Spring 2013 Homework Assignment #3. Due: 8 November 2012, 11:00pm Covers Chapters: 11, 13.
|
|
|
- Corey Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSE 11 Spring 2013 Homework Assignment #3 START EARLY! Due: 8 November 2012, 11:00pm Covers Chapters: 11, 13. You will turn in your assignment electronically Include code means turn in a printed copy of your code. Include output means turn in screen grab of the output of your code. You will turn in several files for this assignment: PR5.txt PR5.pdf Integrate.java MultTable.java Bundle your homework with the program $ /home/linux/ieng6/cs11e/public/bin/bundlep5 For your screen output, create a file called PR5.pdf. It should be portable document format file (See instructions for homework 3, Please make sure to include your NAME: LOGIN: ID: in every file you turn in. PR5.txt should have just that information in it. Problem #1 (20 points) Using the standard Java Scanner class. Look at as an example of using the Scanner class and opening a file for reading. Modify the TextApplet example on page 296 in your book to do the following: 1. Change the applet to a program using the usual technique. 2. The text input box should be relabeled Filename 3. When you type a valid filename into the box and hit enter on your keyboard, your program should read the file indicated and display its contents in the JTextArea (scrollable text area next to Output ) using Scanner. 4. If the file is not found (this is what is called throwing an exception ), the JTextArea should clear the contents and display File Not Found!. This clear and display logic would replace the e.printstacktrace() in the blogspot example. Exceptions have not yet been covered in class, you should simply mimic the try except logic of the blogspot example. 5. Pressing the Clear Output button should clear the JTextArea.
2 Include code Include screen output when what is displayed is the java source code that answers this problem (i.e. your program) Include screen output when a File is not Found! Problem #2 (10 points) Modify your code from Problem #1 to (It is highly suggested to make it a different Program) 1. Add an additional button labeled Count placed next to the clear output button 2. Add an additional JLabel That will display the number of characters of the text that is currently displayed in the JTextArea. This label should be updated when the Count button is pressed by the user. You should use a panel with a FlowLayout for the buttons and label. Include code Include screen output when what is displayed is the java source code that answers this problem (i.e. your program). Your screenshot should be taken after the Count button has been pressed Problem #3 (10 points) JAEA Exercise Modify so that the corrected isprime method is invoked as part of main program called Prime. Prime takes an integer argument from the command line and properly determines if a number is prime. Include code Include output of running Prime with input values of 17, 27, 37, 47, 57, 81 Problem #4 (10 points) Fun with for loops In each of the following, create a valid for( ; ; ) statement to achieve the desired results of the following two-line code segment: for ( ; ; ) System.out.println(i); example: print out integers from 1 to 10 ans: for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) (a) print out integers from 10 to 1 (b) print out 2 k k=0,1,2,3, (c) print out every seventh integer starting at 14 ending at 98 (d) print out the numbers from 1 to 41 that are NOT evenly divisible by 3 (e) print out the numbers 1,3,6,10,15,21,28,36,45,55 (Hint: int j = i = 1; is a legal statement that initializes both i and j to 1) Problem #5 (20 points) Trapezoidal Integration (calculating the area under a curve) In basic calculus, definite integration computes the area under the curve of a function, f(x), when
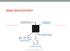
3 graphed on the interval of A,B. One way of numerically computing the definite integral is to sum the area of all trapezoids defined in a particular way. The following picture shows the area of just one of these trapezoids (if you have had calculus, this should look familiar to you). Illustration 1: Area of ONE trapezoid under the curve of a function. The integral sums from 0 to B sums all Trapezoidal areas when f is evaluated a 0,dx,2dx,3dx,...B If A(x) is defined as the trapezoidal area of A(x) = 1/2 (f(x) + f(x + dx)) * dx then the integral from 0 to B is A(0) + A(dx) + A(2*dx) + A(3*dx) A(B dx) As dx becomes smaller this numerical estimate becomes better at computing the actual integral. Write a Function class that provides a static double method called eval(double x) that returns returns the value of the Function evaluated at x (E.g. Function(x)) Write a java program called Integrate that takes two command-line arguments B and ntrapezoid. B is a double the represents the right hand side of the integral, ntrapezoid is an integer that is the number of trapezoids to compute on the interval [0,B]. It should compute the integral of function defined in the class Function It should print out just the computed integral as a double. The basic idea is that one can redefine the function in the Function class and integrate will perform the definite integral over that function Use your program and class to compute the integrals of f(x) = x 2 + 3, B = 1,nTrapezoid = 1 f(x) = x 2 + 3, B = 1,nTrapezoid = 10 f(x) = x 2 + 3, B = 1,nTrapezoid = 100 f(x) = -x 2 + x, B = 1,nTrapezoid = 1 f(x) = -x 2 + x, B = 1,nTrapezoid = 10 f(x) = -x 2 + x, B = 1,nTrapezoid = 100
4 Turnin: Integrate.java Problem #6 (10 points) (a) what is the fundamental difference between do... while(); and a while() loops? (b) JAEA Exercise (c) Look up the definition of the break; statement. What does the following code print out? (attempt this without compiling the code!) int n = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) System.out.print( i + : ); for (int j = 1 ; j <= 5 ; j++) n++; if (j * i >= 15) break; System.out.print(j * i + ); System.out.println( ); System.out.println( Iterations: + n); (d) Look up the definition of the continue; statement. What does the following code print out? (attempt this without compiling the code!) int n = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) System.out.print( i + : ); for (int j = 1 ; j <= 5 ; j++) n++; if (j * i >= 15) continue; System.out.print(j * i + ); System.out.println( ); System.out.println( Iterations: + n); (e) What is different about the two outputs? Explain why one line of code results in very similar but not identical output? Put your answer in your PR5.pdf file. Problem #7 (20 points) Times table with graphical interface.
5 Java has a function called printf() and format() that enables one to have finer control over print formatting that println(). printf() is a used across C, Java, C++, Python and other languages. Printf has the concept of a format string with replaceable parameters. In this exercise you will use the %d format descriptor to print integers in fixed-width field. The String class defines the format() method that behaves nearly identically to printf(). For example int = 10 String S =.format( % 4d,i); will create a String S that has integer i printed in using exactly 4 spaces and is right justified. E.g, 10 Create a program call MultTable that uses JSliders, JTextArea, and JLabel to create a multiplication table that is NxM where N and M are controlled by two different sliders, that range independently from You should not extend WindowController, you should use native JFrames (you could start with HelloWordSwing.java). A JLabel should print out the current value of each slider. The following screen shots show the various configurations that you should be able to support. Illustration 2: Initial Configuration Illustration 3: Sliders when both are at 1
6 Illustration 4: When Sliders are at 7 (columns) and 5 (rows). Notice that the right slider controls number of rows, the bottom the number of columns Hints: The JTextArea in the above uses a fixed-width font. If output is a JTextArea the following will set the font to be fixed-width output.setfont(new Font(Font.MONOSPACED, Font.PLAIN, 12)); To define a ChangeListener, you will need to import javax.swing.event.*. BorderLayout() is probably the simplest layout to use to place sliders, jtextarea, and jlabels. Look up the seteditable() method for JTextArea to insure that you cannot edit the multiplication table You will turn in MultTable.java
Points Missed on Page page 1 of 8
 Midterm II - CSE11 Fall 2013 CLOSED BOOK, CLOSED NOTES 50 minutes, 100 points Total. Name: ID: Problem #1 (8 points) Rewrite the following code segment using a for loop instead of a while loop (that is
Midterm II - CSE11 Fall 2013 CLOSED BOOK, CLOSED NOTES 50 minutes, 100 points Total. Name: ID: Problem #1 (8 points) Rewrite the following code segment using a for loop instead of a while loop (that is
Fall 2013 Program/Homework Assignment #2 (100 points) -(Corrected Version)
 CSE 11 START EARLY! Fall 2013 Program/Homework Assignment #2 (100 points) -(Corrected Version) Due: 11 October 2013 at 11pm (2300) Book Exercises Cover Chapters: 3-4 This is a combination of written responses
CSE 11 START EARLY! Fall 2013 Program/Homework Assignment #2 (100 points) -(Corrected Version) Due: 11 October 2013 at 11pm (2300) Book Exercises Cover Chapters: 3-4 This is a combination of written responses
Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler are denoted using a. Two
Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler are denoted using a. Two
Nested Loops ***** ***** ***** ***** ***** We know we can print out one line of this square as follows: System.out.
 Nested Loops To investigate nested loops, we'll look at printing out some different star patterns. Let s consider that we want to print out a square as follows: We know we can print out one line of this
Nested Loops To investigate nested loops, we'll look at printing out some different star patterns. Let s consider that we want to print out a square as follows: We know we can print out one line of this
Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal
 Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition structures in Java, their syntax, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when
Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition structures in Java, their syntax, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when
Task 1: Print a series of random integers between 0 and 99 until the value 77 is printed. Use the Random class to generate random numbers.
 Task 1: Print a series of random integers between 0 and 99 until the value 77 is printed. Use the Random class to generate random numbers. Task 2: Print a series of random integers between 50 and 99 until
Task 1: Print a series of random integers between 0 and 99 until the value 77 is printed. Use the Random class to generate random numbers. Task 2: Print a series of random integers between 50 and 99 until
Assignment 17 Deadline: Oct pm COSC211 CRN15376 Session 14 (Oct. 29)
 This in-class assignment has 2 points in total. Every bug costs 0.1-0.3 based on its severity. The deadline for this assignment is Tuesday, Oct. 30, NOON, 12 pm. In addition to the 2 points, we have an
This in-class assignment has 2 points in total. Every bug costs 0.1-0.3 based on its severity. The deadline for this assignment is Tuesday, Oct. 30, NOON, 12 pm. In addition to the 2 points, we have an
Midterm I - CSE11 Fall 2013 CLOSED BOOK, CLOSED NOTES 50 minutes, 100 points Total.
 Midterm I - CSE11 Fall 2013 CLOSED BOOK, CLOSED NOTES 50 minutes, 100 points Total. Name: ID: Problem 1) (8 points) For the following code segment, what are the values of i, j, k, and d, after the segment
Midterm I - CSE11 Fall 2013 CLOSED BOOK, CLOSED NOTES 50 minutes, 100 points Total. Name: ID: Problem 1) (8 points) For the following code segment, what are the values of i, j, k, and d, after the segment
Assignment 2.4: Loops
 Writing Programs that Use the Terminal 0. Writing to the Terminal Assignment 2.4: Loops In this project, we will be sending our answers to the terminal for the user to see. To write numbers and text to
Writing Programs that Use the Terminal 0. Writing to the Terminal Assignment 2.4: Loops In this project, we will be sending our answers to the terminal for the user to see. To write numbers and text to
Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler are denoted using a. Two
Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler are denoted using a. Two
Full file at
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.1 Introduction ( none ) Section 2.2 First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler
Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.1 Introduction ( none ) Section 2.2 First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler
Chapter 4 Introduction to Control Statements
 Introduction to Control Statements Fundamentals of Java: AP Computer Science Essentials, 4th Edition 1 Objectives 2 How do you use the increment and decrement operators? What are the standard math methods?
Introduction to Control Statements Fundamentals of Java: AP Computer Science Essentials, 4th Edition 1 Objectives 2 How do you use the increment and decrement operators? What are the standard math methods?
Lecture 14 CSE11 Fall 2013 For loops, Do While, Break, Continue
 Lecture 14 CSE11 Fall 2013 For loops, Do While, Break, Continue General Loops in Java Look at other loop constructions Very common while loop: do a loop a fixed number of times (MAX in the example) int
Lecture 14 CSE11 Fall 2013 For loops, Do While, Break, Continue General Loops in Java Look at other loop constructions Very common while loop: do a loop a fixed number of times (MAX in the example) int
Part I: Learn Common Graphics Components
 OOP GUI Components and Event Handling Page 1 Objectives 1. Practice creating and using graphical components. 2. Practice adding Event Listeners to handle the events and do something. 3. Learn how to connect
OOP GUI Components and Event Handling Page 1 Objectives 1. Practice creating and using graphical components. 2. Practice adding Event Listeners to handle the events and do something. 3. Learn how to connect
Course Outline. Introduction to java
 Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
CS Fall Homework 5 p. 1. CS Homework 5
 CS 235 - Fall 2015 - Homework 5 p. 1 Deadline: CS 235 - Homework 5 Due by 11:59 pm on Wednesday, September 30, 2015. How to submit: Submit your files using ~st10/235submit on nrs-projects, with a homework
CS 235 - Fall 2015 - Homework 5 p. 1 Deadline: CS 235 - Homework 5 Due by 11:59 pm on Wednesday, September 30, 2015. How to submit: Submit your files using ~st10/235submit on nrs-projects, with a homework
Exercises C-Programming
 Exercises C-Programming Claude Fuhrer (claude.fuhrer@bfh.ch) 0 November 016 Contents 1 Serie 1 1 Min function.................................. Triangle surface 1............................... 3 Triangle
Exercises C-Programming Claude Fuhrer (claude.fuhrer@bfh.ch) 0 November 016 Contents 1 Serie 1 1 Min function.................................. Triangle surface 1............................... 3 Triangle
Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements
 Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
Jump Statements. The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls.
 Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
ENCM 339 Fall 2017 Lecture Section 01 Lab 9 for the Week of November 20
 page 1 of 9 ENCM 339 Fall 2017 Lecture Section 01 Lab 9 for the Week of November 20 Steve Norman Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Calgary November 2017 Lab instructions and
page 1 of 9 ENCM 339 Fall 2017 Lecture Section 01 Lab 9 for the Week of November 20 Steve Norman Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Calgary November 2017 Lab instructions and
Programming Assignment 2 ( 100 Points )
 Programming Assignment 2 ( 100 Points ) Due: Thursday, October 16 by 11:59pm This assignment has two programs: one a Java application that reads user input from the command line (TwoLargest) and one a
Programming Assignment 2 ( 100 Points ) Due: Thursday, October 16 by 11:59pm This assignment has two programs: one a Java application that reads user input from the command line (TwoLargest) and one a
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
This page intentionally left blank
 This page intentionally left blank arting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects International Edition - PDF - PDF - PDF Cover Contents Preface Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers and Java
This page intentionally left blank arting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects International Edition - PDF - PDF - PDF Cover Contents Preface Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers and Java
AP Computer Science Unit 3. Programs
 AP Computer Science Unit 3. Programs For most of these programs I m asking that you to limit what you print to the screen. This will help me in quickly running some tests on your code once you submit them
AP Computer Science Unit 3. Programs For most of these programs I m asking that you to limit what you print to the screen. This will help me in quickly running some tests on your code once you submit them
Topic 9: Swing. Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more
 Swing = Java's GUI library Topic 9: Swing Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more Assignment 5: Will be an open-ended Swing project. "Programming Contest"
Swing = Java's GUI library Topic 9: Swing Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more Assignment 5: Will be an open-ended Swing project. "Programming Contest"
Topic 9: Swing. Why are we studying Swing? GUIs Up to now: line-by-line programs: computer displays text user types text. Outline. 1. Useful & fun!
 Swing = Java's GUI library Topic 9: Swing Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more Why are we studying Swing? 1. Useful & fun! 2. Good application of OOP techniques
Swing = Java's GUI library Topic 9: Swing Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more Why are we studying Swing? 1. Useful & fun! 2. Good application of OOP techniques
Math 250A (Fall 2009) - Lab I: Estimate Integrals Numerically with Matlab. Due Date: Monday, September 21, INSTRUCTIONS
 Math 250A (Fall 2009) - Lab I: Estimate Integrals Numerically with Matlab Due Date: Monday, September 21, 2009 4:30 PM 1. INSTRUCTIONS The primary purpose of this lab is to understand how go about numerically
Math 250A (Fall 2009) - Lab I: Estimate Integrals Numerically with Matlab Due Date: Monday, September 21, 2009 4:30 PM 1. INSTRUCTIONS The primary purpose of this lab is to understand how go about numerically
Comp Assignment 2: Object-Oriented Scanning for Numbers, Words, and Quoted Strings
 Comp 401 - Assignment 2: Object-Oriented Scanning for Numbers, Words, and Quoted Strings Date Assigned: Thu Aug 29, 2013 Completion Date: Fri Sep 6, 2013 Early Submission Date: Wed Sep 4, 2013 This work
Comp 401 - Assignment 2: Object-Oriented Scanning for Numbers, Words, and Quoted Strings Date Assigned: Thu Aug 29, 2013 Completion Date: Fri Sep 6, 2013 Early Submission Date: Wed Sep 4, 2013 This work
CONTENTS. Chapter 1 Getting Started with Java SE 6 1. Chapter 2 Exploring Variables, Data Types, Operators and Arrays 13
 CONTENTS Chapter 1 Getting Started with Java SE 6 1 Introduction of Java SE 6... 3 Desktop Improvements... 3 Core Improvements... 4 Getting and Installing Java... 5 A Simple Java Program... 10 Compiling
CONTENTS Chapter 1 Getting Started with Java SE 6 1 Introduction of Java SE 6... 3 Desktop Improvements... 3 Core Improvements... 4 Getting and Installing Java... 5 A Simple Java Program... 10 Compiling
Programming graphics
 Programming graphics Need a window javax.swing.jframe Several essential steps to use (necessary plumbing ): Set the size width and height in pixels Set a title (optional), and a close operation Make it
Programming graphics Need a window javax.swing.jframe Several essential steps to use (necessary plumbing ): Set the size width and height in pixels Set a title (optional), and a close operation Make it
Faculty of Science COMP-202A - Introduction to Computing I (Fall 2008) Midterm Examination
 First Name: Last Name: McGill ID: Section: Faculty of Science COMP-202A - Introduction to Computing I (Fall 2008) Midterm Examination Tuesday, November 4, 2008 Examiners: Mathieu Petitpas [Section 1] 18:30
First Name: Last Name: McGill ID: Section: Faculty of Science COMP-202A - Introduction to Computing I (Fall 2008) Midterm Examination Tuesday, November 4, 2008 Examiners: Mathieu Petitpas [Section 1] 18:30
Repetition, Looping CS101
 Repetition, Looping CS101 Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Repetition, Looping CS101 Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1
 Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1 Write a program which conducts a Monte Carlo simulation to estimate π. 1 See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/monte_carlo_method. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 133 / 149
Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1 Write a program which conducts a Monte Carlo simulation to estimate π. 1 See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/monte_carlo_method. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 133 / 149
Recitation 02/02/07 Defining Classes and Methods. Chapter 4
 Recitation 02/02/07 Defining Classes and Methods 1 Miscellany Project 2 due last night Exam 1 (Ch 1-4) Thursday, Feb. 8, 8:30-9:30pm PHYS 112 Sample Exam posted Project 3 due Feb. 15 10:00pm check newsgroup!
Recitation 02/02/07 Defining Classes and Methods 1 Miscellany Project 2 due last night Exam 1 (Ch 1-4) Thursday, Feb. 8, 8:30-9:30pm PHYS 112 Sample Exam posted Project 3 due Feb. 15 10:00pm check newsgroup!
BASIC INPUT/OUTPUT. Fundamentals of Computer Science
 BASIC INPUT/OUTPUT Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline: Basic Input/Output Screen Output Keyboard Input Simple Screen Output System.out.println("The count is " + count); Outputs the sting literal
BASIC INPUT/OUTPUT Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline: Basic Input/Output Screen Output Keyboard Input Simple Screen Output System.out.println("The count is " + count); Outputs the sting literal
CompSci 125 Lecture 11
 CompSci 125 Lecture 11 switch case The? conditional operator do while for Announcements hw5 Due 10/4 p2 Due 10/5 switch case! The switch case Statement Consider a simple four-function calculator 16 buttons:
CompSci 125 Lecture 11 switch case The? conditional operator do while for Announcements hw5 Due 10/4 p2 Due 10/5 switch case! The switch case Statement Consider a simple four-function calculator 16 buttons:
Java Programming Lecture 6
 Java Programming Lecture 6 Alice E. Fischer Feb 15, 2013 Java Programming - L6... 1/32 Dialog Boxes Class Derivation The First Swing Programs: Snow and Moving The Second Swing Program: Smile Swing Components
Java Programming Lecture 6 Alice E. Fischer Feb 15, 2013 Java Programming - L6... 1/32 Dialog Boxes Class Derivation The First Swing Programs: Snow and Moving The Second Swing Program: Smile Swing Components
Repetition, Looping. While Loop
 Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Lecture 9. Assignment. Logical Operations. Logical Operations - Motivation 2/8/18
 Assignment Lecture 9 Logical Operations Formatted Print Printf Increment and decrement Read through 3.9, 3.10 Read 4.1. 4.2, 4.3 Go through checkpoint exercise 4.1 Logical Operations - Motivation Logical
Assignment Lecture 9 Logical Operations Formatted Print Printf Increment and decrement Read through 3.9, 3.10 Read 4.1. 4.2, 4.3 Go through checkpoint exercise 4.1 Logical Operations - Motivation Logical
Lesson 2: First Java Programs
 Lesson 2: First Java Programs Lesson 2: First Java Programs Objectives: Discuss why Java is an important programming language. Explain the Java virtual machine and byte code. Choose a user interface style.
Lesson 2: First Java Programs Lesson 2: First Java Programs Objectives: Discuss why Java is an important programming language. Explain the Java virtual machine and byte code. Choose a user interface style.
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing. Objectives: Examples: Text-printing program. CSC 209 JAVA I
 AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 2- Arithmetic and Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators Objectives: To use arithmetic operators. The precedence of arithmetic
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 2- Arithmetic and Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators Objectives: To use arithmetic operators. The precedence of arithmetic
CSE Lab 8 Assignment Note: This is the last lab for CSE 1341
 CSE 1341 - Lab 8 Assignment Note: This is the last lab for CSE 1341 Pre-Lab : There is no pre-lab this week. Lab (100 points) The objective of Lab 8 is to get familiar with and utilize the wealth of Java
CSE 1341 - Lab 8 Assignment Note: This is the last lab for CSE 1341 Pre-Lab : There is no pre-lab this week. Lab (100 points) The objective of Lab 8 is to get familiar with and utilize the wealth of Java
Final Examination Semester 2 / Year 2011
 Southern College Kolej Selatan 南方学院 Final Examination Semester 2 / Year 2011 COURSE : FUNDAMENTALS OF SOFTWARE DESIGEN AND DEVELOPMENT COURSE CODE : PROG1003 TIME : 2 1/2 HOURS DEPARTMENT : COMPUTER SCIENCE
Southern College Kolej Selatan 南方学院 Final Examination Semester 2 / Year 2011 COURSE : FUNDAMENTALS OF SOFTWARE DESIGEN AND DEVELOPMENT COURSE CODE : PROG1003 TIME : 2 1/2 HOURS DEPARTMENT : COMPUTER SCIENCE
Jump Statements. The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls.
 Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Welcome to CIS 068! 1. GUIs: JAVA Swing 2. (Streams and Files we ll not cover this in this semester, just a review) CIS 068
 Welcome to! 1. GUIs: JAVA Swing 2. (Streams and Files we ll not cover this in this semester, just a review) Overview JAVA and GUIs: SWING Container, Components, Layouts Using SWING Streams and Files Text
Welcome to! 1. GUIs: JAVA Swing 2. (Streams and Files we ll not cover this in this semester, just a review) Overview JAVA and GUIs: SWING Container, Components, Layouts Using SWING Streams and Files Text
Chapter 2 First Java Programs
 First Java Programs Fundamentals of Java: AP Computer Science Essentials, 4th Edition 1 Objectives Why is Java an important programming language? What is the Java virtual machine and byte code? What are
First Java Programs Fundamentals of Java: AP Computer Science Essentials, 4th Edition 1 Objectives Why is Java an important programming language? What is the Java virtual machine and byte code? What are
CSE 1325 Project Description
 CSE 1325 Summer 2016 Object-Oriented and Event-driven Programming (Using Java) Instructor: Soumyava Das Graphical User Interface (GUI), Event Listeners and Handlers Project IV Assigned On: 07/28/2016 Due
CSE 1325 Summer 2016 Object-Oriented and Event-driven Programming (Using Java) Instructor: Soumyava Das Graphical User Interface (GUI), Event Listeners and Handlers Project IV Assigned On: 07/28/2016 Due
CS Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #1 - Prof. Reed Fall 2009
 CS 102 - Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #1 - Prof. Reed Fall 2009 What is your name?: There are two sections: I. True/False..................... 60 points; ( 30 questions, 2 points each) II.
CS 102 - Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #1 - Prof. Reed Fall 2009 What is your name?: There are two sections: I. True/False..................... 60 points; ( 30 questions, 2 points each) II.
CIS 1068 Program Design and Abstraction Spring2016 Midterm Exam 1. Name SOLUTION
 CIS 1068 Program Design and Abstraction Spring2016 Midterm Exam 1 Name SOLUTION Page Points Score 2 15 3 8 4 18 5 10 6 7 7 7 8 14 9 11 10 10 Total 100 1 P age 1. Program Traces (41 points, 50 minutes)
CIS 1068 Program Design and Abstraction Spring2016 Midterm Exam 1 Name SOLUTION Page Points Score 2 15 3 8 4 18 5 10 6 7 7 7 8 14 9 11 10 10 Total 100 1 P age 1. Program Traces (41 points, 50 minutes)
COMP 202 Java in one week
 COMP 202 Java in one week... Continued CONTENTS: Return to material from previous lecture At-home programming exercises Please Do Ask Questions It's perfectly normal not to understand everything Most of
COMP 202 Java in one week... Continued CONTENTS: Return to material from previous lecture At-home programming exercises Please Do Ask Questions It's perfectly normal not to understand everything Most of
Chapter 7. Iteration. 7.1 Multiple assignment
 Chapter 7 Iteration 7.1 Multiple assignment You can make more than one assignment to the same variable; effect is to replace the old value with the new. int bob = 5; System.out.print(bob); bob = 7; System.out.println(bob);
Chapter 7 Iteration 7.1 Multiple assignment You can make more than one assignment to the same variable; effect is to replace the old value with the new. int bob = 5; System.out.print(bob); bob = 7; System.out.println(bob);
Outline. Topic 9: Swing. GUIs Up to now: line-by-line programs: computer displays text user types text AWT. A. Basics
 Topic 9: Swing Outline Swing = Java's GUI library Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more Assignment 7: Expand moving shapes from Assignment 4 into game. "Programming
Topic 9: Swing Outline Swing = Java's GUI library Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more Assignment 7: Expand moving shapes from Assignment 4 into game. "Programming
Interpreted vs Compiled. Java Compile. Classes, Objects, and Methods. Hello World 10/6/2016. Python Interpreted. Java Compiled
 Interpreted vs Compiled Python 1 Java Interpreted Easy to run and test Quicker prototyping Program runs slower Compiled Execution time faster Virtual Machine compiled code portable Java Compile > javac
Interpreted vs Compiled Python 1 Java Interpreted Easy to run and test Quicker prototyping Program runs slower Compiled Execution time faster Virtual Machine compiled code portable Java Compile > javac
Express Yourself. What is Eclipse?
 CS 170 Java Programming 1 Eclipse and the for Loop A Professional Integrated Development Environment Introducing Iteration Express Yourself Use OpenOffice or Word to create a new document Save the file
CS 170 Java Programming 1 Eclipse and the for Loop A Professional Integrated Development Environment Introducing Iteration Express Yourself Use OpenOffice or Word to create a new document Save the file
Fondamenti di Informatica
 Fondamenti di Informatica Scripts and Functions: examples lesson 9 2012/04/16 Prof. Emiliano Casalicchio emiliano.casalicchio@uniroma2.it Agenda Examples Bisection method Locating roots Secant methods
Fondamenti di Informatica Scripts and Functions: examples lesson 9 2012/04/16 Prof. Emiliano Casalicchio emiliano.casalicchio@uniroma2.it Agenda Examples Bisection method Locating roots Secant methods
This assignment should give you practice with some aspects of working with graphics and windows in Java.
 Assignment 5 Due: Tuesday, July 24 by 11:59 PM Objective This assignment should give you practice with some aspects of working with graphics and windows in Java. Task Write a program utilizing a JDesktopFrame
Assignment 5 Due: Tuesday, July 24 by 11:59 PM Objective This assignment should give you practice with some aspects of working with graphics and windows in Java. Task Write a program utilizing a JDesktopFrame
Constants. Why Use Constants? main Method Arguments. CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD. Lecture 25: Miscellaneous
 CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
Repetition CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal
 Repetition CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Repetition CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Over and Over Again GEEN163
 Over and Over Again GEEN163 There is no harm in repeating a good thing. Plato Homework A programming assignment has been posted on Blackboard You have to convert three flowcharts into programs Upload the
Over and Over Again GEEN163 There is no harm in repeating a good thing. Plato Homework A programming assignment has been posted on Blackboard You have to convert three flowcharts into programs Upload the
Example. Write a program which sums two random integers and lets the user repeatedly enter a new answer until it is correct.
 Example Write a program which sums two random integers and lets the user repeatedly enter a new answer until it is correct. 1... 2 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 3 int x = (int) (Math.random()
Example Write a program which sums two random integers and lets the user repeatedly enter a new answer until it is correct. 1... 2 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 3 int x = (int) (Math.random()
Chapter 12 Advanced GUIs and Graphics
 Chapter 12 Advanced GUIs and Graphics Chapter Objectives Learn about applets Explore the class Graphics Learn about the classfont Explore the classcolor Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program
Chapter 12 Advanced GUIs and Graphics Chapter Objectives Learn about applets Explore the class Graphics Learn about the classfont Explore the classcolor Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program
Java for Non Majors Spring 2018
 Java for Non Majors Spring 2018 Final Study Guide The test consists of 1. Multiple choice questions - 15 x 2 = 30 points 2. Given code, find the output - 3 x 5 = 15 points 3. Short answer questions - 3
Java for Non Majors Spring 2018 Final Study Guide The test consists of 1. Multiple choice questions - 15 x 2 = 30 points 2. Given code, find the output - 3 x 5 = 15 points 3. Short answer questions - 3
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE SCHOOL OF COMPUTING TERM TEST #1 Semester 1 AY2006/2007 CS1101X/Y/Z PROGRAMMING METHODOLOGY 16 September 2006 Time Allowed: 60 Minutes INSTRUCTIONS 1. This question paper
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE SCHOOL OF COMPUTING TERM TEST #1 Semester 1 AY2006/2007 CS1101X/Y/Z PROGRAMMING METHODOLOGY 16 September 2006 Time Allowed: 60 Minutes INSTRUCTIONS 1. This question paper
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals 1 Recall From Last Time: Java Program import java.util.scanner; public class EggBasketEnhanced { public static void main(string[]
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals 1 Recall From Last Time: Java Program import java.util.scanner; public class EggBasketEnhanced { public static void main(string[]
Full file at
 Chapter 2 Console Input and Output Multiple Choice 1) Valid arguments to the System.out object s println method include: (a) Anything with double quotes (b) String variables (c) Variables of type int (d)
Chapter 2 Console Input and Output Multiple Choice 1) Valid arguments to the System.out object s println method include: (a) Anything with double quotes (b) String variables (c) Variables of type int (d)
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations. CONTENTS: The while and for statements
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
Swing/GUI Cheat Sheet
 General reminders To display a Swing component, you must: Swing/GUI Cheat Sheet Construct and initialize the component. Example: button = new JButton ("ButtonLabel"); Add it to the content pane of the
General reminders To display a Swing component, you must: Swing/GUI Cheat Sheet Construct and initialize the component. Example: button = new JButton ("ButtonLabel"); Add it to the content pane of the
CSE 251 PROJECT 1. Andrew Christlieb. Monday Class AND Friday Class Abstract. Web:
 CSE 51 PROJECT 1 Andrew Christlieb Monday Class 0-03-14 AND Friday Class 01-31-14 Abstract Web: http://www.cse.msu.edu/ cse51 Project 1 due date: (Monday Class) 0-17-14 AND (Friday Class)0-14-14, time:
CSE 51 PROJECT 1 Andrew Christlieb Monday Class 0-03-14 AND Friday Class 01-31-14 Abstract Web: http://www.cse.msu.edu/ cse51 Project 1 due date: (Monday Class) 0-17-14 AND (Friday Class)0-14-14, time:
CS 101 Fall 2005 Midterm 2 Name: ID:
 This exam is open text book but closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts (in particular, the final two questions are worth substantially more than any
This exam is open text book but closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts (in particular, the final two questions are worth substantially more than any
1.00 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving. Quiz 1 March 7, 2003
 1.00 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Quiz 1 March 7, 2003 Name: Email Address: TA: Section: You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. For coding questions, you do not need to
1.00 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Quiz 1 March 7, 2003 Name: Email Address: TA: Section: You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. For coding questions, you do not need to
CSCI 1103: File I/O, Scanner, PrintWriter
 CSCI 1103: File I/O, Scanner, PrintWriter Chris Kauffman Last Updated: Mon Dec 4 10:03:11 CST 2017 1 Logistics Reading from Eck Ch 2.1 on Input, File I/O Ch 11.1-2 on File I/O Goals Scanner for input Input
CSCI 1103: File I/O, Scanner, PrintWriter Chris Kauffman Last Updated: Mon Dec 4 10:03:11 CST 2017 1 Logistics Reading from Eck Ch 2.1 on Input, File I/O Ch 11.1-2 on File I/O Goals Scanner for input Input
Programming Assignment 2 (PA2) - DraggingEmoji & ShortLongWords
 Programming Assignment 2 (PA2) - DraggingEmoji & ShortLongWords Due Date: Wednesday, October 10 @ 11:59 pm Assignment Overview Grading Gathering Starter Files Program 1: DraggingEmoji Program 2: ShortLongWords
Programming Assignment 2 (PA2) - DraggingEmoji & ShortLongWords Due Date: Wednesday, October 10 @ 11:59 pm Assignment Overview Grading Gathering Starter Files Program 1: DraggingEmoji Program 2: ShortLongWords
Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to Programming and the Java Language
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Programming and the Java Language 1.1 Basic Computer Concepts 5 1.1.1 Hardware 5 1.1.2 Operating Systems 8 1.1.3 Application Software 9 1.1.4 Computer Networks and the Internet
Chapter 1 Introduction to Programming and the Java Language 1.1 Basic Computer Concepts 5 1.1.1 Hardware 5 1.1.2 Operating Systems 8 1.1.3 Application Software 9 1.1.4 Computer Networks and the Internet
LAB 11: METHODS. CPCS The Lab Note Lab 11 Page 1. Statement Purpose:
 Statement Purpose: The purpose of this Lab. is to practically familiarize student with how to write the common code once and reuse it without rewriting it using the concept of Methods. Activity Outcomes:
Statement Purpose: The purpose of this Lab. is to practically familiarize student with how to write the common code once and reuse it without rewriting it using the concept of Methods. Activity Outcomes:
Exam 2. Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik. Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks:
 كلية الحاسبات وتقنية المعلوما Exam 2 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: November 22, 2015 Student Name: Student ID: Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this
كلية الحاسبات وتقنية المعلوما Exam 2 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: November 22, 2015 Student Name: Student ID: Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this
Loops. Eng. Mohammed Abdualal. Islamic University of Gaza. Faculty of Engineering. Computer Engineering Department
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 6 Loops
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 6 Loops
To gain experience using GUI components and listeners.
 Lab 5 Handout 7 CSCI 134: Fall, 2017 TextPlay Objective To gain experience using GUI components and listeners. Note 1: You may work with a partner on this lab. If you do, turn in only one lab with both
Lab 5 Handout 7 CSCI 134: Fall, 2017 TextPlay Objective To gain experience using GUI components and listeners. Note 1: You may work with a partner on this lab. If you do, turn in only one lab with both
Simple Java Input/Output
 Simple Java Input/Output Prologue They say you can hold seven plus or minus two pieces of information in your mind. I can t remember how to open files in Java. I ve written chapters on it. I ve done it
Simple Java Input/Output Prologue They say you can hold seven plus or minus two pieces of information in your mind. I can t remember how to open files in Java. I ve written chapters on it. I ve done it
ITERATION AND RECURSION 3
 ITERATION AND RECURSION 3 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A June 26, 2012 1 Newton s Method Newton s method is an algorithm that is widely used to compute the zeros of functions. It can be used to approximate a root
ITERATION AND RECURSION 3 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A June 26, 2012 1 Newton s Method Newton s method is an algorithm that is widely used to compute the zeros of functions. It can be used to approximate a root
Problem #3 Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page Mark Sparks 2012
 Problem # Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 490 Mark Sparks 01 Finding Anti-derivatives of Polynomial-Type Functions If you had to explain to someone how to find
Problem # Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 490 Mark Sparks 01 Finding Anti-derivatives of Polynomial-Type Functions If you had to explain to someone how to find
CHAPTER 8: INTEGRALS 8.1 REVIEW: APPROXIMATING INTEGRALS WITH RIEMANN SUMS IN 2-D
 CHAPTER 8: INTEGRALS 8.1 REVIEW: APPROXIMATING INTEGRALS WITH RIEMANN SUMS IN 2-D In two dimensions we have previously used Riemann sums to approximate ( ) following steps: with the 1. Divide the region
CHAPTER 8: INTEGRALS 8.1 REVIEW: APPROXIMATING INTEGRALS WITH RIEMANN SUMS IN 2-D In two dimensions we have previously used Riemann sums to approximate ( ) following steps: with the 1. Divide the region
4.7 Approximate Integration
 4.7 Approximate Integration Some anti-derivatives are difficult to impossible to find. For example, 1 0 e x2 dx or 1 1 1 + x3 dx We came across this situation back in calculus I when we introduced the
4.7 Approximate Integration Some anti-derivatives are difficult to impossible to find. For example, 1 0 e x2 dx or 1 1 1 + x3 dx We came across this situation back in calculus I when we introduced the
Window Interfaces Using Swing. Chapter 12
 Window Interfaces Using Swing 1 Reminders Project 7 due Nov 17 @ 10:30 pm Project 6 grades released: regrades due by next Friday (11-18-2005) at midnight 2 GUIs - Graphical User Interfaces Windowing systems
Window Interfaces Using Swing 1 Reminders Project 7 due Nov 17 @ 10:30 pm Project 6 grades released: regrades due by next Friday (11-18-2005) at midnight 2 GUIs - Graphical User Interfaces Windowing systems
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods
 Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
WOSO Source Code (Java)
 WOSO 2017 - Source Code (Java) Q 1 - Which of the following is false about String? A. String is immutable. B. String can be created using new operator. C. String is a primary data type. D. None of the
WOSO 2017 - Source Code (Java) Q 1 - Which of the following is false about String? A. String is immutable. B. String can be created using new operator. C. String is a primary data type. D. None of the
Proctors are unable to respond to queries about the interpretation of exam questions. Do your best to answer exam questions as written.
 HAND IN Answers Are Recorded on Question Paper QUEEN'S UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF COMPUTING CISC212, FALL TERM, 2006 FINAL EXAMINATION 7pm to 10pm, 19 DECEMBER 2006, Jeffrey Hall 1 st Floor Instructor: Alan
HAND IN Answers Are Recorded on Question Paper QUEEN'S UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF COMPUTING CISC212, FALL TERM, 2006 FINAL EXAMINATION 7pm to 10pm, 19 DECEMBER 2006, Jeffrey Hall 1 st Floor Instructor: Alan
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below.
 C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
Proctors are unable to respond to queries about the interpretation of exam questions. Do your best to answer exam questions as written.
 QUEEN'S UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF COMPUTING HAND IN Answers Are Recorded on Question Paper CISC124, WINTER TERM, 2011 FINAL EXAMINATION 7pm to 10pm, 26 APRIL 2011, Ross Gym Instructor: Alan McLeod If the instructor
QUEEN'S UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF COMPUTING HAND IN Answers Are Recorded on Question Paper CISC124, WINTER TERM, 2011 FINAL EXAMINATION 7pm to 10pm, 26 APRIL 2011, Ross Gym Instructor: Alan McLeod If the instructor
Top-Down Program Development
 Top-Down Program Development Top-down development is a way of thinking when you try to solve a programming problem It involves starting with the entire problem, and breaking it down into more manageable
Top-Down Program Development Top-down development is a way of thinking when you try to solve a programming problem It involves starting with the entire problem, and breaking it down into more manageable
Java for Non Majors. Final Study Guide. April 26, You will have an opportunity to earn 20 extra credit points.
 Java for Non Majors Final Study Guide April 26, 2017 The test consists of 1. Multiple choice questions 2. Given code, find the output 3. Code writing questions 4. Code debugging question 5. Short answer
Java for Non Majors Final Study Guide April 26, 2017 The test consists of 1. Multiple choice questions 2. Given code, find the output 3. Code writing questions 4. Code debugging question 5. Short answer
Frames, GUI and events. Introduction to Swing Structure of Frame based applications Graphical User Interface (GUI) Events and event handling
 Frames, GUI and events Introduction to Swing Structure of Frame based applications Graphical User Interface (GUI) Events and event handling Introduction to Swing The Java AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit)
Frames, GUI and events Introduction to Swing Structure of Frame based applications Graphical User Interface (GUI) Events and event handling Introduction to Swing The Java AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit)
Arithmetic and IO. 25 August 2017
 Arithmetic and IO 25 August 2017 Submissions you can submit multiple times to the homework dropbox file name: uppercase first letter, Yourlastname0829.java the system will use the last submission before
Arithmetic and IO 25 August 2017 Submissions you can submit multiple times to the homework dropbox file name: uppercase first letter, Yourlastname0829.java the system will use the last submission before
Lec 7. for loops and methods
 Lec 7 for loops and methods Announcements Quiz 1 on Friday Review today. 5:00. CENTR 212 Assume there s a method drawrandomfruit() How would you create this: While loops final int DIMENSION = 9; int row
Lec 7 for loops and methods Announcements Quiz 1 on Friday Review today. 5:00. CENTR 212 Assume there s a method drawrandomfruit() How would you create this: While loops final int DIMENSION = 9; int row
CS Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #1 - Prof. Reed Spring 2009
 CS 102 - Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #1 - Prof. Reed Spring 2009 What is your name?: There are two sections: I. True/False..................... 72 points; ( 36 questions, 2 points each) II.
CS 102 - Introduction to Programming Midterm Exam #1 - Prof. Reed Spring 2009 What is your name?: There are two sections: I. True/False..................... 72 points; ( 36 questions, 2 points each) II.
JAVA PROGRAMMING LAB. ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
University of Massachusetts Amherst, Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Massachusetts Amherst, Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 122 Midterm Exam 1 Makeup Answer key March 2, 2018 Instructions: Closed book, Calculators allowed; Duration:120 minutes; Write
University of Massachusetts Amherst, Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 122 Midterm Exam 1 Makeup Answer key March 2, 2018 Instructions: Closed book, Calculators allowed; Duration:120 minutes; Write
Chapter 5 Control Statements: Part 2 Section 5.2 Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition
 Chapter 5 Control Statements: Part 2 Section 5.2 Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition 5.2 Q1: Counter-controlled repetition requires a. A control variable and initial value. b. A control variable
Chapter 5 Control Statements: Part 2 Section 5.2 Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition 5.2 Q1: Counter-controlled repetition requires a. A control variable and initial value. b. A control variable
3. Convert 2E from hexadecimal to decimal. 4. Convert from binary to hexadecimal
 APCS A Midterm Review You will have a copy of the one page Java Quick Reference sheet. This is the same reference that will be available to you when you take the AP Computer Science exam. 1. n bits can
APCS A Midterm Review You will have a copy of the one page Java Quick Reference sheet. This is the same reference that will be available to you when you take the AP Computer Science exam. 1. n bits can
