18-642: Software Architecture & High Level Design
|
|
|
- Clyde Perry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 18-642: Software Architecture & High Level Design 9/27/2018 All the really important mistakes are made the first day. Eberhardt Rechtin, System Architecting 1
2 YOU ARE HERE Product Requirements SPECIFY PRODUCT SPECIFY SOFTWARE Software Requirements TRACEABILITY & VALIDATION Test Plan & Test Results Test Plan & Test Results ACCEPTANCE TEST SOFTWARE TEST Software Test Results Integration Test Results PRODUCT CREATE SW ARCHITECTURE Test Plan & Test Results INTEGRATION TEST High Level Design DESIGN MODULES Detailed Design Test Plan & Test Results UNIT TEST Source Code Unit Test Results IMPLEMENT 2
3 Architecture & High Level Design (HLD) Anti-Patterns: Skipping from requirements to code No picture that shows how all the components fit together Wedding cake layer diagram that omits interface information Elements of High Level Design Architecture: boxes, arrows, interfaces Arrows/interfaces show communication paths between components Recursive: one designer s system is another designer s component High Level Design (HLD) = architecture (nouns) + requirements (verbs) Sequence Diagrams (SDs) show interactions 3
4 Architecture: Boxes and Arrows Software architecture shows the big picture Boxes: software modules/objects Arrows: interfaces Box and arrow semantics well-defined Meaning of box/arrow depends on goal Components all on a single page Nesting of diagrams is OK Many different architecture diagrams are possible, such as: Software architecture (components and data flow types) Hardware architecture with software allocation Controls architecture showing hierarchical control Call graph showing run-time hierarchy 4
5 Sequence Diagram as HLD Notation SD construction: Each object has a time column extending downward Arcs are interactions between objects Each SD shows a scenario Top ovals are preconditions Middle ovals are side effects Bottom ovals are postconditions SD is a partial behavioral description for objects Generally, each object participates in multiple SDs; each SD only has some objects The set of all SDs forms the HLD for all objects in the system 5
6 StateChart to SD Relationship For each object in each SD: identify input & output arcs Detailed Design: design statechart that accounts for all SD behaviors Statechart Must Exhibit All Those Behaviors SD set specifies behaviors 6
7 Requirements Revisited: Levels of Abstraction Modes vs. States State: corresponds to internal state machine When in state S1 the system shall display current time Mode: user-visible change in operations When in stopwatch mode, pressing Button 1 shall do XYZ State-type descriptions in HLD should be modes Input & output behaviors can change depending upon mode GOOD: Pressing X in Mode Y displays Z» Mode Y tells you which sequence diagram applies NOT: Pressing X in state S1 changes state to S2» There is no point describing the detailed design this way 7
8 High Level Design Best Practices HLD should include: One or more architecture diagrams Defines all components & interfaces HW arch., SW arch., Network arch., Sequence Diagrams Both nominal and off-nominal interactions See soda machine for a fully worked example HLD must co-evolve with requirements Need both nouns + verbs to define a system! High Level Design pitfalls: Diagrams that leave out interactions Boxes and arrows don t have well defined meanings HLD that bleeds into detailed design information Should have separate Detailed Design per component /project/sodamachine/index.html 8
9 2011 Health Plan Flow Chart: What s wrong with this as an architecture diagram? e-democrats-health-plan.pdf 9
10 10
18-642: Integration Testing
 18-642: Integration Testing 9/27/2018 It's hard enough to find an error in your code when you're looking for it; it's even harder when you've assumed your code is error-free. Steve McConnell 1 https://goo.gl/pvdmhx
18-642: Integration Testing 9/27/2018 It's hard enough to find an error in your code when you're looking for it; it's even harder when you've assumed your code is error-free. Steve McConnell 1 https://goo.gl/pvdmhx
18-642: Software Development Processes
 18-642: Software Development Processes 9/6/2017 Coding Is Essentially 0% of Creating Software http://e.ubmelectronics.com/2013embeddedstudy/index.html 2 Old-School Waterfall Development Cycle Bugs SPECIFY
18-642: Software Development Processes 9/6/2017 Coding Is Essentially 0% of Creating Software http://e.ubmelectronics.com/2013embeddedstudy/index.html 2 Old-School Waterfall Development Cycle Bugs SPECIFY
Using The Graph Club 1.5
 Using The Graph Club 1.5 Opening The Graph Club Click on the button that reads Skip Introduction. What do you want to Play Screen? Double click on the Create Graphic 1 The Create Data Window Entering Data
Using The Graph Club 1.5 Opening The Graph Club Click on the button that reads Skip Introduction. What do you want to Play Screen? Double click on the Create Graphic 1 The Create Data Window Entering Data
Lecture 8 Requirements Engineering
 Lecture 8 Requirements Engineering Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte September 18, 2008 Lecture Overview
Lecture 8 Requirements Engineering Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte September 18, 2008 Lecture Overview
Activity 1.1.1: A Mysterious Death
 Activity 1.1.1: A Mysterious Death Part II: Processing a Crime Scene Concept Map Although every crime scene is unique, five basic tasks need to be completed in order to properly process a crime scene.
Activity 1.1.1: A Mysterious Death Part II: Processing a Crime Scene Concept Map Although every crime scene is unique, five basic tasks need to be completed in order to properly process a crime scene.
Lesson 11. W.C.Udwela Department of Mathematics & Computer Science
 Lesson 11 INTRODUCING UML W.C.Udwela Department of Mathematics & Computer Science Why we model? Central part of all the activities We build model to Communicate Visualize and control Better understand
Lesson 11 INTRODUCING UML W.C.Udwela Department of Mathematics & Computer Science Why we model? Central part of all the activities We build model to Communicate Visualize and control Better understand
CS352 Lecture - Data Models
 CS352 Lecture - Data Models Objectives: 1. To briefly introduce the entity-relationship model 2. To introduce the relational model. 3. To introduce relational algebra Last revised January 18, 2017 Materials:
CS352 Lecture - Data Models Objectives: 1. To briefly introduce the entity-relationship model 2. To introduce the relational model. 3. To introduce relational algebra Last revised January 18, 2017 Materials:
Static Conformance Checking of Runtime Architectures Tool Demonstration
 Static Conformance Checking of Runtime Architectures Tool Demonstration Marwan Abi-Antoun Jonathan Aldrich School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University The problem: architectural conformance Architects
Static Conformance Checking of Runtime Architectures Tool Demonstration Marwan Abi-Antoun Jonathan Aldrich School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University The problem: architectural conformance Architects
Lecture 26: Testing. Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall Dr. Jamie Payton
 Lecture 26: Testing Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte Dec. 9, 2008 Verification vs validation Verification:
Lecture 26: Testing Software Engineering ITCS 3155 Fall 2008 Dr. Jamie Payton Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte Dec. 9, 2008 Verification vs validation Verification:
Programming in C. main. Level 2. Level 2 Level 2. Level 3 Level 3
 Programming in C main Level 2 Level 2 Level 2 Level 3 Level 3 1 Programmer-Defined Functions Modularize with building blocks of programs Divide and Conquer Construct a program from smaller pieces or components
Programming in C main Level 2 Level 2 Level 2 Level 3 Level 3 1 Programmer-Defined Functions Modularize with building blocks of programs Divide and Conquer Construct a program from smaller pieces or components
Software Design Models, Tools & Processes. Lecture 2: Inception Phase Cecilia Mascolo
 Software Design Models, Tools & Processes Lecture 2: Inception Phase Cecilia Mascolo Inception Phase This is the phase when most of the system requirements are identified. Discover and reach agreement
Software Design Models, Tools & Processes Lecture 2: Inception Phase Cecilia Mascolo Inception Phase This is the phase when most of the system requirements are identified. Discover and reach agreement
Software Life-Cycle Models
 Software Life-Cycle Models CMPSC 487 Lecture 03 Topics: UML Class Diagram Rosenburg Chap 2. Domain Modeling A. UML: Unified Modeling Language UML is a general-purpose, developmental, modeling language
Software Life-Cycle Models CMPSC 487 Lecture 03 Topics: UML Class Diagram Rosenburg Chap 2. Domain Modeling A. UML: Unified Modeling Language UML is a general-purpose, developmental, modeling language
INTRODUCTION TO UNIFIED MODELING MODEL (UML) & DFD. Slides by: Shree Jaswal
 INTRODUCTION TO UNIFIED MODELING MODEL (UML) & DFD Slides by: Shree Jaswal What is UML? 2 It is a standard graphical language for modeling object oriented software. It was developed in mid 90 s by collaborative
INTRODUCTION TO UNIFIED MODELING MODEL (UML) & DFD Slides by: Shree Jaswal What is UML? 2 It is a standard graphical language for modeling object oriented software. It was developed in mid 90 s by collaborative
Software Architectures. Lecture 6 (part 1)
 Software Architectures Lecture 6 (part 1) 2 Roadmap of the course What is software architecture? Designing Software Architecture Requirements: quality attributes or qualities How to achieve requirements
Software Architectures Lecture 6 (part 1) 2 Roadmap of the course What is software architecture? Designing Software Architecture Requirements: quality attributes or qualities How to achieve requirements
Creating Universally Designed Word 2013 Documents - Quick Start Guide
 Creating Universally Designed Word 2013 Documents - Quick Start Guide Overview Creating accessible documents ones that work well with all sorts of technology can be a daunting task. The purpose of this
Creating Universally Designed Word 2013 Documents - Quick Start Guide Overview Creating accessible documents ones that work well with all sorts of technology can be a daunting task. The purpose of this
A Beginners Guide to UML Part II
 A Beginners Guide to UML Part II Dan Brown, Dunstan Thomas Consulting Summary In the first part of this article, I examined the origins and definition of the UML to provide a basic understanding of what
A Beginners Guide to UML Part II Dan Brown, Dunstan Thomas Consulting Summary In the first part of this article, I examined the origins and definition of the UML to provide a basic understanding of what
Fractions / 8 / / 10 1 ½ / 12
 Fractions / 8 / 60 / ½ / 0 / What is a fraction? Loosely speaking, a fraction is a quantity that cannot be represented by a whole number. Why do we need fractions? Consider the following scenario. Can
Fractions / 8 / 60 / ½ / 0 / What is a fraction? Loosely speaking, a fraction is a quantity that cannot be represented by a whole number. Why do we need fractions? Consider the following scenario. Can
Part 1 - Your First algorithm
 California State University, Sacramento College of Engineering and Computer Science Computer Science 10A: Accelerated Introduction to Programming Logic Spring 2017 Activity A Introduction to Flowgorithm
California State University, Sacramento College of Engineering and Computer Science Computer Science 10A: Accelerated Introduction to Programming Logic Spring 2017 Activity A Introduction to Flowgorithm
CSC148H Week 3. Sadia Sharmin. May 24, /20
 CSC148H Week 3 Sadia Sharmin May 24, 2017 1/20 Client vs. Developer I For the first couple of weeks, we have played the role of class designer I However, you are also often in the opposite role: when a
CSC148H Week 3 Sadia Sharmin May 24, 2017 1/20 Client vs. Developer I For the first couple of weeks, we have played the role of class designer I However, you are also often in the opposite role: when a
Creating a Brochure in Publisher
 Creating a Brochure in Publisher If you closed the Flyer, as indicated above, you will see the Microsoft Publisher Task Pane on the left side of your screen. Click the Brochures selection in the Publication
Creating a Brochure in Publisher If you closed the Flyer, as indicated above, you will see the Microsoft Publisher Task Pane on the left side of your screen. Click the Brochures selection in the Publication
AADL Graphical Editor Design
 AADL Graphical Editor Design Peter Feiler Software Engineering Institute phf@sei.cmu.edu Introduction An AADL specification is a set of component type and implementation declarations. They are organized
AADL Graphical Editor Design Peter Feiler Software Engineering Institute phf@sei.cmu.edu Introduction An AADL specification is a set of component type and implementation declarations. They are organized
course 3 Levels of Database Design CSCI 403 Database Management Mines Courses ERD Attributes Entities title 9/26/2018
 3 Levels of Database Design CSCI 403 Database Management 13 Database Modeling with Entity-Relationship Diagrams Conceptual (this lecture) Understand data entities & relationships between them Communication
3 Levels of Database Design CSCI 403 Database Management 13 Database Modeling with Entity-Relationship Diagrams Conceptual (this lecture) Understand data entities & relationships between them Communication
When the player powers up you will first see a CeeNee loading screen followed by the Orchid screen seen below.
 How to setup the CeeNee Orchid Player using a wired Ethernet connection? 1) Carefully insert the supplied SD card into the front of the CeeNee player. It will go in around a 1/2 inch and stop. 2) Connect
How to setup the CeeNee Orchid Player using a wired Ethernet connection? 1) Carefully insert the supplied SD card into the front of the CeeNee player. It will go in around a 1/2 inch and stop. 2) Connect
Chapter 4 Defining Classes I
 Chapter 4 Defining Classes I This chapter introduces the idea that students can create their own classes and therefore their own objects. Introduced is the idea of methods and instance variables as the
Chapter 4 Defining Classes I This chapter introduces the idea that students can create their own classes and therefore their own objects. Introduced is the idea of methods and instance variables as the
Unified Modeling Language (UML) and Modeling
 LECTURE-11 Unified Modeling Language (UML) and Modeling UML is a graphical notation useful for OO analysis and design Allows representing various aspects of the system Various notations are used to build
LECTURE-11 Unified Modeling Language (UML) and Modeling UML is a graphical notation useful for OO analysis and design Allows representing various aspects of the system Various notations are used to build
System Concepts and Architecture. Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Curt Clifton
 System Concepts and Architecture Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Curt Clifton Data Model A set of concepts to describe Database structure Basic operations on the data Categories of Data Models Conceptual
System Concepts and Architecture Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Curt Clifton Data Model A set of concepts to describe Database structure Basic operations on the data Categories of Data Models Conceptual
Shared Variables and Interference
 Solved Shared Variables and Interference CS 536: Science of Programming, Fall 2018 A. Why Parallel programs can coordinate their work using shared variables, but it s important for threads to not interfere
Solved Shared Variables and Interference CS 536: Science of Programming, Fall 2018 A. Why Parallel programs can coordinate their work using shared variables, but it s important for threads to not interfere
Interaction Modelling: Sequence Diagrams
 Interaction Modelling: Sequence Diagrams Fabrizio Maria Maggi Institute of Computer Science (these slides are derived from the book Object-oriented modeling and design with UML ) Interaction Modelling
Interaction Modelling: Sequence Diagrams Fabrizio Maria Maggi Institute of Computer Science (these slides are derived from the book Object-oriented modeling and design with UML ) Interaction Modelling
Architecture and the UML
 Architecture and the UML Models, Views, and A model is a complete description of a system from a particular perspective Use Case Use Case Sequence Use Case Use Case Use Case State State Class State State
Architecture and the UML Models, Views, and A model is a complete description of a system from a particular perspective Use Case Use Case Sequence Use Case Use Case Use Case State State Class State State
Accessibility. EEC 521: Software Engineering. Classes and Objects. Inheritance. Classes and Objects (OO Analysis)
 Accessibility EEC 521: Software Engineering Classes and Objects (OO Analysis) Attributes and Methods can be declared at three levels of accessibility Public (+) Visible everywhere Private (-) Visible only
Accessibility EEC 521: Software Engineering Classes and Objects (OO Analysis) Attributes and Methods can be declared at three levels of accessibility Public (+) Visible everywhere Private (-) Visible only
C14b: Classless Intradomain Routing
 CISC 7332X T6 C14b: Classless Intradomain Routing Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 11/27/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Acknowledgements Some pictures used in this
CISC 7332X T6 C14b: Classless Intradomain Routing Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 11/27/2018 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Acknowledgements Some pictures used in this
Part 1 - Your First algorithm
 California State University, Sacramento College of Engineering and Computer Science Computer Science 10: Introduction to Programming Logic Spring 2016 Activity A Introduction to Flowgorithm Flowcharts
California State University, Sacramento College of Engineering and Computer Science Computer Science 10: Introduction to Programming Logic Spring 2016 Activity A Introduction to Flowgorithm Flowcharts
UML Tutorial. Unified Modeling Language UML Tutorial
 UML Tutorial Unified Modeling Language UML Tutorial A Unified Modeling Language is a language for specifying, constructing, visualizing and documenting the software system and its components. UML is a
UML Tutorial Unified Modeling Language UML Tutorial A Unified Modeling Language is a language for specifying, constructing, visualizing and documenting the software system and its components. UML is a
There are four (4) skills every Drupal editor needs to master:
 There are four (4) skills every Drupal editor needs to master: 1. Create a New Page / Edit an existing page. This entails adding text and formatting the content properly. 2. Adding an image to a page.
There are four (4) skills every Drupal editor needs to master: 1. Create a New Page / Edit an existing page. This entails adding text and formatting the content properly. 2. Adding an image to a page.
Lecture Notes on Quicksort
 Lecture Notes on Quicksort 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 8 September 20, 2012 1 Introduction In this lecture we first sketch two related algorithms for sorting that
Lecture Notes on Quicksort 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 8 September 20, 2012 1 Introduction In this lecture we first sketch two related algorithms for sorting that
Chapter 4. Capturing the Requirements. 4th Edition. Shari L. Pfleeger Joanne M. Atlee
 Chapter 4 Capturing the Requirements Shari L. Pfleeger Joanne M. Atlee 4th Edition It is important to have standard notations for modeling, documenting, and communicating decisions Modeling helps us to
Chapter 4 Capturing the Requirements Shari L. Pfleeger Joanne M. Atlee 4th Edition It is important to have standard notations for modeling, documenting, and communicating decisions Modeling helps us to
Adding EHR-S FM components
 Adding EHR-S FM components This document describes the way new components, sections, headers, functions and/ or conformance criteria can be add to a Functional Model or Profile with support of the EHR-S
Adding EHR-S FM components This document describes the way new components, sections, headers, functions and/ or conformance criteria can be add to a Functional Model or Profile with support of the EHR-S
Object-Oriented Software Engineering Practical Software Development using UML and Java
 Object-Oriented Software Engineering Practical Software Development using UML and Java Chapter 5: Modelling with Classes Lecture 5 5.1 What is UML? The Unified Modelling Language is a standard graphical
Object-Oriented Software Engineering Practical Software Development using UML and Java Chapter 5: Modelling with Classes Lecture 5 5.1 What is UML? The Unified Modelling Language is a standard graphical
Pieter van den Hombergh. Fontys Hogeschool voor Techniek en Logistiek. September 9, 2016
 Pieter van den Hombergh Fontys Hogeschool voor Techniek en Logistiek September 9, 2016 Contents /FHTenL September 9, 2016 2/35 UML State Uses and application In behaviour is modeled with state charts (diagrams)
Pieter van den Hombergh Fontys Hogeschool voor Techniek en Logistiek September 9, 2016 Contents /FHTenL September 9, 2016 2/35 UML State Uses and application In behaviour is modeled with state charts (diagrams)
Computer Architecture. Fall Dongkun Shin, SKKU
 Computer Architecture Fall 2018 1 Syllabus Instructors: Dongkun Shin Office : Room 85470 E-mail : dongkun@skku.edu Office Hours: Wed. 15:00-17:30 or by appointment Lecture notes nyx.skku.ac.kr Courses
Computer Architecture Fall 2018 1 Syllabus Instructors: Dongkun Shin Office : Room 85470 E-mail : dongkun@skku.edu Office Hours: Wed. 15:00-17:30 or by appointment Lecture notes nyx.skku.ac.kr Courses
06. Analysis Modeling
 06. Analysis Modeling Division of Computer Science, College of Computing Hanyang University ERICA Campus 1 st Semester 2017 Overview of Analysis Modeling 1 Requirement Analysis 2 Analysis Modeling Approaches
06. Analysis Modeling Division of Computer Science, College of Computing Hanyang University ERICA Campus 1 st Semester 2017 Overview of Analysis Modeling 1 Requirement Analysis 2 Analysis Modeling Approaches
Access Control Lists. Don Porter CSE 506
 Access Control Lists Don Porter CSE 506 Background (1) ò If everything in Unix is a file ò Everything in Windows is an object ò Why not files? ò Not all OS abstractions make sense as a file ò Examples:
Access Control Lists Don Porter CSE 506 Background (1) ò If everything in Unix is a file ò Everything in Windows is an object ò Why not files? ò Not all OS abstractions make sense as a file ò Examples:
Formal Verification Techniques for GPU Kernels Lecture 1
 École de Recherche: Semantics and Tools for Low-Level Concurrent Programming ENS Lyon Formal Verification Techniques for GPU Kernels Lecture 1 Alastair Donaldson Imperial College London www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~afd
École de Recherche: Semantics and Tools for Low-Level Concurrent Programming ENS Lyon Formal Verification Techniques for GPU Kernels Lecture 1 Alastair Donaldson Imperial College London www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~afd
ProjectXpert Getting Started with your trial
 ProjectXpert Getting Started with your trial Do you find your building projects difficult to manage? Want to streamline your jobs? Looked for the ideal project management solution but never found one?
ProjectXpert Getting Started with your trial Do you find your building projects difficult to manage? Want to streamline your jobs? Looked for the ideal project management solution but never found one?
Modeling Requirements
 Modeling Requirements Critical Embedded Systems Dr. Balázs Polgár Prepared by Budapest University of Technology and Economics Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Informatics Dept. of Measurement and
Modeling Requirements Critical Embedded Systems Dr. Balázs Polgár Prepared by Budapest University of Technology and Economics Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Informatics Dept. of Measurement and
Exam I Principles of Imperative Computation, Summer 2011 William Lovas. May 27, 2011
 Exam I 15-122 Principles of Imperative Computation, Summer 2011 William Lovas May 27, 2011 Name: Sample Solution Andrew ID: wlovas Instructions This exam is closed-book with one sheet of notes permitted.
Exam I 15-122 Principles of Imperative Computation, Summer 2011 William Lovas May 27, 2011 Name: Sample Solution Andrew ID: wlovas Instructions This exam is closed-book with one sheet of notes permitted.
Introduction to UML. Danang Wahyu utomo
 Introduction to UML Danang Wahyu utomo danang.wu@dsn.dinus.ac.id 085 740 955 623 Evolution of OO Development Methods History of OOAD leading to UML Why Model? Analyse the problem domain - Simplify reality
Introduction to UML Danang Wahyu utomo danang.wu@dsn.dinus.ac.id 085 740 955 623 Evolution of OO Development Methods History of OOAD leading to UML Why Model? Analyse the problem domain - Simplify reality
Introduction to UML What is UML? Motivations for UML Types of UML diagrams UML syntax Descriptions of the various diagram types Rational Rose (IBM.. M
 Introduction to UML Part I 1 What is UML? Unified Modeling Language, a standard language for designing and documenting a system in an object- oriented manner. It s a language by which technical architects
Introduction to UML Part I 1 What is UML? Unified Modeling Language, a standard language for designing and documenting a system in an object- oriented manner. It s a language by which technical architects
Computer Science 520/620 Spring 2013 Prof. L. Osterweil" Use Cases" Software Models and Representations" Part 4" More, and Multiple Models"
 Computer Science 520/620 Spring 2013 Prof. L. Osterweil Software Models and Representations Part 4 More, and Multiple Models Use Cases Specify actors and how they interact with various component parts
Computer Science 520/620 Spring 2013 Prof. L. Osterweil Software Models and Representations Part 4 More, and Multiple Models Use Cases Specify actors and how they interact with various component parts
Computer Science 520/620 Spring 2013 Prof. L. Osterweil" Software Models and Representations" Part 4" More, and Multiple Models" Use Cases"
 Computer Science 520/620 Spring 2013 Prof. L. Osterweil Software Models and Representations Part 4 More, and Multiple Models Use Cases Specify actors and how they interact with various component parts
Computer Science 520/620 Spring 2013 Prof. L. Osterweil Software Models and Representations Part 4 More, and Multiple Models Use Cases Specify actors and how they interact with various component parts
Software Engineering Fall 2015 (CSC 4350/6350) TR. 5:30 pm 7:15 pm. Rao Casturi 09/17/2015
 Software Engineering Fall 2015 (CSC 4350/6350) TR. 5:30 pm 7:15 pm Rao Casturi 09/17/2015 http://cs.gsu.edu/~ncasturi1 Requirement Elicitation 2 Requirement Engineering First step for understanding the
Software Engineering Fall 2015 (CSC 4350/6350) TR. 5:30 pm 7:15 pm Rao Casturi 09/17/2015 http://cs.gsu.edu/~ncasturi1 Requirement Elicitation 2 Requirement Engineering First step for understanding the
Absolute C++ Walter Savitch
 Absolute C++ sixth edition Walter Savitch Global edition This page intentionally left blank Absolute C++, Global Edition Cover Title Page Copyright Page Preface Acknowledgments Brief Contents Contents
Absolute C++ sixth edition Walter Savitch Global edition This page intentionally left blank Absolute C++, Global Edition Cover Title Page Copyright Page Preface Acknowledgments Brief Contents Contents
Design of Embedded Systems
 Design of Embedded Systems José Costa Software for Embedded Systems Departamento de Engenharia Informática (DEI) Instituto Superior Técnico 2015-01-02 José Costa (DEI/IST) Design of Embedded Systems 1
Design of Embedded Systems José Costa Software for Embedded Systems Departamento de Engenharia Informática (DEI) Instituto Superior Técnico 2015-01-02 José Costa (DEI/IST) Design of Embedded Systems 1
Use-Case Analysis. Architecture Oriented Analysis. R. Kuehl/J. Scott Hawker p. 1 R I T. Software Engineering
 Use-Case Analysis Architecture Oriented Analysis R. Kuehl/J. Scott Hawker p. 1 Notes The slides are based on UML use-case analysis techniques This is an introduction detailed techniques and notation will
Use-Case Analysis Architecture Oriented Analysis R. Kuehl/J. Scott Hawker p. 1 Notes The slides are based on UML use-case analysis techniques This is an introduction detailed techniques and notation will
ICONIX Process: Use Case Driven Object Modeling. Copyright 2007 ICONIX Software Engineering, Inc. 1
 ICONIX Process: Use Case Driven Object Modeling Copyright 2007 ICONIX Software Engineering, Inc. 1 The goal. Driving a good O-O software design from use cases. Copyright 2007 ICONIX Software Engineering,
ICONIX Process: Use Case Driven Object Modeling Copyright 2007 ICONIX Software Engineering, Inc. 1 The goal. Driving a good O-O software design from use cases. Copyright 2007 ICONIX Software Engineering,
Finite State Machines and Statecharts
 Finite State Machines and Statecharts Hassan Gomaa Dept of Information & Software Engineering George Mason University Reference: H. Gomaa, Chapter 10 - Designing Concurrent, Distributed, and Real-Time
Finite State Machines and Statecharts Hassan Gomaa Dept of Information & Software Engineering George Mason University Reference: H. Gomaa, Chapter 10 - Designing Concurrent, Distributed, and Real-Time
Shared Variables and Interference
 Illinois Institute of Technology Lecture 24 Shared Variables and Interference CS 536: Science of Programming, Spring 2018 A. Why Parallel programs can coordinate their work using shared variables, but
Illinois Institute of Technology Lecture 24 Shared Variables and Interference CS 536: Science of Programming, Spring 2018 A. Why Parallel programs can coordinate their work using shared variables, but
<Project Name> Use Case Specification: <Use-Case Name> Version <1.0>
 1 z 5 2007-02-26 15:57 Use Case Specification: Version [Note: The following template is provided for use with the Rational Unified Process. Text enclosed in square
1 z 5 2007-02-26 15:57 Use Case Specification: Version [Note: The following template is provided for use with the Rational Unified Process. Text enclosed in square
Component Design. Systems Engineering BSc Course. Budapest University of Technology and Economics Department of Measurement and Information Systems
 Component Design Systems Engineering BSc Course Budapest University of Technology and Economics Department of Measurement and Information Systems Traceability Platform-based systems design Verification
Component Design Systems Engineering BSc Course Budapest University of Technology and Economics Department of Measurement and Information Systems Traceability Platform-based systems design Verification
EE Embedded Systems Design
 EE4800-03 Embedded Systems Design Lesson 2 Structured Design, Documentation, and Laboratory Notebooks 1 Overview - Structured Design The divide-and-conquer technique Requirements Partitioning - The Black
EE4800-03 Embedded Systems Design Lesson 2 Structured Design, Documentation, and Laboratory Notebooks 1 Overview - Structured Design The divide-and-conquer technique Requirements Partitioning - The Black
Computer Science 136. Midterm Examination
 Computer Science 136 Bruce - Spring 04 Midterm Examination March 10, 2004 Question Points Score 1 12 2 10 3 11 4 18 5 8 TOTAL 59 Your name (Please print) I have neither given nor received aid on this examination.
Computer Science 136 Bruce - Spring 04 Midterm Examination March 10, 2004 Question Points Score 1 12 2 10 3 11 4 18 5 8 TOTAL 59 Your name (Please print) I have neither given nor received aid on this examination.
Process Modelling. Fault Tolerant Systems Research Group. Budapest University of Technology and Economics
 Process Modelling Budapest University of Technology and Economics Fault Tolerant Systems Research Group Budapest University of Technology and Economics Department of Measurement and Information Systems
Process Modelling Budapest University of Technology and Economics Fault Tolerant Systems Research Group Budapest University of Technology and Economics Department of Measurement and Information Systems
7 Fault Tolerant Distributed Transactions Commit protocols
 7 Fault Tolerant Distributed Transactions Commit protocols 7.1 Subtransactions and distribution 7.2 Fault tolerance and commit processing 7.3 Requirements 7.4 One phase commit 7.5 Two phase commit x based
7 Fault Tolerant Distributed Transactions Commit protocols 7.1 Subtransactions and distribution 7.2 Fault tolerance and commit processing 7.3 Requirements 7.4 One phase commit 7.5 Two phase commit x based
SITE DESIGN & ADVANCED WEB PART FEATURES...
 Overview OVERVIEW... 2 SITE DESIGN & ADVANCED WEB PART FEATURES... 4 SITE HIERARCHY... 4 Planning Your Site Hierarchy & Content... 4 Content Building Tools... 5 Pages vs Sites... 6 Creating Pages... 6
Overview OVERVIEW... 2 SITE DESIGN & ADVANCED WEB PART FEATURES... 4 SITE HIERARCHY... 4 Planning Your Site Hierarchy & Content... 4 Content Building Tools... 5 Pages vs Sites... 6 Creating Pages... 6
Creating a Brochure. The right side of your Publisher screen will now change to Brochures.
 Creating a Brochure Open Microsoft Publisher. You will see the Microsoft Publisher Task Pane on the left side of your screen. Click the Brochures selection in the Publication Types area. The right side
Creating a Brochure Open Microsoft Publisher. You will see the Microsoft Publisher Task Pane on the left side of your screen. Click the Brochures selection in the Publication Types area. The right side
Create a new document: Save your document regularly! The Big Picture: File>New
 Create a new document: File>New 1. On the menu bar, click File, then New. (Note: From now on, this will be indicated using the following notation style: File>New.) 2. Type in the dimensions for the publication
Create a new document: File>New 1. On the menu bar, click File, then New. (Note: From now on, this will be indicated using the following notation style: File>New.) 2. Type in the dimensions for the publication
How to use Excel Spreadsheets for Graphing
 How to use Excel Spreadsheets for Graphing 1. Click on the Excel Program on the Desktop 2. You will notice that a screen similar to the above screen comes up. A spreadsheet is divided into Columns (A,
How to use Excel Spreadsheets for Graphing 1. Click on the Excel Program on the Desktop 2. You will notice that a screen similar to the above screen comes up. A spreadsheet is divided into Columns (A,
CS102 Unit 2. Sets and Mathematical Formalism Programming Languages and Simple Program Execution
 1 CS102 Unit 2 Sets and Mathematical Formalism Programming Languages and Simple Program Execution 2 Review Show how "Hi!\n" would be stored in the memory below Use decimal to represent each byte Remember
1 CS102 Unit 2 Sets and Mathematical Formalism Programming Languages and Simple Program Execution 2 Review Show how "Hi!\n" would be stored in the memory below Use decimal to represent each byte Remember
Tail Calls. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Tail Recursion. Tail Recursion (cont d) Names and Binding. Tail Recursion (cont d)
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Tail Calls A tail call is a function call that is the last thing a function does before it returns let add x y = x + y let f z = add z z (* tail call *)
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Tail Calls A tail call is a function call that is the last thing a function does before it returns let add x y = x + y let f z = add z z (* tail call *)
Program Correctness and Efficiency. Chapter 2
 Program Correctness and Efficiency Chapter 2 Chapter Objectives To understand the differences between the three categories of program errors To understand the effect of an uncaught exception and why you
Program Correctness and Efficiency Chapter 2 Chapter Objectives To understand the differences between the three categories of program errors To understand the effect of an uncaught exception and why you
Exploring Our Family History Web Site Frequently Asked Questions
 Exploring Our Family History Web Site Frequently Asked Questions Q. The site is asking for a user name and password. What do I do? A. You have to be registered. Before registering, review the List of Individuals
Exploring Our Family History Web Site Frequently Asked Questions Q. The site is asking for a user name and password. What do I do? A. You have to be registered. Before registering, review the List of Individuals
Class diagrams. Modeling with UML Chapter 2, part 2. Class Diagrams: details. Class diagram for a simple watch
 Class diagrams Modeling with UML Chapter 2, part 2 CS 4354 Summer II 2014 Jill Seaman Used to describe the internal structure of the system. Also used to describe the application domain. They describe
Class diagrams Modeling with UML Chapter 2, part 2 CS 4354 Summer II 2014 Jill Seaman Used to describe the internal structure of the system. Also used to describe the application domain. They describe
Uldis Donins Janis Osis
 This work has been supported by the European Social Fund within the project «Support for the implementation of doctoral studies at Riga Technical University» Uldis Donins Janis Osis ICEIS 2011, June 8-11,
This work has been supported by the European Social Fund within the project «Support for the implementation of doctoral studies at Riga Technical University» Uldis Donins Janis Osis ICEIS 2011, June 8-11,
CREATING A PAYMENT REQUEST FOR A NEW VENDOR
 CREATING A PAYMENT REQUEST FOR A NEW VENDOR HOW TO PAY AN INVOICE FOR A NEW VENDOR 1 CREATING A PAYMENT REQUEST Click on the Invoice tab at the top of your 'My Concur' homepage This brings you to the invoice
CREATING A PAYMENT REQUEST FOR A NEW VENDOR HOW TO PAY AN INVOICE FOR A NEW VENDOR 1 CREATING A PAYMENT REQUEST Click on the Invoice tab at the top of your 'My Concur' homepage This brings you to the invoice
Editing Objects. Introduction
 M-Graphics User s Manual 6-1 Chapter 6 Editing Objects Introduction This chapter explains how to edit objects in M-Graphic displays. This chapter describes how to: edit the length of a line reposition
M-Graphics User s Manual 6-1 Chapter 6 Editing Objects Introduction This chapter explains how to edit objects in M-Graphic displays. This chapter describes how to: edit the length of a line reposition
Creating Universally Designed Word 2010 Documents - Quick Start Guide
 Creating Universally Designed Word 2010 Documents - Quick Start Guide Overview Creating accessible documents ones that work well with all sorts of technology can be a daunting task. The purpose of this
Creating Universally Designed Word 2010 Documents - Quick Start Guide Overview Creating accessible documents ones that work well with all sorts of technology can be a daunting task. The purpose of this
1 Exporting Files from Maestro Easy Dental Scan Great Lakes Orthodontics
 SMPI122Rev123113 Exporting Files from Maestro Easy Dental Scan The following instructions will explain how to export, or save, models using Maestro Easy Dental Scan. The first section will explain how
SMPI122Rev123113 Exporting Files from Maestro Easy Dental Scan The following instructions will explain how to export, or save, models using Maestro Easy Dental Scan. The first section will explain how
1010 2?= ?= CS 64 Lecture 2 Data Representation. Decimal Numbers: Base 10. Reading: FLD Digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
 CS 64 Lecture 2 Data Representation Reading: FLD 1.2-1.4 Decimal Numbers: Base 10 Digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 Example: 3271 = (3x10 3 ) + (2x10 2 ) + (7x10 1 ) + (1x10 0 ) 1010 10?= 1010 2?= 1
CS 64 Lecture 2 Data Representation Reading: FLD 1.2-1.4 Decimal Numbers: Base 10 Digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 Example: 3271 = (3x10 3 ) + (2x10 2 ) + (7x10 1 ) + (1x10 0 ) 1010 10?= 1010 2?= 1
Software Architecture. Lecture 5
 Software Architecture Lecture 5 Roadmap of the course What is software architecture? Designing Software Architecture Requirements: quality attributes or qualities How to achieve requirements : tactics
Software Architecture Lecture 5 Roadmap of the course What is software architecture? Designing Software Architecture Requirements: quality attributes or qualities How to achieve requirements : tactics
Creating a Box-and-Whisker Graph in Excel: Step One: Step Two:
 Creating a Box-and-Whisker Graph in Excel: It s not as simple as selecting Box and Whisker from the Chart Wizard. But if you ve made a few graphs in Excel before, it s not that complicated to convince
Creating a Box-and-Whisker Graph in Excel: It s not as simple as selecting Box and Whisker from the Chart Wizard. But if you ve made a few graphs in Excel before, it s not that complicated to convince
ME 142 Engineering Computation I. Graphing with Excel
 ME 142 Engineering Computation I Graphing with Excel Common Questions from Unit 1.2 HW 1.2.2 See 1.2.2 Homework Exercise Hints video Use ATAN to find nominal angle in each quadrant Use the AND logical
ME 142 Engineering Computation I Graphing with Excel Common Questions from Unit 1.2 HW 1.2.2 See 1.2.2 Homework Exercise Hints video Use ATAN to find nominal angle in each quadrant Use the AND logical
Getting Started with StrategyBlocks. Training Guide StrategyBlocks 4.0
 Getting Started with StrategyBlocks Training Guide StrategyBlocks 4.0 Section 2: Navigation & Creating a Block Navigation Creating a new block Additional Navigations 2.1 Navigation Here you can manage
Getting Started with StrategyBlocks Training Guide StrategyBlocks 4.0 Section 2: Navigation & Creating a Block Navigation Creating a new block Additional Navigations 2.1 Navigation Here you can manage
Using Choice and Junction Points in RSARTE vs RoseRT
 Using Choice and Junction Points in RSARTE vs RoseRT CHOICE POINTS IN ROSE RT AND RSARTE...2 CHOICE POINTS VS JUNCTION POINTS...5 HOW CHOICE POINTS ARE IMPORTED FROM ROSERT...8 This document discusses
Using Choice and Junction Points in RSARTE vs RoseRT CHOICE POINTS IN ROSE RT AND RSARTE...2 CHOICE POINTS VS JUNCTION POINTS...5 HOW CHOICE POINTS ARE IMPORTED FROM ROSERT...8 This document discusses
Administrivia. Wednesday: Requirements and Specification. CS169 Lecture 4. We assign teams and you start on Monday. Determining Stakeholders and Needs
 Administrivia Requirements and Specification CS169 Lecture 4 Wednesday: Groups and one-sentence idea(s) due at class One per group If you have a small group, still submit so that you will be kept together.
Administrivia Requirements and Specification CS169 Lecture 4 Wednesday: Groups and one-sentence idea(s) due at class One per group If you have a small group, still submit so that you will be kept together.
Testing. Unit, integration, regression, validation, system. OO Testing techniques Application of traditional techniques to OO software
 Testing Basic ideas and principles Traditional testing strategies Unit, integration, regression, validation, system OO Testing techniques Application of traditional techniques to OO software Testing-11,
Testing Basic ideas and principles Traditional testing strategies Unit, integration, regression, validation, system OO Testing techniques Application of traditional techniques to OO software Testing-11,
The following topics will be covered in this course (not necessarily in this order).
 The following topics will be covered in this course (not necessarily in this order). Introduction The course focuses on systematic design of larger object-oriented programs. We will introduce the appropriate
The following topics will be covered in this course (not necessarily in this order). Introduction The course focuses on systematic design of larger object-oriented programs. We will introduce the appropriate
Lecture Notes on Quicksort
 Lecture Notes on Quicksort 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 8 February 5, 2015 1 Introduction In this lecture we consider two related algorithms for sorting that achieve
Lecture Notes on Quicksort 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 8 February 5, 2015 1 Introduction In this lecture we consider two related algorithms for sorting that achieve
MTAT Software Engineering
 MTAT.03.094 Software Engineering Lecture 04: Analysis Dietmar Pfahl Fall 2013 email: dietmar.pfahl@ut.ee Labs Next Week Part of the lab time will be used for assessment your Task 1 solutions Submission
MTAT.03.094 Software Engineering Lecture 04: Analysis Dietmar Pfahl Fall 2013 email: dietmar.pfahl@ut.ee Labs Next Week Part of the lab time will be used for assessment your Task 1 solutions Submission
Basic Structural Modeling. Copyright Joey Paquet,
 Basic Structural Modeling Copyright Joey Paquet, 2000 1 Part I Classes Copyright Joey Paquet, 2000 2 Classes Description of a set of objects sharing the same attributes, operations and semantics Abstraction
Basic Structural Modeling Copyright Joey Paquet, 2000 1 Part I Classes Copyright Joey Paquet, 2000 2 Classes Description of a set of objects sharing the same attributes, operations and semantics Abstraction
A student was asked to point out interface elements in this code: Answer: cout. What is wrong?
 A student was asked to point out interface elements in this code: Answer: cout. What is wrong? Clarification of the concept of INTERFACE The interface we ve been talking about in OOP is not the man-machine
A student was asked to point out interface elements in this code: Answer: cout. What is wrong? Clarification of the concept of INTERFACE The interface we ve been talking about in OOP is not the man-machine
Agenda. Peer Instruction Question 1. Peer Instruction Answer 1. Peer Instruction Question 2 6/22/2011
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Introduction to C (Part II) Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. Patterson http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/sp11 Spring 2011 -- Lecture
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Introduction to C (Part II) Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. Patterson http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/sp11 Spring 2011 -- Lecture
CS 4604: Introduction to Database Management Systems. B. Aditya Prakash Lecture #5: Entity/Relational Models---Part 1
 CS 4604: Introduction to Database Management Systems B. Aditya Prakash Lecture #5: Entity/Relational Models---Part 1 E/R: NOT IN BOOK! IMPORTANT: Follow only lecture slides for this topic! Differences
CS 4604: Introduction to Database Management Systems B. Aditya Prakash Lecture #5: Entity/Relational Models---Part 1 E/R: NOT IN BOOK! IMPORTANT: Follow only lecture slides for this topic! Differences
Transport and TCP. EE122 Fall 2011 Scott Shenker
 Transport and TCP EE122 Fall 2011 Scott Shenker http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee122/ Materials with thanks to Jennifer Rexford, Ion Stoica, Vern Paxson and other colleagues at Princeton and UC Berkeley
Transport and TCP EE122 Fall 2011 Scott Shenker http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee122/ Materials with thanks to Jennifer Rexford, Ion Stoica, Vern Paxson and other colleagues at Princeton and UC Berkeley
Whole Group: Basics of Graphing on your TI Calculator
 Whole Group: Basics of Graphing on your TI Calculator 1. Start by pressing the Y= key on the upper left of your calculator. Notice that there are 10 different lines to write; this means that it is possible
Whole Group: Basics of Graphing on your TI Calculator 1. Start by pressing the Y= key on the upper left of your calculator. Notice that there are 10 different lines to write; this means that it is possible
How invariants help writing loops Author: Sander Kooijmans Document version: 1.0
 How invariants help writing loops Author: Sander Kooijmans Document version: 1.0 Why this document? Did you ever feel frustrated because of a nasty bug in your code? Did you spend hours looking at the
How invariants help writing loops Author: Sander Kooijmans Document version: 1.0 Why this document? Did you ever feel frustrated because of a nasty bug in your code? Did you spend hours looking at the
Software Engineering I (02161)
 Software Engineering I (02161) Week 2 Assoc. Prof. Hubert Baumeister DTU Compute Technical University of Denmark Spring 2017 Contents What are software requirements? Requirements Engineering Process Domain
Software Engineering I (02161) Week 2 Assoc. Prof. Hubert Baumeister DTU Compute Technical University of Denmark Spring 2017 Contents What are software requirements? Requirements Engineering Process Domain
12 Tutorial on UML. TIMe TIMe Electronic Textbook
 TIMe TIMe Electronic Textbook 12 Tutorial on UML Introduction......................................................2.................................................3 Diagrams in UML..................................................3
TIMe TIMe Electronic Textbook 12 Tutorial on UML Introduction......................................................2.................................................3 Diagrams in UML..................................................3
I have chosen to draw the caffeine molecule and will use this as my example throughout this tutorial.
 How to Create a Molecule in ChemDraw and Publish onto Webpage By Sean Wolosin I have chosen to draw the caffeine molecule and will use this as my example throughout this tutorial.. Open ChemDraw Std 8.0..
How to Create a Molecule in ChemDraw and Publish onto Webpage By Sean Wolosin I have chosen to draw the caffeine molecule and will use this as my example throughout this tutorial.. Open ChemDraw Std 8.0..
Domain Analysis. SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering. Department of Software Engineering Rochester Institute of Technology.
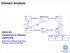 Domain Analysis Die 2 played with Monopoly Game played on Board Count 2 takes turn defines a using location on SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Player 2..8 represents Piece Character 0..8
Domain Analysis Die 2 played with Monopoly Game played on Board Count 2 takes turn defines a using location on SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Player 2..8 represents Piece Character 0..8
Topics. Overview- The UML Functional Model. Structural Model. Behavioral Models. Use Case Diagram (essential and system)
 Topics Overview- The UML Functional Model Use Case Diagram (essential and system) Structural Model Class/object, Component and Deployment Diagram Behavioral Models Activity, State chart, sequence /collaboration
Topics Overview- The UML Functional Model Use Case Diagram (essential and system) Structural Model Class/object, Component and Deployment Diagram Behavioral Models Activity, State chart, sequence /collaboration
