Four sources of packet delay
|
|
|
- Nickolas Sullivan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Outline q Major Internet components q Network architecture and protocols q Switching strategies q Internet protocol stack, history q to network performance Four sources of packet delay q 1. nodal processing: v check bit errors v determine output link q 2. queueing v time waiting at output link for transmission v depends on congestion level of router A transmission propagation B nodal processing queueing
2 Delay in packet-switched networks 3. Transmission delay: q R=link bit rate (bps) q L=packet length (bits) q time to send bits into link = L/R 4. Propagation delay: q d = length of physical link q s = propagation speed in medium (~2x10 8 m/sec) q propagation delay = d/s A transmission propagation B nodal processing queueing How many bits fit on the link?
3 How do loss and delay occur? packets queue in router buffers q packet arrival rate to link exceeds output link capacity q packets queue, wait for turn packet being transmitted (delay) A B packets queueing (delay) free (available) buffers: arriving packets dropped (loss) if no free buffers Nodal delay d = d + d + d + d nodal proc queue trans prop q d proc = processing delay v typically a few microsecs or less q d queue = queueing delay v depends on congestion q d trans = transmission delay v = L/R, significant for low-speed links q d prop = propagation delay v a few microsecs to hundreds of msecs
4 Queueing delay (revisited) q R=link bandwidth (bps) q L=packet length (bits) q a=average packet arrival rate (over long period of time) Average traffic intensity = La/R q La/R ~ 0: average queueing delay small q La/R -> 1: delays become large q La/R > 1: more work arriving than can be serviced, average delay infinite! q NOTE: this does not mean that La cannot exceed R for limited periods of time Packet switching delay example
5 Packet loss q queue (aka buffer) preceding link in buffer has finite capacity q packet arriving to full queue dropped (aka lost) q lost packet may be retransmitted by previous node, by source end system, or not at all A buffer (waiting area) packet being transmitted B packet arriving to full buffer is lost 1-11 Packet loss q Another source of packet loss is noise on the communication channel q Today in wired networks, noise often is not a significant issue q However, in wireless networks it is a HUGE issue q How many transmissions needed to get a frame across the channel?
6 Example Throughput q throughput: rate (bits/time unit) at which bits transferred between sender/receiver v instantaneous: rate at given point in time v average: rate over longer period of time server server, sends with bits (fluid) file of into F bits pipe to send to client pipe link that capacity can carry fluid R s bits/sec at rate R s bits/sec) pipe link that capacity can carry Rfluid c bits/sec at rate R c bits/sec)
7 Throughput (cont.) q R s < R c What is average end-end throughput? R s bits/sec R c bits/sec q R s > R c What is average end-end throughput? R s bits/sec R c bits/sec bottleneck link link on end-end path that constrains end-end throughput Throughput: Internet scenario q per-connection end-end throughput: min(r c,r s,r/10) q in practice: R c or R s is often bottleneck R s R s R s R R c R c R c 10 connections (fairly) share backbone bottleneck link R bits/sec
8 Summary q We have covered a lot of material in this introductory section v Major Internet components v Network architecture and protocols v Switching strategies v Internet protocol stack, history v to network performance q Now we are equipped to work our way down the Internet protocol stack!
end systems, access networks, links circuit switching, packet switching, network structure
 Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 Network core circuit switching, packet switching, network structure 1.4 Delay, loss and throughput
Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 Network core circuit switching, packet switching, network structure 1.4 Delay, loss and throughput
Chapter 1. Computer Networks and the Internet
 Chapter 1 Computer Networks and the Internet Internet traffic What s the Internet? (hardware) PC server wireless laptop cellular handheld wired links millions of connected computing devices: hosts = end
Chapter 1 Computer Networks and the Internet Internet traffic What s the Internet? (hardware) PC server wireless laptop cellular handheld wired links millions of connected computing devices: hosts = end
Computer Networks & Security 2016/2017
 Computer Networks & Security 2016/2017 Protocol Layering (02) Dr. Tanir Ozcelebi Courtesy: Kurose & Ross TU/e Computer Science Security and Embedded Networked Systems Your typical lunch Slide 2 What is
Computer Networks & Security 2016/2017 Protocol Layering (02) Dr. Tanir Ozcelebi Courtesy: Kurose & Ross TU/e Computer Science Security and Embedded Networked Systems Your typical lunch Slide 2 What is
CS 4390 Computer Networks
 CS 4390 Computer Networks UT D application transport network data link physical Session 04 Packet Switching dapted from Computer Networking a Top-Down pproach 1996-2012 by J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, ll
CS 4390 Computer Networks UT D application transport network data link physical Session 04 Packet Switching dapted from Computer Networking a Top-Down pproach 1996-2012 by J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, ll
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these Powerpoint slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations;
Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these Powerpoint slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations;
Computer Networking Introduction
 Computer Networking Introduction Halgurd S. Maghdid Software Engineering Department Koya University-Koya, Kurdistan-Iraq Lecture No.2 Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 what is the Inter? 1.2 work edge end systems,
Computer Networking Introduction Halgurd S. Maghdid Software Engineering Department Koya University-Koya, Kurdistan-Iraq Lecture No.2 Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 what is the Inter? 1.2 work edge end systems,
Overview on the Internet the current and future telecommunication network
 Overview on the Internet the current and future telecommunication network Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 5 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, April 2009. Introduction 1-1 Introduction
Overview on the Internet the current and future telecommunication network Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 5 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, April 2009. Introduction 1-1 Introduction
Chapter I: Introduction
 Chapter I: Introduction UG3 Computer Communications & Networks (COMN) Myungjin Lee myungjin.lee@ed.ac.uk Slides copyright of Kurose and Ross The work core mesh of interconnected routers packet-switching:
Chapter I: Introduction UG3 Computer Communications & Networks (COMN) Myungjin Lee myungjin.lee@ed.ac.uk Slides copyright of Kurose and Ross The work core mesh of interconnected routers packet-switching:
Last Lecture. Nuts-and-bolts description of the Internet. ! The topology. ! The communication links. ! The core. ! The edge
 Last Lecture Nuts-and-bolts description of the Internet! The topology! The core! The edge! The communication links SUNY AT BUFFALO; CSE489/589 MODERN NETWORKING CONCEPTS; Fall 2010; INSTRUCTOR: HUNG Q.
Last Lecture Nuts-and-bolts description of the Internet! The topology! The core! The edge! The communication links SUNY AT BUFFALO; CSE489/589 MODERN NETWORKING CONCEPTS; Fall 2010; INSTRUCTOR: HUNG Q.
CSC 401 Data and Computer Communications Networks
 CSC 401 Data and Computer Communications Networks Computer Networks and The Internet Sec 1.4-1.5 Prof. Lina Battestilli Outline Computer Networks and the Internet (Ch 1) 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 network
CSC 401 Data and Computer Communications Networks Computer Networks and The Internet Sec 1.4-1.5 Prof. Lina Battestilli Outline Computer Networks and the Internet (Ch 1) 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 network
Chapter 1 Computer Networks and the Internet
 CSB051 Computer Networks 電腦網路 Chapter 1 Computer Networks and the Internet 吳俊興 國立高雄大學資訊工程學系 Outline 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge 1.3 Network core 1.4 Access networks and physical media 1.5
CSB051 Computer Networks 電腦網路 Chapter 1 Computer Networks and the Internet 吳俊興 國立高雄大學資訊工程學系 Outline 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge 1.3 Network core 1.4 Access networks and physical media 1.5
Packet-switching: store-and-forward
 Packet-switching: store-and-forward L R R R Takes L/R seconds to transmit (push out) packet of L bits on to link or R bps Entire packet must arrive at router before it can be transmitted on next link:
Packet-switching: store-and-forward L R R R Takes L/R seconds to transmit (push out) packet of L bits on to link or R bps Entire packet must arrive at router before it can be transmitted on next link:
Computer Networks Chapter 1: Introduction. Introduction
 Computer Networks Chapter 1: Introduction CSC 249 January 25, 2018 Introduction What is the Inter? Define work edge: hosts,, physical media Define the work core & Inter structure First glimpse at the layers
Computer Networks Chapter 1: Introduction CSC 249 January 25, 2018 Introduction What is the Inter? Define work edge: hosts,, physical media Define the work core & Inter structure First glimpse at the layers
CMPE 150/L : Introduction to Computer Networks. Chen Qian Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 3
 CMPE 150/L : Introduction to Computer Networks Chen Qian Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 3 1 No Class 1/23 (next Tuesday) Dr. Qian absent to serve a duty for US Department of Energy
CMPE 150/L : Introduction to Computer Networks Chen Qian Computer Engineering UCSC Baskin Engineering Lecture 3 1 No Class 1/23 (next Tuesday) Dr. Qian absent to serve a duty for US Department of Energy
Computer Networks and the Internet. CMPS 4750/6750: Computer Networks
 Computer Networks and the Inter CMPS 4750/6750: Computer Networks Outline What Is the Inter? Access Networks Packet Switching and Circuit Switching A closer look at delay, loss, and throughput Interconnection
Computer Networks and the Inter CMPS 4750/6750: Computer Networks Outline What Is the Inter? Access Networks Packet Switching and Circuit Switching A closer look at delay, loss, and throughput Interconnection
Network core and metrics
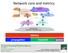 Network core and metrics latency propaga-on transmit queue Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley Some materials copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and
Network core and metrics latency propaga-on transmit queue Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley Some materials copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and
Computer Networks. Wenzhong Li. Nanjing University
 Computer Networks Wenzhong Li Nanjing University 1 Chapter 2. Direct Link Networks Link Service and Framing Error Detection and Reliable Transmission HDLC, PPP, and SONET Token Ring Ethernet Bridges and
Computer Networks Wenzhong Li Nanjing University 1 Chapter 2. Direct Link Networks Link Service and Framing Error Detection and Reliable Transmission HDLC, PPP, and SONET Token Ring Ethernet Bridges and
CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018
 CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018 Introduction II Dmitri Loguinov Texas A& University January 25, 2018 Original slides copyright 1996-2004 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross 1 Chapter
CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018 Introduction II Dmitri Loguinov Texas A& University January 25, 2018 Original slides copyright 1996-2004 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross 1 Chapter
Lecture 2 Communication services The Trasport Layer. Antonio Cianfrani DIET Department Networking Group netlab.uniroma1.it
 Lecture 2 Communication services The Trasport Layer Antonio Cianfrani DIET Department Networking Group netlab.uniroma1.it The structure edge: applications and hosts core: routers of s access s, media:
Lecture 2 Communication services The Trasport Layer Antonio Cianfrani DIET Department Networking Group netlab.uniroma1.it The structure edge: applications and hosts core: routers of s access s, media:
Outline. Computer Communication and Networks. The Network Core. Components of the Internet. The Network Core Packet Switching Circuit Switching
 Outline Computer Communication and Networks 1 Department of Computer Science & Information Technology University of Balochistan Lecture 03 1/26 2/26 Two major components The mesh of packet switches and
Outline Computer Communication and Networks 1 Department of Computer Science & Information Technology University of Balochistan Lecture 03 1/26 2/26 Two major components The mesh of packet switches and
COMP 562: Advanced Topics in Networking
 COMP 562: Advanced Topics in Networking Qian Zhang Spring 2009 HKUST Introduction 1-1 Course Info Instructor: Qian Zhang www.cs.ust.hk/~qianzh Course web site http://www.cs.ust.hk/~qianzh/comp562 2009/comp562
COMP 562: Advanced Topics in Networking Qian Zhang Spring 2009 HKUST Introduction 1-1 Course Info Instructor: Qian Zhang www.cs.ust.hk/~qianzh Course web site http://www.cs.ust.hk/~qianzh/comp562 2009/comp562
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Introduction
 CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Introduction Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge 1.3 Network core 1.4 Delay & loss in packet-switched networks 1.5
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Introduction Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge 1.3 Network core 1.4 Delay & loss in packet-switched networks 1.5
Internet Architecture & Performance. What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view
 Internet Architecture & Performance Internet, Connection, Protocols, Performance measurements What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end systems pc s workstations,
Internet Architecture & Performance Internet, Connection, Protocols, Performance measurements What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end systems pc s workstations,
Slides are an edited mashup of two books
 Slides are an edited mashup of two books Computer Networks: A Systems Approach, 5e Larry L. Peterson and Bruce S. Davie Copyright 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved Computer Networking: A Top Down
Slides are an edited mashup of two books Computer Networks: A Systems Approach, 5e Larry L. Peterson and Bruce S. Davie Copyright 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved Computer Networking: A Top Down
Introduction to Computer Networks. Roadmap
 Introduction to Computer Networks Miguel A. Labrador Department of Computer Science & Engineering labrador@csee.usf.edu http://www.csee.usf.edu/~labrador 1 Dr. Miguel A. Labrador Roadmap 1.1 What is the
Introduction to Computer Networks Miguel A. Labrador Department of Computer Science & Engineering labrador@csee.usf.edu http://www.csee.usf.edu/~labrador 1 Dr. Miguel A. Labrador Roadmap 1.1 What is the
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Internetworking Technology -
 Internetworking Technology - Chapter 1 Computer Networks and the Internet (Cont.) Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge 1.3 Network core 1.4 Network access and physical media 1.5
Internetworking Technology - Chapter 1 Computer Networks and the Internet (Cont.) Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge 1.3 Network core 1.4 Network access and physical media 1.5
Course on Computer Communication and Networks. Lecture 2 Chapter 1: Introduction: Part B: Network structure, performance, security prelude
 Course on Computer Communication and Networks Lecture 2 Chapter 1: Introduction: Part B: Network structure, performance, security prelude CTH EDA344/GU DIT 420 Based on the book Computer Networking: A
Course on Computer Communication and Networks Lecture 2 Chapter 1: Introduction: Part B: Network structure, performance, security prelude CTH EDA344/GU DIT 420 Based on the book Computer Networking: A
CS 3516: Advanced Computer Networks
 Welcome to CS 3516: Advanced Computer Networks Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 9:00am 9:50am M, T, R, and F Location: Fuller 320 Fall 2017 A-term 1 Some slides are originally from the course materials of the textbook
Welcome to CS 3516: Advanced Computer Networks Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 9:00am 9:50am M, T, R, and F Location: Fuller 320 Fall 2017 A-term 1 Some slides are originally from the course materials of the textbook
Chapter 1: roadmap parte B
 Chapter 1: roadmap parte B 1.1 what is the Internet? 1.2 network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 network core packet switching, circuit switching, network structure 1.4 delay, loss, throughput
Chapter 1: roadmap parte B 1.1 what is the Internet? 1.2 network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 network core packet switching, circuit switching, network structure 1.4 delay, loss, throughput
CC451 Computer Networks
 CC451 Computer Networks Lecture 2 Introduction (cont d) Introduction 1-1 Network Core: Packet Switching each end-end data stream divided into packets user A, B packets share network resources each packet
CC451 Computer Networks Lecture 2 Introduction (cont d) Introduction 1-1 Network Core: Packet Switching each end-end data stream divided into packets user A, B packets share network resources each packet
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Slightly adapted from -- Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 5 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, April 2009. All material copyright 1996-2009 J.F Kurose and
Chapter 1 Introduction Slightly adapted from -- Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 5 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, April 2009. All material copyright 1996-2009 J.F Kurose and
Course on Computer Communication and Networks. Lecture 2 Chapter 1: Introduction: Part B: Network structure, performance, security prelude
 Course on Computer Communication and Networks Lecture 2 Chapter 1: Introduction: Part B: Network structure, performance, security prelude CTH EDA344/GU DIT 420 Based on the book Computer Networking: A
Course on Computer Communication and Networks Lecture 2 Chapter 1: Introduction: Part B: Network structure, performance, security prelude CTH EDA344/GU DIT 420 Based on the book Computer Networking: A
A closer look at network structure:
 T1: Introduction 1.1 What is computer network? Examples of computer network The Internet Network structure: edge and core 1.2 Why computer networks 1.3 The way networks work 1.4 Performance metrics: Delay,
T1: Introduction 1.1 What is computer network? Examples of computer network The Internet Network structure: edge and core 1.2 Why computer networks 1.3 The way networks work 1.4 Performance metrics: Delay,
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 All material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Chapter 1:
Chapter 1 Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 All material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Chapter 1:
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Part 1: Introduction. Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview
 Part 1: Introduction Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview Get context Get overview, feel of the Internet Application layer protocols and addressing Network layer / Routing Link layer / Example
Part 1: Introduction Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview Get context Get overview, feel of the Internet Application layer protocols and addressing Network layer / Routing Link layer / Example
Telecommunication Networks Introduction
 Telecommunication Networks Introduction Telemedicina e e-saúde 2011/12 Pedro Brandão References These slides are the companions of Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 5th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith
Telecommunication Networks Introduction Telemedicina e e-saúde 2011/12 Pedro Brandão References These slides are the companions of Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 5th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith
Telecommunication Networks Introduction
 Telecommunication Networks Introduction Telemedicina e e-saúde 2016/17 Pedro Brandão References These slides are the companions of Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 5th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith
Telecommunication Networks Introduction Telemedicina e e-saúde 2016/17 Pedro Brandão References These slides are the companions of Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 5th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction Prof. Sungwook Kim ( 김승욱 ) AS building 903 Tel : 02) 705-8932 E-mail : swkim01@sogang.ac.kr TA : Joonsu Ryu ( 류준수 ) AS building 901 E-mail : sok54833@naver.com Chapter
Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction Prof. Sungwook Kim ( 김승욱 ) AS building 903 Tel : 02) 705-8932 E-mail : swkim01@sogang.ac.kr TA : Joonsu Ryu ( 류준수 ) AS building 901 E-mail : sok54833@naver.com Chapter
A Whirlwind Introduction to the Internet Overview
 Overview What s the Internet What s a protocol? Network edge Network core ccess nets, media Performance: loss, delay Protocol layers, service models ackbones, NPs, ISPs local ISP company regional ISP queuing
Overview What s the Internet What s a protocol? Network edge Network core ccess nets, media Performance: loss, delay Protocol layers, service models ackbones, NPs, ISPs local ISP company regional ISP queuing
CMP-330 Computer Networks
 CMP-330 Computer Networks http://faculty.pucit.edu.pk/fawaz/cmp330 Spring 2013 MW 11:30 1:00 (Morning), Room # 11 MW 4:00 5:30 (Evening), Room # 9 Fawaz Bokhari Office: Senior Faculty Rooms Office Hour:
CMP-330 Computer Networks http://faculty.pucit.edu.pk/fawaz/cmp330 Spring 2013 MW 11:30 1:00 (Morning), Room # 11 MW 4:00 5:30 (Evening), Room # 9 Fawaz Bokhari Office: Senior Faculty Rooms Office Hour:
CSEE 4119 Computer Networks. Chapter 1 Introduction (2/2) Introduction 1-1
 CSEE 4119 Computer Networks Chapter 1 Introduction (2/2) Introduction 1-1 Chapter 1: Introduction Our goal: get feel and terminology more depth, detail later in course approach: use Internet as example
CSEE 4119 Computer Networks Chapter 1 Introduction (2/2) Introduction 1-1 Chapter 1: Introduction Our goal: get feel and terminology more depth, detail later in course approach: use Internet as example
Fundamentals of Information Systems
 Fundamentals of Information Systems Computer Networking Module Year 2017/2018 Master Degree in Data Science Armir Bujari abujari@math.unipd.it Inter structure: work of works Question: given millions of
Fundamentals of Information Systems Computer Networking Module Year 2017/2018 Master Degree in Data Science Armir Bujari abujari@math.unipd.it Inter structure: work of works Question: given millions of
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Master Course Computer Networks IN2097
 Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department of Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Chair for
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department of Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Chair for
CS 3640: Introduction to Networks and Their Applications
 CS 3640: Introduction to Networks and Their Applications Fall 2018, Lecture 4: Packet switching performance metrics Instructor: Rishab Nithyanand Teaching Assistant: Md. Kowsar Hossain 1 You should Be
CS 3640: Introduction to Networks and Their Applications Fall 2018, Lecture 4: Packet switching performance metrics Instructor: Rishab Nithyanand Teaching Assistant: Md. Kowsar Hossain 1 You should Be
Internet: A Brief Overview. Introduction 2-1
 Inter: A Brief Overview Introduction 2-1 Quick Questions v What is the Inter? v How was it invented and developed? https://www.youtube.com/v/9hiqjrmhtv4 Text: http://www.intersociety.org/inter/what-inter/
Inter: A Brief Overview Introduction 2-1 Quick Questions v What is the Inter? v How was it invented and developed? https://www.youtube.com/v/9hiqjrmhtv4 Text: http://www.intersociety.org/inter/what-inter/
Part I: Introduction. 1: Introduction 1
 Part I: Introduction Chapter goal: get context, overview, feel of networking more depth, detail later in course approach: descriptive use Internet as example Overview: what s the Internet what s a protocol?
Part I: Introduction Chapter goal: get context, overview, feel of networking more depth, detail later in course approach: descriptive use Internet as example Overview: what s the Internet what s a protocol?
CSE 434 Spring 2013 Computer Networks
 CSE 434 Spring 2013 Computer Networks Georgios Varsamopoulos Arizona State University What is this course about? Students will learn How works are designed and structured What is the architecture of the
CSE 434 Spring 2013 Computer Networks Georgios Varsamopoulos Arizona State University What is this course about? Students will learn How works are designed and structured What is the architecture of the
Chapter 1 Introduction. Introduction 1-1
 Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 1-1 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view PC server wireless laptop cellular handheld router access points wired links millions of connected computing devices: hosts
Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 1-1 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view PC server wireless laptop cellular handheld router access points wired links millions of connected computing devices: hosts
CSCD 330 Network Programming Spring 2018 Lecture 3 Introduction to Networks. Reading: Chapter 1 - Continued
 CSCD 330 Network Programming Spring 2018 Lecture 3 Introduction to Networks Reading: Chapter 1 - Continued Topics in Chapter 1 What s the Internet? What s a protocol? Network edge; hosts, access net, physical
CSCD 330 Network Programming Spring 2018 Lecture 3 Introduction to Networks Reading: Chapter 1 - Continued Topics in Chapter 1 What s the Internet? What s a protocol? Network edge; hosts, access net, physical
CSIT 561: Computer Networks
 CSIT 561: Computer Networks Fall 2008 HKUST Introduction 1-1 Course Info Instructors: Dr. Jogesh K. Muppala: http://www.cs.ust.hk/~muppala/ Dr. Qian Zhang: http://www.cs.ust.hk/~qianzh Course web site
CSIT 561: Computer Networks Fall 2008 HKUST Introduction 1-1 Course Info Instructors: Dr. Jogesh K. Muppala: http://www.cs.ust.hk/~muppala/ Dr. Qian Zhang: http://www.cs.ust.hk/~qianzh Course web site
Ice-Breaking. COMP 561: Computer Networks. Course Info. Course Info. Qian Zhang Spring 2008 HKUST
 Ice-Breaking COMP 561: Computer Networks Qian Zhang Spring 2008 HKUST Introduction 1-1 Introduction 1-2 Course Info Course Info Instructor: Qian Zhang www.cs.ust.hk/~qianzh Course web site http://www.cs.ust.hk/~qianzh/comp561/spr2008/i
Ice-Breaking COMP 561: Computer Networks Qian Zhang Spring 2008 HKUST Introduction 1-1 Introduction 1-2 Course Info Course Info Instructor: Qian Zhang www.cs.ust.hk/~qianzh Course web site http://www.cs.ust.hk/~qianzh/comp561/spr2008/i
Δίκτυα Μετάδοσης Δεδομένων Data Networks. Introduction 1-1
 Δίκτυα Μετάδοσης Δεδομένων Data Networks Introduction 1-1 Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley All material copyright J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All
Δίκτυα Μετάδοσης Δεδομένων Data Networks Introduction 1-1 Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley All material copyright J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All
ELE 543 Computer Network
 Ken Q. Yang, ECE, URI Ken Q. Yang What Do You Learn? 1. Network Concepts and rchitectures 2. Communication Protocols ELE 543 Computer Network (e.g. TCP/IP, Ethernet, wireless) 3. Doing Useful Work on a
Ken Q. Yang, ECE, URI Ken Q. Yang What Do You Learn? 1. Network Concepts and rchitectures 2. Communication Protocols ELE 543 Computer Network (e.g. TCP/IP, Ethernet, wireless) 3. Doing Useful Work on a
CSC 401 Data and Computer Communications Networks
 CSC 401 Data and Computer Communications Networks Computer Networks and The Inter Sec 1.3 Prof. Lina Battestilli Fall 2017 Outline Computer Networks and the Inter (Ch 1) 1.1 What is the Inter? 1.2 work
CSC 401 Data and Computer Communications Networks Computer Networks and The Inter Sec 1.3 Prof. Lina Battestilli Fall 2017 Outline Computer Networks and the Inter (Ch 1) 1.1 What is the Inter? 1.2 work
CMSC 332: Computer Networks Intro (cont.)
 CMSC 332: Computer Networks Intro (cont.) Professor Doug Szajda Announcements Homework 1 posted Due Thursday, January 30th Get started early - there is a good deal to be done. 2 Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1
CMSC 332: Computer Networks Intro (cont.) Professor Doug Szajda Announcements Homework 1 posted Due Thursday, January 30th Get started early - there is a good deal to be done. 2 Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1
Computer Communication Networks Midterm Review
 Computer Communication Networks Midterm Review ICEN/ICSI 416 Fall 2018 Prof. Aveek Dutta 1 Instructions The exam is closed book, notes, computers, phones. You can use calculator, but not one from your
Computer Communication Networks Midterm Review ICEN/ICSI 416 Fall 2018 Prof. Aveek Dutta 1 Instructions The exam is closed book, notes, computers, phones. You can use calculator, but not one from your
70 CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET
 70 CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET one of these packets arrives to a packet switch, what information in the packet does the switch use to determine the link onto which the packet is forwarded?
70 CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET one of these packets arrives to a packet switch, what information in the packet does the switch use to determine the link onto which the packet is forwarded?
Fall 2009 HKUST. Introduction 1-1
 CSIT 561: Computer Networks Fall 2009 HKUST Introduction 1-1 Course Info Instructors: Dr. Jogesh K. Muppala: http://www.cs.ust.hk/~muppala/ Dr. Qian Zhang: http://www.cs.ust.hk/~qianzh Course web site
CSIT 561: Computer Networks Fall 2009 HKUST Introduction 1-1 Course Info Instructors: Dr. Jogesh K. Muppala: http://www.cs.ust.hk/~muppala/ Dr. Qian Zhang: http://www.cs.ust.hk/~qianzh Course web site
Introduction to computer networking
 edge core Introduction to computer networking Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 The edge core Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 edge core Billions of connected computing
edge core Introduction to computer networking Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 The edge core Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 edge core Billions of connected computing
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations; and can
Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations; and can
Review for Internet Introduction
 Review for Internet Introduction What s the Internet: Two Views View 1: Nuts and Bolts View billions of connected hosts routers and switches protocols control sending, receiving of messages network of
Review for Internet Introduction What s the Internet: Two Views View 1: Nuts and Bolts View billions of connected hosts routers and switches protocols control sending, receiving of messages network of
CS 3516: Computer Networks
 Welcome to CS 3516: Computer Networks Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 9:00am 9:50am M, T, R, and F Location: AK219 Fall 2018 A-term 1 Some slides are originally from the course materials of the textbook Computer
Welcome to CS 3516: Computer Networks Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 9:00am 9:50am M, T, R, and F Location: AK219 Fall 2018 A-term 1 Some slides are originally from the course materials of the textbook Computer
Foundations of Telematics
 Foundations of Telematics Chapter 1 Introduction Acknowledgement: These slides have been prepared by J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Foundations of Telematics (AMW SS 2010): 01 Introduction 1 Chapter 1: Introduction
Foundations of Telematics Chapter 1 Introduction Acknowledgement: These slides have been prepared by J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Foundations of Telematics (AMW SS 2010): 01 Introduction 1 Chapter 1: Introduction
ECEN Final Exam Fall Instructor: Srinivas Shakkottai
 ECEN 424 - Final Exam Fall 2013 Instructor: Srinivas Shakkottai NAME: Problem maximum points your points Problem 1 10 Problem 2 10 Problem 3 20 Problem 4 20 Problem 5 20 Problem 6 20 total 100 1 2 Midterm
ECEN 424 - Final Exam Fall 2013 Instructor: Srinivas Shakkottai NAME: Problem maximum points your points Problem 1 10 Problem 2 10 Problem 3 20 Problem 4 20 Problem 5 20 Problem 6 20 total 100 1 2 Midterm
Network Management & Monitoring Network Delay
 Network Management & Monitoring Network Delay These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 Unported license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) End-to-end
Network Management & Monitoring Network Delay These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 Unported license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) End-to-end
Informática y Comunicaciones. Chapter 1 Introduction to Communications
 Informática y Comunicaciones Chapter 1 Introduction to Communications All material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Introduction to Communications 1-1 Chapter 1: introduction
Informática y Comunicaciones Chapter 1 Introduction to Communications All material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Introduction to Communications 1-1 Chapter 1: introduction
Introduction to Computer Networks. Chapter 1: introduction
 Introduction to Computer Networks EECS 3214 Slides courtesy of J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Introduction 1-1 Chapter 1: introduction our goal: get feel and terminology more depth, detail
Introduction to Computer Networks EECS 3214 Slides courtesy of J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Introduction 1-1 Chapter 1: introduction our goal: get feel and terminology more depth, detail
end systems, access networks, links circuit switching, packet switching, network structure
 Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 Network core circuit switching, packet switching, network structure 1.4 Delay, loss and throughput
Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 Network core circuit switching, packet switching, network structure 1.4 Delay, loss and throughput
Direct Link Communication I: Basic Techniques. Data Transmission. ignore carrier frequency, coding etc.
 Direct Link Communication I: Basic Techniques Link speed unit: bps abstraction Data Transmission ignore carrier frequency, coding etc. Point-to-point link: wired or wireless includes broadcast case Interested
Direct Link Communication I: Basic Techniques Link speed unit: bps abstraction Data Transmission ignore carrier frequency, coding etc. Point-to-point link: wired or wireless includes broadcast case Interested
Transport Layer Congestion Control
 Transport Layer Congestion Control Tom Kelliher, CS 325 Apr. 7, 2008 1 Administrivia Announcements Assignment Read 4.1 4.3. From Last Time TCP Reliability. Outline 1. Congestion control principles. 2.
Transport Layer Congestion Control Tom Kelliher, CS 325 Apr. 7, 2008 1 Administrivia Announcements Assignment Read 4.1 4.3. From Last Time TCP Reliability. Outline 1. Congestion control principles. 2.
Network Management & Monitoring
 Network Management & Monitoring Network Delay These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 Unported license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) End-to-end
Network Management & Monitoring Network Delay These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 Unported license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) End-to-end
Chapter 1 Introduction. Introduction 1-1
 Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 1-1 Chapter 1: Introduction Our goal: q get feel and terminology q more depth, detail later in course q approach: v use Internet as example Overview: q what s the Internet?
Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 1-1 Chapter 1: Introduction Our goal: q get feel and terminology q more depth, detail later in course q approach: v use Internet as example Overview: q what s the Internet?
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction These slides are adapted from the original slides provided by J.Kurose and K.W Ross. Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley,
Chapter 1 Introduction These slides are adapted from the original slides provided by J.Kurose and K.W Ross. Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley,
Data Communications & Computer Networks
 CSE471 Data Communications & Computer Networks Yrd. Doc. Dr. Tacha Serif tserif@cse.yeditepe.edu.tr Department of Computer Engineering Yeditepe University Spring 2009 Introduction 1-1 Introduction Computer
CSE471 Data Communications & Computer Networks Yrd. Doc. Dr. Tacha Serif tserif@cse.yeditepe.edu.tr Department of Computer Engineering Yeditepe University Spring 2009 Introduction 1-1 Introduction Computer
Homework 1 50 points. Quantitative Comparison of Packet Switching and Circuit Switching 20 points Consider the two scenarios below:
 Homework 1 50 points Quantitative Comparison of Packet Switching and Circuit Switching 20 points Consider the two scenarios below: A circuit-switching scenario in which Ncs users, each requiring a bandwidth
Homework 1 50 points Quantitative Comparison of Packet Switching and Circuit Switching 20 points Consider the two scenarios below: A circuit-switching scenario in which Ncs users, each requiring a bandwidth
Internet: A Brief Overview. Chapter 1
 Inter: A Brief Overview Chapter 1 Chapter 1: introduction our goal: v get feel and terminology v more depth, detail later in course v approach: use Inter as example overview: v what s the Inter? v what
Inter: A Brief Overview Chapter 1 Chapter 1: introduction our goal: v get feel and terminology v more depth, detail later in course v approach: use Inter as example overview: v what s the Inter? v what
Multimedia! 23/03/18. Part 3: Lecture 3! Content and multimedia! Internet traffic!
 Part 3: Lecture 3 Content and multimedia Internet traffic Multimedia How can multimedia be transmitted? Interactive/real-time Streaming 1 Voice over IP Interactive multimedia Voice and multimedia sessions
Part 3: Lecture 3 Content and multimedia Internet traffic Multimedia How can multimedia be transmitted? Interactive/real-time Streaming 1 Voice over IP Interactive multimedia Voice and multimedia sessions
Part 3: Lecture 3! Content and multimedia!
 Part 3: Lecture 3! Content and multimedia! Internet traffic! Multimedia! How can multimedia be transmitted?! Interactive/real-time! Streaming! Interactive multimedia! Voice over IP! Voice and multimedia
Part 3: Lecture 3! Content and multimedia! Internet traffic! Multimedia! How can multimedia be transmitted?! Interactive/real-time! Streaming! Interactive multimedia! Voice over IP! Voice and multimedia
CS 557 Congestion and Complexity
 CS 557 Congestion and Complexity Observations on the Dynamics of a Congestion Control Algorithm: The Effects of Two-Way Traffic Zhang, Shenker, and Clark, 1991 Spring 2013 The Story So Far. Transport layer:
CS 557 Congestion and Complexity Observations on the Dynamics of a Congestion Control Algorithm: The Effects of Two-Way Traffic Zhang, Shenker, and Clark, 1991 Spring 2013 The Story So Far. Transport layer:
LECTURE 1 - INTRODUCTION. Jacob Aae Mikkelsen
 LECTURE 1 - INTRODUCTION Jacob Aae Mikkelsen GOALS TODAY History of networks Get "feel" and terminology More depth and details later in the course Approach: Use Internet as example ORIGIN OF THE INTERNET
LECTURE 1 - INTRODUCTION Jacob Aae Mikkelsen GOALS TODAY History of networks Get "feel" and terminology More depth and details later in the course Approach: Use Internet as example ORIGIN OF THE INTERNET
SELECTION OF METRICS (CONT) Gaia Maselli
 SELECTION OF METRICS (CONT) Gaia Maselli maselli@di.uniroma1.it Computer Network Performance 2 Selecting performance metrics Computer Network Performance 3 Selecting performance metrics speed Individual
SELECTION OF METRICS (CONT) Gaia Maselli maselli@di.uniroma1.it Computer Network Performance 2 Selecting performance metrics Computer Network Performance 3 Selecting performance metrics speed Individual
Principles of Reliable Data Transfer
 Principles of Reliable Data Transfer 1 Reliable Delivery Making sure that the packets sent by the sender are correctly and reliably received by the receiver amid network errors, i.e., corrupted/lost packets
Principles of Reliable Data Transfer 1 Reliable Delivery Making sure that the packets sent by the sender are correctly and reliably received by the receiver amid network errors, i.e., corrupted/lost packets
Module 2 Overview of. Computer Networks
 Module Overview of Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link: CS454/654 - Issues How
Module Overview of Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link: CS454/654 - Issues How
Module 2 Overview of Computer Networks
 Module 2 Overview of Computer Networks Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link:
Module 2 Overview of Computer Networks Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link:
Chapter 1: Introduction. Chapter 1 Introduction. Chapter 1: roadmap. What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view
 Chapter 1 Introduction Computer Networking: Top Down pproach, 5 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross ddison-wesley, pril 2009. Introduction 1-1 Chapter 1: Introduction Our goal: get feel and terminology
Chapter 1 Introduction Computer Networking: Top Down pproach, 5 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross ddison-wesley, pril 2009. Introduction 1-1 Chapter 1: Introduction Our goal: get feel and terminology
CSCD 330 Network Programming Spring 2017
 CSCD 330 Network Programming Spring 2017 Lecture 3 Introduction to Networks Reading: Chapter 1 - Continued 1 Topics in Chapter 1 What s the Internet? What s a protocol? Network edge; hosts, access net,
CSCD 330 Network Programming Spring 2017 Lecture 3 Introduction to Networks Reading: Chapter 1 - Continued 1 Topics in Chapter 1 What s the Internet? What s a protocol? Network edge; hosts, access net,
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Lecture 15: TCP over wireless networks. Mythili Vutukuru CS 653 Spring 2014 March 13, Thursday
 Lecture 15: TCP over wireless networks Mythili Vutukuru CS 653 Spring 2014 March 13, Thursday TCP - recap Transport layer TCP is the dominant protocol TCP provides in-order reliable byte stream abstraction
Lecture 15: TCP over wireless networks Mythili Vutukuru CS 653 Spring 2014 March 13, Thursday TCP - recap Transport layer TCP is the dominant protocol TCP provides in-order reliable byte stream abstraction
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
end systems, access networks, links 1.3 network core
 Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 what is the Inter? 1.2 work edge end systems, works, links 1.3 work core packet switching, circuit switching, work structure 1.4 delay, loss, throughput in works 1.5 protocol layers,
Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 what is the Inter? 1.2 work edge end systems, works, links 1.3 work core packet switching, circuit switching, work structure 1.4 delay, loss, throughput in works 1.5 protocol layers,
Direct Link Communication I: Basic Techniques. Data Transmission. ignore carrier frequency, coding etc.
 Direct Link Communication I: Basic Techniques Link speed unit: bps abstraction Data Transmission ignore carrier frequency, coding etc. Point-to-point link: wired or wireless includes broadcast case Interested
Direct Link Communication I: Basic Techniques Link speed unit: bps abstraction Data Transmission ignore carrier frequency, coding etc. Point-to-point link: wired or wireless includes broadcast case Interested
CSCD 330 Network Programming Winter 2016
 CSCD 330 Network Programming Winter 2016 Lecture 3 Introduction to Networks Reading: Chapter 1 - Continued Some Material in these slides from J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross All material copyright 1996-2007 1
CSCD 330 Network Programming Winter 2016 Lecture 3 Introduction to Networks Reading: Chapter 1 - Continued Some Material in these slides from J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross All material copyright 1996-2007 1
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
CS519: Computer Networks
 Lets start at the beginning : Computer Networks Lecture 1: Jan 26, 2004 Intro to Computer Networking What is a for? To allow two or more endpoints to communicate What is a? Nodes connected by links Lets
Lets start at the beginning : Computer Networks Lecture 1: Jan 26, 2004 Intro to Computer Networking What is a for? To allow two or more endpoints to communicate What is a? Nodes connected by links Lets
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete slides (including
Chapter 1 A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete slides (including
