15-780: Problem Set #4
|
|
|
- Corey Singleton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 15-780: Problem Set #4 April 21, Image convolution [10 pts] In this question you will examine a basic property of discrete image convolution. Recall that convolving an m n image J R m n with a p r filters G R p r (for simplicity, we ll assume p and r are both odd) results in a new image (J G) R m p+1 n r+1 where p r (J G) i,j = J i+k 1,j+l 1 G k,l. k=1 l=1 For all the questions below, you can assume that J is large enough so that the (potentially multiple) convolutions all result in a valid return image (e.g., you can assume m > p and n > r anytime we perform a convolution) (a) Is discrete image convolution a commutative operation? That is, if we have two filters G 1 R p 1 r 1 and G 2 R p 2 r 2, does it hold that, using the definition above Prove or give a counterexample. (J G 1 ) G 2 = (J G 2 ) G 1? (b) For image processing, one of the less-than-ideal properties of the convolution as defined above is that the resulting images are smaller than the original image. One of the ways to solve this is by zero-padding the original image J with (p 1)/2 zeros above and below, and (r 1)/2 zeros on the sides. So for example, to convolve and image J R m n with a filter G R 3 5, we would first form the matrix J 11 J 1n J m1 J mn and then convolve this image with G. This results in a new image that is the same size as the original J. Denote this procedure (zero-padding the left-hand matrix, then convolving by ), is it the case that this operation is commutative? That is, does it hold that (J G 1 ) G 2 = (J G 2 ) G 1 for any J R m n, G 1 R p 1 r 1, and G 2 R p 2 r 2? Prove or give a counterexample. 1
2 2. Simple Temporal Network [20 pts] In this written assignment, you are to answer the following questions about a simple temporal network (STN): (a) Draw an STN using the notation on slide 18 of the scheduling lecture for the following set of tasks and constraints: There are three tasks: Task A, Task B, and Task C. Task A must start at tick 5 or later and has a duration of 10 ticks. Task B must start at least 15 ticks after Task A completes and has a duration of 20 ticks. Task C must start immediately after Task B ends, must complete before tick 75, and has a duration of 10 ticks. (b) In the above example, what are the earliest start time, latest start time, earliest finish time, and latest finish time for the three tasks? (c) How would you update the STN in the example above to reflect that the duration of Task B has changed to 50 ticks? What would happen when you make that change and why? (d) At a conceptual level, how is an all-pair-shortest-paths algorithm used to compute the lower bound for a time point? How is it used to compute the upper bound? (e) What type of schedule is supported by an STN? (Hint: note the type of schedule that provides all the bounds you provided in Question 2b for each constituent task) (f) Suppose that a timeline for resource R is represented in an STN as two tasks, A and B, with there being a <0, > constraint from the endpoint of A to the start point of B to represent the sequencing of the tasks resulting from using the same resource. How could the STN be used to check if a new task, C, can be inserted on the timeline for R between tasks A and B? 3. Planar revolute robot [20 pts] This questions will consider the the following robot (x e, y e ) l θ x which has a state represented by the pair (x, θ) where x denotes the posit on of the robot s base along the x axis, and θ denotes the angle of the arm joint with respect to the x axis. The parameters describing the robot are l, m b, m e, where l denotes the length of the arm, m 1 denotes the mass of the robot base represented as a point mass at (x, 0), and m 2 denotes the mass of the end effector represented as a point mass at the end effector location. 2
3 (a) Forward kinematics Denote the location of the end-effector by (x e, y e ). Write the equations for x e and y e as a function of the robot state (x, θ) and parameter l. (b) Jacobian Write an expression for instantaneous velocity of the end-effector (ẋ e, ẏ e ) as a function of state velocities (ẋ, θ). Also derive the Jacobian of the system, and write these equations in terms of this Jacobian. (c) Inverse kinematics Given a desired end-effector location (ẋ e, ẏ e ), determine an equation for the state variables (x, θ) to achieve this position. Discuss the scenarios where there may be zero, one, or multiple solutions to these equations. (d) Lagrangian Write down the the Lagrangian of the system L = T U in terms of the states and velocities of the system (x, θ, ẋ, θ). (e) Dynamics Use the Euler-Lagrange equations to write down the dynamics of the system in the form of the manipulator equations [ ] [ ] ẍ H(x, θ) + C(x, θ, ẋ, θ θ) F + G(x, θ) = τ where F denotes the force applied to the base along the x axis, and τ denotes the torque applied to the robot s joint. Note that not every function in the manipulator equations will depend on all the inputs listed (so for example C(x, θ, ẋ, θ) need not be a function of all of those variables), but these indicate the variables that each element could depend on. 4. Scheduling with Set-Up Dependencies [25 pts] In this programming assignment, you will develop a constraints-based scheduler for a modified version of the taxi-assignment problem, where a dispatcher assigns taxis to pick up fares at a particular time. In this version of the problem, all of the requests are known at the start of the day, and the job of the scheduler is to assign the cabs to service those requests. You will write the following function: def scheduler(duration_matrix,cabs,requests) where duration matrix is a list of lists providing the durations it takes to drive from any location in the input problem to any other location. Locations IDs are consecutive integers from 0 to one less than the number of locations. For example, if there are 3 locations, they are named 0, 1, and 2. The duration matrix is a list of entries for each location, where each entry is a list of durations from the location with the name of the index of the entry to all of the locations. For example, for 3 locations, the duration matrix might look like the following: [[0,2,3],[2,0,5],[3,5,0]]. In this example, the duration from location 0 to location 1 is 2, from location 0 to location 2 is 3, and from location 1 to location 2 is 5. In this example, the reverse durations are the same, but they need not be (think one-way streets). 3
4 cabs is a dict of cabs where the key is the name of the cab and the value is a positive integer representing the number of passengers the cab can carry. An example is { C1 : 3, C2 : 2, C3 : 4}. By definition, all cabs start at location 0. requests is a dict where the key is the ID of the request and the value is a list with the following form: [<number-of-passengers><pickup-time>,<pickup-location>,<dropofflocation>]. <number-of-passenger> is a positive integer. <pickup-time> is a non-negative integer. The start of the day is assumed to begin at time 0. The locations are, as noted above, non-negative integers. Your scheduler should return a dict that contains entries for all of the cabs. Each entry represents an itinerary for the cab and should have the form: [[<order-id>,<pickuptime>],...]. An example return value is { C1 : [[ a,10],[ b,15]], C2 : [[ d,30],[ e,40]]}. In this example, C1 picks up request a at time 10 and then request b at time 15, and C2 picks up request d at time 30 and request e at time 40. Your scheduler should enforce the following constraints: A cab servicing a request must be able to carry the number of passengers in the request. A cab must be at the pick-up location of a request to service a pick-up and at the drop-off location of the request to service the drop-off. While servicing a request, a cab must go directly from the pick-up location to the drop-off location and cannot service any other requests during that transit. All pickups and dropoffs have a duration of 5. A cab must be able to get to the pick-up location of each of its requests on its itinerary by their pick-up times. Your scheduler should find a solution by incrementally scheduling individual requests. Each request should be scheduled by searching the existing itineraries (or timelines) of the cabs to find the time slot that introduces the least amount of travel time. To find that slot, your scheduler should map down each timeline and examine the time slots where the cab is not directly servicing a request. For each candidate time slot, your scheduler should test whether or not the new request can be inserted without violating any of the pick-up times of the downstream requests. If it can be inserted, then the slot should be saved with the additional travel time added to the timeline. Your scheduler should assign the request to the time-slot that introduces the least additional travel. Your scheduler will be tested on a variety of input in which all requests should be feasible, i.e., schedulable. Your schedules will be checked to validate that they are consistent with the constraints. Rapidly-exploring Random Trees [25 pts] In this problem you will implement an RRT for a n-link manipulator. In particular, you will need to implement the function def rrt(theta_start, theta_goal, length, obs, epsilon): 4
5 This function takes as input three length-n lists, theta start, theta goal, and length (these lists specify the joint configuration of the of the start and goal locations, plus the length of each link respectively), a list of length-3 lists obs (each 3-element list describes the 2D location and radius of an obstacles in the form [x,y,r]), and scalar value epsilon. The function needs to return a list of length-n lists specifying a sequence of configurations for the manipulation such that 1) the first element of the path is equal to the start state and the end is equal to the goal; 2) no element of the path is colliding with any of the obstacles (we provide routines for collision detection); and 3) no two elements in the list are more than epsilon apart, i.e., np.linalg.norm(np.array(path[i]) - np.array(path[i+1))) <= epsilon Such a path represents a valid (collision free) trajectory from the start to the goal state. To implement this method, you should use a utility function included in the rrt.py template file: def check_collisions(theta, length, obs): # returns true if the manipulator defined by theta and length # (both lists of n elements) collides with any of the obstances # in obs (defined as an list of lists [x,y,r]) This function will determine if theta is colliding with any of the obstacles or not. You ll want to implement an RRT as described in the slides, where you ll additionally need to check that each node you add to the tree is non-colliding. Furthermore, to ensure that the tree actually reaches the goal, with some probably (say, 0.05) you will want to choose the goal state as the state to expand towards (x rand in the notation of the slides). You can terminate the RRT algorithm when you actually reach this goal at a node in the tree. Then, you ll need to backtrack through the tree you constructed to find the actual path from the start state to the goal state. You can represent the tree in many ways, but a simple way to do this is to maintain a list of tuples (theta,parent) where parent denotes the element in the list that the parent of this node; the initial (root) node can have a parent of -1. Since we ultimately just want to be able to trace back a path from the final element of the tree (which will be the goal), this simple list structure contains everything you need. Also included with the code is a routine draw scene that, given a set of configurations, will draw an animation of these configurations and the obstacle. This routine uses the matplotlib plotting library for Python, and it is not required for the assignment, but it can be helpful for debugging and for visualizing the results of your planning. Since the results of an RRT are inherently random, we can t provide correct paths returned from the tree, but the included test rrt.py file contains code that will validate whether or not a given path is valid (as mentioned before, this just means that it has to go from the start to the goal, have distances less than epsilon between successive points, and have no collisions). 5
Applications. Human and animal motion Robotics control Hair Plants Molecular motion
 Multibody dynamics Applications Human and animal motion Robotics control Hair Plants Molecular motion Generalized coordinates Virtual work and generalized forces Lagrangian dynamics for mass points
Multibody dynamics Applications Human and animal motion Robotics control Hair Plants Molecular motion Generalized coordinates Virtual work and generalized forces Lagrangian dynamics for mass points
Introduction to Robotics
 Université de Strasbourg Introduction to Robotics Bernard BAYLE, 2013 http://eavr.u-strasbg.fr/ bernard Modelling of a SCARA-type robotic manipulator SCARA-type robotic manipulators: introduction SCARA-type
Université de Strasbourg Introduction to Robotics Bernard BAYLE, 2013 http://eavr.u-strasbg.fr/ bernard Modelling of a SCARA-type robotic manipulator SCARA-type robotic manipulators: introduction SCARA-type
A simple example. Assume we want to find the change in the rotation angles to get the end effector to G. Effect of changing s
 CENG 732 Computer Animation This week Inverse Kinematics (continued) Rigid Body Simulation Bodies in free fall Bodies in contact Spring 2006-2007 Week 5 Inverse Kinematics Physically Based Rigid Body Simulation
CENG 732 Computer Animation This week Inverse Kinematics (continued) Rigid Body Simulation Bodies in free fall Bodies in contact Spring 2006-2007 Week 5 Inverse Kinematics Physically Based Rigid Body Simulation
Manipulator trajectory planning
 Manipulator trajectory planning Václav Hlaváč Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Department of Cybernetics Czech Republic http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~hlavac Courtesy to
Manipulator trajectory planning Václav Hlaváč Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Department of Cybernetics Czech Republic http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~hlavac Courtesy to
Forward kinematics and Denavit Hartenburg convention
 Forward kinematics and Denavit Hartenburg convention Prof. Enver Tatlicioglu Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Izmir Institute of Technology Chapter 5 Dr. Tatlicioglu (EEE@IYTE) EE463
Forward kinematics and Denavit Hartenburg convention Prof. Enver Tatlicioglu Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Izmir Institute of Technology Chapter 5 Dr. Tatlicioglu (EEE@IYTE) EE463
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO. Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences
 Page 1 UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam in INF3480 Introduction to Robotics Day of exam: May 31 st 2010 Exam hours: 3 hours This examination paper consists of 5 page(s).
Page 1 UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam in INF3480 Introduction to Robotics Day of exam: May 31 st 2010 Exam hours: 3 hours This examination paper consists of 5 page(s).
Optimization of a two-link Robotic Manipulator
 Optimization of a two-link Robotic Manipulator Zachary Renwick, Yalım Yıldırım April 22, 2016 Abstract Although robots are used in many processes in research and industry, they are generally not customized
Optimization of a two-link Robotic Manipulator Zachary Renwick, Yalım Yıldırım April 22, 2016 Abstract Although robots are used in many processes in research and industry, they are generally not customized
Robots are built to accomplish complex and difficult tasks that require highly non-linear motions.
 Path and Trajectory specification Robots are built to accomplish complex and difficult tasks that require highly non-linear motions. Specifying the desired motion to achieve a specified goal is often a
Path and Trajectory specification Robots are built to accomplish complex and difficult tasks that require highly non-linear motions. Specifying the desired motion to achieve a specified goal is often a
Inverse Kinematics. Given a desired position (p) & orientation (R) of the end-effector
 Inverse Kinematics Given a desired position (p) & orientation (R) of the end-effector q ( q, q, q ) 1 2 n Find the joint variables which can bring the robot the desired configuration z y x 1 The Inverse
Inverse Kinematics Given a desired position (p) & orientation (R) of the end-effector q ( q, q, q ) 1 2 n Find the joint variables which can bring the robot the desired configuration z y x 1 The Inverse
Introduction to Intelligent System ( , Fall 2017) Instruction for Assignment 2 for Term Project. Rapidly-exploring Random Tree and Path Planning
 Instruction for Assignment 2 for Term Project Rapidly-exploring Random Tree and Path Planning Introduction The objective of this semester s term project is to implement a path planning algorithm for a
Instruction for Assignment 2 for Term Project Rapidly-exploring Random Tree and Path Planning Introduction The objective of this semester s term project is to implement a path planning algorithm for a
Jane Li. Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute
 Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) Compare the testing methods for testing path segment and finding first
Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) Compare the testing methods for testing path segment and finding first
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
 Name Code Class Branch Page 1 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : ROBOTICS (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 0 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : A7055 : IV B. Tech I Semester : MECHANICAL
Name Code Class Branch Page 1 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : ROBOTICS (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 0 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : A7055 : IV B. Tech I Semester : MECHANICAL
Planning, Execution and Learning Application: Examples of Planning for Mobile Manipulation and Articulated Robots
 15-887 Planning, Execution and Learning Application: Examples of Planning for Mobile Manipulation and Articulated Robots Maxim Likhachev Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University Two Examples Planning
15-887 Planning, Execution and Learning Application: Examples of Planning for Mobile Manipulation and Articulated Robots Maxim Likhachev Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University Two Examples Planning
Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ x + 5y + 7z 9x + 3y + 11z
 Basic Linear Algebra Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ 1 5 ] 7 9 3 11 Often matrices are used to describe in a simpler way a series of linear equations.
Basic Linear Algebra Linear algebra deals with matrixes: two-dimensional arrays of values. Here s a matrix: [ 1 5 ] 7 9 3 11 Often matrices are used to describe in a simpler way a series of linear equations.
MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control. Lecture 3: Forward and Inverse Kinematics
 MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Forward and Inverse Kinematics Denavit-Hartenberg Convention Reading: SHV Chapter 3 Mechanical Engineering Hanz Richter, PhD MCE503 p.1/12 Aims of
MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Forward and Inverse Kinematics Denavit-Hartenberg Convention Reading: SHV Chapter 3 Mechanical Engineering Hanz Richter, PhD MCE503 p.1/12 Aims of
Serial Manipulator Statics. Robotics. Serial Manipulator Statics. Vladimír Smutný
 Serial Manipulator Statics Robotics Serial Manipulator Statics Vladimír Smutný Center for Machine Perception Czech Institute for Informatics, Robotics, and Cybernetics (CIIRC) Czech Technical University
Serial Manipulator Statics Robotics Serial Manipulator Statics Vladimír Smutný Center for Machine Perception Czech Institute for Informatics, Robotics, and Cybernetics (CIIRC) Czech Technical University
Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces 1/4
 Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces /4 Models of Robot Manipulation - EE 54 - Department of Electrical Engineering - University of Washington Kinematics Relations - Joint & Cartesian Spaces A robot
Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces /4 Models of Robot Manipulation - EE 54 - Department of Electrical Engineering - University of Washington Kinematics Relations - Joint & Cartesian Spaces A robot
Theory of Robotics and Mechatronics
 Theory of Robotics and Mechatronics Final Exam 19.12.2016 Question: 1 2 3 Total Points: 18 32 10 60 Score: Name: Legi-Nr: Department: Semester: Duration: 120 min 1 A4-sheet (double sided) of notes allowed
Theory of Robotics and Mechatronics Final Exam 19.12.2016 Question: 1 2 3 Total Points: 18 32 10 60 Score: Name: Legi-Nr: Department: Semester: Duration: 120 min 1 A4-sheet (double sided) of notes allowed
Kinematics, Kinematics Chains CS 685
 Kinematics, Kinematics Chains CS 685 Previously Representation of rigid body motion Two different interpretations - as transformations between different coord. frames - as operators acting on a rigid body
Kinematics, Kinematics Chains CS 685 Previously Representation of rigid body motion Two different interpretations - as transformations between different coord. frames - as operators acting on a rigid body
Robotics kinematics and Dynamics
 Robotics kinematics and Dynamics C. Sivakumar Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BSA Crescent Institute of Science and Technology 1 Robot kinematics KINEMATICS the analytical study
Robotics kinematics and Dynamics C. Sivakumar Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BSA Crescent Institute of Science and Technology 1 Robot kinematics KINEMATICS the analytical study
Planning in Mobile Robotics
 Planning in Mobile Robotics Part I. Miroslav Kulich Intelligent and Mobile Robotics Group Gerstner Laboratory for Intelligent Decision Making and Control Czech Technical University in Prague Tuesday 26/07/2011
Planning in Mobile Robotics Part I. Miroslav Kulich Intelligent and Mobile Robotics Group Gerstner Laboratory for Intelligent Decision Making and Control Czech Technical University in Prague Tuesday 26/07/2011
Inverse Kinematics (part 1) CSE169: Computer Animation Instructor: Steve Rotenberg UCSD, Winter 2018
 Inverse Kinematics (part 1) CSE169: Computer Animation Instructor: Steve Rotenberg UCSD, Winter 2018 Welman, 1993 Inverse Kinematics and Geometric Constraints for Articulated Figure Manipulation, Chris
Inverse Kinematics (part 1) CSE169: Computer Animation Instructor: Steve Rotenberg UCSD, Winter 2018 Welman, 1993 Inverse Kinematics and Geometric Constraints for Articulated Figure Manipulation, Chris
Chapter 3 Numerical Methods
 Chapter 3 Numerical Methods Part 1 3.1 Linearization and Optimization of Functions of Vectors 1 Problem Notation 2 Outline 3.1.1 Linearization 3.1.2 Optimization of Objective Functions 3.1.3 Constrained
Chapter 3 Numerical Methods Part 1 3.1 Linearization and Optimization of Functions of Vectors 1 Problem Notation 2 Outline 3.1.1 Linearization 3.1.2 Optimization of Objective Functions 3.1.3 Constrained
1 Trajectories. Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733. Figure 1: Robot control system.
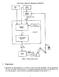 Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
PPGEE Robot Dynamics I
 PPGEE Electrical Engineering Graduate Program UFMG April 2014 1 Introduction to Robotics 2 3 4 5 What is a Robot? According to RIA Robot Institute of America A Robot is a reprogrammable multifunctional
PPGEE Electrical Engineering Graduate Program UFMG April 2014 1 Introduction to Robotics 2 3 4 5 What is a Robot? According to RIA Robot Institute of America A Robot is a reprogrammable multifunctional
Planar Robot Kinematics
 V. Kumar lanar Robot Kinematics The mathematical modeling of spatial linkages is quite involved. t is useful to start with planar robots because the kinematics of planar mechanisms is generally much simpler
V. Kumar lanar Robot Kinematics The mathematical modeling of spatial linkages is quite involved. t is useful to start with planar robots because the kinematics of planar mechanisms is generally much simpler
The Collision-free Workspace of the Tripteron Parallel Robot Based on a Geometrical Approach
 The Collision-free Workspace of the Tripteron Parallel Robot Based on a Geometrical Approach Z. Anvari 1, P. Ataei 2 and M. Tale Masouleh 3 1,2 Human-Robot Interaction Laboratory, University of Tehran
The Collision-free Workspace of the Tripteron Parallel Robot Based on a Geometrical Approach Z. Anvari 1, P. Ataei 2 and M. Tale Masouleh 3 1,2 Human-Robot Interaction Laboratory, University of Tehran
MTRX4700 Experimental Robotics
 MTRX 4700 : Experimental Robotics Lecture 2 Stefan B. Williams Slide 1 Course Outline Week Date Content Labs Due Dates 1 5 Mar Introduction, history & philosophy of robotics 2 12 Mar Robot kinematics &
MTRX 4700 : Experimental Robotics Lecture 2 Stefan B. Williams Slide 1 Course Outline Week Date Content Labs Due Dates 1 5 Mar Introduction, history & philosophy of robotics 2 12 Mar Robot kinematics &
a b c d a b c d e 5 e 7
 COMPSCI 230 Homework 9 Due on April 5, 2016 Work on this assignment either alone or in pairs. You may work with different partners on different assignments, but you can only have up to one partner for
COMPSCI 230 Homework 9 Due on April 5, 2016 Work on this assignment either alone or in pairs. You may work with different partners on different assignments, but you can only have up to one partner for
Robotics. SAAST Robotics Robot Arms
 SAAST Robotics 008 Robot Arms Vijay Kumar Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics and Professor of Computer and Information Science University of Pennsylvania Topics Types of robot arms
SAAST Robotics 008 Robot Arms Vijay Kumar Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics and Professor of Computer and Information Science University of Pennsylvania Topics Types of robot arms
Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces 1/4
 Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces /4 Advanced Robotic - MAE 6D - Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering - UCLA Kinematics Relations - Joint & Cartesian Spaces A robot is often used to manipulate
Jacobian: Velocities and Static Forces /4 Advanced Robotic - MAE 6D - Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering - UCLA Kinematics Relations - Joint & Cartesian Spaces A robot is often used to manipulate
Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates
 433-324 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
433-324 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
CMPUT 412 Motion Control Wheeled robots. Csaba Szepesvári University of Alberta
 CMPUT 412 Motion Control Wheeled robots Csaba Szepesvári University of Alberta 1 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements Kinematic/dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel
CMPUT 412 Motion Control Wheeled robots Csaba Szepesvári University of Alberta 1 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements Kinematic/dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates
 COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
CALCULATING TRANSFORMATIONS OF KINEMATIC CHAINS USING HOMOGENEOUS COORDINATES
 CALCULATING TRANSFORMATIONS OF KINEMATIC CHAINS USING HOMOGENEOUS COORDINATES YINGYING REN Abstract. In this paper, the applications of homogeneous coordinates are discussed to obtain an efficient model
CALCULATING TRANSFORMATIONS OF KINEMATIC CHAINS USING HOMOGENEOUS COORDINATES YINGYING REN Abstract. In this paper, the applications of homogeneous coordinates are discussed to obtain an efficient model
CS354 Computer Graphics Rotations and Quaternions
 Slide Credit: Don Fussell CS354 Computer Graphics Rotations and Quaternions Qixing Huang April 4th 2018 Orientation Position and Orientation The position of an object can be represented as a translation
Slide Credit: Don Fussell CS354 Computer Graphics Rotations and Quaternions Qixing Huang April 4th 2018 Orientation Position and Orientation The position of an object can be represented as a translation
Robotics I. March 27, 2018
 Robotics I March 27, 28 Exercise Consider the 5-dof spatial robot in Fig., having the third and fifth joints of the prismatic type while the others are revolute. z O x Figure : A 5-dof robot, with a RRPRP
Robotics I March 27, 28 Exercise Consider the 5-dof spatial robot in Fig., having the third and fifth joints of the prismatic type while the others are revolute. z O x Figure : A 5-dof robot, with a RRPRP
Trajectory planning in Cartesian space
 Robotics 1 Trajectory planning in Cartesian space Prof. Alessandro De Luca Robotics 1 1 Trajectories in Cartesian space! in general, the trajectory planning methods proposed in the joint space can be applied
Robotics 1 Trajectory planning in Cartesian space Prof. Alessandro De Luca Robotics 1 1 Trajectories in Cartesian space! in general, the trajectory planning methods proposed in the joint space can be applied
Kinematics. Kinematics analyzes the geometry of a manipulator, robot or machine motion. The essential concept is a position.
 Kinematics Kinematics analyzes the geometry of a manipulator, robot or machine motion. The essential concept is a position. 1/31 Statics deals with the forces and moments which are aplied on the mechanism
Kinematics Kinematics analyzes the geometry of a manipulator, robot or machine motion. The essential concept is a position. 1/31 Statics deals with the forces and moments which are aplied on the mechanism
PRACTICAL SESSION 4: FORWARD DYNAMICS. Arturo Gil Aparicio.
 PRACTICAL SESSION 4: FORWARD DYNAMICS Arturo Gil Aparicio arturo.gil@umh.es OBJECTIVES After this practical session, the student should be able to: Simulate the movement of a simple mechanism using the
PRACTICAL SESSION 4: FORWARD DYNAMICS Arturo Gil Aparicio arturo.gil@umh.es OBJECTIVES After this practical session, the student should be able to: Simulate the movement of a simple mechanism using the
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale Politecnico di Milano
 Trajectory optimization and real-time simulation for robotics applications Michele Attolico Pierangelo Masarati Paolo Mantegazza Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale Politecnico di Milano Multibody
Trajectory optimization and real-time simulation for robotics applications Michele Attolico Pierangelo Masarati Paolo Mantegazza Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale Politecnico di Milano Multibody
Homework #2 Posted: February 8 Due: February 15
 CS26N Motion Planning for Robots, Digital Actors and Other Moving Objects (Winter 2012) Homework #2 Posted: February 8 Due: February 15 How to complete this HW: First copy this file; then type your answers
CS26N Motion Planning for Robots, Digital Actors and Other Moving Objects (Winter 2012) Homework #2 Posted: February 8 Due: February 15 How to complete this HW: First copy this file; then type your answers
Jane Li. Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute
 Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) How to generate Delaunay Triangulation? (3 pts) Explain the difference
Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) How to generate Delaunay Triangulation? (3 pts) Explain the difference
Jane Li. Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute
 Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute We know how to describe the transformation of a single rigid object w.r.t. a single
Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute We know how to describe the transformation of a single rigid object w.r.t. a single
CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Robot Arms
 CS83: Fall 016: Robot Arms Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 0.11.016 REVIEW ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 0.11.016 3 General Control Scheme for Mobile
CS83: Fall 016: Robot Arms Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 0.11.016 REVIEW ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 0.11.016 3 General Control Scheme for Mobile
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO. Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam in INF4380 Introduction to Robotics Day of exam: 31 th May, 2017 Exam hours: 14:30, 4 hours This examination paper consists of 7 pages
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam in INF4380 Introduction to Robotics Day of exam: 31 th May, 2017 Exam hours: 14:30, 4 hours This examination paper consists of 7 pages
Kinematics of Wheeled Robots
 CSE 390/MEAM 40 Kinematics of Wheeled Robots Professor Vijay Kumar Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics University of Pennsylvania September 16, 006 1 Introduction In this chapter,
CSE 390/MEAM 40 Kinematics of Wheeled Robots Professor Vijay Kumar Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics University of Pennsylvania September 16, 006 1 Introduction In this chapter,
Kinematics of the Stewart Platform (Reality Check 1: page 67)
 MATH 5: Computer Project # - Due on September 7, Kinematics of the Stewart Platform (Reality Check : page 7) A Stewart platform consists of six variable length struts, or prismatic joints, supporting a
MATH 5: Computer Project # - Due on September 7, Kinematics of the Stewart Platform (Reality Check : page 7) A Stewart platform consists of six variable length struts, or prismatic joints, supporting a
Non-holonomic Planning
 Non-holonomic Planning Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Recap We have learned about RRTs. q new q init q near q rand But the standard
Non-holonomic Planning Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Recap We have learned about RRTs. q new q init q near q rand But the standard
10/25/2018. Robotics and automation. Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi. Chapter two. Introduction To Robot Manipulators
 Robotics and automation Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter two Introduction To Robot Manipulators 1 Robotic Industrial Manipulators A robot manipulator is an electronically controlled mechanism, consisting of
Robotics and automation Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter two Introduction To Robot Manipulators 1 Robotic Industrial Manipulators A robot manipulator is an electronically controlled mechanism, consisting of
Lecture 3.5: Sumary of Inverse Kinematics Solutions
 MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 3.5: Sumary of Inverse Kinematics Solutions Reading: SHV Sect.2.5.1, 3.3 Mechanical Engineering Hanz Richter, PhD MCE647 p.1/13 Inverse Orientation:
MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 3.5: Sumary of Inverse Kinematics Solutions Reading: SHV Sect.2.5.1, 3.3 Mechanical Engineering Hanz Richter, PhD MCE647 p.1/13 Inverse Orientation:
This week. CENG 732 Computer Animation. Warping an Object. Warping an Object. 2D Grid Deformation. Warping an Object.
 CENG 732 Computer Animation Spring 2006-2007 Week 4 Shape Deformation Animating Articulated Structures: Forward Kinematics/Inverse Kinematics This week Shape Deformation FFD: Free Form Deformation Hierarchical
CENG 732 Computer Animation Spring 2006-2007 Week 4 Shape Deformation Animating Articulated Structures: Forward Kinematics/Inverse Kinematics This week Shape Deformation FFD: Free Form Deformation Hierarchical
Jane Li. Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute
 Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute What are the DH parameters for describing the relative pose of the two frames?
Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute What are the DH parameters for describing the relative pose of the two frames?
Automated Parameterization of the Joint Space Dynamics of a Robotic Arm. Josh Petersen
 Automated Parameterization of the Joint Space Dynamics of a Robotic Arm Josh Petersen Introduction The goal of my project was to use machine learning to fully automate the parameterization of the joint
Automated Parameterization of the Joint Space Dynamics of a Robotic Arm Josh Petersen Introduction The goal of my project was to use machine learning to fully automate the parameterization of the joint
Lecture 3. Planar Kinematics
 Matthew T. Mason Mechanics of Manipulation Outline Where are we? s 1. Foundations and general concepts. 2.. 3. Spherical and spatial kinematics. Readings etc. The text: By now you should have read Chapter
Matthew T. Mason Mechanics of Manipulation Outline Where are we? s 1. Foundations and general concepts. 2.. 3. Spherical and spatial kinematics. Readings etc. The text: By now you should have read Chapter
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO. Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam in INF3480 Introduction to Robotics Day of exam: 31 th May, 2017 Exam hours: 14:30, 4 hours This examination paper consists of 6 pages
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam in INF3480 Introduction to Robotics Day of exam: 31 th May, 2017 Exam hours: 14:30, 4 hours This examination paper consists of 6 pages
Control of Industrial and Mobile Robots
 Control of Industrial and Mobile Robots Prof. Rocco, Bascetta January 29, 2019 name: university ID number: signature: Warnings This file consists of 10 pages (including cover). During the exam you are
Control of Industrial and Mobile Robots Prof. Rocco, Bascetta January 29, 2019 name: university ID number: signature: Warnings This file consists of 10 pages (including cover). During the exam you are
Humanoid Robotics. Inverse Kinematics and Whole-Body Motion Planning. Maren Bennewitz
 Humanoid Robotics Inverse Kinematics and Whole-Body Motion Planning Maren Bennewitz 1 Motivation Planning for object manipulation Whole-body motion to reach a desired goal configuration Generate a sequence
Humanoid Robotics Inverse Kinematics and Whole-Body Motion Planning Maren Bennewitz 1 Motivation Planning for object manipulation Whole-body motion to reach a desired goal configuration Generate a sequence
Final Exam Spring 2003
 .8 Final Exam Spring Name Instructions.. Please answer all questions in the exam books that are provided.. Please budget your time carefully. It is often a good idea to read the entire exam first, so that
.8 Final Exam Spring Name Instructions.. Please answer all questions in the exam books that are provided.. Please budget your time carefully. It is often a good idea to read the entire exam first, so that
Lecture 2: Kinematics of medical robotics
 ME 328: Medical Robotics Autumn 2016 Lecture 2: Kinematics of medical robotics Allison Okamura Stanford University kinematics The study of movement The branch of classical mechanics that describes the
ME 328: Medical Robotics Autumn 2016 Lecture 2: Kinematics of medical robotics Allison Okamura Stanford University kinematics The study of movement The branch of classical mechanics that describes the
CS 775: Advanced Computer Graphics. Lecture 3 : Kinematics
 CS 775: Advanced Computer Graphics Lecture 3 : Kinematics Traditional Cell Animation, hand drawn, 2D Lead Animator for keyframes http://animation.about.com/od/flashanimationtutorials/ss/flash31detanim2.htm
CS 775: Advanced Computer Graphics Lecture 3 : Kinematics Traditional Cell Animation, hand drawn, 2D Lead Animator for keyframes http://animation.about.com/od/flashanimationtutorials/ss/flash31detanim2.htm
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematic Control
 Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematic Control 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco Hutter,
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematic Control 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco Hutter,
15-494/694: Cognitive Robotics
 15-494/694: Cognitive Robotics Dave Touretzky Lecture 9: Path Planning with Rapidly-exploring Random Trees Navigating with the Pilot Image from http://www.futuristgerd.com/2015/09/10 Outline How is path
15-494/694: Cognitive Robotics Dave Touretzky Lecture 9: Path Planning with Rapidly-exploring Random Trees Navigating with the Pilot Image from http://www.futuristgerd.com/2015/09/10 Outline How is path
Jacobians. 6.1 Linearized Kinematics. Y: = k2( e6)
 Jacobians 6.1 Linearized Kinematics In previous chapters we have seen how kinematics relates the joint angles to the position and orientation of the robot's endeffector. This means that, for a serial robot,
Jacobians 6.1 Linearized Kinematics In previous chapters we have seen how kinematics relates the joint angles to the position and orientation of the robot's endeffector. This means that, for a serial robot,
Kinematic Control Algorithms for On-Line Obstacle Avoidance for Redundant Manipulators
 Kinematic Control Algorithms for On-Line Obstacle Avoidance for Redundant Manipulators Leon Žlajpah and Bojan Nemec Institute Jožef Stefan, Ljubljana, Slovenia, leon.zlajpah@ijs.si Abstract The paper deals
Kinematic Control Algorithms for On-Line Obstacle Avoidance for Redundant Manipulators Leon Žlajpah and Bojan Nemec Institute Jožef Stefan, Ljubljana, Slovenia, leon.zlajpah@ijs.si Abstract The paper deals
Lecture 18 Kinematic Chains
 CS 598: Topics in AI - Adv. Computational Foundations of Robotics Spring 2017, Rutgers University Lecture 18 Kinematic Chains Instructor: Jingjin Yu Outline What are kinematic chains? C-space for kinematic
CS 598: Topics in AI - Adv. Computational Foundations of Robotics Spring 2017, Rutgers University Lecture 18 Kinematic Chains Instructor: Jingjin Yu Outline What are kinematic chains? C-space for kinematic
Inverse Kinematics Programming Assignment
 Inverse Kinematics Programming Assignment CS 448D: Character Animation Due: Wednesday, April 29 th 11:59PM 1 Logistics In this programming assignment, you will implement a simple inverse kinematics solver
Inverse Kinematics Programming Assignment CS 448D: Character Animation Due: Wednesday, April 29 th 11:59PM 1 Logistics In this programming assignment, you will implement a simple inverse kinematics solver
Motion Control (wheeled robots)
 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground Definition of required motion -> speed control,
Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground Definition of required motion -> speed control,
Manipulation: Mechanisms, Grasping and Inverse Kinematics
 Manipulation: Mechanisms, Grasping and Inverse Kinematics RSS Lectures 14 & 15 Monday & Wednesday, 1 & 3 April 2013 Prof. Seth Teller Overview Mobility and Manipulation Manipulation Strategies Mechanism
Manipulation: Mechanisms, Grasping and Inverse Kinematics RSS Lectures 14 & 15 Monday & Wednesday, 1 & 3 April 2013 Prof. Seth Teller Overview Mobility and Manipulation Manipulation Strategies Mechanism
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE. (Semester I: 1999/2000) EE4304/ME ROBOTICS. October/November Time Allowed: 2 Hours
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.ENG. (Semester I: 1999/000) EE4304/ME445 - ROBOTICS October/November 1999 - Time Allowed: Hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: 1. This paper
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.ENG. (Semester I: 1999/000) EE4304/ME445 - ROBOTICS October/November 1999 - Time Allowed: Hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: 1. This paper
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Laboratory Project #1. Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino
 ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Laboratory Project #1 Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino The structure to be simulated 2 Lab Simulation Project #1: Pan-Tilt (PT) structure (2dof) This system is composed by two
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Laboratory Project #1 Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino The structure to be simulated 2 Lab Simulation Project #1: Pan-Tilt (PT) structure (2dof) This system is composed by two
autorob.github.io Inverse Kinematics UM EECS 398/598 - autorob.github.io
 autorob.github.io Inverse Kinematics Objective (revisited) Goal: Given the structure of a robot arm, compute Forward kinematics: predicting the pose of the end-effector, given joint positions. Inverse
autorob.github.io Inverse Kinematics Objective (revisited) Goal: Given the structure of a robot arm, compute Forward kinematics: predicting the pose of the end-effector, given joint positions. Inverse
Probabilistic Methods for Kinodynamic Path Planning
 16.412/6.834J Cognitive Robotics February 7 th, 2005 Probabilistic Methods for Kinodynamic Path Planning Based on Past Student Lectures by: Paul Elliott, Aisha Walcott, Nathan Ickes and Stanislav Funiak
16.412/6.834J Cognitive Robotics February 7 th, 2005 Probabilistic Methods for Kinodynamic Path Planning Based on Past Student Lectures by: Paul Elliott, Aisha Walcott, Nathan Ickes and Stanislav Funiak
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Laboratory Project #1. Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino
 ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Laboratory Project #1 Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino The structure to be simulated This structure simulates a pan-tilt camera, pointing down to a plane. It is also possible to
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Laboratory Project #1 Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino The structure to be simulated This structure simulates a pan-tilt camera, pointing down to a plane. It is also possible to
Inverse Kinematics of 6 DOF Serial Manipulator. Robotics. Inverse Kinematics of 6 DOF Serial Manipulator
 Inverse Kinematics of 6 DOF Serial Manipulator Robotics Inverse Kinematics of 6 DOF Serial Manipulator Vladimír Smutný Center for Machine Perception Czech Institute for Informatics, Robotics, and Cybernetics
Inverse Kinematics of 6 DOF Serial Manipulator Robotics Inverse Kinematics of 6 DOF Serial Manipulator Vladimír Smutný Center for Machine Perception Czech Institute for Informatics, Robotics, and Cybernetics
1498. End-effector vibrations reduction in trajectory tracking for mobile manipulator
 1498. End-effector vibrations reduction in trajectory tracking for mobile manipulator G. Pajak University of Zielona Gora, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Zielona Góra, Poland E-mail: g.pajak@iizp.uz.zgora.pl
1498. End-effector vibrations reduction in trajectory tracking for mobile manipulator G. Pajak University of Zielona Gora, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Zielona Góra, Poland E-mail: g.pajak@iizp.uz.zgora.pl
4 Kinematic Linkages. Chapter 4. Kinematic Linkages. Department of Computer Science and Engineering 4-1
 Kinematic Linkages 4-1 Introduction In describing an object s motion, it is often useful to relate it to another object. Consider, for eample a coordinate system centered at our sun in which the moon s
Kinematic Linkages 4-1 Introduction In describing an object s motion, it is often useful to relate it to another object. Consider, for eample a coordinate system centered at our sun in which the moon s
Table of Contents Introduction Historical Review of Robotic Orienting Devices Kinematic Position Analysis Instantaneous Kinematic Analysis
 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Background in Robotics 1 1.2 Robot Mechanics 1 1.2.1 Manipulator Kinematics and Dynamics 2 1.3 Robot Architecture 4 1.4 Robotic Wrists 4 1.5 Origins of the Carpal
Table of Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Background in Robotics 1 1.2 Robot Mechanics 1 1.2.1 Manipulator Kinematics and Dynamics 2 1.3 Robot Architecture 4 1.4 Robotic Wrists 4 1.5 Origins of the Carpal
Last 2 modules were about. What the other robot did : Robotics systems and science Lecture 15: Grasping and Manipulation
 6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 15: Grasping and Manipulation Lecture Notes Prepared by Daniela Rus EECS/MIT Spring 2009 What the robot did over Spring break Reading: Chapter3, Craig: Robotics
6.141: Robotics systems and science Lecture 15: Grasping and Manipulation Lecture Notes Prepared by Daniela Rus EECS/MIT Spring 2009 What the robot did over Spring break Reading: Chapter3, Craig: Robotics
ECE276B: Planning & Learning in Robotics Lecture 5: Configuration Space
 ECE276B: Planning & Learning in Robotics Lecture 5: Configuration Space Lecturer: Nikolay Atanasov: natanasov@ucsd.edu Teaching Assistants: Tianyu Wang: tiw161@eng.ucsd.edu Yongxi Lu: yol070@eng.ucsd.edu
ECE276B: Planning & Learning in Robotics Lecture 5: Configuration Space Lecturer: Nikolay Atanasov: natanasov@ucsd.edu Teaching Assistants: Tianyu Wang: tiw161@eng.ucsd.edu Yongxi Lu: yol070@eng.ucsd.edu
Lesson 1: Introduction to Pro/MECHANICA Motion
 Lesson 1: Introduction to Pro/MECHANICA Motion 1.1 Overview of the Lesson The purpose of this lesson is to provide you with a brief overview of Pro/MECHANICA Motion, also called Motion in this book. Motion
Lesson 1: Introduction to Pro/MECHANICA Motion 1.1 Overview of the Lesson The purpose of this lesson is to provide you with a brief overview of Pro/MECHANICA Motion, also called Motion in this book. Motion
3. Manipulator Kinematics. Division of Electronic Engineering Prof. Jaebyung Park
 3. Manipulator Kinematics Division of Electronic Engineering Prof. Jaebyung Park Introduction Kinematics Kinematics is the science of motion which treats motion without regard to the forces that cause
3. Manipulator Kinematics Division of Electronic Engineering Prof. Jaebyung Park Introduction Kinematics Kinematics is the science of motion which treats motion without regard to the forces that cause
Advanced Robotic Manipulation
 Advanced Robotic Manipulation Handout CS327A (Spring 2017) Problem Set #1 Due Wed, Apr 19 th Guidelines: This homework has both problem-solving and programming components. So please start early. In problems
Advanced Robotic Manipulation Handout CS327A (Spring 2017) Problem Set #1 Due Wed, Apr 19 th Guidelines: This homework has both problem-solving and programming components. So please start early. In problems
Redundancy Resolution by Minimization of Joint Disturbance Torque for Independent Joint Controlled Kinematically Redundant Manipulators
 56 ICASE :The Institute ofcontrol,automation and Systems Engineering,KOREA Vol.,No.1,March,000 Redundancy Resolution by Minimization of Joint Disturbance Torque for Independent Joint Controlled Kinematically
56 ICASE :The Institute ofcontrol,automation and Systems Engineering,KOREA Vol.,No.1,March,000 Redundancy Resolution by Minimization of Joint Disturbance Torque for Independent Joint Controlled Kinematically
Solutions to Some Examination Problems MATH 300 Monday 25 April 2016
 Name: s to Some Examination Problems MATH 300 Monday 25 April 2016 Do each of the following. (a) Let [0, 1] denote the unit interval that is the set of all real numbers r that satisfy the contraints that
Name: s to Some Examination Problems MATH 300 Monday 25 April 2016 Do each of the following. (a) Let [0, 1] denote the unit interval that is the set of all real numbers r that satisfy the contraints that
Trajectory Optimization
 Trajectory Optimization Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Recap We heard about RRT*, a sampling-based planning in high-dimensional cost
Trajectory Optimization Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering & Robotics Engineering http://users.wpi.edu/~zli11 Recap We heard about RRT*, a sampling-based planning in high-dimensional cost
Robot Inverse Kinematics Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Mechanical Engieering
 PR 5 Robot Dynamics & Control /8/7 PR 5: Robot Dynamics & Control Robot Inverse Kinematics Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Mechanical Engieering The Inverse Kinematics The determination of all possible
PR 5 Robot Dynamics & Control /8/7 PR 5: Robot Dynamics & Control Robot Inverse Kinematics Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Mechanical Engieering The Inverse Kinematics The determination of all possible
Functions of Several Variables
 Jim Lambers MAT 280 Spring Semester 2009-10 Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Section 11.1 in Stewart and Section 2.1 in Marsden and Tromba. Functions of Several Variables Multi-variable calculus
Jim Lambers MAT 280 Spring Semester 2009-10 Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Section 11.1 in Stewart and Section 2.1 in Marsden and Tromba. Functions of Several Variables Multi-variable calculus
Kinematic Model of Robot Manipulators
 Kinematic Model of Robot Manipulators Claudio Melchiorri Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Energia Elettrica e dell Informazione (DEI) Università di Bologna email: claudio.melchiorri@unibo.it C. Melchiorri
Kinematic Model of Robot Manipulators Claudio Melchiorri Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Energia Elettrica e dell Informazione (DEI) Università di Bologna email: claudio.melchiorri@unibo.it C. Melchiorri
COLLISION-FREE TRAJECTORY PLANNING FOR MANIPULATORS USING GENERALIZED PATTERN SEARCH
 ISSN 1726-4529 Int j simul model 5 (26) 4, 145-154 Original scientific paper COLLISION-FREE TRAJECTORY PLANNING FOR MANIPULATORS USING GENERALIZED PATTERN SEARCH Ata, A. A. & Myo, T. R. Mechatronics Engineering
ISSN 1726-4529 Int j simul model 5 (26) 4, 145-154 Original scientific paper COLLISION-FREE TRAJECTORY PLANNING FOR MANIPULATORS USING GENERALIZED PATTERN SEARCH Ata, A. A. & Myo, T. R. Mechatronics Engineering
10/11/07 1. Motion Control (wheeled robots) Representing Robot Position ( ) ( ) [ ] T
![10/11/07 1. Motion Control (wheeled robots) Representing Robot Position ( ) ( ) [ ] T 10/11/07 1. Motion Control (wheeled robots) Representing Robot Position ( ) ( ) [ ] T](/thumbs/79/79288754.jpg) 3 3 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Introduction: Mobile Robot Kinematics Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground
3 3 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Introduction: Mobile Robot Kinematics Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground
Exercise 1: Kinematics of the ABB IRB 120
 Exercise 1: Kinematics of the ABB IRB 120 Marco Hutter, Michael Blösch, Dario Bellicoso, Samuel Bachmann October 2, 2015 Abstract In this exercise you learn how to calculate the forward and inverse kinematics
Exercise 1: Kinematics of the ABB IRB 120 Marco Hutter, Michael Blösch, Dario Bellicoso, Samuel Bachmann October 2, 2015 Abstract In this exercise you learn how to calculate the forward and inverse kinematics
CSE 4360 / Homework 1- Fall 2018
 CSE 4360 / 5364 Homework 1- Fall 2018 Due Date: Oct. 8 2018 Problems marked with are mandatory only for students of CSE 5364 but will be graded for extra credit for students of CSE 4360. Forward and Inverse
CSE 4360 / 5364 Homework 1- Fall 2018 Due Date: Oct. 8 2018 Problems marked with are mandatory only for students of CSE 5364 but will be graded for extra credit for students of CSE 4360. Forward and Inverse
Simulation-Based Design of Robotic Systems
 Simulation-Based Design of Robotic Systems Shadi Mohammad Munshi* & Erik Van Voorthuysen School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052 shadimunshi@hotmail.com,
Simulation-Based Design of Robotic Systems Shadi Mohammad Munshi* & Erik Van Voorthuysen School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052 shadimunshi@hotmail.com,
Advances in Engineering Research, volume 123 2nd International Conference on Materials Science, Machinery and Energy Engineering (MSMEE 2017)
 Advances in Engineering Research, volume nd International Conference on Materials Science, Machinery and Energy Engineering MSMEE Kinematics Simulation of DOF Manipulator Guangbing Bao,a, Shizhao Liu,b,
Advances in Engineering Research, volume nd International Conference on Materials Science, Machinery and Energy Engineering MSMEE Kinematics Simulation of DOF Manipulator Guangbing Bao,a, Shizhao Liu,b,
Kinematics and Orientations
 Kinematics and Orientations Hierarchies Forward Kinematics Transformations (review) Euler angles Quaternions Yaw and evaluation function for assignment 2 Building a character Just translate, rotate, and
Kinematics and Orientations Hierarchies Forward Kinematics Transformations (review) Euler angles Quaternions Yaw and evaluation function for assignment 2 Building a character Just translate, rotate, and
CSC 418/2504 Computer Graphics, Winter 2012 Assignment 1 (10% of course grade)
 CSC 418/2504 Computer Graphics, Winter 2012 Assignment 1 (10% of course grade) Part A [50 marks in total] Due 11:59pm onwed., Feb. 8, 2012. Below are 4 exercises covering di erent topics from the first
CSC 418/2504 Computer Graphics, Winter 2012 Assignment 1 (10% of course grade) Part A [50 marks in total] Due 11:59pm onwed., Feb. 8, 2012. Below are 4 exercises covering di erent topics from the first
Table of Contents. Chapter 1. Modeling and Identification of Serial Robots... 1 Wisama KHALIL and Etienne DOMBRE
 Chapter 1. Modeling and Identification of Serial Robots.... 1 Wisama KHALIL and Etienne DOMBRE 1.1. Introduction... 1 1.2. Geometric modeling... 2 1.2.1. Geometric description... 2 1.2.2. Direct geometric
Chapter 1. Modeling and Identification of Serial Robots.... 1 Wisama KHALIL and Etienne DOMBRE 1.1. Introduction... 1 1.2. Geometric modeling... 2 1.2.1. Geometric description... 2 1.2.2. Direct geometric
Chapter 4 Dynamics. Part Constrained Kinematics and Dynamics. Mobile Robotics - Prof Alonzo Kelly, CMU RI
 Chapter 4 Dynamics Part 2 4.3 Constrained Kinematics and Dynamics 1 Outline 4.3 Constrained Kinematics and Dynamics 4.3.1 Constraints of Disallowed Direction 4.3.2 Constraints of Rolling without Slipping
Chapter 4 Dynamics Part 2 4.3 Constrained Kinematics and Dynamics 1 Outline 4.3 Constrained Kinematics and Dynamics 4.3.1 Constraints of Disallowed Direction 4.3.2 Constraints of Rolling without Slipping
1. Introduction 1 2. Mathematical Representation of Robots
 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Brief History 1 1.3 Types of Robots 7 1.4 Technology of Robots 9 1.5 Basic Principles in Robotics 12 1.6 Notation 15 1.7 Symbolic Computation and Numerical Analysis
1. Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Brief History 1 1.3 Types of Robots 7 1.4 Technology of Robots 9 1.5 Basic Principles in Robotics 12 1.6 Notation 15 1.7 Symbolic Computation and Numerical Analysis
