Integration Testing Path Based" Chapter 13!
|
|
|
- Kathleen Harper
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Integration Testing Path Based Chapter 13!
2 Call graph based integration Use the call graph instead of the decomposition tree! What is a call graph?! IntP 2
3 Call graph definition Is a directed, labeled graph! Vertices are methods A directed edge joins calling vertex to the called vertex Adjacency matrix is also used Does not scale well, although some insights are useful Nodes of high degree are critical IntP 3
4 SATM call graph example Look at adjacency matrix p IntP 4
5 Call graph integration strategies What types of integration strategies are used?! IntP 5
6 Call graph integration strategies 2 Pair-wise Integration Testing! Neighborhood Integration Testing! IntP 6
7 Pair-wise integration What is pair-wise integration! IntP 7
8 Pair-wise Some integration Pair-wise session Integration example Sessions IntP 8
9 Pair-wise integration 2 The idea behind Pair-Wise integration testing! Eliminate need for developing stubs / drivers Use actual code instead of stubs/drivers IntP 9
10 Pair-wise integration 3 In order not to deteriorate the process to a big-bang strategy! Restrict a testing session to just a pair of units in the call graph Results in one integration test session for each edge in the call graph IntP 10
11 Neighbourhood integration What is neighbourhood integration?! IntP 11
12 Neighbourhood integration example Two Neighborhood Integration Sessions Neighbourhoods for nodes 16 & IntP 12
13 Neighbourhood integration 2 The neighbourhood of a node in a graph! The set of nodes that are one edge away from the given node In a directed graph! All the immediate predecessor nodes and all the immediate successor nodes of a given node IntP 13
14 Neighbourhood integration 3 Neighborhood integration testing! Reduces the number of test sessions Fault isolation is difficult IntP 14
15 Pros of call-graph integration What are the pros of call-graph integration?!! IntP 15
16 Pros of call-graph integration 2 Reduces the need for drivers and stubs! Relative to functional decomposition integration Neighborhoods can be combined to create villages! Closer to a build sequence! Well suited to devising a sequence of builds with which to implement a system IntP 16
17 Cons of call-graph integration What are the cons of call-graph integration?!! IntP 17
18 Cons of call-graph integration 2 Suffers from fault isolation problems! Especially for large neighborhoods Redundancy! Nodes can appear in several neighborhoods Assumes that correct behaviour follows from correct units and correct interfaces! Not always the case! IntP 18
19 Path-based integration What is path-based integration? Why use it?! IntP 19
20 Path-Based Integration 2 Motivation! Combine structural and behavioral type of testing for integration testing as we did for unit testing Basic idea! Focus on interactions among system units Rather than merely to test interfaces among separately developed and tested units Interface-based testing is structural while interactionbased testing is behavioral! IntP 20
21 Source node What is it? IntP 21
22 Source node 2 A program statement fragment at which program execution begins or resumes.! For example the first begin statement in a program. Nodes immediately after nodes that transfer control to other units. IntP 22
23 Sink node What is a sink node?! IntP 23
24 Sink node A statement fragment at which program execution terminates! The final end in a program as well as statements that transfer control to other units IntP 24
25 Module execution path (MEP) What is a module execution path?! IntP 25
26 Module execution path (MEP) 2 A sequence of statements within a module that! Begins with a source node Ends with a sink node With no intervening sink nodes IntP 26
27 Message What is a message?! IntP 27
28 Message 2 A programming language mechanism by which one unit transfers control to another unit! Usually interpreted as subroutine / function invocations! The unit which receives the message always returns control to the message source! IntP 28
29 MM-path What is an MM-path? IntP 29
30 MM-path 2 A module to module path! An interleaved sequence of module execution paths and messages Used to describes sequences of module execution paths that include transfers of control among separate units! MM-paths always represent feasible execution paths, and these paths cross unit boundaries! IntP 30
31 MM-path example 1 A 1 B 1 C Source nodes Sink nodes Module Execution Paths MEP(B,1) = <1, 2> MEP(B,2) = <3, 4> MM-path MEP(A,1) = <1, 2, 3, 6> MEP(A,2) = <1, 2, 4> MEP(A,3) = <5, 6> MEP(C,1) = <1, 2, 4, 5> MEP(C,2) = <1, 3, 4, 5> IntP 31
32 MEPs and DD-paths What is the correspondence between MEPs and a DD-paths?! IntP 32
33 MEPs and DD-paths 2 There is no correspondence between MM execution paths and DD-paths! IntP 33
34 MEPs and slices What is the correspondence between MEPs and slices? IntP 34
35 MEPs and slices 2 There is no correspondence but there is an analog! The intersection of a module execution path with a unit is the analog of a slice with respect to the MMpath function IntP 35
36 MM-path graph What is an MM-path graph? IntP 36
37 MM-path graph 2 Given a set of units their MM-path graph is the directed graph in which! Nodes are module execution paths Edges correspond to messages and returns from one unit to another The definition is with respect to a set of units! It directly supports composition of units and composition-based integration testing IntP 37
38 MM-path graph example MEP(A,2) MEP(A,1) MEP(A,3) MEP(C,2) MEP(B,1) MEP(B,2) MEP(C,1) Solid lines indicate messages (calls) Dashed lines indicate returns from calls IntP 38
39 MM-path guidelines How long, or deep, is an MM-path? What determines the end points?! Quiescence points are natural endpoints for MM-paths! Message quiescence Data quiescence IntP 39
40 Message quiescence Occurs when a unit that sends no messages is reached! Module C in the example IntP 40
41 Data quiescence Occurs when a sequence of processing ends in the creation of stored data that is not immediately used! The causal path Data A has no quiescence The non-causal path D1 and D2 is quiescent at the node P-1 IntP 41
42 MM-path metric What is the minimum number of MM-paths that are sufficient to test a system? IntP 42
43 MM-Path metric 2 What is the minimum number of MM-paths that are sufficient to test a system?! Should cover all source-to-sink paths in the set of units What about loops? How should they be treated? IntP 43
44 MM-Path metric 3 What is the minimum number of MM-paths that are sufficient to test a system?! Should cover all source-to-sink paths in the set of units What about loops? How should they be treated?! Use condensation graphs to get directed acyclic graphs Avoids an excessive number of paths IntP 44
45 Pros of path-based integration Benefits of hybrid of functional and structural testing! Functional represent actions with input and output Structural how they are identified Avoids pitfall of structural testing! Unimplemented behaviours cannot be tested Fairly seamless union with system testing! IntP 45
46 Pros of path-based integration 2 Path-based integration is closely coupled with actual system behaviour! Works well with OO testing No need for stub and driver development! IntP 46
47 Cons of path-based integration There is a significant effort involved in identifying MMpaths! IntP 47
48 MM-path compared to other methods Strategy! Functional decomposition! Ability to test interfaces! Acceptable, can be deceptive! Ability to test co-functionality! Limited to pairs of units! Call-graph! Acceptable! Limited to pairs of units! Fault isolation resolution! Good to faulty unit! Good to faulty unit! MM-path! Excellent! Complete! Excellent to unit path level! IntP 48
TDDD04 Software Testing
 TDDD04 Software Testing Lecture Notes 5 March June 2010 Mohsen Torabzadeh-Tari (presenter), (originator) Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University, Sweden Integration Testing
TDDD04 Software Testing Lecture Notes 5 March June 2010 Mohsen Torabzadeh-Tari (presenter), (originator) Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University, Sweden Integration Testing
Software Testing: A Craftsman s Approach, 4 th Edition. Chapter 13 Integration Testing
 Chapter 13 Integration Testing The Mars Climate Orbiter Mission mission failed in September 1999 completed successful flight: 416,000,000 miles (665.600.600 km) 41 weeks flight duration lost at beginning
Chapter 13 Integration Testing The Mars Climate Orbiter Mission mission failed in September 1999 completed successful flight: 416,000,000 miles (665.600.600 km) 41 weeks flight duration lost at beginning
TDDD04: Integration and System level testing. Lena Buffoni
 TDDD04: Integration and System level testing Lena Buffoni lena.buffoni@liu.se Lecture plan Integration testing System testing Test automation Model-based testing Remember? Testing in the waterfall model
TDDD04: Integration and System level testing Lena Buffoni lena.buffoni@liu.se Lecture plan Integration testing System testing Test automation Model-based testing Remember? Testing in the waterfall model
CSCE 747 Software Testing and Quality Assurance
 CSCE 747 Software Testing and Quality Assurance Lecture 10 Integration Testing 9/30/2013 Lec 10 Integration Testing 1 CSCE 747 Fall 2013 1 Last Time Integration & System Testing Part III Levels of Testing
CSCE 747 Software Testing and Quality Assurance Lecture 10 Integration Testing 9/30/2013 Lec 10 Integration Testing 1 CSCE 747 Fall 2013 1 Last Time Integration & System Testing Part III Levels of Testing
Integration Testing. Rogério Paulo. January 12, 2007
 Integration Testing Rogério Paulo January 12, 2007 Abstract This document is written as a dissertation to complete the module CS339 Advanced Topics in Computer Science: Testing in University of Wales Swansea.
Integration Testing Rogério Paulo January 12, 2007 Abstract This document is written as a dissertation to complete the module CS339 Advanced Topics in Computer Science: Testing in University of Wales Swansea.
Rediscover Web Application Testing
 IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 19, Issue 2, Ver. I (Mar.-Apr. 2017), PP 48-52 www.iosrjournals.org Rediscover Web Application Testing Rajiv
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 19, Issue 2, Ver. I (Mar.-Apr. 2017), PP 48-52 www.iosrjournals.org Rediscover Web Application Testing Rajiv
Mind Q Systems Private Limited
 Software Testing Tools Course Content for Online Training Manual Testing Introduction Introduction to software Testing Software Development Process Project Vs Product Objectives of Testing Testing Principals
Software Testing Tools Course Content for Online Training Manual Testing Introduction Introduction to software Testing Software Development Process Project Vs Product Objectives of Testing Testing Principals
Software Testing Tools
 Software Testing Tools Manual Testing Introduction Introduction to software Testing Software Development Process Project Vs Product Objectives of Testing Testing Principals Software Development Life Cycle
Software Testing Tools Manual Testing Introduction Introduction to software Testing Software Development Process Project Vs Product Objectives of Testing Testing Principals Software Development Life Cycle
Sequential Dependency and Reliability Analysis of Embedded Systems. Yu Jiang Tsinghua university, Beijing, China
 Sequential Dependency and Reliability Analysis of Embedded Systems Yu Jiang Tsinghua university, Beijing, China outline Motivation Background Reliability Block Diagram, Fault Tree Bayesian Network, Dynamic
Sequential Dependency and Reliability Analysis of Embedded Systems Yu Jiang Tsinghua university, Beijing, China outline Motivation Background Reliability Block Diagram, Fault Tree Bayesian Network, Dynamic
Testing: Test design and testing process
 Testing: Test design and testing process Zoltán Micskei Based on István Majzik s slides Dept. of Measurement and Information Systems Budapest University of Technology and Economics Department of Measurement
Testing: Test design and testing process Zoltán Micskei Based on István Majzik s slides Dept. of Measurement and Information Systems Budapest University of Technology and Economics Department of Measurement
Question Bank. Unit 1: Perspective on Testing, Examples. Chapter 1 & 2 from Dr. Paul C. Jorgensen
 Unit 1: Perspective on Testing, Examples Chapter 1 & 2 from Dr. Paul C. Jorgensen Sl no Question Description 1. Make a Venn Diagram that reflects a part of the following statement: we have left undone
Unit 1: Perspective on Testing, Examples Chapter 1 & 2 from Dr. Paul C. Jorgensen Sl no Question Description 1. Make a Venn Diagram that reflects a part of the following statement: we have left undone
Surface Simplification Using Quadric Error Metrics
 Surface Simplification Using Quadric Error Metrics Authors: Michael Garland & Paul Heckbert Presented by: Niu Xiaozhen Disclaimer: Some slides are modified from original slides, which were designed by
Surface Simplification Using Quadric Error Metrics Authors: Michael Garland & Paul Heckbert Presented by: Niu Xiaozhen Disclaimer: Some slides are modified from original slides, which were designed by
Inf 496/596 Topics in Informatics: Analysis of Social Network Data
 Inf 496/596 Topics in Informatics: Analysis of Social Network Data Jagdish S. Gangolly Department of Informatics College of Computing & Information State University of New York at Albany Lecture 1B (Graphs)
Inf 496/596 Topics in Informatics: Analysis of Social Network Data Jagdish S. Gangolly Department of Informatics College of Computing & Information State University of New York at Albany Lecture 1B (Graphs)
Vector-Based GIS Data Processing. Chapter 6
 Vector-Based GIS Data Processing Chapter 6 Vector Data Model Feature Classes points lines polygons Layers limited to one class of data Figure p. 186 Vector Data Model Shapefiles ArcView non-topological
Vector-Based GIS Data Processing Chapter 6 Vector Data Model Feature Classes points lines polygons Layers limited to one class of data Figure p. 186 Vector Data Model Shapefiles ArcView non-topological
ECE332, Week 8. Topics. October 15, Exceptions. Hardware Interrupts Software exceptions
 ECE332, Week 8 October 15, 2007 1 Topics Exceptions Hardware Interrupts Software exceptions Unimplemented instructions Software traps Other exceptions 2 1 Exception An exception is a transfer of control
ECE332, Week 8 October 15, 2007 1 Topics Exceptions Hardware Interrupts Software exceptions Unimplemented instructions Software traps Other exceptions 2 1 Exception An exception is a transfer of control
LECTURE 6: INTERIOR POINT METHOD. 1. Motivation 2. Basic concepts 3. Primal affine scaling algorithm 4. Dual affine scaling algorithm
 LECTURE 6: INTERIOR POINT METHOD 1. Motivation 2. Basic concepts 3. Primal affine scaling algorithm 4. Dual affine scaling algorithm Motivation Simplex method works well in general, but suffers from exponential-time
LECTURE 6: INTERIOR POINT METHOD 1. Motivation 2. Basic concepts 3. Primal affine scaling algorithm 4. Dual affine scaling algorithm Motivation Simplex method works well in general, but suffers from exponential-time
2.5.1: Reforms in Continuous Internal Evaluation (CIE) System at the Institutional Level
 D Y Patil Institute of Engineering and Technology, Ambi, Pune Address:Sr.No.124 & 126, A/p- Ambi, Tal-Maval, MIDC Road, TalegaonDabhade, Pune-410506, Maharashtra, India Tel: 02114306229, E-mail : info@dyptc.edu.in
D Y Patil Institute of Engineering and Technology, Ambi, Pune Address:Sr.No.124 & 126, A/p- Ambi, Tal-Maval, MIDC Road, TalegaonDabhade, Pune-410506, Maharashtra, India Tel: 02114306229, E-mail : info@dyptc.edu.in
Design Patterns. Gunnar Gotshalks A4-1
 Design Patterns A4-1 On Design Patterns A design pattern systematically names, explains and evaluates an important and recurring design problem and its solution Good designers know not to solve every problem
Design Patterns A4-1 On Design Patterns A design pattern systematically names, explains and evaluates an important and recurring design problem and its solution Good designers know not to solve every problem
Outline. Linear Programming (LP): Principles and Concepts. Need for Optimization to Get the Best Solution. Linear Programming
 Outline Linear Programming (LP): Principles and oncepts Motivation enoît hachuat Key Geometric Interpretation McMaster University Department of hemical Engineering 3 LP Standard Form
Outline Linear Programming (LP): Principles and oncepts Motivation enoît hachuat Key Geometric Interpretation McMaster University Department of hemical Engineering 3 LP Standard Form
Chapter 4 Concepts from Geometry
 Chapter 4 Concepts from Geometry An Introduction to Optimization Spring, 2014 Wei-Ta Chu 1 Line Segments The line segment between two points and in R n is the set of points on the straight line joining
Chapter 4 Concepts from Geometry An Introduction to Optimization Spring, 2014 Wei-Ta Chu 1 Line Segments The line segment between two points and in R n is the set of points on the straight line joining
Randomized incremental construction. Trapezoidal decomposition: Special sampling idea: Sample all except one item
 Randomized incremental construction Special sampling idea: Sample all except one item hope final addition makes small or no change Method: process items in order average case analysis randomize order to
Randomized incremental construction Special sampling idea: Sample all except one item hope final addition makes small or no change Method: process items in order average case analysis randomize order to
Boolean Component. Chapter 1. Boolean Operations
 Chapter 1. Boolean Component Component: The Boolean Component (BOOL), in the bool directory, performs Boolean operations on the model topology of bodies, first finding the intersections between bodies,
Chapter 1. Boolean Component Component: The Boolean Component (BOOL), in the bool directory, performs Boolean operations on the model topology of bodies, first finding the intersections between bodies,
Chapter 9. Software Testing
 Chapter 9. Software Testing Table of Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction to software testing... 1 The testers... 2 The developers... 2 An independent testing team... 2 The customer... 2 Principles of
Chapter 9. Software Testing Table of Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction to software testing... 1 The testers... 2 The developers... 2 An independent testing team... 2 The customer... 2 Principles of
Farming Example. Lecture 22. Solving a Linear Program. withthe Simplex Algorithm and with Excel s Solver
 Lecture 22 Solving a Linear Program withthe Simplex Algorithm and with Excel s Solver m j winter, 2 Farming Example Constraints: acreage: x + y < money: x + 7y < 6 time: x + y < 3 y x + y = B (, 8.7) x
Lecture 22 Solving a Linear Program withthe Simplex Algorithm and with Excel s Solver m j winter, 2 Farming Example Constraints: acreage: x + y < money: x + 7y < 6 time: x + y < 3 y x + y = B (, 8.7) x
morphology on binary images
 morphology on binary images Ole-Johan Skrede 10.05.2017 INF2310 - Digital Image Processing Department of Informatics The Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences University of Oslo After original slides
morphology on binary images Ole-Johan Skrede 10.05.2017 INF2310 - Digital Image Processing Department of Informatics The Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences University of Oslo After original slides
On the Computational Complexity of Dynamic Graph Problems
 On the Computational Complexity of Dynamic Graph Problems G. RAMALINGAM and THOMAS REPS University of Wisconsin Madison A common way to evaluate the time complexity of an algorithm is to use asymptotic
On the Computational Complexity of Dynamic Graph Problems G. RAMALINGAM and THOMAS REPS University of Wisconsin Madison A common way to evaluate the time complexity of an algorithm is to use asymptotic
Lecture 4 Introduction to Data Flow Analysis
 Lecture 4 Introduction to Data Flow Analysis I. Structure of data flow analysis II. Example 1: Reaching definition analysis III. Example 2: Liveness analysis IV. Generalization What is Data Flow Analysis?
Lecture 4 Introduction to Data Flow Analysis I. Structure of data flow analysis II. Example 1: Reaching definition analysis III. Example 2: Liveness analysis IV. Generalization What is Data Flow Analysis?
Motivation for B-Trees
 1 Motivation for Assume that we use an AVL tree to store about 20 million records We end up with a very deep binary tree with lots of different disk accesses; log2 20,000,000 is about 24, so this takes
1 Motivation for Assume that we use an AVL tree to store about 20 million records We end up with a very deep binary tree with lots of different disk accesses; log2 20,000,000 is about 24, so this takes
Approximating Fault-Tolerant Steiner Subgraphs in Heterogeneous Wireless Networks
 Approximating Fault-Tolerant Steiner Subgraphs in Heterogeneous Wireless Networks Ambreen Shahnaz and Thomas Erlebach Department of Computer Science University of Leicester University Road, Leicester LE1
Approximating Fault-Tolerant Steiner Subgraphs in Heterogeneous Wireless Networks Ambreen Shahnaz and Thomas Erlebach Department of Computer Science University of Leicester University Road, Leicester LE1
Graph Databases. Graph Databases. May 2015 Alberto Abelló & Oscar Romero
 Graph Databases 1 Knowledge Objectives 1. Describe what a graph database is 2. Explain the basics of the graph data model 3. Enumerate the best use cases for graph databases 4. Name two pros and cons of
Graph Databases 1 Knowledge Objectives 1. Describe what a graph database is 2. Explain the basics of the graph data model 3. Enumerate the best use cases for graph databases 4. Name two pros and cons of
Setting the stage... Key Design Issues. Main purpose - Manage software system complexity by improving software quality factors
 Setting the stage... Dr. Radu Marinescu 1 1946 Key Design Issues Main purpose - Manage software system complexity by...... improving software quality factors... facilitating systematic reuse Dr. Radu Marinescu
Setting the stage... Dr. Radu Marinescu 1 1946 Key Design Issues Main purpose - Manage software system complexity by...... improving software quality factors... facilitating systematic reuse Dr. Radu Marinescu
Systems of Equations and Inequalities. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 5 Systems of Equations and Inequalities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 5.5 Systems of Inequalities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphing an Inequality Systems
5 Systems of Equations and Inequalities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 5.5 Systems of Inequalities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphing an Inequality Systems
ECE276B: Planning & Learning in Robotics Lecture 5: Configuration Space
 ECE276B: Planning & Learning in Robotics Lecture 5: Configuration Space Lecturer: Nikolay Atanasov: natanasov@ucsd.edu Teaching Assistants: Tianyu Wang: tiw161@eng.ucsd.edu Yongxi Lu: yol070@eng.ucsd.edu
ECE276B: Planning & Learning in Robotics Lecture 5: Configuration Space Lecturer: Nikolay Atanasov: natanasov@ucsd.edu Teaching Assistants: Tianyu Wang: tiw161@eng.ucsd.edu Yongxi Lu: yol070@eng.ucsd.edu
6.896 Topics in Algorithmic Game Theory March 1, Lecture 8
 6.896 Topics in Algorithmic Game Theory March 1, 2010 Lecture 8 Lecturer: Constantinos Daskalakis Scribe: Alan Deckelbaum, Anthony Kim NOTE: The content of these notes has not been formally reviewed by
6.896 Topics in Algorithmic Game Theory March 1, 2010 Lecture 8 Lecturer: Constantinos Daskalakis Scribe: Alan Deckelbaum, Anthony Kim NOTE: The content of these notes has not been formally reviewed by
Exemples of LCP. (b,3) (c,3) (d,4) 38 d
 This layout has been presented by G. Even and S. Even [ 00], and it is based on the notion of Layered Cross Product Def. A layered graph of l+1 layers G=(V 0, V 1,, V l, E) consists of l+1 layers of nodes;
This layout has been presented by G. Even and S. Even [ 00], and it is based on the notion of Layered Cross Product Def. A layered graph of l+1 layers G=(V 0, V 1,, V l, E) consists of l+1 layers of nodes;
Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory
 Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory Chapter 8: Topics in Graph Theory Section 8.1: Examples {1,2,3} Section 8.2: Examples {1,2,4} Section 8.3: Examples {1} 8.1 Graphs Graph A graph G consists of a finite
Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory Chapter 8: Topics in Graph Theory Section 8.1: Examples {1,2,3} Section 8.2: Examples {1,2,4} Section 8.3: Examples {1} 8.1 Graphs Graph A graph G consists of a finite
Graphs and Network Flows IE411. Lecture 21. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Graphs and Network Flows IE411 Lecture 21 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE411 Lecture 21 1 Combinatorial Optimization and Network Flows In general, most combinatorial optimization and integer programming problems are
Graphs and Network Flows IE411 Lecture 21 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE411 Lecture 21 1 Combinatorial Optimization and Network Flows In general, most combinatorial optimization and integer programming problems are
Using Machine Learning to Optimize Storage Systems
 Using Machine Learning to Optimize Storage Systems Dr. Kiran Gunnam 1 Outline 1. Overview 2. Building Flash Models using Logistic Regression. 3. Storage Object classification 4. Storage Allocation recommendation
Using Machine Learning to Optimize Storage Systems Dr. Kiran Gunnam 1 Outline 1. Overview 2. Building Flash Models using Logistic Regression. 3. Storage Object classification 4. Storage Allocation recommendation
Chapter 3 Linear Programming: A Geometric Approach
 Chapter 3 Linear Programming: A Geometric Approach Section 3.1 Graphing Systems of Linear Inequalities in Two Variables y 4x + 3y = 12 4 3 4 x 3 y 12 x y 0 x y = 0 2 1 P(, ) 12 12 7 7 1 1 2 3 x We ve seen
Chapter 3 Linear Programming: A Geometric Approach Section 3.1 Graphing Systems of Linear Inequalities in Two Variables y 4x + 3y = 12 4 3 4 x 3 y 12 x y 0 x y = 0 2 1 P(, ) 12 12 7 7 1 1 2 3 x We ve seen
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A process has a: 1) A) pronoun label B) noun phrase label C) verb phrase label D) adjective
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A process has a: 1) A) pronoun label B) noun phrase label C) verb phrase label D) adjective
Software Engineering with Objects and Components Open Issues and Course Summary
 Software Engineering with Objects and Components Open Issues and Course Summary Massimo Felici Software Engineering with Objects and Components Software development process Lifecycle models and main stages
Software Engineering with Objects and Components Open Issues and Course Summary Massimo Felici Software Engineering with Objects and Components Software development process Lifecycle models and main stages
Motivation. CS389L: Automated Logical Reasoning. Lecture 5: Binary Decision Diagrams. Historical Context. Binary Decision Trees
 Motivation CS389L: Automated Logical Reasoning Lecture 5: Binary Decision Diagrams Işıl Dillig Previous lectures: How to determine satisfiability of propositional formulas Sometimes need to efficiently
Motivation CS389L: Automated Logical Reasoning Lecture 5: Binary Decision Diagrams Işıl Dillig Previous lectures: How to determine satisfiability of propositional formulas Sometimes need to efficiently
Mathematics for Business and Economics - I. Chapter7 Linear Inequality Systems and Linear Programming (Lecture11)
 Mathematics for Business and Economics - I Chapter7 Linear Inequality Systems and Linear Programming (Lecture11) A linear inequality in two variables is an inequality that can be written in the form Ax
Mathematics for Business and Economics - I Chapter7 Linear Inequality Systems and Linear Programming (Lecture11) A linear inequality in two variables is an inequality that can be written in the form Ax
Testing. Unit, integration, regression, validation, system. OO Testing techniques Application of traditional techniques to OO software
 Testing Basic ideas and principles Traditional testing strategies Unit, integration, regression, validation, system OO Testing techniques Application of traditional techniques to OO software Testing-11,
Testing Basic ideas and principles Traditional testing strategies Unit, integration, regression, validation, system OO Testing techniques Application of traditional techniques to OO software Testing-11,
Compiler Optimization and Code Generation
 Compiler Optimization and Code Generation Professor: Sc.D., Professor Vazgen Melikyan 1 Course Overview Introduction: Overview of Optimizations 1 lecture Intermediate-Code Generation 2 lectures Machine-Independent
Compiler Optimization and Code Generation Professor: Sc.D., Professor Vazgen Melikyan 1 Course Overview Introduction: Overview of Optimizations 1 lecture Intermediate-Code Generation 2 lectures Machine-Independent
Simple Silhouettes for Complex Surfaces
 Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing(2003) L. Kobbelt, P. Schröder, H. Hoppe (Editors) Simple Silhouettes for Complex Surfaces D. Kirsanov, P. V. Sander, and S. J. Gortler Harvard University Abstract
Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing(2003) L. Kobbelt, P. Schröder, H. Hoppe (Editors) Simple Silhouettes for Complex Surfaces D. Kirsanov, P. V. Sander, and S. J. Gortler Harvard University Abstract
Path Testing + Coverage. Chapter 8
 Path Testing + Coverage Chapter 8 Structural Testing n Also known as glass/white/open box testing n A software testing technique whereby explicit knowledge of the internal workings of the item being tested
Path Testing + Coverage Chapter 8 Structural Testing n Also known as glass/white/open box testing n A software testing technique whereby explicit knowledge of the internal workings of the item being tested
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Scan Converting Polygons and Lines
 COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Scan Converting Polygons and Lines Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Scan conversion Scan-line algorithm Edge coherence
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Scan Converting Polygons and Lines Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Scan conversion Scan-line algorithm Edge coherence
Core Membership Computation for Succinct Representations of Coalitional Games
 Core Membership Computation for Succinct Representations of Coalitional Games Xi Alice Gao May 11, 2009 Abstract In this paper, I compare and contrast two formal results on the computational complexity
Core Membership Computation for Succinct Representations of Coalitional Games Xi Alice Gao May 11, 2009 Abstract In this paper, I compare and contrast two formal results on the computational complexity
Course Outline. Video Game AI: Lecture 7 Heuristics & Smoothing. Finding the best location out of several. Variable size units / special movement?
 Course Outline Video Game AI: Lecture 7 Heuristics & Smoothing Nathan Sturtevant COMP 3705 http://aigamedev.com/ now has free interviews! Miscellaneous details Heuristics How better heuristics can be built
Course Outline Video Game AI: Lecture 7 Heuristics & Smoothing Nathan Sturtevant COMP 3705 http://aigamedev.com/ now has free interviews! Miscellaneous details Heuristics How better heuristics can be built
1 Digraphs. Definition 1
 1 Digraphs Definition 1 Adigraphordirected graphgisatriplecomprisedofavertex set V(G), edge set E(G), and a function assigning each edge an ordered pair of vertices (tail, head); these vertices together
1 Digraphs Definition 1 Adigraphordirected graphgisatriplecomprisedofavertex set V(G), edge set E(G), and a function assigning each edge an ordered pair of vertices (tail, head); these vertices together
The Cyclic Cycle Complex of a Surface
 The Cyclic Cycle Complex of a Surface Allen Hatcher A recent paper [BBM] by Bestvina, Bux, and Margalit contains a construction of a cell complex that gives a combinatorial model for the collection of
The Cyclic Cycle Complex of a Surface Allen Hatcher A recent paper [BBM] by Bestvina, Bux, and Margalit contains a construction of a cell complex that gives a combinatorial model for the collection of
 Orientable Closed/ Boundary-less 2-manifold This wireframe study of a chalice was painted by the Italian Renaissance artist Paolo Uccello around 1460. Today 3D polygonal meshes are the dominant representation
Orientable Closed/ Boundary-less 2-manifold This wireframe study of a chalice was painted by the Italian Renaissance artist Paolo Uccello around 1460. Today 3D polygonal meshes are the dominant representation
4B Summary of some Key SW Testing Concepts 1
 4B Summary of some Key SW Testing Concepts 1 Note: Section 4A presented a particular, specific method for developing (system or requirements level) tests cases from UML use cases. Section 4B provides a
4B Summary of some Key SW Testing Concepts 1 Note: Section 4A presented a particular, specific method for developing (system or requirements level) tests cases from UML use cases. Section 4B provides a
This blog addresses the question: how do we determine the intersection of two circles in the Cartesian plane?
 Intersecting Circles This blog addresses the question: how do we determine the intersection of two circles in the Cartesian plane? This is a problem that a programmer might have to solve, for example,
Intersecting Circles This blog addresses the question: how do we determine the intersection of two circles in the Cartesian plane? This is a problem that a programmer might have to solve, for example,
Road Map Methods. Including material from Howie Choset / G.D. Hager S. Leonard
 Road Map Methods Including material from Howie Choset The Basic Idea Capture the connectivity of Q free by a graph or network of paths. 16-735, Howie Choset, with significant copying from who loosely based
Road Map Methods Including material from Howie Choset The Basic Idea Capture the connectivity of Q free by a graph or network of paths. 16-735, Howie Choset, with significant copying from who loosely based
Algorithm That Mimics Human Perceptual Grouping of Dot Patterns
 Algorithm That Mimics Human Perceptual Grouping of Dot Patterns G. Papari and N. Petkov Institute of Mathematics and Computing Science, University of Groningen, P.O.Box 800, 9700 AV Groningen, The Netherlands
Algorithm That Mimics Human Perceptual Grouping of Dot Patterns G. Papari and N. Petkov Institute of Mathematics and Computing Science, University of Groningen, P.O.Box 800, 9700 AV Groningen, The Netherlands
γ 2 γ 3 γ 1 R 2 (b) a bounded Yin set (a) an unbounded Yin set
 γ 1 γ 3 γ γ 3 γ γ 1 R (a) an unbounded Yin set (b) a bounded Yin set Fig..1: Jordan curve representation of a connected Yin set M R. A shaded region represents M and the dashed curves its boundary M that
γ 1 γ 3 γ γ 3 γ γ 1 R (a) an unbounded Yin set (b) a bounded Yin set Fig..1: Jordan curve representation of a connected Yin set M R. A shaded region represents M and the dashed curves its boundary M that
Techno Expert Solutions An institute for specialized studies! Introduction to Advance QTP course Content
 Introduction to Advance QTP course Content NTRODUCTION TO AUTOMATION Automation Testing Benefits of Automation Testing Automation Testing Vs Manual Testing Automation Test Tools Tool selection criteria
Introduction to Advance QTP course Content NTRODUCTION TO AUTOMATION Automation Testing Benefits of Automation Testing Automation Testing Vs Manual Testing Automation Test Tools Tool selection criteria
Lecture 8: Flow Analysis
 Lecture 8: Flow Analysis Prof. Shervin Shirmohammadi SITE, University of Ottawa Prof. Shervin Shirmohammadi CEG 4185 8-1 Network Analysis Requirement Analysis Gather Requirements Develop Service Metrics
Lecture 8: Flow Analysis Prof. Shervin Shirmohammadi SITE, University of Ottawa Prof. Shervin Shirmohammadi CEG 4185 8-1 Network Analysis Requirement Analysis Gather Requirements Develop Service Metrics
Recognizing Interval Bigraphs by Forbidden Patterns
 Recognizing Interval Bigraphs by Forbidden Patterns Arash Rafiey Simon Fraser University, Vancouver, Canada, and Indiana State University, IN, USA arashr@sfu.ca, arash.rafiey@indstate.edu Abstract Let
Recognizing Interval Bigraphs by Forbidden Patterns Arash Rafiey Simon Fraser University, Vancouver, Canada, and Indiana State University, IN, USA arashr@sfu.ca, arash.rafiey@indstate.edu Abstract Let
Solid Modeling. Michael Kazhdan ( /657) HB , FvDFH 12.1, 12.2, 12.6, 12.7 Marching Cubes, Lorensen et al.
 Solid Modeling Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB 10.15 10.17, 10.22 FvDFH 12.1, 12.2, 12.6, 12.7 Marching Cubes, Lorensen et al. 1987 Announcement OpenGL review session: When: Today @ 9:00 PM Where: Malone
Solid Modeling Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB 10.15 10.17, 10.22 FvDFH 12.1, 12.2, 12.6, 12.7 Marching Cubes, Lorensen et al. 1987 Announcement OpenGL review session: When: Today @ 9:00 PM Where: Malone
Youki Kadobayashi NAIST
 Information Network 1 Routing (1) Image: Part of the entire Internet topology based on CAIDA dataset, using NAIST Internet viewer Youki Kadobayashi NAIST 1 The Routing Problem! How do I get from source
Information Network 1 Routing (1) Image: Part of the entire Internet topology based on CAIDA dataset, using NAIST Internet viewer Youki Kadobayashi NAIST 1 The Routing Problem! How do I get from source
QUIZ #5 - Solutions (5pts each)
 CS 435 Spring 2014 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Department of Computer Science Name QUIZ #5 - Solutions (5pts each) 1. The best reason for using Independent software test teams is that a. software developers do
CS 435 Spring 2014 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Department of Computer Science Name QUIZ #5 - Solutions (5pts each) 1. The best reason for using Independent software test teams is that a. software developers do
Rigidity, connectivity and graph decompositions
 First Prev Next Last Rigidity, connectivity and graph decompositions Brigitte Servatius Herman Servatius Worcester Polytechnic Institute Page 1 of 100 First Prev Next Last Page 2 of 100 We say that a framework
First Prev Next Last Rigidity, connectivity and graph decompositions Brigitte Servatius Herman Servatius Worcester Polytechnic Institute Page 1 of 100 First Prev Next Last Page 2 of 100 We say that a framework
THE LEAFAGE OF A CHORDAL GRAPH
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 18 (1998 ) 23 48 THE LEAFAGE OF A CHORDAL GRAPH In-Jen Lin National Ocean University, Taipei, Taiwan Terry A. McKee 1 Wright State University, Dayton, OH 45435-0001,
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 18 (1998 ) 23 48 THE LEAFAGE OF A CHORDAL GRAPH In-Jen Lin National Ocean University, Taipei, Taiwan Terry A. McKee 1 Wright State University, Dayton, OH 45435-0001,
TDDD04 Software Testing
 TDDD04 Software Testing Lecture Notes 7 March June 2010 Mohsen Torabzadeh-Tari (presenter), (originator) Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University, Sweden Outline of the Lecture
TDDD04 Software Testing Lecture Notes 7 March June 2010 Mohsen Torabzadeh-Tari (presenter), (originator) Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University, Sweden Outline of the Lecture
Introduction to Graphs. common/notes/ppt/
 Introduction to Graphs http://people.cs.clemson.edu/~pargas/courses/cs212/ common/notes/ppt/ Introduction Graphs are a generalization of trees Nodes or verticies Edges or arcs Two kinds of graphs irected
Introduction to Graphs http://people.cs.clemson.edu/~pargas/courses/cs212/ common/notes/ppt/ Introduction Graphs are a generalization of trees Nodes or verticies Edges or arcs Two kinds of graphs irected
AO IBM i Advanced Modernization Workshop Curriculum
 AO IBM i Advanced Modernization Workshop Curriculum This workshop is intended to provide the IBM i professional, specifically the RPG programmer, with an overview of the newest capabilities which have
AO IBM i Advanced Modernization Workshop Curriculum This workshop is intended to provide the IBM i professional, specifically the RPG programmer, with an overview of the newest capabilities which have
CS 5630/6630 Scientific Visualization. Volume Rendering III: Unstructured Grid Techniques
 CS 5630/6630 Scientific Visualization Volume Rendering III: Unstructured Grid Techniques Unstructured Grids Image-space techniques Ray-Casting Object-space techniques Projected Tetrahedra Hybrid Incremental
CS 5630/6630 Scientific Visualization Volume Rendering III: Unstructured Grid Techniques Unstructured Grids Image-space techniques Ray-Casting Object-space techniques Projected Tetrahedra Hybrid Incremental
Introduction to Graphs. CS2110, Spring 2011 Cornell University
 Introduction to Graphs CS2110, Spring 2011 Cornell University A graph is a data structure for representing relationships. Each graph is a set of nodes connected by edges. Synonym Graph Hostile Slick Icy
Introduction to Graphs CS2110, Spring 2011 Cornell University A graph is a data structure for representing relationships. Each graph is a set of nodes connected by edges. Synonym Graph Hostile Slick Icy
Graph Theory for Modelling a Survey Questionnaire Pierpaolo Massoli, ISTAT via Adolfo Ravà 150, Roma, Italy
 Graph Theory for Modelling a Survey Questionnaire Pierpaolo Massoli, ISTAT via Adolfo Ravà 150, 00142 Roma, Italy e-mail: pimassol@istat.it 1. Introduction Questions can be usually asked following specific
Graph Theory for Modelling a Survey Questionnaire Pierpaolo Massoli, ISTAT via Adolfo Ravà 150, 00142 Roma, Italy e-mail: pimassol@istat.it 1. Introduction Questions can be usually asked following specific
A subquery is a nested query inserted inside a large query Generally occurs with select, from, where Also known as inner query or inner select,
 Sub queries A subquery is a nested query inserted inside a large query Generally occurs with select, from, where Also known as inner query or inner select, Result of the inner query is passed to the main
Sub queries A subquery is a nested query inserted inside a large query Generally occurs with select, from, where Also known as inner query or inner select, Result of the inner query is passed to the main
Paths. Path is a sequence of edges that begins at a vertex of a graph and travels from vertex to vertex along edges of the graph.
 Paths Path is a sequence of edges that begins at a vertex of a graph and travels from vertex to vertex along edges of the graph. Formal Definition of a Path (Undirected) Let n be a nonnegative integer
Paths Path is a sequence of edges that begins at a vertex of a graph and travels from vertex to vertex along edges of the graph. Formal Definition of a Path (Undirected) Let n be a nonnegative integer
Chapter 11. Topological Spaces: General Properties
 11.1. Open Sets, Closed Sets, Bases, and Subbases 1 Chapter 11. Topological Spaces: General Properties Section 11.1. Open Sets, Closed Sets, Bases, and Subbases Note. In this section, we define a topological
11.1. Open Sets, Closed Sets, Bases, and Subbases 1 Chapter 11. Topological Spaces: General Properties Section 11.1. Open Sets, Closed Sets, Bases, and Subbases Note. In this section, we define a topological
Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees
 Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo
Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo
DISCUSSION 5min 2/24/2009. DTD to relational schema. Inlining. Basic inlining
 XML DTD Relational Databases for Querying XML Documents: Limitations and Opportunities Semi-structured SGML Emerging as a standard E.g. john 604xxxxxxxx 778xxxxxxxx
XML DTD Relational Databases for Querying XML Documents: Limitations and Opportunities Semi-structured SGML Emerging as a standard E.g. john 604xxxxxxxx 778xxxxxxxx
Auto-calibration. Computer Vision II CSE 252B
 Auto-calibration Computer Vision II CSE 252B 2D Affine Rectification Solve for planar projective transformation that maps line (back) to line at infinity Solve as a Householder matrix Euclidean Projective
Auto-calibration Computer Vision II CSE 252B 2D Affine Rectification Solve for planar projective transformation that maps line (back) to line at infinity Solve as a Householder matrix Euclidean Projective
Review for Mastery Using Graphs and Tables to Solve Linear Systems
 3-1 Using Graphs and Tables to Solve Linear Systems A linear system of equations is a set of two or more linear equations. To solve a linear system, find all the ordered pairs (x, y) that make both equations
3-1 Using Graphs and Tables to Solve Linear Systems A linear system of equations is a set of two or more linear equations. To solve a linear system, find all the ordered pairs (x, y) that make both equations
Chapter 14. Graphs Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1
 Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
1 Trajectories. Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733. Figure 1: Robot control system.
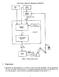 Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
BETA. CAE data and process management. ANSA Data Management ANSA Task Manager. CAE Systems SA
 BETA CAE Systems SA CAE data and process management ANSA Data Management ANSA Task Manager 28 June 2010 Overview 1. Motivation and objectives 2. ANSA Data Management for CAE data organization 3. Assembly
BETA CAE Systems SA CAE data and process management ANSA Data Management ANSA Task Manager 28 June 2010 Overview 1. Motivation and objectives 2. ANSA Data Management for CAE data organization 3. Assembly
Domain Driven Design IS. An architectural methodology for evolving a software system that closely aligns to business requirements
 Domain Driven Design IS An architectural methodology for evolving a software system that closely aligns to business requirements Domain Driven Design IS Domain First Focus on the Object Model Focus on
Domain Driven Design IS An architectural methodology for evolving a software system that closely aligns to business requirements Domain Driven Design IS Domain First Focus on the Object Model Focus on
Database Management Systems
 Database Management Systems Distributed Databases Doug Shook What does it mean to be distributed? Multiple nodes connected by a network Data on the nodes is logically related The nodes do not need to be
Database Management Systems Distributed Databases Doug Shook What does it mean to be distributed? Multiple nodes connected by a network Data on the nodes is logically related The nodes do not need to be
Design Pattern Detection
 Design Pattern Detection Design Patterns EECS 6431 Design Pattern Detection 2/22 A design pattern systematically names, explains and evaluates an important and recurring design problem and its solution
Design Pattern Detection Design Patterns EECS 6431 Design Pattern Detection 2/22 A design pattern systematically names, explains and evaluates an important and recurring design problem and its solution
Introduction to NoSQL Databases
 Introduction to NoSQL Databases Roman Kern KTI, TU Graz 2017-10-16 Roman Kern (KTI, TU Graz) Dbase2 2017-10-16 1 / 31 Introduction Intro Why NoSQL? Roman Kern (KTI, TU Graz) Dbase2 2017-10-16 2 / 31 Introduction
Introduction to NoSQL Databases Roman Kern KTI, TU Graz 2017-10-16 Roman Kern (KTI, TU Graz) Dbase2 2017-10-16 1 / 31 Introduction Intro Why NoSQL? Roman Kern (KTI, TU Graz) Dbase2 2017-10-16 2 / 31 Introduction
Developer s Guide to Azure RemoteApp Hybrid Collection Deployment
 Developer s Guide to Azure RemoteApp Hybrid Collection Deployment ABSTRACT I. II. ABSTRACT AZURE REMOTEAPP 1. What is Azure RemoteApp? 2. How It Works Behind the Scene 3. Advantages of Azure RemoteApp
Developer s Guide to Azure RemoteApp Hybrid Collection Deployment ABSTRACT I. II. ABSTRACT AZURE REMOTEAPP 1. What is Azure RemoteApp? 2. How It Works Behind the Scene 3. Advantages of Azure RemoteApp
AOSA - Betriebssystemkomponenten und der Aspektmoderatoransatz
 AOSA - Betriebssystemkomponenten und der Aspektmoderatoransatz Results obtained by researchers in the aspect-oriented programming are promoting the aim to export these ideas to whole software development
AOSA - Betriebssystemkomponenten und der Aspektmoderatoransatz Results obtained by researchers in the aspect-oriented programming are promoting the aim to export these ideas to whole software development
Resiliency at Scale in the Distributed Storage Cloud
 Resiliency at Scale in the Distributed Storage Cloud Alma Riska Advanced Storage Division EMC Corporation In collaboration with many at Cloud Infrastructure Group Outline Wi topic but this talk will focus
Resiliency at Scale in the Distributed Storage Cloud Alma Riska Advanced Storage Division EMC Corporation In collaboration with many at Cloud Infrastructure Group Outline Wi topic but this talk will focus
Testing Theory. Agenda - What will you learn today? A Software Life-cycle Model Which part will we talk about today? Theory Lecture Plan
 heory Lecture Plan 2 esting heory Lecture 8 Software Engineering DDC88/DDC93 autumn 28 Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University, Sweden L - Course Introduction and Overview L2
heory Lecture Plan 2 esting heory Lecture 8 Software Engineering DDC88/DDC93 autumn 28 Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University, Sweden L - Course Introduction and Overview L2
Graphs. A graph is a data structure consisting of nodes (or vertices) and edges. An edge is a connection between two nodes
 Graphs Graphs A graph is a data structure consisting of nodes (or vertices) and edges An edge is a connection between two nodes A D B E C Nodes: A, B, C, D, E Edges: (A, B), (A, D), (D, E), (E, C) Nodes
Graphs Graphs A graph is a data structure consisting of nodes (or vertices) and edges An edge is a connection between two nodes A D B E C Nodes: A, B, C, D, E Edges: (A, B), (A, D), (D, E), (E, C) Nodes
V10 Metabolic networks - Graph connectivity
 V10 Metabolic networks - Graph connectivity Graph connectivity is related to analyzing biological networks for - finding cliques - edge betweenness - modular decomposition that have been or will be covered
V10 Metabolic networks - Graph connectivity Graph connectivity is related to analyzing biological networks for - finding cliques - edge betweenness - modular decomposition that have been or will be covered
Chapter 15. Object-Oriented Testing. Software Testing: A Craftsman s Approach, 4 th Edition. Chapter 15 O-O Testing
 Chapter 15 Object-Oriented Testing Software Testing: A Craftsman s Approach, 3 rd Edition Object- Issues in Testing Object-Oriented Software How is object-oriented (o-o) software different/special? Need
Chapter 15 Object-Oriented Testing Software Testing: A Craftsman s Approach, 3 rd Edition Object- Issues in Testing Object-Oriented Software How is object-oriented (o-o) software different/special? Need
arxiv: v5 [cs.dm] 9 May 2016
![arxiv: v5 [cs.dm] 9 May 2016 arxiv: v5 [cs.dm] 9 May 2016](/thumbs/94/122228531.jpg) Tree spanners of bounded degree graphs Ioannis Papoutsakis Kastelli Pediados, Heraklion, Crete, reece, 700 06 October 21, 2018 arxiv:1503.06822v5 [cs.dm] 9 May 2016 Abstract A tree t-spanner of a graph
Tree spanners of bounded degree graphs Ioannis Papoutsakis Kastelli Pediados, Heraklion, Crete, reece, 700 06 October 21, 2018 arxiv:1503.06822v5 [cs.dm] 9 May 2016 Abstract A tree t-spanner of a graph
RUNNING TIME ANALYSIS. Problem Solving with Computers-II
 RUNNING TIME ANALYSIS Problem Solving with Computers-II Performance questions 4 How efficient is a particular algorithm? CPU time usage (Running time complexity) Memory usage Disk usage Network usage Why
RUNNING TIME ANALYSIS Problem Solving with Computers-II Performance questions 4 How efficient is a particular algorithm? CPU time usage (Running time complexity) Memory usage Disk usage Network usage Why
Securing IoT-based Cyber-Physical Human Systems against Collaborative Attacks
 Securing IoT-based Cyber-Physical Human Systems against Collaborative Attacks Sathish A.P Kumar, Coastal Carolina University, Conway, SC, USA Bharat Bhargava and Ganapathy Mani Purdue University, West
Securing IoT-based Cyber-Physical Human Systems against Collaborative Attacks Sathish A.P Kumar, Coastal Carolina University, Conway, SC, USA Bharat Bhargava and Ganapathy Mani Purdue University, West
CSC 8301 Design and Analysis of Algorithms: Exhaustive Search
 CSC 8301 Design and Analysis of Algorithms: Exhaustive Search Professor Henry Carter Fall 2016 Recap Brute force is the use of iterative checking or solving a problem by its definition The straightforward
CSC 8301 Design and Analysis of Algorithms: Exhaustive Search Professor Henry Carter Fall 2016 Recap Brute force is the use of iterative checking or solving a problem by its definition The straightforward
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CS SOFTWARE ENGINEERING
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CS 6403 - SOFTWARE ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK TWO MARKS UNIT I SOFTWARE PROCESS AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT 1. What is software engineering? Software engineering
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CS 6403 - SOFTWARE ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK TWO MARKS UNIT I SOFTWARE PROCESS AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT 1. What is software engineering? Software engineering
Question Points Score TOTAL 50
 UCSD CSE 101 Section B00, Winter 2015 MIDTERM February 5, 2015 NAME: Student ID: Question Points Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 TOTAL 50 INSTRUCTIONS. Be clear and concise. Write your answers in the space
UCSD CSE 101 Section B00, Winter 2015 MIDTERM February 5, 2015 NAME: Student ID: Question Points Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 TOTAL 50 INSTRUCTIONS. Be clear and concise. Write your answers in the space
Lecture 4: Walks, Trails, Paths and Connectivity
 Lecture 4: Walks, Trails, Paths and Connectivity Rosa Orellana Math 38 April 6, 2015 Graph Decompositions Def: A decomposition of a graph is a list of subgraphs such that each edge appears in exactly one
Lecture 4: Walks, Trails, Paths and Connectivity Rosa Orellana Math 38 April 6, 2015 Graph Decompositions Def: A decomposition of a graph is a list of subgraphs such that each edge appears in exactly one
