyHarvest is the rate (per day) at which the forest food is decreasing, and the rate (per day) at which the total harvest is increasing. Simile can use these equations to predict the future Total Harvest and the Food at the end of each day. To do this we have to input this quantitative information into the model. Prepare to set component properties Click on the pointer button in the toolbar. Assign an initial value for a compartment Click on the compartment labelled Food. Enter the value 100 into the equation bar. Click on the green tick mark or press the Return key. Repeat this for the compartment labelled Total Harvest and set its value to 0 in the equation bar. As the initial values of the compartments are set they turn black, showing that all the information for this compartment has been specified. 7
8 Quantitative Model Add the harvest rate equation Click on the flow labelled Daily Harvest. The variable Food is listed as an influence upon Daily Harvest. These influences are visible by clicking on the x s button. Selecting an influence from the dropdown list, places the text in the equation bar. Enter the expression 0.1*Food into the equation bar. Click on the green tick mark. A full discussion of defining equations in Simile can be found on the Simile help pages. When you have finished, you should notice that every component of the model diagram is now black, rather than red as it was before. This indicates that every component has been mathematically specified, and so the model is ready for running. Simile has enough information to work out the flows, and thus to update the amount of food in the forest and the total harvest forward through time. Seeing the equations and data in a model You can see all the equations in a model by selecting Model/List equations from the menu bar, or by typing Ctrl+L. This will open a window with all the components in the model, their equations and their values. You can compare the equations with those on the previous page. 8
9 Evaluate and Analyse the Model Running the model Now all components have been defined we can run the model to predict the effect of harvesting the forest food. First compile the model: Open the Model menu Select the Run item. Simile creates a new window: the execution window. This contains the controls for running the model; a list of the variables in the model; and an area where any of a variety of tools for showing model results can be displayed. Change the time step Simile uses default time step of 0.1 to update the model (the default method for updating the model is Euler s method). For this model we want a daily time steps, so we will set the time-step to 1. Change the value for Time step #1 from 0.1 to 1. The Run Settings tab contains other options which should not be changed. Note: Leave the time units at their default value (unit) Change the duration of the simulation run Change the value for Execute for from 100 to 30. This is because there are 30 days in November. Select the graph-plot display Simile has several graphical tools to display results. A list of the graphics can be found by clicking on the Spectacles button in the toolbar. Click on the "Plotter" display tool on the toolbar; or select it from the list in the Add menu. 9
10 Evaluate and Analyse the Model Choose the variable to be displayed Note the graph window that appears. This is initially scaled with default values on both axes, but will rescale itself as needed. You can re-size the panel containing the graph by dragging on the little boxes on the horizontal and vertical panel separators. Click on the "Add a variable" button on the plotter toolbar Click on the compartment labelled Food in the list of model variables. Click on the "Add a variable" button on the plotter toolbar Click on the compartment labelled Total Harvest in the list of model variables. Start the simulation Click on the "Play" button in the Run control dialogue window. Note the line that appears on the graph. By placing the mouse over the variable Food in the bottom left window shows the value of food after 30 days. The same can be done for Total Harvest and Daily Harvest. Continue the simulation Click on the "Play" button again. The simulation carries on for another 30 days. Resetting the simulation The simulation can be reset to time=0, and run again. The stop button will stop the simulation and set the current time to zero Click on the "Play" button to run the model again Resetting the graphics display All the graphics can be cleared by clicking the clear button in the toolbar. Individual graphics can be cleared by clicking the same icon in each graphics panel. Changing parameter values and rerunning the model Now run a simulation where there is less initial food in the forest due to deforestation. Click on the "Go to Model Window" toolbar button. Or select the model window directly. 10
11 Evaluate and Analyse the Model Now select the Food compartment and set its initial value to 80 Recompile the model, using Model/Run in the menu bar. Rerun the model for the first 30 days. The new simulation results are shown as run 2. Is the harvest at the end of November greater than the 75 units necessary for the huntergather s survival over the winter? At what initial food abundance will the hunter-gathers find it difficult to survive the winter? Displaying numerical data It is often more useful to display the numerical values from a simulation. Displaying data as a table is useful if you want to read the data into Excel. To do this: Create a new Notebook by clicking on the Add notebook page button Click on the Create table icon Click on the "Add a variable" button as you did to add a variable to the plotter Then rerun a simulation (output shown on the right) The online help manual explains all the aspects of customizing a table at Saving the model graphics The graph of simulation results can be copied and inserted into a Word document. Select the graph and then select Edit/Copy in the menu bar to copy the figure onto the clipboard. The figure can then be pasted into a Word document. 11
12 Problems to answer Use your model to answer some problems about the system Here are some problems which you can use your Simile model to answer (answers can be found on the last page). 1. How long does it take to harvest 75 food items before deforestation took place (i.e. when there are 100 food items at the start of November)? 2. How long does it take to gather 75 food items now that deforestation has happened (i.e. when there are 80 food items at the start of November)? 3. Create a word document which contains a figure showing the model s structure and a figure (with caption) showing the simulation results from one model run. 4. Include a variable in the model (see additional skills below) that adds together the food in the forest and the total harvest. This variable will keep track of the total amount of food in the system. Does the total amount of food change during the month of November? Explain what you have found. 5. Food in the harvest can rot. Roughly 0.05% of the food in the harvest is lost each day due to rotting. Modify your conceptual model to include this new information. To receive some feedback on you work, you can submit this report or your report from practical 2, via Blackboard before 6pm Friday. 12
13 Additional Simile Skills Additional Simile Skills Adding a variable to a model Another component that hasn t been discussed is a variable. A variable in Simile is just a number, but we can give it a name. This will be useful when calculating output results, or defining initial parameter values. We do not need this at the moment, but we will later on. Here is how a variable is added. Click on the variable symbol in the toolbar. Move the mouse to the blank area of the model canvas and click once. Type in the label for the variable. Adding a source/sink into a model The final component that hasn t been discussed is a source/sink. A source/sink is represented by three overlapping circles (akin to a cloud), and is very similar to a compartment, which was introduced on page 4. The only difference between a compartment and a source/sink is that the source/sink is inexhaustible. You create a source by left-clicking on the flow icon, left-clicking on a blank piece of canvas. This will create a source with a flow arrow coming out from the source (pictured on the right). By dragging the end of the flow arrow you can link this source to any existing compartment. You create a sink by: left-clicking on the flow icon, left-clicking on a compartment that has already been created. keep the left button help down and drag the flow arrow to a blank piece of the canvas. This will create a flow arrow from a compartment into a sink (pictured on the right). 13
14 Additional Simile Skills Defining a variable parameter with the equation dialogue window The Initial food in the forest can be changed without recompiling the model every time. To do this: Return to the Model Window. Create a new variable for the Initial food in the forest and label it initfood Next define this variable as having a range of possible values rather than one fixed value (this will enable us to set the value when the model is running). Under data source click the "Variable parameter" option and then type in the minimum and maximum values of the efficiency (we ll take the minimum to be 50 and the maximum 150). In the window at the bottom type in 100 as a default value for the initial food, and the press the OK button. In the model, initfood now has a line through it to show that it is defined with a range of values. Draw influence arrows from initfood to the Food compartment. Click on the Food compartment and in the equation bar set its initial value to be initfood (as shown). The initial food is now defined by a new variable (initfood) that has a well defined range. The model should be ready to compile using Model/Run in the menu bar. This reopens the execution window, with the old simulation results. Now we want to be able to change the values of initfood. Click on the "Split pane horizontally" button in the tool bar Click on the "Create input sliders" button in the toolbar Add the variable initfood by clicking on the "Add a variable" button, and then the variable The sliders can be used to set the value for the variable. Clear the graph by selecting the "Clear" button Reset the simulation with the "Stop" button Run the model by clicking on the "Play" button. The slider can be used to change parameter values without recompiling. The Stop button must be pressed after the slider has been moved to select the initial value. 14
15 Additional Simile Skills Random numbers in a simulation Every variable we have defined up to now has been a well defined number. Simile can also model variables which have random values (e.g. a random number between 0 and 1). For example, the hunting efficiency may not be constant during a simulation (we have set it to 0.1), but may randomly fluctuate about some mean value. Create a new variable and label it efficiency Double click on the efficiency variable to open up the equation dialogue window In the top left of the window is a section called Functions:. Click on the Statistics folder and double click on the top entry, which is rand_var(). This function creates a new random number every time step from within a range of possible values. rand_var() will have appeared in the box at the bottom of the equation dialogue box. We must now set the range of possible values, which we ll take as being between 0.05 and Enters these values between the brackets on rand_var, so that the full expression looks like rand_var(0.05, 0.15). You can then click on the OK button to save this definition. Finally we must draw an influence arrow from the variable efficiency to the flow Daily Harvest, and redefine the Daily Harvest flow to be efficiency*food (instead of 0.1*Food). The harvesting efficiency is now a random variable which fluctuates daily between 0.05 and Running the model and plotting the output gives the following result. We can see that the efficiency is randomly jumping around from one day to the next, but always within our defined range. The effect of this random variation can be seen in the graph of Total Harvest and Food. 15
16 Additional Simile Skills Submodels We can enclose all or part of a model within a rectangle, which will define the contents as a submodel. Submodels are useful to make the model diagram easier to read. They are also useful for creating several copies of the same model diagram (e.g. in a spatial population model the same population dynamics could describe populations at different spatial locations, we can use the submodel to create multiple copies of a model, one for each spatial location). We want to define our entire model as a submodel. Click on the submodel button in the component bar. Use the mouse to draw a box around all the model components, and enter the label as Hunter-Gatherer Model. Vectors and matrices So far all the variables in our model have been single numbers. Simile can define variables which are vectors or matrices (e.g the variable x=[9, 10, 11, 12, 13] is a vector with five elements which happen to be the numbers from 9 to 13). Simile calls a vector a one-dimensional array, and a matrix a two-dimensional array. Arrays are explained in the Simile s help. We could define 5 copies of the whole model by defining the Forest Model submodel into an array. To do this we Select the submodel, so that it turns blue. Double click in the interior of the submodel to bring up the Properties window. Select Fixed array from the list (shown above right) To create five copies of the submodel enter 5 in the text box that appears. Click OK. Multiple copies of the submodel are shown in the model diagram by the boundary of the submodel having several lines (shown opposite). 16
17 Additional Simile Skills Exporting results from Simile into Excel Once you have created a table and run the model so that the table contains some data you can save this data in a format that can be read by Excel. You do this my clicking on the Save button in the table s notebook and then typing in the name of the file where you want the data to be saved. By default this will be a Comma Separated Variable file ( a CSV file) which is a text file that can be read by Excel. Changing the look of the model diagram Sometimes the default look of the model diagram will be unclear. For instance you may want to make the compartment boxes larger, or change the size of text, thickness of lines, etc. The look of a Simile model diagram can be changed under the menu item View/Customise. For example, if you want to change the way compartments are displayed select View/Customise/Compartments which will open up a window called Customise compartment appearance where you can change the look of all the compartments in your model. You also have some flexibility to change the way the model look under the menu item Edit/Preferences. This opens up a window called Preferences. Under the Edit tab you can change several aspects of model look. Perhaps the most useful is the Rectilinear Flow Routing option. Final Note This has been a very quick look at Simile. Simile allows you to create and analyse quite sophisticated models, and generate a range of output interfaces. Now to properly understand how to use all these components you re going to have to get stuck in to a modeling project and use Simile. References Grant, W. E. and T. M. Swannack (2007). Ecological Modelling: A common-sense approach to theory and practice. New York, Wiley-Blackwell. 17
18 Answers to Problems Question 1. How long does it take to harvest 75 food items before deforestation took place (i.e. when there are 100 food items at the start of November)? On the end of day 13 the model predicts that the total harvest will be 74.6 food items, and at the end of day 14 it will be 77.1 food items (this is quoting food items to 1 decimal place accuracy). So 75 food items will take 14 days to collect (if you round up to a whole number of food items then 13 days could also be correct, showing that model results are dependent upon the accuracy, and your interpretation of the results to a certain extent). Since the model only considers whole days, we cannot say when on day 14 the harvest will hit 75 food items. Besides, this would be tending to make a precise prediction which is not consistent with the simplicity of the model. Question 2. How long does it take to gather 75 food items now that deforestation has happened (i.e. when there are 80 food items at the start of November)? On the end of day 26 the model predicts that the total harvest will be 74.8 food items, and at the end of day 27 it will be 75.3 food items. So 75 food items will take 27 days to collect. 18
19 Food Items Answers to Problems Question 3. Create a word document which contains a figure showing the model s structure and a figure (with caption) showing the simulation results from one model run. Food Daily Harvest Total Harvest Figure 1: A diagram of the hunter-gatherer model, showing the movement of food from the forest (Food compartment) into the yearly harvest (compartment Total Harvest) Time [days] Figure 2: The food items in the forest (green line) and the total harvest (black line) as a function of days in November. At day 0 the total harvest was zero and there were 80 food items in the forest. To answer this question I have used Excel to produce the graph because Simile does not produce graphs of sufficient quality for reports. The axes are clearly labeled, the text is readable and the units of the axes are included. The caption explains the two lines and other details about the simulation used to produce these results (in this case the initial conditions). 19
20 Answers to Problems Question 4. Include a variable in the model (see additional skills below) that adds together the food in the forest and the total harvest. This variable will keep track of the total amount of food in the system. Does the total amount of food change during the month of November? Below is the model with a variable added that calculates the sum of Food and Total Harvest Running this model shows that the total amount of food in the model does not change. This is because the model represents a closed system. There are no sources of new food and no sinks for the food, food can only move between the forest (food compartment) and the Total Harvest. 20
21 Question 5. Food in the harvest can rot. Roughly 0.05% of the food in the harvest is lost each day due to rotting. Modify your conceptual model to include this new information. Below is the conceptual model which includes the rotting of the harvest. The quantitative information has also been included. Notice that 0.05% gives a daily rotting rate of 0.05/100 * Total_Harvest = * Total_Harvest in units of food items per day 21
The Mathcad Workspace 7
 For information on system requirements and how to install Mathcad on your computer, refer to Chapter 1, Welcome to Mathcad. When you start Mathcad, you ll see a window like that shown in Figure 2-1. By
For information on system requirements and how to install Mathcad on your computer, refer to Chapter 1, Welcome to Mathcad. When you start Mathcad, you ll see a window like that shown in Figure 2-1. By
Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals
 1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
For more info and downloads go to: Gerrit Stols
 For more info and downloads go to: http://school-maths.com Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source (free) software for learning and teaching mathematics in schools. It
For more info and downloads go to: http://school-maths.com Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source (free) software for learning and teaching mathematics in schools. It
5.13 Exercise: Sampling variation - numeric data
 5.13 Exercise: Sampling variation - numeric data In this exercise you will begin using the Visual Inferential Tools (VIT) software. VIT will enable you to see the variation in estimates from sample to
5.13 Exercise: Sampling variation - numeric data In this exercise you will begin using the Visual Inferential Tools (VIT) software. VIT will enable you to see the variation in estimates from sample to
A Simple First-Model Using the Berkeley-Madonna Program
 A Simple First-Model Using the Berkeley-Madonna Program For this introduction, we will be creating a model of a simple system with two compartments analogous to containers of a liquid which can flow between
A Simple First-Model Using the Berkeley-Madonna Program For this introduction, we will be creating a model of a simple system with two compartments analogous to containers of a liquid which can flow between
Exercise 1.1 A First NetLogo Session Turtle commands and properties
 Exercise 1.1 A First NetLogo Session NetLogo is an interpreted language meaning you can type commands directly into a command line and see the results. In order to introduce NetLogo we will first type
Exercise 1.1 A First NetLogo Session NetLogo is an interpreted language meaning you can type commands directly into a command line and see the results. In order to introduce NetLogo we will first type
Spreadsheet View and Basic Statistics Concepts
 Spreadsheet View and Basic Statistics Concepts GeoGebra 3.2 Workshop Handout 9 Judith and Markus Hohenwarter www.geogebra.org Table of Contents 1. Introduction to GeoGebra s Spreadsheet View 2 2. Record
Spreadsheet View and Basic Statistics Concepts GeoGebra 3.2 Workshop Handout 9 Judith and Markus Hohenwarter www.geogebra.org Table of Contents 1. Introduction to GeoGebra s Spreadsheet View 2 2. Record
HBS Training - IT Solutions. PlanWeb. Intermediate
 HBS Training - IT Solutions PlanWeb Intermediate CONTENTS Logging on to the system...3 The PlanWeb Window...5 The Tool Bar...6 The Status Bar...6 The Map Window...6 The Information Window...7 Changing
HBS Training - IT Solutions PlanWeb Intermediate CONTENTS Logging on to the system...3 The PlanWeb Window...5 The Tool Bar...6 The Status Bar...6 The Map Window...6 The Information Window...7 Changing
Synoptics Limited reserves the right to make changes without notice both to this publication and to the product that it describes.
 GeneTools Getting Started Although all possible care has been taken in the preparation of this publication, Synoptics Limited accepts no liability for any inaccuracies that may be found. Synoptics Limited
GeneTools Getting Started Although all possible care has been taken in the preparation of this publication, Synoptics Limited accepts no liability for any inaccuracies that may be found. Synoptics Limited
Using Mapmaker s Toolkit. In this tutorial, you will learn the following basic elements of Mapmaker s Toolkit:
 Using Mapmaker s Toolkit Mapmaker s Toolkit is a useful piece of software that allows you and your students to create customized physical, cultural and historical maps of hundreds of countries, states
Using Mapmaker s Toolkit Mapmaker s Toolkit is a useful piece of software that allows you and your students to create customized physical, cultural and historical maps of hundreds of countries, states
COMP : Practical 6 Buttons and First Script Instructions
 COMP126-2006: Practical 6 Buttons and First Script Instructions In Flash, we are able to create movies. However, the Flash idea of movie is not quite the usual one. A normal movie is (technically) a series
COMP126-2006: Practical 6 Buttons and First Script Instructions In Flash, we are able to create movies. However, the Flash idea of movie is not quite the usual one. A normal movie is (technically) a series
IGSS 13 Configuration Workshop - Exercises
 IGSS 13 Configuration Workshop - Exercises Contents IGSS 13 Configuration Workshop - Exercises... 1 Exercise 1: Working as an Operator in IGSS... 2 Exercise 2: Creating a new IGSS Project... 28 Exercise
IGSS 13 Configuration Workshop - Exercises Contents IGSS 13 Configuration Workshop - Exercises... 1 Exercise 1: Working as an Operator in IGSS... 2 Exercise 2: Creating a new IGSS Project... 28 Exercise
Insight: Measurement Tool. User Guide
 OMERO Beta v2.2: Measurement Tool User Guide - 1 - October 2007 Insight: Measurement Tool User Guide Open Microscopy Environment: http://www.openmicroscopy.org OMERO Beta v2.2: Measurement Tool User Guide
OMERO Beta v2.2: Measurement Tool User Guide - 1 - October 2007 Insight: Measurement Tool User Guide Open Microscopy Environment: http://www.openmicroscopy.org OMERO Beta v2.2: Measurement Tool User Guide
Intermediate Excel 2003
 Intermediate Excel 2003 Introduction The aim of this document is to introduce some techniques for manipulating data within Excel, including sorting, filtering and how to customise the charts you create.
Intermediate Excel 2003 Introduction The aim of this document is to introduce some techniques for manipulating data within Excel, including sorting, filtering and how to customise the charts you create.
AODstats. Guide to using the Victorian data maps. Powered by StatPlanet
 AODstats Guide to using the Victorian data maps Powered by StatPlanet Contents Quick start guide Interface: Start page Main page Indicator selector panel Indicator details Indicator search box Graph panel
AODstats Guide to using the Victorian data maps Powered by StatPlanet Contents Quick start guide Interface: Start page Main page Indicator selector panel Indicator details Indicator search box Graph panel
Lines and Circles Guided Practice: Teacher Instructions
 Lines and Circles Guided Practice: Teacher Instructions Overview 1. Together, as a class, go through the Lines and Circles Guided Practice (exercises 1-22) described below. 2. Then have student teams conduct
Lines and Circles Guided Practice: Teacher Instructions Overview 1. Together, as a class, go through the Lines and Circles Guided Practice (exercises 1-22) described below. 2. Then have student teams conduct
HBS Training - IT Solutions. PlanWeb. Introduction
 HBS Training - IT Solutions PlanWeb Introduction CONTENTS Logging on to the system...3 The PlanWeb Window...5 The Tool Bar...6 The Status Bar...6 The Map Window...6 The Information Window...7 Changing
HBS Training - IT Solutions PlanWeb Introduction CONTENTS Logging on to the system...3 The PlanWeb Window...5 The Tool Bar...6 The Status Bar...6 The Map Window...6 The Information Window...7 Changing
MET 107 Drawing Tool (Shapes) Notes Day 3
 MET 107 Drawing Tool (Shapes) Notes Day 3 Shapes: (Insert Tab Shapes) Example: Select on the rounded rectangle Then use the mouse to position the upper left corner and produce the size by dragging out
MET 107 Drawing Tool (Shapes) Notes Day 3 Shapes: (Insert Tab Shapes) Example: Select on the rounded rectangle Then use the mouse to position the upper left corner and produce the size by dragging out
Discovering Computers & Microsoft Office Office 2010 and Windows 7: Essential Concepts and Skills
 Discovering Computers & Microsoft Office 2010 Office 2010 and Windows 7: Essential Concepts and Skills Objectives Perform basic mouse operations Start Windows and log on to the computer Identify the objects
Discovering Computers & Microsoft Office 2010 Office 2010 and Windows 7: Essential Concepts and Skills Objectives Perform basic mouse operations Start Windows and log on to the computer Identify the objects
DOING MORE WITH EXCEL: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2013
 DOING MORE WITH EXCEL: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2013 GETTING STARTED PAGE 02 Prerequisites What You Will Learn MORE TASKS IN MICROSOFT EXCEL PAGE 03 Cutting, Copying, and Pasting Data Basic Formulas Filling Data
DOING MORE WITH EXCEL: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2013 GETTING STARTED PAGE 02 Prerequisites What You Will Learn MORE TASKS IN MICROSOFT EXCEL PAGE 03 Cutting, Copying, and Pasting Data Basic Formulas Filling Data
CHAPTER 1 COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Getting to Know AutoCAD. Opening a new drawing. Getting familiar with the AutoCAD and AutoCAD LT Graphics windows
 CHAPTER 1 Getting to Know AutoCAD Opening a new drawing Getting familiar with the AutoCAD and AutoCAD LT Graphics windows Modifying the display Displaying and arranging toolbars COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 2
CHAPTER 1 Getting to Know AutoCAD Opening a new drawing Getting familiar with the AutoCAD and AutoCAD LT Graphics windows Modifying the display Displaying and arranging toolbars COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 2
AEMLog Users Guide. Version 1.01
 AEMLog Users Guide Version 1.01 INTRODUCTION...2 DOCUMENTATION...2 INSTALLING AEMLOG...4 AEMLOG QUICK REFERENCE...5 THE MAIN GRAPH SCREEN...5 MENU COMMANDS...6 File Menu...6 Graph Menu...7 Analysis Menu...8
AEMLog Users Guide Version 1.01 INTRODUCTION...2 DOCUMENTATION...2 INSTALLING AEMLOG...4 AEMLOG QUICK REFERENCE...5 THE MAIN GRAPH SCREEN...5 MENU COMMANDS...6 File Menu...6 Graph Menu...7 Analysis Menu...8
Geographical Information Systems Institute. Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University. LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap
 Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
Tutorial 3: Using the Waveform Viewer Introduces the basics of using the waveform viewer. Read Tutorial SIMPLIS Tutorials SIMPLIS provide a range of t
 Tutorials Introductory Tutorials These tutorials are designed to give new users a basic understanding of how to use SIMetrix and SIMetrix/SIMPLIS. Tutorial 1: Getting Started Guides you through getting
Tutorials Introductory Tutorials These tutorials are designed to give new users a basic understanding of how to use SIMetrix and SIMetrix/SIMPLIS. Tutorial 1: Getting Started Guides you through getting
Microsoft Windows 7 - Illustrated Unit A: Introducing Windows 7
 Microsoft Windows 7 - Illustrated Unit A: Introducing Windows 7 Objectives Start Windows and view the desktop Use pointing devices Use the Start button Use the taskbar Work with windows 2 Objectives Use
Microsoft Windows 7 - Illustrated Unit A: Introducing Windows 7 Objectives Start Windows and view the desktop Use pointing devices Use the Start button Use the taskbar Work with windows 2 Objectives Use
CREATING A NEW SURVEY IN
 CREATING A NEW SURVEY IN 1. Click to start a new survey 2. Type a name for the survey in the Survey field dialog box e.g., Quick 3. Enter a descriptive title for the survey in the Title field. - Quick
CREATING A NEW SURVEY IN 1. Click to start a new survey 2. Type a name for the survey in the Survey field dialog box e.g., Quick 3. Enter a descriptive title for the survey in the Title field. - Quick
Microsoft Excel XP. Intermediate
 Microsoft Excel XP Intermediate Jonathan Thomas March 2006 Contents Lesson 1: Headers and Footers...1 Lesson 2: Inserting, Viewing and Deleting Cell Comments...2 Options...2 Lesson 3: Printing Comments...3
Microsoft Excel XP Intermediate Jonathan Thomas March 2006 Contents Lesson 1: Headers and Footers...1 Lesson 2: Inserting, Viewing and Deleting Cell Comments...2 Options...2 Lesson 3: Printing Comments...3
MICROSOFT POWERPOINT 2016 Quick Reference Guide
 MICROSOFT POWERPOINT 2016 Quick Reference Guide PowerPoint What is it? What s new in PowerPoint 2016? PowerPoint is a computer program that allows you to create, edit and produce slide show presentations.
MICROSOFT POWERPOINT 2016 Quick Reference Guide PowerPoint What is it? What s new in PowerPoint 2016? PowerPoint is a computer program that allows you to create, edit and produce slide show presentations.
Press the Plus + key to zoom in. Press the Minus - key to zoom out. Scroll the mouse wheel away from you to zoom in; towards you to zoom out.
 Navigate Around the Map Interactive maps provide many choices for displaying information, searching for more details, and moving around the map. Most navigation uses the mouse, but at times you may also
Navigate Around the Map Interactive maps provide many choices for displaying information, searching for more details, and moving around the map. Most navigation uses the mouse, but at times you may also
StitchGraph User Guide V1.8
 StitchGraph User Guide V1.8 Thanks for buying StitchGraph: the easy way to create stitch layouts for hardanger and other complex embroidery stitch types. StitchGraph is intended to allow you to create
StitchGraph User Guide V1.8 Thanks for buying StitchGraph: the easy way to create stitch layouts for hardanger and other complex embroidery stitch types. StitchGraph is intended to allow you to create
QUEEN MARY, UNIVERSITY OF LONDON. Introduction to Statistics
 QUEEN MARY, UNIVERSITY OF LONDON MTH 4106 Introduction to Statistics Practical 1 10 January 2012 In this practical you will be introduced to the statistical computing package called Minitab. You will use
QUEEN MARY, UNIVERSITY OF LONDON MTH 4106 Introduction to Statistics Practical 1 10 January 2012 In this practical you will be introduced to the statistical computing package called Minitab. You will use
Learning Microsoft Word By Greg Bowden. Chapter 10. Drawing Tools. Guided Computer Tutorials
 Learning Microsoft Word 2007 By Greg Bowden Chapter 10 Drawing Tools Guided Computer Tutorials www.gct.com.au PUBLISHED BY GUIDED COMPUTER TUTORIALS PO Box 311 Belmont, Victoria, 3216, Australia www.gct.com.au
Learning Microsoft Word 2007 By Greg Bowden Chapter 10 Drawing Tools Guided Computer Tutorials www.gct.com.au PUBLISHED BY GUIDED COMPUTER TUTORIALS PO Box 311 Belmont, Victoria, 3216, Australia www.gct.com.au
ArcView QuickStart Guide. Contents. The ArcView Screen. Elements of an ArcView Project. Creating an ArcView Project. Adding Themes to Views
 ArcView QuickStart Guide Page 1 ArcView QuickStart Guide Contents The ArcView Screen Elements of an ArcView Project Creating an ArcView Project Adding Themes to Views Zoom and Pan Tools Querying Themes
ArcView QuickStart Guide Page 1 ArcView QuickStart Guide Contents The ArcView Screen Elements of an ArcView Project Creating an ArcView Project Adding Themes to Views Zoom and Pan Tools Querying Themes
In this chapter we explain the structure and use of BestDose, with examples.
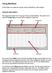 Using BestDose In this chapter we explain the structure and use of BestDose, with examples. General description The image below shows the view you get when you start BestDose. The actual view is called
Using BestDose In this chapter we explain the structure and use of BestDose, with examples. General description The image below shows the view you get when you start BestDose. The actual view is called
IT82: Multimedia Macromedia Director Practical 1
 IT82: Multimedia Macromedia Director Practical 1 Over the course of these labs, you will be introduced Macromedia s Director multimedia authoring tool. This is the de facto standard for time-based multimedia
IT82: Multimedia Macromedia Director Practical 1 Over the course of these labs, you will be introduced Macromedia s Director multimedia authoring tool. This is the de facto standard for time-based multimedia
Exploring extreme weather with Excel - The basics
 Exploring extreme weather with Excel - The basics These activities will help to develop your data skills using Excel and explore extreme weather in the UK. This activity introduces the basics of using
Exploring extreme weather with Excel - The basics These activities will help to develop your data skills using Excel and explore extreme weather in the UK. This activity introduces the basics of using
Grade 8 FSA Mathematics Practice Test Guide
 Grade 8 FSA Mathematics Practice Test Guide This guide serves as a walkthrough of the Grade 8 Florida Standards Assessments (FSA) Mathematics practice test. By reviewing the steps listed below, you will
Grade 8 FSA Mathematics Practice Test Guide This guide serves as a walkthrough of the Grade 8 Florida Standards Assessments (FSA) Mathematics practice test. By reviewing the steps listed below, you will
Clip Art and Graphics. Inserting Clip Art. Inserting Other Graphics. Creating Your Own Shapes. Formatting the Shape
 1 of 1 Clip Art and Graphics Inserting Clip Art Click where you want the picture to go (you can change its position later.) From the Insert tab, find the Illustrations Area and click on the Clip Art button
1 of 1 Clip Art and Graphics Inserting Clip Art Click where you want the picture to go (you can change its position later.) From the Insert tab, find the Illustrations Area and click on the Clip Art button
Parametric Modeling. With. Autodesk Inventor. Randy H. Shih. Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS
 Parametric Modeling With Autodesk Inventor R10 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric
Parametric Modeling With Autodesk Inventor R10 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric
Bill Analyser User Guide
 Bill Analyser User Guide emobile.ie/business Contents 1.0 Basic Concepts... 3 1.1 Users and Roles... 3 Standard Users... 3 Global Users... 3 eircom User Roles... 3 Available user roles... 3 1.2 Data Structure...
Bill Analyser User Guide emobile.ie/business Contents 1.0 Basic Concepts... 3 1.1 Users and Roles... 3 Standard Users... 3 Global Users... 3 eircom User Roles... 3 Available user roles... 3 1.2 Data Structure...
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis
 Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Stamina Software Pty Ltd. TRAINING MANUAL Viságe BIT VIEWER
 Stamina Software Pty Ltd TRAINING MANUAL Viságe BIT VIEWER Version: 3 31 st October 2011 Viságe BIT Viewer TABLE OF CONTENTS VISÁGE BIT VIEWER... 2 ELEMENTS OF THE VISÁGE BIT VIEWER SCREEN... 3 TITLE...
Stamina Software Pty Ltd TRAINING MANUAL Viságe BIT VIEWER Version: 3 31 st October 2011 Viságe BIT Viewer TABLE OF CONTENTS VISÁGE BIT VIEWER... 2 ELEMENTS OF THE VISÁGE BIT VIEWER SCREEN... 3 TITLE...
Beginning Tutorial the Lego
 Beginning Tutorial the Lego In this tutorial, you will construct a simple hollowed-out block with a hole in it (looks like a Lego). You will learn the basics of creating and modifying sketches and features.
Beginning Tutorial the Lego In this tutorial, you will construct a simple hollowed-out block with a hole in it (looks like a Lego). You will learn the basics of creating and modifying sketches and features.
PowerPoint 2016 Building a Presentation
 PowerPoint 2016 Building a Presentation What is PowerPoint? PowerPoint is presentation software that helps users quickly and efficiently create dynamic, professional-looking presentations through the use
PowerPoint 2016 Building a Presentation What is PowerPoint? PowerPoint is presentation software that helps users quickly and efficiently create dynamic, professional-looking presentations through the use
On the Web sun.com/aboutsun/comm_invest STAROFFICE 8 DRAW
 STAROFFICE 8 DRAW Graphics They say a picture is worth a thousand words. Pictures are often used along with our words for good reason. They help communicate our thoughts. They give extra information that
STAROFFICE 8 DRAW Graphics They say a picture is worth a thousand words. Pictures are often used along with our words for good reason. They help communicate our thoughts. They give extra information that
Slides & Presentations
 Section 2 Slides & Presentations ECDL Section 2 Slides & Presentations By the end of this section you should be able to: Understand and Use Different Views Understand Slide Show Basics Save, Close and
Section 2 Slides & Presentations ECDL Section 2 Slides & Presentations By the end of this section you should be able to: Understand and Use Different Views Understand Slide Show Basics Save, Close and
Microsoft Excel 2007
 Learning computers is Show ezy Microsoft Excel 2007 301 Excel screen, toolbars, views, sheets, and uses for Excel 2005-8 Steve Slisar 2005-8 COPYRIGHT: The copyright for this publication is owned by Steve
Learning computers is Show ezy Microsoft Excel 2007 301 Excel screen, toolbars, views, sheets, and uses for Excel 2005-8 Steve Slisar 2005-8 COPYRIGHT: The copyright for this publication is owned by Steve
4 TRANSFORMING OBJECTS
 4 TRANSFORMING OBJECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Add, edit, rename, and reorder artboards in an existing document. Navigate artboards. Select individual objects,
4 TRANSFORMING OBJECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Add, edit, rename, and reorder artboards in an existing document. Navigate artboards. Select individual objects,
Working with Objects. Chapter 6. Objectives
 Working with Objects Chapter 6 Objects can easily be inserted into documents to illustrate the points you are making in the document. You can use drawing objects, clipart and other images. Objectives In
Working with Objects Chapter 6 Objects can easily be inserted into documents to illustrate the points you are making in the document. You can use drawing objects, clipart and other images. Objectives In
Getting Started with Crazy Talk 6
 Getting Started with Crazy Talk 6 Crazy Talk 6 is an application that generates talking characters from an image or photo, as well as facial animation for video. Importing an Image Launch Crazy Talk and
Getting Started with Crazy Talk 6 Crazy Talk 6 is an application that generates talking characters from an image or photo, as well as facial animation for video. Importing an Image Launch Crazy Talk and
Title of Resource Introduction to SPSS 22.0: Assignment and Grading Rubric Kimberly A. Barchard. Author(s)
 Title of Resource Introduction to SPSS 22.0: Assignment and Grading Rubric Kimberly A. Barchard Author(s) Leiszle Lapping-Carr Institution University of Nevada, Las Vegas Students learn the basics of SPSS,
Title of Resource Introduction to SPSS 22.0: Assignment and Grading Rubric Kimberly A. Barchard Author(s) Leiszle Lapping-Carr Institution University of Nevada, Las Vegas Students learn the basics of SPSS,
Data logger. Overview. PDF created with FinePrint pdffactory trial version
 Data logger Overview The PC control software now includes a data logger that can record 8 channels of information from the ECU. Selecting Data logger from the Graph drop down menu accesses the data logger
Data logger Overview The PC control software now includes a data logger that can record 8 channels of information from the ECU. Selecting Data logger from the Graph drop down menu accesses the data logger
Use the Move tool to drag A around and see how the automatically constructed objects (like G or the perpendicular and parallel lines) are updated.
 Math 5335 Fall 2015 Lab #0: Installing and using GeoGebra This semester you will have a number of lab assignments which require you to use GeoGebra, a dynamic geometry program. GeoGebra lets you explore
Math 5335 Fall 2015 Lab #0: Installing and using GeoGebra This semester you will have a number of lab assignments which require you to use GeoGebra, a dynamic geometry program. GeoGebra lets you explore
In the first class, you'll learn how to create a simple single-view app, following a 3-step process:
 Class 1 In the first class, you'll learn how to create a simple single-view app, following a 3-step process: 1. Design the app's user interface (UI) in Xcode's storyboard. 2. Open the assistant editor,
Class 1 In the first class, you'll learn how to create a simple single-view app, following a 3-step process: 1. Design the app's user interface (UI) in Xcode's storyboard. 2. Open the assistant editor,
Autodesk Fusion 360: Model. Overview. Modeling techniques in Fusion 360
 Overview Modeling techniques in Fusion 360 Modeling in Fusion 360 is quite a different experience from how you would model in conventional history-based CAD software. Some users have expressed that it
Overview Modeling techniques in Fusion 360 Modeling in Fusion 360 is quite a different experience from how you would model in conventional history-based CAD software. Some users have expressed that it
To complete this activity, you will need the following files:
 CHAPTER 1 Windows XP More Skills 12 Move Data Between Windows You can open several application windows at the same time; they do not need to be files created by the same program. Having more than one window
CHAPTER 1 Windows XP More Skills 12 Move Data Between Windows You can open several application windows at the same time; they do not need to be files created by the same program. Having more than one window
Creating a Title Block & Border Using Chief Architect. Architectural Design & Residential Construction Penncrest High School
 Creating a Title Block & Border Using Chief Architect Architectural Design & Residential Construction Penncrest High School 2017-2018 Select New Layout to begin designing your Title Block. Note: Once the
Creating a Title Block & Border Using Chief Architect Architectural Design & Residential Construction Penncrest High School 2017-2018 Select New Layout to begin designing your Title Block. Note: Once the
Veco User Guides. Grids, Views, and Grid Reports
 Veco User Guides Grids, Views, and Grid Reports Introduction A Grid is defined as being a list of data records presented to the user. A grid is shown generally when an option is selected from the Tree
Veco User Guides Grids, Views, and Grid Reports Introduction A Grid is defined as being a list of data records presented to the user. A grid is shown generally when an option is selected from the Tree
Session 3: Cartography in ArcGIS. Mapping population data
 Exercise 3: Cartography in ArcGIS Mapping population data Background GIS is well known for its ability to produce high quality maps. ArcGIS provides useful tools that allow you to do this. It is important
Exercise 3: Cartography in ArcGIS Mapping population data Background GIS is well known for its ability to produce high quality maps. ArcGIS provides useful tools that allow you to do this. It is important
Links to Activities ACTIVITY 1.1. Links to Activities Links to Activities
 EXCEL Analyzing Data Using Excel Section 1 Skills Start Excel and identify features in the Excel window Enter labels and values Use the fill handle to enter a series Enter formulas Create a formula using
EXCEL Analyzing Data Using Excel Section 1 Skills Start Excel and identify features in the Excel window Enter labels and values Use the fill handle to enter a series Enter formulas Create a formula using
MAKING TABLES WITH WORD BASIC INSTRUCTIONS. Setting the Page Orientation. Inserting the Basic Table. Daily Schedule
 MAKING TABLES WITH WORD BASIC INSTRUCTIONS Setting the Page Orientation Once in word, decide if you want your paper to print vertically (the normal way, called portrait) or horizontally (called landscape)
MAKING TABLES WITH WORD BASIC INSTRUCTIONS Setting the Page Orientation Once in word, decide if you want your paper to print vertically (the normal way, called portrait) or horizontally (called landscape)
Status Bar: Right click on the Status Bar to add or remove features.
 Excel 2013 Quick Start Guide The Excel Window File Tab: Click to access actions like Print, Save As, etc. Also to set Excel options. Ribbon: Logically organizes actions onto Tabs, Groups, and Buttons to
Excel 2013 Quick Start Guide The Excel Window File Tab: Click to access actions like Print, Save As, etc. Also to set Excel options. Ribbon: Logically organizes actions onto Tabs, Groups, and Buttons to
Introducing Gupta Report Builder
 Business Reporting Chapter 1 Introducing Gupta Report Builder You can use Report Builder to design reports. This chapter describes: Our approach to building reports. Some of the reports you can build.
Business Reporting Chapter 1 Introducing Gupta Report Builder You can use Report Builder to design reports. This chapter describes: Our approach to building reports. Some of the reports you can build.
Sample Chapters. To learn more about this book, visit the detail page at: go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=192147
 Sample Chapters Copyright 2010 by Online Training Solutions, Inc. All rights reserved. To learn more about this book, visit the detail page at: go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=192147 Chapter at a Glance
Sample Chapters Copyright 2010 by Online Training Solutions, Inc. All rights reserved. To learn more about this book, visit the detail page at: go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=192147 Chapter at a Glance
Study Guide. PCIC 3 B2 GS3- Key Applications-Excel. Copyright 2010 Teknimedia Corporation
 Study Guide PCIC 3 B2 GS3- Key Applications-Excel Copyright 2010 Teknimedia Corporation Teknimedia grants permission to any licensed owner of PCIC 3 B GS3 Key Applications-Excel to duplicate the contents
Study Guide PCIC 3 B2 GS3- Key Applications-Excel Copyright 2010 Teknimedia Corporation Teknimedia grants permission to any licensed owner of PCIC 3 B GS3 Key Applications-Excel to duplicate the contents
Student Success Guide
 Student Success Guide Contents Like a web page, links in this document can be clicked and they will take you to where you want to go. Using a Mouse 6 The Left Button 6 The Right Button 7 The Scroll Wheel
Student Success Guide Contents Like a web page, links in this document can be clicked and they will take you to where you want to go. Using a Mouse 6 The Left Button 6 The Right Button 7 The Scroll Wheel
Intro To Excel Spreadsheet for use in Introductory Sciences
 INTRO TO EXCEL SPREADSHEET (World Population) Objectives: Become familiar with the Excel spreadsheet environment. (Parts 1-5) Learn to create and save a worksheet. (Part 1) Perform simple calculations,
INTRO TO EXCEL SPREADSHEET (World Population) Objectives: Become familiar with the Excel spreadsheet environment. (Parts 1-5) Learn to create and save a worksheet. (Part 1) Perform simple calculations,
Academic Word Processing with Word 2003
 Academic Word Processing with Word 2003 Doc 5.133 Ver 1 John Matthews May 2005 Central Computing Services Prerequisites This document assumes that you are familiar with the use of a computer keyboard and
Academic Word Processing with Word 2003 Doc 5.133 Ver 1 John Matthews May 2005 Central Computing Services Prerequisites This document assumes that you are familiar with the use of a computer keyboard and
C omputer D riving L icence
 E uropean C omputer D riving L icence E C D L S y l l a b u s 5. 0 Module 6 Presentation ECDL Syllabus 5 Courseware Module 6 Contents USING THE APPLICATION... 1 OPENING & CLOSING MS POWERPOINT & PRESENTATIONS...
E uropean C omputer D riving L icence E C D L S y l l a b u s 5. 0 Module 6 Presentation ECDL Syllabus 5 Courseware Module 6 Contents USING THE APPLICATION... 1 OPENING & CLOSING MS POWERPOINT & PRESENTATIONS...
FSA Algebra 1 EOC Practice Test Guide
 FSA Algebra 1 EOC Practice Test Guide This guide serves as a walkthrough of the Florida Standards Assessments (FSA) Algebra 1 End-of- Course (EOC) practice test. By reviewing the steps listed below, you
FSA Algebra 1 EOC Practice Test Guide This guide serves as a walkthrough of the Florida Standards Assessments (FSA) Algebra 1 End-of- Course (EOC) practice test. By reviewing the steps listed below, you
Unit 21 - Creating a Navigation Bar in Macromedia Fireworks
 Unit 21 - Creating a Navigation Bar in Macromedia Fireworks Items needed to complete the Navigation Bar: Unit 21 - House Style Unit 21 - Graphics Sketch Diagrams Document ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Unit 21 - Creating a Navigation Bar in Macromedia Fireworks Items needed to complete the Navigation Bar: Unit 21 - House Style Unit 21 - Graphics Sketch Diagrams Document ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2.1 System Dynamics Tool: Vensim PLE Version 6.2 Tutorial 1
 2.1 System Dynamics Tool: Vensim PLE Version 6.2 Tutorial 1 Introduction to Computational Science: Modeling and Simulation for the Sciences, 2nd Edition Angela B. Shiflet and George W. Shiflet Wofford
2.1 System Dynamics Tool: Vensim PLE Version 6.2 Tutorial 1 Introduction to Computational Science: Modeling and Simulation for the Sciences, 2nd Edition Angela B. Shiflet and George W. Shiflet Wofford
Using Microsoft Word. Tables
 Using Microsoft Word are a useful way of arranging information on a page. In their simplest form, tables can be used to place information in lists. More complex tables can be used to arrange graphics on
Using Microsoft Word are a useful way of arranging information on a page. In their simplest form, tables can be used to place information in lists. More complex tables can be used to arrange graphics on
In this lesson, you ll learn how to:
 LESSON 5: ADVANCED DRAWING TECHNIQUES OBJECTIVES In this lesson, you ll learn how to: apply gradient fills modify graphics by smoothing, straightening, and optimizing understand the difference between
LESSON 5: ADVANCED DRAWING TECHNIQUES OBJECTIVES In this lesson, you ll learn how to: apply gradient fills modify graphics by smoothing, straightening, and optimizing understand the difference between
Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2010
 Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2010 This class is designed to cover the following basics: What you can do with Excel Excel Ribbon Moving and selecting cells Formatting cells Adding Worksheets, Rows and
Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2010 This class is designed to cover the following basics: What you can do with Excel Excel Ribbon Moving and selecting cells Formatting cells Adding Worksheets, Rows and
WAIPA DISTRICT COUNCIL. Maps Online 9. Updated January This document contains an overview of IntraMaps/Maps Online version 9.
 WAIPA DISTRICT COUNCIL Maps Online 9 Updated January 2018 This document contains an overview of IntraMaps/Maps Online version 9.0 Contents Starting Maps Online... 3 Menu Bar... 4 Tools... 5 View Tab...
WAIPA DISTRICT COUNCIL Maps Online 9 Updated January 2018 This document contains an overview of IntraMaps/Maps Online version 9.0 Contents Starting Maps Online... 3 Menu Bar... 4 Tools... 5 View Tab...
Creating and Modifying Charts
 Creating and Modifying Charts Introduction When you re ready to share data with others, a worksheet might not be the most effective way to present the information. A page full of numbers, even if formatted
Creating and Modifying Charts Introduction When you re ready to share data with others, a worksheet might not be the most effective way to present the information. A page full of numbers, even if formatted
Introduction to MS Office Somy Kuriakose Principal Scientist, FRAD, CMFRI
 Introduction to MS Office Somy Kuriakose Principal Scientist, FRAD, CMFRI Email: somycmfri@gmail.com 29 Word, Excel and Power Point Microsoft Office is a productivity suite which integrates office tools
Introduction to MS Office Somy Kuriakose Principal Scientist, FRAD, CMFRI Email: somycmfri@gmail.com 29 Word, Excel and Power Point Microsoft Office is a productivity suite which integrates office tools
Section 3 Formatting
 Section 3 Formatting ECDL 5.0 Section 3 Formatting By the end of this Section you should be able to: Apply Formatting, Text Effects and Bullets Use Undo and Redo Change Alignment and Spacing Use Cut, Copy
Section 3 Formatting ECDL 5.0 Section 3 Formatting By the end of this Section you should be able to: Apply Formatting, Text Effects and Bullets Use Undo and Redo Change Alignment and Spacing Use Cut, Copy
Using SymPrint to Make Overlays, Templates & More...
 Welcome to SymPrint SymPrint is an easy-to-use tool for creating communication overlays, worksheets, classroom activities and more using a modern toolbar and common-sense interface modeled after the programs
Welcome to SymPrint SymPrint is an easy-to-use tool for creating communication overlays, worksheets, classroom activities and more using a modern toolbar and common-sense interface modeled after the programs
Websites Geogebra Homepage: Use the Webstart Version of Geogebra or download a stand alone version.
 GeoGebra Workshop 24 th May 2010 Paul Robinson, IT Tallaght Websites Geogebra Homepage: http://www.geogebra.org/cms/ Use the Webstart Version of Geogebra or download a stand alone version. Geogebra Forum:
GeoGebra Workshop 24 th May 2010 Paul Robinson, IT Tallaght Websites Geogebra Homepage: http://www.geogebra.org/cms/ Use the Webstart Version of Geogebra or download a stand alone version. Geogebra Forum:
Creating a Basic Chart in Excel 2007
 Creating a Basic Chart in Excel 2007 A chart is a pictorial representation of the data you enter in a worksheet. Often, a chart can be a more descriptive way of representing your data. As a result, those
Creating a Basic Chart in Excel 2007 A chart is a pictorial representation of the data you enter in a worksheet. Often, a chart can be a more descriptive way of representing your data. As a result, those
To complete this database, you will need the following file:
 = CHAPTER 6 Access More Skills 11 Add Option Groups to Forms An option group is a frame with a set of check boxes, toggle buttons, or option buttons. Option groups can be bound or unbound to a field. When
= CHAPTER 6 Access More Skills 11 Add Option Groups to Forms An option group is a frame with a set of check boxes, toggle buttons, or option buttons. Option groups can be bound or unbound to a field. When
Digital Media. Seasons Assignment. 1. Copy and open the file seasonsbegin.fla from the Read folder.
 Digital Media Seasons Assignment 1. Copy and open the file seasonsbegin.fla from the Read folder. 2. Make a new layer for buttons. Create a button that the user will click to start the interaction. (Be
Digital Media Seasons Assignment 1. Copy and open the file seasonsbegin.fla from the Read folder. 2. Make a new layer for buttons. Create a button that the user will click to start the interaction. (Be
Visual Insights system
 Visual Insights system Supplier User Guide Packaged (Pick by store) version Date: September 2016 1 Contents Visual Insights system... 1 Supplier User Guide... 1 Grocery version... 1 1.0 Overview and Purpose...
Visual Insights system Supplier User Guide Packaged (Pick by store) version Date: September 2016 1 Contents Visual Insights system... 1 Supplier User Guide... 1 Grocery version... 1 1.0 Overview and Purpose...
Navigator Software User s Manual. User Manual. Navigator Software. Monarch Instrument Rev 0.98 May Page 1 of 17
 User Manual Navigator Software Monarch Instrument Rev 0.98 May 2006 Page 1 of 17 Contents 1. NAVIGATOR SOFTWARE 2. INSTALLATION 3. USING NAVIGATOR SOFTWARE 3.1 STARTING THE PROGRAM 3.2 SYSTEM SET UP 3.3
User Manual Navigator Software Monarch Instrument Rev 0.98 May 2006 Page 1 of 17 Contents 1. NAVIGATOR SOFTWARE 2. INSTALLATION 3. USING NAVIGATOR SOFTWARE 3.1 STARTING THE PROGRAM 3.2 SYSTEM SET UP 3.3
Using Microsoft Word. Text Editing
 Using Microsoft Word A word processor is all about working with large amounts of text, so learning the basics of text editing is essential to being able to make the most of the program. The first thing
Using Microsoft Word A word processor is all about working with large amounts of text, so learning the basics of text editing is essential to being able to make the most of the program. The first thing
How to...create a Video VBOX Gauge in Inkscape. So you want to create your own gauge? How about a transparent background for those text elements?
 BASIC GAUGE CREATION The Video VBox setup software is capable of using many different image formats for gauge backgrounds, static images, or logos, including Bitmaps, JPEGs, or PNG s. When the software
BASIC GAUGE CREATION The Video VBox setup software is capable of using many different image formats for gauge backgrounds, static images, or logos, including Bitmaps, JPEGs, or PNG s. When the software
Part 1: Basics. Page Sorter:
 Part 1: Basics Page Sorter: The Page Sorter displays all the pages in an open file as thumbnails and automatically updates as you add content. The page sorter can do the following. Display Pages Create
Part 1: Basics Page Sorter: The Page Sorter displays all the pages in an open file as thumbnails and automatically updates as you add content. The page sorter can do the following. Display Pages Create
3.1 System Dynamics Tool: Vensim PLE Tutorial 1. Introduction to Computational Science: Modeling and Simulation for the Sciences
 3.1 System Dynamics Tool: Vensim PLE Tutorial 1 Introduction to Computational Science: Modeling and Simulation for the Sciences Angela B. Shiflet and George W. Shiflet Wofford College 2011 by Princeton
3.1 System Dynamics Tool: Vensim PLE Tutorial 1 Introduction to Computational Science: Modeling and Simulation for the Sciences Angela B. Shiflet and George W. Shiflet Wofford College 2011 by Princeton
MatDeck User Manual. Contents
 MatDeck User Manual Contents Table of Pictures... 2 1 Activate license - Help tab... 6 2 MatDeck basics... 7 2.1 Document list area... 7 2.2 Document area... 8 2.2.1 Data types... 8 2.2.2 Variables...
MatDeck User Manual Contents Table of Pictures... 2 1 Activate license - Help tab... 6 2 MatDeck basics... 7 2.1 Document list area... 7 2.2 Document area... 8 2.2.1 Data types... 8 2.2.2 Variables...
Let s Make a Front Panel using FrontCAD
 Let s Make a Front Panel using FrontCAD By Jim Patchell FrontCad is meant to be a simple, easy to use CAD program for creating front panel designs and artwork. It is a free, open source program, with the
Let s Make a Front Panel using FrontCAD By Jim Patchell FrontCad is meant to be a simple, easy to use CAD program for creating front panel designs and artwork. It is a free, open source program, with the
6.3. Applying Designs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER Now we ll look at the overall appearance of the slides. The slides could do with brightening up a bit to increase the impact of the presentation. We ll also insert some pictures to add interest.
CHAPTER Now we ll look at the overall appearance of the slides. The slides could do with brightening up a bit to increase the impact of the presentation. We ll also insert some pictures to add interest.
Colony Counting User Manual A D I V I S I O N O F S Y N O P T I C S L T D
 ProtoCOL Colony Counting User Manual S Y N B I O S I S A D I V I S I O N O F S Y N O P T I C S L T D All possible care has been taken in the preparation of this publication, but Synoptics Limited accepts
ProtoCOL Colony Counting User Manual S Y N B I O S I S A D I V I S I O N O F S Y N O P T I C S L T D All possible care has been taken in the preparation of this publication, but Synoptics Limited accepts
Information Technology and Media Services. Office Excel. Charts
 Information Technology and Media Services Office 2010 Excel Charts August 2014 Information Technology and Media Services CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 CHART TYPES... 3 CHOOSING A CHART... 4 CREATING A COLUMN
Information Technology and Media Services Office 2010 Excel Charts August 2014 Information Technology and Media Services CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 CHART TYPES... 3 CHOOSING A CHART... 4 CREATING A COLUMN
Handout Objectives: a. b. c. d. 3. a. b. c. d. e a. b. 6. a. b. c. d. Overview:
 Computer Basics I Handout Objectives: 1. Control program windows and menus. 2. Graphical user interface (GUI) a. Desktop b. Manage Windows c. Recycle Bin d. Creating a New Folder 3. Control Panel. a. Appearance
Computer Basics I Handout Objectives: 1. Control program windows and menus. 2. Graphical user interface (GUI) a. Desktop b. Manage Windows c. Recycle Bin d. Creating a New Folder 3. Control Panel. a. Appearance
Lastly, in case you don t already know this, and don t have Excel on your computers, you can get it for free through IT s website under software.
 Welcome to Basic Excel, presented by STEM Gateway as part of the Essential Academic Skills Enhancement, or EASE, workshop series. Before we begin, I want to make sure we are clear that this is by no means
Welcome to Basic Excel, presented by STEM Gateway as part of the Essential Academic Skills Enhancement, or EASE, workshop series. Before we begin, I want to make sure we are clear that this is by no means
Contents. Introduction. CDI V3 Help Quick Search
 Contents Introduction... 1 A The interface... 2 A-1 Introduction... 2 A-2. Results list... 2 A-3: Additional menu options... 3 B. Searching the CDI entries metadata... 4 B-1 Narrowing down your result
Contents Introduction... 1 A The interface... 2 A-1 Introduction... 2 A-2. Results list... 2 A-3: Additional menu options... 3 B. Searching the CDI entries metadata... 4 B-1 Narrowing down your result
Working with PDF s. To open a recent file on the Start screen, double click on the file name.
 Working with PDF s Acrobat DC Start Screen (Home Tab) When Acrobat opens, the Acrobat Start screen (Home Tab) populates displaying a list of recently opened files. The search feature on the top of the
Working with PDF s Acrobat DC Start Screen (Home Tab) When Acrobat opens, the Acrobat Start screen (Home Tab) populates displaying a list of recently opened files. The search feature on the top of the
FSA Geometry EOC Practice Test Guide
 FSA Geometry EOC Practice Test Guide This guide serves as a walkthrough of the Florida Standards Assessments (FSA) Geometry End-of- Course (EOC) practice test. By reviewing the steps listed below, you
FSA Geometry EOC Practice Test Guide This guide serves as a walkthrough of the Florida Standards Assessments (FSA) Geometry End-of- Course (EOC) practice test. By reviewing the steps listed below, you
