Behavior of Cisco Discovery Protocol between Routers and Switches
|
|
|
- Gyles Copeland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Behavior of Cisco Discovery Protocol between Routers and Switches Document ID: Contributed by Meghana Tandon, Sumanth Srinath, and Vishnu Asok, Cisco TAC Engineers. May 06, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used CDP Timer and CDP Hold Time Topology Scenario 1: The Switch Ss a Tagged CDP Packet Scenario 2: The Switch Ss an Untagged CDP Packet Introduction This document describes the behavior of Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) between a router and a switch that run Cisco IOS. CDP is Cisco proprietary Layer 2 protocol that is media and protocol indepent, and runs on all Cisco manufactured equipment. Cisco devices s CDP announcements to the multicast destination address c cc cc cc out each connected network interface. These multicast packets are received by Cisco switches and other network devices that support CDP through their connected network interface. Prerequisites Requirements There are no specific requirements for this document. Components Used This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions. This document applies to all Cisco routers and switches that run Cisco IOS. The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
2 CDP Timer and CDP Hold Time By default, CDP announcements are sent every 60 seconds on interfaces that support Subnetwork Access Protocol (SNAP) headers, which include Ethernet, Frame Relay, and ATM. The hold time specifies the lifetime of an entry in the table. That is, if no announcements are received from a device for a period in excess of the holdtime, the device information is discarded (default 180 seconds). In order to change the default CDP timer (60 seconds) and CDP holdtime (180 seconds), enter the cdp timer and cdp holdtime Cisco IOS configuration commands respectively. The changes can be verified with the show cdp command, which shows the current devices' CDP setting. Router#show cdp Global CDP information: Sing CDP packets every 60 seconds Sing a holdtime value of 180 seconds Sing CDPv2 advertisements is enabled CDP, by default, is enabled on all interfaces. However, there is an option to disable CDP for the router as a whole or on a per interface basis. Topology Switch Configuration Switch#show run int fa1/0/23 Building configuration... Current configuration : 267 bytes! interface FastEthernet1/0/23 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 10 switchport mode trunk power inline never spanning tree portfast spanning tree guard root Router Configuration Router#show run int gi0/1 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address no ip redirects duplex auto speed auto media type rj45 encapsulation dot1q 1 shutdown int vlan 10 ip address int vlan 21 ip address encapsulation dot1q 10 The interface on the router has dot1q subinterfaces gi0/0.1, gi0/0.10, and gi0/0.21 configured with VLAN 1, 10, and 21 respectively. The interface on the switch is a trunk link where all the VLANs are allowed. Router#show ip int brief
3 Interface IP Address OK? Method Status Protocol GigabitEthernet0/ YES DHCP up up GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES NVRAM up up GigabitEthernet0/1.1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down GigabitEthernet0/ YES manual up up GigabitEthernet0/ YES manual up up The switch shows the router as a valid CDP neighbor as shown here: Router Fas 1/0/ R S I 3845 Gig 0/1.10 The same command on the router does not reveal the directly connected switch. Router#show cdp neighbor Run a debug for CDP in order to help determine the reason ( debug cdp { packets adjacency events } ). This entry is found in the cache. CDP PA: version 2 packet sent out on GigabitEthernet0/1 >the packet is sent out on gi0/1 CDP EV: No space for insertion of civic location CDP EV: No space (1068) for insertion of location information. As per the previous logs, the router did not receive any CDP packets from the switch on any of the connected interfaces. The interface with dot1q encapsulation is administratively shut down. Thus, when the switch ss the CDP packet, the packet is discarded by the router. Note: On the router, the subinterface with the lowest VLAN/dot1q encapsulation is selected as the preferred subinterface to carry the CDP packets. On the switch, the CDP traffic is always preferred on the lowest VLAN configured. That is, VLAN 1 always, which cannot be deleted from the VLAN database. The CDP protocol behaves differently when the switch ss CDP as a tagged packet or untagged packet depent upon the native VLAN configured on the trunk link. On the switch, the CDP traffic is always preferred on the lowest VLAN configured. That is, VLAN 1 always, which cannot be deleted from the VLAN database. The CDP protocol behaves differently when the switch ss CDP as a tagged packet or untagged packet depent upon the native VLAN configured on the trunk link.
4 Scenario 1: The Switch Ss a Tagged CDP Packet Switch configuration: interface FastEthernet1/0/1 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 10 switchport mode trunk Case 1: The Subinterface Which Has VLAN 1 Configured on the Router Is Up/Up encapsulation dot1q 1 0 encapsulation dot1q 10 GL.S #show ip int brief Interface IP Address OK? Method Status Protocol GigabitEthernet0/ YES DHCP up up GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES NVRAM up up GigabitEthernet0/1.1 unassigned YES unset up up GigabitEthernet0/ YES manual up up GigabitEthernet0/ YES manual up up The switch ss the CDP packet on VLAN 1 which will be received by the router as a tagged packet. The router checks to see if any of its subinterfaces are configured with VLAN1 dot1q encapsulation and is UP. If this check is successful then the CDP packet is processed by the router on GigabitEthernet 0/1.1. The router will generate a CDP packet on the lowest numbered subinterface which is up/up and configured with VLAN1 dot1q encapsulation (or the lowest VLAN). In this scenario, the router ss untagged CDP packets on gi0/1.1 which are received by the switch on FastEthernet1/0/23.. This entry is found in the cache. CDP PA: version 2 packet sent out on GigabitEthernet0/1.1. CDP PA: Packet received from Switch on. This entry is found in the cache. CDP EV: Lookup for ip phone with idb= GigabitEthernet0/1.1 ip= mac= e.e219 platform= cisco WS C P
5 Enter the show cdp neighbor command on the router. Router Fas 1/0/ R S I 3845 Gig 0/1.1 Enter the show cdp neigh command on the router. Router#show cdp neigh > > > > Switch Gig 0/ S I WS C3750 Fas 1/0/23 Case 2: Change the Configuration on the Router Interfaces so That You Do Not Have Any Subinterface with VLAN 1!! Router#show ip interface brief Interface IP Address OK? Method Status Protocol GigabitEthernet0/ YES DHCP up up GigabitEthernet0/0.1 unassigned YES unset up up GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES NVRAM up up GigabitEthernet0/1.1 unassigned YES unset up up GigabitEthernet0/ YES manual up up GigabitEthernet0/ YES manual up up Analysis The switch ss the CDP tagged packet on fa1/0/23. When the router receives the packet, it checks to see if a subinterface on the router is configured for encapsulation dot1q for VLAN 1. Currently there is no subinterface configured. Thus the router receives the CDP packet on the main interface. The reason the router receives the packet on the main interface is because VLAN 1 is active. Enter the show vlan switch command for confirmation. Even if the router does not have any interface configured for VLAN 1 the CDP packet is still received. Router#show vlan switch VLAN Name Status Ports 1 default active 1002 fddi default act/unsup 1003 token ring default act/unsup 1004 fddinet default act/unsup 1005 trnet default act/unsup
6 VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2 1 enet fddi tr srb fdnet ibm trnet ibm 0 0 In such scenarios the CDP packet from the router is sent through gi0/1. This entry is found in the cache. CDP PA: version 2 packet sent out on GigabitEthernet0/1> CDP PA: Packet received from Switch on interface GigabitEthernet0/1 This entry is found in the cache. CDP EV: Lookup for ip phone with idb= GigabitEthernet0/1 ip= mac= e.e219 platform= cisco WS C P On the switch: Router Fas 1/0/ R S I 3845 Gig 0/1 On the router: Router#show cdp neighbor Switch Gig 0/1 160 S I WS C3750 Fas 1/0/23 You see similar behavior when any interface is configured with the encapsulation VLAN as native. Scenario 2: The Switch Ss an Untagged CDP Packet Switch configuration:
7 interface FastEthernet1/0/1 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 1 switchport mode trunk Case 1: The Interface Where the VLAN 1 Is Configured Is Up/Up encapsulation dot1q 1 0 encapsulation dot1q 10 When the switch ss the CDP packet to the router, it ss an untagged packet as native VLAN is used for this communication. Thus the router receives the packet on the interface where VLAN 1 is configured. The router checks if it has dot1q encapsulation VLAN 1 configured and the interface is up/up. If this check is successful, the router ss the packet through that interface. Router Fas 1/0/23 5 R S I 3845 Gig 0/1.1 Router#show cdp neighbor Switch Gig 0/1.1 8 S I WS C3750 Fas 1/0/23 CDP PA: version 2 packet sent out on GigabitEthernet0/1.1 CDP PA: Packet received from Switch on CDP AD: Aging entry for Router, on interface FastEthernet1/0/23
8 Case 2: The Interface on the Router Where the VLAN Is Configured Is Up/Up and Neither of the Interfaces Has a Native VLAN Specified encapsulation dot1q 1 0 encapsulation dot1q 10 native Analysis When the switch ss the CDP packet to the router, it ss the untagged packet as native VLAN is used for communication. The router receives the packet over gi0/1.1 as it has VLAN 1 configured on itself. The router checks whether it has VLAN 1 configured or any other native VLAN configured. In the current case, the interface gi0/1.10 is configured with the native keyword. Thus the router ss the packet through gi0/1.10 subinterface. This output is seen in this scenario: Router Fas 1/0/23 5 R S I 3845 Gig 0/1.1 The CDP neighbor result on the router is shown here: Router#show cdp neighbor Switch Gig 0/ S I WS C3750 Fas 1/0/23 CDP PA: version 2 packet sent out on GigabitEthernet0/1.10 CDP PA: Packet received from Switch on CDP AD: Aging entry for Router, on interface FastEthernet1/0/23
9 Case 3: There Is No Interface Where the VLAN 1 Is Configured, but Neither of the Interfaces Has a Native Keyword Configured 0 encapsulation dot1q 10 native When the switch ss the packet to the router, it ss the untagged packet over native VLAN. The router receives the packet over gi0/1. The router checks whether it has VLAN 1 configured or any other native VLAN configured. Here, the gi0/1.10 interface is configured for encapsulation as native, thus the router ss the packet through gi0/1.10. Router Fas 1/0/ R S I 3845 Gig 0/1 Router#sh cdp neigh Switch Gig 0/ S I WS C3750 Fas 1/0/23 CDP PA: version 2 packet sent out on GigabitEthernet0/1.10 CDP PA: Packet received from Switch on interface GigabitEthernet0/1 CDP AD: Aging entry for Router, on interface FastEthernet1/0/23
10 Case 4: The Router Does Not Have a VLAN dot1q Encapsulation and Native VLAN Is Not Specified 0 encapsulation dot1q 10 When the switch ss the packet to the router, it ss the untagged CDP packet as the communication is over native VLAN. The router receives the packet over gi0/1. The router checks whether it has VLAN 1 configured or any other native VLAN configured. Here there is no interface as such, thus the router ss the packet through gi0/1 (over the main interface). This output is seen in this scenario : Router Fas 1/0/23 7 R S I 3845 Gig 0/1 The output on the router is shown here: Router#show cdp neighbor Switch Gig 0/1 7 S I WS C3750 Fas 1/0/23 CDP PA: version 2 packet sent out on GigabitEthernet0/1 CDP PA: Packet received from Switch on interface GigabitEthernet0/1 CDP AD: Aging entry for Router, on interface FastEthernet1/0/23
11 Summary The router receives a tagged CDP packet: The subinterface configured with VLAN1 is administratively down/down. The subinterface configured with VLAN1 is UP/UP. A Native VLAN is not specified. The router does not have VLAN1 configured and any of the subinterfaces is configured with/without native keyword. The router discards the CDP packet. The switch would not be listed as a CDP neighbor. The router ss and receives the packet on this subinterface. The packets traverse over the main interface. CDP works in both direction. The router receives an untagged CDP packet: The subinterface configured with VLAN1 is administratively down/down. The subinterface configured with VLAN1 is UP/UP. A Native VLAN is not specified. The router does not have VLAN1 configured and none of the subinterfaces is configured with the native keyword. The router has neither VLAN1 nor native keyword configured. The router discards the CDP packet. The switch would not be listed as a CDP neighbor. The router ss and receives the packets on this subinterface. CDP works in both directions. The router receives the CDP packets on the main interface, but ss them over the subinterface where the native keyword is configured. The CDP packets traverse over the main interface. CDP works in both directions. Updated: May 06, 2015 Document ID:
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
ISP /24. Fas0/0. Fas1/0/1. Fas1/0/22 NYCORE1. Cisco PS. Fas0/1. Lab Nic /24
 Introduction The Configuring VLANs and Trunks module provides you with the instructions and Cisco hardware to develop your hands on skills in configuring layer 2 technologies VLANs and trunking. This module
Introduction The Configuring VLANs and Trunks module provides you with the instructions and Cisco hardware to develop your hands on skills in configuring layer 2 technologies VLANs and trunking. This module
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
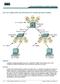 Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Netw 3000 VLAN 1 LAB Darlene Redmond Ryan Gamblin January 19 th 2012
 Netw 3000 VLAN 1 LAB Darlene Redmond Ryan Gamblin January 19 th 2012 3. Attach a workstation to the Management VLAN and demonstrate a successful login to the switch at the privileged exec mode, with a
Netw 3000 VLAN 1 LAB Darlene Redmond Ryan Gamblin January 19 th 2012 3. Attach a workstation to the Management VLAN and demonstrate a successful login to the switch at the privileged exec mode, with a
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Note: Use two 2960 switches for ALS1 and ALS2 and two 3560 switches for DLS1 and DLS2
 LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF).
 Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol
 Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
1 of :22
 Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS
 Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example
 EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
Question 5.1. Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain.
 Question 5.1 Q 5.1.1 Number of Collision Domains: = 14 Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain. Number of Broadcast Domains: = 5 Every port on a router
Question 5.1 Q 5.1.1 Number of Collision Domains: = 14 Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain. Number of Broadcast Domains: = 5 Every port on a router
All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example
 All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 81682 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 81682 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
This chapter describes how to configure VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers.
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco 7600 Series
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco 7600 Series
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Cisco Discovery Protocol Version 2
 Cisco Discovery Protocol (formerly known as CDP) is a Layer 2, media-independent, and network-independent protocol that runs on Cisco devices and enables networking applications to learn about directly
Cisco Discovery Protocol (formerly known as CDP) is a Layer 2, media-independent, and network-independent protocol that runs on Cisco devices and enables networking applications to learn about directly
Lab Configuring Fast EtherChannel
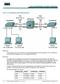 Lab 3.7.5 Configuring Fast EtherChannel Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to provide more bandwidth between Ethernet switches. Two 100-Mb links will be combined together to form a full duplex
Lab 3.7.5 Configuring Fast EtherChannel Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to provide more bandwidth between Ethernet switches. Two 100-Mb links will be combined together to form a full duplex
VLANs. Traditional Campus Networks. Performance Issues. Broadcast Issues. Bridges terminate collision domains
 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLAN Commands. Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Denali 16.3.x (Catalyst 3650 Switches) 1
 client vlan, page 2 clear vtp counters, page 3 debug platform vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan, page 5 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 7 debug sw-vlan notification, page 8 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 10 interface vlan,
client vlan, page 2 clear vtp counters, page 3 debug platform vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan, page 5 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 7 debug sw-vlan notification, page 8 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 10 interface vlan,
Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
Cisco Discovery Protocol Version 2
 Cisco Discovery Protocol (formerly known as CDP) is a Layer 2, media-independent, and network-independent protocol that runs on Cisco devices and enables networking applications to learn about directly
Cisco Discovery Protocol (formerly known as CDP) is a Layer 2, media-independent, and network-independent protocol that runs on Cisco devices and enables networking applications to learn about directly
Understanding and Configuring CDP
 CHAPTER 17 This chapter describes how to configure Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
CHAPTER 17 This chapter describes how to configure Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
IEEE 802.1Q Configuration
 CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0
 Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Switching-I Questions & Answers CCIE R&S by Narbik Kocharians Advanced
Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Switching-I Questions & Answers CCIE R&S by Narbik Kocharians Advanced
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
Configuring Network Access to the GGSN
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure access from the gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) to a serving GPRS support node (SGSN), public data network (PDN), and optionally to a Virtual Private
CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure access from the gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) to a serving GPRS support node (SGSN), public data network (PDN), and optionally to a Virtual Private
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
 CHAPTER 14 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling With Release 12.1(13)E and later, the Catalyst 6500 series switches support IEEE 802.1Q tunneling and Layer 2 protocol tunneling.
CHAPTER 14 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling With Release 12.1(13)E and later, the Catalyst 6500 series switches support IEEE 802.1Q tunneling and Layer 2 protocol tunneling.
VLAN. Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 3850 Switches) 1
 clear vtp counters, page 2 debug platform vlan, page 3 debug sw-vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 6 debug sw-vlan notification, page 7 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 9 interface vlan, page 11 private-vlan,
clear vtp counters, page 2 debug platform vlan, page 3 debug sw-vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 6 debug sw-vlan notification, page 7 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 9 interface vlan, page 11 private-vlan,
Lab Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
Using Cisco Discovery Protocol
 Using Cisco Discovery Protocol First Published: February 1, 1995 Last Updated: August 12, 2010 Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a Layer 2 media-independent and network-independent protocol that runs on
Using Cisco Discovery Protocol First Published: February 1, 1995 Last Updated: August 12, 2010 Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a Layer 2 media-independent and network-independent protocol that runs on
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
VLAN Configuration. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification. Comparing ISL and 802.1Q. VLAN Trunking
 Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.)
 Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior
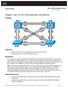 Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. VLANs, Trunking, & VTP. VLANs Overview
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Buy full file at
 14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree.
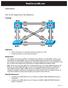 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Additional Scenarios A P P E N D I X
 A P P E N D I X F Additional Scenarios Each chapter of this book focuses on a small set of related topics so that you can more easily digest the material. However, the CCNA exams require that you be able
A P P E N D I X F Additional Scenarios Each chapter of this book focuses on a small set of related topics so that you can more easily digest the material. However, the CCNA exams require that you be able
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
Lab Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 The Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) support clients on both physical LANs and VLANs. The routers can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to enable
CHAPTER 15 The Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) support clients on both physical LANs and VLANs. The routers can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to enable
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series
 Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
2] Chapter 2 Cisco IOS Commands traceroute mac
![2] Chapter 2 Cisco IOS Commands traceroute mac 2] Chapter 2 Cisco IOS Commands traceroute mac](/thumbs/72/68003916.jpg) 2] Chapter 2 traceroute mac traceroute mac Use the traceroute mac privileged EXEC command on the switch stack or on a standalone switch to display the Layer 2 path taken by the packets from the specified
2] Chapter 2 traceroute mac traceroute mac Use the traceroute mac privileged EXEC command on the switch stack or on a standalone switch to display the Layer 2 path taken by the packets from the specified
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
Table of Contents. isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ
 king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1
 CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
RealCiscoLAB.com. Securing Spanning Tree Protocol. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 SWITCH
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
Lab 7.5.3: Troubleshooting the Wireless WRT300N
 Lab 7.5.3: Troubleshooting the Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/1.5 5.5.5.10 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/1.10 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 7.5.3: Troubleshooting the Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/1.5 5.5.5.10 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/1.10 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces
 Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces Ethernet interfaces can be configured either as access ports or trunk ports. Trunks carry the traffic of multiple VLANs over a single link and allow you to extend
Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces Ethernet interfaces can be configured either as access ports or trunk ports. Trunks carry the traffic of multiple VLANs over a single link and allow you to extend
CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0)
 CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Cisco 200-125 Dumps Available Here at: /cisco-exam/200-125-dumps.html Enrolling now you will get access to 455 questions in a unique set of 200-125 dumps
CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Cisco 200-125 Dumps Available Here at: /cisco-exam/200-125-dumps.html Enrolling now you will get access to 455 questions in a unique set of 200-125 dumps
Describing the STP. Enhancements to STP. Configuring PortFast. Describing PortFast. Configuring. Verifying
 Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
Lab 6.4.1: Basic Inter-VLAN Routing
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
Cisco Discovery Protocol Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S (Cisco ASR 920 Series)
 Cisco Discovery Protocol Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S (Cisco ASR 920 Series) Cisco Discovery Protocol Version 2 2 Finding Feature Information 2 Prerequisites for Using Cisco Discovery Protocol
Cisco Discovery Protocol Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S (Cisco ASR 920 Series) Cisco Discovery Protocol Version 2 2 Finding Feature Information 2 Prerequisites for Using Cisco Discovery Protocol
Configuring VLANs. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software
 Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software Document ID: 8759 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Theory Important
Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software Document ID: 8759 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Theory Important
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
LAN Troubleshooting. Ethernet Troubleshooting
 CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
Extending Switched Networks with Virtual LANs. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7-1
 Extending Switched Networks with Virtual LANs 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Configure a VLAN Configure VLAN
Extending Switched Networks with Virtual LANs 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Configure a VLAN Configure VLAN
For information about configuring these settings from Cluster Management Suite (CMS), refer to the online help.
 Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 일년무료업데이트서비스제공
 itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트
 PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트 http://www.pass4test.net 일년동안무료업데이트 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 10 Get Latest & Valid 640-802 Exam's Question
PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트 http://www.pass4test.net 일년동안무료업데이트 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 10 Get Latest & Valid 640-802 Exam's Question
Configuring VLANs. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 8 Monitoring VLANs, page 22 Where to Go Next,
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 8 Monitoring VLANs, page 22 Where to Go Next,
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
 CHAPTER 26 This chapter describes how to configure IEEE 802.1Q tunneling in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS
CHAPTER 26 This chapter describes how to configure IEEE 802.1Q tunneling in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
Configuring CDP. Understanding CDP CHAPTER. This chapter describes how to configure Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on the Catalyst 3560 switch.
 21 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on the Catalyst 3560 switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
21 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on the Catalyst 3560 switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Internetwork Communications C:>ping 172.16.30.100 Can two hosts on different subnets communicate without a router? No
Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Internetwork Communications C:>ping 172.16.30.100 Can two hosts on different subnets communicate without a router? No
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
Chapter 3: VLANs. Routing & Switching
 Chapter 3: VLANs Routing & Switching VLAN Definitions A VLAN is a logical partition of a Layer 2 network. VLANs logically group hosts, regardless of physical location. Multiple partitions can be created,
Chapter 3: VLANs Routing & Switching VLAN Definitions A VLAN is a logical partition of a Layer 2 network. VLANs logically group hosts, regardless of physical location. Multiple partitions can be created,
Cisco HWIC-4ESW and HWIC-D-9ESW EtherSwitch Interface Cards
 Cisco HWIC-4ESW and HWIC-D-9ESW EtherSwitch Interface Cards This document provides configuration tasks for the 4-port Cisco HWIC-4ESW and the 9-port Cisco HWIC-D-9ESW EtherSwitch high-speed WAN interface
Cisco HWIC-4ESW and HWIC-D-9ESW EtherSwitch Interface Cards This document provides configuration tasks for the 4-port Cisco HWIC-4ESW and the 9-port Cisco HWIC-D-9ESW EtherSwitch high-speed WAN interface
VLAN Range. Feature Overview
 VLAN Range Feature History Release 12.0(7)XE 12.1(5)T 12.2(2)DD 12.2(4)B 12.2(8)T 12.2(13)T Modification The interface range command was introduced. The interface range command was integrated into Cisco
VLAN Range Feature History Release 12.0(7)XE 12.1(5)T 12.2(2)DD 12.2(4)B 12.2(8)T 12.2(13)T Modification The interface range command was introduced. The interface range command was integrated into Cisco
Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Enchilada Solutions
 Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Solutions Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: LAB Book Chapter Book Page The 18 1161 Overview... 3 Technical Details... 3 Table 54-1:
Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Solutions Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: LAB Book Chapter Book Page The 18 1161 Overview... 3 Technical Details... 3 Table 54-1:
Cisco Switch VLAN Setup (IOS)
 Summary WirelessTrakker requires that the switch ports involved for connecting the components for WirelessTrakker be 802.1q VLAN tagged / trunked ports. These directions tell you how to do that. Note:
Summary WirelessTrakker requires that the switch ports involved for connecting the components for WirelessTrakker be 802.1q VLAN tagged / trunked ports. These directions tell you how to do that. Note:
Configuring Private VLANs
 36 CHAPTER This chapter describes private VLANs (PVLANs) on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides restrictions, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major
36 CHAPTER This chapter describes private VLANs (PVLANs) on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides restrictions, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major
VLAN Range. Feature Overview
 VLAN Range Feature History Release 12.0(7)XE 12.1(5)T 12.2(2)DD Modification The interface range command was introduced. The interface range command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.1(5)T. The
VLAN Range Feature History Release 12.0(7)XE 12.1(5)T 12.2(2)DD Modification The interface range command was introduced. The interface range command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.1(5)T. The
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
 CHAPTER 8 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Virtual private networks (VPNs) provide enterprise-scale connectivity on a shared infrastructure, often Ethernet-based, with the same security,
CHAPTER 8 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Virtual private networks (VPNs) provide enterprise-scale connectivity on a shared infrastructure, often Ethernet-based, with the same security,
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. Understanding Interface Types, page 9-1 Using Interface Configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. Understanding Interface Types, page 9-1 Using Interface Configuration
CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual
 CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, Indiana 46240 USA ii CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual CCNA SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Copyright 2011
CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, Indiana 46240 USA ii CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual CCNA SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Copyright 2011
Table of Contents 1 LLDP Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 LLDP Configuration 1-1 Over 1-1 Background 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-1 How LLDP Works 1-5 Protocols and Standards 1-6 LLDP Configuration Task List 1-6 Performing Basic LLDP Configuration
Table of Contents 1 LLDP Configuration 1-1 Over 1-1 Background 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-1 How LLDP Works 1-5 Protocols and Standards 1-6 LLDP Configuration Task List 1-6 Performing Basic LLDP Configuration
Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Identify what a VLAN is and how it operates. Configure a VLAN to
 Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Identify what a VLAN is and how it operates. Configure a VLAN to improve network performance. Identify what role the switch
Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Identify what a VLAN is and how it operates. Configure a VLAN to improve network performance. Identify what role the switch
CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0)
 200-125 - CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) 1.What is one benefit of PVST+? A. PVST+ supports Layer 3 load balancing without loops. B. PVST+ reduces the CPU cycles for all the switches
200-125 - CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) 1.What is one benefit of PVST+? A. PVST+ supports Layer 3 load balancing without loops. B. PVST+ reduces the CPU cycles for all the switches
Configuring Private VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
 24 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and Remote SPAN (RSPAN) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for
24 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and Remote SPAN (RSPAN) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for
Lab Configuring Basic Switch Settings (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Cisco HWIC-4ESW and HWIC-D-9ESW EtherSwitch Interface Cards
 Cisco HWIC-4ESW and HWIC-D-9ESW EtherSwitch Interface Cards First Published: May 17, 2005 Last Updated: July 28, 2010 This document provides configuration tasks for the 4-port Cisco HWIC-4ESW and the 9-port
Cisco HWIC-4ESW and HWIC-D-9ESW EtherSwitch Interface Cards First Published: May 17, 2005 Last Updated: July 28, 2010 This document provides configuration tasks for the 4-port Cisco HWIC-4ESW and the 9-port
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. The chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Types,
CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. The chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Types,
