Elastic Multicast. Brian Adamson NRL Claudiu Danilov Boeing Joe Macker NRL. dra;- adamson- elas=cmcast November 2013 IETF 88 - Vancouver
|
|
|
- Austen Anderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Elastic Multicast Brian Adamson NRL Claudiu Danilov Boeing Joe Macker NRL dra;- adamson- elas=cmcast November 2013 IETF 88 - Vancouver
2 Outline Background and Main Concept Protocol Descrip6on Some Experimental Results Implementa6on Status Protocol Design Considera6ons Document Status 2
3 Background - SMF Simplified Mul=cast Forwarding (SMF) MANET Mul6cast (broadcast) protocol. Packets are disseminated to the en6re MANET. Duplicates are eliminated (no loops). Op6mized through use of Connected Domina6ng Set (CDS). No knowledge of group membership. Very efficient in small, highly dynamic mobile networks. Not intended to scale to large networks. 3
4 Main Concept Dynamic pruning of broadcas6ng nodes in SMF. Keep the por)on of SMF mesh ac)ve only where needed Converges to single path mul6cast trees in stable networks Expands to full network broadcast in highly dynamic networks Maintains no topology or global membership informa6on. Applied to higher bandwidth traffic Lower bandwidth traffic s6ll broadcasted to the en6re MANET Proposed provision for surrogate message to adver)se ac)ve flows instead of flooding user traffic for some flows if desired 4
5 Definitions Group: An IP Mul6cast address. Node: A wireless network node running SMF. Flow: Traffic being characterized by a source address, des6na6on group, and a set of op6onal parameters such as protocol, traffic class, port, etc. Subscriber: A node that subscribes to (joins) that group. Ac=ve forwarder for a flow: An SMF node that does not limit packet broadcas6ng for that flow. EM- ACK message for a flow: A unicast control packet being sent to an upstream (previous hop) forwarder, indica6ng interest in a flow. EM- ADV message: Op6onal message with a list of ac6ve flows that can be disseminated as surrogate for lower rate flooding 5
6 Elastic Multicast Protocol (1) Each node limits the forwarding rate through a separate token bucket created for each flow they observe. DPD and SMF relay sets (CDS) are also applied. Packets are forwarded via local broadcast. Lower traffic flows get floded to the en6re MANET, as with SMF. Higher bandwidth flows are throsled, and get most of their packets dropped. All packets that exceed the token bucket rate for their flow are dropped. Some packets s6ll make it to the en6re MANET. Ini6al empty token bucket can allow for start up of some mul6cast protocols Subscribers send periodic EM- ACK messages to an upstream forwarder only if/when they receive new packetsfor groups that are subscribed to from that node. DPD determines new packets. No link is established to the upstream nodes. EM- ACK messages con6nue to be sent periodically to an upstream node, as long as new subscribed packets con6nue to be received from that node. 6
7 Elastic Multicast Protocol (2) Upon receiving an EM- ACK message for a flow, a node becomes an ac6ve forwarder for that flow, for a limited interval. A new EM- ACK message received refreshes the interval for that flow. Ac6ve forwarders send periodic EM- ACK messages to upstream forwarders only if/when they receive new packets that match flows for which they are ac6ve forwarders. EM- ACK messages con6nue to be sent periodically to an upstream forwarder, as long as new packets for their flows con6nue to be received from that node. 7
8 Sta=c network Dynamic Behavior Mul6ple trees (backbones) of high speed forwarders are established from sources to mul6cast des6na6ons. Trees are maintained through periodic Join messages. Dynamic network More nodes become high speed forwarders due to topology changes The set/number of ac6ve forwarders depends of the network dynamics in different parts of the network. Poten6ally all SMF relays can become ac6ve forwarders. When/where mobility slows down, some of the ac6ve forwarder 6mers expire, and they start throsling down the flows they forward. Eventually, if the network becomes sta6c, only a small number of ac6ve forwarders will form trees/backbones derived from the full SMF mesh 8
9 Elastic Multicast Protocol Messages EM- ACK router- id : iden)fier of previous hop forwarder group- addr: group des)na)on address of flow source- addr: source address of flow protocol, traffic class, ports (op)onal descriptors) EM- ADV op)onal list of ac)ve flows, each with: group- addr: group des)na)on address of flow source- addr: source address of flow protocol, traffic class, ports (op)onal descriptors) dpd- id: DPD iden)fier of packet triggering flow adver)sement tagger- id: originator of flow adver)sement 9
10 Current Implementation Architecture Two separate processes Packets intercepted and forwarded by SMF process. Forwarding decisions done in the Rou6ng Daemon. The Rou6ng Daemon processes handles subscrip6ons and sends EM- ACK messages Approach DPD pcap capture netfilter queue SMF ECDS IP Data Packets Raw sockets / firewallforward Routing Daemon Local Subscriptions Rate Limiting DataAcks 10
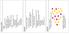
11 Static Grid Topology S 1 20 nodes, sta6c topology Single sender at node S 7 SMF (Classic Flooding) compared with EM Measured traffic at each node. D D1 Single receiver D1 (EM1) Forwarding nodes: 7, 13, 19 Two receivers D1 and D2 (EM2) Forwarding nodes: 7, 12, 13, 19 Mbytes SMF EM 1 EM Nodes 11
12 Gauntlet Scenario S D 30 nodes, random mobility. 200 x 800 grid; wireless range 200 Two end nodes are sta6c (S, D). Nodes in the middle of the network move faster. Node mobility slows down gradually towards the ends Mul6cast UDP streams sent from S to D for 300 seconds. 12
13 Gauntlet Topology Overhead S D Static Mobile MBytes SMF MBytes SMF 10 EM 10 EM Nodes Nodes 13
14 Random Waypoint Delivery Ratio Delivery Ratio (%) Delivery Ratio (%) static medium slow fast Time (s) Time (s) 40 mobile nodes; 5 subscribers; one sender; four different scenarios 14
15 Random Waypoint Overhead Overhead Ratio Overhead Ratio static medium slow fast Time (s) Time (s) 40 mobile nodes; 5 subscribers; one sender; four different scenarios 15
16 Implementation Status EM- ACK implemented as UDP message format Will be updated to PacketBB format EM- ADV, dynamic group membership not yet implemented nrlsmf and arouted processes both in packet forwarding path Plan to define forwarding informa6on base (FIB) structure for SMF that supports this and poten6ally other protocol needs for beser control and forwarding plane separa6on Will refactor nrlsmf, arouted, and nrlnhdp implementa6ons to support updated design 16
17 Protocol Design Considerations IGMP and MLD ASM and SSM support possible Local host associa6on paradigms Collocated processes joining groups OS- specific IGMP/MLD join/leave intercep6on Directly asached hosts on non- MANET interfaces Standard IGMP/MLD querier opera6on sufficient Neighboring non- router MANET hosts Border Gateways Modified IGMP/MLD querier opera6on needed EM- ADV mechanism useful for gateway purposes Concept for wildcard EM- ADV message to collect rou6ng area membership and/or pre- plumb set of ac6ve forwarders for joined groups Proac6ve Elas6c Mul6cast Nodes joining groups as sources could generated EM- ADV messages SMF Relay Set Selec6on Algorithm considera6ons ECDS and CF accommodated by EM- ACK genera6on as described S- MPR and other relay set algorithms may need modified behavior E.g., only send EM- ACK to S- MPR selector previous hop forwarders 17
18 Document Status draft-adamson-elasticmcast-00! It s a rough drak. PacketBB (RFC 5444) message formats not yet defined Elas6c Mul6cast could piggy- back with other MANET protocol signaling (e.g. NHDP, etc) Protocol 6meouts not explicitly described Details on various protocol design considera6ons need to be completed 18
19 Elastic Multicast Summary Dynamic pruning of SMF relays for specific group memberships Converges to single path mul6cast trees in stable networks Expands to full network flood in highly dynamic networks Maintains no topology or global membership informa6on. Relay set reduc6on applied to higher bandwidth traffic Lower bandwidth traffic s6ll flooded to the en6re MANET Or surrogate flow adver6sements 19
Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) Multicast Routing Perspective. Brian Adamson Internet Engineering Task Force 101 March London
 Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) Multicast Routing Perspective Brian Adamson Internet Engineering Task Force 101 March 2018 - London Outline MANET Routing Protocol Synopsis Multicast Routing for MANET Simplified
Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) Multicast Routing Perspective Brian Adamson Internet Engineering Task Force 101 March 2018 - London Outline MANET Routing Protocol Synopsis Multicast Routing for MANET Simplified
Elastic Multicast: Design Extensions and Experimentation Results
 Elastic Multicast: Design Extensions and Experimentation Results Brian Adamson, Joseph P. Macker, Jeffery W. Weston Information Technology Division, Naval Research Laboratory, Washington DC Email: brian.adamson@nrl.navy.mil,
Elastic Multicast: Design Extensions and Experimentation Results Brian Adamson, Joseph P. Macker, Jeffery W. Weston Information Technology Division, Naval Research Laboratory, Washington DC Email: brian.adamson@nrl.navy.mil,
IPv6 PIM. Based on the forwarding mechanism, IPv6 PIM falls into two modes:
 Overview Protocol Independent Multicast for IPv6 () provides IPv6 multicast forwarding by leveraging static routes or IPv6 unicast routing tables generated by any IPv6 unicast routing protocol, such as
Overview Protocol Independent Multicast for IPv6 () provides IPv6 multicast forwarding by leveraging static routes or IPv6 unicast routing tables generated by any IPv6 unicast routing protocol, such as
ASM. Engineering Workshops
 1 ASM 2 ASM Allows SPTs and RPTs RP: Matches senders with receivers Provides network source discovery Typically uses RPT to bootstrap SPT RPs can be learned via: Static configuration recommended Anycast-RP
1 ASM 2 ASM Allows SPTs and RPTs RP: Matches senders with receivers Provides network source discovery Typically uses RPT to bootstrap SPT RPs can be learned via: Static configuration recommended Anycast-RP
Table of Contents 1 PIM Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 PIM Configuration 1-1 PIM Overview 1-1 Introduction to PIM-DM 1-2 How PIM-DM Works 1-2 Introduction to PIM-SM 1-4 How PIM-SM Works 1-5 Introduction to Administrative Scoping in PIM-SM
Table of Contents 1 PIM Configuration 1-1 PIM Overview 1-1 Introduction to PIM-DM 1-2 How PIM-DM Works 1-2 Introduction to PIM-SM 1-4 How PIM-SM Works 1-5 Introduction to Administrative Scoping in PIM-SM
Mul7cast protocols. IP Mul7cast and IGMP SRM (Scalable Reliable Mul7cast) PGM (Pragma7c General Mul7cast)
 IP ANYCAST and MULTICAST; OVERLAYS and UNDERLAYS 1 IP Anycast Outline today Mul7cast protocols IP Mul7cast and IGMP SRM (Scalable Reliable Mul7cast) PGM (Pragma7c General Mul7cast) Overlay networks Tunnels
IP ANYCAST and MULTICAST; OVERLAYS and UNDERLAYS 1 IP Anycast Outline today Mul7cast protocols IP Mul7cast and IGMP SRM (Scalable Reliable Mul7cast) PGM (Pragma7c General Mul7cast) Overlay networks Tunnels
ICS 351: Today's plan. routing protocol comparison encapsulation network dynamics multicasting in general IP multicasting IGMP PIM
 ICS 351: Today's plan routing protocol comparison encapsulation network dynamics multicasting in general IP multicasting IGMP PIM what routing is not: Ethernet switching does not use IP addresses in any
ICS 351: Today's plan routing protocol comparison encapsulation network dynamics multicasting in general IP multicasting IGMP PIM what routing is not: Ethernet switching does not use IP addresses in any
MANET WG Overview 96 th IETF Berlin Manet WG Chairs
 MANET WG Overview 96 th IETF Berlin 2016 Manet WG Chairs What is MANET? Mobile Ad hoc Network The vision: to support robust and efficient operagon in mobile wireless networks by incorporagng IP rougng
MANET WG Overview 96 th IETF Berlin 2016 Manet WG Chairs What is MANET? Mobile Ad hoc Network The vision: to support robust and efficient operagon in mobile wireless networks by incorporagng IP rougng
Link State Rou.ng Reading: Sec.ons 4.2 and 4.3.4
 Link State Rou.ng Reading: Sec.ons. and.. COS 6: Computer Networks Spring 009 (MW :0 :50 in COS 05) Michael Freedman Teaching Assistants: WyaN Lloyd and Jeff Terrace hnp://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spring09/cos6/
Link State Rou.ng Reading: Sec.ons. and.. COS 6: Computer Networks Spring 009 (MW :0 :50 in COS 05) Michael Freedman Teaching Assistants: WyaN Lloyd and Jeff Terrace hnp://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spring09/cos6/
MFTP: a Clean- Slate Transport Protocol for the Informa8on Centric MobilityFirst Network
 MFTP: a Clean- Slate Transport Protocol for the Informa8on Centric MobilityFirst Network Kai Su (presen8ng), Francesco Bronzino, K. K. Ramakrishnan*, and Dipankar Raychaudhuri WINLAB, Rutgers University
MFTP: a Clean- Slate Transport Protocol for the Informa8on Centric MobilityFirst Network Kai Su (presen8ng), Francesco Bronzino, K. K. Ramakrishnan*, and Dipankar Raychaudhuri WINLAB, Rutgers University
Internet Protocol (IP)
 (IP) Guevara Noubir Textbook: Chapter 4. Computer Networks: A Systems Approach, L. Peterson, B. Davie, Morgan Kaufmann Lecture Outline Addressing IP over LAN Rou;ng IPv6 IP Internet Concatena;on of Networks
(IP) Guevara Noubir Textbook: Chapter 4. Computer Networks: A Systems Approach, L. Peterson, B. Davie, Morgan Kaufmann Lecture Outline Addressing IP over LAN Rou;ng IPv6 IP Internet Concatena;on of Networks
Table of Contents Chapter 1 IPv6 PIM Configuration
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 IPv6 PIM Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to IPv6 PIM-DM... 1-2 1.1.2 How IPv6 PIM-DM Works... 1-2 1.1.3 Introduction to IPv6 PIM-SM... 1-5 1.1.4 How IPv6
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 IPv6 PIM Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to IPv6 PIM-DM... 1-2 1.1.2 How IPv6 PIM-DM Works... 1-2 1.1.3 Introduction to IPv6 PIM-SM... 1-5 1.1.4 How IPv6
List of groups known at each router. Router gets those using IGMP. And where they are in use Where members are located. Enhancement to OSPF
 Multicast OSPF OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link State Protocol Use Dijkstra s algorithm (SPF) Calculate shortest path from the router to every possible destination Areas Limit the information volume
Multicast OSPF OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link State Protocol Use Dijkstra s algorithm (SPF) Calculate shortest path from the router to every possible destination Areas Limit the information volume
IP Multicast. What is multicast?
 IP Multicast 1 What is multicast? IP(v4) allows a host to send packets to a single host (unicast), or to all hosts (broadcast). Multicast allows a host to send packets to a subset of all host called a
IP Multicast 1 What is multicast? IP(v4) allows a host to send packets to a single host (unicast), or to all hosts (broadcast). Multicast allows a host to send packets to a subset of all host called a
Distributed Conditional Multicast Access for IP TV in High-Speed Wireless Networks (Destination Specific Multicast)
 137 Distributed Conditional Multicast Access for IP TV in High-Speed Wireless Networks (Destination Specific Multicast) 1, 2 Jan Fesl, 1 Richard Klee, 1 Marie Dolezalova 1 Institute of Applied Informatics,
137 Distributed Conditional Multicast Access for IP TV in High-Speed Wireless Networks (Destination Specific Multicast) 1, 2 Jan Fesl, 1 Richard Klee, 1 Marie Dolezalova 1 Institute of Applied Informatics,
Mobile Ad-hoc Networks
 Mobile Ad-hoc Networks Fred Baker 1 The manet problem Mobile Random and perhaps constantly changing Ad-hoc Not engineered Networks Elastic data applications which use networks to communicate 2 Examples
Mobile Ad-hoc Networks Fred Baker 1 The manet problem Mobile Random and perhaps constantly changing Ad-hoc Not engineered Networks Elastic data applications which use networks to communicate 2 Examples
Multicast Technology White Paper
 Multicast Technology White Paper Keywords: Multicast, IGMP, IGMP Snooping, PIM, MBGP, MSDP, and SSM Mapping Abstract: The multicast technology implements high-efficiency point-to-multipoint data transmission
Multicast Technology White Paper Keywords: Multicast, IGMP, IGMP Snooping, PIM, MBGP, MSDP, and SSM Mapping Abstract: The multicast technology implements high-efficiency point-to-multipoint data transmission
Mobile Communications. Ad-hoc and Mesh Networks
 Ad-hoc+mesh-net 1 Mobile Communications Ad-hoc and Mesh Networks Manuel P. Ricardo Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto Ad-hoc+mesh-net 2 What is an ad-hoc network? What are differences between
Ad-hoc+mesh-net 1 Mobile Communications Ad-hoc and Mesh Networks Manuel P. Ricardo Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto Ad-hoc+mesh-net 2 What is an ad-hoc network? What are differences between
IPv6 PIM-DM configuration example 36 IPv6 PIM-SM non-scoped zone configuration example 39 IPv6 PIM-SM admin-scoped zone configuration example 42 IPv6
 Contents Configuring IPv6 PIM 1 Overview 1 IPv6 PIM-DM overview 1 IPv6 PIM-SM overview 3 IPv6 BIDIR-PIM overview 8 IPv6 administrative scoping overview 11 IPv6 PIM-SSM overview 13 Relationship among IPv6
Contents Configuring IPv6 PIM 1 Overview 1 IPv6 PIM-DM overview 1 IPv6 PIM-SM overview 3 IPv6 BIDIR-PIM overview 8 IPv6 administrative scoping overview 11 IPv6 PIM-SSM overview 13 Relationship among IPv6
Advanced Network Training Multicast
 Division of Brocade Advanced Network Training Multicast Larry Mathews Systems Engineer lmathews@brocade.com Training Objectives Session will concentrate on Multicast with emphasis on Protocol Independent
Division of Brocade Advanced Network Training Multicast Larry Mathews Systems Engineer lmathews@brocade.com Training Objectives Session will concentrate on Multicast with emphasis on Protocol Independent
Iden%fying Defunct DAGs in RPL dra7- goyal- roll- defunct- dags- 00. Mukul Goyal University of Wisconsin Milwaukee
 Iden%fying Defunct DAGs in RPL dra7- goyal- roll- defunct- dags- 00 Mukul Goyal University of Wisconsin Milwaukee Main Idea Need a mechanism that allows a node to iden;fy defunct DAGs and delete the state
Iden%fying Defunct DAGs in RPL dra7- goyal- roll- defunct- dags- 00 Mukul Goyal University of Wisconsin Milwaukee Main Idea Need a mechanism that allows a node to iden;fy defunct DAGs and delete the state
Configuring multicast VPN
 Contents Configuring multicast VPN 1 Multicast VPN overview 1 Multicast VPN overview 1 MD-VPN overview 3 Protocols and standards 6 How MD-VPN works 6 Share-MDT establishment 6 Share-MDT-based delivery
Contents Configuring multicast VPN 1 Multicast VPN overview 1 Multicast VPN overview 1 MD-VPN overview 3 Protocols and standards 6 How MD-VPN works 6 Share-MDT establishment 6 Share-MDT-based delivery
Politecnico di Milano Advanced Network Technologies Laboratory. ZigBee Revealed
 Politecnico di Milano Advanced Network Technologies Laboratory ZigBee Revealed Zigbee: Communica4on Stack APPLICATIONS Customer APPLICATION INTERFACE SECURITY NETWORK LAYER Star/Cluster/Mesh ZigBee Alliance
Politecnico di Milano Advanced Network Technologies Laboratory ZigBee Revealed Zigbee: Communica4on Stack APPLICATIONS Customer APPLICATION INTERFACE SECURITY NETWORK LAYER Star/Cluster/Mesh ZigBee Alliance
BIER. Bit Indexed Explicit Replica0on. MBONED, IETF 92 Greg Shepherd
 BIER Bit Indexed Explicit Replica0on MBONED, IETF 92 Greg Shepherd The BIER Epiphany Only encode the end- receivers in the packet header. Not the intermediate nodes. Assign end- receivers a Bit Posi0on
BIER Bit Indexed Explicit Replica0on MBONED, IETF 92 Greg Shepherd The BIER Epiphany Only encode the end- receivers in the packet header. Not the intermediate nodes. Assign end- receivers a Bit Posi0on
Configuring MLD. Overview. MLD versions. How MLDv1 operates. MLD querier election
 Contents Configuring MLD 1 Overview 1 MLD versions 1 How MLDv1 operates 1 How MLDv2 operates 3 MLD message types 4 MLD SSM mapping 7 MLD proxying 8 Protocols and standards 9 MLD configuration task list
Contents Configuring MLD 1 Overview 1 MLD versions 1 How MLDv1 operates 1 How MLDv2 operates 3 MLD message types 4 MLD SSM mapping 7 MLD proxying 8 Protocols and standards 9 MLD configuration task list
IP Multicast Technology Overview
 IP multicast is a bandwidth-conserving technology that reduces traffic by delivering a single stream of information simultaneously to potentially thousands of businesses and homes. Applications that take
IP multicast is a bandwidth-conserving technology that reduces traffic by delivering a single stream of information simultaneously to potentially thousands of businesses and homes. Applications that take
Institute of Computer Technology - Vienna University of Technology. L73 - IP QoS Integrated Services Model. Integrated Services Model
 Integrated Services Model IP QoS IntServ Integrated Services Model Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) Agenda Integrated Services Principles Resource Reservation Protocol RSVP Message Formats RSVP in
Integrated Services Model IP QoS IntServ Integrated Services Model Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) Agenda Integrated Services Principles Resource Reservation Protocol RSVP Message Formats RSVP in
Configuring PIM. Information About PIM. Send document comments to CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes how to configure the Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) features on Cisco NX-OS switches in your IPv4 networks. This chapter includes the following sections: Information
CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes how to configure the Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) features on Cisco NX-OS switches in your IPv4 networks. This chapter includes the following sections: Information
Design Intentions. IP QoS IntServ. Agenda. Design Intentions. L73 - IP QoS Integrated Services Model. L73 - IP QoS Integrated Services Model
 Design Intentions Integrated Services Model IP QoS IntServ Integrated Services Model Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) The Internet was based on a best effort packet delivery service, but nowadays the
Design Intentions Integrated Services Model IP QoS IntServ Integrated Services Model Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) The Internet was based on a best effort packet delivery service, but nowadays the
MANET Architecture and address auto-configuration issue
 MANET Architecture and address auto-configuration issue Namhi Kang Catholic University E-mail: kang@catholic.ac.kr Contents Background Information Overview Common MANET misperception Multilink subnet issue
MANET Architecture and address auto-configuration issue Namhi Kang Catholic University E-mail: kang@catholic.ac.kr Contents Background Information Overview Common MANET misperception Multilink subnet issue
Wireless Mul*hop Ad Hoc Networks
 Wireless Mul*hop Guevara Noubir noubir@ccs.neu.edu Some slides are from Nitin Vaidya s tutorial. Infrastructure vs. Ad Hoc Wireless Networks Infrastructure networks: One or several Access- Points (AP)
Wireless Mul*hop Guevara Noubir noubir@ccs.neu.edu Some slides are from Nitin Vaidya s tutorial. Infrastructure vs. Ad Hoc Wireless Networks Infrastructure networks: One or several Access- Points (AP)
3. Evaluation of Selected Tree and Mesh based Routing Protocols
 33 3. Evaluation of Selected Tree and Mesh based Routing Protocols 3.1 Introduction Construction of best possible multicast trees and maintaining the group connections in sequence is challenging even in
33 3. Evaluation of Selected Tree and Mesh based Routing Protocols 3.1 Introduction Construction of best possible multicast trees and maintaining the group connections in sequence is challenging even in
ANYCAST and MULTICAST READING: SECTION 4.4
 1 ANYCAST and MULTICAST READING: SECTION 4.4 COS 461: Computer Networks Spring 2011 Mike Freedman h>p://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spring11/cos461/ 2 Outline today IP Anycast N deshnahons, 1
1 ANYCAST and MULTICAST READING: SECTION 4.4 COS 461: Computer Networks Spring 2011 Mike Freedman h>p://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spring11/cos461/ 2 Outline today IP Anycast N deshnahons, 1
Multicast Communications
 Multicast Communications Multicast communications refers to one-to-many or many-tomany communications. Unicast Broadcast Multicast Dragkedja IP Multicasting refers to the implementation of multicast communication
Multicast Communications Multicast communications refers to one-to-many or many-tomany communications. Unicast Broadcast Multicast Dragkedja IP Multicasting refers to the implementation of multicast communication
Internetworking. Problem: There is more than one network (heterogeneity & scale)
 Internetworking Problem: There is more than one network (heterogeneity & scale) Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Internetworking: Internet Protocol (IP) Routing and scalability Group Communication
Internetworking Problem: There is more than one network (heterogeneity & scale) Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Internetworking: Internet Protocol (IP) Routing and scalability Group Communication
Comparison of proposed path selection protocols for IEEE s WLAN mesh networks
 Comparison of proposed path selection protocols for IEEE 802.11s WLAN mesh networks Sana Ghannay, Sonia Mettali Gammar and Farouk Kamoun CRISTAL lab, National School of Computer Sciences, ENSI, 2010, Manouba
Comparison of proposed path selection protocols for IEEE 802.11s WLAN mesh networks Sana Ghannay, Sonia Mettali Gammar and Farouk Kamoun CRISTAL lab, National School of Computer Sciences, ENSI, 2010, Manouba
Performance Evaluation of Mesh - Based Multicast Routing Protocols in MANET s
 Performance Evaluation of Mesh - Based Multicast Routing Protocols in MANET s M. Nagaratna Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE JNTUH, Hyderabad, India V. Kamakshi Prasad Prof & Additional Cont. of. Examinations
Performance Evaluation of Mesh - Based Multicast Routing Protocols in MANET s M. Nagaratna Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE JNTUH, Hyderabad, India V. Kamakshi Prasad Prof & Additional Cont. of. Examinations
Link State Rou.ng Reading: Sec.ons 4.2 and 4.3.4
 Link State Rou.ng Reading: Sec.ons. and.. COS 6: Computer Networks Spring 0 Mike Freedman hep://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spring/cos6/ Inside a router Goals of Today s Lecture Control plane:
Link State Rou.ng Reading: Sec.ons. and.. COS 6: Computer Networks Spring 0 Mike Freedman hep://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spring/cos6/ Inside a router Goals of Today s Lecture Control plane:
Name-Based Content Routing in Information Centric Networks Using Distance Information
 Name-Based Content Routing in Information Centric Networks Using Distance Information J.J. Garcia-Luna-Aceves Palo Alto Research Center UC Santa Cruz jj@soe.ucsc.edu Origins of Routing for Packet Switching
Name-Based Content Routing in Information Centric Networks Using Distance Information J.J. Garcia-Luna-Aceves Palo Alto Research Center UC Santa Cruz jj@soe.ucsc.edu Origins of Routing for Packet Switching
Switching and bridging
 Switching and bridging CSCI 466: Networks Keith Vertanen Fall 2011 Last chapter: Overview Crea7ng networks from: Point- to- point links Shared medium (wireless) This chapter: SoCware and hardware connec7ng
Switching and bridging CSCI 466: Networks Keith Vertanen Fall 2011 Last chapter: Overview Crea7ng networks from: Point- to- point links Shared medium (wireless) This chapter: SoCware and hardware connec7ng
What is Multicasting? Multicasting Fundamentals. Unicast Transmission. Agenda. L70 - Multicasting Fundamentals. L70 - Multicasting Fundamentals
 What is Multicasting? Multicasting Fundamentals Unicast transmission transmitting a packet to one receiver point-to-point transmission used by most applications today Multicast transmission transmitting
What is Multicasting? Multicasting Fundamentals Unicast transmission transmitting a packet to one receiver point-to-point transmission used by most applications today Multicast transmission transmitting
Table of Contents 1 Multicast VPN Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 Multicast VPN Configuration 1-1 Multicast VPN Overview 1-1 Introduction to MPLS L3VPN 1-1 Introduction to Multicast VPN 1-2 Introduction to MD-VPN 1-4 Protocols and Standards 1-7 How
Table of Contents 1 Multicast VPN Configuration 1-1 Multicast VPN Overview 1-1 Introduction to MPLS L3VPN 1-1 Introduction to Multicast VPN 1-2 Introduction to MD-VPN 1-4 Protocols and Standards 1-7 How
ITEC310 Computer Networks II
 ITEC310 Computer Networks II Chapter 22 Network Layer:, and Routing Department of Information Technology Eastern Mediterranean University Objectives 2/131 After completing this chapter you should be able
ITEC310 Computer Networks II Chapter 22 Network Layer:, and Routing Department of Information Technology Eastern Mediterranean University Objectives 2/131 After completing this chapter you should be able
Content. 1. Introduction. 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm. 3. Simulation and Results. 4. Future Work. 5.
 Rahem Abri Content 1. Introduction 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm Path Discovery Reverse Path Setup Forward Path Setup Route Table Management Path Management Local Connectivity Management
Rahem Abri Content 1. Introduction 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm Path Discovery Reverse Path Setup Forward Path Setup Route Table Management Path Management Local Connectivity Management
IGMP and MLD Op-miza-on for Mobile Hosts and Routers
 76 th IETF, Nov. 2009, Hiroshima, Japan IGMP and MLD Op-miza-on for Mobile Hosts and Routers dra< asaeda mul-mob igmp mld op-miza-on 01 Hitoshi Asaeda (Keio University) 1 Overview This dra< aims to describe
76 th IETF, Nov. 2009, Hiroshima, Japan IGMP and MLD Op-miza-on for Mobile Hosts and Routers dra< asaeda mul-mob igmp mld op-miza-on 01 Hitoshi Asaeda (Keio University) 1 Overview This dra< aims to describe
Broadcast and Multicast Routing
 Broadcast and Multicast Routing Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Group Communication 2/34 How can the Internet provide efficient group communication? send the same copy
Broadcast and Multicast Routing Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Group Communication 2/34 How can the Internet provide efficient group communication? send the same copy
MLD. MLDv1 (defined in RFC 2710), which is derived from IGMPv2. MLDv2 (defined in RFC 3810), which is derived from IGMPv3.
 Introduction to Multicast listener discovery protocol () is used by an IPv6 router to discover the presence of multicast listeners on directly-attached subnets. Multicast listeners are nodes wishing to
Introduction to Multicast listener discovery protocol () is used by an IPv6 router to discover the presence of multicast listeners on directly-attached subnets. Multicast listeners are nodes wishing to
Configuring IGMP Snooping
 This chapter describes how to configure Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping on a Cisco NX-OS device. About IGMP Snooping, page 1 Licensing Requirements for IGMP Snooping, page 4 Prerequisites
This chapter describes how to configure Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping on a Cisco NX-OS device. About IGMP Snooping, page 1 Licensing Requirements for IGMP Snooping, page 4 Prerequisites
Mul$cast and Anycast. Outline today TODAY 3/11/14. Mike Freedman COS 461: Computer Networks. IP Anycast
 Mul$cast and Anycast Mike Freedman COS 461: Computer Networks TODAY h=p://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spr14/cos461/ Outline today 3 4 IP Anycast N desfnafons, 1 should receive the message Providing
Mul$cast and Anycast Mike Freedman COS 461: Computer Networks TODAY h=p://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spr14/cos461/ Outline today 3 4 IP Anycast N desfnafons, 1 should receive the message Providing
Introduction to IGMP for IPTV Networks
 White Paper Introduction to for IPTV Networks Understanding Processing in the Broadband Access Network Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408.745.2000 1.888
White Paper Introduction to for IPTV Networks Understanding Processing in the Broadband Access Network Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408.745.2000 1.888
IP MULTICAST EXPLAINED
 IP MULTICAST EXPLAINED June 2004 Jon Hardwick Data Connection Ltd. Jon.Hardwick@dataconnection.com Data Connection Limited 100 Church Street Enfield, UK Tel: +44 20 8366 1177 / Copyright 2004 Data Connection
IP MULTICAST EXPLAINED June 2004 Jon Hardwick Data Connection Ltd. Jon.Hardwick@dataconnection.com Data Connection Limited 100 Church Street Enfield, UK Tel: +44 20 8366 1177 / Copyright 2004 Data Connection
BASIC MULTICAST TROUBLESHOOTING. Piotr Wojciechowski (CCIE #25543)
 BASIC MULTICAST TROUBLESHOOTING Piotr Wojciechowski (CCIE #25543) ABOUT ME Senior Network Engineer MSO at VeriFone Inc. Previously Network Solutions Architect at one of top polish IT integrators CCIE #25543
BASIC MULTICAST TROUBLESHOOTING Piotr Wojciechowski (CCIE #25543) ABOUT ME Senior Network Engineer MSO at VeriFone Inc. Previously Network Solutions Architect at one of top polish IT integrators CCIE #25543
Multicast overview. Introduction to multicast. Information transmission techniques. Unicast
 Contents Multicast overview 1 Introduction to multicast 1 Information transmission techniques 1 Multicast features 3 Common notations in multicast 4 Multicast advantages and applications 4 Multicast models
Contents Multicast overview 1 Introduction to multicast 1 Information transmission techniques 1 Multicast features 3 Common notations in multicast 4 Multicast advantages and applications 4 Multicast models
! Naive n-way unicast does not scale. ! IP multicast to the rescue. ! Extends IP architecture for efficient multi-point delivery. !
 Bayeux: An Architecture for Scalable and Fault-tolerant Wide-area Data Dissemination ACM NOSSDAV 001 Shelley Q. Zhuang, Ben Y. Zhao, Anthony D. Joseph, Randy H. Katz, John D. Kubiatowicz {shelleyz, ravenben,
Bayeux: An Architecture for Scalable and Fault-tolerant Wide-area Data Dissemination ACM NOSSDAV 001 Shelley Q. Zhuang, Ben Y. Zhao, Anthony D. Joseph, Randy H. Katz, John D. Kubiatowicz {shelleyz, ravenben,
Contents. Overview Multicast = Send to a group of hosts. Overview. Overview. Implementation Issues. Motivation: ISPs charge by bandwidth
 EECS Contents Motivation Overview Implementation Issues Ethernet Multicast IGMP Routing Approaches Reliability Application Layer Multicast Summary Motivation: ISPs charge by bandwidth Broadcast Center
EECS Contents Motivation Overview Implementation Issues Ethernet Multicast IGMP Routing Approaches Reliability Application Layer Multicast Summary Motivation: ISPs charge by bandwidth Broadcast Center
Link Layer. w/ credit to Rick Graziani (Cabrillo) for some of the anima<ons
 Link Layer w/ credit to Rick Graziani (Cabrillo) for some of the anima
Link Layer w/ credit to Rick Graziani (Cabrillo) for some of the anima
Network layer overview
 Network layer overview understand principles behind layer services: layer service models forwarding versus rou:ng how a router works rou:ng (path selec:on) broadcast, mul:cast instan:a:on, implementa:on
Network layer overview understand principles behind layer services: layer service models forwarding versus rou:ng how a router works rou:ng (path selec:on) broadcast, mul:cast instan:a:on, implementa:on
FSOS Multicast Configuration Guide
 FSOS Multicast Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Multicast-Routing...6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Configuration... 6 1.3 Validation... 6 2 Configuring IGMP... 8 2.1 Overview...8 2.2 References...9
FSOS Multicast Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Multicast-Routing...6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Configuration... 6 1.3 Validation... 6 2 Configuring IGMP... 8 2.1 Overview...8 2.2 References...9
Why multicast? The concept of multicast Multicast groups Multicast addressing Multicast routing protocols MBONE Multicast applications Conclusions
 Tuomo Karhapää tuomo.karhapaa@otaverkko.fi Otaverkko Oy Why multicast? The concept of multicast Multicast groups Multicast addressing Multicast routing protocols MBONE Multicast applications Conclusions
Tuomo Karhapää tuomo.karhapaa@otaverkko.fi Otaverkko Oy Why multicast? The concept of multicast Multicast groups Multicast addressing Multicast routing protocols MBONE Multicast applications Conclusions
IP Multicast Jean Yves Le Boudec 2017
 IP Multicast Jean Yves Le Boudec 2017 1 IP Multicast Unicast = send to one destination Multicast = send to a group of destinations IP has multicast addresses: 224.0.0.0/4 (i.e. 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255)
IP Multicast Jean Yves Le Boudec 2017 1 IP Multicast Unicast = send to one destination Multicast = send to a group of destinations IP has multicast addresses: 224.0.0.0/4 (i.e. 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255)
Configuring a Rendezvous Point
 Version History Version Number Date Notes 1 03/15/2002 This document was created. The purpose of this document is to outline four recommended methods for configuring a rendezvous point (RP) in a Protocol
Version History Version Number Date Notes 1 03/15/2002 This document was created. The purpose of this document is to outline four recommended methods for configuring a rendezvous point (RP) in a Protocol
A Comparative and Performance Study of On Demand Multicast Routing Protocols for Ad Hoc Networks
 A Comparative and Performance Study of On Demand Multicast Routing Protocols for Ad Hoc Networks P.Madhan Mohan #, J.James Johnson #, K.Murugan $ and V.Ramachandran % # Under Graduate Student $ Senior
A Comparative and Performance Study of On Demand Multicast Routing Protocols for Ad Hoc Networks P.Madhan Mohan #, J.James Johnson #, K.Murugan $ and V.Ramachandran % # Under Graduate Student $ Senior
Table of Contents 1 IGMP Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 IGMP Configuration 1-1 IGMP Overview 1-1 IGMP Versions 1-1 Introduction to IGMPv1 1-2 Enhancements in IGMPv2 1-3 Enhancements in IGMPv3 1-4 IGMP SSM Mapping 1-5 Protocols and Standards
Table of Contents 1 IGMP Configuration 1-1 IGMP Overview 1-1 IGMP Versions 1-1 Introduction to IGMPv1 1-2 Enhancements in IGMPv2 1-3 Enhancements in IGMPv3 1-4 IGMP SSM Mapping 1-5 Protocols and Standards
IP Multicast. Overview. Casts. Tarik Čičić University of Oslo December 2001
 IP Multicast Tarik Čičić University of Oslo December 00 Overview One-to-many communication, why and how Algorithmic approach (IP) multicast protocols: host-router intra-domain (router-router) inter-domain
IP Multicast Tarik Čičić University of Oslo December 00 Overview One-to-many communication, why and how Algorithmic approach (IP) multicast protocols: host-router intra-domain (router-router) inter-domain
ECE 1749H: Interconnec1on Networks for Parallel Computer Architectures: Rou1ng. Prof. Natalie Enright Jerger
 ECE 1749H: Interconnec1on Networks for Parallel Computer Architectures: Rou1ng Prof. Natalie Enright Jerger Announcements Feedback on your project proposals This week Scheduled extended 1 week Next week:
ECE 1749H: Interconnec1on Networks for Parallel Computer Architectures: Rou1ng Prof. Natalie Enright Jerger Announcements Feedback on your project proposals This week Scheduled extended 1 week Next week:
CSE 473 Introduction to Computer Networks. Final Exam. Your Name: 12/17/2014 PLEASE WRITE LEGIBLY NO POINTS FOR ILLEGIBLE ANSWERS
 CSE 47 Introduction to Computer Networks Roch Guérin Final Exam Your Name: 12/17/2014 PLEASE WRITE LEGIBLY NO POINTS FOR ILLEGIBLE ANSWERS 1. [10 points] Bob has been provided with the following pair of
CSE 47 Introduction to Computer Networks Roch Guérin Final Exam Your Name: 12/17/2014 PLEASE WRITE LEGIBLY NO POINTS FOR ILLEGIBLE ANSWERS 1. [10 points] Bob has been provided with the following pair of
ECE 1749H: Interconnec1on Networks for Parallel Computer Architectures: Rou1ng. Prof. Natalie Enright Jerger
 ECE 1749H: Interconnec1on Networks for Parallel Computer Architectures: Rou1ng Prof. Natalie Enright Jerger Rou1ng Overview Discussion of topologies assumed ideal rou1ng In prac1ce Rou1ng algorithms are
ECE 1749H: Interconnec1on Networks for Parallel Computer Architectures: Rou1ng Prof. Natalie Enright Jerger Rou1ng Overview Discussion of topologies assumed ideal rou1ng In prac1ce Rou1ng algorithms are
Ad Hoc Networks: Issues and Routing
 Ad Hoc Networks: Issues and Routing Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-08/
Ad Hoc Networks: Issues and Routing Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-08/
Multicast routing protocols
 Multicast routing protocols IGMP IP Group Management Protocol PIM Protocol Independent Multicast MOSPF Multicast OSPF DVMRP DV Multicast Routing Protocol E7310-Multicast-2/Comnet 1 Multicast in local area
Multicast routing protocols IGMP IP Group Management Protocol PIM Protocol Independent Multicast MOSPF Multicast OSPF DVMRP DV Multicast Routing Protocol E7310-Multicast-2/Comnet 1 Multicast in local area
Quick Start Guide MU120131A/32A. IP Multicast Measurement MD1230B/MP1590B. Data Quality Analyzer / Network Performance Tester
 Quick Start Guide MU120131A/32A IP Multicast Measurement MD1230B/MP1590B Data Quality Analyzer / Network Performance Tester Contents MU120131A/32A IP Multicast Measurement Quck Start Guide 1. Introduction...
Quick Start Guide MU120131A/32A IP Multicast Measurement MD1230B/MP1590B Data Quality Analyzer / Network Performance Tester Contents MU120131A/32A IP Multicast Measurement Quck Start Guide 1. Introduction...
draft-ietf-magma-igmp-proxy-04.txt Brian Haberman, Caspian Networks Hal Sandick, Sheperd Middle School Expire: March, 2004 September, 2003
 MAGMA Working Group Bill Fenner, AT&T Research INTERNET-DRAFT Haixiang He, Nortel Networks draft-ietf-magma-igmp-proxy-04.txt Brian Haberman, Caspian Networks Hal Sandick, Sheperd Middle School Expire:
MAGMA Working Group Bill Fenner, AT&T Research INTERNET-DRAFT Haixiang He, Nortel Networks draft-ietf-magma-igmp-proxy-04.txt Brian Haberman, Caspian Networks Hal Sandick, Sheperd Middle School Expire:
Implementation and simulation of OLSR protocol with QoS in Ad Hoc Networks
 Implementation and simulation of OLSR protocol with QoS in Ad Hoc Networks Mounir FRIKHA, Manel MAAMER Higher School of Communication of Tunis (SUP COM), Network Department, m.frikha@supcom.rnu.tn ABSTRACT
Implementation and simulation of OLSR protocol with QoS in Ad Hoc Networks Mounir FRIKHA, Manel MAAMER Higher School of Communication of Tunis (SUP COM), Network Department, m.frikha@supcom.rnu.tn ABSTRACT
Multicasting in Ad-Hoc Networks: Comparing MAODV and ODMRP
 Multicasting in Ad-Hoc Networks: Comparing MAODV and ODMRP Thomas Kunz and Ed Cheng Carleton University tkunz@sce.carleton.ca Abstract. Multicasting can efficiently support a variety of applications that
Multicasting in Ad-Hoc Networks: Comparing MAODV and ODMRP Thomas Kunz and Ed Cheng Carleton University tkunz@sce.carleton.ca Abstract. Multicasting can efficiently support a variety of applications that
Real-Time Applications. Delay-adaptive: applications that can adjust their playback point (delay or advance over time).
 Real-Time Applications Tolerant: can tolerate occasional loss of data. Intolerant: cannot tolerate such losses. Delay-adaptive: applications that can adjust their playback point (delay or advance over
Real-Time Applications Tolerant: can tolerate occasional loss of data. Intolerant: cannot tolerate such losses. Delay-adaptive: applications that can adjust their playback point (delay or advance over
OSPF Protocol Overview on page 187. OSPF Standards on page 188. OSPF Area Terminology on page 188. OSPF Routing Algorithm on page 190
 Chapter 17 OSPF Protocol Overview The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) that routes packets within a single autonomous system (AS). OSPF uses link-state information
Chapter 17 OSPF Protocol Overview The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) that routes packets within a single autonomous system (AS). OSPF uses link-state information
IP Multicast Technology Overview
 IP multicast is a bandwidth-conserving technology that reduces traffic by delivering a single stream of information simultaneously to potentially thousands of businesses and homes. Applications that take
IP multicast is a bandwidth-conserving technology that reduces traffic by delivering a single stream of information simultaneously to potentially thousands of businesses and homes. Applications that take
Fast, Efficient, and Robust Multicast in Wireless Mesh Networks
 fast efficient and robust networking FERN Fast, Efficient, and Robust Multicast in Wireless Mesh Networks Ian Chakeres Chivukula Koundinya Pankaj Aggarwal Outline IEEE 802.11s mesh multicast FERM algorithms
fast efficient and robust networking FERN Fast, Efficient, and Robust Multicast in Wireless Mesh Networks Ian Chakeres Chivukula Koundinya Pankaj Aggarwal Outline IEEE 802.11s mesh multicast FERM algorithms
Configuring SSM. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for Configuring SSM
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 1 Restrictions for, page 2 Information About SSM, page 3 How to Configure SSM, page 7 Monitoring SSM, page 15 Configuration Examples for Source
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 1 Restrictions for, page 2 Information About SSM, page 3 How to Configure SSM, page 7 Monitoring SSM, page 15 Configuration Examples for Source
Configuring Basic IP Multicast
 IP multicast is a bandwidth-conserving technology that reduces traffic by delivering a single stream of information simultaneously to potentially thousands of corporate businesses and homes. Applications
IP multicast is a bandwidth-conserving technology that reduces traffic by delivering a single stream of information simultaneously to potentially thousands of corporate businesses and homes. Applications
! Purpose of Multicasting Routing is to reduce cost for applications that send same data to Multiple recipients.
 PAPER OVERVIEW:! Evaluation of two Multicasting protocols namely CBT and PIM.! Comparison of protocols in terms of End-to-end delay, Network resource usage, Join time, Size of the tables containing multicast
PAPER OVERVIEW:! Evaluation of two Multicasting protocols namely CBT and PIM.! Comparison of protocols in terms of End-to-end delay, Network resource usage, Join time, Size of the tables containing multicast
Internet2 Multicast Workshop
 Internet2 Multicast Workshop University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC May, 2004 Acknowledgements Greg Shepherd Beau Williamson Marshall Eubanks Bill Nickless Caren Litvanyi Patrick Dorn Leonard Giuliano
Internet2 Multicast Workshop University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC May, 2004 Acknowledgements Greg Shepherd Beau Williamson Marshall Eubanks Bill Nickless Caren Litvanyi Patrick Dorn Leonard Giuliano
CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018
 CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018 Network Layer V Dmitri Loguinov Texas A&M University April 17, 2018 Original slides copyright 1996-2004 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross Chapter 4:
CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018 Network Layer V Dmitri Loguinov Texas A&M University April 17, 2018 Original slides copyright 1996-2004 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross Chapter 4:
Lab 7-3 Routing IP Multicast with PIM Sparse Mode
 Lab 7-3 Routing IP Multicast with PIM Sparse Mode Learning Objectives Implement and verify PIM-SM operation and adjacencies Implement and verify the use of a static rendezvous point Observe the shared
Lab 7-3 Routing IP Multicast with PIM Sparse Mode Learning Objectives Implement and verify PIM-SM operation and adjacencies Implement and verify the use of a static rendezvous point Observe the shared
Missing pieces + Putting the pieces together
 Missing pieces + Putting the pieces together CS 168, Fall 2014 Sylvia Ratnasamy Material thanks to Ion Stoica, Scott Shenker, Jennifer Rexford, Nick McKeown, and many other colleagues Today Switched Ethernet
Missing pieces + Putting the pieces together CS 168, Fall 2014 Sylvia Ratnasamy Material thanks to Ion Stoica, Scott Shenker, Jennifer Rexford, Nick McKeown, and many other colleagues Today Switched Ethernet
Objectives. Chapter 10. Upon completion you will be able to:
 Chapter 10 Figure 10.1 Position of IGMP in the network layer Objectives Upon completion you will be able to: Know the purpose of IGMP Know the types of IGMP messages Understand how a member joins a group
Chapter 10 Figure 10.1 Position of IGMP in the network layer Objectives Upon completion you will be able to: Know the purpose of IGMP Know the types of IGMP messages Understand how a member joins a group
CHAPTER 3 EFFECTIVE ADMISSION CONTROL MECHANISM IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS
 28 CHAPTER 3 EFFECTIVE ADMISSION CONTROL MECHANISM IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS Introduction Measurement-based scheme, that constantly monitors the network, will incorporate the current network state in the
28 CHAPTER 3 EFFECTIVE ADMISSION CONTROL MECHANISM IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS Introduction Measurement-based scheme, that constantly monitors the network, will incorporate the current network state in the
What is the difference between unicast and multicast? (P# 114)
 1 FINAL TERM FALL2011 (eagle_eye) CS610 current final term subjective all solved data by eagle_eye MY paper of CS610 COPUTER NETWORKS There were 30 MCQs Question no. 31 (Marks2) Find the class in 00000001.001011.1001.111
1 FINAL TERM FALL2011 (eagle_eye) CS610 current final term subjective all solved data by eagle_eye MY paper of CS610 COPUTER NETWORKS There were 30 MCQs Question no. 31 (Marks2) Find the class in 00000001.001011.1001.111
Performance Comparison of Ad Hoc Routing Protocols over IEEE DCF and TDMA MAC Layer Protocols
 Performance Comparison of Ad Hoc Routing Protocols over IEEE 82.11 DCF and TDMA MAC Layer Protocols Govind. P. Gupta Computer Science Department R.K.G.I.T, Ghaziabad (India) er_gpgupta@yahoo.com A. K.
Performance Comparison of Ad Hoc Routing Protocols over IEEE 82.11 DCF and TDMA MAC Layer Protocols Govind. P. Gupta Computer Science Department R.K.G.I.T, Ghaziabad (India) er_gpgupta@yahoo.com A. K.
IP Multicast: PIM Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 12.4T
 IP Multicast: PIM Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 12.4T Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS
IP Multicast: PIM Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 12.4T Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS
4.2 Multicast IP supports multicast to support one-to-many (radio, news, IP multicast was originally a many-to-many (any source MC or
 CS475 Networks Lecture 14 Chapter 4 Advanced Internetworking Assignments Reading for Lecture 15: Sections 5.1-5.2 Homework 5, Wireshark Project 3 posted, due next Thursday; Programming Project 3 posted,
CS475 Networks Lecture 14 Chapter 4 Advanced Internetworking Assignments Reading for Lecture 15: Sections 5.1-5.2 Homework 5, Wireshark Project 3 posted, due next Thursday; Programming Project 3 posted,
Viewing IP and MPLS Multicast Configurations
 CHAPTER 19 These topics provide an overview of the IP Multicast technology and describe how to view IP and multicast configurations in Prime Network Vision: IP and MPLS Multicast Configuration: Overview,
CHAPTER 19 These topics provide an overview of the IP Multicast technology and describe how to view IP and multicast configurations in Prime Network Vision: IP and MPLS Multicast Configuration: Overview,
IP Multicast. Falko Dressler Regionales Rechenzentrum Grundzüge der Datenkommunikation IP Multicast
 Falko Dressler Regionales Rechenzentrum falko.dressler@rrze.uni-erlangen.de 1 Agenda Basics Principles of IP multicast, addressing, TTL Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) IGMPv1, v2, v3 Layer-2
Falko Dressler Regionales Rechenzentrum falko.dressler@rrze.uni-erlangen.de 1 Agenda Basics Principles of IP multicast, addressing, TTL Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) IGMPv1, v2, v3 Layer-2
Implementing IPv6 Multicast
 Implementing IPv6 Multicast Last Updated: November 14, 2011 Traditional IP communication allows a host to send packets to a single host (unicast transmission) or to all hosts (broadcast transmission).
Implementing IPv6 Multicast Last Updated: November 14, 2011 Traditional IP communication allows a host to send packets to a single host (unicast transmission) or to all hosts (broadcast transmission).
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to use the multicast routing protocol.
 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to use the multicast routing protocol. About, page 1 Guidelines for, page 4 Enable, page 4 Customize, page 5 Monitoring for PIM, page 16 Example for,
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to use the multicast routing protocol. About, page 1 Guidelines for, page 4 Enable, page 4 Customize, page 5 Monitoring for PIM, page 16 Example for,
MRT- FRR: Architecture, Algorithms, Analysis, and Extensions
 MRT- FRR: Architecture, Algorithms, Analysis, and Extensions Alia Atlas, Gabor Enyedi, Andras Csaszar, Bob Kebler, Shraddha Hegde, Chris Bowers, Jeff Tantsura, Abishek Gopalan, Kishore Tiruveedhula, Russ
MRT- FRR: Architecture, Algorithms, Analysis, and Extensions Alia Atlas, Gabor Enyedi, Andras Csaszar, Bob Kebler, Shraddha Hegde, Chris Bowers, Jeff Tantsura, Abishek Gopalan, Kishore Tiruveedhula, Russ
ETSI TS V1.1.1 ( )
 TS 102 294 V1.1.1 (2004-02) Technical Specification Satellite Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Broadband Satellite Multimedia (BSM) services and architectures; IP interworking via satellite; Multicast
TS 102 294 V1.1.1 (2004-02) Technical Specification Satellite Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Broadband Satellite Multimedia (BSM) services and architectures; IP interworking via satellite; Multicast
Routing Protocols. Autonomous System (AS)
 Routing Protocols Two classes of protocols: 1. Interior Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) 2. Exterior Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Autonomous System (AS) What is an AS?
Routing Protocols Two classes of protocols: 1. Interior Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) 2. Exterior Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Autonomous System (AS) What is an AS?
CSE/ISE 311: Systems Administra5on Basic Network Organiza5on
 Basic Network Organiza5on Por$ons Courtesy Ellen Liu Outline Internet and Internet Standards Protocols and Protocol Layering Packet- switching Segment, packet, frame TCP segment header and IP packet header
Basic Network Organiza5on Por$ons Courtesy Ellen Liu Outline Internet and Internet Standards Protocols and Protocol Layering Packet- switching Segment, packet, frame TCP segment header and IP packet header
Key Nego(a(on Protocol & Trust Router
 Key Nego(a(on Protocol & Trust Router dra6- howle:- radsec- knp ABFAB, IETF 80 31 March, Prague. Introduc(on The ABFAB architecture does not require any par(cular AAA strategy for connec(ng RPs to IdPs.
Key Nego(a(on Protocol & Trust Router dra6- howle:- radsec- knp ABFAB, IETF 80 31 March, Prague. Introduc(on The ABFAB architecture does not require any par(cular AAA strategy for connec(ng RPs to IdPs.
Chapter 24 PIM Commands
 Chapter 24 PIM Commands bsr-candidate Configures the Routing Switch as a candidate PIM Sparse Bootstrap Router (BSR). To configure the Routing Switch as a candidate BSR, enter a command such as the following:
Chapter 24 PIM Commands bsr-candidate Configures the Routing Switch as a candidate PIM Sparse Bootstrap Router (BSR). To configure the Routing Switch as a candidate BSR, enter a command such as the following:
