Unit4: Inferencefornumericaldata. 2. Bootstrapping
|
|
|
- Emily Hamilton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Announcements Unit4: Inferencefornumericaldata 2. Bootstrapping Sta Summer 2017 Duke University, Department of Statistical Science Project Description now posted on course page Project time in lab on Monday, July 24. Discuss with your team members, ask questions if you re stuck! Lab due on Monday PS 4 and PA 4 both due next Wednesday Prof. Burris Slides posted at 1 Readiness assessment Rotten horrors Individual: 15 minutes, using bubble sheets is a movie aggregator, where the audience is also able to review and score the movies. We want to estimate the average audience score of horror movies on RottenTomatoes.com. We start with a random sample of 20 horror movies. Team: 10 minutes, using scratch off sheets (1 per team) 2 3
2 Data First look 1 Patrick 52 2 Demon Seed 43 3 Tormented 34 4 Under the Bed 12 5 Phantasm IV: Oblivion 41 6 Fright Night Part House of 1000 Corpses 65 8 Creepshow The Forsaken All the Boys Love Mandy Lane Jason Lives: Friday the 13th Part VI Vampire's Kiss The Witches of Eastwick Yellowbrickroad Dying Breed Carrie Whoever Slew Auntie Roo? The Mangler Primal The Twilight Saga: New Moon 65 The histogram below shows the distribution of the audience scores of these movies (ranging from 0 to 100). The median score in the sample is Can we apply CLT based methods we have learned so far to construct a confidence interval for the median RottenTomatoes score of horror movies. Why or why not? audience scores 4 5 Bootstrapping Bootstrapping An alternative approach to constructing confidence intervals is bootstrapping. This term comes from the phrase pulling oneself up by one s bootstraps, which is a metaphor for accomplishing an impossible task without any outside help. In this case the impossible task is estimating a population parameter, and we ll accomplish it using data from only the given sample. Bootstrapping works as follows: (1) take a bootstrap sample - a random sample taken with replacement from the original sample, of the same size as the original sample (2) calculate the bootstrap statistic - a statistic such as mean, median, proportion, etc. computed on the bootstrap samples (3) repeat steps (1) and (2) many times to create a bootstrap distribution - a distribution of bootstrap statistics The XX% bootstrap confidence interval can be estimated by the cutoff values for the middle XX% of the bootstrap distribution, OR point estimate ± t SE boot 6 7
3 Bootstrap sample 1 Bootstrap sample 2 (1)Takeabootstrapsample: 1 Vampire's Kiss 48 2 Phantasm IV: Oblivion 41 3 House of 1000 Corpses 65 4 Dying Breed 27 5 Whoever Slew Auntie Roo? 56 6 The Forsaken 44 7 The Twilight Saga: New Moon 65 8 The Twilight Saga: New Moon 65 9 Whoever Slew Auntie Roo? The Twilight Saga: New Moon The Mangler Dying Breed Creepshow House of 1000 Corpses Whoever Slew Auntie Roo? Tormented Jason Lives: Friday the 13th Part VI Vampire's Kiss Primal The Witches of Eastwick 60 23, 27, 27, 29, 34, 41, 44, 46, 48, 48, 56, 56, 56, 57, 60, 65, 65, 65, 65, 65 median = ( ) / 2 = 52 (1)Takeanotherbootstrapsample: 1 Fright Night Part Carrie 73 3 The Forsaken 44 4 The Mangler 23 5 Primal 29 6 Patrick 52 7 Jason Lives: Friday the 13th Part VI 57 8 The Mangler 23 9 Vampire's Kiss All the Boys Love Mandy Lane The Twilight Saga: New Moon All the Boys Love Mandy Lane Yellowbrickroad Vampire's Kiss Tormented The Mangler Phantasm IV: Oblivion Patrick House of 1000 Corpses The Twilight Saga: New Moon 65 23, 23, 23, 28, 29, 34, 34, 34, 41, 42, 44, 48, 48, 52, 52, 57, 65, 65, 65, 73 median = ( ) / 2 = Bootstrap sample 3 Many more bootstrap samples (1)Takeanotherbootstrapsample: 1 Tormented 34 2 The Witches of Eastwick 60 3 The Witches of Eastwick 60 4 The Witches of Eastwick 60 5 The Mangler 23 6 The Witches of Eastwick 60 7 Patrick 52 8 Phantasm IV: Oblivion 41 9 Yellowbrickroad Jason Lives: Friday the 13th Part VI Yellowbrickroad Jason Lives: Friday the 13th Part VI Fright Night Part Primal Fright Night Part Whoever Slew Auntie Roo? Fright Night Part Fright Night Part Under the Bed Phantasm IV: Oblivion repeat 12, 23, 28, 28, 29, 34, 41, 41, 42, 42, 42, 42, 52, 56, 57, 57, 60, 60, 60, 60 median = ( ) / 2 =
4 Question The dot plot below is the bootstrap distribution of medians constructed using 100 simulations. What does each dot on the dot plot represent? Question The dot plot below shows the distribution of 100. Estimate the 90% bootstrap confidence interval for the median RT score of horror movies using the percentile method. (a) Score of a horror movie in the original sample (b) Score of a horror movie in the population (c) Median from one bootstrap sample from the original sample (d) Median from one sample from the population (a) (29, 58.5) (b) (34, 57) (c) (37.5, 52) (d) (40, 49.5) Bootstrap interval, standard error Bootstrap testing for a mean The dot plot below shows the distribution of 100. The median of the original sample is 43.5 and the bootstrap standard error is Estimate the 90% bootstrap confidence interval for the median RT score of horror movies using the standard error method. This is very similar to bootstrapping, i.e. we randomly sample with replacement from the sample, but this time we shift the bootstrap distribution to be centered at the null value. The p-value is then defined as the proportion of simulations that yield a sample statistic at least as favorable to the alternative hypothesis as the observed sample statistic
5 Bootstrap vs. sampling distributions Do these data provide convincing evidence that the median audience score of horror movies is greater than 40? Remember that the median of the original sample was Application exercise: 4.2 Bootstrap intervals See the course webpage for details. H 0 : median = 40 H A : median > 40 p-value: proportion of simulations where the simulated bootstrap sample median is at least as extreme as the one observed (43.5). 20 / 100 = Summary of main ideas 1. Bootstrapping = sampling with replacement from the observed sample 2. Bootstrap percentile intervals: middle XX% of the bootstrap distribution 3. Bootstrap SE intervals: point estimate ± ME 4. Bootstrap testing for a single numerical variable requires shifting the bootstrap distribution to be centered at the null value 18
Unit4: Inferencefornumericaldata. 2. Bootstrapping
 Announcements Unit4: Inferencefornumericaldata 2. Bootstrapping Sta 101 - Fall 2015 Duke University, Department of Statistical Science Feedback from midterm evaluation: n = 10 :( or :)? Majority think
Announcements Unit4: Inferencefornumericaldata 2. Bootstrapping Sta 101 - Fall 2015 Duke University, Department of Statistical Science Feedback from midterm evaluation: n = 10 :( or :)? Majority think
Unit4: Inferencefornumericaldata. 2. Bootstrapping. Sta Fall Duke University, Department of Statistical Science
 Unit4: Inferencefornumericaldata 2. Bootstrapping Sta 101 - Fall 2015 Duke University, Department of Statistical Science Dr. Çetinkaya-Rundel Slides posted at http://bit.ly/sta101_f15 Outline 1. Housekeeping
Unit4: Inferencefornumericaldata 2. Bootstrapping Sta 101 - Fall 2015 Duke University, Department of Statistical Science Dr. Çetinkaya-Rundel Slides posted at http://bit.ly/sta101_f15 Outline 1. Housekeeping
Announcements. Unit 4: Inference for Numerical Data Lecture 1: Bootstrapping. Rotten horrors. Data
 Housekeeping Announcements Unit 4: Inference for Numerical Data Lecture 1: Statistics 101 Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel October 9, 2014 Midterms will be distributed at the end of class. Extra credit opportunity:
Housekeeping Announcements Unit 4: Inference for Numerical Data Lecture 1: Statistics 101 Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel October 9, 2014 Midterms will be distributed at the end of class. Extra credit opportunity:
Descriptive Statistics, Standard Deviation and Standard Error
 AP Biology Calculations: Descriptive Statistics, Standard Deviation and Standard Error SBI4UP The Scientific Method & Experimental Design Scientific method is used to explore observations and answer questions.
AP Biology Calculations: Descriptive Statistics, Standard Deviation and Standard Error SBI4UP The Scientific Method & Experimental Design Scientific method is used to explore observations and answer questions.
1. Probability and conditional probability
 Unit2: Probabilityanddistributions 1. Probability and conditional probability Sta 101 - Fall 2015 Duke University, Department of Statistical Science Dr. Çetinkaya-Rundel Slides posted at http://bit.ly/sta101_f15
Unit2: Probabilityanddistributions 1. Probability and conditional probability Sta 101 - Fall 2015 Duke University, Department of Statistical Science Dr. Çetinkaya-Rundel Slides posted at http://bit.ly/sta101_f15
Confidence Intervals. Dennis Sun Data 301
 Dennis Sun Data 301 Statistical Inference probability Population / Box Sample / Data statistics The goal of statistics is to infer the unknown population from the sample. We ve already seen one mode of
Dennis Sun Data 301 Statistical Inference probability Population / Box Sample / Data statistics The goal of statistics is to infer the unknown population from the sample. We ve already seen one mode of
Practice 1 f = 12 2 m = 5 3 a = 7 g = 3 8 q = 96 9 c = y = 6. Warm-up. 1 x = 2 2 x = 20 3 y = 6 4 y = 3. Warm-up
 s Math Part B Lesson Manual Chapter Lesson Exploring Equations and Inequalities > < Lesson Solving Equations by Substitution Lesson Solving Equations with Addition and Subtraction Lesson Solving Equations
s Math Part B Lesson Manual Chapter Lesson Exploring Equations and Inequalities > < Lesson Solving Equations by Substitution Lesson Solving Equations with Addition and Subtraction Lesson Solving Equations
Confidence Interval of a Proportion
 Confidence Interval of a Proportion FPP 20-21 Using the sample to learn about the box Box models and CLT assume we know the contents of the box (the population). In real-world problems, we do not. In random
Confidence Interval of a Proportion FPP 20-21 Using the sample to learn about the box Box models and CLT assume we know the contents of the box (the population). In real-world problems, we do not. In random
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers
 IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
Mean,Median, Mode Teacher Twins 2015
 Mean,Median, Mode Teacher Twins 2015 Warm Up How can you change the non-statistical question below to make it a statistical question? How many pets do you have? Possible answer: What is your favorite type
Mean,Median, Mode Teacher Twins 2015 Warm Up How can you change the non-statistical question below to make it a statistical question? How many pets do you have? Possible answer: What is your favorite type
STA Module 4 The Normal Distribution
 STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA /25/12. Module 4 The Normal Distribution. Learning Objectives. Let s Look at Some Examples of Normal Curves
 STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
Question. Dinner at the Urquhart House. Data, Statistics, and Spreadsheets. Data. Types of Data. Statistics and Data
 Question What are data and what do they mean to a scientist? Dinner at the Urquhart House Brought to you by the Briggs Multiracial Alliance Sunday night All food provided (probably Chinese) Contact Mimi
Question What are data and what do they mean to a scientist? Dinner at the Urquhart House Brought to you by the Briggs Multiracial Alliance Sunday night All food provided (probably Chinese) Contact Mimi
Guide to Running TEMAP2.R. The R-program, TEMAP2.R, fits the TE models to the data; it can also
 Guide to Running TEMAP2.R The R-program, TEMAP2.R, fits the TE models to the data; it can also construct Monte Carlo simulation of the test statistic, and it can perform bootstrapping to construct distributions
Guide to Running TEMAP2.R The R-program, TEMAP2.R, fits the TE models to the data; it can also construct Monte Carlo simulation of the test statistic, and it can perform bootstrapping to construct distributions
Cross-validation and the Bootstrap
 Cross-validation and the Bootstrap In the section we discuss two resampling methods: cross-validation and the bootstrap. These methods refit a model of interest to samples formed from the training set,
Cross-validation and the Bootstrap In the section we discuss two resampling methods: cross-validation and the bootstrap. These methods refit a model of interest to samples formed from the training set,
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers HW 34. Sketch
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers HW 34. Sketch
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Lecture 1: Exploratory data analysis
 Lecture 1: Exploratory data analysis Statistics 101 Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel January 17, 2012 Announcements Announcements Any questions about the syllabus? If you sent me your gmail address your RStudio account
Lecture 1: Exploratory data analysis Statistics 101 Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel January 17, 2012 Announcements Announcements Any questions about the syllabus? If you sent me your gmail address your RStudio account
STAT 113: Lab 9. Colin Reimer Dawson. Last revised November 10, 2015
 STAT 113: Lab 9 Colin Reimer Dawson Last revised November 10, 2015 We will do some of the following together. The exercises with a (*) should be done and turned in as part of HW9. Before we start, let
STAT 113: Lab 9 Colin Reimer Dawson Last revised November 10, 2015 We will do some of the following together. The exercises with a (*) should be done and turned in as part of HW9. Before we start, let
Quantitative - One Population
 Quantitative - One Population The Quantitative One Population VISA procedures allow the user to perform descriptive and inferential procedures for problems involving one population with quantitative (interval)
Quantitative - One Population The Quantitative One Population VISA procedures allow the user to perform descriptive and inferential procedures for problems involving one population with quantitative (interval)
Day 4 Percentiles and Box and Whisker.notebook. April 20, 2018
 Day 4 Box & Whisker Plots and Percentiles In a previous lesson, we learned that the median divides a set a data into 2 equal parts. Sometimes it is necessary to divide the data into smaller more precise
Day 4 Box & Whisker Plots and Percentiles In a previous lesson, we learned that the median divides a set a data into 2 equal parts. Sometimes it is necessary to divide the data into smaller more precise
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
EXERCISE: GETTING STARTED WITH SAV
 Sequencing Analysis Viewer (SAV) Overview 1 EXERCISE: GETTING STARTED WITH SAV Purpose This exercise explores the following topics: How to load run data into SAV How to explore run metrics with SAV Getting
Sequencing Analysis Viewer (SAV) Overview 1 EXERCISE: GETTING STARTED WITH SAV Purpose This exercise explores the following topics: How to load run data into SAV How to explore run metrics with SAV Getting
Learner Expectations UNIT 1: GRAPICAL AND NUMERIC REPRESENTATIONS OF DATA. Sept. Fathom Lab: Distributions and Best Methods of Display
 CURRICULUM MAP TEMPLATE Priority Standards = Approximately 70% Supporting Standards = Approximately 20% Additional Standards = Approximately 10% HONORS PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS Essential Questions &
CURRICULUM MAP TEMPLATE Priority Standards = Approximately 70% Supporting Standards = Approximately 20% Additional Standards = Approximately 10% HONORS PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS Essential Questions &
Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary
 1 Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary Z-score: Is the distance of each data value from the mean in standard deviation Standardizes data values Standardization changes the mean and the standard deviation: o Z
1 Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary Z-score: Is the distance of each data value from the mean in standard deviation Standardizes data values Standardization changes the mean and the standard deviation: o Z
Frequency Distributions
 Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
Chapter 3: Data Description - Part 3. Homework: Exercises 1-21 odd, odd, odd, 107, 109, 118, 119, 120, odd
 Chapter 3: Data Description - Part 3 Read: Sections 1 through 5 pp 92-149 Work the following text examples: Section 3.2, 3-1 through 3-17 Section 3.3, 3-22 through 3.28, 3-42 through 3.82 Section 3.4,
Chapter 3: Data Description - Part 3 Read: Sections 1 through 5 pp 92-149 Work the following text examples: Section 3.2, 3-1 through 3-17 Section 3.3, 3-22 through 3.28, 3-42 through 3.82 Section 3.4,
MAT 110 WORKSHOP. Updated Fall 2018
 MAT 110 WORKSHOP Updated Fall 2018 UNIT 3: STATISTICS Introduction Choosing a Sample Simple Random Sample: a set of individuals from the population chosen in a way that every individual has an equal chance
MAT 110 WORKSHOP Updated Fall 2018 UNIT 3: STATISTICS Introduction Choosing a Sample Simple Random Sample: a set of individuals from the population chosen in a way that every individual has an equal chance
Laboratory #11. Bootstrap Estimates
 Name Laboratory #11. Bootstrap Estimates Randomization methods so far have been used to compute p-values for hypothesis testing. Randomization methods can also be used to place confidence limits around
Name Laboratory #11. Bootstrap Estimates Randomization methods so far have been used to compute p-values for hypothesis testing. Randomization methods can also be used to place confidence limits around
Humanoid Robots Exercise Sheet 9 - Inverse reachability maps (IRM) and statistical testing
 Prof. Dr. Maren Bennewitz M.Sc. Stefan Oßwald M.Sc. AbdElMoniem Bayoumi Bonn, 2 July 2015 Humanoid Robots Exercise Sheet 9 - Inverse reachability maps (IRM) and statistical testing Exercise 17 In this
Prof. Dr. Maren Bennewitz M.Sc. Stefan Oßwald M.Sc. AbdElMoniem Bayoumi Bonn, 2 July 2015 Humanoid Robots Exercise Sheet 9 - Inverse reachability maps (IRM) and statistical testing Exercise 17 In this
Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution
 Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution 2.1 Density Curves and the Normal Distributions 2.2 Standard Normal Calculations 1 2 Histogram for Strength of Yarn Bobbins 15.60 16.10 16.60 17.10 17.60 18.10 18.60
Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution 2.1 Density Curves and the Normal Distributions 2.2 Standard Normal Calculations 1 2 Histogram for Strength of Yarn Bobbins 15.60 16.10 16.60 17.10 17.60 18.10 18.60
Box and Whisker Plot Review A Five Number Summary. October 16, Box and Whisker Lesson.notebook. Oct 14 5:21 PM. Oct 14 5:21 PM.
 Oct 14 5:21 PM Oct 14 5:21 PM Box and Whisker Plot Review A Five Number Summary Activities Practice Labeling Title Page 1 Click on each word to view its definition. Outlier Median Lower Extreme Upper Extreme
Oct 14 5:21 PM Oct 14 5:21 PM Box and Whisker Plot Review A Five Number Summary Activities Practice Labeling Title Page 1 Click on each word to view its definition. Outlier Median Lower Extreme Upper Extreme
Section 9: One Variable Statistics
 The following Mathematics Florida Standards will be covered in this section: MAFS.912.S-ID.1.1 MAFS.912.S-ID.1.2 MAFS.912.S-ID.1.3 Represent data with plots on the real number line (dot plots, histograms,
The following Mathematics Florida Standards will be covered in this section: MAFS.912.S-ID.1.1 MAFS.912.S-ID.1.2 MAFS.912.S-ID.1.3 Represent data with plots on the real number line (dot plots, histograms,
CHAPTER 6. The Normal Probability Distribution
 The Normal Probability Distribution CHAPTER 6 The normal probability distribution is the most widely used distribution in statistics as many statistical procedures are built around it. The central limit
The Normal Probability Distribution CHAPTER 6 The normal probability distribution is the most widely used distribution in statistics as many statistical procedures are built around it. The central limit
Chapter 3. Bootstrap. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 The general idea
 Chapter 3 Bootstrap 3.1 Introduction The estimation of parameters in probability distributions is a basic problem in statistics that one tends to encounter already during the very first course on the subject.
Chapter 3 Bootstrap 3.1 Introduction The estimation of parameters in probability distributions is a basic problem in statistics that one tends to encounter already during the very first course on the subject.
GenStat for Schools. Disappearing Rock Wren in Fiordland
 GenStat for Schools Disappearing Rock Wren in Fiordland A possible decrease in number of Rock Wren in the Fiordland area of New Zealand between 1985 and 2005 was investigated. Numbers were recorded in
GenStat for Schools Disappearing Rock Wren in Fiordland A possible decrease in number of Rock Wren in the Fiordland area of New Zealand between 1985 and 2005 was investigated. Numbers were recorded in
Common R commands used in Data Analysis and Statistical Inference
 Common R commands used in Data Analysis and Statistical Inference 1 One numerical variable summary(x) # most summary statitstics at once mean(x) median(x) sd(x) hist(x) boxplot(x) # horizontal = TRUE for
Common R commands used in Data Analysis and Statistical Inference 1 One numerical variable summary(x) # most summary statitstics at once mean(x) median(x) sd(x) hist(x) boxplot(x) # horizontal = TRUE for
Minitab Study Card J ENNIFER L EWIS P RIESTLEY, PH.D.
 Minitab Study Card J ENNIFER L EWIS P RIESTLEY, PH.D. Introduction to Minitab The interface for Minitab is very user-friendly, with a spreadsheet orientation. When you first launch Minitab, you will see
Minitab Study Card J ENNIFER L EWIS P RIESTLEY, PH.D. Introduction to Minitab The interface for Minitab is very user-friendly, with a spreadsheet orientation. When you first launch Minitab, you will see
Chapter 7 Assignment due Wednesday, May 24
 due Wednesday, May 24 Calculating Probabilities for Normal Distributions Overview What you re going to do in this assignment is use an online applet to calculate: probabilities associated with given -scores
due Wednesday, May 24 Calculating Probabilities for Normal Distributions Overview What you re going to do in this assignment is use an online applet to calculate: probabilities associated with given -scores
STA215 Inference about comparing two populations
 STA215 Inference about comparing two populations Al Nosedal. University of Toronto. Summer 2017 June 22, 2017 Two-sample problems The goal of inference is to compare the responses to two treatments or
STA215 Inference about comparing two populations Al Nosedal. University of Toronto. Summer 2017 June 22, 2017 Two-sample problems The goal of inference is to compare the responses to two treatments or
Cross-validation and the Bootstrap
 Cross-validation and the Bootstrap In the section we discuss two resampling methods: cross-validation and the bootstrap. 1/44 Cross-validation and the Bootstrap In the section we discuss two resampling
Cross-validation and the Bootstrap In the section we discuss two resampling methods: cross-validation and the bootstrap. 1/44 Cross-validation and the Bootstrap In the section we discuss two resampling
Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach
 i Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach Computer software help: SAS SAS (originally Statistical Analysis Software ) is a commercial statistical software package based on a powerful programming
i Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach Computer software help: SAS SAS (originally Statistical Analysis Software ) is a commercial statistical software package based on a powerful programming
MAT 142 College Mathematics. Module ST. Statistics. Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015
 MAT 142 College Mathematics Statistics Module ST Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015 2 Statistics Data Organization and Visualization Basic Terms. A population is the set of all objects under study, a sample
MAT 142 College Mathematics Statistics Module ST Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015 2 Statistics Data Organization and Visualization Basic Terms. A population is the set of all objects under study, a sample
Week 7: The normal distribution and sample means
 Week 7: The normal distribution and sample means Goals Visualize properties of the normal distribution. Learning the Tools Understand the Central Limit Theorem. Calculate sampling properties of sample
Week 7: The normal distribution and sample means Goals Visualize properties of the normal distribution. Learning the Tools Understand the Central Limit Theorem. Calculate sampling properties of sample
Minitab Notes for Activity 1
 Minitab Notes for Activity 1 Creating the Worksheet 1. Label the columns as team, heat, and time. 2. Have Minitab automatically enter the team data for you. a. Choose Calc / Make Patterned Data / Simple
Minitab Notes for Activity 1 Creating the Worksheet 1. Label the columns as team, heat, and time. 2. Have Minitab automatically enter the team data for you. a. Choose Calc / Make Patterned Data / Simple
MS&E 226: Small Data
 MS&E 226: Small Data Lecture 13: The bootstrap (v3) Ramesh Johari ramesh.johari@stanford.edu 1 / 30 Resampling 2 / 30 Sampling distribution of a statistic For this lecture: There is a population model
MS&E 226: Small Data Lecture 13: The bootstrap (v3) Ramesh Johari ramesh.johari@stanford.edu 1 / 30 Resampling 2 / 30 Sampling distribution of a statistic For this lecture: There is a population model
JEOPARDY! JEOPARDY JEOPARDY. April 18, Unit 04, Review Jeopardy.notebook $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $400 $400
 Increasing / Critical Decreasing? Numbers Discont. & Concavity Asymptotes & POI Graph Me! Menu! $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 c $200 $200 $200 $200 d Category Setup Directions Examples Question
Increasing / Critical Decreasing? Numbers Discont. & Concavity Asymptotes & POI Graph Me! Menu! $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 c $200 $200 $200 $200 d Category Setup Directions Examples Question
Data 8 Final Review #1
 Data 8 Final Review #1 Topics we ll cover: Visualizations Arrays and Table Manipulations Programming constructs (functions, for loops, conditional statements) Chance, Simulation, Sampling and Distributions
Data 8 Final Review #1 Topics we ll cover: Visualizations Arrays and Table Manipulations Programming constructs (functions, for loops, conditional statements) Chance, Simulation, Sampling and Distributions
LESSON 3: CENTRAL TENDENCY
 LESSON 3: CENTRAL TENDENCY Outline Arithmetic mean, median and mode Ungrouped data Grouped data Percentiles, fractiles, and quartiles Ungrouped data Grouped data 1 MEAN Mean is defined as follows: Sum
LESSON 3: CENTRAL TENDENCY Outline Arithmetic mean, median and mode Ungrouped data Grouped data Percentiles, fractiles, and quartiles Ungrouped data Grouped data 1 MEAN Mean is defined as follows: Sum
Statistical Methods. Instructor: Lingsong Zhang. Any questions, ask me during the office hour, or me, I will answer promptly.
 Statistical Methods Instructor: Lingsong Zhang 1 Issues before Class Statistical Methods Lingsong Zhang Office: Math 544 Email: lingsong@purdue.edu Phone: 765-494-7913 Office Hour: Monday 1:00 pm - 2:00
Statistical Methods Instructor: Lingsong Zhang 1 Issues before Class Statistical Methods Lingsong Zhang Office: Math 544 Email: lingsong@purdue.edu Phone: 765-494-7913 Office Hour: Monday 1:00 pm - 2:00
An Introduction to the Bootstrap
 An Introduction to the Bootstrap Bradley Efron Department of Statistics Stanford University and Robert J. Tibshirani Department of Preventative Medicine and Biostatistics and Department of Statistics,
An Introduction to the Bootstrap Bradley Efron Department of Statistics Stanford University and Robert J. Tibshirani Department of Preventative Medicine and Biostatistics and Department of Statistics,
Lab #9: ANOVA and TUKEY tests
 Lab #9: ANOVA and TUKEY tests Objectives: 1. Column manipulation in SAS 2. Analysis of variance 3. Tukey test 4. Least Significant Difference test 5. Analysis of variance with PROC GLM 6. Levene test for
Lab #9: ANOVA and TUKEY tests Objectives: 1. Column manipulation in SAS 2. Analysis of variance 3. Tukey test 4. Least Significant Difference test 5. Analysis of variance with PROC GLM 6. Levene test for
CS 126 Lecture P1: Introduction to C
 CS 126 Lecture P1: Introduction to C Administrivia Background Syntax Libraries Algorithms Outline CS126 2-1 Randy Wang To Get Started Visit course web page: - http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/cs126
CS 126 Lecture P1: Introduction to C Administrivia Background Syntax Libraries Algorithms Outline CS126 2-1 Randy Wang To Get Started Visit course web page: - http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/cs126
AOE 5204: Homework Assignment 4 Due: Wednesday, 9/21 in class. Extended to Friday 9/23 Online Students:
 AOE 5204: Homework Assignment 4 Due: Wednesday, 9/21 in class. Extended to Friday 9/23 Online Students: Email (cdhall@vt.edu) by 5 PM Suppose F b is initially aligned with F i and at t = 0 begins to rotate
AOE 5204: Homework Assignment 4 Due: Wednesday, 9/21 in class. Extended to Friday 9/23 Online Students: Email (cdhall@vt.edu) by 5 PM Suppose F b is initially aligned with F i and at t = 0 begins to rotate
Learning Objectives. Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution. Continuous Random Variable
 Learning Objectives Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution 1. Understand characteristics about continuous random variables and probability distributions 2. Understand the uniform
Learning Objectives Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution 1. Understand characteristics about continuous random variables and probability distributions 2. Understand the uniform
CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA
 CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA This presentation is based on material and graphs from Open Stax and is copyrighted by Open Stax and Georgia Highlands College. OUTLINE 2.1 Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots),
CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA This presentation is based on material and graphs from Open Stax and is copyrighted by Open Stax and Georgia Highlands College. OUTLINE 2.1 Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots),
How individual data points are positioned within a data set.
 Section 3.4 Measures of Position Percentiles How individual data points are positioned within a data set. P k is the value such that k% of a data set is less than or equal to P k. For example if we said
Section 3.4 Measures of Position Percentiles How individual data points are positioned within a data set. P k is the value such that k% of a data set is less than or equal to P k. For example if we said
Bootstrapping Methods
 Bootstrapping Methods example of a Monte Carlo method these are one Monte Carlo statistical method some Bayesian statistical methods are Monte Carlo we can also simulate models using Monte Carlo methods
Bootstrapping Methods example of a Monte Carlo method these are one Monte Carlo statistical method some Bayesian statistical methods are Monte Carlo we can also simulate models using Monte Carlo methods
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
Vocabulary. 5-number summary Rule. Area principle. Bar chart. Boxplot. Categorical data condition. Categorical variable.
 5-number summary 68-95-99.7 Rule Area principle Bar chart Bimodal Boxplot Case Categorical data Categorical variable Center Changing center and spread Conditional distribution Context Contingency table
5-number summary 68-95-99.7 Rule Area principle Bar chart Bimodal Boxplot Case Categorical data Categorical variable Center Changing center and spread Conditional distribution Context Contingency table
AP Physics 1 and 2 Summer Assignment
 AP Physics 1 and 2 Summer Assignment Due: First Day of Class Welcome to AP Physics! You are responsible for the material covered in the first three chapters of your textbook. The questions that follow
AP Physics 1 and 2 Summer Assignment Due: First Day of Class Welcome to AP Physics! You are responsible for the material covered in the first three chapters of your textbook. The questions that follow
MHPE 494: Data Analysis. Welcome! The Analytic Process
 MHPE 494: Data Analysis Alan Schwartz, PhD Department of Medical Education Memoona Hasnain,, MD, PhD, MHPE Department of Family Medicine College of Medicine University of Illinois at Chicago Welcome! Your
MHPE 494: Data Analysis Alan Schwartz, PhD Department of Medical Education Memoona Hasnain,, MD, PhD, MHPE Department of Family Medicine College of Medicine University of Illinois at Chicago Welcome! Your
Probability and Statistics. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Probability and Statistics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 14.6 Descriptive Statistics (Graphical) Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Data in Categories Histograms
Probability and Statistics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 14.6 Descriptive Statistics (Graphical) Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Data in Categories Histograms
Unit 7 Statistics. AFM Mrs. Valentine. 7.1 Samples and Surveys
 Unit 7 Statistics AFM Mrs. Valentine 7.1 Samples and Surveys v Obj.: I will understand the different methods of sampling and studying data. I will be able to determine the type used in an example, and
Unit 7 Statistics AFM Mrs. Valentine 7.1 Samples and Surveys v Obj.: I will understand the different methods of sampling and studying data. I will be able to determine the type used in an example, and
Evaluating generalization (validation) Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.951J: Medical Decision Support
 Evaluating generalization (validation) Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.951J: Medical Decision Support Topics Validation of biomedical models Data-splitting Resampling Cross-validation
Evaluating generalization (validation) Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.951J: Medical Decision Support Topics Validation of biomedical models Data-splitting Resampling Cross-validation
IPS9 in R: Bootstrap Methods and Permutation Tests (Chapter 16)
 IPS9 in R: Bootstrap Methods and Permutation Tests (Chapter 6) Bonnie Lin and Nicholas Horton (nhorton@amherst.edu) July, 8 Introduction and background These documents are intended to help describe how
IPS9 in R: Bootstrap Methods and Permutation Tests (Chapter 6) Bonnie Lin and Nicholas Horton (nhorton@amherst.edu) July, 8 Introduction and background These documents are intended to help describe how
Page 1. Graphical and Numerical Statistics
 TOPIC: Description Statistics In this tutorial, we show how to use MINITAB to produce descriptive statistics, both graphical and numerical, for an existing MINITAB dataset. The example data come from Exercise
TOPIC: Description Statistics In this tutorial, we show how to use MINITAB to produce descriptive statistics, both graphical and numerical, for an existing MINITAB dataset. The example data come from Exercise
Homework Packet Week #3
 Lesson 8.1 Choose the term that best completes statements # 1-12. 10. A data distribution is if the peak of the data is in the middle of the graph. The left and right sides of the graph are nearly mirror
Lesson 8.1 Choose the term that best completes statements # 1-12. 10. A data distribution is if the peak of the data is in the middle of the graph. The left and right sides of the graph are nearly mirror
Notes on Simulations in SAS Studio
 Notes on Simulations in SAS Studio If you are not careful about simulations in SAS Studio, you can run into problems. In particular, SAS Studio has a limited amount of memory that you can use to write
Notes on Simulations in SAS Studio If you are not careful about simulations in SAS Studio, you can run into problems. In particular, SAS Studio has a limited amount of memory that you can use to write
Ms Nurazrin Jupri. Frequency Distributions
 Frequency Distributions Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and simplify the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results.
Frequency Distributions Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and simplify the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results.
Processing, representing and interpreting data
 Processing, representing and interpreting data 21 CHAPTER 2.1 A head CHAPTER 17 21.1 polygons A diagram can be drawn from grouped discrete data. A diagram looks the same as a bar chart except that the
Processing, representing and interpreting data 21 CHAPTER 2.1 A head CHAPTER 17 21.1 polygons A diagram can be drawn from grouped discrete data. A diagram looks the same as a bar chart except that the
Integrated Math 1 Module 7 Honors Connecting Algebra and Geometry Ready, Set, Go! Homework Solutions
 1 Integrated Math 1 Module 7 Honors Connecting Algebra and Geometry Ready, Set, Go! Homework Solutions Adapted from The Mathematics Vision Project: Scott Hendrickson, Joleigh Honey, Barbara Kuehl, Travis
1 Integrated Math 1 Module 7 Honors Connecting Algebra and Geometry Ready, Set, Go! Homework Solutions Adapted from The Mathematics Vision Project: Scott Hendrickson, Joleigh Honey, Barbara Kuehl, Travis
MATH : EXAM 3 INFO/LOGISTICS/ADVICE
 MATH 3342-004: EXAM 3 INFO/LOGISTICS/ADVICE INFO: WHEN: Friday (04/22) at 10:00am DURATION: 50 mins PROBLEM COUNT: Appropriate for a 50-min exam BONUS COUNT: At least one TOPICS CANDIDATE FOR THE EXAM:
MATH 3342-004: EXAM 3 INFO/LOGISTICS/ADVICE INFO: WHEN: Friday (04/22) at 10:00am DURATION: 50 mins PROBLEM COUNT: Appropriate for a 50-min exam BONUS COUNT: At least one TOPICS CANDIDATE FOR THE EXAM:
Name Date Types of Graphs and Creating Graphs Notes
 Name Date Types of Graphs and Creating Graphs Notes Graphs are helpful visual representations of data. Different graphs display data in different ways. Some graphs show individual data, but many do not.
Name Date Types of Graphs and Creating Graphs Notes Graphs are helpful visual representations of data. Different graphs display data in different ways. Some graphs show individual data, but many do not.
Z-TEST / Z-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses about. µ when the population standard deviation is unknown
 Z-TEST / Z-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses about µ when the population standard deviation is known and population distribution is normal or sample size is large T-TEST / T-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses
Z-TEST / Z-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses about µ when the population standard deviation is known and population distribution is normal or sample size is large T-TEST / T-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses
M7D1.a: Formulate questions and collect data from a census of at least 30 objects and from samples of varying sizes.
 M7D1.a: Formulate questions and collect data from a census of at least 30 objects and from samples of varying sizes. Population: Census: Biased: Sample: The entire group of objects or individuals considered
M7D1.a: Formulate questions and collect data from a census of at least 30 objects and from samples of varying sizes. Population: Census: Biased: Sample: The entire group of objects or individuals considered
HS Mathematics Item Specification C1 TP
 Task Model 1 Multiple Choice, single correct response S-ID.A.1 Represent data with plots on the real number line (dot plots, histograms, and box plots). 1. The student will be able to represent data on
Task Model 1 Multiple Choice, single correct response S-ID.A.1 Represent data with plots on the real number line (dot plots, histograms, and box plots). 1. The student will be able to represent data on
Distributions of random variables
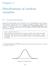 Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
DATA VISUALIZATION Prepare the data for visualization Data presentation architecture (DPA) is a skill-set that seeks to identify, locate, manipulate,
 DATA VISUALIZATION Prepare the data for visualization Data presentation architecture (DPA) is a skill-set that seeks to identify, locate, manipulate, format and present data in such a way as to optimally
DATA VISUALIZATION Prepare the data for visualization Data presentation architecture (DPA) is a skill-set that seeks to identify, locate, manipulate, format and present data in such a way as to optimally
AMC FearFest 2015 Schedule
 Monday, October 19, 2015 AMC FearFest 2015 Schedule 9:00am Halloween 11:00am Halloween II 1:00pm Halloween 4: The Return of Michael Myers 3:00pm Halloween 5: The Revenge of Michael Myers 5:00pm Halloween
Monday, October 19, 2015 AMC FearFest 2015 Schedule 9:00am Halloween 11:00am Halloween II 1:00pm Halloween 4: The Return of Michael Myers 3:00pm Halloween 5: The Revenge of Michael Myers 5:00pm Halloween
Continuous Improvement Toolkit. Normal Distribution. Continuous Improvement Toolkit.
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Normal Distribution The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Normal Distribution The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
Numerical Summaries of Data Section 14.3
 MATH 11008: Numerical Summaries of Data Section 14.3 MEAN mean: The mean (or average) of a set of numbers is computed by determining the sum of all the numbers and dividing by the total number of observations.
MATH 11008: Numerical Summaries of Data Section 14.3 MEAN mean: The mean (or average) of a set of numbers is computed by determining the sum of all the numbers and dividing by the total number of observations.
INFO Wednesday, September 14, 2016
 INFO 1301 Wednesday, September 14, 2016 Topics to be covered Last class we spoke about the middle (central tendency) of a data set. Today we talk about variability in a data set. Variability of Data Variance
INFO 1301 Wednesday, September 14, 2016 Topics to be covered Last class we spoke about the middle (central tendency) of a data set. Today we talk about variability in a data set. Variability of Data Variance
The Normal Distribution & z-scores
 & z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
& z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
Box Plots. OpenStax College
 Connexions module: m46920 1 Box Plots OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Box plots (also called box-and-whisker
Connexions module: m46920 1 Box Plots OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Box plots (also called box-and-whisker
Understanding Statistical Questions
 Unit 6: Statistics Standards, Checklist and Concept Map Common Core Georgia Performance Standards (CCGPS): MCC6.SP.1: Recognize a statistical question as one that anticipates variability in the data related
Unit 6: Statistics Standards, Checklist and Concept Map Common Core Georgia Performance Standards (CCGPS): MCC6.SP.1: Recognize a statistical question as one that anticipates variability in the data related
Minitab Guide for MA330
 Minitab Guide for MA330 The purpose of this guide is to show you how to use the Minitab statistical software to carry out the statistical procedures discussed in your textbook. The examples usually are
Minitab Guide for MA330 The purpose of this guide is to show you how to use the Minitab statistical software to carry out the statistical procedures discussed in your textbook. The examples usually are
The Normal Distribution. John McGready, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 The Normal Distribution John McGready, PhD Johns Hopkins University General Properties of The Normal Distribution The material in this video is subject to the copyright of the owners of the material and
The Normal Distribution John McGready, PhD Johns Hopkins University General Properties of The Normal Distribution The material in this video is subject to the copyright of the owners of the material and
More Summer Program t-shirts
 ICPSR Blalock Lectures, 2003 Bootstrap Resampling Robert Stine Lecture 2 Exploring the Bootstrap Questions from Lecture 1 Review of ideas, notes from Lecture 1 - sample-to-sample variation - resampling
ICPSR Blalock Lectures, 2003 Bootstrap Resampling Robert Stine Lecture 2 Exploring the Bootstrap Questions from Lecture 1 Review of ideas, notes from Lecture 1 - sample-to-sample variation - resampling
Using the Dashboard. The dashboard allows you to see, and drill into, important summary information about the health of your reliability solution.
 Using the Dashboard The dashboard allows you to see, and drill into, important summary information about the health of your reliability solution. Opening the Dashboard: You can see part of the dashboard
Using the Dashboard The dashboard allows you to see, and drill into, important summary information about the health of your reliability solution. Opening the Dashboard: You can see part of the dashboard
DM4U_B P 1 W EEK 1 T UNIT
 MDM4U_B Per 1 WEEK 1 Tuesday Feb 3 2015 UNIT 1: Organizing Data for Analysis 1) THERE ARE DIFFERENT TYPES OF DATA THAT CAN BE SURVEYED. 2) DATA CAN BE EFFECTIVELY DISPLAYED IN APPROPRIATE TABLES AND GRAPHS.
MDM4U_B Per 1 WEEK 1 Tuesday Feb 3 2015 UNIT 1: Organizing Data for Analysis 1) THERE ARE DIFFERENT TYPES OF DATA THAT CAN BE SURVEYED. 2) DATA CAN BE EFFECTIVELY DISPLAYED IN APPROPRIATE TABLES AND GRAPHS.
STA Rev. F Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives (Cont.) Module 3 Descriptive Measures
 STA 2023 Module 3 Descriptive Measures Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Explain the purpose of a measure of center. 2. Obtain and interpret the mean, median, and
STA 2023 Module 3 Descriptive Measures Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Explain the purpose of a measure of center. 2. Obtain and interpret the mean, median, and
Chapter 3. Descriptive Measures. Slide 3-2. Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 3 Descriptive Measures Slide 3-2 Section 3.1 Measures of Center Slide 3-3 Definition 3.1 Mean of a Data Set The mean of a data set is the sum of the observations divided by the number of observations.
Chapter 3 Descriptive Measures Slide 3-2 Section 3.1 Measures of Center Slide 3-3 Definition 3.1 Mean of a Data Set The mean of a data set is the sum of the observations divided by the number of observations.
Prepare a stem-and-leaf graph for the following data. In your final display, you should arrange the leaves for each stem in increasing order.
 Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Middle Years Data Analysis Display Methods
 Middle Years Data Analysis Display Methods Double Bar Graph A double bar graph is an extension of a single bar graph. Any bar graph involves categories and counts of the number of people or things (frequency)
Middle Years Data Analysis Display Methods Double Bar Graph A double bar graph is an extension of a single bar graph. Any bar graph involves categories and counts of the number of people or things (frequency)
Statistics with a Hemacytometer
 Statistics with a Hemacytometer Overview This exercise incorporates several different statistical analyses. Data gathered from cell counts with a hemacytometer is used to explore frequency distributions
Statistics with a Hemacytometer Overview This exercise incorporates several different statistical analyses. Data gathered from cell counts with a hemacytometer is used to explore frequency distributions
Assignments Fill out this form to do the assignments or see your scores.
 Assignments Assignment schedule General instructions for online assignments Troubleshooting technical problems Fill out this form to do the assignments or see your scores. Login Course: Statistics W21,
Assignments Assignment schedule General instructions for online assignments Troubleshooting technical problems Fill out this form to do the assignments or see your scores. Login Course: Statistics W21,
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
 CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is how the data is spread or distributed over the range of the data values. This is one of
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is how the data is spread or distributed over the range of the data values. This is one of
Introductory Applied Statistics: A Variable Approach TI Manual
 Introductory Applied Statistics: A Variable Approach TI Manual John Gabrosek and Paul Stephenson Department of Statistics Grand Valley State University Allendale, MI USA Version 1.1 August 2014 2 Copyright
Introductory Applied Statistics: A Variable Approach TI Manual John Gabrosek and Paul Stephenson Department of Statistics Grand Valley State University Allendale, MI USA Version 1.1 August 2014 2 Copyright

![1. Select[] is used to select items meeting a specified criterion. 1. Select[] is used to select items meeting a specified criterion.](/thumbs/94/118473170.jpg)