A binary search tree or BST is a binary tree that is either empty or in which the data element of each node has a key and satisfies the conditions:
|
|
|
- Catherine Andrews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 The general binary tree shown is not terribly useful in practice. The chief use of binary trees is for providing rapid access to data (indexing, if you will) and the general binary tree does not have good performance. Suppose that we wish to store data elements that contain a number of fields, and that one of those fields is distinguished as the key upon which searches will be performed. A binary search tree or ST is a binary tree that is either empty or in which the data element of each node has a key and satisfies the conditions: 1. The key of the left child (if there is one) is less than the key of its parent node. 2. The key of the right child (if there is one) is greater than or equal to the key of its parent node. 3. The left and right subtrees of the root are binary search trees.
2 ST Insertion 2 ere, the key values are characters (and only key values are shown). Inserting the following key values in the given order yields the given ST: In a ST, insertion is always at the leaf level. Traverse the ST, comparing the new value to existing ones, until you find the right spot, then add a new leaf node holding that value. What is the resulting tree if the (same) key values are inserted in the order: or
3 Searching in a ST 3 ecause of the key ordering imposed by a ST, searching resembles the binary search algorithm on a sorted array, which is O(log N) for an array of N elements. A ST offers the advantage of purely dynamic storage, no wasted array cells and no shifting of the array tail on insertion and deletion. A Trace searching for the key value.
4 ST eletion 4 eletion is perhaps the most complex operation on a ST, because the algorithm must result in a ST. The question is: what value should replace the one deleted? As with the general tree, we have cases: - Removing a leaf node is trivial, just set the relevant child pointer in the parent node to NULL. - Removing an internal node which has only one subtree is also trivial, just set the relevant child pointer in the parent node to target the root of the subtree. NULL
5 ST eletion 5 - Removing an internal node which has two subtrees is more complex Simply removing the node would disconnect the tree. ut what value should replace the one in the targeted node? To preserve the ST property, we must take the smallest value from the right subtree, which would be the closest succcessor of the value being deleted. ortunately, the smallest value will always lie in the left-most node of the subtree.
6 ST eletion 6 So, we first find the left-most node of the right subtree, and then swap data values between it and the targeted node. Note that at this point we don t necessarily have a ST. Now we must delete the swapped value from the right subtree. That looks straightforward here since the node in question is a leaf. owever - the node will NOT be a leaf in all cases - the occurrence of duplicate values is a complicating factor (so we might want to have a eleterightminimum() function to clean up at this point).
7 eleting the Minimum Value 7 Suppose we want to delete the value from the ST: After swapping the with the, we must delete We must be careful to not confuse this with the other node containing an. Also, consider deleting the value. In this case, the right subtree is just a leaf node, whose parent is the node originally targeted for deletion. Moral: be careful to consider ALL cases when designing.
8 ST lass Interface 8 A ST class may be derived from a general binary tree class, saving some work of implementation. template <class ata> class STreeT : public inarytreet<ata> { protected: bool Insertelper(ata, innodet<ata>* sroot); bool eleteelper(ata, innodet<ata>* sroot); bool movetoataelper(ata, innodet<ata>* sroot); public: STreeT(); STreeT(ata newata); ; bool Insert(ata ); bool elete(ata ); bool movetoata(ata ); bool seturrentata(ata ); ~STreeT(); The insert/delete rules are different for a ST, so we must override the base class versions of those. Searching is different in a ST, so we must override that as well. inally, we should override the set data function in order to prevent a client from breaking the data organization required in a ST. //... continues...
9 ST onstructors and estructor 9 The ST constructors can just use the base class constructors since the data members are identical. template <class ata> STreeT<ata>::STreeT() : inarytreet<ata>() { template <class ata> STreeT<ata>::STreeT(ata newata) : inarytreet<ata>(newata) { An empty ST destructor is provided. Recall that the base class destructor will be invoked automatically for a derived class object. template <class ata> STreeT<ata>::~STreeT() {
10 ST Search Implementation 10 The ST function takes advantage of the data organization: template <class ata> bool STreeT<ata>::moveToata(ata toind) { if (Root == NULL) return false; return (movetoataelper(toind, Root)); template <class ata> bool STreeT<ata>::moveToataelper(ata toind, innodet<ata>* sroot) { if (sroot == NULL) return false; if (sroot->getata() == toind) { urrent = sroot; return true; Uses operator== for the class ata, which is customized by the client for the particular application at hand. if (toind < sroot->getata()) return movetoataelper(toind, sroot->getleft()); else return movetoataelper(toind, sroot->getright()); Search direction is determined by relationship of target data to data in current node.
11 ST Insert Implementation 11 The public Insert function is logically identical to that in the base class: template <class ata> bool STreeT<ata>::Insert(ata ) { if (Root == NULL) { innodet<ata>* Temp = new innodet<ata>(); if (Temp == NULL) return false; Root = urrent = Temp; return true; return Insertelper(, Root); Warning: because the ST definition in these notes allows for duplicate data values to occur, the logic of insertion is slightly different from that presented in Kruse/Ryba. owever, the implementation of the helper function is substantially different. In the ST, we must follow the route determined by comparing the new data value to the existing data values in order to reach the appropriate point for an insertion. The modifications are left to the reader there are substantial differences from the implementation given in Kruse/Ryba due to the encapsulation of the data in the innodet class.
12 ST elete Implementation 12 The public elete function is very different from that in the base class. The public function still needs to handle deletion of the Root node; however, the logic is entirely different in the case where the Root node has two children: template <class ata> bool STreeT<ata>::elete(ata ) { if (Root == NULL) return false; if (Root->getata() == ) { innodet<ata>* toelete = Root; if (Root->getLeft() == NULL) { Root = Root->getRight(); delete toelete; return true; else if (Root->getRight() == NULL) { Root = Root->getLeft(); delete toelete; return true; asy cases, where Root node has no left subtree Root node has a left subtree, but no right subtree //... continues...
13 ST elete Implementation 13 The public elete function is very different from that in the base class. The public function still needs to handle deletion of the Root node; however, the logic is entirely different in the case where the Root node has two children: //... continued... else { innodet<ata>* Look = Root->getRight(); while (Look->getLeft()!= NULL) Look = Look->getLeft(); Root->setata(Look->getata()); Look->setata(); ard case where Root node has both a left subtree and a right subtree must find the closest successor of the data value in the Root node that will be in the left-most node of the right subtree then swap that data value into the Root node return eleterightminimum(root); and then chase that data value down the right subtree and delete it there return eleteelper(, Root);
14 ST elete elper unction 14 The protected elete helper function shares similarities with, but is also very different from, that in the base class. The changes are logically similar to those shown in the public elete function, and are left to the reader Warnings: The logic of deletion in a ST differs from that shown earlier for a general binary tree, since in a ST the search is driven by the organization of the data elements in the ST. The logic of deletion is different than that shown in Kruse/Ryba because we allow duplicate key values to occur. The implementation is (again) also very different because of the encapsulation of the private data in the innodet class, in contrast to the public struct elements used in Kruse/Ryba. QTP: ould we use the maximum value from the left subtree (as in Kruse/Ryba) when deleting a node with two subtrees?
15 alance in a ST 15 owever, a ST with N nodes does not always provide O(log N) search times. A A well-balanced ST. This will have log(n) search times in the worst case. A What if we inserted the values in the order: A A poorly-balanced ST. This will not have log(n) search times in the worst case.
Binary Trees. BSTs. For example: Jargon: Data Structures & Algorithms. root node. level: internal node. edge.
 Binary Trees 1 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the root, which are disjoint from
Binary Trees 1 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the root, which are disjoint from
Trees can be used to store entire records from a database, serving as an in-memory representation of the collection of records in a file.
 Large Trees 1 Trees can be used to store entire records from a database, serving as an in-memory representation of the collection of records in a file. Trees can also be used to store indices of the collection
Large Trees 1 Trees can be used to store entire records from a database, serving as an in-memory representation of the collection of records in a file. Trees can also be used to store indices of the collection
Binary Trees. For example: Jargon: General Binary Trees. root node. level: internal node. edge. leaf node. Data Structures & File Management
 Binary Trees 1 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the root, which are disjoint from
Binary Trees 1 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the root, which are disjoint from
Chapter 20: Binary Trees
 Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Binary Trees. For example: Jargon: General Binary Trees. root node. level: internal node. edge. leaf node. Data Structures & File Management
 Binary Trees 1 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the root, which are disjoint from
Binary Trees 1 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the root, which are disjoint from
Binary Tree Node Relationships. Binary Trees. Quick Application: Expression Trees. Traversals
 Binary Trees 1 Binary Tree Node Relationships 2 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the
Binary Trees 1 Binary Tree Node Relationships 2 A binary tree is either empty, or it consists of a node called the root together with two binary trees called the left subtree and the right subtree of the
ITEC2620 Introduction to Data Structures
 9//201 T2620 ntroduction to ata Structures Lecture b nserting and eleting into Linked ata Structures nserting into Linked Lists nsert an element into a linked sorted from smallest to largest.g..insert(newvalue)
9//201 T2620 ntroduction to ata Structures Lecture b nserting and eleting into Linked ata Structures nserting into Linked Lists nsert an element into a linked sorted from smallest to largest.g..insert(newvalue)
Trees can be used to store entire records from a database, serving as an in-memory representation of the collection of records in a file.
 Large Trees 1 Trees can be used to store entire records from a database, serving as an in-memory representation of the collection of records in a file. Trees can also be used to store indices of the collection
Large Trees 1 Trees can be used to store entire records from a database, serving as an in-memory representation of the collection of records in a file. Trees can also be used to store indices of the collection
CS 2604 Data Structures Midterm Summer 2000 U T. Do not start the test until instructed to do so!
 VIRG INIA POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE AND STATE U T PROSI M UNI VERSI TY Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes. No calculators or other computing
VIRG INIA POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE AND STATE U T PROSI M UNI VERSI TY Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes. No calculators or other computing
CS102 Binary Search Trees
 CS102 Binary Search Trees Prof Tejada 1 To speed up insertion, removal and search, modify the idea of a Binary Tree to create a Binary Search Tree (BST) Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees have one
CS102 Binary Search Trees Prof Tejada 1 To speed up insertion, removal and search, modify the idea of a Binary Tree to create a Binary Search Tree (BST) Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees have one
Generic BST Interface
 Generic BST Interface Here s a partial generic BST interface: public class BST
Generic BST Interface Here s a partial generic BST interface: public class BST
A set of nodes (or vertices) with a single starting point
 Binary Search Trees Understand tree terminology Understand and implement tree traversals Define the binary search tree property Implement binary search trees Implement the TreeSort algorithm 2 A set of
Binary Search Trees Understand tree terminology Understand and implement tree traversals Define the binary search tree property Implement binary search trees Implement the TreeSort algorithm 2 A set of
Priority Queues. 1 Introduction. 2 Naïve Implementations. CSci 335 Software Design and Analysis III Chapter 6 Priority Queues. Prof.
 Priority Queues 1 Introduction Many applications require a special type of queuing in which items are pushed onto the queue by order of arrival, but removed from the queue based on some other priority
Priority Queues 1 Introduction Many applications require a special type of queuing in which items are pushed onto the queue by order of arrival, but removed from the queue based on some other priority
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
CSCI Trees. Mark Redekopp David Kempe
 CSCI 104 2-3 Trees Mark Redekopp David Kempe Trees & Maps/Sets C++ STL "maps" and "sets" use binary search trees internally to store their keys (and values) that can grow or contract as needed This allows
CSCI 104 2-3 Trees Mark Redekopp David Kempe Trees & Maps/Sets C++ STL "maps" and "sets" use binary search trees internally to store their keys (and values) that can grow or contract as needed This allows
Lec 17 April 8. Topics: binary Trees expression trees. (Chapter 5 of text)
 Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Trees. Chapter 6. strings. 3 Both position and Enumerator are similar in concept to C++ iterators, although the details are quite different.
 Chapter 6 Trees In a hash table, the items are not stored in any particular order in the table. This is fine for implementing Sets and Maps, since for those abstract data types, the only thing that matters
Chapter 6 Trees In a hash table, the items are not stored in any particular order in the table. This is fine for implementing Sets and Maps, since for those abstract data types, the only thing that matters
Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi Section Webpage:
 Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs32 Trees Definitions Yet another data structure -- trees. Just like a linked
Discussion 2C Notes (Week 8, February 25) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs32 Trees Definitions Yet another data structure -- trees. Just like a linked
! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges. ! Parent: source node of directed edge. ! Child: terminal node of directed edge
 Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges. ! Parent: source node of directed edge. ! Child: terminal node of directed edge
 Trees & Heaps Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every
Trees & Heaps Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every
BINARY SEARCH TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015
 BINARY SEARCH TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 7 due tonight at midnight -asking for regrades through assignment 5 and midterm must
BINARY SEARCH TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 7 due tonight at midnight -asking for regrades through assignment 5 and midterm must
Tree: non-recursive definition. Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps. Tree: recursive definition. Tree: example.
 Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015
 CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015 Lecture #17, Implementing Binary Search Trees John Ridgway April 2, 2015 1 Implementing Binary Search Trees Review: The BST Interface Binary search
CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015 Lecture #17, Implementing Binary Search Trees John Ridgway April 2, 2015 1 Implementing Binary Search Trees Review: The BST Interface Binary search
Binary Search Tree. Revised based on textbook author s notes.
 Binary Search Tree Revised based on textbook author s notes. Search Trees The tree structure can be used for searching. Each node contains a search key as part of its data or payload. Nodes are organized
Binary Search Tree Revised based on textbook author s notes. Search Trees The tree structure can be used for searching. Each node contains a search key as part of its data or payload. Nodes are organized
Spring 2018 Mentoring 8: March 14, Binary Trees
 CSM 6B Binary Trees Spring 08 Mentoring 8: March 4, 08 Binary Trees. Define a procedure, height, which takes in a Node and outputs the height of the tree. Recall that the height of a leaf node is 0. private
CSM 6B Binary Trees Spring 08 Mentoring 8: March 4, 08 Binary Trees. Define a procedure, height, which takes in a Node and outputs the height of the tree. Recall that the height of a leaf node is 0. private
ITEC2620 Introduction to Data Structures
 T2620 ntroduction to ata Structures Lecture 4a inary Trees Review of Linked Lists Linked-Lists dynamic length arbitrary memory locations access by following links an only traverse link in forward direction
T2620 ntroduction to ata Structures Lecture 4a inary Trees Review of Linked Lists Linked-Lists dynamic length arbitrary memory locations access by following links an only traverse link in forward direction
Binary Search Trees. Contents. Steven J. Zeil. July 11, Definition: Binary Search Trees The Binary Search Tree ADT...
 Steven J. Zeil July 11, 2013 Contents 1 Definition: Binary Search Trees 2 1.1 The Binary Search Tree ADT.................................................... 3 2 Implementing Binary Search Trees 7 2.1 Searching
Steven J. Zeil July 11, 2013 Contents 1 Definition: Binary Search Trees 2 1.1 The Binary Search Tree ADT.................................................... 3 2 Implementing Binary Search Trees 7 2.1 Searching
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1
 CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
Sorted Arrays. Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min
 Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Heaps & Priority Queues. (Walls & Mirrors - Remainder of Chapter 11)
 Heaps & Priority Queues (Walls & Mirrors - Remainder of Chapter 11) 1 Overview Array-Based Representation of a Complete Binary Tree Heaps The ADT Priority Queue Heap Implementation of the ADT Priority
Heaps & Priority Queues (Walls & Mirrors - Remainder of Chapter 11) 1 Overview Array-Based Representation of a Complete Binary Tree Heaps The ADT Priority Queue Heap Implementation of the ADT Priority
Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees
 COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
Recall: Properties of B-Trees
 CSE 326 Lecture 10: B-Trees and Heaps It s lunch time what s cookin? B-Trees Insert/Delete Examples and Run Time Analysis Summary of Search Trees Introduction to Heaps and Priority Queues Covered in Chapters
CSE 326 Lecture 10: B-Trees and Heaps It s lunch time what s cookin? B-Trees Insert/Delete Examples and Run Time Analysis Summary of Search Trees Introduction to Heaps and Priority Queues Covered in Chapters
8. Binary Search Tree
 8 Binary Search Tree Searching Basic Search Sequential Search : Unordered Lists Binary Search : Ordered Lists Tree Search Binary Search Tree Balanced Search Trees (Skipped) Sequential Search int Seq-Search
8 Binary Search Tree Searching Basic Search Sequential Search : Unordered Lists Binary Search : Ordered Lists Tree Search Binary Search Tree Balanced Search Trees (Skipped) Sequential Search int Seq-Search
CS 234. Module 8. November 15, CS 234 Module 8 ADT Priority Queue 1 / 22
 CS 234 Module 8 November 15, 2018 CS 234 Module 8 ADT Priority Queue 1 / 22 ADT Priority Queue Data: (key, element pairs) where keys are orderable but not necessarily distinct, and elements are any data.
CS 234 Module 8 November 15, 2018 CS 234 Module 8 ADT Priority Queue 1 / 22 ADT Priority Queue Data: (key, element pairs) where keys are orderable but not necessarily distinct, and elements are any data.
Binary Trees and Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees and Binary Search Trees Learning Goals After this unit, you should be able to... Determine if a given tree is an instance of a particular type (e.g. binary, and later heap, etc.) Describe
Binary Trees and Binary Search Trees Learning Goals After this unit, you should be able to... Determine if a given tree is an instance of a particular type (e.g. binary, and later heap, etc.) Describe
CMSC 341 Lecture 10 Binary Search Trees
 CMSC 341 Lecture 10 Binary Search Trees John Park Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Review: Tree Traversals 2 Traversal Preorder, Inorder, Postorder H X M A K B E N Y L G W UMBC CMSC
CMSC 341 Lecture 10 Binary Search Trees John Park Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Review: Tree Traversals 2 Traversal Preorder, Inorder, Postorder H X M A K B E N Y L G W UMBC CMSC
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees
 Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
- 1 - Handout #22S May 24, 2013 Practice Second Midterm Exam Solutions. CS106B Spring 2013
 CS106B Spring 2013 Handout #22S May 24, 2013 Practice Second Midterm Exam Solutions Based on handouts by Eric Roberts and Jerry Cain Problem One: Reversing a Queue One way to reverse the queue is to keep
CS106B Spring 2013 Handout #22S May 24, 2013 Practice Second Midterm Exam Solutions Based on handouts by Eric Roberts and Jerry Cain Problem One: Reversing a Queue One way to reverse the queue is to keep
Multi-Way Search Trees
 Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees
 Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
* Due 11:59pm on Sunday 10/4 for Monday lab and Tuesday 10/6 Wednesday Lab
 ===Lab Info=== *100 points * Due 11:59pm on Sunday 10/4 for Monday lab and Tuesday 10/6 Wednesday Lab ==Assignment== In this assignment you will work on designing a class for a binary search tree. You
===Lab Info=== *100 points * Due 11:59pm on Sunday 10/4 for Monday lab and Tuesday 10/6 Wednesday Lab ==Assignment== In this assignment you will work on designing a class for a binary search tree. You
Computational Optimization ISE 407. Lecture 16. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees. Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler
 Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Multiway Seach Tree: a new type of search trees: for ordered d dictionary
Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Multiway Seach Tree: a new type of search trees: for ordered d dictionary
Multi-Way Search Trees
 Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
STUDENT LESSON AB30 Binary Search Trees
 STUDENT LESSON AB30 Binary Search Trees Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson AB30 1 STUDENT LESSON AB30 Binary Search Trees INTRODUCTION: A binary tree is a different kind of data structure
STUDENT LESSON AB30 Binary Search Trees Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson AB30 1 STUDENT LESSON AB30 Binary Search Trees INTRODUCTION: A binary tree is a different kind of data structure
CSC 421: Algorithm Design Analysis. Spring 2013
 CSC 421: Algorithm Design Analysis Spring 2013 Transform & conquer transform-and-conquer approach presorting balanced search trees, heaps Horner's Rule problem reduction 1 Transform & conquer the idea
CSC 421: Algorithm Design Analysis Spring 2013 Transform & conquer transform-and-conquer approach presorting balanced search trees, heaps Horner's Rule problem reduction 1 Transform & conquer the idea
void insert( Type const & ) void push_front( Type const & )
 6.1 Binary Search Trees A binary search tree is a data structure that can be used for storing sorted data. We will begin by discussing an Abstract Sorted List or Sorted List ADT and then proceed to describe
6.1 Binary Search Trees A binary search tree is a data structure that can be used for storing sorted data. We will begin by discussing an Abstract Sorted List or Sorted List ADT and then proceed to describe
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 13: Index structure. The Lecture Contains: Index structure. Binary search tree (BST) B-tree. B+-tree.
 The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
Multi-way Search Trees. (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 25
 Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2
 CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2 1) Shown below is an AVL tree T. Nov 14, 2012 Solutions to OPEN BOOK section. (a) Suggest a key whose insertion does not require any rotation. 18 (b) Suggest a key, if
CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2 1) Shown below is an AVL tree T. Nov 14, 2012 Solutions to OPEN BOOK section. (a) Suggest a key whose insertion does not require any rotation. 18 (b) Suggest a key, if
HEAPS: IMPLEMENTING EFFICIENT PRIORITY QUEUES
 HEAPS: IMPLEMENTING EFFICIENT PRIORITY QUEUES 2 5 6 9 7 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H., Wiley, 2014
HEAPS: IMPLEMENTING EFFICIENT PRIORITY QUEUES 2 5 6 9 7 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H., Wiley, 2014
TREES. Trees - Introduction
 TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Priority Queues Outline Priority Queues 1 Priority Queues Jumping the Queue Priority Queues In normal queue, the mode of selection is first in,
Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Priority Queues Outline Priority Queues 1 Priority Queues Jumping the Queue Priority Queues In normal queue, the mode of selection is first in,
Heaps. Heaps. A heap is a complete binary tree.
 A heap is a complete binary tree. 1 A max-heap is a complete binary tree in which the value in each internal node is greater than or equal to the values in the children of that node. A min-heap is defined
A heap is a complete binary tree. 1 A max-heap is a complete binary tree in which the value in each internal node is greater than or equal to the values in the children of that node. A min-heap is defined
MIDTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 CS301- Data Structures
 MIDTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the
MIDTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the
CIS265/ Trees Red-Black Trees. Some of the following material is from:
 CIS265/506 2-3-4 Trees Red-Black Trees Some of the following material is from: Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp ISBN 0-13-047724-9 Chapter 27 Balanced Search Trees Bret Ford 2005,
CIS265/506 2-3-4 Trees Red-Black Trees Some of the following material is from: Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp ISBN 0-13-047724-9 Chapter 27 Balanced Search Trees Bret Ford 2005,
Balanced Search Trees
 Balanced Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Review: Balanced Trees A tree is balanced if, for each node, the node s subtrees have the same height or have
Balanced Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Review: Balanced Trees A tree is balanced if, for each node, the node s subtrees have the same height or have
Priority Queues (Heaps)
 Priority Queues (Heaps) 1 Priority Queues Many applications require that we process records with keys in order, but not necessarily in full sorted order. Often we collect a set of items and process the
Priority Queues (Heaps) 1 Priority Queues Many applications require that we process records with keys in order, but not necessarily in full sorted order. Often we collect a set of items and process the
Algorithms in Systems Engineering ISE 172. Lecture 16. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Algorithms in Systems Engineering ISE 172 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 172 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms
Algorithms in Systems Engineering ISE 172 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 172 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises
 Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises A Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises A Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will
Self-Balancing Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
CSE 326: Data Structures Binary Search Trees
 nnouncements (1/3/0) S 36: ata Structures inary Search Trees Steve Seitz Winter 0 HW # due now HW #3 out today, due at beginning of class next riday. Project due next Wed. night. Read hapter 4 1 Ts Seen
nnouncements (1/3/0) S 36: ata Structures inary Search Trees Steve Seitz Winter 0 HW # due now HW #3 out today, due at beginning of class next riday. Project due next Wed. night. Read hapter 4 1 Ts Seen
Advanced Programming Handout 5. Purely Functional Data Structures: A Case Study in Functional Programming
 Advanced Programming Handout 5 Purely Functional Data Structures: A Case Study in Functional Programming Persistent vs. Ephemeral An ephemeral data structure is one for which only one version is available
Advanced Programming Handout 5 Purely Functional Data Structures: A Case Study in Functional Programming Persistent vs. Ephemeral An ephemeral data structure is one for which only one version is available
Binary Trees. Directed, Rooted Tree. Terminology. Trees. Binary Trees. Possible Implementation 4/18/2013
 Directed, Rooted Tree Binary Trees Chapter 5 CPTR 318 Every non-empty directed, rooted tree has A unique element called root One or more elements called leaves Every element except root has a unique parent
Directed, Rooted Tree Binary Trees Chapter 5 CPTR 318 Every non-empty directed, rooted tree has A unique element called root One or more elements called leaves Every element except root has a unique parent
(2,4) Trees. 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
12 July, Red-Black Trees. Red-Black Trees
 1 BST work well if the data is inserted into the tree in random order. They work much slower if the data is inserted in already sorted order. When the values to be inserted are already ordered, a binary
1 BST work well if the data is inserted into the tree in random order. They work much slower if the data is inserted in already sorted order. When the values to be inserted are already ordered, a binary
Binary Search Trees > = 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser. Binary Search Trees 1
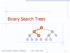 Binary Search Trees < > = Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionary (Map) ADT get (k): record with key k put (k,data): add record (k,data) remove (k): delete record with key k smallest(): record with smallest
Binary Search Trees < > = Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionary (Map) ADT get (k): record with key k put (k,data): add record (k,data) remove (k): delete record with key k smallest(): record with smallest
Binary Search Trees. Analysis of Algorithms
 Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Multi-Way Search Tree
 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two and at most d children and stores d -1 data items (k i, D i ) Rule: Number of children = 1
Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two and at most d children and stores d -1 data items (k i, D i ) Rule: Number of children = 1
Data Structures in Java
 Data Structures in Java Lecture 9: Binary Search Trees. 10/7/015 Daniel Bauer 1 Contents 1. Binary Search Trees. Implementing Maps with BSTs Map ADT A map is collection of (key, value) pairs. Keys are
Data Structures in Java Lecture 9: Binary Search Trees. 10/7/015 Daniel Bauer 1 Contents 1. Binary Search Trees. Implementing Maps with BSTs Map ADT A map is collection of (key, value) pairs. Keys are
Advanced Programming Handout 6. Purely Functional Data Structures: A Case Study in Functional Programming
 Advanced Programming Handout 6 Purely Functional Data Structures: A Case Study in Functional Programming Persistent vs. Ephemeral An ephemeral data structure is one for which only one version is available
Advanced Programming Handout 6 Purely Functional Data Structures: A Case Study in Functional Programming Persistent vs. Ephemeral An ephemeral data structure is one for which only one version is available
IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10)
 IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) -1- A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following: a. If Loc >= length
IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) -1- A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following: a. If Loc >= length
Heaps, Heap Sort, and Priority Queues.
 Heaps, Heap Sort, and Priority Queues Sorting III / Slide 2 Background: Binary Trees Has a root at the topmost level Each node has zero, one or two children A node that has no child is called a leaf For
Heaps, Heap Sort, and Priority Queues Sorting III / Slide 2 Background: Binary Trees Has a root at the topmost level Each node has zero, one or two children A node that has no child is called a leaf For
Balanced Binary Search Trees. Victor Gao
 Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Priority Queues. e.g. jobs sent to a printer, Operating system job scheduler in a multi-user environment. Simulation environments
 Heaps 1 Priority Queues Many applications require that we process records with keys in order, but not necessarily in full sorted order. Often we collect a set of items and process the one with the current
Heaps 1 Priority Queues Many applications require that we process records with keys in order, but not necessarily in full sorted order. Often we collect a set of items and process the one with the current
Week 8. BinaryTrees. 1 Binary trees. 2 The notion of binary search tree. 3 Tree traversal. 4 Queries in binary search trees. 5 Insertion.
 Week 8 Binarys 1 2 of 3 4 of 5 6 7 General remarks We consider, another important data structure. We learn how to use them, by making efficient queries. And we learn how to build them. Reading from CLRS
Week 8 Binarys 1 2 of 3 4 of 5 6 7 General remarks We consider, another important data structure. We learn how to use them, by making efficient queries. And we learn how to build them. Reading from CLRS
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures. Lecture #28: Binary Search Trees 21 November 2011
 CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture #28: Binary Search Trees 21 November 2011 Binary Search Trees The Idea of a Binary Search Tree The BinarySearchTreeADT Interface The LinkedBinarySearchTree
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture #28: Binary Search Trees 21 November 2011 Binary Search Trees The Idea of a Binary Search Tree The BinarySearchTreeADT Interface The LinkedBinarySearchTree
Week 8. BinaryTrees. 1 Binary trees. 2 The notion of binary search tree. 3 Tree traversal. 4 Queries in binary search trees. 5 Insertion.
 Week 8 Binarys 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 General remarks We consider, another important data structure. We learn how to use them, by making efficient queries. And we learn how to build them. Reading from CLRS for
Week 8 Binarys 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 General remarks We consider, another important data structure. We learn how to use them, by making efficient queries. And we learn how to build them. Reading from CLRS for
2-3 Tree. Outline B-TREE. catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } ADD SLIDES ON DISJOINT SETS
 Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Balanced Search Trees. CS 3110 Fall 2010
 Balanced Search Trees CS 3110 Fall 2010 Some Search Structures Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Balanced Search Trees CS 3110 Fall 2010 Some Search Structures Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
CMSC 341. Binary Search Trees CMSC 341 BST
 CMSC 341 Binary Search Trees CMSC 341 BST Announcements Homework #3 dues Thursday (10/5/2017) Exam #1 next Thursday (10/12/2017) CMSC 341 BST A Generic Tree CMSC 341 BST Binary Tree CMSC 341 BST The Binary
CMSC 341 Binary Search Trees CMSC 341 BST Announcements Homework #3 dues Thursday (10/5/2017) Exam #1 next Thursday (10/12/2017) CMSC 341 BST A Generic Tree CMSC 341 BST Binary Tree CMSC 341 BST The Binary
CS-301 Data Structure. Tariq Hanif
 1. The tree data structure is a Linear data structure Non-linear data structure Graphical data structure Data structure like queue FINALTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2012 CS301- Data Structure 25-07-2012 2.
1. The tree data structure is a Linear data structure Non-linear data structure Graphical data structure Data structure like queue FINALTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2012 CS301- Data Structure 25-07-2012 2.
Operations on Heap Tree The major operations required to be performed on a heap tree are Insertion, Deletion, and Merging.
 Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
Hash Tables. CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides. Wednesday, April 22, Glenn G. Chappell
 Hash Tables CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Wednesday, April 22, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005
Hash Tables CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Wednesday, April 22, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005
CS 3114 Data Structures and Algorithms READ THIS NOW!
 READ THIS NOW! Print your name in the space provided below. There are 7 short-answer questions, priced as marked. The maximum score is 100. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from
READ THIS NOW! Print your name in the space provided below. There are 7 short-answer questions, priced as marked. The maximum score is 100. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from
CSE100. Advanced Data Structures. Lecture 13. (Based on Paul Kube course materials)
 CSE100 Advanced Data Structures Lecture 13 (Based on Paul Kube course materials) CSE 100 Priority Queues in Huffman s algorithm Heaps and Priority Queues Time and space costs of coding with Huffman codes
CSE100 Advanced Data Structures Lecture 13 (Based on Paul Kube course materials) CSE 100 Priority Queues in Huffman s algorithm Heaps and Priority Queues Time and space costs of coding with Huffman codes
INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1
 Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk A. Maus, R.K. Runde, I. Yu INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Trees & estimation of running time (Exercises with hints for solution) Issued:
Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk A. Maus, R.K. Runde, I. Yu INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Trees & estimation of running time (Exercises with hints for solution) Issued:
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2017 Lecture 18 Trees, Part II
 CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2017 Lecture 18 Trees, Part II Review from Lecture 17 and Lab 9 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees, & Balanced Trees STL set container class (like STL map, but without the
CSCI-1200 Data Structures Fall 2017 Lecture 18 Trees, Part II Review from Lecture 17 and Lab 9 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees, & Balanced Trees STL set container class (like STL map, but without the
ECE 244 Programming Fundamentals Fall Lab Assignment #5: Binary Search Trees
 ECE 244 Programming Fundamentals Fall 2012 1. Objectives Lab Assignment #5: Binary Search Trees The objectives of this assignment are to provide you with more practice on the use of the various C++ concepts/constructs
ECE 244 Programming Fundamentals Fall 2012 1. Objectives Lab Assignment #5: Binary Search Trees The objectives of this assignment are to provide you with more practice on the use of the various C++ concepts/constructs
Unit III - Tree TREES
 TREES Unit III - Tree Consider a scenario where you are required to represent the directory structure of your operating system. The directory structure contains various folders and files. A folder may
TREES Unit III - Tree Consider a scenario where you are required to represent the directory structure of your operating system. The directory structure contains various folders and files. A folder may
MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI KUALA LUMPUR
 STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION PSD2023 ALGORITHM & DATA STRUCTURE DSEW-E-F-2/13 25 MAY 2015 9.00 AM
STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION PSD2023 ALGORITHM & DATA STRUCTURE DSEW-E-F-2/13 25 MAY 2015 9.00 AM
Lecture Notes on Tries
 Lecture Notes on Tries 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Thomas Cortina Notes by Frank Pfenning Lecture 24 April 19, 2011 1 Introduction In the data structures implementing associative arrays
Lecture Notes on Tries 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Thomas Cortina Notes by Frank Pfenning Lecture 24 April 19, 2011 1 Introduction In the data structures implementing associative arrays
SCJ2013 Data Structure & Algorithms. Binary Search Tree. Nor Bahiah Hj Ahmad
 SCJ2013 Data Structure & Algorithms Binary Search Tree Nor Bahiah Hj Ahmad Binary Search Tree A binary search tree has the following properties: For every node n in the tree Value of n is greater than
SCJ2013 Data Structure & Algorithms Binary Search Tree Nor Bahiah Hj Ahmad Binary Search Tree A binary search tree has the following properties: For every node n in the tree Value of n is greater than
Tree Data Structures CSC 221
 Tree Data Structures CSC 221 BSTree Deletion - Merging template // LOOK AT THIS PARAMETER!!! void BST::deleteByMerging(BSTNode* & nodepointer) { BSTNode* temp= nodepointer;
Tree Data Structures CSC 221 BSTree Deletion - Merging template // LOOK AT THIS PARAMETER!!! void BST::deleteByMerging(BSTNode* & nodepointer) { BSTNode* temp= nodepointer;
SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES. Chapter 11
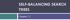 SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES Chapter 11 Tree Balance and Rotation Section 11.1 Algorithm for Rotation BTNode root = left right = data = 10 BTNode = left right = data = 20 BTNode NULL = left right = NULL
SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES Chapter 11 Tree Balance and Rotation Section 11.1 Algorithm for Rotation BTNode root = left right = data = 10 BTNode = left right = data = 20 BTNode NULL = left right = NULL
(2,4) Trees Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
Expression Trees and the Heap
 Expression Trees and the Heap 1 Binary Expression Trees evaluating expressions splitting strings in operators and operands 2 C++ Binary Tree of Strings header files defining the methods 3 the Heap or Priority
Expression Trees and the Heap 1 Binary Expression Trees evaluating expressions splitting strings in operators and operands 2 C++ Binary Tree of Strings header files defining the methods 3 the Heap or Priority
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall Topic Notes: Priority Queues and Heaps
 Computer Science 0 Data Structures Siena College Fall 08 Topic Notes: Priority Queues and Heaps Heaps and Priority Queues From here, we will look at some ways that trees are used in other structures. First,
Computer Science 0 Data Structures Siena College Fall 08 Topic Notes: Priority Queues and Heaps Heaps and Priority Queues From here, we will look at some ways that trees are used in other structures. First,
