Embedded System Design
|
|
|
- Veronica Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Embedded System Design Lecture 5 Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University
2 What We Have Covered So Far Instruction Set Architecture How CPU interacts with I/O controllers Today, we will talk about how CPU interacts with memory in greater details Memory system mechanism (Chapter 3.5 in Wolf s book) Chung EPC6071 2
3 Memory Management Units (MMU) Most OSes require CPU to have MMU If multi-tasking is needed in your embedded system, buy CPU with MMU There are some OSes that do not need MMU Ex) uclinux ( MMUs provide virtualization for memory Entities share a resource, but they are perceived as if each has its own resource Chung EPC6071 3
4 Resource Sharing When more than one process (i.e., program being executed) run Processes fight for resources (CPU, memories, and IO devices) OSes manage processes and resources with authority (i.e., OS is supervisor) Scheduling time management, core allocation Memory management CPU provides hardware to support OS MMU for memory management Chung EPC6071 4
5 Memory Management Processes fight for memory Needs memory protection Memory virtualization Elegant mechanism to share memory Process 1 Virtual address Virtual memory Physical memory Process 2 Virtual address Virtual memory Space for 1 Space for 2 Physical address Space for 3 Process 3 Virtual address Virtual memory Memory mapping /address translation Chung EPC6071 5
6 Memory Management Units Memory management unit (MMU) translates addresses: CPU Logical (virtual) address memory management unit physical address main memory Chung EPC6071 6
7 Address Translation Requires some sort of register/table to allow arbitrary mappings of logical to physical addresses. Two basic schemes: Contiguous Allocation Base and limit registers Non-contiguous Allocation Paging Segmentation Segmentation and paging can be combined (x86). Chung EPC6071 7
8 Base and Limit Registers Memory Process 1 Virtual Mem. 0 Base register Process Process 2 Virtual Mem. 0 Process [Silberschartz et al] Chung EPC6071 8
9 Base and Limit Registers 100 Process [Silberschartz et al] Chung EPC6071 9
10 Activity Process 1 is running and is writing 10 to 0x4 addr. Where is it stored in physical memory? How base register change when process 2 runs? Process 1 s Virtual address space Process 2 s Virtual address space Physical memory 0x0 0x1 0x2 0x3 0x4 0x5 0x6 0x7 0x8 0x9 0xA 0xB 0xC 0xD 0xE 0xF x0 0x1 0x2 0x3 0x4 0x5 0x6 0x7 0x8 0x9 0xA 0xB 0xC 0xD 0xE 0xF PC IR R0 R1 R2 R3 CPU CORE Base register CPU 5 MMU ADDR[0] ADDR[1] ADDR[2] ADDR[3] DATA[7:0] x0 0x1 0x2 0x3 0x4 0x5 0x6 0x7 0x8 0x9 0xA 0xB 0xC 0xD 0xE 0xF Chung EPC
11 Swapping If we run out of contiguous memory space, [Silberschartz et al] Chung EPC
12 Fragmentation Base-and-limit-register scheme suffers from external fragmentation External Fragmentation total memory space exists to satisfy q request, but it is not contiguous Internal Fragmentation allocated memory may be slightly larger than requested memory Chung EPC
13 Paging Divide memory space into same-size blocks Can handle external & internal fragmentation Use non-contiguous memory allocation for external frag. Make blocks small for internal frag. [Silberschartz et al] Chung EPC
14 Paging Hardware [Silberschartz et al] Chung EPC
15 Activity Use paging and page size is 4 bytes How many frames? How many pages? How many entries in page table? Allocate 8 bytes. How many bits are in offset field? Process 1 s Virtual address space 0x0 0x1 0x2 0x3 0x4 0x5 0x6 0x7 0x8 0x9 0xA 0xB 0xC 0xD 0xE 0xF PC IR R0 R1 R2 R3 CPU CORE Page table CPU MMU ADDR[0] ADDR[1] ADDR[2] ADDR[3] DATA[7:0] Physical memory used 0x0 0x1 0x2 0x3 0x4 0x5 0x6 0x7 0x8 0x9 0xA 0xB 0xC 0xD 0xE 0xF Chung EPC
16 Caching Address Translations Large translation tables require main memory access. TLB: cache for address translation. Typically small. Chung EPC
17 Paging Hardware w/ TLB [Silberschartz et al] Chung EPC
18 Advantages of Paging Some pages are present in memory and others can be in secondary storage Page level swapping Demand paging Being able to conceptually use more memory than might be physically available Chung EPC
19 Page Fault A trap to the software raised by the hardware when a program accesses a page that is mapped in the virtual address space, but not loaded in physical memory. A page may be swapped out (Swapping) A page may not be loaded at all (Demand paging) When a page fault occurs, Check if the memory reference is a valid reference to a location on secondary memory. If not, the process is terminated (illegal memory access). Otherwise, we have to page in the required page Schedule disk operation to read the desired page into main memory and restart the instruction that was interrupted by the operating system trap Chung EPC
20 Demand Paging When pure demand paging is used, page loading only occurs at the time of the data request, and not before. In particular, when a demand pager is used, a program usually begins execution with none of its pages pre-loaded in RAM. Pages are copied from the executable file into RAM the first time the executing code references them, usually in response to page faults. As a consequence, pages of the executable file containing code not executed during a particular run will never be loaded into memory Chung EPC
21 Page Sharing [Silberschartz et al] Chung EPC
22 ARM Memory Management Memory region types: section: 1 Mbyte block; large page: 64 kbytes; small page: 4 kbytes. Two-level translation scheme. Chung EPC
23 Large Page Table Problem 32bit virtual address space 4K (2^12) page size Each entry in page table is 4bytes (a word) Each process needs 4MB physical memory for its page table alone Chung EPC
24 Two-Level Page-Table Scheme Chung EPC
25 Two-Level Page-Table Scheme Advantages Individual page tables are smaller, and easier to allocate space for Page tables themselves may be paged Efficiently represents scattered virtual memory Chung EPC
26 Segmentation Hardware [Silberschartz et al] Chung EPC
27 Segmentation Hardware [Silberschartz et al] Chung EPC
28 Linux (Virtual) address space int global_data; int global_data2 = 5; int foo() { } int *a; int b[100]; a = malloc(sizeof(int)*100); Chung EPC
Virtual Memory. Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. November 15, MIT Fall 2018 L20-1
 Virtual Memory Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L20-1 Reminder: Operating Systems Goals of OS: Protection and privacy: Processes cannot access each other s data Abstraction:
Virtual Memory Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L20-1 Reminder: Operating Systems Goals of OS: Protection and privacy: Processes cannot access each other s data Abstraction:
CS399 New Beginnings. Jonathan Walpole
 CS399 New Beginnings Jonathan Walpole Memory Management Memory Management Memory a linear array of bytes - Holds O.S. and programs (processes) - Each cell (byte) is named by a unique memory address Recall,
CS399 New Beginnings Jonathan Walpole Memory Management Memory Management Memory a linear array of bytes - Holds O.S. and programs (processes) - Each cell (byte) is named by a unique memory address Recall,
Virtual Memory. Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. April 12, 2018 L16-1
 Virtual Memory Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L16-1 Reminder: Operating Systems Goals of OS: Protection and privacy: Processes cannot access each other s data Abstraction:
Virtual Memory Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L16-1 Reminder: Operating Systems Goals of OS: Protection and privacy: Processes cannot access each other s data Abstraction:
Operating Systems. Paging... Memory Management 2 Overview. Lecture 6 Memory management 2. Paging (contd.)
 Operating Systems Lecture 6 Memory management 2 Memory Management 2 Overview Paging (contd.) Structure of page table Shared memory Segmentation Segmentation with paging Virtual memory Just to remind you...
Operating Systems Lecture 6 Memory management 2 Memory Management 2 Overview Paging (contd.) Structure of page table Shared memory Segmentation Segmentation with paging Virtual memory Just to remind you...
14 May 2012 Virtual Memory. Definition: A process is an instance of a running program
 Virtual Memory (VM) Overview and motivation VM as tool for caching VM as tool for memory management VM as tool for memory protection Address translation 4 May 22 Virtual Memory Processes Definition: A
Virtual Memory (VM) Overview and motivation VM as tool for caching VM as tool for memory management VM as tool for memory protection Address translation 4 May 22 Virtual Memory Processes Definition: A
CS 153 Design of Operating Systems Winter 2016
 CS 153 Design of Operating Systems Winter 2016 Lecture 16: Memory Management and Paging Announcement Homework 2 is out To be posted on ilearn today Due in a week (the end of Feb 19 th ). 2 Recap: Fixed
CS 153 Design of Operating Systems Winter 2016 Lecture 16: Memory Management and Paging Announcement Homework 2 is out To be posted on ilearn today Due in a week (the end of Feb 19 th ). 2 Recap: Fixed
Computer Systems II. Memory Management" Subdividing memory to accommodate many processes. A program is loaded in main memory to be executed
 Computer Systems II Memory Management" Memory Management" Subdividing memory to accommodate many processes A program is loaded in main memory to be executed Memory needs to be allocated efficiently to
Computer Systems II Memory Management" Memory Management" Subdividing memory to accommodate many processes A program is loaded in main memory to be executed Memory needs to be allocated efficiently to
198:231 Intro to Computer Organization. 198:231 Introduction to Computer Organization Lecture 14
 98:23 Intro to Computer Organization Lecture 4 Virtual Memory 98:23 Introduction to Computer Organization Lecture 4 Instructor: Nicole Hynes nicole.hynes@rutgers.edu Credits: Several slides courtesy of
98:23 Intro to Computer Organization Lecture 4 Virtual Memory 98:23 Introduction to Computer Organization Lecture 4 Instructor: Nicole Hynes nicole.hynes@rutgers.edu Credits: Several slides courtesy of
Introduction to Virtual Memory Management
 Introduction to Virtual Memory Management Minsoo Ryu Department of Computer Science and Engineering Virtual Memory Management Page X Demand Paging Page X Q & A Page X Memory Allocation Three ways of memory
Introduction to Virtual Memory Management Minsoo Ryu Department of Computer Science and Engineering Virtual Memory Management Page X Demand Paging Page X Q & A Page X Memory Allocation Three ways of memory
Learning Outcomes. An understanding of page-based virtual memory in depth. Including the R3000 s support for virtual memory.
 Virtual Memory 1 Learning Outcomes An understanding of page-based virtual memory in depth. Including the R3000 s support for virtual memory. 2 Memory Management Unit (or TLB) The position and function
Virtual Memory 1 Learning Outcomes An understanding of page-based virtual memory in depth. Including the R3000 s support for virtual memory. 2 Memory Management Unit (or TLB) The position and function
CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems
 CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems Spring 2018 Lecture 10: Paging Geoffrey M. Voelker Lecture Overview Today we ll cover more paging mechanisms: Optimizations Managing page tables (space) Efficient
CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems Spring 2018 Lecture 10: Paging Geoffrey M. Voelker Lecture Overview Today we ll cover more paging mechanisms: Optimizations Managing page tables (space) Efficient
Learning Outcomes. An understanding of page-based virtual memory in depth. Including the R3000 s support for virtual memory.
 Virtual Memory Learning Outcomes An understanding of page-based virtual memory in depth. Including the R000 s support for virtual memory. Memory Management Unit (or TLB) The position and function of the
Virtual Memory Learning Outcomes An understanding of page-based virtual memory in depth. Including the R000 s support for virtual memory. Memory Management Unit (or TLB) The position and function of the
Processes, Address Spaces, and Memory Management. CS449 Spring 2016
 Processes, Address Spaces, and Memory Management CS449 Spring 2016 Process A running program and its associated data Process s Address Space 0x7fffffff Stack Data (Heap) Data (Heap) Globals Text (Code)
Processes, Address Spaces, and Memory Management CS449 Spring 2016 Process A running program and its associated data Process s Address Space 0x7fffffff Stack Data (Heap) Data (Heap) Globals Text (Code)
Simple idea 1: load-time linking. Our main questions. Some terminology. Simple idea 2: base + bound register. Protection mechanics.
 Our main questions! How is protection enforced?! How are processes relocated?! How is ory partitioned? Simple idea 1: load-time linking! Link as usual, but keep the list of references! At load time, determine
Our main questions! How is protection enforced?! How are processes relocated?! How is ory partitioned? Simple idea 1: load-time linking! Link as usual, but keep the list of references! At load time, determine
CSE 351. Virtual Memory
 CSE 351 Virtual Memory Virtual Memory Very powerful layer of indirection on top of physical memory addressing We never actually use physical addresses when writing programs Every address, pointer, etc
CSE 351 Virtual Memory Virtual Memory Very powerful layer of indirection on top of physical memory addressing We never actually use physical addresses when writing programs Every address, pointer, etc
Memory Management. Goals of Memory Management. Mechanism. Policies
 Memory Management Design, Spring 2011 Department of Computer Science Rutgers Sakai: 01:198:416 Sp11 (https://sakai.rutgers.edu) Memory Management Goals of Memory Management Convenient abstraction for programming
Memory Management Design, Spring 2011 Department of Computer Science Rutgers Sakai: 01:198:416 Sp11 (https://sakai.rutgers.edu) Memory Management Goals of Memory Management Convenient abstraction for programming
Introduction to Operating Systems Prof. Chester Rebeiro Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Introduction to Operating Systems Prof. Chester Rebeiro Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Week 02 Lecture 06 Virtual Memory Hello. In this video, we
Introduction to Operating Systems Prof. Chester Rebeiro Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Week 02 Lecture 06 Virtual Memory Hello. In this video, we
Memory Management - Demand Paging and Multi-level Page Tables
 Memory Management - Demand Paging and Multi-level Page Tables CS 416: Operating Systems Design, Spring 2011 Department of Computer Science Rutgers Sakai: 01:198:416 Sp11 (https://sakai.rutgers.edu) Topics
Memory Management - Demand Paging and Multi-level Page Tables CS 416: Operating Systems Design, Spring 2011 Department of Computer Science Rutgers Sakai: 01:198:416 Sp11 (https://sakai.rutgers.edu) Topics
Modeling Page Replacement: Stack Algorithms. Design Issues for Paging Systems
 Modeling Page Replacement: Stack Algorithms 7 4 6 5 State of memory array, M, after each item in reference string is processed CS450/550 Memory.45 Design Issues for Paging Systems Local page replacement
Modeling Page Replacement: Stack Algorithms 7 4 6 5 State of memory array, M, after each item in reference string is processed CS450/550 Memory.45 Design Issues for Paging Systems Local page replacement
How to create a process? What does process look like?
 How to create a process? On Unix systems, executable read by loader Compile time runtime Ken Birman ld loader Cache Compiler: generates one object file per source file Linker: combines all object files
How to create a process? On Unix systems, executable read by loader Compile time runtime Ken Birman ld loader Cache Compiler: generates one object file per source file Linker: combines all object files
May 19, Answer pieces in italics were not required to receive full points.
 (2 pts) Name: (2 pts) User Id: CMPSCI 377: Operating Systems Final Exam May 19, 2003 Answer pieces in italics were not required to receive full points. Problem Topic Max Grade 0-4 1 Memory 30 2 Disk Support
(2 pts) Name: (2 pts) User Id: CMPSCI 377: Operating Systems Final Exam May 19, 2003 Answer pieces in italics were not required to receive full points. Problem Topic Max Grade 0-4 1 Memory 30 2 Disk Support
Performance of Various Levels of Storage. Movement between levels of storage hierarchy can be explicit or implicit
 Memory Management All data in memory before and after processing All instructions in memory in order to execute Memory management determines what is to be in memory Memory management activities Keeping
Memory Management All data in memory before and after processing All instructions in memory in order to execute Memory management determines what is to be in memory Memory management activities Keeping
Addresses in the source program are generally symbolic. A compiler will typically bind these symbolic addresses to re-locatable addresses.
 1 Memory Management Address Binding The normal procedures is to select one of the processes in the input queue and to load that process into memory. As the process executed, it accesses instructions and
1 Memory Management Address Binding The normal procedures is to select one of the processes in the input queue and to load that process into memory. As the process executed, it accesses instructions and
Memory Management Topics. CS 537 Lecture 11 Memory. Virtualizing Resources
 Memory Management Topics CS 537 Lecture Memory Michael Swift Goals of memory management convenient abstraction for programming isolation between processes allocate scarce memory resources between competing
Memory Management Topics CS 537 Lecture Memory Michael Swift Goals of memory management convenient abstraction for programming isolation between processes allocate scarce memory resources between competing
Outline. V Computer Systems Organization II (Honors) (Introductory Operating Systems) Advantages of Multi-level Page Tables
 Outline V22.0202-001 Computer Systems Organization II (Honors) (Introductory Operating Systems) Lecture 15 Memory Management (cont d) Virtual Memory March 30, 2005 Announcements Lab 4 due next Monday (April
Outline V22.0202-001 Computer Systems Organization II (Honors) (Introductory Operating Systems) Lecture 15 Memory Management (cont d) Virtual Memory March 30, 2005 Announcements Lab 4 due next Monday (April
Memory management. Last modified: Adaptation of Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne slides for the textbook Applied Operating Systems Concepts
 Memory management Last modified: 26.04.2016 1 Contents Background Logical and physical address spaces; address binding Overlaying, swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of
Memory management Last modified: 26.04.2016 1 Contents Background Logical and physical address spaces; address binding Overlaying, swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of
Operating Systems. Memory Management. Lecture 9 Michael O Boyle
 Operating Systems Memory Management Lecture 9 Michael O Boyle 1 Memory Management Background Logical/Virtual Address Space vs Physical Address Space Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Goals
Operating Systems Memory Management Lecture 9 Michael O Boyle 1 Memory Management Background Logical/Virtual Address Space vs Physical Address Space Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Goals
CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 16: Virtual Memory. Robert Wagner
 CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 16: Virtual Memory Robert Wagner cps 104 VM.1 RW Fall 2000 Outline of Today s Lecture Virtual Memory. Paged virtual memory. Virtual to Physical translation:
CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 16: Virtual Memory Robert Wagner cps 104 VM.1 RW Fall 2000 Outline of Today s Lecture Virtual Memory. Paged virtual memory. Virtual to Physical translation:
Memory Management. Memory Management
 Memory Management Gordon College Stephen Brinton Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Allocation Paging Segmentation Segmentation with Paging 1 Background Program must be brought into memory
Memory Management Gordon College Stephen Brinton Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Allocation Paging Segmentation Segmentation with Paging 1 Background Program must be brought into memory
Today. Process Memory Layout. CSCI 4061 Introduction to Operating Systems. Where does the memory come from?
 Today CSCI 4061 Introduction to Operating Systems OS Management Virtual Paging and Swapping Instructor: Abhishek Chandra 2 Process Layout Where does the memory come from? High Address Args, environment
Today CSCI 4061 Introduction to Operating Systems OS Management Virtual Paging and Swapping Instructor: Abhishek Chandra 2 Process Layout Where does the memory come from? High Address Args, environment
Virtual Memory. User memory model so far:! In reality they share the same memory space! Separate Instruction and Data memory!!
 Virtual Memory User memory model so far:! Separate Instruction and Data memory!! In reality they share the same memory space!!! 0x00000000 User space Instruction memory 0x7fffffff Data memory MicroComuter
Virtual Memory User memory model so far:! Separate Instruction and Data memory!! In reality they share the same memory space!!! 0x00000000 User space Instruction memory 0x7fffffff Data memory MicroComuter
CS 537: Introduction to Operating Systems Fall 2015: Midterm Exam #1
 CS 537: Introduction to Operating Systems Fall 2015: Midterm Exam #1 This exam is closed book, closed notes. All cell phones must be turned off. No calculators may be used. You have two hours to complete
CS 537: Introduction to Operating Systems Fall 2015: Midterm Exam #1 This exam is closed book, closed notes. All cell phones must be turned off. No calculators may be used. You have two hours to complete
Changelog. Virtual Memory (2) exercise: 64-bit system. exercise: 64-bit system
 Changelog Virtual Memory (2) Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 21 November 2017: 1-level example: added final answer of memory value, not just location 21 November 2017: two-level
Changelog Virtual Memory (2) Changes made in this version not seen in first lecture: 21 November 2017: 1-level example: added final answer of memory value, not just location 21 November 2017: two-level
CSE 4/521 Introduction to Operating Systems. Lecture 15 Virtual Memory I (Background, Demand Paging) Summer 2018
 CSE 4/521 Introduction to Operating Systems Lecture 15 Virtual Memory I (Background, Demand Paging) Summer 2018 Overview Objective: To describe the benefits of a virtual memory system. To explain the concept
CSE 4/521 Introduction to Operating Systems Lecture 15 Virtual Memory I (Background, Demand Paging) Summer 2018 Overview Objective: To describe the benefits of a virtual memory system. To explain the concept
CS370 Operating Systems
 CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2017 Lecture 20 Main Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 Pages Pages and frames Page
CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2017 Lecture 20 Main Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 Pages Pages and frames Page
CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems Spring 2017
 CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems Spring 2017 Lecture 12: Paging Lecture Overview Today we ll cover more paging mechanisms: Optimizations Managing page tables (space) Efficient translations (TLBs)
CSE 120 Principles of Operating Systems Spring 2017 Lecture 12: Paging Lecture Overview Today we ll cover more paging mechanisms: Optimizations Managing page tables (space) Efficient translations (TLBs)
Embedded System Design
 Embedded System Design Lecture 4 Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University CPUs Takes inputs from input devices (sensors, keyboards, ) Process inputs and produce results
Embedded System Design Lecture 4 Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University CPUs Takes inputs from input devices (sensors, keyboards, ) Process inputs and produce results
Systems Programming and Computer Architecture ( ) Timothy Roscoe
 Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Systems Programming and Computer Architecture (252-6-) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 26 AS 26 Virtual Memory 8: Virtual Memory Computer Architecture
Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Systems Programming and Computer Architecture (252-6-) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 26 AS 26 Virtual Memory 8: Virtual Memory Computer Architecture
Memory Management Cache Base and Limit Registers base limit Binding of Instructions and Data to Memory Compile time absolute code Load time
 Memory Management To provide a detailed description of various ways of organizing memory hardware To discuss various memory-management techniques, including paging and segmentation To provide a detailed
Memory Management To provide a detailed description of various ways of organizing memory hardware To discuss various memory-management techniques, including paging and segmentation To provide a detailed
Virtual or Logical. Logical Addr. MMU (Memory Mgt. Unit) Physical. Addr. 1. (50 ns access)
 Virtual Memory - programmer views memory as large address space without concerns about the amount of physical memory or memory management. (What do the terms 3-bit (or 6-bit) operating system or overlays
Virtual Memory - programmer views memory as large address space without concerns about the amount of physical memory or memory management. (What do the terms 3-bit (or 6-bit) operating system or overlays
CS5460: Operating Systems Lecture 14: Memory Management (Chapter 8)
 CS5460: Operating Systems Lecture 14: Memory Management (Chapter 8) Important from last time We re trying to build efficient virtual address spaces Why?? Virtual / physical translation is done by HW and
CS5460: Operating Systems Lecture 14: Memory Management (Chapter 8) Important from last time We re trying to build efficient virtual address spaces Why?? Virtual / physical translation is done by HW and
Processes and Tasks What comprises the state of a running program (a process or task)?
 Processes and Tasks What comprises the state of a running program (a process or task)? Microprocessor Address bus Control DRAM OS code and data special caches code/data cache EAXEBP EIP DS EBXESP EFlags
Processes and Tasks What comprises the state of a running program (a process or task)? Microprocessor Address bus Control DRAM OS code and data special caches code/data cache EAXEBP EIP DS EBXESP EFlags
Virtual Memory 1. Virtual Memory
 Virtual Memory 1 Virtual Memory key concepts virtual memory, physical memory, address translation, MMU, TLB, relocation, paging, segmentation, executable file, swapping, page fault, locality, page replacement
Virtual Memory 1 Virtual Memory key concepts virtual memory, physical memory, address translation, MMU, TLB, relocation, paging, segmentation, executable file, swapping, page fault, locality, page replacement
Virtual Memory 1. Virtual Memory
 Virtual Memory 1 Virtual Memory key concepts virtual memory, physical memory, address translation, MMU, TLB, relocation, paging, segmentation, executable file, swapping, page fault, locality, page replacement
Virtual Memory 1 Virtual Memory key concepts virtual memory, physical memory, address translation, MMU, TLB, relocation, paging, segmentation, executable file, swapping, page fault, locality, page replacement
Chapter 8 & Chapter 9 Main Memory & Virtual Memory
 Chapter 8 & Chapter 9 Main Memory & Virtual Memory 1. Various ways of organizing memory hardware. 2. Memory-management techniques: 1. Paging 2. Segmentation. Introduction Memory consists of a large array
Chapter 8 & Chapter 9 Main Memory & Virtual Memory 1. Various ways of organizing memory hardware. 2. Memory-management techniques: 1. Paging 2. Segmentation. Introduction Memory consists of a large array
For The following Exercises, mark the answers True and False
 1 For The following Exercises, mark the answers True and False 1. An operating system is an example of application software. False 2. 3. 4. 6. 7. 9. 10. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. An operating system
1 For The following Exercises, mark the answers True and False 1. An operating system is an example of application software. False 2. 3. 4. 6. 7. 9. 10. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. An operating system
 Part-A QUESTION BANK UNIT-III 1. Define Dynamic Loading. To obtain better memory-space utilization dynamic loading is used. With dynamic loading, a routine is not loaded until it is called. All routines
Part-A QUESTION BANK UNIT-III 1. Define Dynamic Loading. To obtain better memory-space utilization dynamic loading is used. With dynamic loading, a routine is not loaded until it is called. All routines
Chapter 8: Memory- Management Strategies. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 8: Memory- Management Strategies Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Strategies Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation
Chapter 8: Memory- Management Strategies Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Strategies Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation
Chapter 8: Main Memory
 Chapter 8: Main Memory Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel 32 and 64-bit Architectures Example:
Chapter 8: Main Memory Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel 32 and 64-bit Architectures Example:
Virtual Memory. Stefanos Kaxiras. Credits: Some material and/or diagrams adapted from Hennessy & Patterson, Hill, online sources.
 Virtual Memory Stefanos Kaxiras Credits: Some material and/or diagrams adapted from Hennessy & Patterson, Hill, online sources. Caches Review & Intro Intended to make the slow main memory look fast by
Virtual Memory Stefanos Kaxiras Credits: Some material and/or diagrams adapted from Hennessy & Patterson, Hill, online sources. Caches Review & Intro Intended to make the slow main memory look fast by
Memory management units
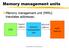 Memory management units Memory management unit (MMU) translates addresses: CPU logical address memory management unit physical address main memory Computers as Components 1 Access time comparison Media
Memory management units Memory management unit (MMU) translates addresses: CPU logical address memory management unit physical address main memory Computers as Components 1 Access time comparison Media
CMSC 313 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING LECTURE 27, FALL 2012
 CMSC 313 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING LECTURE 27, FALL 2012 ANNOUNCEMENTS Need student input on Lecturer Search Max Morawski Lecture 2:30pm 3:15pm, Fri 12/7, ITE 217 Meet with
CMSC 313 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING LECTURE 27, FALL 2012 ANNOUNCEMENTS Need student input on Lecturer Search Max Morawski Lecture 2:30pm 3:15pm, Fri 12/7, ITE 217 Meet with
Virtual Memory. CS61, Lecture 15. Prof. Stephen Chong October 20, 2011
 Virtual Memory CS6, Lecture 5 Prof. Stephen Chong October 2, 2 Announcements Midterm review session: Monday Oct 24 5:3pm to 7pm, 6 Oxford St. room 33 Large and small group interaction 2 Wall of Flame Rob
Virtual Memory CS6, Lecture 5 Prof. Stephen Chong October 2, 2 Announcements Midterm review session: Monday Oct 24 5:3pm to 7pm, 6 Oxford St. room 33 Large and small group interaction 2 Wall of Flame Rob
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 12 -- Virtual Memory 2014-2-27 John Lazzaro (not a prof - John is always OK) TA: Eric Love www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/ Play: CS 152 L12: Virtual
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 12 -- Virtual Memory 2014-2-27 John Lazzaro (not a prof - John is always OK) TA: Eric Love www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/ Play: CS 152 L12: Virtual
virtual memory Page 1 CSE 361S Disk Disk
 CSE 36S Motivations for Use DRAM a for the Address space of a process can exceed physical memory size Sum of address spaces of multiple processes can exceed physical memory Simplify Management 2 Multiple
CSE 36S Motivations for Use DRAM a for the Address space of a process can exceed physical memory size Sum of address spaces of multiple processes can exceed physical memory Simplify Management 2 Multiple
CPS 104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 20: Virtual Memory
 CPS 104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 20: Virtual Nov. 10, 1999 Dietolf (Dee) Ramm http://www.cs.duke.edu/~dr/cps104.html CPS 104 Lecture 20.1 Outline of Today s Lecture O Virtual. 6 Paged
CPS 104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 20: Virtual Nov. 10, 1999 Dietolf (Dee) Ramm http://www.cs.duke.edu/~dr/cps104.html CPS 104 Lecture 20.1 Outline of Today s Lecture O Virtual. 6 Paged
Chapter 8: Memory-Management Strategies
 Chapter 8: Memory-Management Strategies Chapter 8: Memory Management Strategies Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel 32 and
Chapter 8: Memory-Management Strategies Chapter 8: Memory Management Strategies Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel 32 and
CS307: Operating Systems
 CS307: Operating Systems Chentao Wu 吴晨涛 Associate Professor Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University SEIEE Building 3-513 wuct@cs.sjtu.edu.cn Download Lectures ftp://public.sjtu.edu.cn
CS307: Operating Systems Chentao Wu 吴晨涛 Associate Professor Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University SEIEE Building 3-513 wuct@cs.sjtu.edu.cn Download Lectures ftp://public.sjtu.edu.cn
CS370 Operating Systems
 CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Spring 2018 L17 Main Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 FAQ Was Great Dijkstra a magician?
CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Spring 2018 L17 Main Memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 FAQ Was Great Dijkstra a magician?
Memory Hierarchy. Goal: Fast, unlimited storage at a reasonable cost per bit.
 Memory Hierarchy Goal: Fast, unlimited storage at a reasonable cost per bit. Recall the von Neumann bottleneck - single, relatively slow path between the CPU and main memory. Fast: When you need something
Memory Hierarchy Goal: Fast, unlimited storage at a reasonable cost per bit. Recall the von Neumann bottleneck - single, relatively slow path between the CPU and main memory. Fast: When you need something
CS 318 Principles of Operating Systems
 CS 318 Principles of Operating Systems Fall 2018 Lecture 10: Virtual Memory II Ryan Huang Slides adapted from Geoff Voelker s lectures Administrivia Next Tuesday project hacking day No class My office
CS 318 Principles of Operating Systems Fall 2018 Lecture 10: Virtual Memory II Ryan Huang Slides adapted from Geoff Voelker s lectures Administrivia Next Tuesday project hacking day No class My office
! What is main memory? ! What is static and dynamic allocation? ! What is segmentation? Maria Hybinette, UGA. High Address (0x7fffffff) !
 Memory Questions? CSCI [4 6]730 Operating Systems Main Memory! What is main memory?! How does multiple processes share memory space?» Key is how do they refer to memory addresses?! What is static and dynamic
Memory Questions? CSCI [4 6]730 Operating Systems Main Memory! What is main memory?! How does multiple processes share memory space?» Key is how do they refer to memory addresses?! What is static and dynamic
Lecture 8 Memory Management Strategies (chapter 8)
 Bilkent University Department of Computer Engineering CS342 Operating Systems Lecture 8 Memory Management Strategies (chapter 8) Dr. İbrahim Körpeoğlu http://www.cs.bilkent.edu.tr/~korpe 1 References The
Bilkent University Department of Computer Engineering CS342 Operating Systems Lecture 8 Memory Management Strategies (chapter 8) Dr. İbrahim Körpeoğlu http://www.cs.bilkent.edu.tr/~korpe 1 References The
6 - Main Memory EECE 315 (101) ECE UBC 2013 W2
 6 - Main Memory EECE 315 (101) ECE UBC 2013 W2 Acknowledgement: This set of slides is partly based on the PPTs provided by the Wiley s companion website (including textbook images, when not explicitly
6 - Main Memory EECE 315 (101) ECE UBC 2013 W2 Acknowledgement: This set of slides is partly based on the PPTs provided by the Wiley s companion website (including textbook images, when not explicitly
The memory of a program. Paging and Virtual Memory. Swapping. Paging. Physical to logical address mapping. Memory management: Review
 The memory of a program Paging and Virtual Memory Operating Systems Spring 4 Source-code is compiled into linkable object modules Memory addresses given as relative offsets Libraries contain object modules
The memory of a program Paging and Virtual Memory Operating Systems Spring 4 Source-code is compiled into linkable object modules Memory addresses given as relative offsets Libraries contain object modules
CHAPTER 8 - MEMORY MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES
 CHAPTER 8 - MEMORY MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES OBJECTIVES Detailed description of various ways of organizing memory hardware Various memory-management techniques, including paging and segmentation To provide
CHAPTER 8 - MEMORY MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES OBJECTIVES Detailed description of various ways of organizing memory hardware Various memory-management techniques, including paging and segmentation To provide
Tutorial on Memory Management, Deadlock and Operating System Types
 Operating Systems and Systems Integration Tutorial on Memory Management, Deadlock and Operating System Types 1 Background 1.1 Memory management Virtual memory: is a method of managing memory automatically
Operating Systems and Systems Integration Tutorial on Memory Management, Deadlock and Operating System Types 1 Background 1.1 Memory management Virtual memory: is a method of managing memory automatically
ECE 341. Lecture # 18
 ECE 341 Lecture # 18 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@ece.pdx.edu December 1, 2014 Portland State University Lecture Topics The Memory System Cache Memories Performance Considerations Hit Ratios and Miss
ECE 341 Lecture # 18 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@ece.pdx.edu December 1, 2014 Portland State University Lecture Topics The Memory System Cache Memories Performance Considerations Hit Ratios and Miss
CHAPTER 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT. By I-Chen Lin Textbook: Operating System Concepts 9th Ed.
 CHAPTER 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT By I-Chen Lin Textbook: Operating System Concepts 9th Ed. Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the
CHAPTER 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT By I-Chen Lin Textbook: Operating System Concepts 9th Ed. Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the
CMSC 313 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING LECTURE 27, SPRING 2013
 CMSC 313 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING LECTURE 27, SPRING 2013 CACHING Why: bridge speed difference between CPU and RAM Modern RAM allows blocks of memory to be read quickly Principle
CMSC 313 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING LECTURE 27, SPRING 2013 CACHING Why: bridge speed difference between CPU and RAM Modern RAM allows blocks of memory to be read quickly Principle
Operating Systems. Designed and Presented by Dr. Ayman Elshenawy Elsefy
 Operating Systems Designed and Presented by Dr. Ayman Elshenawy Elsefy Dept. of Systems & Computer Eng.. AL-AZHAR University Website : eaymanelshenawy.wordpress.com Email : eaymanelshenawy@yahoo.com Reference
Operating Systems Designed and Presented by Dr. Ayman Elshenawy Elsefy Dept. of Systems & Computer Eng.. AL-AZHAR University Website : eaymanelshenawy.wordpress.com Email : eaymanelshenawy@yahoo.com Reference
Virtual Memory II. CSE 351 Autumn Instructor: Justin Hsia
 Virtual Memory II CSE 35 Autumn 27 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Lucas Wotton Michael Zhang Parker DeWilde Ryan Wong Sam Gehman Sam Wolfson Savanna Yee Vinny Palaniappan https://xkcd.com/495/
Virtual Memory II CSE 35 Autumn 27 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Lucas Wotton Michael Zhang Parker DeWilde Ryan Wong Sam Gehman Sam Wolfson Savanna Yee Vinny Palaniappan https://xkcd.com/495/
Chapter 8: Main Memory. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 8: Main Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel
Chapter 8: Main Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel
Memory Management. Dr. Yingwu Zhu
 Memory Management Dr. Yingwu Zhu Big picture Main memory is a resource A process/thread is being executing, the instructions & data must be in memory Assumption: Main memory is super big to hold a program
Memory Management Dr. Yingwu Zhu Big picture Main memory is a resource A process/thread is being executing, the instructions & data must be in memory Assumption: Main memory is super big to hold a program
Virtual Memory. Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University
 Virtual Memory Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Precise Definition of Virtual Memory Virtual memory is a mechanism for translating logical
Virtual Memory Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Precise Definition of Virtual Memory Virtual memory is a mechanism for translating logical
Virtual Memory. Jinkyu Jeong Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Virtual Memory Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu SSE3044: Operating Systems, Fall 2017, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Virtual Memory:
Virtual Memory Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu SSE3044: Operating Systems, Fall 2017, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Virtual Memory:
Memory Management. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1
 Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 Recap Paged MMU: Two main Issues Translation speed can be slow TLB Table size is big Multi-level page table
Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 Recap Paged MMU: Two main Issues Translation speed can be slow TLB Table size is big Multi-level page table
Memory Allocation. Copyright : University of Illinois CS 241 Staff 1
 Memory Allocation Copyright : University of Illinois CS 241 Staff 1 Recap: Virtual Addresses A virtual address is a memory address that a process uses to access its own memory Virtual address actual physical
Memory Allocation Copyright : University of Illinois CS 241 Staff 1 Recap: Virtual Addresses A virtual address is a memory address that a process uses to access its own memory Virtual address actual physical
Topics: Memory Management (SGG, Chapter 08) 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.5, 8.6 CS 3733 Operating Systems
 Topics: Memory Management (SGG, Chapter 08) 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.5, 8.6 CS 3733 Operating Systems Instructor: Dr. Turgay Korkmaz Department Computer Science The University of Texas at San Antonio Office: NPB
Topics: Memory Management (SGG, Chapter 08) 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.5, 8.6 CS 3733 Operating Systems Instructor: Dr. Turgay Korkmaz Department Computer Science The University of Texas at San Antonio Office: NPB
Chapter 8: Memory Management. Operating System Concepts with Java 8 th Edition
 Chapter 8: Memory Management 8.1 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Background Program must be brought (from disk) into memory and placed within a process for it to be run Main memory and registers are
Chapter 8: Memory Management 8.1 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Background Program must be brought (from disk) into memory and placed within a process for it to be run Main memory and registers are
UNIT III MEMORY MANAGEMENT
 UNIT III MEMORY MANAGEMENT TOPICS TO BE COVERED 3.1 Memory management 3.2 Contiguous allocation i Partitioned memory allocation ii Fixed & variable partitioning iii Swapping iv Relocation v Protection
UNIT III MEMORY MANAGEMENT TOPICS TO BE COVERED 3.1 Memory management 3.2 Contiguous allocation i Partitioned memory allocation ii Fixed & variable partitioning iii Swapping iv Relocation v Protection
Chapter 8: Memory- Management Strategies. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 8: Memory- Management Strategies Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Strategies Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation
Chapter 8: Memory- Management Strategies Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Strategies Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation
Chapter 8: Memory- Management Strategies
 Chapter 8: Memory Management Strategies Chapter 8: Memory- Management Strategies Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel 32 and
Chapter 8: Memory Management Strategies Chapter 8: Memory- Management Strategies Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel 32 and
Embedded Systems Dr. Santanu Chaudhury Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Embedded Systems Dr. Santanu Chaudhury Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 13 Virtual memory and memory management unit In the last class, we had discussed
Embedded Systems Dr. Santanu Chaudhury Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 13 Virtual memory and memory management unit In the last class, we had discussed
CS 162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Professor: Anthony D. Joseph Spring Lecture 13: Address Translation
 CS 162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Professor: Anthony D. Joseph Spring 2004 Lecture 13: Address Translation 13.0 Main Points 13.1 Hardware Translation Overview CPU Virtual Address Translation
CS 162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Professor: Anthony D. Joseph Spring 2004 Lecture 13: Address Translation 13.0 Main Points 13.1 Hardware Translation Overview CPU Virtual Address Translation
Part Three - Memory Management. Chapter 8: Memory-Management Strategies
 Part Three - Memory Management Chapter 8: Memory-Management Strategies Chapter 8: Memory-Management Strategies 8.1 Background 8.2 Swapping 8.3 Contiguous Memory Allocation 8.4 Segmentation 8.5 Paging 8.6
Part Three - Memory Management Chapter 8: Memory-Management Strategies Chapter 8: Memory-Management Strategies 8.1 Background 8.2 Swapping 8.3 Contiguous Memory Allocation 8.4 Segmentation 8.5 Paging 8.6
Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging. Cache Performance
 6.823, L11--1 Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 Cache Performance 6.823,
6.823, L11--1 Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 Cache Performance 6.823,
Chapter 8: Main Memory
 Chapter 8: Main Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel
Chapter 8: Main Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 8: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of the Page Table Example: The Intel
Paging. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Paging Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Today s Topics Virtual memory implementation Paging Segmentation 2 Paging (1) Paging Permits
Paging Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Today s Topics Virtual memory implementation Paging Segmentation 2 Paging (1) Paging Permits
Computer System Architecture Midterm Examination Spring 2002
 Computer System Architecture 6.823 Midterm Examination Spring 2002 Name: This is an open book, open notes exam. 110 Minutes 1 Pages Notes: Not all questions are of equal difficulty, so look over the entire
Computer System Architecture 6.823 Midterm Examination Spring 2002 Name: This is an open book, open notes exam. 110 Minutes 1 Pages Notes: Not all questions are of equal difficulty, so look over the entire
Chapter 7: Main Memory. Operating System Concepts Essentials 8 th Edition
 Chapter 7: Main Memory Operating System Concepts Essentials 8 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2011 Chapter 7: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Paging Structure
Chapter 7: Main Memory Operating System Concepts Essentials 8 th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2011 Chapter 7: Memory Management Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Paging Structure
Memory Management. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1
 Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 CPU management Roadmap Process, thread, synchronization, scheduling Memory management Virtual memory Disk
Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 CPU management Roadmap Process, thread, synchronization, scheduling Memory management Virtual memory Disk
CS 153 Design of Operating Systems Winter 2016
 CS 153 Design of Operating Systems Winter 2016 Lecture 17: Paging Lecture Overview Recap: Today: Goal of virtual memory management: map 2^32 byte address space to physical memory Internal fragmentation
CS 153 Design of Operating Systems Winter 2016 Lecture 17: Paging Lecture Overview Recap: Today: Goal of virtual memory management: map 2^32 byte address space to physical memory Internal fragmentation
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory
 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Multiprogramming Memory Management so far 1. Dynamic Loading The main Program gets loaded into memory Routines are stored in Relocatable Load format on disk As main program (or
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Multiprogramming Memory Management so far 1. Dynamic Loading The main Program gets loaded into memory Routines are stored in Relocatable Load format on disk As main program (or
CPUs. Caching: The Basic Idea. Cache : MainMemory :: Window : Caches. Memory management. CPU performance. 1. Door 2. Bigger Door 3. The Great Outdoors
 CPUs Caches. Memory management. CPU performance. Cache : MainMemory :: Window : 1. Door 2. Bigger Door 3. The Great Outdoors 4. Horizontal Blinds 18% 9% 64% 9% Door Bigger Door The Great Outdoors Horizontal
CPUs Caches. Memory management. CPU performance. Cache : MainMemory :: Window : 1. Door 2. Bigger Door 3. The Great Outdoors 4. Horizontal Blinds 18% 9% 64% 9% Door Bigger Door The Great Outdoors Horizontal
Memory Management. Contents: Memory Management. How to generate code? Background
 TDIU11 Operating systems Contents: Memory Management Memory Management [SGG7/8/9] Chapter 8 Background Relocation Dynamic loading and linking Swapping Contiguous Allocation Paging Segmentation Copyright
TDIU11 Operating systems Contents: Memory Management Memory Management [SGG7/8/9] Chapter 8 Background Relocation Dynamic loading and linking Swapping Contiguous Allocation Paging Segmentation Copyright
Virtual Memory Oct. 29, 2002
 5-23 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Virtual Memory Oct. 29, 22 Topics Motivations for VM Address translation Accelerating translation with TLBs class9.ppt Motivations for Virtual Memory Use Physical
5-23 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Virtual Memory Oct. 29, 22 Topics Motivations for VM Address translation Accelerating translation with TLBs class9.ppt Motivations for Virtual Memory Use Physical
PROCESS VIRTUAL MEMORY. CS124 Operating Systems Winter , Lecture 18
 PROCESS VIRTUAL MEMORY CS124 Operating Systems Winter 2015-2016, Lecture 18 2 Programs and Memory Programs perform many interactions with memory Accessing variables stored at specific memory locations
PROCESS VIRTUAL MEMORY CS124 Operating Systems Winter 2015-2016, Lecture 18 2 Programs and Memory Programs perform many interactions with memory Accessing variables stored at specific memory locations
Paging. Jinkyu Jeong Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Paging Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Today s Topics Virtual memory implementation Paging Segmentation 2 Paging (1) Paging Permits
Paging Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Today s Topics Virtual memory implementation Paging Segmentation 2 Paging (1) Paging Permits
Chapter 8: Main Memory
 Chapter 8: Main Memory Operating System Concepts 8 th Edition,! Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009! Chapter 8: Memory Management Background" Swapping " Contiguous Memory Allocation" Paging" Structure
Chapter 8: Main Memory Operating System Concepts 8 th Edition,! Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009! Chapter 8: Memory Management Background" Swapping " Contiguous Memory Allocation" Paging" Structure
