ROSS: A Design of Read-Oriented STT-MRAM Storage for Energy-Efficient Non-Uniform Cache Architecture
|
|
|
- Doreen Rich
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ROSS: A Design of Read-Oriented STT-MRAM Storage for Energy-Efficient Non-Uniform Cache Architecture Jie Zhang, Miryeong Kwon, Changyoung Park, Myoungsoo Jung, Songkuk Kim Computer Architecture and Memory System Lab, Yonsei University
2 Summary Motivation: There is a huge demand to increase the last-level cache size. However, SRAM suffers from the high leakage power and low density. STT-MRAM can be a good candidate to replace SRAM, due to its small cell size and low leakage power. Challenge: Conventional STT-MRAM cannot directly substitute SRAM, because of - High write latency - High write energy Solution: We observe read-oriented data pattern in real applications; We propose ROSS, a read-oriented STT-MRAM storage that can - dynamically detect the read-oriented data pattern - reduce the write frequency in STT-MRAM - accommodate as many read misses as possible in LLC
3 Motivation Data set size increases explosively. Webs Videos Graphs Scientific Computing 1 Billion Web Pages 300-hour new videos/min 30 Billion Photos 10-month Spacecraft Simulation
4 Motivation Huge demand to increase on-chip last-level cache size in future
5 Traditional SRAM Challenges Read Latency Write Latency Read Energy Write Energy 397ps 397ps 35pJ 35pJ Fast speed Reasonable energy Cell Area (F^2) 50~120 Low density Leakage 75.7mW High Leakage
6 Traditional SRAM Challenges STT-MRAM Read Latency Write Latency Read Energy Write Energy 397ps 397ps 35pJ 35pJ 238ps 6932ps High Write 13pJ High density Latency/Energy 90pJ Cell Area (F^2) 50~120 6~40 High density Leakage 75.7mW 6.6mW Low leakage
7 Prior work Read Preemption: suspend write operation and give priority to read operation Mitigate the impact of long write latency to read access; Cannot reduce the write latency Write Request Rerouting: accommodate write requests with idle blocks Parallelize write requests to hide long write latency; Cannot reduce the write energy; Deadwrite bypass: predict and bypass the deadwrite (single write no read). Effectively avoid unnecessary write access on STT-MRAM; Bypassing deadwrite is not sufficient to avoid massive write on STT-MRAM
8 ROSS-key observation How the application behavior can impact LLC data access? Last Level Cache eviction trend Large working sets result in frequent cache eviction Read-miss distribution What if we can detect the singular write blocks and put in STT-MRAM?
9 ROSS Target: build a hybrid last-level cache to i. avoid many cache read misses with larger STT-MRAM; ii. accommodate write updates in SRAM; iii. intelligent data migration algorithm;
10 Hybrid-NUCA Conventional cache hierarchy Uniform latency Severe wire delay Non-uniform cache architecture Different wire latency latency
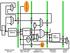
11 Hybrid-NUCA 1-way STT-MRAM banks Migration policy Address map policy LLC Controller SRAM banks SRAM-SRAM migrat. 3-way SRAM->STT-MRAM migration Cache Bank Set Less flexibility, but simplified design
12 3-way Decoder 1-way Migration policy Address map policy Hybrid-NUCA Data search policy Tag Index Bank set Tag Array Data Array S/A S/A Comparator Match? Request routes to specific cache bank set Tag broadcast to each bank for searching
13 Data Flow L2 Cache 2 Write-Back Miss 5 Write Hit L1 Cache 5 Write Hit 3 Read Hit 4 STT-MRAM 6 Evict Block HB: Migrate one cache line ER: Migrate multiple cache lines MEM 1 Block Fill SRAM
14 Singular write detection LLC Controller 1-bit status reg. C C C C C 8-bit counter Write hit Evict Initialize Poll Evict
15 Experiment Setup Evaluation model: ND-NUCA: traditional SRAM NUCA model; DB-NUCA: STT-MRAM NUCA model aware of deadblock; HB-ROSS: Hybrid Read-Oriented STT-MRAM Storage; ER-ROSS: Early Retirement aware Raed-Oriented STT-MRAM Storage; Gem5 simulation parameters and workloads:
16 Evaluation DB-NUCA: suffer from long write latency HB-ROSS: larger capacity and less STT-MRAM write ER-ROSS: benefits from early retirement
17 Evaluation DB-NUCA: suffer from evicting singular write blocks ROSS: STT-MRAM accommodates read-intensive data
18 Evaluation ND-NUCA: consume more leakage energy ROSS: reduce the write energy overhead in STT-MRAM
19 Thank You
STLAC: A Spatial and Temporal Locality-Aware Cache and Networkon-Chip
 STLAC: A Spatial and Temporal Locality-Aware Cache and Networkon-Chip Codesign for Tiled Manycore Systems Mingyu Wang and Zhaolin Li Institute of Microelectronics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084,
STLAC: A Spatial and Temporal Locality-Aware Cache and Networkon-Chip Codesign for Tiled Manycore Systems Mingyu Wang and Zhaolin Li Institute of Microelectronics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084,
Couture: Tailoring STT-MRAM for Persistent Main Memory. Mustafa M Shihab Jie Zhang Shuwen Gao Joseph Callenes-Sloan Myoungsoo Jung
 Couture: Tailoring STT-MRAM for Persistent Main Memory Mustafa M Shihab Jie Zhang Shuwen Gao Joseph Callenes-Sloan Myoungsoo Jung Executive Summary Motivation: DRAM plays an instrumental role in modern
Couture: Tailoring STT-MRAM for Persistent Main Memory Mustafa M Shihab Jie Zhang Shuwen Gao Joseph Callenes-Sloan Myoungsoo Jung Executive Summary Motivation: DRAM plays an instrumental role in modern
BIBIM: A Prototype Multi-Partition Aware Heterogeneous New Memory
 HotStorage 18 BIBIM: A Prototype Multi-Partition Aware Heterogeneous New Memory Gyuyoung Park 1, Miryeong Kwon 1, Pratyush Mahapatra 2, Michael Swift 2, and Myoungsoo Jung 1 Yonsei University Computer
HotStorage 18 BIBIM: A Prototype Multi-Partition Aware Heterogeneous New Memory Gyuyoung Park 1, Miryeong Kwon 1, Pratyush Mahapatra 2, Michael Swift 2, and Myoungsoo Jung 1 Yonsei University Computer
Cache/Memory Optimization. - Krishna Parthaje
 Cache/Memory Optimization - Krishna Parthaje Hybrid Cache Architecture Replacing SRAM Cache with Future Memory Technology Suji Lee, Jongpil Jung, and Chong-Min Kyung Department of Electrical Engineering,KAIST
Cache/Memory Optimization - Krishna Parthaje Hybrid Cache Architecture Replacing SRAM Cache with Future Memory Technology Suji Lee, Jongpil Jung, and Chong-Min Kyung Department of Electrical Engineering,KAIST
A Spherical Placement and Migration Scheme for a STT-RAM Based Hybrid Cache in 3D chip Multi-processors
 , July 4-6, 2018, London, U.K. A Spherical Placement and Migration Scheme for a STT-RAM Based Hybrid in 3D chip Multi-processors Lei Wang, Fen Ge, Hao Lu, Ning Wu, Ying Zhang, and Fang Zhou Abstract As
, July 4-6, 2018, London, U.K. A Spherical Placement and Migration Scheme for a STT-RAM Based Hybrid in 3D chip Multi-processors Lei Wang, Fen Ge, Hao Lu, Ning Wu, Ying Zhang, and Fang Zhou Abstract As
FlashShare: Punching Through Server Storage Stack from Kernel to Firmware for Ultra-Low Latency SSDs
 FlashShare: Punching Through Server Storage Stack from Kernel to Firmware for Ultra-Low Latency SSDs Jie Zhang, Miryeong Kwon, Donghyun Gouk, Sungjoon Koh, Changlim Lee, Mohammad Alian, Myoungjun Chun,
FlashShare: Punching Through Server Storage Stack from Kernel to Firmware for Ultra-Low Latency SSDs Jie Zhang, Miryeong Kwon, Donghyun Gouk, Sungjoon Koh, Changlim Lee, Mohammad Alian, Myoungjun Chun,
Lecture 14: Cache Innovations and DRAM. Today: cache access basics and innovations, DRAM (Sections )
 Lecture 14: Cache Innovations and DRAM Today: cache access basics and innovations, DRAM (Sections 5.1-5.3) 1 Reducing Miss Rate Large block size reduces compulsory misses, reduces miss penalty in case
Lecture 14: Cache Innovations and DRAM Today: cache access basics and innovations, DRAM (Sections 5.1-5.3) 1 Reducing Miss Rate Large block size reduces compulsory misses, reduces miss penalty in case
Lecture 8: Virtual Memory. Today: DRAM innovations, virtual memory (Sections )
 Lecture 8: Virtual Memory Today: DRAM innovations, virtual memory (Sections 5.3-5.4) 1 DRAM Technology Trends Improvements in technology (smaller devices) DRAM capacities double every two years, but latency
Lecture 8: Virtual Memory Today: DRAM innovations, virtual memory (Sections 5.3-5.4) 1 DRAM Technology Trends Improvements in technology (smaller devices) DRAM capacities double every two years, but latency
Lecture 11: Large Cache Design
 Lecture 11: Large Cache Design Topics: large cache basics and An Adaptive, Non-Uniform Cache Structure for Wire-Dominated On-Chip Caches, Kim et al., ASPLOS 02 Distance Associativity for High-Performance
Lecture 11: Large Cache Design Topics: large cache basics and An Adaptive, Non-Uniform Cache Structure for Wire-Dominated On-Chip Caches, Kim et al., ASPLOS 02 Distance Associativity for High-Performance
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Reducing DRAM Latency at Low Cost by Exploiting Heterogeneity. Donghyuk Lee Carnegie Mellon University
 Reducing DRAM Latency at Low Cost by Exploiting Heterogeneity Donghyuk Lee Carnegie Mellon University Problem: High DRAM Latency processor stalls: waiting for data main memory high latency Major bottleneck
Reducing DRAM Latency at Low Cost by Exploiting Heterogeneity Donghyuk Lee Carnegie Mellon University Problem: High DRAM Latency processor stalls: waiting for data main memory high latency Major bottleneck
OAP: An Obstruction-Aware Cache Management Policy for STT-RAM Last-Level Caches
 OAP: An Obstruction-Aware Cache Management Policy for STT-RAM Last-Level Caches Jue Wang, Xiangyu Dong, Yuan Xie Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Pennsylvania State University Qualcomm Technology,
OAP: An Obstruction-Aware Cache Management Policy for STT-RAM Last-Level Caches Jue Wang, Xiangyu Dong, Yuan Xie Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Pennsylvania State University Qualcomm Technology,
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Lecture: Large Caches, Virtual Memory. Topics: cache innovations (Sections 2.4, B.4, B.5)
 Lecture: Large Caches, Virtual Memory Topics: cache innovations (Sections 2.4, B.4, B.5) 1 More Cache Basics caches are split as instruction and data; L2 and L3 are unified The /L2 hierarchy can be inclusive,
Lecture: Large Caches, Virtual Memory Topics: cache innovations (Sections 2.4, B.4, B.5) 1 More Cache Basics caches are split as instruction and data; L2 and L3 are unified The /L2 hierarchy can be inclusive,
A Comparison of Capacity Management Schemes for Shared CMP Caches
 A Comparison of Capacity Management Schemes for Shared CMP Caches Carole-Jean Wu and Margaret Martonosi Princeton University 7 th Annual WDDD 6/22/28 Motivation P P1 P1 Pn L1 L1 L1 L1 Last Level On-Chip
A Comparison of Capacity Management Schemes for Shared CMP Caches Carole-Jean Wu and Margaret Martonosi Princeton University 7 th Annual WDDD 6/22/28 Motivation P P1 P1 Pn L1 L1 L1 L1 Last Level On-Chip
Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory
 Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
Migration Based Page Caching Algorithm for a Hybrid Main Memory of DRAM and PRAM
 Migration Based Page Caching Algorithm for a Hybrid Main Memory of DRAM and PRAM Hyunchul Seok Daejeon, Korea hcseok@core.kaist.ac.kr Youngwoo Park Daejeon, Korea ywpark@core.kaist.ac.kr Kyu Ho Park Deajeon,
Migration Based Page Caching Algorithm for a Hybrid Main Memory of DRAM and PRAM Hyunchul Seok Daejeon, Korea hcseok@core.kaist.ac.kr Youngwoo Park Daejeon, Korea ywpark@core.kaist.ac.kr Kyu Ho Park Deajeon,
Rethinking Last-Level Cache Management for Multicores Operating at Near-Threshold
 Rethinking Last-Level Cache Management for Multicores Operating at Near-Threshold Farrukh Hijaz, Omer Khan University of Connecticut Power Efficiency Performance/Watt Multicores enable efficiency Power-performance
Rethinking Last-Level Cache Management for Multicores Operating at Near-Threshold Farrukh Hijaz, Omer Khan University of Connecticut Power Efficiency Performance/Watt Multicores enable efficiency Power-performance
Optimizing Replication, Communication, and Capacity Allocation in CMPs
 Optimizing Replication, Communication, and Capacity Allocation in CMPs Zeshan Chishti, Michael D Powell, and T. N. Vijaykumar School of ECE Purdue University Motivation CMP becoming increasingly important
Optimizing Replication, Communication, and Capacity Allocation in CMPs Zeshan Chishti, Michael D Powell, and T. N. Vijaykumar School of ECE Purdue University Motivation CMP becoming increasingly important
Lecture: Large Caches, Virtual Memory. Topics: cache innovations (Sections 2.4, B.4, B.5)
 Lecture: Large Caches, Virtual Memory Topics: cache innovations (Sections 2.4, B.4, B.5) 1 Techniques to Reduce Cache Misses Victim caches Better replacement policies pseudo-lru, NRU Prefetching, cache
Lecture: Large Caches, Virtual Memory Topics: cache innovations (Sections 2.4, B.4, B.5) 1 Techniques to Reduce Cache Misses Victim caches Better replacement policies pseudo-lru, NRU Prefetching, cache
Architectural Aspects in Design and Analysis of SOTbased
 Architectural Aspects in Design and Analysis of SOTbased Memories Rajendra Bishnoi, Mojtaba Ebrahimi, Fabian Oboril & Mehdi Tahoori INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING (ITEC) CHAIR FOR DEPENDABLE NANO COMPUTING
Architectural Aspects in Design and Analysis of SOTbased Memories Rajendra Bishnoi, Mojtaba Ebrahimi, Fabian Oboril & Mehdi Tahoori INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING (ITEC) CHAIR FOR DEPENDABLE NANO COMPUTING
Lecture: Cache Hierarchies. Topics: cache innovations (Sections B.1-B.3, 2.1)
 Lecture: Cache Hierarchies Topics: cache innovations (Sections B.1-B.3, 2.1) 1 Types of Cache Misses Compulsory misses: happens the first time a memory word is accessed the misses for an infinite cache
Lecture: Cache Hierarchies Topics: cache innovations (Sections B.1-B.3, 2.1) 1 Types of Cache Misses Compulsory misses: happens the first time a memory word is accessed the misses for an infinite cache
EFFICIENTLY ENABLING CONVENTIONAL BLOCK SIZES FOR VERY LARGE DIE- STACKED DRAM CACHES
 EFFICIENTLY ENABLING CONVENTIONAL BLOCK SIZES FOR VERY LARGE DIE- STACKED DRAM CACHES MICRO 2011 @ Porte Alegre, Brazil Gabriel H. Loh [1] and Mark D. Hill [2][1] December 2011 [1] AMD Research [2] University
EFFICIENTLY ENABLING CONVENTIONAL BLOCK SIZES FOR VERY LARGE DIE- STACKED DRAM CACHES MICRO 2011 @ Porte Alegre, Brazil Gabriel H. Loh [1] and Mark D. Hill [2][1] December 2011 [1] AMD Research [2] University
Hybrid Cache Architecture (HCA) with Disparate Memory Technologies
 Hybrid Cache Architecture (HCA) with Disparate Memory Technologies Xiaoxia Wu, Jian Li, Lixin Zhang, Evan Speight, Ram Rajamony, Yuan Xie Pennsylvania State University IBM Austin Research Laboratory Acknowledgement:
Hybrid Cache Architecture (HCA) with Disparate Memory Technologies Xiaoxia Wu, Jian Li, Lixin Zhang, Evan Speight, Ram Rajamony, Yuan Xie Pennsylvania State University IBM Austin Research Laboratory Acknowledgement:
3118 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 24, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2016
 3118 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 24, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2016 Hybrid L2 NUCA Design and Management Considering Data Access Latency, Energy Efficiency, and Storage
3118 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 24, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2016 Hybrid L2 NUCA Design and Management Considering Data Access Latency, Energy Efficiency, and Storage
Middleware and Flash Translation Layer Co-Design for the Performance Boost of Solid-State Drives
 Middleware and Flash Translation Layer Co-Design for the Performance Boost of Solid-State Drives Chao Sun 1, Asuka Arakawa 1, Ayumi Soga 1, Chihiro Matsui 1 and Ken Takeuchi 1 1 Chuo University Santa Clara,
Middleware and Flash Translation Layer Co-Design for the Performance Boost of Solid-State Drives Chao Sun 1, Asuka Arakawa 1, Ayumi Soga 1, Chihiro Matsui 1 and Ken Takeuchi 1 1 Chuo University Santa Clara,
A Memory Management Scheme for Hybrid Memory Architecture in Mission Critical Computers
 A Memory Management Scheme for Hybrid Memory Architecture in Mission Critical Computers Soohyun Yang and Yeonseung Ryu Department of Computer Engineering, Myongji University Yongin, Gyeonggi-do, Korea
A Memory Management Scheme for Hybrid Memory Architecture in Mission Critical Computers Soohyun Yang and Yeonseung Ryu Department of Computer Engineering, Myongji University Yongin, Gyeonggi-do, Korea
A Comprehensive Analytical Performance Model of DRAM Caches
 A Comprehensive Analytical Performance Model of DRAM Caches Authors: Nagendra Gulur *, Mahesh Mehendale *, and R Govindarajan + Presented by: Sreepathi Pai * Texas Instruments, + Indian Institute of Science
A Comprehensive Analytical Performance Model of DRAM Caches Authors: Nagendra Gulur *, Mahesh Mehendale *, and R Govindarajan + Presented by: Sreepathi Pai * Texas Instruments, + Indian Institute of Science
15-740/ Computer Architecture Lecture 5: Project Example. Jus%n Meza Yoongu Kim Fall 2011, 9/21/2011
 15-740/18-740 Computer Architecture Lecture 5: Project Example Jus%n Meza Yoongu Kim Fall 2011, 9/21/2011 Reminder: Project Proposals Project proposals due NOON on Monday 9/26 Two to three pages consisang
15-740/18-740 Computer Architecture Lecture 5: Project Example Jus%n Meza Yoongu Kim Fall 2011, 9/21/2011 Reminder: Project Proposals Project proposals due NOON on Monday 9/26 Two to three pages consisang
A Superblock-based Memory Adapter Using Decoupled Dual Buffers for Hiding the Access Latency of Non-volatile Memory
 , October 19-21, 2011, San Francisco, USA A Superblock-based Memory Adapter Using Decoupled Dual Buffers for Hiding the Access Latency of Non-volatile Memory Kwang-Su Jung, Jung-Wook Park, Charles C. Weems
, October 19-21, 2011, San Francisco, USA A Superblock-based Memory Adapter Using Decoupled Dual Buffers for Hiding the Access Latency of Non-volatile Memory Kwang-Su Jung, Jung-Wook Park, Charles C. Weems
Rethinking On-chip DRAM Cache for Simultaneous Performance and Energy Optimization
 Rethinking On-chip DRAM Cache for Simultaneous Performance and Energy Optimization Fazal Hameed and Jeronimo Castrillon Center for Advancing Electronics Dresden (cfaed), Technische Universität Dresden,
Rethinking On-chip DRAM Cache for Simultaneous Performance and Energy Optimization Fazal Hameed and Jeronimo Castrillon Center for Advancing Electronics Dresden (cfaed), Technische Universität Dresden,
Announcements. ECE4750/CS4420 Computer Architecture L6: Advanced Memory Hierarchy. Edward Suh Computer Systems Laboratory
 ECE4750/CS4420 Computer Architecture L6: Advanced Memory Hierarchy Edward Suh Computer Systems Laboratory suh@csl.cornell.edu Announcements Lab 1 due today Reading: Chapter 5.1 5.3 2 1 Overview How to
ECE4750/CS4420 Computer Architecture L6: Advanced Memory Hierarchy Edward Suh Computer Systems Laboratory suh@csl.cornell.edu Announcements Lab 1 due today Reading: Chapter 5.1 5.3 2 1 Overview How to
Caches. Hiding Memory Access Times
 Caches Hiding Memory Access Times PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O N T R O L ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH INSTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMORY
Caches Hiding Memory Access Times PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O N T R O L ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH INSTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMORY
1/19/2009. Data Locality. Exploiting Locality: Caches
 Spring 2009 Prof. Hyesoon Kim Thanks to Prof. Loh & Prof. Prvulovic Data Locality Temporal: if data item needed now, it is likely to be needed again in near future Spatial: if data item needed now, nearby
Spring 2009 Prof. Hyesoon Kim Thanks to Prof. Loh & Prof. Prvulovic Data Locality Temporal: if data item needed now, it is likely to be needed again in near future Spatial: if data item needed now, nearby
Speeding Up Crossbar Resistive Memory by Exploiting In-memory Data Patterns
 March 12, 2018 Speeding Up Crossbar Resistive Memory by Exploiting In-memory Data Patterns Wen Wen Lei Zhao, Youtao Zhang, Jun Yang Executive Summary Problems: performance and reliability of write operations
March 12, 2018 Speeding Up Crossbar Resistive Memory by Exploiting In-memory Data Patterns Wen Wen Lei Zhao, Youtao Zhang, Jun Yang Executive Summary Problems: performance and reliability of write operations
Multilevel Memories. Joel Emer Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 1 Multilevel Memories Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Based on the material prepared by Krste Asanovic and Arvind CPU-Memory Bottleneck 6.823
1 Multilevel Memories Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Based on the material prepared by Krste Asanovic and Arvind CPU-Memory Bottleneck 6.823
MARACAS: A Real-Time Multicore VCPU Scheduling Framework
 : A Real-Time Framework Computer Science Department Boston University Overview 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Motivation platforms are gaining popularity in embedded and real-time systems concurrent workload support less
: A Real-Time Framework Computer Science Department Boston University Overview 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Motivation platforms are gaining popularity in embedded and real-time systems concurrent workload support less
A Comprehensive Review of the Challenges and Opportunities Confronting Cache Memory System Performance
 A Comprehensive Review of the Challenges and Opportunities Confronting Cache Memory System Performance Richard A. Kramer, Mathias Elmlinger, Abhishek Ramamurthy, Siva Pranav Kumar Timmireddy kramerri@oregonstate.edu,
A Comprehensive Review of the Challenges and Opportunities Confronting Cache Memory System Performance Richard A. Kramer, Mathias Elmlinger, Abhishek Ramamurthy, Siva Pranav Kumar Timmireddy kramerri@oregonstate.edu,
A Low-Power Hybrid Magnetic Cache Architecture Exploiting Narrow-Width Values
 A Low-Power Hybrid Magnetic Cache Architecture Exploiting Narrow-Width Values Mohsen Imani, Abbas Rahimi, Yeseong Kim, Tajana Rosing Computer Science and Engineering, UC San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093,
A Low-Power Hybrid Magnetic Cache Architecture Exploiting Narrow-Width Values Mohsen Imani, Abbas Rahimi, Yeseong Kim, Tajana Rosing Computer Science and Engineering, UC San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093,
Cache Designs and Tricks. Kyle Eli, Chun-Lung Lim
 Cache Designs and Tricks Kyle Eli, Chun-Lung Lim Why is cache important? CPUs already perform computations on data faster than the data can be retrieved from main memory and microprocessor execution speeds
Cache Designs and Tricks Kyle Eli, Chun-Lung Lim Why is cache important? CPUs already perform computations on data faster than the data can be retrieved from main memory and microprocessor execution speeds
Caches. Samira Khan March 23, 2017
 Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Agenda Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Agenda Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
Caches 3/23/17. Agenda. The Dataflow Model (of a Computer)
 Agenda Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
Agenda Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
Lecture-14 (Memory Hierarchy) CS422-Spring
 Lecture-14 (Memory Hierarchy) CS422-Spring 2018 Biswa@CSE-IITK The Ideal World Instruction Supply Pipeline (Instruction execution) Data Supply - Zero-cycle latency - Infinite capacity - Zero cost - Perfect
Lecture-14 (Memory Hierarchy) CS422-Spring 2018 Biswa@CSE-IITK The Ideal World Instruction Supply Pipeline (Instruction execution) Data Supply - Zero-cycle latency - Infinite capacity - Zero cost - Perfect
Comparative Analysis of Contemporary Cache Power Reduction Techniques
 Comparative Analysis of Contemporary Cache Power Reduction Techniques Ph.D. Dissertation Proposal Samuel V. Rodriguez Motivation Power dissipation is important across the board, not just portable devices!!
Comparative Analysis of Contemporary Cache Power Reduction Techniques Ph.D. Dissertation Proposal Samuel V. Rodriguez Motivation Power dissipation is important across the board, not just portable devices!!
Lecture: Large Caches, Virtual Memory. Topics: cache innovations (Sections 2.4, B.4, B.5)
 Lecture: Large Caches, Virtual Memory Topics: cache innovations (Sections 2.4, B.4, B.5) 1 Intel Montecito Cache Two cores, each with a private 12 MB L3 cache and 1 MB L2 Naffziger et al., Journal of Solid-State
Lecture: Large Caches, Virtual Memory Topics: cache innovations (Sections 2.4, B.4, B.5) 1 Intel Montecito Cache Two cores, each with a private 12 MB L3 cache and 1 MB L2 Naffziger et al., Journal of Solid-State
ECE 30 Introduction to Computer Engineering
 ECE 0 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #9 Spring 01 1. Given the following series of address references given as word addresses:,,, 1, 1, 1,, 8, 19,,,,, 7,, and. Assuming a direct-mapped
ECE 0 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #9 Spring 01 1. Given the following series of address references given as word addresses:,,, 1, 1, 1,, 8, 19,,,,, 7,, and. Assuming a direct-mapped
ARCHITECTURAL APPROACHES TO REDUCE LEAKAGE ENERGY IN CACHES
 ARCHITECTURAL APPROACHES TO REDUCE LEAKAGE ENERGY IN CACHES Shashikiran H. Tadas & Chaitali Chakrabarti Department of Electrical Engineering Arizona State University Tempe, AZ, 85287. tadas@asu.edu, chaitali@asu.edu
ARCHITECTURAL APPROACHES TO REDUCE LEAKAGE ENERGY IN CACHES Shashikiran H. Tadas & Chaitali Chakrabarti Department of Electrical Engineering Arizona State University Tempe, AZ, 85287. tadas@asu.edu, chaitali@asu.edu
Power Reduction Techniques in the Memory System. Typical Memory Hierarchy
 Power Reduction Techniques in the Memory System Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial Memories.1 Typical Memory Hierarchy On-Chip Components Control edram Datapath RegFile ITLB DTLB Instr Data Cache
Power Reduction Techniques in the Memory System Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial Memories.1 Typical Memory Hierarchy On-Chip Components Control edram Datapath RegFile ITLB DTLB Instr Data Cache
Using Transparent Compression to Improve SSD-based I/O Caches
 Using Transparent Compression to Improve SSD-based I/O Caches Thanos Makatos, Yannis Klonatos, Manolis Marazakis, Michail D. Flouris, and Angelos Bilas {mcatos,klonatos,maraz,flouris,bilas}@ics.forth.gr
Using Transparent Compression to Improve SSD-based I/O Caches Thanos Makatos, Yannis Klonatos, Manolis Marazakis, Michail D. Flouris, and Angelos Bilas {mcatos,klonatos,maraz,flouris,bilas}@ics.forth.gr
WALL: A Writeback-Aware LLC Management for PCM-based Main Memory Systems
 : A Writeback-Aware LLC Management for PCM-based Main Memory Systems Bahareh Pourshirazi *, Majed Valad Beigi, Zhichun Zhu *, and Gokhan Memik * University of Illinois at Chicago Northwestern University
: A Writeback-Aware LLC Management for PCM-based Main Memory Systems Bahareh Pourshirazi *, Majed Valad Beigi, Zhichun Zhu *, and Gokhan Memik * University of Illinois at Chicago Northwestern University
Lecture: DRAM Main Memory. Topics: virtual memory wrap-up, DRAM intro and basics (Section 2.3)
 Lecture: DRAM Main Memory Topics: virtual memory wrap-up, DRAM intro and basics (Section 2.3) 1 TLB and Cache 2 Virtually Indexed Caches 24-bit virtual address, 4KB page size 12 bits offset and 12 bits
Lecture: DRAM Main Memory Topics: virtual memory wrap-up, DRAM intro and basics (Section 2.3) 1 TLB and Cache 2 Virtually Indexed Caches 24-bit virtual address, 4KB page size 12 bits offset and 12 bits
Page 1. Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash )
 Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Lecture 14: Large Cache Design II. Topics: Cache partitioning and replacement policies
 Lecture 14: Large Cache Design II Topics: Cache partitioning and replacement policies 1 Page Coloring CACHE VIEW Bank number with Page-to-Bank Tag Set Index Bank number with Set-interleaving Block offset
Lecture 14: Large Cache Design II Topics: Cache partitioning and replacement policies 1 Page Coloring CACHE VIEW Bank number with Page-to-Bank Tag Set Index Bank number with Set-interleaving Block offset
AC-DIMM: Associative Computing with STT-MRAM
 AC-DIMM: Associative Computing with STT-MRAM Qing Guo, Xiaochen Guo, Ravi Patel Engin Ipek, Eby G. Friedman University of Rochester Published In: ISCA-2013 Motivation Prevalent Trends in Modern Computing:
AC-DIMM: Associative Computing with STT-MRAM Qing Guo, Xiaochen Guo, Ravi Patel Engin Ipek, Eby G. Friedman University of Rochester Published In: ISCA-2013 Motivation Prevalent Trends in Modern Computing:
CONTENT-AWARE SPIN-TRANSFER TORQUE MAGNETORESISTIVE RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY (STT-MRAM) CACHE DESIGNS
 CONTENT-AWARE SPIN-TRANSFER TORQUE MAGNETORESISTIVE RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY (STT-MRAM) CACHE DESIGNS By QI ZENG A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
CONTENT-AWARE SPIN-TRANSFER TORQUE MAGNETORESISTIVE RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY (STT-MRAM) CACHE DESIGNS By QI ZENG A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
Low-power Architecture. By: Jonathan Herbst Scott Duntley
 Low-power Architecture By: Jonathan Herbst Scott Duntley Why low power? Has become necessary with new-age demands: o Increasing design complexity o Demands of and for portable equipment Communication Media
Low-power Architecture By: Jonathan Herbst Scott Duntley Why low power? Has become necessary with new-age demands: o Increasing design complexity o Demands of and for portable equipment Communication Media
Emerging NVM Memory Technologies
 Emerging NVM Memory Technologies Yuan Xie Associate Professor The Pennsylvania State University Department of Computer Science & Engineering www.cse.psu.edu/~yuanxie yuanxie@cse.psu.edu Position Statement
Emerging NVM Memory Technologies Yuan Xie Associate Professor The Pennsylvania State University Department of Computer Science & Engineering www.cse.psu.edu/~yuanxie yuanxie@cse.psu.edu Position Statement
Evaluating STT-RAM as an Energy-Efficient Main Memory Alternative
 Evaluating STT-RAM as an Energy-Efficient Main Memory Alternative Emre Kültürsay *, Mahmut Kandemir *, Anand Sivasubramaniam *, and Onur Mutlu * Pennsylvania State University Carnegie Mellon University
Evaluating STT-RAM as an Energy-Efficient Main Memory Alternative Emre Kültürsay *, Mahmut Kandemir *, Anand Sivasubramaniam *, and Onur Mutlu * Pennsylvania State University Carnegie Mellon University
EE414 Embedded Systems Ch 5. Memory Part 2/2
 EE414 Embedded Systems Ch 5. Memory Part 2/2 Byung Kook Kim School of Electrical Engineering Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Overview 6.1 introduction 6.2 Memory Write Ability and Storage
EE414 Embedded Systems Ch 5. Memory Part 2/2 Byung Kook Kim School of Electrical Engineering Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Overview 6.1 introduction 6.2 Memory Write Ability and Storage
Module 9: Addendum to Module 6: Shared Memory Multiprocessors Lecture 17: Multiprocessor Organizations and Cache Coherence. The Lecture Contains:
 The Lecture Contains: Shared Memory Multiprocessors Shared Cache Private Cache/Dancehall Distributed Shared Memory Shared vs. Private in CMPs Cache Coherence Cache Coherence: Example What Went Wrong? Implementations
The Lecture Contains: Shared Memory Multiprocessors Shared Cache Private Cache/Dancehall Distributed Shared Memory Shared vs. Private in CMPs Cache Coherence Cache Coherence: Example What Went Wrong? Implementations
An Energy Improvement in Cache System by Using Write Through Policy
 An Energy Improvement in Cache System by Using Write Through Policy Vigneshwari.S 1 PG Scholar, Department of ECE VLSI Design, SNS College of Technology, CBE-641035, India 1 ABSTRACT: This project presents
An Energy Improvement in Cache System by Using Write Through Policy Vigneshwari.S 1 PG Scholar, Department of ECE VLSI Design, SNS College of Technology, CBE-641035, India 1 ABSTRACT: This project presents
TAPAS: Temperature-aware Adaptive Placement for 3D Stacked Hybrid Caches
 TAPAS: Temperature-aware Adaptive Placement for 3D Stacked Hybrid Caches Majed Valad Beigi and Gokhan Memik Department of EECS, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL majed.beigi@northwestern.edu and memik@eecs.northwestern.edu
TAPAS: Temperature-aware Adaptive Placement for 3D Stacked Hybrid Caches Majed Valad Beigi and Gokhan Memik Department of EECS, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL majed.beigi@northwestern.edu and memik@eecs.northwestern.edu
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
Simultaneous Multithreading Processor
 Simultaneous Multithreading Processor Paper presented: Exploiting Choice: Instruction Fetch and Issue on an Implementable Simultaneous Multithreading Processor James Lue Some slides are modified from http://hassan.shojania.com/pdf/smt_presentation.pdf
Simultaneous Multithreading Processor Paper presented: Exploiting Choice: Instruction Fetch and Issue on an Implementable Simultaneous Multithreading Processor James Lue Some slides are modified from http://hassan.shojania.com/pdf/smt_presentation.pdf
Registers. Instruction Memory A L U. Data Memory C O N T R O L M U X A D D A D D. Sh L 2 M U X. Sign Ext M U X ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH
 PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O T R O L ALU CTL ISTRUCTIO FETCH ISTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMOR ACCESS WRITE BACK A D D A D D A L U
PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O T R O L ALU CTL ISTRUCTIO FETCH ISTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMOR ACCESS WRITE BACK A D D A D D A L U
Novel Nonvolatile Memory Hierarchies to Realize "Normally-Off Mobile Processors" ASP-DAC 2014
 Novel Nonvolatile Memory Hierarchies to Realize "Normally-Off Mobile Processors" ASP-DAC 2014 Shinobu Fujita, Kumiko Nomura, Hiroki Noguchi, Susumu Takeda, Keiko Abe Toshiba Corporation, R&D Center Advanced
Novel Nonvolatile Memory Hierarchies to Realize "Normally-Off Mobile Processors" ASP-DAC 2014 Shinobu Fujita, Kumiko Nomura, Hiroki Noguchi, Susumu Takeda, Keiko Abe Toshiba Corporation, R&D Center Advanced
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization. More Caches Measuring Performance
 ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 28 More s Measuring Performance Announcements HW7 due tomorrow :59pm Prelab 5(c) due Saturday 3pm Lab 6 (last one) released HW8 (last one) to be released
ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 28 More s Measuring Performance Announcements HW7 due tomorrow :59pm Prelab 5(c) due Saturday 3pm Lab 6 (last one) released HW8 (last one) to be released
Compiler-Assisted Refresh Minimization for Volatile STT-RAM Cache
 Compiler-Assisted Refresh Minimization for Volatile STT-RAM Cache Qingan Li, Jianhua Li, Liang Shi, Chun Jason Xue, Yiran Chen, Yanxiang He City University of Hong Kong University of Pittsburg Outline
Compiler-Assisted Refresh Minimization for Volatile STT-RAM Cache Qingan Li, Jianhua Li, Liang Shi, Chun Jason Xue, Yiran Chen, Yanxiang He City University of Hong Kong University of Pittsburg Outline
Reactive NUCA: Near-Optimal Block Placement and Replication in Distributed Caches
 Reactive NUCA: Near-Optimal Block Placement and Replication in Distributed Caches Nikos Hardavellas Michael Ferdman, Babak Falsafi, Anastasia Ailamaki Carnegie Mellon and EPFL Data Placement in Distributed
Reactive NUCA: Near-Optimal Block Placement and Replication in Distributed Caches Nikos Hardavellas Michael Ferdman, Babak Falsafi, Anastasia Ailamaki Carnegie Mellon and EPFL Data Placement in Distributed
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory / DRAM SRAM = Static RAM SRAM vs. DRAM As long as power is present, data is retained DRAM = Dynamic RAM If you don t do anything, you lose the data SRAM: 6T per bit
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory / DRAM SRAM = Static RAM SRAM vs. DRAM As long as power is present, data is retained DRAM = Dynamic RAM If you don t do anything, you lose the data SRAM: 6T per bit
and data combined) is equal to 7% of the number of instructions. Miss Rate with Second- Level Cache, Direct- Mapped Speed
 5.3 By convention, a cache is named according to the amount of data it contains (i.e., a 4 KiB cache can hold 4 KiB of data); however, caches also require SRAM to store metadata such as tags and valid
5.3 By convention, a cache is named according to the amount of data it contains (i.e., a 4 KiB cache can hold 4 KiB of data); however, caches also require SRAM to store metadata such as tags and valid
Module 9: "Introduction to Shared Memory Multiprocessors" Lecture 16: "Multiprocessor Organizations and Cache Coherence" Shared Memory Multiprocessors
 Shared Memory Multiprocessors Shared memory multiprocessors Shared cache Private cache/dancehall Distributed shared memory Shared vs. private in CMPs Cache coherence Cache coherence: Example What went
Shared Memory Multiprocessors Shared memory multiprocessors Shared cache Private cache/dancehall Distributed shared memory Shared vs. private in CMPs Cache coherence Cache coherence: Example What went
Lecture 16: Checkpointed Processors. Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University
 Lecture 16: Checkpointed Processors Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee382a Lecture 18-1 Announcements Reading for today: class notes Your main focus:
Lecture 16: Checkpointed Processors Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee382a Lecture 18-1 Announcements Reading for today: class notes Your main focus:
Spring 2016 :: CSE 502 Computer Architecture. Caches. Nima Honarmand
 Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
ADAPTIVE BLOCK PINNING BASED: DYNAMIC CACHE PARTITIONING FOR MULTI-CORE ARCHITECTURES
 ADAPTIVE BLOCK PINNING BASED: DYNAMIC CACHE PARTITIONING FOR MULTI-CORE ARCHITECTURES Nitin Chaturvedi 1 Jithin Thomas 1, S Gurunarayanan 2 1 Birla Institute of Technology and Science, EEE Group, Pilani,
ADAPTIVE BLOCK PINNING BASED: DYNAMIC CACHE PARTITIONING FOR MULTI-CORE ARCHITECTURES Nitin Chaturvedi 1 Jithin Thomas 1, S Gurunarayanan 2 1 Birla Institute of Technology and Science, EEE Group, Pilani,
Improving System. Performance: Caches
 Improving System Performance: Caches December 04 CSC201 Section 002 Fall, 2000 A Motivating Example Application: making a (mechanical) clock dozens of tools and pages of instructions, hundreds of parts
Improving System Performance: Caches December 04 CSC201 Section 002 Fall, 2000 A Motivating Example Application: making a (mechanical) clock dozens of tools and pages of instructions, hundreds of parts
Lecture: DRAM Main Memory. Topics: virtual memory wrap-up, DRAM intro and basics (Section 2.3)
 Lecture: DRAM Main Memory Topics: virtual memory wrap-up, DRAM intro and basics (Section 2.3) 1 TLB and Cache Is the cache indexed with virtual or physical address? To index with a physical address, we
Lecture: DRAM Main Memory Topics: virtual memory wrap-up, DRAM intro and basics (Section 2.3) 1 TLB and Cache Is the cache indexed with virtual or physical address? To index with a physical address, we
An Efficient STT-RAM Last Level Cache Architecture for GPUs
 An Efficient STT-RAM Last Level Cache Architecture for GPUs Mohammad Hossein Samavatian, Hamed Abbasitabar, Mohammad Arjomand, and Hamid Sarbazi-Azad, HPCAN Lab, Computer Engineering Department, Sharif
An Efficient STT-RAM Last Level Cache Architecture for GPUs Mohammad Hossein Samavatian, Hamed Abbasitabar, Mohammad Arjomand, and Hamid Sarbazi-Azad, HPCAN Lab, Computer Engineering Department, Sharif
CPS101 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 13: The Memory System. Outline of Today s Lecture. The Big Picture: Where are We Now?
 cps 14 memory.1 RW Fall 2 CPS11 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 13 The System Robert Wagner Outline of Today s Lecture System the BIG Picture? Technology Technology DRAM A Real Life Example
cps 14 memory.1 RW Fall 2 CPS11 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 13 The System Robert Wagner Outline of Today s Lecture System the BIG Picture? Technology Technology DRAM A Real Life Example
Lecture 17: Virtual Memory, Large Caches. Today: virtual memory, shared/pvt caches, NUCA caches
 Lecture 17: Virtual Memory, Large Caches Today: virtual memory, shared/pvt caches, NUCA caches 1 Virtual Memory Processes deal with virtual memory they have the illusion that a very large address space
Lecture 17: Virtual Memory, Large Caches Today: virtual memory, shared/pvt caches, NUCA caches 1 Virtual Memory Processes deal with virtual memory they have the illusion that a very large address space
Caches (Writing) P & H Chapter 5.2 3, 5.5. Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2013 Computer Science Cornell University
 Caches (Writing) P & H Chapter 5.2 3, 5.5 Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2013 Computer Science Cornell University Big Picture: Memory Code Stored in Memory (also, data and stack) memory PC +4 new pc
Caches (Writing) P & H Chapter 5.2 3, 5.5 Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2013 Computer Science Cornell University Big Picture: Memory Code Stored in Memory (also, data and stack) memory PC +4 new pc
Cache Memories. From Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems. A Programmer s Perspective. Chapter 6.
 Cache Memories From Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems. A Programmer s Perspective. Chapter 6. Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging
Cache Memories From Bryant and O Hallaron, Computer Systems. A Programmer s Perspective. Chapter 6. Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging
Area, Power, and Latency Considerations of STT-MRAM to Substitute for Main Memory
 Area, Power, and Latency Considerations of STT-MRAM to Substitute for Main Memory Youngbin Jin, Mustafa Shihab, and Myoungsoo Jung Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory Department of Electrical
Area, Power, and Latency Considerations of STT-MRAM to Substitute for Main Memory Youngbin Jin, Mustafa Shihab, and Myoungsoo Jung Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory Department of Electrical
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
CS 33. Architecture and Optimization (3) CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XVI 1 Copyright 2018 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved.
 CS 33 Architecture and Optimization (3) CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XVI 1 Copyright 2018 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Hyper Threading Instruction Control Instruction Control Retirement Unit
CS 33 Architecture and Optimization (3) CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XVI 1 Copyright 2018 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Hyper Threading Instruction Control Instruction Control Retirement Unit
A Row Buffer Locality-Aware Caching Policy for Hybrid Memories. HanBin Yoon Justin Meza Rachata Ausavarungnirun Rachael Harding Onur Mutlu
 A Row Buffer Locality-Aware Caching Policy for Hybrid Memories HanBin Yoon Justin Meza Rachata Ausavarungnirun Rachael Harding Onur Mutlu Overview Emerging memories such as PCM offer higher density than
A Row Buffer Locality-Aware Caching Policy for Hybrid Memories HanBin Yoon Justin Meza Rachata Ausavarungnirun Rachael Harding Onur Mutlu Overview Emerging memories such as PCM offer higher density than
Energy Efficient Data Access and Storage through HW/SW Co-design
 Energy Efficient Data Access and Storage through HW/SW Co-design Minyi Guo Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China MCSOC 2014, Japan 24 September, 2014 Outline! Power: A first--class data center constraint!
Energy Efficient Data Access and Storage through HW/SW Co-design Minyi Guo Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China MCSOC 2014, Japan 24 September, 2014 Outline! Power: A first--class data center constraint!
A Buffer Replacement Algorithm Exploiting Multi-Chip Parallelism in Solid State Disks
 A Buffer Replacement Algorithm Exploiting Multi-Chip Parallelism in Solid State Disks Jinho Seol, Hyotaek Shim, Jaegeuk Kim, and Seungryoul Maeng Division of Computer Science School of Electrical Engineering
A Buffer Replacement Algorithm Exploiting Multi-Chip Parallelism in Solid State Disks Jinho Seol, Hyotaek Shim, Jaegeuk Kim, and Seungryoul Maeng Division of Computer Science School of Electrical Engineering
Topic 18: Virtual Memory
 Topic 18: Virtual Memory COS / ELE 375 Computer Architecture and Organization Princeton University Fall 2015 Prof. David August 1 Virtual Memory Any time you see virtual, think using a level of indirection
Topic 18: Virtual Memory COS / ELE 375 Computer Architecture and Organization Princeton University Fall 2015 Prof. David August 1 Virtual Memory Any time you see virtual, think using a level of indirection
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization. Caches
 ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 217 s Lecture 2: 1 Announcements HW7 will be posted tonight Lab sessions resume next week Lecture 2: 2 Course Content Binary numbers and logic gates
ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 217 s Lecture 2: 1 Announcements HW7 will be posted tonight Lab sessions resume next week Lecture 2: 2 Course Content Binary numbers and logic gates
Design and Implementation of High Performance DDR3 SDRAM controller
 Design and Implementation of High Performance DDR3 SDRAM controller Mrs. Komala M 1 Suvarna D 2 Dr K. R. Nataraj 3 Research Scholar PG Student(M.Tech) HOD, Dept. of ECE Jain University, Bangalore SJBIT,Bangalore
Design and Implementation of High Performance DDR3 SDRAM controller Mrs. Komala M 1 Suvarna D 2 Dr K. R. Nataraj 3 Research Scholar PG Student(M.Tech) HOD, Dept. of ECE Jain University, Bangalore SJBIT,Bangalore
Efficient Page Caching Algorithm with Prediction and Migration for a Hybrid Main Memory
 Efficient Page Caching Algorithm with Prediction and Migration for a Hybrid Main Memory Hyunchul Seok, Youngwoo Park, Ki-Woong Park, and Kyu Ho Park KAIST Daejeon, Korea {hcseok, ywpark, woongbak}@core.kaist.ac.kr
Efficient Page Caching Algorithm with Prediction and Migration for a Hybrid Main Memory Hyunchul Seok, Youngwoo Park, Ki-Woong Park, and Kyu Ho Park KAIST Daejeon, Korea {hcseok, ywpark, woongbak}@core.kaist.ac.kr
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures)
 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Instructors: Randy H Katz David A PaHerson hhp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa Direct Mapped (contnued) - Interface CharacterisTcs of the
CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Instructors: Randy H Katz David A PaHerson hhp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa Direct Mapped (contnued) - Interface CharacterisTcs of the
Computer Sciences Department
 Computer Sciences Department SIP: Speculative Insertion Policy for High Performance Caching Hongil Yoon Tan Zhang Mikko H. Lipasti Technical Report #1676 June 2010 SIP: Speculative Insertion Policy for
Computer Sciences Department SIP: Speculative Insertion Policy for High Performance Caching Hongil Yoon Tan Zhang Mikko H. Lipasti Technical Report #1676 June 2010 SIP: Speculative Insertion Policy for
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching
 CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 Reminder: Memory Hierarchy L0: Registers CPU registers hold words retrieved from L1 cache Smaller, faster,
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 Reminder: Memory Hierarchy L0: Registers CPU registers hold words retrieved from L1 cache Smaller, faster,
Couture: Tailoring STT-MRAM for Persistent Main Memory
 : Tailoring for Persistent Main Memory Mustafa M Shihab 1, Jie Zhang 3, Shuwen Gao 2, Joseph Callenes-Sloan 1, and Myoungsoo Jung 3 1 University of Texas at Dallas, 2 Intel Corporation 3 School of Integrated
: Tailoring for Persistent Main Memory Mustafa M Shihab 1, Jie Zhang 3, Shuwen Gao 2, Joseph Callenes-Sloan 1, and Myoungsoo Jung 3 1 University of Texas at Dallas, 2 Intel Corporation 3 School of Integrated
Memory. Lecture 22 CS301
 Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
Cache memory. Lecture 4. Principles, structure, mapping
 Cache memory Lecture 4 Principles, structure, mapping Computer memory overview Computer memory overview By analyzing memory hierarchy from top to bottom, the following conclusions can be done: a. Cost
Cache memory Lecture 4 Principles, structure, mapping Computer memory overview Computer memory overview By analyzing memory hierarchy from top to bottom, the following conclusions can be done: a. Cost
TIMELINE SCHEDULING FOR OUT-OF-CORE RAY BATCHING. SGVR Lab KAIST
 TIMELINE SCHEDLIN FOR OT-OF-CORE RAY BATCHIN Myungbae Son SVR Lab KAIST Sung-EuiYoon Our Scenario Complex scenes Out-of-core model: Too big data! Cannot be stored in main / memory Complex device configurations
TIMELINE SCHEDLIN FOR OT-OF-CORE RAY BATCHIN Myungbae Son SVR Lab KAIST Sung-EuiYoon Our Scenario Complex scenes Out-of-core model: Too big data! Cannot be stored in main / memory Complex device configurations
Baoping Wang School of software, Nanyang Normal University, Nanyang , Henan, China
 doi:10.21311/001.39.7.41 Implementation of Cache Schedule Strategy in Solid-state Disk Baoping Wang School of software, Nanyang Normal University, Nanyang 473061, Henan, China Chao Yin* School of Information
doi:10.21311/001.39.7.41 Implementation of Cache Schedule Strategy in Solid-state Disk Baoping Wang School of software, Nanyang Normal University, Nanyang 473061, Henan, China Chao Yin* School of Information
