Numerical Methods with Matlab: Implementations and Applications. Gerald W. Recktenwald. Chapter 11 Numerical Integration
|
|
|
- William Paul
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Selected Solutions for Exercises in Numerical Methods with Matlab: Implementations and Applications Gerald W. Recktenwald Chapter 11 Numerical Integration The following pages contain solutions to selected end-of-chapter Exercises from the book Numerical Methods with Matlab: Implementations and Applications, by Gerald W. Recktenwald, c 21, Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. The solutions are c 21 Gerald W. Recktenwald. The PDF version of the solutions may be downloaded or stored or printed only for noncommercial, educational use. Repackaging and sale of these solutions in any form, without the written consent of the author, is prohibited. The latest version of this PDF file, along with other supplemental material for the book, can be found at
2 2 Numerical Integration 11.2 Write a polyint function that uses the built-in polyval function to evaluate the definite integral of a polynomial. The inputs to polyint should be a vector of polynomial coefficients and the lower and upper limits of integration. Test your function by evaluating the two integrals in the preceding exercise. Update for Matlab version 6: Version 6 includes a polyint function that comes close to solving this Exercise. To avoid the name clash, the solution presented here is to develop a polyintegral function. Partial Solution: A correct implementation of polyintegral gives >> I1 = polyintegral([1 1 1],-pi/2,pi) I1 = 2.48 >> I1exact = (3/8)*pi^3 + (3/8)*pi^2 + (3/2)*pi; >> err1 = I1 - I1exact err1 = >> I2 = polyintegral([1-1],sqrt(3),-5) I2 = >> I2exact = ( (-5)^4/4 + 5 ) - ( 9/4 - sqrt(3) ); >> err2 = I2 - I2exact err2 = How would the built-in polyint (Matlab version 6) function be used to evaluate the definite integral of a polynomial?
3 Chapter 11: Numerical Integration Use the symbolic capability of the Student Edition of Matlab or the Symbolic Mathematics Toolbox, to find the definite integral of the generalized humps function f(x) = 1 (x c 1 ) 2 + c (x c 3 ) 2 + c 4 + c 5 Solution: The following Matlab session requires a version of the Symbolic Mathematics Toolbox. >> syms a b c1 c2 c3 c4 c5 f x >> f = 1/( (x-c1)^2 + c2 ) + 1/( (x-c3)^2 + c4 ) + c5 f = 1/((x-c1)^2+c2)+1/((x-c3)^2+c4)+c5 >> g = int(f,x,a,b) g = ( atan( (b-c1)/c2^(1/2) )*c4^(1/2) + atan( (b-c3)/c4^(1/2) )*c2^(1/2) + c5*b*c2^(1/2)*c4^(1/2) )/c2^(1/2)/c4^(1/2) - ( atan( (a-c1)/c2^(1/2) )*c4^(1/2) + atan( (a-c3)/c4^(1/2) )*c2^(1/2) + c5*a*c2^(1/2)*c4^(1/2) )/c2^(1/2)/c4^(1/2) which can be rearranged as g = ( atan((c1-a)/sqrt(c2)) - atan((c1-b)/sqrt(c2)) )/sqrt(c2)... + ( atan((c3-a)/sqrt(c4)) - atan((c3-b)/sqrt(c4)) )/sqrt(c4)... + c5*(b-a);
4 4 Numerical Integration 11.8 F.M. White (Fluid Mechanics, fourth edition, 1999, McGraw-Hill, New York., problem 6.57) gives the following data for the velocity profile in a round pipe r/r u/u c r is the radial position, R =12.35 cm is the radius of the pipe, u is the velocity at the position r, and u c is the velocity at the centerline r =. Theaverage velocity in a round pipe is defined by V = 1 πr 2 R u 2πr dr, or V u c = 1 2 V u c ηdη, where η = r/r. What is the value of V for the given data if u c =3.5m/s? Do not forget to include the implied data point u/u c =atr/r = 1. The data in the table is in the vprofile.dat file in the data directory of the NMM toolbox. Typographical Error: A factor of 2 is missing from the second integral expression. The correct formula for V/u c is V u c = 1 2 V u c ηdη Numerical Answer: Using trapzdat function with the correct form of the integral for V/u c, gives V = m/s.
5 Chapter 11: Numerical Integration Use the Trapezoid rule to evaluate β(m, n) = 1 x m 1 (1 x) n 1 dx for any m and n and for a sequence of decreasing panel sizes h. Print the value of β(m, n), and the error relative to the value returned by the built-in beta function. Use your function to evaluate β(1, 2), β(1.5, 2.5), β(2, 3), and β(2, 5). Comment on the convergence rate. (Hint: The values of m and n can be passed around (not through) trapezoid with global variables.) Partial Solution: The solution is obtained by writing two m-file functions. One function evaluates the integrand, and the other calls trapezoid with a sequence of decreasing panel sizes. This second m-file is obtained with minor modifications to the demotrap function. I ve called it betatrap. The prologue of the betatrap function is function betatrap(m,n) betatrap Evaluate beta function with trapezoid rule Synopsis: betatrap betatrap(m,n) Input: m,n = (optional) parameters of the beta function Default: m = 1, n = 2 Output: Table of integral values as a function of decreasing panel size Running betatrap for m =1andn = 2 gives >> betatrap Iexact =.5 n h I error alpha The numerical integral is exact in this case becuase the integrand reduces to (1 x). The trapezoid rule integrates a linear function with no truncation error. Running betatrap for m =1.5 andn =2.5 gives >> betatrap(1.5,2.5) Iexact =
6 6 Numerical Integration n h I error alpha The theoretical value of α = 2 is not obtained becuase the derivative of the integrand is not defined at the lower limit of integration. The truncation error for the composite trapezoid rule is bounded by Ch 2 f (ξ) where C is a constant and f (ξ) is the second derivative of the integrand evaluated at some point ξ in the limits of integration. For m =1.5 andn =2.5, f = x(1 x) 3/2 and f (x) as x approaches zero. Although the formulas in the trapezoid rule do not encounter a division by zero, the truncation error reduces more slowly than O(h 2 ) because of the contribution of f (ξ).
7 Chapter 11: Numerical Integration Evaluate I = 1 xdx using the NMM routines trapezoid, simpson, andgaussquad. For each routine, evaluate the integral for at least three different panel sizes. Present a table comparing the measured truncation error as a function of panel size. Report any problems in obtaining values of I. Which routine works best for this problem? Partial Solution: The solution is obtained by modifying the code in the demotrap, demosimp, and demogauss functions. For convenience the modified code from these function is combined into a single m-file called intsqrt. Running intsqrt gives: >> intsqrt Evaluate Integral with Trapezoid Rule: Iexact = n h I error alpha Evaluate Integral with Simpson s Rule: Iexact = n h I error alpha Evaluate Integral with Gauss-Legendre Rule: Iexact = Gauss-Legendre quadrature with 4 panels, H =.25 nodes I error e e e e e e e e-5
8 8Numerical Integration Gauss-Legendre quadrature with 8 nodes panels H I error alpha e e e e e e e e None of the integration rules achieves its theoretical truncation error. The reason is that the integrand is not sufficiently differentiable at the lower limit of integration. (See also the solution to Exercise ) The Gauss Legendre rule with eight nodes per panel obtains the result with the smallest error, though its performance is considerable worse on this integrand than on the integrands demonstrated in the Examples in the text.
9 Chapter 11: Numerical Integration Write an m-file function that evaluates 2π sin 2 (x) dx using the composite trapezoid rule, composite Simpson s rule, and composite Gauss Legendre quadrature with four nodes per panel. Place the calls to trapezoid, simpson, andgaussquad inside a loop and repeat the calculations for np = [ ], where np is the number of panels. Record the number of function evaluations, n, for each method. Print the absolute error I I exact for the three methods versus n. (See, for example, [13, 2.9] for help in explaining the results.) Partial Solution: The computations are carried out with the compint_sinx2 function. The prologue for compint_sinx2 is function compint_sinx2(a,b) compint_sinx2 Compare quadrature rules for integral of (sin(x))^2 Synopsis: compint_sinx2 compint_sinx2(a,b) Input: a,b = (optional) limits of integration. Default: a=; b=pi Output: Values of integral obtained by trapezoid and simpsons rules for increasing number of panels Running compint_sinx2 with the default inputs gives: >> compint_sinx2 Integral of (sin(x))^2 from *pi to 1*pi Iexact = Trapezoid Simpson Gauss-Legendre n error n error n error 3.e+ 5.e+ 8.e+ 5.e+ 9.e+ 16.e+ 9.e+ 17.e+ 32.e+ 17.e+ 33.e e e+ 65.e+ 128.e+ 65.e+ 129.e+ 256.e+ Note that n is the number of nodes at which the integrand is evaluated, not the number of panels used by the various composite rules. All methods give neglible errors regardless of the number of panels. The trapezoid rule is known to rapidly converge for a periodic integrand when the limits of the integral are points at which the integrand and its derivative assume periodic values. See Davis and Rabinowitz [13, 2.9] for details. sin 2 x is an extreme example of the special behavior for periodic integrands. A slightly more interesting results is obtained if np = [ ] and the Gauss Legendre rule with two (instead of four) points per panel is used. Making these changes and running the modified compint_sinx2 gives >> compint_sinx2 Integral of (sin(x))^2 from *pi to 1*pi Iexact =
10 1 Numerical Integration Trapezoid Simpson Gauss-Legendre n error n error n error e e e-1 3.e+ 5.e+ 4.e+ 5.e+ 9.e+ 8.e+ 9.e+ 17.e+ 16.e+ 17.e+ 33.e+ 32.e+ 33.e+ 65.e+ 64.e+ This result allows direct comparison with somewhat more comparable number of nodes in each row. The first row shows the error for applying the basic rule for each method. If, for the integral in this Exercise, the limits of the integral are shifted to and some nonrational multiple of π, the integration schemes behave as usual. Rerunning the modified version of compint_sinx2 gives >> compint_sinx2(,5.12*pi) Integral of (sin(x))^2 from *pi to 5.12*pi Iexact = Trapezoid Simpson Gauss-Legendre n error n error n error e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e e-5 Now the truncation errors do not decrease so dramatically because the limits of the integral do not produce periodic values of the integrand and its derivatives.
Unavoidable Errors in Computing
 Unavoidable Errors in Computing Gerald W. Recktenwald Department of Mechanical Engineering Portland State University gerry@me.pdx.edu These slides are a supplement to the book Numerical Methods with Matlab:
Unavoidable Errors in Computing Gerald W. Recktenwald Department of Mechanical Engineering Portland State University gerry@me.pdx.edu These slides are a supplement to the book Numerical Methods with Matlab:
SYDE 312 UNIT 4: EXTRA QUADRATURE PROBLEMS
 SYDE 3 UNIT 4: EXTRA QUADRATURE PROBLEMS Problem E x x + Use f(x) = /x x + You can t use the Matlab gaussquad file in the provided form, because it implements composite Gauss-Legendre quadrature with multiple
SYDE 3 UNIT 4: EXTRA QUADRATURE PROBLEMS Problem E x x + Use f(x) = /x x + You can t use the Matlab gaussquad file in the provided form, because it implements composite Gauss-Legendre quadrature with multiple
Numerical Methods with Matlab: Implementations and Applications. Gerald W. Recktenwald. Chapter 10 Interpolation
 Selected Solutions for Exercises in Numerical Methods with Matlab: Implementations and Applications Gerald W. Recktenwald Chapter 10 Interpolation The following pages contain solutions to selected end-of-chapter
Selected Solutions for Exercises in Numerical Methods with Matlab: Implementations and Applications Gerald W. Recktenwald Chapter 10 Interpolation The following pages contain solutions to selected end-of-chapter
Math 226A Homework 4 Due Monday, December 11th
 Math 226A Homework 4 Due Monday, December 11th 1. (a) Show that the polynomial 2 n (T n+1 (x) T n 1 (x)), is the unique monic polynomial of degree n + 1 with roots at the Chebyshev points x k = cos ( )
Math 226A Homework 4 Due Monday, December 11th 1. (a) Show that the polynomial 2 n (T n+1 (x) T n 1 (x)), is the unique monic polynomial of degree n + 1 with roots at the Chebyshev points x k = cos ( )
A MIXED QUADRATURE FORMULA USING RULES OF LOWER ORDER
 Bulletin of the Marathwada Mathematical Society Vol.5, No., June 004, Pages 6-4 ABSTRACT A MIXED QUADRATURE FORMULA USING RULES OF LOWER ORDER Namita Das And Sudhir Kumar Pradhan P.G. Department of Mathematics
Bulletin of the Marathwada Mathematical Society Vol.5, No., June 004, Pages 6-4 ABSTRACT A MIXED QUADRATURE FORMULA USING RULES OF LOWER ORDER Namita Das And Sudhir Kumar Pradhan P.G. Department of Mathematics
Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 361 / 761 Fall 2018 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane
 Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 36 / 76 Fall 28 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane c Sateesh R. Mane 28 6 Homework lecture 6: numerical integration If you write the
Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 36 / 76 Fall 28 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane c Sateesh R. Mane 28 6 Homework lecture 6: numerical integration If you write the
Numerical Integration
 Numerical Integration Numerical Integration is the process of computing the value of a definite integral, when the values of the integrand function, are given at some tabular points. As in the case of
Numerical Integration Numerical Integration is the process of computing the value of a definite integral, when the values of the integrand function, are given at some tabular points. As in the case of
D01ARF NAG Fortran Library Routine Document
 D01ARF NAG Fortran Library Routine Document Note. Before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of bold italicised terms and other implementation-dependent
D01ARF NAG Fortran Library Routine Document Note. Before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of bold italicised terms and other implementation-dependent
Introduction to Computer Programming with MATLAB Calculation and Programming Errors. Selis Önel, PhD
 Introduction to Computer Programming with MATLAB Calculation and Programming Errors Selis Önel, PhD Today you will learn Numbers, Significant figures Error analysis Absolute error Relative error Chopping
Introduction to Computer Programming with MATLAB Calculation and Programming Errors Selis Önel, PhD Today you will learn Numbers, Significant figures Error analysis Absolute error Relative error Chopping
PHYS 210: Introduction to Computational Physics Octave/MATLAB Exercises 1
 PHYS 210: Introduction to Computational Physics Octave/MATLAB Exercises 1 1. Problems from Gilat, Ch. 1.10 Open a terminal window, change to directory /octave, and using your text editor, create the file
PHYS 210: Introduction to Computational Physics Octave/MATLAB Exercises 1 1. Problems from Gilat, Ch. 1.10 Open a terminal window, change to directory /octave, and using your text editor, create the file
LECTURE 0: Introduction and Background
 1 LECTURE 0: Introduction and Background September 10, 2012 1 Computational science The role of computational science has become increasingly significant during the last few decades. It has become the
1 LECTURE 0: Introduction and Background September 10, 2012 1 Computational science The role of computational science has become increasingly significant during the last few decades. It has become the
nag 1d quad gauss (d01bac)
 1. Purpose nag 1d quad gauss () nag 1d quad gauss () computes an estimate of the definite integral of a function of known analytical form, using a Gaussian quadrature formula with a specified number of
1. Purpose nag 1d quad gauss () nag 1d quad gauss () computes an estimate of the definite integral of a function of known analytical form, using a Gaussian quadrature formula with a specified number of
Integration. Volume Estimation
 Monte Carlo Integration Lab Objective: Many important integrals cannot be evaluated symbolically because the integrand has no antiderivative. Traditional numerical integration techniques like Newton-Cotes
Monte Carlo Integration Lab Objective: Many important integrals cannot be evaluated symbolically because the integrand has no antiderivative. Traditional numerical integration techniques like Newton-Cotes
Organizing and Debugging Matlab Programs
 Organizing and Debugging Matlab Programs Gerald Recktenwald Portland State University Department of Mechanical Engineering These slides are a supplement to the book Numerical Methods with Matlab: Implementations
Organizing and Debugging Matlab Programs Gerald Recktenwald Portland State University Department of Mechanical Engineering These slides are a supplement to the book Numerical Methods with Matlab: Implementations
APPM/MATH Problem Set 4 Solutions
 APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
nag 1d quad gauss 1 (d01tac)
 1. Purpose nag 1d quad gauss 1 () nag 1d quad gauss 1 () computes an estimate of the definite integral of a function of known analytical form, using a Gaussian quadrature formula with a specified number
1. Purpose nag 1d quad gauss 1 () nag 1d quad gauss 1 () computes an estimate of the definite integral of a function of known analytical form, using a Gaussian quadrature formula with a specified number
AMSC/CMSC 460 Final Exam, Fall 2007
 AMSC/CMSC 460 Final Exam, Fall 2007 Show all work. You may leave arithmetic expressions in any form that a calculator could evaluate. By putting your name on this paper, you agree to abide by the university
AMSC/CMSC 460 Final Exam, Fall 2007 Show all work. You may leave arithmetic expressions in any form that a calculator could evaluate. By putting your name on this paper, you agree to abide by the university
NUMERICAL INTEGRATION AND FUNCTION FUNCTIONS
 NUMERICAL INTEGRATION AND FUNCTION FUNCTIONS The arguments of functions previously considered had constants, or vector or matrix variables as arguments. In this section we will see how to set up a function
NUMERICAL INTEGRATION AND FUNCTION FUNCTIONS The arguments of functions previously considered had constants, or vector or matrix variables as arguments. In this section we will see how to set up a function
Excel Tool: Calculations with Data Sets
 Excel Tool: Calculations with Data Sets The best thing about Excel for the scientist is that it makes it very easy to work with data sets. In this assignment, we learn how to do basic calculations that
Excel Tool: Calculations with Data Sets The best thing about Excel for the scientist is that it makes it very easy to work with data sets. In this assignment, we learn how to do basic calculations that
MATLAB QUICK START TUTORIAL
 MATLAB QUICK START TUTORIAL This tutorial is a brief introduction to MATLAB which is considered one of the most powerful languages of technical computing. In the following sections, the basic knowledge
MATLAB QUICK START TUTORIAL This tutorial is a brief introduction to MATLAB which is considered one of the most powerful languages of technical computing. In the following sections, the basic knowledge
CS321 Introduction To Numerical Methods
 CS3 Introduction To Numerical Methods Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington KY 456-46 - - Table of Contents Errors and Number Representations 3 Error Types
CS3 Introduction To Numerical Methods Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington KY 456-46 - - Table of Contents Errors and Number Representations 3 Error Types
NAG Library Routine Document D01BAF.1
 NAG Library Routine Document Note: before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of bold italicised terms and other implementation-dependent
NAG Library Routine Document Note: before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of bold italicised terms and other implementation-dependent
Homework Project #6. Math 365, Spring Due Wednesday April 27th
 Name : Homework Project #6 Math 365, Spring 2016 Due Wednesday April 27th You may work with a partner on this assignment and turn in a single assignment for the both of you. 1. (Using fzero) Consider the
Name : Homework Project #6 Math 365, Spring 2016 Due Wednesday April 27th You may work with a partner on this assignment and turn in a single assignment for the both of you. 1. (Using fzero) Consider the
MA 113 Calculus I Fall 2015 Exam 2 Tuesday, 20 October Multiple Choice Answers. Question
 MA 113 Calculus I Fall 2015 Exam 2 Tuesday, 20 October 2015 Name: Section: Last digits of student ID #: This exam has ten multiple choice questions (five points each) and five free response questions (ten
MA 113 Calculus I Fall 2015 Exam 2 Tuesday, 20 October 2015 Name: Section: Last digits of student ID #: This exam has ten multiple choice questions (five points each) and five free response questions (ten
Exercises for a Numerical Methods Course
 Exercises for a Numerical Methods Course Brian Heinold Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Mount St. Mary s University November 18, 2017 1 / 73 About the class Mix of Math and CS students, mostly
Exercises for a Numerical Methods Course Brian Heinold Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Mount St. Mary s University November 18, 2017 1 / 73 About the class Mix of Math and CS students, mostly
A Curve-Fitting Cookbook for use with the NMM Toolbox
 A Curve-Fitting Cookbook for use with the NMM Toolbox Gerald Recktenwald October 17, 2000 Abstract Computational steps for obtaining curve fits with Matlab are described. The steps include reading data
A Curve-Fitting Cookbook for use with the NMM Toolbox Gerald Recktenwald October 17, 2000 Abstract Computational steps for obtaining curve fits with Matlab are described. The steps include reading data
Computer Arithmetic. 1. Floating-point representation of numbers (scientific notation) has four components, for example, 3.
 ECS231 Handout Computer Arithmetic I: Floating-point numbers and representations 1. Floating-point representation of numbers (scientific notation) has four components, for example, 3.1416 10 1 sign significandbase
ECS231 Handout Computer Arithmetic I: Floating-point numbers and representations 1. Floating-point representation of numbers (scientific notation) has four components, for example, 3.1416 10 1 sign significandbase
University of Alberta
 A Brief Introduction to MATLAB University of Alberta M.G. Lipsett 2008 MATLAB is an interactive program for numerical computation and data visualization, used extensively by engineers for analysis of systems.
A Brief Introduction to MATLAB University of Alberta M.G. Lipsett 2008 MATLAB is an interactive program for numerical computation and data visualization, used extensively by engineers for analysis of systems.
When implementing FEM for solving two-dimensional partial differential equations, integrals of the form
 Quadrature Formulas in Two Dimensions Math 57 - Finite Element Method Section, Spring Shaozhong Deng, PhD (shaodeng@unccedu Dept of Mathematics and Statistics, UNC at Charlotte When implementing FEM for
Quadrature Formulas in Two Dimensions Math 57 - Finite Element Method Section, Spring Shaozhong Deng, PhD (shaodeng@unccedu Dept of Mathematics and Statistics, UNC at Charlotte When implementing FEM for
Review Questions 26 CHAPTER 1. SCIENTIFIC COMPUTING
 26 CHAPTER 1. SCIENTIFIC COMPUTING amples. The IEEE floating-point standard can be found in [131]. A useful tutorial on floating-point arithmetic and the IEEE standard is [97]. Although it is no substitute
26 CHAPTER 1. SCIENTIFIC COMPUTING amples. The IEEE floating-point standard can be found in [131]. A useful tutorial on floating-point arithmetic and the IEEE standard is [97]. Although it is no substitute
Exercises C-Programming
 Exercises C-Programming Claude Fuhrer (claude.fuhrer@bfh.ch) 0 November 016 Contents 1 Serie 1 1 Min function.................................. Triangle surface 1............................... 3 Triangle
Exercises C-Programming Claude Fuhrer (claude.fuhrer@bfh.ch) 0 November 016 Contents 1 Serie 1 1 Min function.................................. Triangle surface 1............................... 3 Triangle
Practice Reading if Constructs
 ME 350 Lab Exercise 4 Fall 2017 if constructs, while loops Practice Reading if Constructs What is the output of the following command sequences? Some of the sequences may print messages that are not correct
ME 350 Lab Exercise 4 Fall 2017 if constructs, while loops Practice Reading if Constructs What is the output of the following command sequences? Some of the sequences may print messages that are not correct
1. Fill in the right hand side of the following equation by taking the derivative: (x sin x) =
 7.1 What is x cos x? 1. Fill in the right hand side of the following equation by taking the derivative: (x sin x = 2. Integrate both sides of the equation. Instructor: When instructing students to integrate
7.1 What is x cos x? 1. Fill in the right hand side of the following equation by taking the derivative: (x sin x = 2. Integrate both sides of the equation. Instructor: When instructing students to integrate
NAG Fortran Library Routine Document D01AJF.1
 D01 Quadrature NAG Fortran Library Routine Document Note: before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of bold italicised terms and other implementation-dependent
D01 Quadrature NAG Fortran Library Routine Document Note: before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of bold italicised terms and other implementation-dependent
Dr Richard Greenaway
 SCHOOL OF PHYSICS, ASTRONOMY & MATHEMATICS 4PAM1008 MATLAB 2 Basic MATLAB Operation Dr Richard Greenaway 2 Basic MATLAB Operation 2.1 Overview 2.1.1 The Command Line In this Workshop you will learn how
SCHOOL OF PHYSICS, ASTRONOMY & MATHEMATICS 4PAM1008 MATLAB 2 Basic MATLAB Operation Dr Richard Greenaway 2 Basic MATLAB Operation 2.1 Overview 2.1.1 The Command Line In this Workshop you will learn how
Lab1: Use of Word and Excel
 Dr. Fritz Wilhelm; physics 230 Lab1: Use of Word and Excel Page 1 of 9 Lab partners: Download this page onto your computer. Also download the template file which you can use whenever you start your lab
Dr. Fritz Wilhelm; physics 230 Lab1: Use of Word and Excel Page 1 of 9 Lab partners: Download this page onto your computer. Also download the template file which you can use whenever you start your lab
A. Matrix-wise and element-wise operations
 USC GSBME MATLAB CLASS Reviewing previous session Second session A. Matrix-wise and element-wise operations A.1. Matrix-wise operations So far we learned how to define variables and how to extract data
USC GSBME MATLAB CLASS Reviewing previous session Second session A. Matrix-wise and element-wise operations A.1. Matrix-wise operations So far we learned how to define variables and how to extract data
An interesting related problem is Buffon s Needle which was first proposed in the mid-1700 s.
 Using Monte Carlo to Estimate π using Buffon s Needle Problem An interesting related problem is Buffon s Needle which was first proposed in the mid-1700 s. Here s the problem (in a simplified form). Suppose
Using Monte Carlo to Estimate π using Buffon s Needle Problem An interesting related problem is Buffon s Needle which was first proposed in the mid-1700 s. Here s the problem (in a simplified form). Suppose
Introduction to Programming for Engineers Spring Final Examination. May 10, Questions, 170 minutes
 Final Examination May 10, 2011 75 Questions, 170 minutes Notes: 1. Before you begin, please check that your exam has 28 pages (including this one). 2. Write your name and student ID number clearly on your
Final Examination May 10, 2011 75 Questions, 170 minutes Notes: 1. Before you begin, please check that your exam has 28 pages (including this one). 2. Write your name and student ID number clearly on your
Session 2. a. Follow-ups to Session Session 2 (last revised: January 6, 2013) 2 1
 6810 Session 2 (last revised: January 6, 2013) 2 1 2. 6810 Session 2 a. Follow-ups to Session 1 First, a couple of general comments on the 1094 sessions. Please try to not skip items if you have time;
6810 Session 2 (last revised: January 6, 2013) 2 1 2. 6810 Session 2 a. Follow-ups to Session 1 First, a couple of general comments on the 1094 sessions. Please try to not skip items if you have time;
Computational Mathematics/Information Technology. Worksheet 2 Iteration and Excel
 Computational Mathematics/Information Technology Worksheet 2 Iteration and Excel This sheet uses Excel and the method of iteration to solve the problem f(x) = 0. It introduces user functions and self referencing
Computational Mathematics/Information Technology Worksheet 2 Iteration and Excel This sheet uses Excel and the method of iteration to solve the problem f(x) = 0. It introduces user functions and self referencing
A Brief Introduction to Mathematica
 A Brief Introduction to Mathematica Objectives: (1) To learn to use Mathematica as a calculator. (2) To learn to write expressions in Mathematica, and to evaluate them at given point. (3) To learn to plot
A Brief Introduction to Mathematica Objectives: (1) To learn to use Mathematica as a calculator. (2) To learn to write expressions in Mathematica, and to evaluate them at given point. (3) To learn to plot
Unit #11 : Integration by Parts, Average of a Function. Goals: Learning integration by parts. Computing the average value of a function.
 Unit #11 : Integration by Parts, Average of a Function Goals: Learning integration by parts. Computing the average value of a function. Integration Method - By Parts - 1 Integration by Parts So far in
Unit #11 : Integration by Parts, Average of a Function Goals: Learning integration by parts. Computing the average value of a function. Integration Method - By Parts - 1 Integration by Parts So far in
Problem #3 Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page Mark Sparks 2012
 Problem # Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 490 Mark Sparks 01 Finding Anti-derivatives of Polynomial-Type Functions If you had to explain to someone how to find
Problem # Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 490 Mark Sparks 01 Finding Anti-derivatives of Polynomial-Type Functions If you had to explain to someone how to find
ME 261: Numerical Analysis. ME 261: Numerical Analysis
 ME 261: Numerical Analysis 3. credit hours Prereq.: ME 163/ME 171 Course content Approximations and error types Roots of polynomials and transcendental equations Determinants and matrices Solution of linear
ME 261: Numerical Analysis 3. credit hours Prereq.: ME 163/ME 171 Course content Approximations and error types Roots of polynomials and transcendental equations Determinants and matrices Solution of linear
Errors in Computation
 Theory of Errors Content Errors in computation Absolute Error Relative Error Roundoff Errors Truncation Errors Floating Point Numbers Normalized Floating Point Numbers Roundoff Error in Floating Point
Theory of Errors Content Errors in computation Absolute Error Relative Error Roundoff Errors Truncation Errors Floating Point Numbers Normalized Floating Point Numbers Roundoff Error in Floating Point
Computer exercise 1 Introduction to Matlab.
 Chalmers-University of Gothenburg Department of Mathematical Sciences Probability, Statistics and Risk MVE300 Computer exercise 1 Introduction to Matlab. Understanding Distributions In this exercise, you
Chalmers-University of Gothenburg Department of Mathematical Sciences Probability, Statistics and Risk MVE300 Computer exercise 1 Introduction to Matlab. Understanding Distributions In this exercise, you
Review of Trigonometry
 Worksheet 8 Properties of Trigonometric Functions Section Review of Trigonometry This section reviews some of the material covered in Worksheets 8, and The reader should be familiar with the trig ratios,
Worksheet 8 Properties of Trigonometric Functions Section Review of Trigonometry This section reviews some of the material covered in Worksheets 8, and The reader should be familiar with the trig ratios,
Final Exam May 2, 2017
 Math 07 Calculus II Name: Final Exam May, 07 Circle the name of your instructor and, in the appropriate column, the name of your recitation leader. The second row is the time of your lecture. Radu Ledder
Math 07 Calculus II Name: Final Exam May, 07 Circle the name of your instructor and, in the appropriate column, the name of your recitation leader. The second row is the time of your lecture. Radu Ledder
University of California, Berkeley
 University of California, Berkeley FINAL EXAMINATION, Fall 2012 DURATION: 3 hours Department of Mathematics MATH 53 Multivariable Calculus Examiner: Sean Fitzpatrick Total: 100 points Family Name: Given
University of California, Berkeley FINAL EXAMINATION, Fall 2012 DURATION: 3 hours Department of Mathematics MATH 53 Multivariable Calculus Examiner: Sean Fitzpatrick Total: 100 points Family Name: Given
Practice Reading for Loops
 ME 350 Lab Exercise 3 Fall 07 for loops, fprintf, if constructs Practice Reading for Loops For each of the following code snippets, fill out the table to the right with the values displayed when the code
ME 350 Lab Exercise 3 Fall 07 for loops, fprintf, if constructs Practice Reading for Loops For each of the following code snippets, fill out the table to the right with the values displayed when the code
Hybrid Newton-Cotes Integrals
 Hybrid Newton-Cotes Integrals 1 Hybrid Newton-Cotes Integrals By Namir C. Shammas Introduction Newton-Cotes integration methods are numerical methods for integration. These methods calculate the estimate
Hybrid Newton-Cotes Integrals 1 Hybrid Newton-Cotes Integrals By Namir C. Shammas Introduction Newton-Cotes integration methods are numerical methods for integration. These methods calculate the estimate
Introduction to Matlab
 Introduction to Matlab Kristian Sandberg Department of Applied Mathematics University of Colorado Goal The goal with this worksheet is to give a brief introduction to the mathematical software Matlab.
Introduction to Matlab Kristian Sandberg Department of Applied Mathematics University of Colorado Goal The goal with this worksheet is to give a brief introduction to the mathematical software Matlab.
Chapter 3. Numerical Differentiation, Interpolation, and Integration. Instructor: Dr. Ming Ye
 Chapter 3 Numerical Differentiation, Interpolation, and Integration Instructor: Dr. Ming Ye Measuring Flow in Natural Channels Mean-Section Method (1) Divide the stream into a number of rectangular elements
Chapter 3 Numerical Differentiation, Interpolation, and Integration Instructor: Dr. Ming Ye Measuring Flow in Natural Channels Mean-Section Method (1) Divide the stream into a number of rectangular elements
Introduction to MATLAB
 Introduction to MATLAB Basics MATLAB is a high-level interpreted language, and uses a read-evaluate-print loop: it reads your command, evaluates it, then prints the answer. This means it works a lot like
Introduction to MATLAB Basics MATLAB is a high-level interpreted language, and uses a read-evaluate-print loop: it reads your command, evaluates it, then prints the answer. This means it works a lot like
Introduction to Matrix Operations in Matlab
 Introduction to Matrix Operations in Matlab Gerald W. Recktenwald Department of Mechanical Engineering Portland State University gerry@pdx.edu ME 350: Introduction to Matrix Operations in Matlab Overview
Introduction to Matrix Operations in Matlab Gerald W. Recktenwald Department of Mechanical Engineering Portland State University gerry@pdx.edu ME 350: Introduction to Matrix Operations in Matlab Overview
AC : MATHEMATICAL MODELING AND SIMULATION US- ING LABVIEW AND LABVIEW MATHSCRIPT
 AC 2012-4561: MATHEMATICAL MODELING AND SIMULATION US- ING LABVIEW AND LABVIEW MATHSCRIPT Dr. Nikunja Swain, South Carolina State University Nikunja Swain is a professor in the College of Science, Mathematics,
AC 2012-4561: MATHEMATICAL MODELING AND SIMULATION US- ING LABVIEW AND LABVIEW MATHSCRIPT Dr. Nikunja Swain, South Carolina State University Nikunja Swain is a professor in the College of Science, Mathematics,
LAB 1 General MATLAB Information 1
 LAB 1 General MATLAB Information 1 General: To enter a matrix: > type the entries between square brackets, [...] > enter it by rows with elements separated by a space or comma > rows are terminated by
LAB 1 General MATLAB Information 1 General: To enter a matrix: > type the entries between square brackets, [...] > enter it by rows with elements separated by a space or comma > rows are terminated by
0.1 Numerical Integration Rules Using Maple
 > restart; Numerical Integration Note: While reading this worksheet make sure that you re-execute each command by placing the cursor on the command line and pressing Enter. You should do this with every
> restart; Numerical Integration Note: While reading this worksheet make sure that you re-execute each command by placing the cursor on the command line and pressing Enter. You should do this with every
Classes of Real Numbers 1/2. The Real Line
 Classes of Real Numbers All real numbers can be represented by a line: 1/2 π 1 0 1 2 3 4 real numbers The Real Line { integers rational numbers non-integral fractions irrational numbers Rational numbers
Classes of Real Numbers All real numbers can be represented by a line: 1/2 π 1 0 1 2 3 4 real numbers The Real Line { integers rational numbers non-integral fractions irrational numbers Rational numbers
HSC Mathematics integration 5.3 numerical methods
 MD53a HSC Mathematics integration 5.3 numerical methods student name....................... Monday, 3 May 6 number о number о 3 6 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 a 8 b 9 9 a b a 3 b 4
MD53a HSC Mathematics integration 5.3 numerical methods student name....................... Monday, 3 May 6 number о number о 3 6 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 a 8 b 9 9 a b a 3 b 4
4.7 Approximate Integration
 4.7 Approximate Integration Some anti-derivatives are difficult to impossible to find. For example, 1 0 e x2 dx or 1 1 1 + x3 dx We came across this situation back in calculus I when we introduced the
4.7 Approximate Integration Some anti-derivatives are difficult to impossible to find. For example, 1 0 e x2 dx or 1 1 1 + x3 dx We came across this situation back in calculus I when we introduced the
Education Resources. This section is designed to provide examples which develop routine skills necessary for completion of this section.
 Education Resources Trigonometry Higher Mathematics Supplementary Resources Section A This section is designed to provide examples which develop routine skills necessary for completion of this section.
Education Resources Trigonometry Higher Mathematics Supplementary Resources Section A This section is designed to provide examples which develop routine skills necessary for completion of this section.
Chapter 1. Math review. 1.1 Some sets
 Chapter 1 Math review This book assumes that you understood precalculus when you took it. So you used to know how to do things like factoring polynomials, solving high school geometry problems, using trigonometric
Chapter 1 Math review This book assumes that you understood precalculus when you took it. So you used to know how to do things like factoring polynomials, solving high school geometry problems, using trigonometric
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE MA MATHEMATICS 1. AY2013/2014 : Semester 2. Time allowed : 2 hours
 Matriculation Number: NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE MA1505 - MATHEMATICS 1 AY2013/2014 : Semester 2 Time allowed : 2 hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. Write your matriculation number neatly in the
Matriculation Number: NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE MA1505 - MATHEMATICS 1 AY2013/2014 : Semester 2 Time allowed : 2 hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. Write your matriculation number neatly in the
Study Guide for Test 2
 Study Guide for Test Math 6: Calculus October, 7. Overview Non-graphing calculators will be allowed. You will need to know the following:. Set Pieces 9 4.. Trigonometric Substitutions (Section 7.).. Partial
Study Guide for Test Math 6: Calculus October, 7. Overview Non-graphing calculators will be allowed. You will need to know the following:. Set Pieces 9 4.. Trigonometric Substitutions (Section 7.).. Partial
Illustrative Mathematics. G-MG Paper Clip. Alignment 1: G-MG.A.3. This paper clip is just over 4 cm long.
 Illustrative Mathematics G-MG Paper Clip Alignment : G-MG.A.3 This paper clip is just over 4 cm long. How many paper clips like this may be made from a straight piece of wire 0 meters long? Commentary:
Illustrative Mathematics G-MG Paper Clip Alignment : G-MG.A.3 This paper clip is just over 4 cm long. How many paper clips like this may be made from a straight piece of wire 0 meters long? Commentary:
Computational Mathematics: Models, Methods and Analysis. Zhilin Li
 Computational Mathematics: Models, Methods and Analysis Zhilin Li Chapter 1 Introduction Why is this course important (motivations)? What is the role of this class in the problem solving process using
Computational Mathematics: Models, Methods and Analysis Zhilin Li Chapter 1 Introduction Why is this course important (motivations)? What is the role of this class in the problem solving process using
Interactive Computing with Matlab. Gerald W. Recktenwald Department of Mechanical Engineering Portland State University
 Interactive Computing with Matlab Gerald W. Recktenwald Department of Mechanical Engineering Portland State University gerry@me.pdx.edu Starting Matlab Double click on the Matlab icon, or on unix systems
Interactive Computing with Matlab Gerald W. Recktenwald Department of Mechanical Engineering Portland State University gerry@me.pdx.edu Starting Matlab Double click on the Matlab icon, or on unix systems
8 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation
 Applied Math Notes by R. J. LeVeque 8 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation 8. Pitfalls of high order interpolation Suppose we know the value of a function at several points on an interval and we wish to
Applied Math Notes by R. J. LeVeque 8 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation 8. Pitfalls of high order interpolation Suppose we know the value of a function at several points on an interval and we wish to
Collocation and optimization initialization
 Boundary Elements and Other Mesh Reduction Methods XXXVII 55 Collocation and optimization initialization E. J. Kansa 1 & L. Ling 2 1 Convergent Solutions, USA 2 Hong Kong Baptist University, Hong Kong
Boundary Elements and Other Mesh Reduction Methods XXXVII 55 Collocation and optimization initialization E. J. Kansa 1 & L. Ling 2 1 Convergent Solutions, USA 2 Hong Kong Baptist University, Hong Kong
Introduction to numerical algorithms
 Introduction to numerical algorithms Given an algebraic equation or formula, we may want to approximate the value, and while in calculus, we deal with equations or formulas that are well defined at each
Introduction to numerical algorithms Given an algebraic equation or formula, we may want to approximate the value, and while in calculus, we deal with equations or formulas that are well defined at each
HSC Mathematics - Extension 1. Workshop E2
 HSC Mathematics - Extension Workshop E Presented by Richard D. Kenderdine BSc, GradDipAppSc(IndMaths), SurvCert, MAppStat, GStat School of Mathematics and Applied Statistics University of Wollongong Moss
HSC Mathematics - Extension Workshop E Presented by Richard D. Kenderdine BSc, GradDipAppSc(IndMaths), SurvCert, MAppStat, GStat School of Mathematics and Applied Statistics University of Wollongong Moss
1. Practice the use of the C ++ repetition constructs of for, while, and do-while. 2. Use computer-generated random numbers.
 1 Purpose This lab illustrates the use of looping structures by introducing a class of programming problems called numerical algorithms. 1. Practice the use of the C ++ repetition constructs of for, while,
1 Purpose This lab illustrates the use of looping structures by introducing a class of programming problems called numerical algorithms. 1. Practice the use of the C ++ repetition constructs of for, while,
Wiswall, Applied Microeconometrics, Lecture Notes 1. In this section we focus on three very common computational tasks in applied
 Wiswall, Applied Microeconometrics, Lecture Notes 1 1 Numerical Methods In this section we focus on three very common computational tasks in applied microeconomics: i) calculating derivatives numerically
Wiswall, Applied Microeconometrics, Lecture Notes 1 1 Numerical Methods In this section we focus on three very common computational tasks in applied microeconomics: i) calculating derivatives numerically
Measurement and Geometry: Area and Volume of Geometric Figures and Objects *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m35023 1 Measurement and Geometry: and Volume of Geometric Figures and Objects * Wade Ellis Denny Burzynski This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m35023 1 Measurement and Geometry: and Volume of Geometric Figures and Objects * Wade Ellis Denny Burzynski This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Interpolation by Spline Functions
 Interpolation by Spline Functions Com S 477/577 Sep 0 007 High-degree polynomials tend to have large oscillations which are not the characteristics of the original data. To yield smooth interpolating curves
Interpolation by Spline Functions Com S 477/577 Sep 0 007 High-degree polynomials tend to have large oscillations which are not the characteristics of the original data. To yield smooth interpolating curves
Approximate First and Second Derivatives
 MTH229 Project 6 Exercises Approximate First and Second Derivatives NAME: SECTION: INSTRUCTOR: Exercise 1: Let f(x) = sin(x 2 ). We wish to find the derivative of f when x = π/4. a. Make a function m-file
MTH229 Project 6 Exercises Approximate First and Second Derivatives NAME: SECTION: INSTRUCTOR: Exercise 1: Let f(x) = sin(x 2 ). We wish to find the derivative of f when x = π/4. a. Make a function m-file
LINEARIZATION, NEWTON S METHOD BACKGROUND PREPARATIONS
 LINEARIZATION, NEWTON S METHOD COMPUTER SESSION D3 BACKGROUND Question 1 PREPARATIONS The session is divided into two parts. The first part involves experimenting in the Mathematics Laboratory and the
LINEARIZATION, NEWTON S METHOD COMPUTER SESSION D3 BACKGROUND Question 1 PREPARATIONS The session is divided into two parts. The first part involves experimenting in the Mathematics Laboratory and the
MATH 104 Sample problems for first exam - Fall MATH 104 First Midterm Exam - Fall (d) 256 3
 MATH 14 Sample problems for first exam - Fall 1 MATH 14 First Midterm Exam - Fall 1. Find the area between the graphs of y = 9 x and y = x + 1. (a) 4 (b) (c) (d) 5 (e) 4 (f) 81. A solid has as its base
MATH 14 Sample problems for first exam - Fall 1 MATH 14 First Midterm Exam - Fall 1. Find the area between the graphs of y = 9 x and y = x + 1. (a) 4 (b) (c) (d) 5 (e) 4 (f) 81. A solid has as its base
NUMERICAL INTEGRATION
 NUMERICAL INTEGRATION f(x) MISN-0-349 NUMERICAL INTEGRATION by Robert Ehrlich George Mason University 1. Numerical Integration Algorithms a. Introduction.............................................1 b.
NUMERICAL INTEGRATION f(x) MISN-0-349 NUMERICAL INTEGRATION by Robert Ehrlich George Mason University 1. Numerical Integration Algorithms a. Introduction.............................................1 b.
Getting Started with MATLAB
 APPENDIX B Getting Started with MATLAB MATLAB software is a computer program that provides the user with a convenient environment for many types of calculations in particular, those that are related to
APPENDIX B Getting Started with MATLAB MATLAB software is a computer program that provides the user with a convenient environment for many types of calculations in particular, those that are related to
Integration by parts, sometimes multiple times in the same problem. a. Show your choices. b. Evaluate the integral. a.
 Instructions Complete the homework with a pencil. Show your work. Use extra paper if necessary. Homework can be turned in as follows Turn in homework in person at KPC Scan and e-mail to UAACalculus@yahoo.com
Instructions Complete the homework with a pencil. Show your work. Use extra paper if necessary. Homework can be turned in as follows Turn in homework in person at KPC Scan and e-mail to UAACalculus@yahoo.com
Truncation Errors. Applied Numerical Methods with MATLAB for Engineers and Scientists, 2nd ed., Steven C. Chapra, McGraw Hill, 2008, Ch. 4.
 Chapter 4: Roundoff and Truncation Errors Applied Numerical Methods with MATLAB for Engineers and Scientists, 2nd ed., Steven C. Chapra, McGraw Hill, 2008, Ch. 4. 1 Outline Errors Accuracy and Precision
Chapter 4: Roundoff and Truncation Errors Applied Numerical Methods with MATLAB for Engineers and Scientists, 2nd ed., Steven C. Chapra, McGraw Hill, 2008, Ch. 4. 1 Outline Errors Accuracy and Precision
Definition. A Taylor series of a function f is said to represent function f, iff the error term converges to 0 for n going to infinity.
 Definition A Taylor series of a function f is said to represent function f, iff the error term converges to 0 for n going to infinity. 120202: ESM4A - Numerical Methods 32 f(x) = e x at point c = 0. Taylor
Definition A Taylor series of a function f is said to represent function f, iff the error term converges to 0 for n going to infinity. 120202: ESM4A - Numerical Methods 32 f(x) = e x at point c = 0. Taylor
We can conclude that if f is differentiable in an interval containing a, then. f(x) L(x) = f(a) + f (a)(x a).
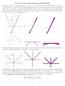 = sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
= sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
Numerical Integration
 Lecture 12: Numerical Integration (with a focus on Monte Carlo integration) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2015 Review: fundamental theorem of calculus Z b f(x)dx = F (b) F (a) a f(x) = d dx
Lecture 12: Numerical Integration (with a focus on Monte Carlo integration) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2015 Review: fundamental theorem of calculus Z b f(x)dx = F (b) F (a) a f(x) = d dx
2.0 MATLAB Fundamentals
 2.0 MATLAB Fundamentals 2.1 INTRODUCTION MATLAB is a computer program for computing scientific and engineering problems that can be expressed in mathematical form. The name MATLAB stands for MATrix LABoratory,
2.0 MATLAB Fundamentals 2.1 INTRODUCTION MATLAB is a computer program for computing scientific and engineering problems that can be expressed in mathematical form. The name MATLAB stands for MATrix LABoratory,
New Mexico Tech Hyd 510
 Numerics Motivation Modeling process (JLW) To construct a model we assemble and synthesize data and other information to formulate a conceptual model of the situation. The model is conditioned on the science
Numerics Motivation Modeling process (JLW) To construct a model we assemble and synthesize data and other information to formulate a conceptual model of the situation. The model is conditioned on the science
Math 2250 MATLAB TUTORIAL Fall 2005
 Math 2250 MATLAB TUTORIAL Fall 2005 Math Computer Lab The Mathematics Computer Lab is located in the T. Benny Rushing Mathematics Center (located underneath the plaza connecting JWB and LCB) room 155C.
Math 2250 MATLAB TUTORIAL Fall 2005 Math Computer Lab The Mathematics Computer Lab is located in the T. Benny Rushing Mathematics Center (located underneath the plaza connecting JWB and LCB) room 155C.
Univ. of Illinois Due Wednesday, Sept 13, 2017 Prof. Allen
 ECE 298JA NS #2 Version.28 April 22, 208 Fall 207 Univ. of Illinois Due Wednesday, Sept 3, 207 Prof. Allen Topic of this homework: Prime numbers, greatest common divisors, the continued fraction algorithm
ECE 298JA NS #2 Version.28 April 22, 208 Fall 207 Univ. of Illinois Due Wednesday, Sept 3, 207 Prof. Allen Topic of this homework: Prime numbers, greatest common divisors, the continued fraction algorithm
2.1.1 Fixed-Point (or Integer) Arithmetic
 x = approximation to true value x error = x x, relative error = x x. x 2.1.1 Fixed-Point (or Integer) Arithmetic A base 2 (base 10) fixed-point number has a fixed number of binary (decimal) places. 1.
x = approximation to true value x error = x x, relative error = x x. x 2.1.1 Fixed-Point (or Integer) Arithmetic A base 2 (base 10) fixed-point number has a fixed number of binary (decimal) places. 1.
Math 250A (Fall 2009) - Lab I: Estimate Integrals Numerically with Matlab. Due Date: Monday, September 21, INSTRUCTIONS
 Math 250A (Fall 2009) - Lab I: Estimate Integrals Numerically with Matlab Due Date: Monday, September 21, 2009 4:30 PM 1. INSTRUCTIONS The primary purpose of this lab is to understand how go about numerically
Math 250A (Fall 2009) - Lab I: Estimate Integrals Numerically with Matlab Due Date: Monday, September 21, 2009 4:30 PM 1. INSTRUCTIONS The primary purpose of this lab is to understand how go about numerically
AMS527: Numerical Analysis II
 AMS527: Numerical Analysis II A Brief Overview of Finite Element Methods Xiangmin Jiao SUNY Stony Brook Xiangmin Jiao SUNY Stony Brook AMS527: Numerical Analysis II 1 / 25 Overview Basic concepts Mathematical
AMS527: Numerical Analysis II A Brief Overview of Finite Element Methods Xiangmin Jiao SUNY Stony Brook Xiangmin Jiao SUNY Stony Brook AMS527: Numerical Analysis II 1 / 25 Overview Basic concepts Mathematical
Computational Methods. Sources of Errors
 Computational Methods Sources of Errors Manfred Huber 2011 1 Numerical Analysis / Scientific Computing Many problems in Science and Engineering can not be solved analytically on a computer Numeric solutions
Computational Methods Sources of Errors Manfred Huber 2011 1 Numerical Analysis / Scientific Computing Many problems in Science and Engineering can not be solved analytically on a computer Numeric solutions
Introduction to Engineering gii
 25.108 Introduction to Engineering gii Dr. Jay Weitzen Lecture Notes I: Introduction to Matlab from Gilat Book MATLAB - Lecture # 1 Starting with MATLAB / Chapter 1 Topics Covered: 1. Introduction. 2.
25.108 Introduction to Engineering gii Dr. Jay Weitzen Lecture Notes I: Introduction to Matlab from Gilat Book MATLAB - Lecture # 1 Starting with MATLAB / Chapter 1 Topics Covered: 1. Introduction. 2.
What is MATLAB? What is MATLAB? Programming Environment MATLAB PROGRAMMING. Stands for MATrix LABoratory. A programming environment
 What is MATLAB? MATLAB PROGRAMMING Stands for MATrix LABoratory A software built around vectors and matrices A great tool for numerical computation of mathematical problems, such as Calculus Has powerful
What is MATLAB? MATLAB PROGRAMMING Stands for MATrix LABoratory A software built around vectors and matrices A great tool for numerical computation of mathematical problems, such as Calculus Has powerful
Integration Using the Gauss Quadrature Rule - Convergence
 Integration Using the Gauss Quadrature Rule - Convergence 2004 Autar Kaw, Loubna Guennoun, University of South Florida, kaw@eng.usf.edu, http://numericalmethods.eng.usf.edu NOTE: This worksheet demonstrates
Integration Using the Gauss Quadrature Rule - Convergence 2004 Autar Kaw, Loubna Guennoun, University of South Florida, kaw@eng.usf.edu, http://numericalmethods.eng.usf.edu NOTE: This worksheet demonstrates
SOME PROPERTIES OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS. 5! x7 7! + = 6! + = 4! x6
 SOME PROPERTIES OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS PO-LAM YUNG We defined earlier the sine cosine by the following series: sin x = x x3 3! + x5 5! x7 7! + = k=0 cos x = 1 x! + x4 4! x6 6! + = k=0 ( 1) k x k+1
SOME PROPERTIES OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS PO-LAM YUNG We defined earlier the sine cosine by the following series: sin x = x x3 3! + x5 5! x7 7! + = k=0 cos x = 1 x! + x4 4! x6 6! + = k=0 ( 1) k x k+1
Math 98 - Introduction to MATLAB Programming. Fall Lecture 1
 Syllabus Instructor: Chris Policastro Class Website: https://math.berkeley.edu/~cpoli/math98/fall2016.html See website for 1 Class Number 2 Oce hours 3 Textbooks 4 Lecture schedule slides programs Syllabus
Syllabus Instructor: Chris Policastro Class Website: https://math.berkeley.edu/~cpoli/math98/fall2016.html See website for 1 Class Number 2 Oce hours 3 Textbooks 4 Lecture schedule slides programs Syllabus
