Lists Revisited: Cache Conscious STL lists
|
|
|
- Roxanne Wheeler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lists Revisited: Cache Conscious STL lists Leonor Frias, Jordi Petit, Salvador Roura Departament de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya.
2 Overview Goal: Improve STL lists perfomance in most common settings using a cache-conscious data structure. Previous work: Either double-linked lists implementations: easily cope with standard requirements theoretical cache-conscious data structures: do not take into account any of these requirements Main contribution: merging both approaches. Main problem: dealing with STL lists iterator functionality. Work done: analysis, design, implementation and comprehensive experimental study.
3 Index 1. Introduction and motivation 2. Problem and our approach 3. Design 4. Experiments 5. Conclusions and further work
4 Standard Template Library (STL) Core of C ++ standard library [International Standard ISO/IEC ]. Elements: containers: list, vector, map... iterators: high-level pointers algorithms: sort, reverse, find... Implementation: classical literature on algorithms and data structures.
5 Improve performance Use memory hierarchy effectively for known / regular access patterns cache-conscious algorithms & data structures General idea: organize data s.t. logical access pattern physical memory locations. Models: cache-aware cache-oblivious [Frigo et al. 1999]
6 STL lists Forward and backward traversal container, that supports insertion and deletion in constant time. STL list iterators properties: arbitrary number operations cannot invalidate them Straightforward implementation: This is what all known STL implementations do!
7 Double-linked lists cache performance Pointer-based data structures cannot guarantee good cache performance. scaled time (in microsec) no-modification 1-insert-erase 2-insert-erase 4-insert-erase 8-insert-erase 16-insert-erase 32-insert-erase 64-insert-erase sort Traversal using libstdc list size (in 10^4) It is worth trying a cache-conscious approach!
8 Index 1. Introduction and motivation 2. Problem and our approach 3. Design 4. Experiments 5. Conclusions and further work
9 Previous work on cache-conscious lists [Demaine 2002] Cache-aware: partition of Θ(n/B) pieces with (B/2, B) elems. Traversal: O(n/B) amortized Update: constant Cache-oblivious: uses the packed memory structure, array of Θ(n) size with uniformly distributed gaps. Traversal: O(n/B) amortized Update: O((log 2 n)/b) (lower by partitioning the array) Amortized constant with self-organizing structures (updates may break the uniformity until the list is reorganized when traversed).
10 Problem Pointers + cache-conscious data structure: physical/logical location are not independent. No trivial pointers reach iterators whenever a modification occurs. Main issue: unbounded number of iterators pointing to the same element. Achieving Θ(1) operations: number of iterators arbitrarily restricted iterators pointing to the same element share some data STL lists are not traversed as a whole but step by step NO self-organizing strategies.
11 Our approach Efficient data access + full iterator functionality + (constant) worst case costs compliant with the Standard Base: cache-aware solution. Common list usages: Only a few iterators on a list instance Many traversals are performed due to sequential access Frequent modifications at any position Small/Plain old data (POD) types (*)Implicit or explicit in general cache-conscious literature
12 Index 1. Introduction and motivation 2. Problem and our approach 3. Design 4. Experiments 5. Conclusions and further work
13 Basic design Double-linked list of buckets. What more? 1. how to arrange the elements inside a bucket 2. how to reorganize the buckets on insertion/deletion 3. how to manage iterators 4. bucket capacity? Experimentally
14 Arrangement of elements
15 Reorganization of buckets Preserve data structure invariant after modification minimum bucket occupancy arrangement coherency... Main issue: Keeping balance between: high occupancy few bucket accessed few elements movements
16 Iterators management Key idea: all the iterators referred to an element are identified with a dynamic node (relayer) that points to it. Figure 1: Bucket of pairs 2-level- Figure 2: list
17 Index 1. Introduction and motivation 2. Problem and our approach 3. Design 4. Experiments 5. Conclusions and further work
18 Set up Our three implementations: bucket-pairs 2-level-cont 2-level-link against libstdc ++ in GCC Basic environment: 64-bit Sun Workstation, AMD Opteron CPU at 2.4 Ghz 1 GB main memory 64 KB + 64 KB 2-associative L1 cache, 1024 KB 16-associative L2 cache and 64 bytes per cache line. Other: Pentium 4, 3.06 GHz hyperthreading CPU, 900 Mb of main memory and 512 Kb L2 cache.
19 Which experiments Performance measures: wall-clock times cache performance data: Pin [Luk et al. 2005] Types of experiments: lists with no iterators lists with iterators lists with several bucket capacities LEDA Lists before and after elements reorganization (by sorting).
20 Traversal before 0.08 Traversal before shuffling (0% it load and bucket capacity 100) scaled time (in microsec) list size (in 10^4) gcc bucket-pairs 2-level-cont 2-level-link
21 Traversal after scaled time (in microsec) Traversal after shuffling (0% it load and bucket capacity 100) gcc bucket-pairs 2-level-cont 2-level-link list size (in 10^4)
22 Pin Traversal after scaled number of L2 cache accesses e-04 1e-05 Traversal after shuffling (0% it load and bucket capacity 100) gcc (misses) bucket-pairs (misses) 2-level-cont (misses) 2-level-link (misses) gcc (total) bucket-pairs (total) 2-level-cont (total) 2-level-link (total) list size (in 10^4)
23 Insert before 0.25 Insert traversal before shuffling (0% it load and bucket capacity 100) scaled time (in microsec) list size (in 10^4) gcc bucket-pairs 2-level-cont 2-level-link
24 Insert after scaled time (in microsec) Insert traversal after shuffling (0% it load and bucket capacity 100) gcc bucket-pairs 2-level-cont 2-level-link list size (in 10^4)
25 Intensive insertion scaled time (in microsec) Insert after shuffling (0% it load and bucket capacity 100) gcc bucket-pairs 2-level-cont 2-level-link list size (in 10^4)
26 Internal sort scaled time (in microsec) gcc bucket-pairs 2-level-cont 2-level-link Sort (0% it load and bucket capacity 100) list size (in 10^4)
27 Effect of bucket capacity scaled time (in microsec) Insert traversal after shuffling (486* 10^4 list size and 0% it load) gcc bucket-pairs 2-level-cont 2-level-link bucket capacity
28 Iterators 0.7 Traversal after shuffling (486* 10^4 list size and bucket capacity 100) 0.6 scaled time (in microsec) percentage of iterator load gcc bucket-pairs 2-level-cont 2-level-link
29 LEDA scaled time (in microsec) Traversal after shuffling (0% it load and bucket capacity 100) gcc leda 2-level-link list size (in 10^4)
30 Index 1. Introduction and motivation 2. Problem and our approach 3. Design 4. Experiments 5. Conclusions and further work
31 Conclusions (1) Pioneering to show the importance of porting existing theory and practice on cache-conscious data structures to standard libraries, as the STL. Provided three standard compliant cache-conscious lists implementations. This is not straightforward, although based on simple existing data structures. Kept with standard requirements, in particular with iterators. We have provided two standard compliant iterators designs. The algorithms involved must be designed carefully to keep up some properties.
32 Conclusions (2) Provided a comprehensive experimental study. Our implementations are prefferable in many (common) situations to classical double-linked list implementations, such as GCC (or LEDA). Specifically, 5-10 times faster traversals 3-5 times faster internal sort still competitive with (unusual) big load of iterators bucket capacity is not a critical parameter Between our implementations: 2-level linked implementation linked bucket implementation
33 What next? My webpage: Extended article: reorganization algorithm analysed in detail. Using amortized analysis, we show that the number of created/destroyed buckets is assymptotically optimal.
34 Thank you Questions?
35 References Demaine, E. (2002). Cache-oblivious algorithms and data structures. In EEF Summer School on Massive Data Sets, LNCS. Frigo, M., C. Leiserson, H. Prokop, and S. Ramachandran (1999). Cache-oblivious algorithms. In FOCS 99, pp IEEE Computer Society. International Standard ISO/IEC (1998). Programming languages C ++ (1st ed.). American National Standard Institute. Luk, C., R. Cohn, R. Muth, H. Patil, A. Klauser, G. Lowney, S. Wallace, V. J. Reddi, and K. Hazelwood (2005, June). Pin: Building customized program analysis tools with dynamic instrumentation. In PLDI 05, Chicago, IL.
Lists Revisited: Cache Conscious STL Lists
 Lists Revisited: Cache Conscious STL Lists Leonor Frias, Jordi Petit, and Salvador Roura Departament de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Campus Nord, edifici Omega
Lists Revisited: Cache Conscious STL Lists Leonor Frias, Jordi Petit, and Salvador Roura Departament de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Campus Nord, edifici Omega
Lists Revisited: Cache Conscious STL Lists
 Lists Revisited: Cache Conscious STL Lists Leonor Frias,JordiPetit, and Salvador Roura Departament de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Campus Nord, edifici Omega,
Lists Revisited: Cache Conscious STL Lists Leonor Frias,JordiPetit, and Salvador Roura Departament de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Campus Nord, edifici Omega,
Single-Pass List Partitioning
 Single-Pass List Partitioning Leonor Frias 1 Johannes Singler 2 Peter Sanders 2 1 Dep. de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya 2 Institut für Theoretische Informatik,
Single-Pass List Partitioning Leonor Frias 1 Johannes Singler 2 Peter Sanders 2 1 Dep. de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya 2 Institut für Theoretische Informatik,
Report Seminar Algorithm Engineering
 Report Seminar Algorithm Engineering G. S. Brodal, R. Fagerberg, K. Vinther: Engineering a Cache-Oblivious Sorting Algorithm Iftikhar Ahmad Chair of Algorithm and Complexity Department of Computer Science
Report Seminar Algorithm Engineering G. S. Brodal, R. Fagerberg, K. Vinther: Engineering a Cache-Oblivious Sorting Algorithm Iftikhar Ahmad Chair of Algorithm and Complexity Department of Computer Science
Parallel Partition Revisited
 Parallel Partition Revisited Leonor Frias and Jordi Petit Dep. de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya WEA 2008 Overview Partitioning an array with respect to a pivot
Parallel Partition Revisited Leonor Frias and Jordi Petit Dep. de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya WEA 2008 Overview Partitioning an array with respect to a pivot
Massive Data Algorithmics. Lecture 12: Cache-Oblivious Model
 Typical Computer Hierarchical Memory Basics Data moved between adjacent memory level in blocks A Trivial Program A Trivial Program: d = 1 A Trivial Program: d = 1 A Trivial Program: n = 2 24 A Trivial
Typical Computer Hierarchical Memory Basics Data moved between adjacent memory level in blocks A Trivial Program A Trivial Program: d = 1 A Trivial Program: d = 1 A Trivial Program: n = 2 24 A Trivial
Cache-Oblivious Algorithms A Unified Approach to Hierarchical Memory Algorithms
 Cache-Oblivious Algorithms A Unified Approach to Hierarchical Memory Algorithms Aarhus University Cache-Oblivious Current Trends Algorithms in Algorithms, - A Unified Complexity Approach to Theory, Hierarchical
Cache-Oblivious Algorithms A Unified Approach to Hierarchical Memory Algorithms Aarhus University Cache-Oblivious Current Trends Algorithms in Algorithms, - A Unified Complexity Approach to Theory, Hierarchical
External Memory. Philip Bille
 External Memory Philip Bille Outline Computationals models Modern computers (word) RAM I/O Cache-oblivious Shortest path in implicit grid graphs RAM algorithm I/O algorithms Cache-oblivious algorithm Computational
External Memory Philip Bille Outline Computationals models Modern computers (word) RAM I/O Cache-oblivious Shortest path in implicit grid graphs RAM algorithm I/O algorithms Cache-oblivious algorithm Computational
Cache-Oblivious Traversals of an Array s Pairs
 Cache-Oblivious Traversals of an Array s Pairs Tobias Johnson May 7, 2007 Abstract Cache-obliviousness is a concept first introduced by Frigo et al. in [1]. We follow their model and develop a cache-oblivious
Cache-Oblivious Traversals of an Array s Pairs Tobias Johnson May 7, 2007 Abstract Cache-obliviousness is a concept first introduced by Frigo et al. in [1]. We follow their model and develop a cache-oblivious
Extending STL maps using LBSTs
 Extending STL maps using LBSTs LEONOR FRIAS Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Associative containers are basic generic classes of the C ++ standard library. Access to the elements can be done by key
Extending STL maps using LBSTs LEONOR FRIAS Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Associative containers are basic generic classes of the C ++ standard library. Access to the elements can be done by key
Lecture 19 Apr 25, 2007
 6.851: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2007 Prof. Erik Demaine Lecture 19 Apr 25, 2007 Scribe: Aditya Rathnam 1 Overview Previously we worked in the RA or cell probe models, in which the cost of an algorithm
6.851: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2007 Prof. Erik Demaine Lecture 19 Apr 25, 2007 Scribe: Aditya Rathnam 1 Overview Previously we worked in the RA or cell probe models, in which the cost of an algorithm
Lecture 24 November 24, 2015
 CS 229r: Algorithms for Big Data Fall 2015 Prof. Jelani Nelson Lecture 24 November 24, 2015 Scribes: Zhengyu Wang 1 Cache-oblivious Model Last time we talked about disk access model (as known as DAM, or
CS 229r: Algorithms for Big Data Fall 2015 Prof. Jelani Nelson Lecture 24 November 24, 2015 Scribes: Zhengyu Wang 1 Cache-oblivious Model Last time we talked about disk access model (as known as DAM, or
Buffer Heap Implementation & Evaluation. Hatem Nassrat. CSCI 6104 Instructor: N.Zeh Dalhousie University Computer Science
 Buffer Heap Implementation & Evaluation Hatem Nassrat CSCI 6104 Instructor: N.Zeh Dalhousie University Computer Science Table of Contents Introduction...3 Cache Aware / Cache Oblivious Algorithms...3 Buffer
Buffer Heap Implementation & Evaluation Hatem Nassrat CSCI 6104 Instructor: N.Zeh Dalhousie University Computer Science Table of Contents Introduction...3 Cache Aware / Cache Oblivious Algorithms...3 Buffer
Report on Cache-Oblivious Priority Queue and Graph Algorithm Applications[1]
![Report on Cache-Oblivious Priority Queue and Graph Algorithm Applications[1] Report on Cache-Oblivious Priority Queue and Graph Algorithm Applications[1]](/thumbs/75/71592945.jpg) Report on Cache-Oblivious Priority Queue and Graph Algorithm Applications[1] Marc André Tanner May 30, 2014 Abstract This report contains two main sections: In section 1 the cache-oblivious computational
Report on Cache-Oblivious Priority Queue and Graph Algorithm Applications[1] Marc André Tanner May 30, 2014 Abstract This report contains two main sections: In section 1 the cache-oblivious computational
Multi-core Computing Lecture 2
 Multi-core Computing Lecture 2 MADALGO Summer School 2012 Algorithms for Modern Parallel and Distributed Models Phillip B. Gibbons Intel Labs Pittsburgh August 21, 2012 Multi-core Computing Lectures: Progress-to-date
Multi-core Computing Lecture 2 MADALGO Summer School 2012 Algorithms for Modern Parallel and Distributed Models Phillip B. Gibbons Intel Labs Pittsburgh August 21, 2012 Multi-core Computing Lectures: Progress-to-date
BRICS Research Activities Algorithms
 BRICS Research Activities Algorithms Gerth Stølting Brodal BRICS Retreat, Sandbjerg, 21 23 October 2002 1 Outline of Talk The Algorithms Group Courses Algorithm Events Expertise within BRICS Examples Algorithms
BRICS Research Activities Algorithms Gerth Stølting Brodal BRICS Retreat, Sandbjerg, 21 23 October 2002 1 Outline of Talk The Algorithms Group Courses Algorithm Events Expertise within BRICS Examples Algorithms
Lecture 2: Memory Systems
 Lecture 2: Memory Systems Basic components Memory hierarchy Cache memory Virtual Memory Zebo Peng, IDA, LiTH Many Different Technologies Zebo Peng, IDA, LiTH 2 Internal and External Memories CPU Date transfer
Lecture 2: Memory Systems Basic components Memory hierarchy Cache memory Virtual Memory Zebo Peng, IDA, LiTH Many Different Technologies Zebo Peng, IDA, LiTH 2 Internal and External Memories CPU Date transfer
Cache-Oblivious Algorithms
 Cache-Oblivious Algorithms Paper Reading Group Matteo Frigo Charles E. Leiserson Harald Prokop Sridhar Ramachandran Presents: Maksym Planeta 03.09.2015 Table of Contents Introduction Cache-oblivious algorithms
Cache-Oblivious Algorithms Paper Reading Group Matteo Frigo Charles E. Leiserson Harald Prokop Sridhar Ramachandran Presents: Maksym Planeta 03.09.2015 Table of Contents Introduction Cache-oblivious algorithms
Cache-Oblivious and Data-Oblivious Sorting and Applications
 Cache-Oblivious and Data-Oblivious Sorting and Applications T-H. Hubert Chan, Yue Guo, Wei-Kai Lin, and Elaine Shi Jan, 2018 External Memory Model Cache efficiency: # of blocks Time: # of words Memory
Cache-Oblivious and Data-Oblivious Sorting and Applications T-H. Hubert Chan, Yue Guo, Wei-Kai Lin, and Elaine Shi Jan, 2018 External Memory Model Cache efficiency: # of blocks Time: # of words Memory
Effect of memory latency
 CACHE AWARENESS Effect of memory latency Consider a processor operating at 1 GHz (1 ns clock) connected to a DRAM with a latency of 100 ns. Assume that the processor has two ALU units and it is capable
CACHE AWARENESS Effect of memory latency Consider a processor operating at 1 GHz (1 ns clock) connected to a DRAM with a latency of 100 ns. Assume that the processor has two ALU units and it is capable
Massive Data Algorithmics. Lecture 1: Introduction
 . Massive Data Massive datasets are being collected everywhere Storage management software is billion-dollar industry . Examples Phone: AT&T 20TB phone call database, wireless tracking Consumer: WalMart
. Massive Data Massive datasets are being collected everywhere Storage management software is billion-dollar industry . Examples Phone: AT&T 20TB phone call database, wireless tracking Consumer: WalMart
Introduction to I/O Efficient Algorithms (External Memory Model)
 Introduction to I/O Efficient Algorithms (External Memory Model) Jeff M. Phillips August 30, 2013 Von Neumann Architecture Model: CPU and Memory Read, Write, Operations (+,,,...) constant time polynomially
Introduction to I/O Efficient Algorithms (External Memory Model) Jeff M. Phillips August 30, 2013 Von Neumann Architecture Model: CPU and Memory Read, Write, Operations (+,,,...) constant time polynomially
Memory Management Algorithms on Distributed Systems. Katie Becker and David Rodgers CS425 April 15, 2005
 Memory Management Algorithms on Distributed Systems Katie Becker and David Rodgers CS425 April 15, 2005 Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Coarse Grained Memory 2.1. Bottlenecks 2.2. Simulations 2.3.
Memory Management Algorithms on Distributed Systems Katie Becker and David Rodgers CS425 April 15, 2005 Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Coarse Grained Memory 2.1. Bottlenecks 2.2. Simulations 2.3.
Algorithms and Data Structures: Efficient and Cache-Oblivious
 7 Ritika Angrish and Dr. Deepak Garg Algorithms and Data Structures: Efficient and Cache-Oblivious Ritika Angrish* and Dr. Deepak Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Thapar University,
7 Ritika Angrish and Dr. Deepak Garg Algorithms and Data Structures: Efficient and Cache-Oblivious Ritika Angrish* and Dr. Deepak Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Thapar University,
Lecture 7 8 March, 2012
 6.851: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2012 Lecture 7 8 arch, 2012 Prof. Erik Demaine Scribe: Claudio A Andreoni 2012, Sebastien Dabdoub 2012, Usman asood 2012, Eric Liu 2010, Aditya Rathnam 2007 1 emory
6.851: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2012 Lecture 7 8 arch, 2012 Prof. Erik Demaine Scribe: Claudio A Andreoni 2012, Sebastien Dabdoub 2012, Usman asood 2012, Eric Liu 2010, Aditya Rathnam 2007 1 emory
The Cost of Address Translation
 The Cost of Address Translation Tomasz Jurkiewicz Kurt Mehlhorn Pat Nicholson Max Planck Institute for Informatics full version of paper by TJ and KM available at arxiv preliminary version presented at
The Cost of Address Translation Tomasz Jurkiewicz Kurt Mehlhorn Pat Nicholson Max Planck Institute for Informatics full version of paper by TJ and KM available at arxiv preliminary version presented at
Cache-efficient string sorting for Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Advait D. Karande Sriram Saroop
 Cache-efficient string sorting for Burrows-Wheeler Transform Advait D. Karande Sriram Saroop What is Burrows-Wheeler Transform? A pre-processing step for data compression Involves sorting of all rotations
Cache-efficient string sorting for Burrows-Wheeler Transform Advait D. Karande Sriram Saroop What is Burrows-Wheeler Transform? A pre-processing step for data compression Involves sorting of all rotations
Multithreaded Architectures and The Sort Benchmark. Phil Garcia Hank Korth Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Lehigh University
 Multithreaded Architectures and The Sort Benchmark Phil Garcia Hank Korth Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Lehigh University About our Sort Benchmark Based on the benchmark proposed in A measure
Multithreaded Architectures and The Sort Benchmark Phil Garcia Hank Korth Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Lehigh University About our Sort Benchmark Based on the benchmark proposed in A measure
Algorithm Performance Factors. Memory Performance of Algorithms. Processor-Memory Performance Gap. Moore s Law. Program Model of Memory I
 Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
Chapter 12: Query Processing
 Chapter 12: Query Processing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Overview Chapter 12: Query Processing Measures of Query Cost Selection Operation Sorting Join
Chapter 12: Query Processing Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Overview Chapter 12: Query Processing Measures of Query Cost Selection Operation Sorting Join
Mismatch of CPU and MM Speeds
 Fö 3 Cache-Minne Introduction Cache design Replacement and write policy Zebo Peng, IDA, LiTH Mismatch of CPU and MM Speeds Cycle Time (nano second) 0 4 0 3 0 0 Main Memory CPU Speed Gap (ca. one order
Fö 3 Cache-Minne Introduction Cache design Replacement and write policy Zebo Peng, IDA, LiTH Mismatch of CPU and MM Speeds Cycle Time (nano second) 0 4 0 3 0 0 Main Memory CPU Speed Gap (ca. one order
Pathfinder/MonetDB: A High-Performance Relational Runtime for XQuery
 Introduction Problems & Solutions Join Recognition Experimental Results Introduction GK Spring Workshop Waldau: Pathfinder/MonetDB: A High-Performance Relational Runtime for XQuery Database & Information
Introduction Problems & Solutions Join Recognition Experimental Results Introduction GK Spring Workshop Waldau: Pathfinder/MonetDB: A High-Performance Relational Runtime for XQuery Database & Information
On the number of string lookups in BSTs (and related algorithms) with digital access
 On the number of string lookups in BSTs (and related algorithms) with digital access Leonor Frias Departament de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya lfrias@lsi.upc.edu
On the number of string lookups in BSTs (and related algorithms) with digital access Leonor Frias Departament de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya lfrias@lsi.upc.edu
Advanced Database Systems
 Lecture IV Query Processing Kyumars Sheykh Esmaili Basic Steps in Query Processing 2 Query Optimization Many equivalent execution plans Choosing the best one Based on Heuristics, Cost Will be discussed
Lecture IV Query Processing Kyumars Sheykh Esmaili Basic Steps in Query Processing 2 Query Optimization Many equivalent execution plans Choosing the best one Based on Heuristics, Cost Will be discussed
Algorithm Performance Factors. Memory Performance of Algorithms. Processor-Memory Performance Gap. Moore s Law. Program Model of Memory II
 Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
Memory Hierarchies && The New Bottleneck == Cache Conscious Data Access. Martin Grund
 Memory Hierarchies && The New Bottleneck == Cache Conscious Data Access Martin Grund Agenda Key Question: What is the memory hierarchy and how to exploit it? What to take home How is computer memory organized.
Memory Hierarchies && The New Bottleneck == Cache Conscious Data Access Martin Grund Agenda Key Question: What is the memory hierarchy and how to exploit it? What to take home How is computer memory organized.
External-Memory Algorithms with Applications in GIS - (L. Arge) Enylton Machado Roberto Beauclair
 External-Memory Algorithms with Applications in GIS - (L. Arge) Enylton Machado Roberto Beauclair {machado,tron}@visgraf.impa.br Theoretical Models Random Access Machine Memory: Infinite Array. Access
External-Memory Algorithms with Applications in GIS - (L. Arge) Enylton Machado Roberto Beauclair {machado,tron}@visgraf.impa.br Theoretical Models Random Access Machine Memory: Infinite Array. Access
Introduction to Computers and Programming. Today
 Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 10 April 8 2004 Today How to determine Big-O Compare data structures and algorithms Sorting algorithms 2 How to determine Big-O Partition
Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 10 April 8 2004 Today How to determine Big-O Compare data structures and algorithms Sorting algorithms 2 How to determine Big-O Partition
Memory management. Last modified: Adaptation of Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne slides for the textbook Applied Operating Systems Concepts
 Memory management Last modified: 26.04.2016 1 Contents Background Logical and physical address spaces; address binding Overlaying, swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of
Memory management Last modified: 26.04.2016 1 Contents Background Logical and physical address spaces; address binding Overlaying, swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of
Chapter 13: Query Processing
 Chapter 13: Query Processing! Overview! Measures of Query Cost! Selection Operation! Sorting! Join Operation! Other Operations! Evaluation of Expressions 13.1 Basic Steps in Query Processing 1. Parsing
Chapter 13: Query Processing! Overview! Measures of Query Cost! Selection Operation! Sorting! Join Operation! Other Operations! Evaluation of Expressions 13.1 Basic Steps in Query Processing 1. Parsing
Algorithms for dealing with massive data
 Computer Science Department Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul Porto Alegre, Brazil Outline of the talk Introduction Outline of the talk Algorithms models for dealing with massive datasets : Motivation,
Computer Science Department Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul Porto Alegre, Brazil Outline of the talk Introduction Outline of the talk Algorithms models for dealing with massive datasets : Motivation,
Lecture 3: Sorting 1
 Lecture 3: Sorting 1 Sorting Arranging an unordered collection of elements into monotonically increasing (or decreasing) order. S = a sequence of n elements in arbitrary order After sorting:
Lecture 3: Sorting 1 Sorting Arranging an unordered collection of elements into monotonically increasing (or decreasing) order. S = a sequence of n elements in arbitrary order After sorting:
Cache Oblivious Matrix Transpositions using Sequential Processing
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 225-321, p-issn: 2278-8719 Vol. 3, Issue 11 (November. 213), V4 PP 5-55 Cache Oblivious Matrix s using Sequential Processing korde P.S., and Khanale P.B 1
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 225-321, p-issn: 2278-8719 Vol. 3, Issue 11 (November. 213), V4 PP 5-55 Cache Oblivious Matrix s using Sequential Processing korde P.S., and Khanale P.B 1
Main Memory and the CPU Cache
 Main Memory and the CPU Cache CPU cache Unrolled linked lists B Trees Our model of main memory and the cost of CPU operations has been intentionally simplistic The major focus has been on determining
Main Memory and the CPU Cache CPU cache Unrolled linked lists B Trees Our model of main memory and the cost of CPU operations has been intentionally simplistic The major focus has been on determining
Lecture 8 13 March, 2012
 6.851: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2012 Prof. Erik Demaine Lecture 8 13 March, 2012 1 From Last Lectures... In the previous lecture, we discussed the External Memory and Cache Oblivious memory models.
6.851: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2012 Prof. Erik Demaine Lecture 8 13 March, 2012 1 From Last Lectures... In the previous lecture, we discussed the External Memory and Cache Oblivious memory models.
CS370 Operating Systems
 CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2017 Lecture 20 Main Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 Pages Pages and frames Page
CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2017 Lecture 20 Main Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 Pages Pages and frames Page
Lecture April, 2010
 6.851: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2010 Prof. Eri Demaine Lecture 20 22 April, 2010 1 Memory Hierarchies and Models of Them So far in class, we have wored with models of computation lie the word RAM
6.851: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2010 Prof. Eri Demaine Lecture 20 22 April, 2010 1 Memory Hierarchies and Models of Them So far in class, we have wored with models of computation lie the word RAM
! A relational algebra expression may have many equivalent. ! Cost is generally measured as total elapsed time for
 Chapter 13: Query Processing Basic Steps in Query Processing! Overview! Measures of Query Cost! Selection Operation! Sorting! Join Operation! Other Operations! Evaluation of Expressions 1. Parsing and
Chapter 13: Query Processing Basic Steps in Query Processing! Overview! Measures of Query Cost! Selection Operation! Sorting! Join Operation! Other Operations! Evaluation of Expressions 1. Parsing and
Chapter 13: Query Processing Basic Steps in Query Processing
 Chapter 13: Query Processing Basic Steps in Query Processing! Overview! Measures of Query Cost! Selection Operation! Sorting! Join Operation! Other Operations! Evaluation of Expressions 1. Parsing and
Chapter 13: Query Processing Basic Steps in Query Processing! Overview! Measures of Query Cost! Selection Operation! Sorting! Join Operation! Other Operations! Evaluation of Expressions 1. Parsing and
Disk Scheduling COMPSCI 386
 Disk Scheduling COMPSCI 386 Topics Disk Structure (9.1 9.2) Disk Scheduling (9.4) Allocation Methods (11.4) Free Space Management (11.5) Hard Disk Platter diameter ranges from 1.8 to 3.5 inches. Both sides
Disk Scheduling COMPSCI 386 Topics Disk Structure (9.1 9.2) Disk Scheduling (9.4) Allocation Methods (11.4) Free Space Management (11.5) Hard Disk Platter diameter ranges from 1.8 to 3.5 inches. Both sides
Cache Memories. From Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems. A Programmer s Perspective. Chapter 6.
 Cache Memories From Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems. A Programmer s Perspective. Chapter 6. Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging
Cache Memories From Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems. A Programmer s Perspective. Chapter 6. Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging
Lab Determining Data Storage Capacity
 Lab 1.3.2 Determining Data Storage Capacity Objectives Determine the amount of RAM (in MB) installed in a PC. Determine the size of the hard disk drive (in GB) installed in a PC. Determine the used and
Lab 1.3.2 Determining Data Storage Capacity Objectives Determine the amount of RAM (in MB) installed in a PC. Determine the size of the hard disk drive (in GB) installed in a PC. Determine the used and
Query Processing. Debapriyo Majumdar Indian Sta4s4cal Ins4tute Kolkata DBMS PGDBA 2016
 Query Processing Debapriyo Majumdar Indian Sta4s4cal Ins4tute Kolkata DBMS PGDBA 2016 Slides re-used with some modification from www.db-book.com Reference: Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. By Silberschatz,
Query Processing Debapriyo Majumdar Indian Sta4s4cal Ins4tute Kolkata DBMS PGDBA 2016 Slides re-used with some modification from www.db-book.com Reference: Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. By Silberschatz,
Cache-Adaptive Analysis
 Cache-Adaptive Analysis Michael A. Bender1 Erik Demaine4 Roozbeh Ebrahimi1 Jeremy T. Fineman3 Rob Johnson1 Andrea Lincoln4 Jayson Lynch4 Samuel McCauley1 1 3 4 Available Memory Can Fluctuate in Real Systems
Cache-Adaptive Analysis Michael A. Bender1 Erik Demaine4 Roozbeh Ebrahimi1 Jeremy T. Fineman3 Rob Johnson1 Andrea Lincoln4 Jayson Lynch4 Samuel McCauley1 1 3 4 Available Memory Can Fluctuate in Real Systems
Multi-core Computing Lecture 1
 Hi-Spade Multi-core Computing Lecture 1 MADALGO Summer School 2012 Algorithms for Modern Parallel and Distributed Models Phillip B. Gibbons Intel Labs Pittsburgh August 20, 2012 Lecture 1 Outline Multi-cores:
Hi-Spade Multi-core Computing Lecture 1 MADALGO Summer School 2012 Algorithms for Modern Parallel and Distributed Models Phillip B. Gibbons Intel Labs Pittsburgh August 20, 2012 Lecture 1 Outline Multi-cores:
4. A Comparison of Cache Aware and Cache Oblivious Static Search Trees Using Program Instrumentation
 4. A Comparison of Cache Aware and Cache Oblivious Static Search Trees Using Program Instrumentation Richard E. Ladner, Ray Fortna, and Bao-Hoang Nguyen Department of Computer Science & Engineering Universityof
4. A Comparison of Cache Aware and Cache Oblivious Static Search Trees Using Program Instrumentation Richard E. Ladner, Ray Fortna, and Bao-Hoang Nguyen Department of Computer Science & Engineering Universityof
Performance of Various Levels of Storage. Movement between levels of storage hierarchy can be explicit or implicit
 Memory Management All data in memory before and after processing All instructions in memory in order to execute Memory management determines what is to be in memory Memory management activities Keeping
Memory Management All data in memory before and after processing All instructions in memory in order to execute Memory management determines what is to be in memory Memory management activities Keeping
The History of I/O Models Erik Demaine
 The History of I/O Models Erik Demaine MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Memory Hierarchies in Practice CPU 750 ps Registers 100B Level 1 Cache 100KB Level 2 Cache 1MB 10GB 14 ns Main Memory 1EB-1ZB
The History of I/O Models Erik Demaine MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Memory Hierarchies in Practice CPU 750 ps Registers 100B Level 1 Cache 100KB Level 2 Cache 1MB 10GB 14 ns Main Memory 1EB-1ZB
3.2 Cache Oblivious Algorithms
 3.2 Cache Oblivious Algorithms Cache-Oblivious Algorithms by Matteo Frigo, Charles E. Leiserson, Harald Prokop, and Sridhar Ramachandran. In the 40th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science,
3.2 Cache Oblivious Algorithms Cache-Oblivious Algorithms by Matteo Frigo, Charles E. Leiserson, Harald Prokop, and Sridhar Ramachandran. In the 40th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science,
Chapter 8: Main Memory
 Chapter 8: Main Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel
Chapter 8: Main Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel
CS307 Operating Systems Main Memory
 CS307 Main Memory Fan Wu Department of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Spring 2018 Background Program must be brought (from disk) into memory and placed within a process
CS307 Main Memory Fan Wu Department of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Spring 2018 Background Program must be brought (from disk) into memory and placed within a process
High Performance Comparison-Based Sorting Algorithm on Many-Core GPUs
 High Performance Comparison-Based Sorting Algorithm on Many-Core GPUs Xiaochun Ye, Dongrui Fan, Wei Lin, Nan Yuan, and Paolo Ienne Key Laboratory of Computer System and Architecture ICT, CAS, China Outline
High Performance Comparison-Based Sorting Algorithm on Many-Core GPUs Xiaochun Ye, Dongrui Fan, Wei Lin, Nan Yuan, and Paolo Ienne Key Laboratory of Computer System and Architecture ICT, CAS, China Outline
Sorting. Overview. External sorting. Warm up: in memory sorting. Purpose. Overview. Sort benchmarks
 15-823 Advanced Topics in Database Systems Performance Sorting Shimin Chen School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University 22 March 2001 Sort benchmarks A base case: AlphaSort Improving Sort Performance
15-823 Advanced Topics in Database Systems Performance Sorting Shimin Chen School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University 22 March 2001 Sort benchmarks A base case: AlphaSort Improving Sort Performance
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-201 971 Comparative Performance Analysis Of Sorting Algorithms Abhinav Yadav, Dr. Sanjeev Bansal Abstract Sorting Algorithms
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-201 971 Comparative Performance Analysis Of Sorting Algorithms Abhinav Yadav, Dr. Sanjeev Bansal Abstract Sorting Algorithms
Outlook. File-System Interface Allocation-Methods Free Space Management
 File System Outlook File-System Interface Allocation-Methods Free Space Management 2 File System Interface File Concept File system is the most visible part of an OS Files storing related data Directory
File System Outlook File-System Interface Allocation-Methods Free Space Management 2 File System Interface File Concept File system is the most visible part of an OS Files storing related data Directory
Cache Memories. University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario (Canada) Marc Moreno Maza. CS2101 October 2012
 Cache Memories Marc Moreno Maza University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario (Canada) CS2101 October 2012 Plan 1 Hierarchical memories and their impact on our 2 Cache Analysis in Practice Plan 1 Hierarchical
Cache Memories Marc Moreno Maza University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario (Canada) CS2101 October 2012 Plan 1 Hierarchical memories and their impact on our 2 Cache Analysis in Practice Plan 1 Hierarchical
Pharmacy college.. Assist.Prof. Dr. Abdullah A. Abdullah
 The kinds of memory:- 1. RAM(Random Access Memory):- The main memory in the computer, it s the location where data and programs are stored (temporally). RAM is volatile means that the data is only there
The kinds of memory:- 1. RAM(Random Access Memory):- The main memory in the computer, it s the location where data and programs are stored (temporally). RAM is volatile means that the data is only there
School of Computer and Information Science
 School of Computer and Information Science CIS Research Placement Report Multiple threads in floating-point sort operations Name: Quang Do Date: 8/6/2012 Supervisor: Grant Wigley Abstract Despite the vast
School of Computer and Information Science CIS Research Placement Report Multiple threads in floating-point sort operations Name: Quang Do Date: 8/6/2012 Supervisor: Grant Wigley Abstract Despite the vast
Benchmarking the Memory Hierarchy of Modern GPUs
 1 of 30 Benchmarking the Memory Hierarchy of Modern GPUs In 11th IFIP International Conference on Network and Parallel Computing Xinxin Mei, Kaiyong Zhao, Chengjian Liu, Xiaowen Chu CS Department, Hong
1 of 30 Benchmarking the Memory Hierarchy of Modern GPUs In 11th IFIP International Conference on Network and Parallel Computing Xinxin Mei, Kaiyong Zhao, Chengjian Liu, Xiaowen Chu CS Department, Hong
The levels of a memory hierarchy. Main. Memory. 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms
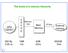 The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
Cache-Oblivious String Dictionaries
 Cache-Oblivious String Dictionaries Gerth Stølting Brodal University of Aarhus Joint work with Rolf Fagerberg #"! Outline of Talk Cache-oblivious model Basic cache-oblivious techniques Cache-oblivious
Cache-Oblivious String Dictionaries Gerth Stølting Brodal University of Aarhus Joint work with Rolf Fagerberg #"! Outline of Talk Cache-oblivious model Basic cache-oblivious techniques Cache-oblivious
CS307: Operating Systems
 CS307: Operating Systems Chentao Wu 吴晨涛 Associate Professor Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University SEIEE Building 3-513 wuct@cs.sjtu.edu.cn Download Lectures ftp://public.sjtu.edu.cn
CS307: Operating Systems Chentao Wu 吴晨涛 Associate Professor Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University SEIEE Building 3-513 wuct@cs.sjtu.edu.cn Download Lectures ftp://public.sjtu.edu.cn
Chapter 7: Main Memory. Operating System Concepts Essentials 8 th Edition
 Chapter 7: Main Memory Operating System Concepts Essentials 8 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2011 Chapter 7: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Paging Structure
Chapter 7: Main Memory Operating System Concepts Essentials 8 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2011 Chapter 7: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Paging Structure
Performance comparison between a massive SMP machine and clusters
 Performance comparison between a massive SMP machine and clusters Martin Scarcia, Stefano Alberto Russo Sissa/eLab joint Democritos/Sissa Laboratory for e-science Via Beirut 2/4 34151 Trieste, Italy Stefano
Performance comparison between a massive SMP machine and clusters Martin Scarcia, Stefano Alberto Russo Sissa/eLab joint Democritos/Sissa Laboratory for e-science Via Beirut 2/4 34151 Trieste, Italy Stefano
Fast and Cache-Oblivious Dynamic Programming with Local Dependencies
 Fast and Cache-Oblivious Dynamic Programming with Local Dependencies Philip Bille and Morten Stöckel Technical University of Denmark, DTU Informatics, Copenhagen, Denmark Abstract. String comparison such
Fast and Cache-Oblivious Dynamic Programming with Local Dependencies Philip Bille and Morten Stöckel Technical University of Denmark, DTU Informatics, Copenhagen, Denmark Abstract. String comparison such
ECE 7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture ---- A Systems Perspective. Part I: Operating system overview: Memory Management
 ECE 7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture ---- A Systems Perspective Part I: Operating system overview: Memory Management 1 Hardware background The role of primary memory Program
ECE 7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture ---- A Systems Perspective Part I: Operating system overview: Memory Management 1 Hardware background The role of primary memory Program
Indexing. Week 14, Spring Edited by M. Naci Akkøk, , Contains slides from 8-9. April 2002 by Hector Garcia-Molina, Vera Goebel
 Indexing Week 14, Spring 2005 Edited by M. Naci Akkøk, 5.3.2004, 3.3.2005 Contains slides from 8-9. April 2002 by Hector Garcia-Molina, Vera Goebel Overview Conventional indexes B-trees Hashing schemes
Indexing Week 14, Spring 2005 Edited by M. Naci Akkøk, 5.3.2004, 3.3.2005 Contains slides from 8-9. April 2002 by Hector Garcia-Molina, Vera Goebel Overview Conventional indexes B-trees Hashing schemes
Clustering and Reclustering HEP Data in Object Databases
 Clustering and Reclustering HEP Data in Object Databases Koen Holtman CERN EP division CH - Geneva 3, Switzerland We formulate principles for the clustering of data, applicable to both sequential HEP applications
Clustering and Reclustering HEP Data in Object Databases Koen Holtman CERN EP division CH - Geneva 3, Switzerland We formulate principles for the clustering of data, applicable to both sequential HEP applications
Memory Hierarchy Computing Systems & Performance MSc Informatics Eng. Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed)
 Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2012/13 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2012/13 1 2
Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2012/13 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2012/13 1 2
Funnel Heap - A Cache Oblivious Priority Queue
 Alcom-FT Technical Report Series ALCOMFT-TR-02-136 Funnel Heap - A Cache Oblivious Priority Queue Gerth Stølting Brodal, Rolf Fagerberg Abstract The cache oblivious model of computation is a two-level
Alcom-FT Technical Report Series ALCOMFT-TR-02-136 Funnel Heap - A Cache Oblivious Priority Queue Gerth Stølting Brodal, Rolf Fagerberg Abstract The cache oblivious model of computation is a two-level
CS 310: Memory Hierarchy and B-Trees
 CS 310: Memory Hierarchy and B-Trees Chris Kauffman Week 14-1 Matrix Sum Given an M by N matrix X, sum its elements M rows, N columns Sum R given X, M, N sum = 0 for i=0 to M-1{ for j=0 to N-1 { sum +=
CS 310: Memory Hierarchy and B-Trees Chris Kauffman Week 14-1 Matrix Sum Given an M by N matrix X, sum its elements M rows, N columns Sum R given X, M, N sum = 0 for i=0 to M-1{ for j=0 to N-1 { sum +=
ICS RESEARCH TECHNICAL TALK DRAKE TETREAULT, ICS H197 FALL 2013
 ICS RESEARCH TECHNICAL TALK DRAKE TETREAULT, ICS H197 FALL 2013 TOPIC: RESEARCH PAPER Title: Data Management for SSDs for Large-Scale Interactive Graphics Applications Authors: M. Gopi, Behzad Sajadi,
ICS RESEARCH TECHNICAL TALK DRAKE TETREAULT, ICS H197 FALL 2013 TOPIC: RESEARCH PAPER Title: Data Management for SSDs for Large-Scale Interactive Graphics Applications Authors: M. Gopi, Behzad Sajadi,
I/O Model. Cache-Oblivious Algorithms : Algorithms in the Real World. Advantages of Cache-Oblivious Algorithms 4/9/13
 I/O Model 15-853: Algorithms in the Real World Locality II: Cache-oblivious algorithms Matrix multiplication Distribution sort Static searching Abstracts a single level of the memory hierarchy Fast memory
I/O Model 15-853: Algorithms in the Real World Locality II: Cache-oblivious algorithms Matrix multiplication Distribution sort Static searching Abstracts a single level of the memory hierarchy Fast memory
Chapter 8: Main Memory. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 8: Main Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel
Chapter 8: Main Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel
CHAPTER 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT. By I-Chen Lin Textbook: Operating System Concepts 9th Ed.
 CHAPTER 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT By I-Chen Lin Textbook: Operating System Concepts 9th Ed. Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the
CHAPTER 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT By I-Chen Lin Textbook: Operating System Concepts 9th Ed. Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the
Short-term Memory for Self-collecting Mutators. Martin Aigner, Andreas Haas, Christoph Kirsch, Ana Sokolova Universität Salzburg
 Short-term Memory for Self-collecting Mutators Martin Aigner, Andreas Haas, Christoph Kirsch, Ana Sokolova Universität Salzburg CHESS Seminar, UC Berkeley, September 2010 Heap Management explicit heap
Short-term Memory for Self-collecting Mutators Martin Aigner, Andreas Haas, Christoph Kirsch, Ana Sokolova Universität Salzburg CHESS Seminar, UC Berkeley, September 2010 Heap Management explicit heap
Flexible Architecture Research Machine (FARM)
 Flexible Architecture Research Machine (FARM) RAMP Retreat June 25, 2009 Jared Casper, Tayo Oguntebi, Sungpack Hong, Nathan Bronson Christos Kozyrakis, Kunle Olukotun Motivation Why CPUs + FPGAs make sense
Flexible Architecture Research Machine (FARM) RAMP Retreat June 25, 2009 Jared Casper, Tayo Oguntebi, Sungpack Hong, Nathan Bronson Christos Kozyrakis, Kunle Olukotun Motivation Why CPUs + FPGAs make sense
CMSC 341 Hashing (Continued) Based on slides from previous iterations of this course
 CMSC 341 Hashing (Continued) Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Today s Topics Review Uses and motivations of hash tables Major concerns with hash tables Properties Hash function Hash
CMSC 341 Hashing (Continued) Based on slides from previous iterations of this course Today s Topics Review Uses and motivations of hash tables Major concerns with hash tables Properties Hash function Hash
COMPUTER ARCHITECTURES
 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURES Cache memory Gábor Horváth BUTE Department of Networked Systems and Services ghorvath@hit.bme.hu Budapest, 2019. 04. 07. 1 SPEED OF MEMORY OPERATIONS The memory is a serious bottleneck
COMPUTER ARCHITECTURES Cache memory Gábor Horváth BUTE Department of Networked Systems and Services ghorvath@hit.bme.hu Budapest, 2019. 04. 07. 1 SPEED OF MEMORY OPERATIONS The memory is a serious bottleneck
Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 465
 Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 465 LECTURE 2 Analysis of Algorithms Insertion Sort Loop invariants Asymptotic analysis Sofya Raskhodnikova and Adam Smith The problem of sorting Input: sequence a 1,
Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 465 LECTURE 2 Analysis of Algorithms Insertion Sort Loop invariants Asymptotic analysis Sofya Raskhodnikova and Adam Smith The problem of sorting Input: sequence a 1,
Optimal Cache-Oblivious Implicit Dictionaries
 Optimal Cache-Oblivious Implicit Dictionaries Gianni Franceschini and Roberto Grossi Dipartimento di Informatica, Università di Pisa via Filippo Buonarroti 2, 56127 Pisa, Italy {francesc,grossi}@di.unipi.it
Optimal Cache-Oblivious Implicit Dictionaries Gianni Franceschini and Roberto Grossi Dipartimento di Informatica, Università di Pisa via Filippo Buonarroti 2, 56127 Pisa, Italy {francesc,grossi}@di.unipi.it
Dense Matrix Multiplication
 Dense Matrix Multiplication Abhishek Somani, Debdeep Mukhopadhyay Mentor Graphics, IIT Kharagpur October 7, 2015 Abhishek, Debdeep (IIT Kgp) Matrix Mult. October 7, 2015 1 / 56 Overview 1 The Problem 2
Dense Matrix Multiplication Abhishek Somani, Debdeep Mukhopadhyay Mentor Graphics, IIT Kharagpur October 7, 2015 Abhishek, Debdeep (IIT Kgp) Matrix Mult. October 7, 2015 1 / 56 Overview 1 The Problem 2
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing. Basic Concepts
 Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing! Basic Concepts! Ordered Indices! B+-Tree Index Files! B-Tree Index Files! Static Hashing! Dynamic Hashing! Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing! Index Definition
Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing! Basic Concepts! Ordered Indices! B+-Tree Index Files! B-Tree Index Files! Static Hashing! Dynamic Hashing! Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing! Index Definition
Dynamic programming in faulty memory hierarchies (cache-obliviously)
 Dynamic programming in faulty memory hierarchies (cache-obliviously) S. Caminiti 1, I. Finocchi 1, E. G. Fusco 1, and F. Silvestri 2 1 Computer Science Department, Sapienza University of Rome 2 Department
Dynamic programming in faulty memory hierarchies (cache-obliviously) S. Caminiti 1, I. Finocchi 1, E. G. Fusco 1, and F. Silvestri 2 1 Computer Science Department, Sapienza University of Rome 2 Department
I.-C. Lin, Assistant Professor. Textbook: Operating System Concepts 8ed CHAPTER 8: MEMORY
 I.-C. Lin, Assistant Professor. Textbook: Operating System Concepts 8ed CHAPTER 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Paging Structure of the
I.-C. Lin, Assistant Professor. Textbook: Operating System Concepts 8ed CHAPTER 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Paging Structure of the
L9: Storage Manager Physical Data Organization
 L9: Storage Manager Physical Data Organization Disks and files Record and file organization Indexing Tree-based index: B+-tree Hash-based index c.f. Fig 1.3 in [RG] and Fig 2.3 in [EN] Functional Components
L9: Storage Manager Physical Data Organization Disks and files Record and file organization Indexing Tree-based index: B+-tree Hash-based index c.f. Fig 1.3 in [RG] and Fig 2.3 in [EN] Functional Components
Chapter 8: Main Memory
 Chapter 8: Main Memory Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel 32 and 64-bit Architectures Example:
Chapter 8: Main Memory Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel 32 and 64-bit Architectures Example:
Analyze the obvious algorithm, 5 points Here is the most obvious algorithm for this problem: (LastLargerElement[A[1..n]:
![Analyze the obvious algorithm, 5 points Here is the most obvious algorithm for this problem: (LastLargerElement[A[1..n]: Analyze the obvious algorithm, 5 points Here is the most obvious algorithm for this problem: (LastLargerElement[A[1..n]:](/thumbs/90/104324109.jpg) CSE 101 Homework 1 Background (Order and Recurrence Relations), correctness proofs, time analysis, and speeding up algorithms with restructuring, preprocessing and data structures. Due Thursday, April
CSE 101 Homework 1 Background (Order and Recurrence Relations), correctness proofs, time analysis, and speeding up algorithms with restructuring, preprocessing and data structures. Due Thursday, April
The Limits of Sorting Divide-and-Conquer Comparison Sorts II
 The Limits of Sorting Divide-and-Conquer Comparison Sorts II CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Monday, October 12, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of
The Limits of Sorting Divide-and-Conquer Comparison Sorts II CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Monday, October 12, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of
First Swedish Workshop on Multi-Core Computing MCC 2008 Ronneby: On Sorting and Load Balancing on Graphics Processors
 First Swedish Workshop on Multi-Core Computing MCC 2008 Ronneby: On Sorting and Load Balancing on Graphics Processors Daniel Cederman and Philippas Tsigas Distributed Computing Systems Chalmers University
First Swedish Workshop on Multi-Core Computing MCC 2008 Ronneby: On Sorting and Load Balancing on Graphics Processors Daniel Cederman and Philippas Tsigas Distributed Computing Systems Chalmers University
