The Normal Distribution & z-scores
|
|
|
- Loren Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 & z-scores
2 Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we know something about the probability that one of those events is likely to occur
3 Distributions and Probabilities Whose course would you rather take? Professor A Professor B C/C+ 30% D 8% F 5% A 19% B/B+ 38% D 4% C/C+ 22% F 7% B/B+ 35% A 32%
4 Distributions and Probabilities Whose course would you rather take? Professor A Professor B D 4% F 5% D 8% C 30% B 38% A 19% F 7% C 22% B 35% A 32%
5 A Note on Continuous Versus Discrete Distributions Y-axis represents density Probability density function Probability of any exact value is zero Y-axis represents probability Probability mass function Probability of exact values can be positive
6 The Normal Distribution Okay, distributions can be useful. But why should we care about this particular distribution? Most prominent distribution in statistics Normally distributed data Computational convenience Normality of sample means
7 Normally Distributed Data Many of the dependent variables that we deal with are approximately normally distributed in the population Originally used to describe errors in astronomical measurements Examples of normally distributed data Height Weight Normalized test scores Speed of cars on Route 18 Anything averaged across a large number of observations
8 Normally Distributed Data
9 Computational Convenience Many statistics related to the normal distribution, along with their sampling distributions are analytically tractable If we can assume that a variable is at least approximately normally distributed, then we can use standard techniques (i.e., those that make up most of this book) to make inferences about values of that variable
10 Normality of Sample Means Regardless of the distribution of the underlying variable (with limited exceptions), the distribution of sample means approaches normality as the sample size n grows. We will discuss this in greater detail later in the next lecture when we cover the central limit theorem. Generally, this means that the sampling distribution of the mean can be approximated by a normal distribution
11 The Standard Normal Distribution The Normal Distribution σ 2.1% 13.6% 34.1% 34.1% 13.6% 2.1%
12 Standardizing Normal Variables By itself, a raw score or x value provides very little information about how that particular score compares with other values in the distribution. A score of x = 53, for example, may be a relatively low score, or an average score, or an extremely high score depending on the mean and standard deviation for the distribution from which the score was obtained. If the raw score is transformed into a z-score, however, the value of the z-score tells you where the score is located relative to all the other scores in the distribution.
13 Standardizing Normal Variables To transform an x value into a z-score: z x To transform a z-score into an x value: x z
14 Standardizing Normal Variables In addition to knowing the basic definition of a z-score and the formula for a z-score, it is useful to be able to visualize z- scores as locations in a distribution. Remember, z = 0 is in the center (at the mean), and the extreme tails correspond to z-scores of approximately 2.00 on the left and on the right. 95.4% of the distribution is contained between z = -2 and z = % of the distribution is contained between z = -3 and z = 3
15 Standardizing Normal Distributions The Normal Distribution z x : x :
16 Standard Normal Tables (z-tables) Another important advantage of standardizing distributions is that it allows us to compute and use a single probability table for all normal distributions The Normal Distribution
17 Standard Normal Tables (z-tables) Upper-Tail Probabilities The Normal Distribution z
18 Standard Normal Tables: Meaning The Normal Distribution
19 Standard Normal Tables: Meaning The Normal Distribution
20 Standard Normal Tables: Meaning The Normal Distribution
21 Standard Normal Tables: Meaning The Normal Distribution
22 Standard Normal Tables: Meaning The Normal Distribution
23 Using z-tables Area under curve sums to 1 The normal distribution is symmetrical E.g., P(Z < -z) = P(Z > +z) (non-overlapping) areas sum E.g., P(0.0 < Z < 1.0) = P(Z > 0.0) P(Z > 1.0) Note: In this slide and in the rest of this lecture, I m using Z (capital) to indicate a randomly selected value of a standard normal variable, and z (lower-case) to indicate a particular value of that variable.
24 What is the probability that a randomly selected woman is taller than 5 6 (66 inches)?
25 Using z-tables to Compute Interval Probabilities Step 1: standardize value (i.e., compute z-score) z(66) Step 2: Look up upper-tail area (66) 0.73 P Z z P Z
26 Standard Normal Tables (z-tables) Upper-Tail Probabilities The Normal Distribution z
27 Using z-tables to Compute Interval Probabilities Step 1: standardize value (i.e., compute z-score) z(66) Step 2: Look up upper-tail area P Z
28 What is the probability that a randomly selected woman is between 64 and 68 inches tall?
29 Using z-tables to Compute Interval Probabilities Step 1: standardize values (i.e., compute z-scores) z(64) z(68) Step 2: Look up upper-tail area(s) P Z z(64) P Z z(68) Step 3: Compute difference (64) (68) P Z P Z z P Z z
30 Standard Normal Tables (z-tables) Upper-Tail Probabilities The Normal Distribution z
31 Using z-tables to Compute Interval Probabilities Step 1: standardize values (i.e., compute z-scores) z(64) z(68) Step 2: Look up upper-tail area(s) P Z P Z Step 3: Compute difference P 0.0 Z 1.45 P Z 0.0 P Z
32 What is the probability that a randomly selected woman is between 62 and 66 inches tall?
33 Using z-tables to Compute Interval Probabilities Step 1: standardize values (i.e., compute z-scores) z(62) z(66) Step 2: Look up tail area(s) P Z 0.73 P Z 0.73 Step 3: Compute difference P 0.73 Z 0.73
34 Standard Normal Tables (z-tables) Upper-Tail Probabilities The Normal Distribution z
35 Using z-tables to Compute Interval Probabilities Step 1: standardize values (i.e., compute z-scores) z(62) z(66) Step 2: Look up tail area(s) P Z P Z 0.73 P( Z 0.73) Step 3: Compute difference P 0.73 Z P Z 0.73 P( Z 0.73) 1 2(0.2327)
36 What is the probability that a randomly selected woman is between 60 and 66 inches tall?
37 Using z-tables to Compute Interval Probabilities Step 1: standardize values (i.e., compute z-scores) z(60) z(66) Step 2: Look up tail area(s) P Z 0.73 P Z 1.45 Step 3: Compute difference P 1.45 Z 0.73
38 Standard Normal Tables (z-tables) Upper-Tail Probabilities The Normal Distribution z
39 Using z-tables to Compute Interval Probabilities Step 1: standardize values (i.e., compute z-scores) z(60) z(66) Step 2: Look up tail area(s) P Z P Z 1.45 P( Z 1.45) Step 3: Compute difference P 1.45 Z P Z 0.73 P( Z 1.45)
40 What height would place a woman at the 95 th Percentile (i.e., taller than 95% of women)?
41 Using z-tables to Compute Probable Intervals Step 1: look up z-score corresponding to 95 th percentile (Hint: p in tail = 100%- percentile rank) z 0.05 P Z z? Step 2: (inverse) transform z-score to height x z 1.645(2.75)
42 Standard Normal Tables (z-tables) Upper-Tail Probabilities The Normal Distribution z
43 Using z-tables to Compute Probable Intervals Step 1: look up z-score corresponding to 95 th percentile (Hint: p in tail = 100%- percentile rank) z 0.05 P Z z 1.45 Step 2: (inverse) transform z-score to height x z 1.645(2.75)
44 Computing Probable Intervals 95% 2.5% 2.5%
45 Standard Normal Tables (z-tables) Upper-Tail Probabilities The Normal Distribution z
46 Using z-tables to Compute Probable Intervals Step 1: look up z-score corresponding to 2.5% (0.0250) z P Z z z 1.96 z 1.96 Step 2: transform z-scores to heights x x z z
The Normal Distribution & z-scores
 & z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
& z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
The Normal Distribution & z-scores
 & z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
& z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
Ch6: The Normal Distribution
 Ch6: The Normal Distribution Introduction Review: A continuous random variable can assume any value between two endpoints. Many continuous random variables have an approximately normal distribution, which
Ch6: The Normal Distribution Introduction Review: A continuous random variable can assume any value between two endpoints. Many continuous random variables have an approximately normal distribution, which
Lecture Slides. Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition. by Mario F. Triola. and the Triola Statistics Series. Section 6.2-1
 Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Section 6.2-1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard
Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Section 6.2-1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard
Prepare a stem-and-leaf graph for the following data. In your final display, you should arrange the leaves for each stem in increasing order.
 Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Frequency Distributions
 Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe
 Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe Section 1.3 Homework Answers Assignment 5 1.80 If you ask a computer to generate "random numbers between 0 and 1, you uniform will
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe Section 1.3 Homework Answers Assignment 5 1.80 If you ask a computer to generate "random numbers between 0 and 1, you uniform will
Density Curve (p52) Density curve is a curve that - is always on or above the horizontal axis.
 1.3 Density curves p50 Some times the overall pattern of a large number of observations is so regular that we can describe it by a smooth curve. It is easier to work with a smooth curve, because the histogram
1.3 Density curves p50 Some times the overall pattern of a large number of observations is so regular that we can describe it by a smooth curve. It is easier to work with a smooth curve, because the histogram
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers
 IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
Normal Distribution. 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution
 Normal Distribution 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution 1 /20 Homework Read Sec 6-4. Discussion question p316 Do p316 probs 1-10, 16-22, 31, 32, 34-37, 39 2 /20 3 /20 Objective Find the probabilities
Normal Distribution 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution 1 /20 Homework Read Sec 6-4. Discussion question p316 Do p316 probs 1-10, 16-22, 31, 32, 34-37, 39 2 /20 3 /20 Objective Find the probabilities
Math 14 Lecture Notes Ch. 6.1
 6.1 Normal Distribution What is normal? a 10-year old boy that is 4' tall? 5' tall? 6' tall? a 25-year old woman with a shoe size of 5? 7? 9? an adult alligator that weighs 200 pounds? 500 pounds? 800
6.1 Normal Distribution What is normal? a 10-year old boy that is 4' tall? 5' tall? 6' tall? a 25-year old woman with a shoe size of 5? 7? 9? an adult alligator that weighs 200 pounds? 500 pounds? 800
Confidence Intervals: Estimators
 Confidence Intervals: Estimators Point Estimate: a specific value at estimates a parameter e.g., best estimator of e population mean ( ) is a sample mean problem is at ere is no way to determine how close
Confidence Intervals: Estimators Point Estimate: a specific value at estimates a parameter e.g., best estimator of e population mean ( ) is a sample mean problem is at ere is no way to determine how close
MATH 1070 Introductory Statistics Lecture notes Descriptive Statistics and Graphical Representation
 MATH 1070 Introductory Statistics Lecture notes Descriptive Statistics and Graphical Representation Objectives: 1. Learn the meaning of descriptive versus inferential statistics 2. Identify bar graphs,
MATH 1070 Introductory Statistics Lecture notes Descriptive Statistics and Graphical Representation Objectives: 1. Learn the meaning of descriptive versus inferential statistics 2. Identify bar graphs,
6-1 THE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 6-1 THE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION The major focus of this chapter is the concept of a normal probability distribution, but we begin with a uniform distribution so that we can see the following two very
6-1 THE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION The major focus of this chapter is the concept of a normal probability distribution, but we begin with a uniform distribution so that we can see the following two very
23.2 Normal Distributions
 1_ Locker LESSON 23.2 Normal Distributions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: S-ID.4 Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate
1_ Locker LESSON 23.2 Normal Distributions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: S-ID.4 Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate
Sections 4.3 and 4.4
 Sections 4.3 and 4.4 Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 205: Elementary Statistics for the Biological and Life Sciences 1 / 32 4.3 Areas under normal densities Every
Sections 4.3 and 4.4 Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 205: Elementary Statistics for the Biological and Life Sciences 1 / 32 4.3 Areas under normal densities Every
Math 120 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency
 Math 1 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency lowest value + highest value midrange The word average: is very ambiguous and can actually refer to the mean,
Math 1 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency lowest value + highest value midrange The word average: is very ambiguous and can actually refer to the mean,
2) In the formula for the Confidence Interval for the Mean, if the Confidence Coefficient, z(α/2) = 1.65, what is the Confidence Level?
 Pg.431 1)The mean of the sampling distribution of means is equal to the mean of the population. T-F, and why or why not? True. If you were to take every possible sample from the population, and calculate
Pg.431 1)The mean of the sampling distribution of means is equal to the mean of the population. T-F, and why or why not? True. If you were to take every possible sample from the population, and calculate
appstats6.notebook September 27, 2016
 Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model Objectives: 1.Students will calculate and interpret z scores. 2.Students will compare/contrast values from different distributions using
Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model Objectives: 1.Students will calculate and interpret z scores. 2.Students will compare/contrast values from different distributions using
Chapter 5: The standard deviation as a ruler and the normal model p131
 Chapter 5: The standard deviation as a ruler and the normal model p131 Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12? Is it fair to say: 67 is
Chapter 5: The standard deviation as a ruler and the normal model p131 Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12? Is it fair to say: 67 is
Probability and Statistics. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Probability and Statistics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 14.6 Descriptive Statistics (Graphical) Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Data in Categories Histograms
Probability and Statistics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 14.6 Descriptive Statistics (Graphical) Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Data in Categories Histograms
The Normal Distribution
 The Normal Distribution Lecture 20 Section 6.3.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 28, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, 2011 1 / 41 Outline
The Normal Distribution Lecture 20 Section 6.3.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 28, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, 2011 1 / 41 Outline
CHAPTER 6. The Normal Probability Distribution
 The Normal Probability Distribution CHAPTER 6 The normal probability distribution is the most widely used distribution in statistics as many statistical procedures are built around it. The central limit
The Normal Probability Distribution CHAPTER 6 The normal probability distribution is the most widely used distribution in statistics as many statistical procedures are built around it. The central limit
Measures of Position
 Measures of Position In this section, we will learn to use fractiles. Fractiles are numbers that partition, or divide, an ordered data set into equal parts (each part has the same number of data entries).
Measures of Position In this section, we will learn to use fractiles. Fractiles are numbers that partition, or divide, an ordered data set into equal parts (each part has the same number of data entries).
Chapter 6: Continuous Random Variables & the Normal Distribution. 6.1 Continuous Probability Distribution
 Chapter 6: Continuous Random Variables & the Normal Distribution 6.1 Continuous Probability Distribution and the Normal Probability Distribution 6.2 Standardizing a Normal Distribution 6.3 Applications
Chapter 6: Continuous Random Variables & the Normal Distribution 6.1 Continuous Probability Distribution and the Normal Probability Distribution 6.2 Standardizing a Normal Distribution 6.3 Applications
Distributions of random variables
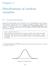 Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Unit 8: Normal Calculations
 Unit 8: Normal Calculations Prerequisites This unit requires familiarity with basic facts about normal distributions, which are covered in Unit 7, Normal Curves. In addition, students need some background
Unit 8: Normal Calculations Prerequisites This unit requires familiarity with basic facts about normal distributions, which are covered in Unit 7, Normal Curves. In addition, students need some background
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
 CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is how the data is spread or distributed over the range of the data values. This is one of
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is how the data is spread or distributed over the range of the data values. This is one of
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers HW 34. Sketch
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers HW 34. Sketch
AP Statistics. Study Guide
 Measuring Relative Standing Standardized Values and z-scores AP Statistics Percentiles Rank the data lowest to highest. Counting up from the lowest value to the select data point we discover the percentile
Measuring Relative Standing Standardized Values and z-scores AP Statistics Percentiles Rank the data lowest to highest. Counting up from the lowest value to the select data point we discover the percentile
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture:
 Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution
 Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution 2.1 Density Curves and the Normal Distributions 2.2 Standard Normal Calculations 1 2 Histogram for Strength of Yarn Bobbins 15.60 16.10 16.60 17.10 17.60 18.10 18.60
Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution 2.1 Density Curves and the Normal Distributions 2.2 Standard Normal Calculations 1 2 Histogram for Strength of Yarn Bobbins 15.60 16.10 16.60 17.10 17.60 18.10 18.60
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture:
 Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Example 1. Find the x value that has a left tail area of.1131 P ( x <??? ) =. 1131
 Section 6 4D: Finding a Value of x with a Given tail arae Label the shaded area for both graphs. Find the value for z and label the z axis. Find the value for x for the given area under the normal curve
Section 6 4D: Finding a Value of x with a Given tail arae Label the shaded area for both graphs. Find the value for z and label the z axis. Find the value for x for the given area under the normal curve
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions
 Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
Ms Nurazrin Jupri. Frequency Distributions
 Frequency Distributions Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and simplify the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results.
Frequency Distributions Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and simplify the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results.
Chapter 7 Assignment SOLUTIONS WOMEN: Plus, add your pulse rate to the histogram.
 Instructor: Linda C. Stephenson WOMEN: Plus, add your pulse rate to the histogram. Instructor: Linda C. Stephenson MEN: Plus, add your pulse rate to the histogram. 1a. For z = -1.17: P (below) = 0.1210
Instructor: Linda C. Stephenson WOMEN: Plus, add your pulse rate to the histogram. Instructor: Linda C. Stephenson MEN: Plus, add your pulse rate to the histogram. 1a. For z = -1.17: P (below) = 0.1210
Z-TEST / Z-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses about. µ when the population standard deviation is unknown
 Z-TEST / Z-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses about µ when the population standard deviation is known and population distribution is normal or sample size is large T-TEST / T-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses
Z-TEST / Z-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses about µ when the population standard deviation is known and population distribution is normal or sample size is large T-TEST / T-STATISTIC: used to test hypotheses
MAT 110 WORKSHOP. Updated Fall 2018
 MAT 110 WORKSHOP Updated Fall 2018 UNIT 3: STATISTICS Introduction Choosing a Sample Simple Random Sample: a set of individuals from the population chosen in a way that every individual has an equal chance
MAT 110 WORKSHOP Updated Fall 2018 UNIT 3: STATISTICS Introduction Choosing a Sample Simple Random Sample: a set of individuals from the population chosen in a way that every individual has an equal chance
CHAPTER 2: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Lecture Notes for Introductory Statistics 1. Daphne Skipper, Augusta University (2016)
 CHAPTER 2: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Lecture Notes for Introductory Statistics 1 Daphne Skipper, Augusta University (2016) 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is
CHAPTER 2: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Lecture Notes for Introductory Statistics 1 Daphne Skipper, Augusta University (2016) 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is
7.2. The Standard Normal Distribution
 7.2 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal The standard normal curve is the one with mean μ = 0 and standard deviation σ = 1 We have related the general normal random variable to the standard
7.2 The Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal The standard normal curve is the one with mean μ = 0 and standard deviation σ = 1 We have related the general normal random variable to the standard
Chapter 2: Frequency Distributions
 Chapter 2: Frequency Distributions Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction to Frequency Distributions 2.2 Frequency Distribution Tables Obtaining ΣX from a Frequency Distribution Table Proportions and Percentages
Chapter 2: Frequency Distributions Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction to Frequency Distributions 2.2 Frequency Distribution Tables Obtaining ΣX from a Frequency Distribution Table Proportions and Percentages
BIOL Gradation of a histogram (a) into the normal curve (b)
 (التوزيع الطبيعي ( Distribution Normal (Gaussian) One of the most important distributions in statistics is a continuous distribution called the normal distribution or Gaussian distribution. Consider the
(التوزيع الطبيعي ( Distribution Normal (Gaussian) One of the most important distributions in statistics is a continuous distribution called the normal distribution or Gaussian distribution. Consider the
MAT 142 College Mathematics. Module ST. Statistics. Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015
 MAT 142 College Mathematics Statistics Module ST Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015 2 Statistics Data Organization and Visualization Basic Terms. A population is the set of all objects under study, a sample
MAT 142 College Mathematics Statistics Module ST Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015 2 Statistics Data Organization and Visualization Basic Terms. A population is the set of all objects under study, a sample
The Normal Distribution
 Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution Continuous random variables are used to approximate probabilities where there are many possibilities or an infinite number of possibilities on a given trial. One of the
Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution Continuous random variables are used to approximate probabilities where there are many possibilities or an infinite number of possibilities on a given trial. One of the
Unit 5: Estimating with Confidence
 Unit 5: Estimating with Confidence Section 8.3 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Unit 5 Estimating with Confidence 8.1 8.2 8.3 Confidence Intervals: The Basics Estimating
Unit 5: Estimating with Confidence Section 8.3 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Unit 5 Estimating with Confidence 8.1 8.2 8.3 Confidence Intervals: The Basics Estimating
Learning Objectives. Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution. Continuous Random Variable
 Learning Objectives Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution 1. Understand characteristics about continuous random variables and probability distributions 2. Understand the uniform
Learning Objectives Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution 1. Understand characteristics about continuous random variables and probability distributions 2. Understand the uniform
Chapter 1. Looking at Data-Distribution
 Chapter 1. Looking at Data-Distribution Statistics is the scientific discipline that provides methods to draw right conclusions: 1)Collecting the data 2)Describing the data 3)Drawing the conclusions Raw
Chapter 1. Looking at Data-Distribution Statistics is the scientific discipline that provides methods to draw right conclusions: 1)Collecting the data 2)Describing the data 3)Drawing the conclusions Raw
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
Today s Topics. Percentile ranks and percentiles. Standardized scores. Using standardized scores to estimate percentiles
 Today s Topics Percentile ranks and percentiles Standardized scores Using standardized scores to estimate percentiles Using µ and σ x to learn about percentiles Percentiles, standardized scores, and the
Today s Topics Percentile ranks and percentiles Standardized scores Using standardized scores to estimate percentiles Using µ and σ x to learn about percentiles Percentiles, standardized scores, and the
Chapter 3 - Displaying and Summarizing Quantitative Data
 Chapter 3 - Displaying and Summarizing Quantitative Data 3.1 Graphs for Quantitative Data (LABEL GRAPHS) August 25, 2014 Histogram (p. 44) - Graph that uses bars to represent different frequencies or relative
Chapter 3 - Displaying and Summarizing Quantitative Data 3.1 Graphs for Quantitative Data (LABEL GRAPHS) August 25, 2014 Histogram (p. 44) - Graph that uses bars to represent different frequencies or relative
MAT 102 Introduction to Statistics Chapter 6. Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions and the Normal Distribution
 MAT 102 Introduction to Statistics Chapter 6 Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions and the Normal Distribution 6.2 Continuous Probability Distributions Characteristics of a Continuous Probability
MAT 102 Introduction to Statistics Chapter 6 Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions and the Normal Distribution 6.2 Continuous Probability Distributions Characteristics of a Continuous Probability
Chapter 7 Assignment SOLUTIONS WOMEN:
 SOLUTIONS WOMEN: MEN: 1a. For z -0.79: P (below) 0.2148 1b. For z 1.46: 0.9279 P(above) 1 0.9279 0.0721 1c. For z 1.23: 0.1093 For z 1.65: 0.9505 P(between) 0.9505 0.1093 0.8412 1d. For z 0.71: 0.2389
SOLUTIONS WOMEN: MEN: 1a. For z -0.79: P (below) 0.2148 1b. For z 1.46: 0.9279 P(above) 1 0.9279 0.0721 1c. For z 1.23: 0.1093 For z 1.65: 0.9505 P(between) 0.9505 0.1093 0.8412 1d. For z 0.71: 0.2389
STA Module 4 The Normal Distribution
 STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA /25/12. Module 4 The Normal Distribution. Learning Objectives. Let s Look at Some Examples of Normal Curves
 STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
How individual data points are positioned within a data set.
 Section 3.4 Measures of Position Percentiles How individual data points are positioned within a data set. P k is the value such that k% of a data set is less than or equal to P k. For example if we said
Section 3.4 Measures of Position Percentiles How individual data points are positioned within a data set. P k is the value such that k% of a data set is less than or equal to P k. For example if we said
Lecture 21 Section Fri, Oct 3, 2008
 Lecture 21 Section 6.3.1 Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 3, 2008 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 Exercise 6.15, page 378. A young woman needs a 15-ampere fuse for the electrical system in her apartment and has decided
Lecture 21 Section 6.3.1 Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 3, 2008 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 Exercise 6.15, page 378. A young woman needs a 15-ampere fuse for the electrical system in her apartment and has decided
Chapter 2 Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Data
 Slide 1 Chapter 2 Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Data Slide 2 2-1 Overview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Visualizing Data 2-4 Measures of Center 2-5 Measures of Variation 2-6 Measures of Relative
Slide 1 Chapter 2 Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Data Slide 2 2-1 Overview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Visualizing Data 2-4 Measures of Center 2-5 Measures of Variation 2-6 Measures of Relative
CHAPTER 2: Describing Location in a Distribution
 CHAPTER 2: Describing Location in a Distribution 2.1 Goals: 1. Compute and use z-scores given the mean and sd 2. Compute and use the p th percentile of an observation 3. Intro to density curves 4. More
CHAPTER 2: Describing Location in a Distribution 2.1 Goals: 1. Compute and use z-scores given the mean and sd 2. Compute and use the p th percentile of an observation 3. Intro to density curves 4. More
Normal Data ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning
 Normal Data ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning Histogram for Different Sample Sizes For a small sample, the choice of class (group) size dramatically affects how the histogram appears. Say we
Normal Data ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning Histogram for Different Sample Sizes For a small sample, the choice of class (group) size dramatically affects how the histogram appears. Say we
1. The Normal Distribution, continued
 Math 1125-Introductory Statistics Lecture 16 10/9/06 1. The Normal Distribution, continued Recall that the standard normal distribution is symmetric about z = 0, so the area to the right of zero is 0.5000.
Math 1125-Introductory Statistics Lecture 16 10/9/06 1. The Normal Distribution, continued Recall that the standard normal distribution is symmetric about z = 0, so the area to the right of zero is 0.5000.
+ Statistical Methods in
 9/4/013 Statistical Methods in Practice STA/MTH 379 Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Mathematics & Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Discovering Statistics
9/4/013 Statistical Methods in Practice STA/MTH 379 Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Mathematics & Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Discovering Statistics
Sampling Distribution Examples Sections 15.4, 15.5
 Sampling Distribution Examples Sections 15.4, 15.5 Lecture 27 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Mar 2, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)Sampling Distribution ExamplesSections 15.4,
Sampling Distribution Examples Sections 15.4, 15.5 Lecture 27 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Mar 2, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)Sampling Distribution ExamplesSections 15.4,
Downloaded from
 UNIT 2 WHAT IS STATISTICS? Researchers deal with a large amount of data and have to draw dependable conclusions on the basis of data collected for the purpose. Statistics help the researchers in making
UNIT 2 WHAT IS STATISTICS? Researchers deal with a large amount of data and have to draw dependable conclusions on the basis of data collected for the purpose. Statistics help the researchers in making
adjacent angles Two angles in a plane which share a common vertex and a common side, but do not overlap. Angles 1 and 2 are adjacent angles.
 Angle 1 Angle 2 Angles 1 and 2 are adjacent angles. Two angles in a plane which share a common vertex and a common side, but do not overlap. adjacent angles 2 5 8 11 This arithmetic sequence has a constant
Angle 1 Angle 2 Angles 1 and 2 are adjacent angles. Two angles in a plane which share a common vertex and a common side, but do not overlap. adjacent angles 2 5 8 11 This arithmetic sequence has a constant
Continuous Improvement Toolkit. Normal Distribution. Continuous Improvement Toolkit.
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Normal Distribution The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Normal Distribution The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
Data can be in the form of numbers, words, measurements, observations or even just descriptions of things.
 + What is Data? Data is a collection of facts. Data can be in the form of numbers, words, measurements, observations or even just descriptions of things. In most cases, data needs to be interpreted and
+ What is Data? Data is a collection of facts. Data can be in the form of numbers, words, measurements, observations or even just descriptions of things. In most cases, data needs to be interpreted and
Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary
 1 Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary Z-score: Is the distance of each data value from the mean in standard deviation Standardizes data values Standardization changes the mean and the standard deviation: o Z
1 Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary Z-score: Is the distance of each data value from the mean in standard deviation Standardizes data values Standardization changes the mean and the standard deviation: o Z
Sec 6.3. Bluman, Chapter 6 1
 Sec 6.3 Bluman, Chapter 6 1 Bluman, Chapter 6 2 Review: Find the z values; the graph is symmetrical. z = ±1. 96 z 0 z the total area of the shaded regions=5% Bluman, Chapter 6 3 Review: Find the z values;
Sec 6.3 Bluman, Chapter 6 1 Bluman, Chapter 6 2 Review: Find the z values; the graph is symmetrical. z = ±1. 96 z 0 z the total area of the shaded regions=5% Bluman, Chapter 6 3 Review: Find the z values;
Condence Intervals about a Single Parameter:
 Chapter 9 Condence Intervals about a Single Parameter: 9.1 About a Population Mean, known Denition 9.1.1 A point estimate of a parameter is the value of a statistic that estimates the value of the parameter.
Chapter 9 Condence Intervals about a Single Parameter: 9.1 About a Population Mean, known Denition 9.1.1 A point estimate of a parameter is the value of a statistic that estimates the value of the parameter.
The Normal Distribution. John McGready, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 The Normal Distribution John McGready, PhD Johns Hopkins University General Properties of The Normal Distribution The material in this video is subject to the copyright of the owners of the material and
The Normal Distribution John McGready, PhD Johns Hopkins University General Properties of The Normal Distribution The material in this video is subject to the copyright of the owners of the material and
Measures of Dispersion
 Measures of Dispersion 6-3 I Will... Find measures of dispersion of sets of data. Find standard deviation and analyze normal distribution. Day 1: Dispersion Vocabulary Measures of Variation (Dispersion
Measures of Dispersion 6-3 I Will... Find measures of dispersion of sets of data. Find standard deviation and analyze normal distribution. Day 1: Dispersion Vocabulary Measures of Variation (Dispersion
Exam 2 Review. 2. What the difference is between an equation and an expression?
 Exam 2 Review Chapter 1 Section1 Do You Know: 1. What does it mean to solve an equation? 2. What the difference is between an equation and an expression? 3. How to tell if an equation is linear? 4. How
Exam 2 Review Chapter 1 Section1 Do You Know: 1. What does it mean to solve an equation? 2. What the difference is between an equation and an expression? 3. How to tell if an equation is linear? 4. How
Lab 4: Distributions of random variables
 Lab 4: Distributions of random variables In this lab we ll investigate the probability distribution that is most central to statistics: the normal distribution If we are confident that our data are nearly
Lab 4: Distributions of random variables In this lab we ll investigate the probability distribution that is most central to statistics: the normal distribution If we are confident that our data are nearly
Data Analysis & Probability
 Unit 5 Probability Distributions Name: Date: Hour: Section 7.2: The Standard Normal Distribution (Area under the curve) Notes By the end of this lesson, you will be able to Find the area under the standard
Unit 5 Probability Distributions Name: Date: Hour: Section 7.2: The Standard Normal Distribution (Area under the curve) Notes By the end of this lesson, you will be able to Find the area under the standard
Chapter 2 - Graphical Summaries of Data
 Chapter 2 - Graphical Summaries of Data Data recorded in the sequence in which they are collected and before they are processed or ranked are called raw data. Raw data is often difficult to make sense
Chapter 2 - Graphical Summaries of Data Data recorded in the sequence in which they are collected and before they are processed or ranked are called raw data. Raw data is often difficult to make sense
1 Overview of Statistics; Essential Vocabulary
 1 Overview of Statistics; Essential Vocabulary Statistics: the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data in order to make decisions Population and sample Population: the entire
1 Overview of Statistics; Essential Vocabulary Statistics: the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data in order to make decisions Population and sample Population: the entire
Student Learning Objectives
 Student Learning Objectives A. Understand that the overall shape of a distribution of a large number of observations can be summarized by a smooth curve called a density curve. B. Know that an area under
Student Learning Objectives A. Understand that the overall shape of a distribution of a large number of observations can be summarized by a smooth curve called a density curve. B. Know that an area under
MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY
 11.1 Find Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion STATISTICS Numerical values used to summarize and compare sets of data MEASURE OF CENTRAL TENDENCY A number used to represent the center or middle
11.1 Find Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion STATISTICS Numerical values used to summarize and compare sets of data MEASURE OF CENTRAL TENDENCY A number used to represent the center or middle
CHAPTER 8: INTEGRALS 8.1 REVIEW: APPROXIMATING INTEGRALS WITH RIEMANN SUMS IN 2-D
 CHAPTER 8: INTEGRALS 8.1 REVIEW: APPROXIMATING INTEGRALS WITH RIEMANN SUMS IN 2-D In two dimensions we have previously used Riemann sums to approximate ( ) following steps: with the 1. Divide the region
CHAPTER 8: INTEGRALS 8.1 REVIEW: APPROXIMATING INTEGRALS WITH RIEMANN SUMS IN 2-D In two dimensions we have previously used Riemann sums to approximate ( ) following steps: with the 1. Divide the region
Measures of Central Tendency
 Page of 6 Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean The sum of all data values divided by the number of
Page of 6 Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean The sum of all data values divided by the number of
Chapter 7 Assignment due Wednesday, May 24
 due Wednesday, May 24 Calculating Probabilities for Normal Distributions Overview What you re going to do in this assignment is use an online applet to calculate: probabilities associated with given -scores
due Wednesday, May 24 Calculating Probabilities for Normal Distributions Overview What you re going to do in this assignment is use an online applet to calculate: probabilities associated with given -scores
The Normal Curve. June 20, Bryan T. Karazsia, M.A.
 The Normal Curve June 20, 2006 Bryan T. Karazsia, M.A. Overview Hand-in Homework Why are distributions so important (particularly the normal distribution)? What is the normal distribution? Z-scores Using
The Normal Curve June 20, 2006 Bryan T. Karazsia, M.A. Overview Hand-in Homework Why are distributions so important (particularly the normal distribution)? What is the normal distribution? Z-scores Using
Chapter 5snow year.notebook March 15, 2018
 Chapter 5: Statistical Reasoning Section 5.1 Exploring Data Measures of central tendency (Mean, Median and Mode) attempt to describe a set of data by identifying the central position within a set of data
Chapter 5: Statistical Reasoning Section 5.1 Exploring Data Measures of central tendency (Mean, Median and Mode) attempt to describe a set of data by identifying the central position within a set of data
The standard deviation 1 n
 The standard deviation 1 SD = (xj x) n 2 The SD gives a measure of how the data are clustered around the mean. If the SD is larger, then the data are more spread out we are more likely to find data that
The standard deviation 1 SD = (xj x) n 2 The SD gives a measure of how the data are clustered around the mean. If the SD is larger, then the data are more spread out we are more likely to find data that
Unit 7 Statistics. AFM Mrs. Valentine. 7.1 Samples and Surveys
 Unit 7 Statistics AFM Mrs. Valentine 7.1 Samples and Surveys v Obj.: I will understand the different methods of sampling and studying data. I will be able to determine the type used in an example, and
Unit 7 Statistics AFM Mrs. Valentine 7.1 Samples and Surveys v Obj.: I will understand the different methods of sampling and studying data. I will be able to determine the type used in an example, and
Section 10.4 Normal Distributions
 Section 10.4 Normal Distributions Random Variables Suppose a bank is interested in improving its services to customers. The manager decides to begin by finding the amount of time tellers spend on each
Section 10.4 Normal Distributions Random Variables Suppose a bank is interested in improving its services to customers. The manager decides to begin by finding the amount of time tellers spend on each
IQR = number. summary: largest. = 2. Upper half: Q3 =
 Step by step box plot Height in centimeters of players on the 003 Women s Worldd Cup soccer team. 157 1611 163 163 164 165 165 165 168 168 168 170 170 170 171 173 173 175 180 180 Determine the 5 number
Step by step box plot Height in centimeters of players on the 003 Women s Worldd Cup soccer team. 157 1611 163 163 164 165 165 165 168 168 168 170 170 170 171 173 173 175 180 180 Determine the 5 number
4.3 The Normal Distribution
 4.3 The Normal Distribution Objectives. Definition of normal distribution. Standard normal distribution. Specialties of the graph of the standard normal distribution. Percentiles of the standard normal
4.3 The Normal Distribution Objectives. Definition of normal distribution. Standard normal distribution. Specialties of the graph of the standard normal distribution. Percentiles of the standard normal
Section 2.2 Normal Distributions. Normal Distributions
 Section 2.2 Normal Distributions Normal Distributions One particularly important class of density curves are the Normal curves, which describe Normal distributions. All Normal curves are symmetric, single-peaked,
Section 2.2 Normal Distributions Normal Distributions One particularly important class of density curves are the Normal curves, which describe Normal distributions. All Normal curves are symmetric, single-peaked,
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER STATISTICS 1 (The presentation of data) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 18.1 STATISTICS 1 (The presentation of data) by A.J.Hobson 18.1.1 Introduction 18.1.2 The tabulation of data 18.1.3 The graphical representation of data 18.1.4 Exercises 18.1.5
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 18.1 STATISTICS 1 (The presentation of data) by A.J.Hobson 18.1.1 Introduction 18.1.2 The tabulation of data 18.1.3 The graphical representation of data 18.1.4 Exercises 18.1.5
Learner Expectations UNIT 1: GRAPICAL AND NUMERIC REPRESENTATIONS OF DATA. Sept. Fathom Lab: Distributions and Best Methods of Display
 CURRICULUM MAP TEMPLATE Priority Standards = Approximately 70% Supporting Standards = Approximately 20% Additional Standards = Approximately 10% HONORS PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS Essential Questions &
CURRICULUM MAP TEMPLATE Priority Standards = Approximately 70% Supporting Standards = Approximately 20% Additional Standards = Approximately 10% HONORS PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS Essential Questions &
Measures of Central Tendency. A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set.
 Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean the sum of all data values divided by the number of values in
Measures of Central Tendency A measure of central tendency is a value used to represent the typical or average value in a data set. The Mean the sum of all data values divided by the number of values in
CHAPTER 3: Data Description
 CHAPTER 3: Data Description You ve tabulated and made pretty pictures. Now what numbers do you use to summarize your data? Ch3: Data Description Santorico Page 68 You ll find a link on our website to a
CHAPTER 3: Data Description You ve tabulated and made pretty pictures. Now what numbers do you use to summarize your data? Ch3: Data Description Santorico Page 68 You ll find a link on our website to a
Topic 5 - Joint distributions and the CLT
 Topic 5 - Joint distributions and the CLT Joint distributions Calculation of probabilities, mean and variance Expectations of functions based on joint distributions Central Limit Theorem Sampling distributions
Topic 5 - Joint distributions and the CLT Joint distributions Calculation of probabilities, mean and variance Expectations of functions based on joint distributions Central Limit Theorem Sampling distributions
(Refer Slide Time: 0:38)
 Digital Image Processing. Professor P. K. Biswas. Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Lecture-37. Histogram Implementation-II.
Digital Image Processing. Professor P. K. Biswas. Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Lecture-37. Histogram Implementation-II.
8: Statistics. Populations and Samples. Histograms and Frequency Polygons. Page 1 of 10
 8: Statistics Statistics: Method of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data, as well as drawing conclusions based on the data. Methodology is divided into two main areas. Descriptive Statistics:
8: Statistics Statistics: Method of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data, as well as drawing conclusions based on the data. Methodology is divided into two main areas. Descriptive Statistics:
