Step 1: IP Configuration: On R1: On R2: On R3: R1(config)#int s1/2 R1(config-if)#ip addr R1(config-if)#no shu
|
|
|
- Julius Gardner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Step 1: IP Configuration: n R1: R1(config)#int s1/2 R1(config-if)#ip addr R1(config-if)#no shu R1(config-if)#int lo0 R1(config-if)#ip addr R1(config-if)#int lo1 R1(config-if)#ip addr n R2: R2(config)#int s1/1 R2(config-if)#ip addr R2(config-if)#no shu R2(config)#int s1/3 R2(config-if)#ip addr R2(config-if)#no shut R2(config)#int lo0 R2(config-if)#ip addr n R3: R3(config)#int s1/2 R3(config-if)#ip addr R3(config-if)#no shut R3(config)#int lo0 R3(config-if)#ip addr R3(config)#int s2/0 R3(config-if)#ip addr R3(config-if)#no shu
2 n R4: R4(config)#int s1/3 R4(config-if)#ip addr R4(config-if)#no shut R4(config)#int s2/1 R4(config-if)#ip addr R4(config-if)#no shu R4(config)#int lo0 R4(config-if)#ip addr n R5: R5(config)#int s2/0 R5(config-if)#ip addr R5(config-if)#no shut R5(config)#int s2/2 R5(config-if)#ip addr R5(config-if)#no shu R5(config)#int lo0 R5(config-if)#ip addr n R6: R6(config)#int lo0 R6(config-if)#ip addr R6(config)#int s2/1 R6(config-if)#ip addr R6(config-if)#no shu After each step we MUST verify: n R2: R2#ping Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/8/9 ms
3 R2#ping Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/8/9 ms n R4: R4#ping Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/8/9 ms R4#ping Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/8/9 ms n R6: R6#ping Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/8/9 ms Perfect let s go to the second step: Step 2 Configure IGP in the core: The core routers in this topology are R2 R5, therefore, we will run SPF on all these routers and their loopbacks: n R2: R2(config)#router ospf 1 R2(config-router)#netw a 0 R2(config-router)#netw a 0 NTE: We are NT running SPF on the interface facing R1, the customer router.
4 n R3: R3(config)#router ospf 1 R3(config-router)#netw a 0 R3(config-router)#netw a 0 R3(config-router)#netw a 0 *Sep 19 18:39:50.510: %SPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr on Serial1/2 from LADING to FULL, Loading Done n R4: R4(config)#router ospf 1 R4(config-router)#netw a 0 R4(config-router)#netw a 0 R4(config-router)#netw a 0 *Sep 19 18:40:35.574: %SPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr on Serial1/3 from LADING to FULL, Loading Done n R5: R5(config)#router ospf 1 R5(config-router)#netw a 0 R5(config-router)#netw a 0 *Sep 19 18:41:23.433: %SPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr on Serial2/0 from LADING to FULL, Loading Done Let s verify: n R2: R2#sh ip rou ospf b Gate Gateway of last resort is not set /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/65] via , 00:00:05, Serial1/ /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/129] via , 00:01:53, Serial1/ /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/193] via , 00:01:05, Serial1/ /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/128] via , 00:02:38, Serial1/ /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/192] via , 00:01:53, Serial1/3
5 n R5: R5#sh ip rou ospf b Gate Gateway of last resort is not set /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/193] via , 00:01:36, Serial2/ /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/129] via , 00:00:26, Serial2/ /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/65] via , 00:01:36, Serial2/ /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/192] via , 00:01:36, Serial2/ /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/128] via , 00:01:36, Serial2/0 Step 3: Configure LDP: n R2: R2(config)#mpls label range R2(config)#mpls label protocol ldp R2(config)#router ospf 1 R2(config-router)#mpls ldp autoconfig are 0 n R3: R3(config)#mpls label range R3(config)#mpls label proto ldp R3(config)#router ospf 1 R3(config-router)#mpls ldp auto area 0 *Sep 19 18:45:39.229: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor :0 (1) is UP We can see that the LDP session came up between R2 and R3. n R4: R4(config)#mpls label range R4(config)#mpls label protocol ldp
6 R4(config)#router ospf 1 R4(config-router)#mpls ldp auto are 0 *Sep 19 18:46:44.902: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor :0 (1) is UP n R5: R5(config)#mpls label range R5(config)#mpls label protocol ldp R5(config)#router ospf 1 R5(config-router)#mpls ldp auto are 0 *Sep 19 18:47:36.213: %LDP-5-NBRCHG: LDP Neighbor :0 (1) is UP To verify the configuration: n R3: R3#sh mpls inter Interface IP Tunnel BGP Static perational Serial1/2 Yes (ldp) No No No Yes Serial2/0 Yes (ldp) No No No Yes R3#sh mpls ldp nei Peer LDP Ident: :0; Local LDP Ident :0 TCP connection: State: per; Msgs sent/rcvd: 13/14; Downstream Up time: 00:02:59 LDP discovery sources: Serial1/2, Src IP addr: Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident: Peer LDP Ident: :0; Local LDP Ident :0 TCP connection: State: per; Msgs sent/rcvd: 12/12; Downstream Up time: 00:01:53 LDP discovery sources: Serial2/0, Src IP addr: Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident:
7 n R5: R5#sh mpls inter Interface IP Tunnel BGP Static perational Serial2/0 Yes (ldp) No No No Yes R5#sh mpls ldp nei Step 4: Peer LDP Ident: :0; Local LDP Ident :0 TCP connection: State: per; Msgs sent/rcvd: 12/11; Downstream Up time: 00:01:23 LDP discovery sources: Serial2/0, Src IP addr: Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident: Configure ibgp: This ibgp peer session MUST be established between the PE routers: n R2: R2(config)#router bgp 100 R2(config-router)#no bgp default ipv4-unicast R2(config-router)#neigh remote 100 R2(config-router)#neigh update lo0 n R5: R5(config)#router bgp 100 R5(config-router)#no bgp default ipv4-unicast R5(config-router)#neigh remote 100 R5(config-router)#neigh update lo0 NTE: The peer session is NT up. This is because we configured the two BGP routers NT to form a peer session using IPv4. This means that we need to activate the peers under the address-family VPNv4: n R2: R2(config)#router bgp 100
8 R2(config-router)#address-family vpnv4 R2(config-router-af)#neigh act n R5: R5(config)#router bgp 100 R5(config-router)#address-family vpnv4 R5(config-router-af)#neigh act *Sep 19 18:55:18.118: %BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor Up And sure enough the peer session between the PE routers is up. Step 5: Configure VRFs: NTE : This is configured on the PE routers: n R2: R2(config)#ip vrf 11 R2(config-vrf)#rd 1:10 R2(config-vrf)#route-target both 1:100 Before applying the VRF to the interface: R5#sh run int s1/1 Building configuration... Current configuration : 86 bytes! interface Serial1/1 ip address serial restart-delay 0 end R2(config)#int s1/1 R2(config-if)#ip vrf forwarding 11 You should see the following console message: % Interface Serial1/1 IPv4 disabled and address(es) removed due to disabling VRF 11
9 R2(config-if)#ip address To verify: R2#ping vrf Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/9/13 ms n R5: R5(config)#ip vrf 66 R5(config-vrf)#rd 1:10 R5(config-vrf)#route-target both 1:100 You should see the following console message: *Sep 19 18:59:18.584: %SYS-5-CNFIG_I: Configured from console by console R5#sh run int s2/2 Building configuration... Current configuration : 86 bytes! interface Serial2/2 ip address serial restart-delay 0 end R5(config)#int s2/2 R5(config-if)#ip vrf forwarding 66 % Interface Serial2/2 IPv4 disabled and address(es) removed due to disabling VRF 66 R5(config-if)#ip addr To verify the configuration: R5#ping vrf Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:
10 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/9/10 ms Step 6: Configuring Routing Protocols between PE and the CE routers: n R1: R1(config-if)#route-map tst R1(config-route-map)#match ip addr 1 R1(config-route-map)#router ospf 1 R1(config-router)#router-id R1(config-router)#netw a 0 R1(config-router)#netw a 0 R1(config-router)#redistri conn route-map tst sub n R2: R2(config)#router ospf 2 vrf 11 R2(config-router)#netw a 0 *Sep 19 19:03:24.304: %SPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 2, Nbr on Serial1/1 from LADING to FULL, Loading Done To verify: n R2: R2#sh ip rou vrf 11 ospf b Gate Gateway of last resort is not set E /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/65] via , 00:00:42, Serial1/ /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/20] via , 00:00:42, Serial1/1 n R6: R6(config)#router ospf 1 R6(config-router)#netw a 0 R6(config-router)#netw a 0
11 n R5: R5(config)#router ospf 2 vrf 66 R5(config-router)#netw a 0 *Sep 19 19:05:22.801: %SPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 2, Nbr on Serial2/2 from LADING to FULL, Loading Done To verify: n R5: R5#sh ip rou vrf 66 ospf b Gate Gateway of last resort is not set /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/65] via , 00:00:26, Serial2/2 Step 7: Redistribution: NTE : You should perform a one way redistribution and verify if everything is working before configuring redistribution in the other direction: n R2: R2(config)#router bgp 100 R2(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf 11 R2(config-router-af)#redistr ospf 2 Let s verify: R2#sh ip route vrf 11 ospf b Gate Gateway of last resort is not set E /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/65] via , 00:05:01, Serial1/ /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/20] via , 00:05:01, Serial1/1 R2#sh ip bgp vpnv4 all BGP table version is 3, local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
12 r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, rigin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path Route Distinguisher: 1:10 (default for vrf 11) *> / ? *> / ? NTE : the external SPF route is not redistributed, in order to redistribute the external routes we have to do the following: R2(config)#router bgp 100 R2(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf 11 R2(config-router-af)#redistr ospf 2 match internal external 1 external 2 To verify: R2#sh ip bgp vpnv4 all BGP table version is 4, local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, rigin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path Route Distinguisher: 1:10 (default for vrf 11) *> / ? *> / ? *> / ? Perfect. These three routes should be in R5 s BGP table, let s verify: n R5: R5#sh ip bgp vpnv4 all BGP table version is 7, local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, rigin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path Route Distinguisher: 1:10 (default for vrf 66) *>i / ?
13 *>i / ? *>i / ? This is good. Now, we need to redistribute BGP into SPF so R6 can see the routes: n R5: R5(config)#router ospf 2 vrf 66 R5(config-router)#redistribute bgp 100 sub To verify: n R6: R6#sh ip route ospf b Gate Gateway of last resort is not set IA E2 IA /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/129] via , 00:00:19, Serial2/ /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/20] via , 00:00:19, Serial2/ /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/65] via , 00:00:19, Serial2/1 The routes are there, but do we have reachability? n R1: R1#deb ip icmp ICMP packet debugging is on n R6: R6#ping Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:... Success rate is 0 percent (0/5) We knew that this ping was not going to be successful, but let s see if R1 can see the ICMP echo messages:
14 n R1: *Sep 19 19:13:44.496: ICMP: echo reply sent, src , dst , topology BASE, dscp 0 topoid 0 R1# *Sep 19 19:13:46.495: ICMP: echo reply sent, src , dst , topology BASE, dscp 0 topoid 0 R1# *Sep 19 19:13:48.496: ICMP: echo reply sent, src , dst , topology BASE, dscp 0 topoid 0 R1# *Sep 19 19:13:50.497: ICMP: echo reply sent, src , dst , topology BASE, dscp 0 topoid 0 R1# *Sep 19 19:13:52.496: ICMP: echo reply sent, src , dst , topology BASE, dscp 0 topoid 0 We can see that R1 did receive the ICMP messages, now we can redistribute going in the other direction: n R5: R5(config)#router bgp 100 R5(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf 66 R5(config-router-af)#redistr ospf 2 To verify: R5#sh ip bgp vpnv4 all BGP table version is 9, local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, rigin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path Route Distinguisher: 1:10 (default for vrf 66) *>i / ? *> / ? *>i / ? *>i / ? *> / ? The routes are redistributed, these routes should show up on R2. Let s verify:
15 n R2: R2#sh ip bgp vpnv4 all BGP table version is 8, local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, rigin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path Route Distinguisher: 1:10 (default for vrf 11) *> / ? *>i / ? *> / ? *> / ? *>i / ? Perfect! Now we need to redistribute BGP into SPF so the customer router (R1) can see the routes: R2(config)#router ospf 2 vrf 11 R2(config-router)#redistr bgp 100 sub To verify: n R1: R1#show ip route ospf b Gate Gateway of last resort is not set IA IA /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/129] via , 00:00:26, Serial1/ /24 is subnetted, 1 subnets [110/65] via , 00:00:26, Serial1/2 R1#ping Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 37/40/42 ms
AS 100 AS 300. Lab -1 Private Communities - II .1 S1/2. Task 1. On R1: / / /24. Configure the above topology.
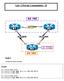 Lab -1 Private Communities - II AS 100.1 R1 S1/2 12.1.1.0/24 S1/1.2 R2 S1/3 S1/3 13.1.1.0/24 23.1.1.0/24 S1/1.3 R3 S1/2 Lo0 6.6.6.0/24 Lo1 7.7.7.0/24 AS 300 Task 1 Configure the above topology. On R1:
Lab -1 Private Communities - II AS 100.1 R1 S1/2 12.1.1.0/24 S1/1.2 R2 S1/3 S1/3 13.1.1.0/24 23.1.1.0/24 S1/1.3 R3 S1/2 Lo0 6.6.6.0/24 Lo1 7.7.7.0/24 AS 300 Task 1 Configure the above topology. On R1:
Lab 1 BGP Automatic-tag, AS-path tag and Table-map
 Lab 1 BGP Automatic-tag, AS-path tag and Table-map Lo0 1.1.1.1 /24 AS 100.1 R1 S1/3 13.1.1.0/24 S1/1 S1/2 AS 300 AS 400.3 R3 34.1.1.0/24 S2/0 S1/3.4 R4 Lo0 2.2.2.2 /24.2 R2 AS 200 S1/3 23.1.1.0/24 Task
Lab 1 BGP Automatic-tag, AS-path tag and Table-map Lo0 1.1.1.1 /24 AS 100.1 R1 S1/3 13.1.1.0/24 S1/1 S1/2 AS 300 AS 400.3 R3 34.1.1.0/24 S2/0 S1/3.4 R4 Lo0 2.2.2.2 /24.2 R2 AS 200 S1/3 23.1.1.0/24 Task
Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE
 MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
LAB 5: DMVPN BGP. LAB 5: Diagram. Note: This Lab was developed on Cisco IOS Version15.2(4) M1 ADVENTERPRISEK9-M.
 LAB 5: DMVPN BGP LAB 5: Diagram Note: This Lab was developed on Cisco IOS Version15.2(4) M1 ADVENTERPRISEK9-M. LAB 5: Configure BGP over DMVPN Configuration Step 1: Enable loopback and physical interfaces
LAB 5: DMVPN BGP LAB 5: Diagram Note: This Lab was developed on Cisco IOS Version15.2(4) M1 ADVENTERPRISEK9-M. LAB 5: Configure BGP over DMVPN Configuration Step 1: Enable loopback and physical interfaces
v5.0 Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Physical or Logical
 CCIE Foundation v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Physical or Logical R&S Foundation by Narbik Kocharians CCIE R&S Foundation v5.0 Page 1 of 90 LAB 2
CCIE Foundation v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Physical or Logical R&S Foundation by Narbik Kocharians CCIE R&S Foundation v5.0 Page 1 of 90 LAB 2
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing
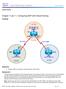 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Chapter 7 Lab 7-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute
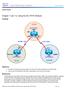 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Layer3 VPN with RIP protocol between CE-PE
 MPLS Layer3 VPN with IP protocol between E-PE Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to
MPLS Layer3 VPN with IP protocol between E-PE Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to
Adapted from the Synchronization example in g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html
 Adapted from the Synchronization example in http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/internetworkin g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html When an AS provides transit service to other ASs when there are non-bgp routers in
Adapted from the Synchronization example in http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/internetworkin g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html When an AS provides transit service to other ASs when there are non-bgp routers in
Lab 2 - EIGRP Stub / / /24
 Lab 2 - EIGRP Stub Lo0 1.1.0.1/24 1.1.1.1/24 Lo1 200.1.1.1/24 200.2.2.2/24 F0/0.1.2 F0/0 R1 1.1.2.1/24 Lo2.1 S1/2 CE 1.1.3.1/24 Lo3 12.1.1.0 /24.2 S1/1 2.2.3.2/24 Lo3 R2 2.2.2.2/24 Lo2 Lo0 2.2.0.2/24 2.2.1.2/24
Lab 2 - EIGRP Stub Lo0 1.1.0.1/24 1.1.1.1/24 Lo1 200.1.1.1/24 200.2.2.2/24 F0/0.1.2 F0/0 R1 1.1.2.1/24 Lo2.1 S1/2 CE 1.1.3.1/24 Lo3 12.1.1.0 /24.2 S1/1 2.2.3.2/24 Lo3 R2 2.2.2.2/24 Lo2 Lo0 2.2.0.2/24 2.2.1.2/24
LAB1: BGP IPv4. BGP: Initial Config. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
CCIE ROUTING & SWITCHING v5.0 LAB EXAM CONFIGURATION SECTION -H3 Lead2pass.
 CCIE ROUTING & SWITCHING v5.0 LAB EXAM CONFIGURATION SECTION -H3 H3 Topology Diagrams Collection SECTION 1 Layer 2 Technologies Section 1.1: LAN Access Section 1.2: LAN Distribution Section 1.3: LAN Resiliency:
CCIE ROUTING & SWITCHING v5.0 LAB EXAM CONFIGURATION SECTION -H3 H3 Topology Diagrams Collection SECTION 1 Layer 2 Technologies Section 1.1: LAN Access Section 1.2: LAN Distribution Section 1.3: LAN Resiliency:
CCIE Service Provider v3.0 Lab Workbook. Copyright Information. Copyright Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Copyright Information Copyright 2003-2012 Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE Service Provider v3.0 Lab Workbook, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All
Copyright Information Copyright 2003-2012 Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE Service Provider v3.0 Lab Workbook, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All
MultiVRF Deployment Example
 MultiVRF Deployment Example BGP Session Per VRF Loopback13 192.168.1.13/32 AVPN VLAN10/VE10/RED VRF/172.16.16.2/30 VLAN11/VE11/GREEN VRF/172.16.16.6/30 VLAN13/VE13/Manage VRF/172.16.16.10/30 (2) Customer
MultiVRF Deployment Example BGP Session Per VRF Loopback13 192.168.1.13/32 AVPN VLAN10/VE10/RED VRF/172.16.16.2/30 VLAN11/VE11/GREEN VRF/172.16.16.6/30 VLAN13/VE13/Manage VRF/172.16.16.10/30 (2) Customer
UniNets MPLS LAB MANUAL MPLS. UNiNets Multiprotocol label Switching MPLS LAB MANUAL. UniNets MPLS LAB MANUAL
 MPLS UNiNets Multiprotocol label Switching MPLS LAB MANUAL CCNP TOPOLOGY Lab: OSPF Routing VPN Topology: Task1: Perform the basic Configuration to provide the reachability as per diagram. SW1 Configuration
MPLS UNiNets Multiprotocol label Switching MPLS LAB MANUAL CCNP TOPOLOGY Lab: OSPF Routing VPN Topology: Task1: Perform the basic Configuration to provide the reachability as per diagram. SW1 Configuration
Configuring IPv6 Provider Edge over MPLS (6PE)
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
Deploy MPLS L3 VPN. APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by:
 Deploy MPLS L3 VPN APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems Course Outline MPLS L3 VPN Models L3
Deploy MPLS L3 VPN APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems Course Outline MPLS L3 VPN Models L3
Route Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks
 Route Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks Document ID: 47807 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Route Leaking from a Global Routing Table into a VRF and Route
Route Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks Document ID: 47807 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Route Leaking from a Global Routing Table into a VRF and Route
IP NAT Troubleshooting. Solutions. Luke Bibby, CCIE #45527
 IP NAT Troubleshooting Solutions Luke Bibby, CCIE #45527 Quick Overview of Scenario Solutions Scenario #1 R2 s E0/0 should be NAT inside not NAT outside ACL 100 is configured incorrectly NAT policy missing
IP NAT Troubleshooting Solutions Luke Bibby, CCIE #45527 Quick Overview of Scenario Solutions Scenario #1 R2 s E0/0 should be NAT inside not NAT outside ACL 100 is configured incorrectly NAT policy missing
Failover with EIGRP Using VRF Configuration Example
 Failover with EIGRP Using VRF onfiguration Example ocument I: 113446 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Hardware and Software Versions onventions onfigure Network iagram onfigurations Verify Show ommands
Failover with EIGRP Using VRF onfiguration Example ocument I: 113446 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Hardware and Software Versions onventions onfigure Network iagram onfigurations Verify Show ommands
Configuration and Management of Networks 2012
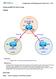 Configuring BGP with default routing Topology Objectives Background Instructions Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on
Configuring BGP with default routing Topology Objectives Background Instructions Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on
May 14, 2006 Nairobi, Kenya
 AfNOG MPLS Lab May 14, 2006 Nairobi, Kenya Page 1 of 30 Table of Contents Assignment...3 Topology...3 Connection information...3 IP Addressing...4 Initial Configuration...4 Lab Modules...5 Module 1: Basic
AfNOG MPLS Lab May 14, 2006 Nairobi, Kenya Page 1 of 30 Table of Contents Assignment...3 Topology...3 Connection information...3 IP Addressing...4 Initial Configuration...4 Lab Modules...5 Module 1: Basic
BGP Best External. Finding Feature Information
 The feature provides the network with a backup external route to avoid loss of connectivity of the primary external route. The feature advertises the most preferred route among those received from external
The feature provides the network with a backup external route to avoid loss of connectivity of the primary external route. The feature advertises the most preferred route among those received from external
address-family ipv4 vrf vrf-name - Selects a per-vrf instance of a routing protocol.
 LAB 1: Initial MPLS VPN Setup LAB 2: Running OSPF between PE and CE Routers LAB 3: Running BGP between PE and CE Routers LAB 4: Overlapping VPNs LAB 1: Initial MPLS VPN Setup Introduction: Introduction
LAB 1: Initial MPLS VPN Setup LAB 2: Running OSPF between PE and CE Routers LAB 3: Running BGP between PE and CE Routers LAB 4: Overlapping VPNs LAB 1: Initial MPLS VPN Setup Introduction: Introduction
BGP Persistence. Restrictions for BGP Persistence. Information About BGP Persistence
 BGP persistence enables the router to retain routes that it has learnt from the configured neighbor even when the neighbor session is down. BGP persistence is also referred as long lived graceful restart
BGP persistence enables the router to retain routes that it has learnt from the configured neighbor even when the neighbor session is down. BGP persistence is also referred as long lived graceful restart
3 ROUTER SETUP WITH FRAME RELAY CONFIGURATION OF FRAME RELAY ROUTER
 3 ROUTER SETUP WITH FRAME RELAY R2 s0 Network 192.168.1.0 s1 DCE * Frame Relay Network * s0 192.168.1.0 s0 DCE R1 Hardware Requirement: 1 Router with t 2 Serials 2 Router with 1 Serial 2 DTE/DCE Serial
3 ROUTER SETUP WITH FRAME RELAY R2 s0 Network 192.168.1.0 s1 DCE * Frame Relay Network * s0 192.168.1.0 s0 DCE R1 Hardware Requirement: 1 Router with t 2 Serials 2 Router with 1 Serial 2 DTE/DCE Serial
MPLS for R&S CCIE Candidates
 MPLS for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 2 About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since the late 1980s CCIE R&S #6458 CCSI 97168 Cisco 360 R&S Master Instructor Course director
MPLS for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 2 About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since the late 1980s CCIE R&S #6458 CCSI 97168 Cisco 360 R&S Master Instructor Course director
MPLS VPN Multipath Support for Inter-AS VPNs
 The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing. Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing Topology Objectives Background Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing Topology Objectives Background Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel
Configuration and Management of Networks
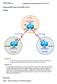 Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements. Components Used
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations OSPF EIGRP RIP Troubleshoot Introduction This document describes how to redistribute Internal Border
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations OSPF EIGRP RIP Troubleshoot Introduction This document describes how to redistribute Internal Border
CCNP ROUTE LAB MANUAL
 CCNP ROUTE 300-101 UNiNets CCNP Cisco Certified Network Professional ROUTE LAB MANUAL CCNP TOPOLOGY Lab: ibgp Synchronization TASK Configure BGP per the diagram to obtain connectivity from AS 1 to R4 and
CCNP ROUTE 300-101 UNiNets CCNP Cisco Certified Network Professional ROUTE LAB MANUAL CCNP TOPOLOGY Lab: ibgp Synchronization TASK Configure BGP per the diagram to obtain connectivity from AS 1 to R4 and
MPLS VPN--Inter-AS Option AB
 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0
 Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
LAB5: OSPF IPv4. OSPF: Stub. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB5: SPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB5: SPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN
 Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN Document ID: 23565 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Router Configurations Problem Cause of the LSP Failure
Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN Document ID: 23565 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Router Configurations Problem Cause of the LSP Failure
MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB
 First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
Page1. Cisco IOS Software, Linux Software (I86BI_LINUX-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 15.2(4)M1, DEVELOPMENT TEST SOFTWARE
 BGP Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as complete
BGP Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as complete
BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing
 2016/09/08 10:01 1/6 BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Apply the concepts of BGP policy learned in class to achieve the
2016/09/08 10:01 1/6 BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Apply the concepts of BGP policy learned in class to achieve the
H3C BGP Configuration Examples
 H3C BGP Configuration Examples Copyright 2017 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
H3C BGP Configuration Examples Copyright 2017 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example
 Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example Document ID: 113361 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Related Information
Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example Document ID: 113361 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Related Information
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
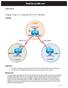 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
ibgp Multipath Load Sharing
 ibgp Multipath Load haring Feature History Release 12.2(2)T 12.2(14) Modification This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into. This feature module describes the ibgp Multipath Load haring
ibgp Multipath Load haring Feature History Release 12.2(2)T 12.2(14) Modification This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into. This feature module describes the ibgp Multipath Load haring
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador July 06)
 South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Multiprotocol BGP configuration Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Laboratory
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Multiprotocol BGP configuration Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Laboratory
EIGRP Lab / lo1. .1 lo / /30
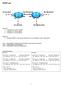 EIGRP Lab 172,16,1.0/24.1 lo1 192.168.20.0/30.2.1 Merida fa0 fa0 Vargas lo2.1 lo2.5.1 lo1 192.168.30.0/24 172.16.2.0/24 192.168.20.4.0/30 Scenario: Loopback0 is used for RouterID Loopback1 is a virtual
EIGRP Lab 172,16,1.0/24.1 lo1 192.168.20.0/30.2.1 Merida fa0 fa0 Vargas lo2.1 lo2.5.1 lo1 192.168.30.0/24 172.16.2.0/24 192.168.20.4.0/30 Scenario: Loopback0 is used for RouterID Loopback1 is a virtual
Label Distribution Protocol and Basic MPLS Configuration. APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by:
 Label Distribution Protocol and Basic MPLS Configuration APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Label Distribution Protocol 2
Label Distribution Protocol and Basic MPLS Configuration APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Label Distribution Protocol 2
The information in this document is based on Cisco IOS Software Release 15.4 version.
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
MPLS VPN C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T. BGP Advertising IPv4 Prefixes with a Label
 7 C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T This online supplement of Chapter 7 focuses on two important developments. The first one is Inter-Autonomous. Inter-Autonomous is a concept whereby two service provider
7 C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T This online supplement of Chapter 7 focuses on two important developments. The first one is Inter-Autonomous. Inter-Autonomous is a concept whereby two service provider
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) What Is BGP?
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) http:// What Is BGP? Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 Standards based RFC 4271 A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Exterior Gateway Protocol
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) http:// What Is BGP? Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 Standards based RFC 4271 A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Exterior Gateway Protocol
Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6 Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a manual IPv6 tunnel. Configure EIGRP for IPv6 across the tunnel. Background In this
Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6 Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a manual IPv6 tunnel. Configure EIGRP for IPv6 across the tunnel. Background In this
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
BGP Attributes and Path Selection
 BGP Attributes and Path Selection ISP Training Workshops 1 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 2 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop AS Path MED...... Part of a BGP Update Describes the characteristics
BGP Attributes and Path Selection ISP Training Workshops 1 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 2 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop AS Path MED...... Part of a BGP Update Describes the characteristics
BGP FlowSpec Route-reflector Support
 The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Flowspec (Flow Specification) Route Reflector feature enables service providers to control traffic flows in their network. This helps in filtering traffic and helps in
The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Flowspec (Flow Specification) Route Reflector feature enables service providers to control traffic flows in their network. This helps in filtering traffic and helps in
Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration
 Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Module 6 Implementing BGP
 Module 6 Implementing BGP Lesson 1 Explaining BGP Concepts and Terminology BGP Border Gateway Protocol Using BGP to Connect to the Internet If only one ISP, do not need BGP. If multiple ISPs, use BGP,
Module 6 Implementing BGP Lesson 1 Explaining BGP Concepts and Terminology BGP Border Gateway Protocol Using BGP to Connect to the Internet If only one ISP, do not need BGP. If multiple ISPs, use BGP,
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab. Part 2 of 7
 CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 2 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 2 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0
 Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Switching-I Questions & Answers CCIE R&S by Narbik Kocharians Advanced
Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Switching-I Questions & Answers CCIE R&S by Narbik Kocharians Advanced
Introduction to BGP. ISP Workshops. Last updated 30 October 2013
 Introduction to BGP ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 Border Gateway Protocol p A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks n Exterior gateway protocol
Introduction to BGP ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 Border Gateway Protocol p A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks n Exterior gateway protocol
Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands
 Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor multiprotocol BGP. Multiprotocol BGP is based on RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for
Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor multiprotocol BGP. Multiprotocol BGP is based on RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for
IOS Implementation of the ibgp PE CE Feature
 IOS Implementation of the ibgp PE CE Feature Document ID: 117567 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Apr 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Background Information Implement ibgp PE CE BGP Customer
IOS Implementation of the ibgp PE CE Feature Document ID: 117567 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Apr 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Background Information Implement ibgp PE CE BGP Customer
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
 IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 22, 2013 Last Modified: January 22, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 22, 2013 Last Modified: January 22, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network
 Anas Al-Selwi Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Bachelor of Engineering Information Technology Thesis 08 May 2013 Abstract Author(s)
Anas Al-Selwi Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Bachelor of Engineering Information Technology Thesis 08 May 2013 Abstract Author(s)
BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family
 BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute L2VPN endpoint provisioning information. BGP uses a separate L2VPN
BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute L2VPN endpoint provisioning information. BGP uses a separate L2VPN
Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Configure. Requirements. Components Used
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations CE1 CE2 PE1 PE2 Verify Case 1: Accepting and exchanging customer routes over MP-BGP Case 2: Leaking
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations CE1 CE2 PE1 PE2 Verify Case 1: Accepting and exchanging customer routes over MP-BGP Case 2: Leaking
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example
 Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
EVPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) Single Homed
 EVPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) Single Homed EVPN-VPWS single homed is a BGP control plane solution for point-to-point services. It has the ability to forward traffic from or to one network to
EVPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) Single Homed EVPN-VPWS single homed is a BGP control plane solution for point-to-point services. It has the ability to forward traffic from or to one network to
EVPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) Single Homed
 EVPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) Single Homed Effective Release Cisco IOS XE 3.18, this feature is now supported on Cisco ASR 920 Series Aggregation Services Router, EVPN-VPWS single homed is a
EVPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) Single Homed Effective Release Cisco IOS XE 3.18, this feature is now supported on Cisco ASR 920 Series Aggregation Services Router, EVPN-VPWS single homed is a
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one MPLS VPN-based service provider
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one MPLS VPN-based service provider
Configure L2VPN Autodiscovery and Signaling
 This chapter describes the L2VPN Autodiscovery and Signaling feature which enables the discovery of remote Provider Edge (PE) routers and the associated signaling in order to provision the pseudowires.
This chapter describes the L2VPN Autodiscovery and Signaling feature which enables the discovery of remote Provider Edge (PE) routers and the associated signaling in order to provision the pseudowires.
CCIE R&S Techtorial MPLS
 CCIE R&S Techtorial MPLS Ing. Tomáš Kelemen Partner Systems Engineer CCIE #24395 Ing. Peter Mesjar Systems Engineer CCIE #17428 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda Introduction to MPLS
CCIE R&S Techtorial MPLS Ing. Tomáš Kelemen Partner Systems Engineer CCIE #24395 Ing. Peter Mesjar Systems Engineer CCIE #17428 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda Introduction to MPLS
BGP Link-State. Finding Feature Information. Overview of Link-State Information in BGP
 (LS) is an Address Family Identifier (AFI) and Sub-address Family Identifier (SAFI) defined to carry interior gateway protocol (IGP) link-state database through BGP. BGP-LS delivers network topology information
(LS) is an Address Family Identifier (AFI) and Sub-address Family Identifier (SAFI) defined to carry interior gateway protocol (IGP) link-state database through BGP. BGP-LS delivers network topology information
MPLS VPN Route Target Rewrite
 The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA ( )
 STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA (640-802) Developed By, Router Infotech Career Academy LAB: 09 Static Route Configuration Objective: To configure & implement Static Route successfully on said devices and test its
STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA (640-802) Developed By, Router Infotech Career Academy LAB: 09 Static Route Configuration Objective: To configure & implement Static Route successfully on said devices and test its
Lab Guide CIERS1. Overview. Outline
 CIERS1 Lab Guide Overview Outline This guide presents the instructions and other information concerning the activities for this course. You can find the recommended solutions in the Answer Key. This guide
CIERS1 Lab Guide Overview Outline This guide presents the instructions and other information concerning the activities for this course. You can find the recommended solutions in the Answer Key. This guide
BGP Event-Based VPN Import
 The feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced BGP path import is driven by events; when a BGP path changes, all of its imported copies
The feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced BGP path import is driven by events; when a BGP path changes, all of its imported copies
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Last Updated: December 14, 2011 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Last Updated: December 14, 2011 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one
IPv6 BGP AS Path. R1 Router Config:! ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef. R4 Router Config:! ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef Page1
 IPv6 IPv6 BGP AS Path Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
IPv6 IPv6 BGP AS Path Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Configuring Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) and VPLS BGP-Based Autodiscovery
 Configuring Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) and VPLS BGP-Based Autodiscovery Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring VPLS, page 1 Configuring VPLS BGP-based Autodiscovery, page 17 Finding Feature
Configuring Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) and VPLS BGP-Based Autodiscovery Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring VPLS, page 1 Configuring VPLS BGP-based Autodiscovery, page 17 Finding Feature
Implementing DCI VXLAN Layer 3 Gateway
 This chapter module provides conceptual and configuration information for Data Center Interconnect (DCI) VXLAN Layer 3 Gateway on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. Release Modification Release 5.3.2 This feature
This chapter module provides conceptual and configuration information for Data Center Interconnect (DCI) VXLAN Layer 3 Gateway on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. Release Modification Release 5.3.2 This feature
APNIC elearning: MPLS L3 VPN
 ANIC elearning: MLS L3 VN 18 JANUARY 2017 11:00 AM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Issue Date: 07 July 2015 Revision: 2.0 Introduction resenter/s Jessica Bei Wei Training Officer jwei@apnic.net Specialties: Routing
ANIC elearning: MLS L3 VN 18 JANUARY 2017 11:00 AM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Issue Date: 07 July 2015 Revision: 2.0 Introduction resenter/s Jessica Bei Wei Training Officer jwei@apnic.net Specialties: Routing
SDN Workshop. Contact: WSDN01_v0.1
 SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS - Lab SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS Configuration 3 Configuration Example
SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS - Lab SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS Configuration 3 Configuration Example
Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support
 Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support Last Updated: December 23, 2011 The Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support feature enables Multicast Distribution Trees (MDTs) used for Multicast VPNs (MVPNs) to span
Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support Last Updated: December 23, 2011 The Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support feature enables Multicast Distribution Trees (MDTs) used for Multicast VPNs (MVPNs) to span
Rev External BGP
 Rev. 00.. External BGP c c n a c o o k b o o k. c o m C O N C E P T S AS (Autonomous System) A network under a single administrative control, like a single company or a single ISP. ASN (AS Number) used
Rev. 00.. External BGP c c n a c o o k b o o k. c o m C O N C E P T S AS (Autonomous System) A network under a single administrative control, like a single company or a single ISP. ASN (AS Number) used
BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family
 BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family Last Updated: November 21, 2012 BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute
BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family Last Updated: November 21, 2012 BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature lets you configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes and Multiprotocol
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature lets you configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes and Multiprotocol
MPLS Troubleshooting. Contents. Prerequisites. Document ID: Requirements. Components Used
 MPLS Troubleshooting Document ID: 12492 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions Troubleshoot Procedures Verify That Routing Protocol Runs Verify EF Switching Verify MPLS
MPLS Troubleshooting Document ID: 12492 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions Troubleshoot Procedures Verify That Routing Protocol Runs Verify EF Switching Verify MPLS
Deploy VPLS. APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by:
 Deploy VPLS APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems 2 VPLS Overview 3 Virtual Private LAN Service
Deploy VPLS APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems 2 VPLS Overview 3 Virtual Private LAN Service
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab. Part 1 of 7
 CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 1 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 1 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
Fortinet Auto Discovery VPN (ADVPN)
 Fortinet Auto Discovery VPN (ADVPN) Stéphane HAMELIN Support Engineering Team Copyright Fortinet Inc. All rights reserved. Change Log Date Author 2017-09-14 S. Hamelin IKEv2 is supported as of FortiOS
Fortinet Auto Discovery VPN (ADVPN) Stéphane HAMELIN Support Engineering Team Copyright Fortinet Inc. All rights reserved. Change Log Date Author 2017-09-14 S. Hamelin IKEv2 is supported as of FortiOS
CCNP Route Questions/Answers Labs
 Refer to the exhibit. R2 is an ASBR for EIGRP AS 100 and OSPF Area 24. R3 is an ASBR for EIGRP AS 100 and OSPF Area 34. R1 is configured for EIGRP AS 100, and is router where you can ping from. R4 has
Refer to the exhibit. R2 is an ASBR for EIGRP AS 100 and OSPF Area 24. R3 is an ASBR for EIGRP AS 100 and OSPF Area 34. R1 is configured for EIGRP AS 100, and is router where you can ping from. R4 has
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature enables you to configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature enables you to configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes
BGP Route Reflector Commands
 This chapter provides details of the commands used for configuring Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Route Reflector (RR). address-family (BGP), on page 2 keychain, on page 5 neighbor (BGP), on page 7 remote-as
This chapter provides details of the commands used for configuring Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Route Reflector (RR). address-family (BGP), on page 2 keychain, on page 5 neighbor (BGP), on page 7 remote-as
Lab 3.2 Configuring a Basic GRE Tunnel
 Lab 3.2 onfiguring a Basic GRE Tunnel Learning Objectives onfigure a GRE tunnel onfigure EIGRP on a router onfigure and test routing over the tunnel interfaces Topology iagram Scenario This lab is designed
Lab 3.2 onfiguring a Basic GRE Tunnel Learning Objectives onfigure a GRE tunnel onfigure EIGRP on a router onfigure and test routing over the tunnel interfaces Topology iagram Scenario This lab is designed
BGP Cost Community. Prerequisites for the BGP Cost Community Feature
 The feature introduces the cost extended community attribute. The cost community is a non-transitive extended community attribute that is passed to internal BGP (ibgp) and confederation peers but not to
The feature introduces the cost extended community attribute. The cost community is a non-transitive extended community attribute that is passed to internal BGP (ibgp) and confederation peers but not to
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking
 The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
