10/9/2012. Comparison and Logical Operators The if Statement The if else Statement Nested if Statements The switch case. switch case Statement
|
|
|
- Annabella Jefferson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 I l Implementing ti Control C t ll Logic i iin C# 5 5. Comparison and Logical Operators The if Statement The if Statement Nested if Statements The switch case switch case Statement 2 Operator Notation in C# Equals == Not Equals!= Greater Than > Greater Than or Equals >= Less Than Less Than or Equals < <= Example: bool result = 5 <= 6; (result); // True 4 Operator Notation in C# Logical NOT! Logical AND && Logical OR Logical Exclusive OR (XOR) ^ Implementing Conditional Logic De Morgan laws!!a!(a B) A!(A && B)!A &&!B!A!B 5 1
2 The condition can be: Boolean variable Boolean logical expression Comparison expression The most simple conditional Enables you to test for a condition Branch to different parts of the code depending on the result The simplest form of an if : if (condition) s; The condition Th diti cannott be b iinteger t variable i bl (lik (like in i C / C++) The can be: Single ending with a semicolon Block enclosed in braces 7 condition 8 static void Main() ("Enter ("Enter two numbers."); false true int biggernumber = int.parse(console.readline()); int smallernumber = int.parse(console.readline()); if (smallernumber > biggernumber biggernumber) ) biggernumber = smallernumber smallernumber; ; The condition is evaluated If it is true, the is executed If it is false, the is skipped ("The greater number is: 0", biggernumber); biggernumber ); 9 10 Live De Demo mo example03a01 More complex and useful conditional Executes one branch if the condition is true, and another if it is false The simplest form of an if : if (expression) 1; 1 ; 2; 2 ; 12 2
3 conditio n false second string s = Console.ReadLine(); int number = int.parse(s); true first if ( (number number % 2 == 0) ("This ("This number is even."); ("This ("This number is odd."); The condition is evaluated Checking a number if it is odd or even If it is true, the first is executed If it is false, the second is executed Demo--look at the example03a03 Creating More Complex Logic if and if s can be nested, i.e. used inside another if or Every corresponds to its closest preceding if if (expression) if (expression) ; ; ; Always use blocks to avoid ambiguity 17 Even when a single follows Avoid using more than three levels of nested if s Put the case y you normally y expect p to p process first,, then write the unusual cases Arrange the code to make it more readable 18 3
4 if ( (first first == second) ( "These two numbers are equal."); if (first (first > second) ( "The first number is bigger."); ("The ("The second is bigger."); example03a03 19 Sometimes we need to use another ifconstruction in the block Thus if can be used: int ch = 'X'; if (ch == 'A' A ch == 'a') a ) ("Vowel [ei]"); if (ch == 'E' ch == 'e') ("Vowel [i:]"); Demo-example03a04 if 21 Making Several Comparisons at Once Selects for execution a from a list depending on the value of the switch expression switch (day) case 1: ("Monday"); case 2: ("Tuesday"); case 3: ("Wednesday ("Wednesday"); "); case 4: ("Thursday"); case 5: ("Friday"); case 6: ("Saturday"); case 7: ("Sunday"); default: ("Error!"); 24 4
5 2. The expression is evaluated When one of the constants specified in a case label is equal to the expression 3. If no case is equal q to the expression p 1. The that corresponds to that case is executed If there is default case, it is executed Otherwise the control is transferred to the end point of the switch Demo--example03a05 25 Variables types like string, enum and integral types can be used for switch expression The value null is permitted as a case label constant The keyword break exits the switch "No fall through" rule you are obligated to use break after each case Multiple labels that correspond to the same are permitted You can use multiple labels to execute the same in more than one case switch (animal) case "dog" : ("MAMMAL"); b k case "crocodile" : case "tortoise" : case "snake" : ("REPTILE"); default : ("There is no such animal!"); There must be a separate case for every normal situation Put the normal case first Li DemoLive Demo D -example03a06; l and d 07 Put the most frequently executed cases first and the least frequently executed last Order cases alphabetically or numerically In default use case that cannot be reached under normal circumstances 30 5
6 Comparison and logical operators are used to compose logical conditions The conditional s if and if provide conditional execution of blocks of code p Questions? Constantly used in computer programming Conditional s can be nested The switch easily and elegantly checks an expression for a sequence of values Write an if that examines two integer variables and exchanges their values if the first one is greater than the second one. Write a p program g that shows the sign g of the product of three real numbers without calculating it. Use a sequence of if s. Write a program that finds the biggest of three integers using nested if s. Sort 3 real values in descending order using nested if s Write a program that, depending on the user's choice inputs int, double or string variable. If the variable is integer or double, increases it with 1. If the variable is string, appends "*" at its end. The program must show the value of that variable as a console output. Use switch. We are given 5 integer numbers. Write a program that checks if the sum of some subset of them is 0. Example: 3, 2, 1, 1, = Write program that asks for a digit and depending on the input shows the name of that digit (in English) using a switch. Write a p program g that enters the coefficients a, b and c of a quadratic equation a*x2 + b*x + c = 0 and calculates and prints its real roots. Note that quadratic equations may have 0, 1 or 2 real roots. Write a program that finds the greatest of given 5 variables. 34 Write a program that applies bonus scores to given scores in the range [1..9]. The program reads a digit as an input. If the digit is between 1 and 3, the program multiplies it by 10; if it is b between 4 and d 6, multiplies l l it b by 100; iff it is between 7 and 9, multiplies it by If it is zero or if the value is not a digit, the program must report an error. Use a switch and at the end print the calculated new value in the console. 36 6
7 11. * Write a program that converts a number in the range [ ] to a text corresponding to its English pronunciation. Examples: 0 "Zero" 273 "Two hundred seventy three" 400 "Four hundred" 501 "Five hundred and one" 711 "Severn hundred and eleven" 37 7
DECISION CONTROL AND LOOPING STATEMENTS
 DECISION CONTROL AND LOOPING STATEMENTS DECISION CONTROL STATEMENTS Decision control statements are used to alter the flow of a sequence of instructions. These statements help to jump from one part of
DECISION CONTROL AND LOOPING STATEMENTS DECISION CONTROL STATEMENTS Decision control statements are used to alter the flow of a sequence of instructions. These statements help to jump from one part of
Other conditional and loop constructs. Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen
 Other conditional and loop constructs Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Overview Current loop constructs: for, while, do-while New loop constructs Get out of loop early: break Skip rest of
Other conditional and loop constructs Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Overview Current loop constructs: for, while, do-while New loop constructs Get out of loop early: break Skip rest of
CHAPTER : 9 FLOW OF CONTROL
 CHAPTER 9 FLOW OF CONTROL Statements-Statements are the instructions given to the Computer to perform any kind of action. Null Statement-A null statement is useful in those case where syntax of the language
CHAPTER 9 FLOW OF CONTROL Statements-Statements are the instructions given to the Computer to perform any kind of action. Null Statement-A null statement is useful in those case where syntax of the language
Programming Language. Control Structures: Selection (switch) Eng. Anis Nazer First Semester
 Programming Language Control Structures: Selection (switch) Eng. Anis Nazer First Semester 2018-2019 Multiple selection choose one of two things if/else choose one from many things multiple selection using
Programming Language Control Structures: Selection (switch) Eng. Anis Nazer First Semester 2018-2019 Multiple selection choose one of two things if/else choose one from many things multiple selection using
CHRIST THE KING BOYS MATRIC HR. SEC. SCHOOL, KUMBAKONAM CHAPTER 9 C++
 CHAPTER 9 C++ 1. WRITE ABOUT THE BINARY OPERATORS USED IN C++? ARITHMETIC OPERATORS: Arithmetic operators perform simple arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division etc.,
CHAPTER 9 C++ 1. WRITE ABOUT THE BINARY OPERATORS USED IN C++? ARITHMETIC OPERATORS: Arithmetic operators perform simple arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division etc.,
Chapter 3, Selection. Liang, Introduction to Programming with C++, Second Edition, (c) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3, Selection 1 The bool Type and Operators 2 One-way if Statements if (booleanexpression) { statement(s); } if (radius >= 0) { area = radius * radius * PI; cout
Chapter 3, Selection 1 The bool Type and Operators 2 One-way if Statements if (booleanexpression) { statement(s); } if (radius >= 0) { area = radius * radius * PI; cout
bool bool - either true or false
 Strings & Branching bool bool - either true or false You have the common math comparisons: > (greater than), e.g. 7 > 2.5 is true == (equals), e.g. 5 == 4 is false
Strings & Branching bool bool - either true or false You have the common math comparisons: > (greater than), e.g. 7 > 2.5 is true == (equals), e.g. 5 == 4 is false
204111: Computer and Programming
 204111: Computer and Programming Week 4: Control Structures t Monchai Sopitkamon, Ph.D. Overview Types of control structures Using selection structure Using repetition structure Types of control ol structures
204111: Computer and Programming Week 4: Control Structures t Monchai Sopitkamon, Ph.D. Overview Types of control structures Using selection structure Using repetition structure Types of control ol structures
Announcements. HW0 is posted on schedule, due next Friday at 9pm (pretty easy)
 Branching Announcements HW0 is posted on schedule, due next Friday at 9pm (pretty easy) Office hours (attempt problems before going): - HW only or Lab only (check calendar) - Write name on whiteboard if
Branching Announcements HW0 is posted on schedule, due next Friday at 9pm (pretty easy) Office hours (attempt problems before going): - HW only or Lab only (check calendar) - Write name on whiteboard if
Data Types and Variables in C language
 Data Types and Variables in C language Basic structure of C programming To write a C program, we first create functions and then put them together. A C program may contain one or more sections. They are
Data Types and Variables in C language Basic structure of C programming To write a C program, we first create functions and then put them together. A C program may contain one or more sections. They are
Boolean Data-Type. Boolean Data Type (false, true) i.e. 3/6/2018. The type bool is also described as being an integer: bool bflag; bflag = true;
 Programming in C++ If Statements If the sun is shining Choice Statements if (the sun is shining) go to the beach; True Beach False Class go to class; End If 2 1 Boolean Data Type (false, ) i.e. bool bflag;
Programming in C++ If Statements If the sun is shining Choice Statements if (the sun is shining) go to the beach; True Beach False Class go to class; End If 2 1 Boolean Data Type (false, ) i.e. bool bflag;
Lecture 9. Monday, January 31 CS 205 Programming for the Sciences - Lecture 9 1
 Lecture 9 Reminder: Programming Assignment 3 is due Wednesday by 4:30pm. Exam 1 is on Friday. Exactly like Prog. Assign. 2; no collaboration or help from the instructor. Log into Windows/ACENET. Start
Lecture 9 Reminder: Programming Assignment 3 is due Wednesday by 4:30pm. Exam 1 is on Friday. Exactly like Prog. Assign. 2; no collaboration or help from the instructor. Log into Windows/ACENET. Start
if Statement Numeric Rela5onal Operators The if Statement Flow of Control: Branching (Savitch, Chapter 3)
 if Statement Flow of Control: Branching (Savitch, Chapter 3) TOPICS Conditional Execution if and Statement Boolean Data switch Statement Ensures that a statement is executed only when some condi5on is
if Statement Flow of Control: Branching (Savitch, Chapter 3) TOPICS Conditional Execution if and Statement Boolean Data switch Statement Ensures that a statement is executed only when some condi5on is
if Statement Numeric Rela7onal Operators The if Statement Flow of Control: Branching (Savitch, Chapter 3)
 if Statement Flow of Control: Branching (Savitch, Chapter 3) TOPICS Conditional Execution if,, and if boolean data switch statements CS 160, Fall Semester 2015 1 Programs o-en contain statements that may
if Statement Flow of Control: Branching (Savitch, Chapter 3) TOPICS Conditional Execution if,, and if boolean data switch statements CS 160, Fall Semester 2015 1 Programs o-en contain statements that may
Laboratory 0 Week 0 Advanced Structured Programming An Introduction to Visual Studio and C++
 Laboratory 0 Week 0 Advanced Structured Programming An Introduction to Visual Studio and C++ 0.1 Introduction This is a session to familiarize working with the Visual Studio development environment. It
Laboratory 0 Week 0 Advanced Structured Programming An Introduction to Visual Studio and C++ 0.1 Introduction This is a session to familiarize working with the Visual Studio development environment. It
AQA Decision 1 Algorithms. Section 1: Communicating an algorithm
 AQA Decision 1 Algorithms Section 1: Communicating an algorithm Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Flow charts Pseudo code Loops in algorithms Programs for the TI-83 graphical calculator
AQA Decision 1 Algorithms Section 1: Communicating an algorithm Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Flow charts Pseudo code Loops in algorithms Programs for the TI-83 graphical calculator
Flow Control. CSC215 Lecture
 Flow Control CSC215 Lecture Outline Blocks and compound statements Conditional statements if - statement if-else - statement switch - statement? : opertator Nested conditional statements Repetitive statements
Flow Control CSC215 Lecture Outline Blocks and compound statements Conditional statements if - statement if-else - statement switch - statement? : opertator Nested conditional statements Repetitive statements
CIS 3260 Intro to Programming in C#
 Iteration (looping) McGraw-Hill 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Understand the necessity of this program control structure Describe while loops Describe do while loops Describe
Iteration (looping) McGraw-Hill 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Understand the necessity of this program control structure Describe while loops Describe do while loops Describe
Making Decisions. C# Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design 2nd Edition. David McDonald, Ph.D. Director of Emerging Technologies
 5 ec Making Decisions s C# Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design 2nd Edition David McDonald, Ph.D. Director of Emerging Technologies Chapter Objectives Learn about conditional expressions
5 ec Making Decisions s C# Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design 2nd Edition David McDonald, Ph.D. Director of Emerging Technologies Chapter Objectives Learn about conditional expressions
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
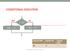 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
Lexical Considerations
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Fall 2005 Handout 6 Decaf Language Wednesday, September 7 The project for the course is to write a
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Fall 2005 Handout 6 Decaf Language Wednesday, September 7 The project for the course is to write a
Iosif Ignat, Marius Joldoș Laboratory Guide 4. Statements. STATEMENTS in C
 STATEMENTS in C 1. Overview The learning objective of this lab is: To understand and proper use statements of C/C++ language, both the simple and structured ones: the expression statement, the empty statement,
STATEMENTS in C 1. Overview The learning objective of this lab is: To understand and proper use statements of C/C++ language, both the simple and structured ones: the expression statement, the empty statement,
Chapter 2. The Algorithmic Foundations of. Computer Science INVITATION TO. Computer Science. Tuesday, September 10, 13
 Chapter 2 The Algorithmic Foundations of Computer Science INVITATION TO Computer Science 1 Objectives After studying this chapter, students will be able to: Explain the benefits of pseudocode over natural
Chapter 2 The Algorithmic Foundations of Computer Science INVITATION TO Computer Science 1 Objectives After studying this chapter, students will be able to: Explain the benefits of pseudocode over natural
Michele Van Dyne Museum 204B CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II, Spring
 Michele Van Dyne Museum 204B mvandyne@mtech.edu http://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II, Spring 2016 1 Review of Java Basics Data Types Arrays NEW: multidimensional
Michele Van Dyne Museum 204B mvandyne@mtech.edu http://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II, Spring 2016 1 Review of Java Basics Data Types Arrays NEW: multidimensional
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Introduction. C provides two styles of flow control:
 Introduction C provides two styles of flow control: Branching Looping Branching is deciding what actions to take and looping is deciding how many times to take a certain action. Branching constructs: if
Introduction C provides two styles of flow control: Branching Looping Branching is deciding what actions to take and looping is deciding how many times to take a certain action. Branching constructs: if
CMSC 104 -Lecture 11 John Y. Park, adapted by C Grasso
 CMSC 104 -Lecture 11 John Y. Park, adapted by C Grasso 1 Topics Multiple Selection vs Binary Selection switch Statement char data type and getchar( ) function Reading newline characters 2 So far, we have
CMSC 104 -Lecture 11 John Y. Park, adapted by C Grasso 1 Topics Multiple Selection vs Binary Selection switch Statement char data type and getchar( ) function Reading newline characters 2 So far, we have
Lecture 3 MATLAB programming (1) Dr.Qi Ying
 Lecture 3 MATLAB programming (1) Dr.Qi Ying Objectives Data types Logical operators/functions Branching Debugging of a program Data types in MATLAB Basic: Numeric (integer, floating-point, complex) Logical:
Lecture 3 MATLAB programming (1) Dr.Qi Ying Objectives Data types Logical operators/functions Branching Debugging of a program Data types in MATLAB Basic: Numeric (integer, floating-point, complex) Logical:
Subject: PROBLEM SOLVING THROUGH C Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 100
 Code: DC-05 Subject: PROBLEM SOLVING THROUGH C Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 100 NOTE: There are 11 Questions in all. Question 1 is compulsory and carries 16 marks. Answer to Q. 1. must be written in the space
Code: DC-05 Subject: PROBLEM SOLVING THROUGH C Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 100 NOTE: There are 11 Questions in all. Question 1 is compulsory and carries 16 marks. Answer to Q. 1. must be written in the space
Announcements. Homework 0: using cin with 10/3 is NOT the same as (directly)
 Branching Announcements Homework 0: using cin with 10/3 is NOT the same as 3.3333 (directly) With cin, it will stop as soon as it reaches a type that does not match the variable (into which it is storing)
Branching Announcements Homework 0: using cin with 10/3 is NOT the same as 3.3333 (directly) With cin, it will stop as soon as it reaches a type that does not match the variable (into which it is storing)
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Recap. ANSI C Reserved Words C++ Multimedia Programming Lecture 2. Erwin M. Bakker Joachim Rijsdam
 Multimedia Programming 2004 Lecture 2 Erwin M. Bakker Joachim Rijsdam Recap Learning C++ by example No groups: everybody should experience developing and programming in C++! Assignments will determine
Multimedia Programming 2004 Lecture 2 Erwin M. Bakker Joachim Rijsdam Recap Learning C++ by example No groups: everybody should experience developing and programming in C++! Assignments will determine
Section 1.1. Inductive Reasoning. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 1.1 Inductive Reasoning What You Will Learn Inductive and deductive reasoning processes 1.1-2 Natural Numbers The set of natural numbers is also called the set of counting numbers. N = {1, 2, 3,
Section 1.1 Inductive Reasoning What You Will Learn Inductive and deductive reasoning processes 1.1-2 Natural Numbers The set of natural numbers is also called the set of counting numbers. N = {1, 2, 3,
I SEMESTER EXAM : : XI :COMPUTER SCIENCE : MAX MARK a) What is the difference between Hardware and Software? Give one example for each.
 I SEMESTER EXAM : : XI :COMPUTER SCIENCE : MAX MARK 70. a) What is the difference between Hardware and Software? Give one example for each. b) Give two differences between primary and secondary memory.
I SEMESTER EXAM : : XI :COMPUTER SCIENCE : MAX MARK 70. a) What is the difference between Hardware and Software? Give one example for each. b) Give two differences between primary and secondary memory.
5. Selection: If and Switch Controls
 Computer Science I CS 135 5. Selection: If and Switch Controls René Doursat Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Nevada, Reno Fall 2005 Computer Science I CS 135 0. Course Presentation
Computer Science I CS 135 5. Selection: If and Switch Controls René Doursat Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Nevada, Reno Fall 2005 Computer Science I CS 135 0. Course Presentation
B.V. Patel Institute of Business Management, Computer & Information Technology, Uka Tarsadia University
 Unit 1 Programming Language and Overview of C 1. State whether the following statements are true or false. a. Every line in a C program should end with a semicolon. b. In C language lowercase letters are
Unit 1 Programming Language and Overview of C 1. State whether the following statements are true or false. a. Every line in a C program should end with a semicolon. b. In C language lowercase letters are
Chapter. Solving Problems that Require Decisions. Objectives: At the end of the chapter students should be able to:
 Chapter 13 Solving Problems that Require Decisions Objectives: At the end of the chapter students should be able to: Design programs that correctly use decision logic Correctly write and evaluate simple
Chapter 13 Solving Problems that Require Decisions Objectives: At the end of the chapter students should be able to: Design programs that correctly use decision logic Correctly write and evaluate simple
Objectives. Introduce the core C# language features class Main types variables basic input and output operators arrays control constructs comments
 Basics Objectives Introduce the core C# language features class Main types variables basic input and output operators arrays control constructs comments 2 Class Keyword class used to define new type specify
Basics Objectives Introduce the core C# language features class Main types variables basic input and output operators arrays control constructs comments 2 Class Keyword class used to define new type specify
Programming - 1. Computer Science Department 011COMP-3 لغة البرمجة 1 لطالب كلية الحاسب اآللي ونظم المعلومات 011 عال- 3
 Programming - 1 Computer Science Department 011COMP-3 لغة البرمجة 1 011 عال- 3 لطالب كلية الحاسب اآللي ونظم المعلومات 1 1.1 Machine Language A computer programming language which has binary instructions
Programming - 1 Computer Science Department 011COMP-3 لغة البرمجة 1 011 عال- 3 لطالب كلية الحاسب اآللي ونظم المعلومات 1 1.1 Machine Language A computer programming language which has binary instructions
Unit-II Programming and Problem Solving (BE1/4 CSE-2)
 Unit-II Programming and Problem Solving (BE1/4 CSE-2) Problem Solving: Algorithm: It is a part of the plan for the computer program. An algorithm is an effective procedure for solving a problem in a finite
Unit-II Programming and Problem Solving (BE1/4 CSE-2) Problem Solving: Algorithm: It is a part of the plan for the computer program. An algorithm is an effective procedure for solving a problem in a finite
CHAPTER 5 FLOW OF CONTROL
 CHAPTER 5 FLOW OF CONTROL PROGRAMMING CONSTRUCTS - In a program, statements may be executed sequentially, selectively or iteratively. - Every programming language provides constructs to support sequence,
CHAPTER 5 FLOW OF CONTROL PROGRAMMING CONSTRUCTS - In a program, statements may be executed sequentially, selectively or iteratively. - Every programming language provides constructs to support sequence,
Lecture 12. Data Types and Strings
 Lecture 12 Data Types and Strings Class v. Object A Class represents the generic description of a type. An Object represents a specific instance of the type. Video Game=>Class, WoW=>Instance Members of
Lecture 12 Data Types and Strings Class v. Object A Class represents the generic description of a type. An Object represents a specific instance of the type. Video Game=>Class, WoW=>Instance Members of
YOLOP Language Reference Manual
 YOLOP Language Reference Manual Sasha McIntosh, Jonathan Liu & Lisa Li sam2270, jl3516 and ll2768 1. Introduction YOLOP (Your Octothorpean Language for Optical Processing) is an image manipulation language
YOLOP Language Reference Manual Sasha McIntosh, Jonathan Liu & Lisa Li sam2270, jl3516 and ll2768 1. Introduction YOLOP (Your Octothorpean Language for Optical Processing) is an image manipulation language
Warm Up. Factor the following numbers and expressions. Multiply the following factors using either FOIL or Box Method
 Warm Up Factor the following numbers and expressions 1. 36 2. 36x 3 + 48x 2 + 24x Multiply the following factors using either FOIL or Box Method 3. (3x 2)(x 1) 4. (x 2)(x + 3) Objectives Recognize standard
Warm Up Factor the following numbers and expressions 1. 36 2. 36x 3 + 48x 2 + 24x Multiply the following factors using either FOIL or Box Method 3. (3x 2)(x 1) 4. (x 2)(x + 3) Objectives Recognize standard
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Princes Nora bint Abdul Rahman University College of Computer Since and Information System CS240 BRANCHING STATEMENTS
 Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Princes Nora bint Abdul Rahman University College of Computer Since and Information System CS240 BRANCHING STATEMENTS Objectives By the end of this section you should be able to:
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Princes Nora bint Abdul Rahman University College of Computer Since and Information System CS240 BRANCHING STATEMENTS Objectives By the end of this section you should be able to:
Chapter 21: Introduction to C Programming Language
 Ref. Page Slide 1/65 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Features of C Various constructs and their syntax Data types and operators in C Control and Loop Structures in C Functions
Ref. Page Slide 1/65 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Features of C Various constructs and their syntax Data types and operators in C Control and Loop Structures in C Functions
COMP 208 Computers in Engineering
 COMP 208 Computers in Engineering Lecture 14 Jun Wang School of Computer Science McGill University Fall 2007 COMP 208 - Lecture 14 1 Review: basics of C C is case sensitive 2 types of comments: /* */,
COMP 208 Computers in Engineering Lecture 14 Jun Wang School of Computer Science McGill University Fall 2007 COMP 208 - Lecture 14 1 Review: basics of C C is case sensitive 2 types of comments: /* */,
IT 374 C# and Applications/ IT695 C# Data Structures
 IT 374 C# and Applications/ IT695 C# Data Structures Module 2.1: Introduction to C# App Programming Xianrong (Shawn) Zheng Spring 2017 1 Outline Introduction Creating a Simple App String Interpolation
IT 374 C# and Applications/ IT695 C# Data Structures Module 2.1: Introduction to C# App Programming Xianrong (Shawn) Zheng Spring 2017 1 Outline Introduction Creating a Simple App String Interpolation
Chapter 3. More Flow of Control. Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Chapter 3 More Flow of Control Overview 3.1 Using Boolean Expressions 3.2 Multiway Branches 3.3 More about C++ Loop Statements 3.4 Designing Loops Slide 3-3 Flow Of Control Flow of control refers to the
Chapter 3 More Flow of Control Overview 3.1 Using Boolean Expressions 3.2 Multiway Branches 3.3 More about C++ Loop Statements 3.4 Designing Loops Slide 3-3 Flow Of Control Flow of control refers to the
Oct Decision Structures cont d
 Oct. 29 - Decision Structures cont d Programming Style and the if Statement Even though an if statement usually spans more than one line, it is really one statement. For instance, the following if statements
Oct. 29 - Decision Structures cont d Programming Style and the if Statement Even though an if statement usually spans more than one line, it is really one statement. For instance, the following if statements
1 Lexical Considerations
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Spring 2013 Handout Decaf Language Thursday, Feb 7 The project for the course is to write a compiler
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Spring 2013 Handout Decaf Language Thursday, Feb 7 The project for the course is to write a compiler
Example: Which of the following expressions must be an even integer if x is an integer? a. x + 5
 8th Grade Honors Basic Operations Part 1 1 NUMBER DEFINITIONS UNDEFINED On the ACT, when something is divided by zero, it is considered undefined. For example, the expression a bc is undefined if either
8th Grade Honors Basic Operations Part 1 1 NUMBER DEFINITIONS UNDEFINED On the ACT, when something is divided by zero, it is considered undefined. For example, the expression a bc is undefined if either
CHAPTER 9 FLOW OF CONTROL
 CHAPTER 9 FLOW OF CONTROL FLOW CONTROL In a program statement may be executed sequentially, selectively or iteratively. Every program language provides constructs to support sequence, selection or iteration.
CHAPTER 9 FLOW OF CONTROL FLOW CONTROL In a program statement may be executed sequentially, selectively or iteratively. Every program language provides constructs to support sequence, selection or iteration.
Chapter 4: Making Decisions
 Chapter 4: Making Decisions 4.1 Relational Operators Relational Operators Used to compare numbers to determine relative order Operators: > Greater than < Less than >= Greater than or equal to
Chapter 4: Making Decisions 4.1 Relational Operators Relational Operators Used to compare numbers to determine relative order Operators: > Greater than < Less than >= Greater than or equal to
Course Outline. Introduction to java
 Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
In Java, data type boolean is used to represent Boolean data. Each boolean constant or variable can contain one of two values: true or false.
 CS101, Mock Boolean Conditions, If-Then Boolean Expressions and Conditions The physical order of a program is the order in which the statements are listed. The logical order of a program is the order in
CS101, Mock Boolean Conditions, If-Then Boolean Expressions and Conditions The physical order of a program is the order in which the statements are listed. The logical order of a program is the order in
Put the following equations to slope-intercept form then use 2 points to graph
 Tuesday September 23, 2014 Warm-up: Put the following equations to slope-intercept form then use 2 points to graph 1. 4x - 3y = 8 8 x 6y = 16 2. 2x + y = 4 2x + y = 1 Tuesday September 23, 2014 Warm-up:
Tuesday September 23, 2014 Warm-up: Put the following equations to slope-intercept form then use 2 points to graph 1. 4x - 3y = 8 8 x 6y = 16 2. 2x + y = 4 2x + y = 1 Tuesday September 23, 2014 Warm-up:
Math 202 Test Problem Solving, Sets, and Whole Numbers 19 September, 2008
 Math 202 Test Problem Solving, Sets, and Whole Numbers 19 September, 2008 Ten questions, each worth the same amount. Complete six of your choice. I will only grade the first six I see. Make sure your name
Math 202 Test Problem Solving, Sets, and Whole Numbers 19 September, 2008 Ten questions, each worth the same amount. Complete six of your choice. I will only grade the first six I see. Make sure your name
Chapter 4: Making Decisions
 Chapter 4: Making Decisions CSE 142 - Computer Programming I 1 4.1 Relational Operators Relational Operators Used to compare numbers to determine relative order Operators: > Greater than < Less than >=
Chapter 4: Making Decisions CSE 142 - Computer Programming I 1 4.1 Relational Operators Relational Operators Used to compare numbers to determine relative order Operators: > Greater than < Less than >=
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
V2 2/4/ Ch Programming in C. Flow of Control. Flow of Control. Flow of control The order in which statements are executed
 Programming in C 1 Flow of Control Flow of control The order in which statements are executed Transfer of control When the next statement executed is not the next one in sequence 2 Flow of Control Control
Programming in C 1 Flow of Control Flow of control The order in which statements are executed Transfer of control When the next statement executed is not the next one in sequence 2 Flow of Control Control
View a Students Schedule Through Student Services Trigger:
 Department Responsibility/Role File Name Version Document Generation Date 6/10/2007 Date Modified 6/10/2007 Last Changed by Status View a Students Schedule Through Student Services_BUSPROC View a Students
Department Responsibility/Role File Name Version Document Generation Date 6/10/2007 Date Modified 6/10/2007 Last Changed by Status View a Students Schedule Through Student Services_BUSPROC View a Students
Chapter 7. Additional Control Structures
 Chapter 7 Additional Control Structures 1 Chapter 7 Topics Switch Statement for Multi-Way Branching Do-While Statement for Looping For Statement for Looping Using break and continue Statements 2 Chapter
Chapter 7 Additional Control Structures 1 Chapter 7 Topics Switch Statement for Multi-Way Branching Do-While Statement for Looping For Statement for Looping Using break and continue Statements 2 Chapter
Flow of Control. Flow of control The order in which statements are executed. Transfer of control
 1 Programming in C Flow of Control Flow of control The order in which statements are executed Transfer of control When the next statement executed is not the next one in sequence 2 Flow of Control Control
1 Programming in C Flow of Control Flow of control The order in which statements are executed Transfer of control When the next statement executed is not the next one in sequence 2 Flow of Control Control
Chapter 4: Making Decisions
 Chapter 4: Making Decisions Understanding Logic-Planning Tools and Pseudocode Decision Making A tool that helps programmers plan a program s logic by writing plain English statements Flowchart You write
Chapter 4: Making Decisions Understanding Logic-Planning Tools and Pseudocode Decision Making A tool that helps programmers plan a program s logic by writing plain English statements Flowchart You write
CS349/SE382 A1 C Programming Tutorial
 CS349/SE382 A1 C Programming Tutorial Erin Lester January 2005 Outline Comments Variable Declarations Objects Dynamic Memory Boolean Type structs, enums and unions Other Differences The Event Loop Comments
CS349/SE382 A1 C Programming Tutorial Erin Lester January 2005 Outline Comments Variable Declarations Objects Dynamic Memory Boolean Type structs, enums and unions Other Differences The Event Loop Comments
Objectives. Describe ways to create constants const readonly enum
 Constants Objectives Describe ways to create constants const readonly enum 2 Motivation Idea of constant is useful makes programs more readable allows more compile time error checking 3 Const Keyword const
Constants Objectives Describe ways to create constants const readonly enum 2 Motivation Idea of constant is useful makes programs more readable allows more compile time error checking 3 Const Keyword const
Lecture Programming in C++ PART 1. By Assistant Professor Dr. Ali Kattan
 Lecture 08-1 Programming in C++ PART 1 By Assistant Professor Dr. Ali Kattan 1 The Conditional Operator The conditional operator is similar to the if..else statement but has a shorter format. This is useful
Lecture 08-1 Programming in C++ PART 1 By Assistant Professor Dr. Ali Kattan 1 The Conditional Operator The conditional operator is similar to the if..else statement but has a shorter format. This is useful
Structures and Pointers
 Structures and Pointers Comp-206 : Introduction to Software Systems Lecture 11 Alexandre Denault Computer Science McGill University Fall 2006 Note on Assignment 1 Please note that handin does not allow
Structures and Pointers Comp-206 : Introduction to Software Systems Lecture 11 Alexandre Denault Computer Science McGill University Fall 2006 Note on Assignment 1 Please note that handin does not allow
3/12/2018. Structures. Programming in C++ Sequential Branching Repeating. Loops (Repetition)
 Structures Programming in C++ Sequential Branching Repeating Loops (Repetition) 2 1 Loops Repetition is referred to the ability of repeating a statement or a set of statements as many times this is necessary.
Structures Programming in C++ Sequential Branching Repeating Loops (Repetition) 2 1 Loops Repetition is referred to the ability of repeating a statement or a set of statements as many times this is necessary.
Section 1.1. Inductive Reasoning. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 1.1 Inductive Reasoning What You Will Learn Inductive and deductive reasoning processes 1.1-2 Natural Numbers The set of natural numbers is also called the set of counting numbers. N = {1, 2, 3,
Section 1.1 Inductive Reasoning What You Will Learn Inductive and deductive reasoning processes 1.1-2 Natural Numbers The set of natural numbers is also called the set of counting numbers. N = {1, 2, 3,
Software Design & Programming I
 Software Design & Programming I Starting Out with C++ (From Control Structures through Objects) 7th Edition Written by: Tony Gaddis Pearson - Addison Wesley ISBN: 13-978-0-132-57625-3 Chapter 4 Making
Software Design & Programming I Starting Out with C++ (From Control Structures through Objects) 7th Edition Written by: Tony Gaddis Pearson - Addison Wesley ISBN: 13-978-0-132-57625-3 Chapter 4 Making
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College October 24, 2018 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 8: A C++ Introduction For Python Programmers Expressions and Operator Precedence
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College October 24, 2018 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 8: A C++ Introduction For Python Programmers Expressions and Operator Precedence
! A set is a collection of objects of the same. ! {6,9,11,-5} and {11,9,6,-5} are equivalent. ! There is no first element, and no successor. of 9.
 Sets & Hash Tables Week 13 Weiss: chapter 20 CS 5301 Fall 2015 What are sets?! A set is a collection of objects of the same type that has the following two properties: - there are no duplicates in the
Sets & Hash Tables Week 13 Weiss: chapter 20 CS 5301 Fall 2015 What are sets?! A set is a collection of objects of the same type that has the following two properties: - there are no duplicates in the
Lexical Considerations
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Spring 2010 Handout Decaf Language Tuesday, Feb 2 The project for the course is to write a compiler
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Spring 2010 Handout Decaf Language Tuesday, Feb 2 The project for the course is to write a compiler
9/23/2013. Chapter 2. Objectives. Introduction. Objectives (continued) Representing Algorithms. Representing Algorithms
 Chapter 2 The Algorithmic Foundations of Computer Science Objectives After studying this chapter, students will be able to: Explain the benefits of pseudocode over natural language or a programming language
Chapter 2 The Algorithmic Foundations of Computer Science Objectives After studying this chapter, students will be able to: Explain the benefits of pseudocode over natural language or a programming language
CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall Office hours:
 CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall alphonce@buffalo.edu Office hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM 12:00 PM * Wednesday 4:00 PM 5:00 PM Friday 11:00 AM 12:00 PM OR
CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall alphonce@buffalo.edu Office hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM 12:00 PM * Wednesday 4:00 PM 5:00 PM Friday 11:00 AM 12:00 PM OR
Topic 5: Enumerated Types and Switch Statements
 Topic 5: Enumerated Types and Switch Statements Reading: JBD Sections 6.1, 6.2, 3.9 1 What's wrong with this code? if (pressure > 85.0) excesspressure = pressure - 85.0; else safetymargin = 85.0 - pressure;!
Topic 5: Enumerated Types and Switch Statements Reading: JBD Sections 6.1, 6.2, 3.9 1 What's wrong with this code? if (pressure > 85.0) excesspressure = pressure - 85.0; else safetymargin = 85.0 - pressure;!
Armstrong State University Engineering Studies MATLAB Marina Switch-Case Statements Primer
 Armstrong State University Engineering Studies MATLAB Marina Switch-Case Statements Primer Prerequisites The Switch-Case Statements Primer assumes knowledge of the MATLAB IDE, MATLAB help, arithmetic operations,
Armstrong State University Engineering Studies MATLAB Marina Switch-Case Statements Primer Prerequisites The Switch-Case Statements Primer assumes knowledge of the MATLAB IDE, MATLAB help, arithmetic operations,
Chapter 4: Making Decisions. Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Sunday, September 7, 14
 Chapter 4: Making Decisions 4.1 Relational Operators Relational Operators Used to compare numbers to determine relative order Operators: > Greater than < Less than >= Greater than or equal to
Chapter 4: Making Decisions 4.1 Relational Operators Relational Operators Used to compare numbers to determine relative order Operators: > Greater than < Less than >= Greater than or equal to
Introduction to OOP with Java. Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017
 Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 03: Control Flow Statements: Selection Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor
Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 03: Control Flow Statements: Selection Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor
Introduction to C# Applications
 1 2 3 Introduction to C# Applications OBJECTIVES To write simple C# applications To write statements that input and output data to the screen. To declare and use data of various types. To write decision-making
1 2 3 Introduction to C# Applications OBJECTIVES To write simple C# applications To write statements that input and output data to the screen. To declare and use data of various types. To write decision-making
Lecture 8. Daily Puzzle
 Lecture 8 if and switch Statements Daily Puzzle If a bottle, partly filled with liquid, has a round, square or rectangular bottom which is flat, can you find its volume using only a ruler? You may not
Lecture 8 if and switch Statements Daily Puzzle If a bottle, partly filled with liquid, has a round, square or rectangular bottom which is flat, can you find its volume using only a ruler? You may not
BITG 1223: Selection Control Structure by: ZARITA (FTMK) LECTURE 4 (Sem 1, 16/17)
 BITG 1223: Selection Control Structure by: ZARITA (FTMK) LECTURE 4 (Sem 1, 16/17) 1 Learning Outcomes At the end of this lecture, you should be able to: 1. Explain the concept of selection control structure
BITG 1223: Selection Control Structure by: ZARITA (FTMK) LECTURE 4 (Sem 1, 16/17) 1 Learning Outcomes At the end of this lecture, you should be able to: 1. Explain the concept of selection control structure
Agenda: Discussion Week 7. May 11, 2009
 Agenda: Discussion Week 7 Method signatures Static vs. instance compareto Exceptions Interfaces 2 D arrays Recursion varargs enum Suggestions? May 11, 2009 Method signatures [protection] [static] [return
Agenda: Discussion Week 7 Method signatures Static vs. instance compareto Exceptions Interfaces 2 D arrays Recursion varargs enum Suggestions? May 11, 2009 Method signatures [protection] [static] [return
If Control Construct
 If Control Construct A mechanism for deciding whether an action should be taken JPC and JWD 2002 McGraw-Hill, Inc. 1 Boolean Algebra Logical expressions have the one of two values - true or false A rectangle
If Control Construct A mechanism for deciding whether an action should be taken JPC and JWD 2002 McGraw-Hill, Inc. 1 Boolean Algebra Logical expressions have the one of two values - true or false A rectangle
DECISION MAKING STATEMENTS
 DECISION MAKING STATEMENTS If, else if, switch case These statements allow the execution of selective statements based on certain decision criteria. C language provides the following statements: if statement
DECISION MAKING STATEMENTS If, else if, switch case These statements allow the execution of selective statements based on certain decision criteria. C language provides the following statements: if statement
All copyrights reserved - KV NAD, Aluva. Dinesh Kumar Ram PGT(CS) KV NAD Aluva
 All copyrights reserved - KV NAD, Aluva Dinesh Kumar Ram PGT(CS) KV NAD Aluva Overview Looping Introduction While loops Syntax Examples Points to Observe Infinite Loops Examples using while loops do..
All copyrights reserved - KV NAD, Aluva Dinesh Kumar Ram PGT(CS) KV NAD Aluva Overview Looping Introduction While loops Syntax Examples Points to Observe Infinite Loops Examples using while loops do..
Computer Programming : C++
 The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2003 Muath i.alnabris Computer Programming : C++ Experiment #1 Basics Contents Structure of a program
The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2003 Muath i.alnabris Computer Programming : C++ Experiment #1 Basics Contents Structure of a program
Relational & Logical Operators, if and switch Statements
 1 Relational & Logical Operators, if and switch Statements Topics Relational Operators and Expressions The if Statement The if- Statement Nesting of if- Statements switch Logical Operators and Expressions
1 Relational & Logical Operators, if and switch Statements Topics Relational Operators and Expressions The if Statement The if- Statement Nesting of if- Statements switch Logical Operators and Expressions
Operators. Java operators are classified into three categories:
 Operators Operators are symbols that perform arithmetic and logical operations on operands and provide a meaningful result. Operands are data values (variables or constants) which are involved in operations.
Operators Operators are symbols that perform arithmetic and logical operations on operands and provide a meaningful result. Operands are data values (variables or constants) which are involved in operations.
ALGORITHMS AND FLOWCHARTS
 ALGORITHMS AND FLOWCHARTS ALGORITHMS AND FLOWCHARTS A typical programming task can be divided into two phases: Problem solving phase produce an ordered sequence of steps that describe solution of problem
ALGORITHMS AND FLOWCHARTS ALGORITHMS AND FLOWCHARTS A typical programming task can be divided into two phases: Problem solving phase produce an ordered sequence of steps that describe solution of problem
The Further Mathematics Support Programme
 The Further Mathematics Support Programme Algorithms An algorithm is a precise set of instructions which is used to accomplish a specific process. We come across algorithms in every-day life, for example:
The Further Mathematics Support Programme Algorithms An algorithm is a precise set of instructions which is used to accomplish a specific process. We come across algorithms in every-day life, for example:
CHAPTER 4 CONTROL STRUCTURES
 CHAPTER 4 CONTROL STRUCTURES 1 Control Structures A program is usually not limited to a linear sequence of instructions. During its process it may deviate, repeat code or take decisions. For that purpose,
CHAPTER 4 CONTROL STRUCTURES 1 Control Structures A program is usually not limited to a linear sequence of instructions. During its process it may deviate, repeat code or take decisions. For that purpose,
Algorithm Discovery and Design
 Algorithm Discovery and Design Chapter 2 The Algorithmic Foundations of Computer Science Algorithms Algorithm Step-by-step method for accomplishing some task Operations used to construct algorithms Sequential,
Algorithm Discovery and Design Chapter 2 The Algorithmic Foundations of Computer Science Algorithms Algorithm Step-by-step method for accomplishing some task Operations used to construct algorithms Sequential,
x = 3 * y + 1; // x becomes 3 * y + 1 a = b = 0; // multiple assignment: a and b both get the value 0
 6 Statements 43 6 Statements The statements of C# do not differ very much from those of other programming languages. In addition to assignments and method calls there are various sorts of selections and
6 Statements 43 6 Statements The statements of C# do not differ very much from those of other programming languages. In addition to assignments and method calls there are various sorts of selections and
CSc Introduction to Computing
 CSc 10200 Introduction to Computing Lecture 2 Edgardo Molina Fall 2011 - City College of New York Thursday, September 1, 2011 Introduction to C++ Modular program: A program consisting of interrelated segments
CSc 10200 Introduction to Computing Lecture 2 Edgardo Molina Fall 2011 - City College of New York Thursday, September 1, 2011 Introduction to C++ Modular program: A program consisting of interrelated segments
Task 1: Print a series of random integers between 0 and 99 until the value 77 is printed. Use the Random class to generate random numbers.
 Task 1: Print a series of random integers between 0 and 99 until the value 77 is printed. Use the Random class to generate random numbers. Task 2: Print a series of random integers between 50 and 99 until
Task 1: Print a series of random integers between 0 and 99 until the value 77 is printed. Use the Random class to generate random numbers. Task 2: Print a series of random integers between 50 and 99 until
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
The following expression causes a divide by zero error:
 Chapter 2 - Test Questions These test questions are true-false, fill in the blank, multiple choice, and free form questions that may require code. The multiple choice questions may have more than one correct
Chapter 2 - Test Questions These test questions are true-false, fill in the blank, multiple choice, and free form questions that may require code. The multiple choice questions may have more than one correct
