CHAPTER 6. The Normal Probability Distribution
|
|
|
- Pearl Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Normal Probability Distribution CHAPTER 6 The normal probability distribution is the most widely used distribution in statistics as many statistical procedures are built around it. The central limit theorem is probably the main reason that contributes to the importance of the normal distribution. It is essential for statistics students to learn how to use the normal probability distribution for solving applied problems. In this Chapter we are going to study the normal probability distribution using the appropriate functions in JMP. Also, we are going to perform simulations using a random function to generate a normally distributed random variable with a specified mean and standard deviation. We are going to perform a statistical experiment to demonstrate numerically the central limit theorem, and finally we are going to assess the normality of a given dataset. Class Exercises: Compute probabilities for the normal distribution Class example 1: According to the National Health Survey, heights of adult males are normally distributed with a mean of 69 and a standard deviation of 2.9. Compute the percentage of the population of adult males that falls between 64 and 76. First, let s open a new data table, Figure 6.1 then, right click at the heading of Column 1 Chapter 6 Page 1
2 Figure 6.2 click on the text box for Column Name and change the name to x, as follows: Figure 6.3 left click twice at the right side of the first column heading to open a new column Figure 6.4 you can save the file as Normal Dist (or anything you like), then right click over Column 2, select Column Info and change the name to P(x), then click over Column Properties and select formula, as shown below, Chapter 6 Page 2
3 Figure 6.5 a new window will open, then choose Probability from Functions (grouped) and select Normal Distribution as shown below Figure 6.6 then click twice over variable x, and click inside the parenthesis, then after the variable x, type,69,2.8 as shown below: Chapter 6 Page 3
4 Figure 6.7 click over Apply, you are going to see the following screen: Figure 6.8 then click over OK on this window and in the next window, next we want to compute the cumulative probability for x=64 and x = 76, let s input these numbers in the first column as shown below: Chapter 6 Page 4
5 Figure 6.9 the cumulative probabilities for these numbers are shown above. Thus, the probability that the height of one person is between 64 and 76 is (rounding to three digits): P(64<x<76) = = Class Exercise 2: We can also perform probability computations using a simulation, for example, let s generate 10,000 random numbers from a normal distribution with a mean of 69 and standard deviation of 2.9, to do this, let s open a new data table as follows, Figure 6.10 then, right click at the heading of Column 1 and click over Column Info Figure 6.11 Chapter 6 Page 5
6 click on the text box for Column Name and change the name to x, as follows: Figure 6.12 then click over Column Properties and select Formula, Figure 6.13 next, click over Edit Formula and select Random, then select Random Normal Chapter 6 Page 6
7 Figure 6.14 click inside the parenthesis, and input the numbers, 69 and 2.8 separated by a comma as follows: Figure 6.15 click over OK on this window and in the next window, then right click over the first column (below the red arrow) and select Add Rows, as below Chapter 6 Page 7
8 Figure 6.16 type at the dialog box and click OK Figure 6.17 at this point, you are going to see a sequence of randomly generated numbers from a normal distribution, Figure 6.18 Chapter 6 Page 8
9 you can draw a histogram using the Analyze menu and choosing the Distribution option, (see Chapter 3 for more details, this procedure is not shown here). You can check the shape of the distribution and take a look at the summary statistics that will be approximately equal to the requested mean and standard deviation (this activity is highly recommended, please ask you lab instructor if you do not know how to do it). Next, you need to sort the numbers from lowest to highest, by selecting Tables and Sort, then choose the variable x and click over By, you will see the next window Figure 6.19 click over OK, and you are going to see the sequence of random numbers ordered from lowest to highest as follows: Figure 6.20 Chapter 6 Page 9
10 computing the simulated probabilities is just a matter of counting the number of observations that match the requirements for this problem. To compute the requested probabilities, you need to count the number of observations that are less than 64, you can do it by scanning the ordered dataset, and looking at the index number on the left side of the screen, Figure 6.21 we can see at the Figure above that there are 349 observations less than 64, then this probability is computed as follows: P(x<64) = 349/10,0000 = Which is close to the computed probability using the normal distribution formula (see Figure 6.9) of , please do not forget that this is a numeric simulation and the results shown here are approximations to the true probabilities, but this result is close enough. Next, we need to find the probability that a man selected at random has a height less than 76, to do it we need to count the number of observations that are less than 76 as shown below: Chapter 6 Page 10
11 Figure 6.22 we found 9940 observations that are less than 76, thus the probability associated with that event is computed as follows =9,940/10,000 = 0.994, then the computation for the probability that one man selected at random is between 64 and 76 is as follows: P(64<x<76) = = 0.959, which is very close to the probability computed using the formulas, as you can see here, the simulation provided acceptable results! Class Exercise: The Central Limit Theorem Please go to the website: or search in your browser Rice virtual labs 1) Select Simulations and Demonstrations, and select Sampling Distribution Simulation 2) Select a normal distribution and choose a small sample size, then you can take 50,000 samples (or more) and look at the graph for the sampling distribution of the mean 3) Select a skewed distribution and choose a small sample size (n = 2 or 5), repeat the same procedure and see what happens. 4) Select a skewed distribution and choose the largest sample size available (n=25) and generate again the sampling distribution of the means 5) What are your conclusions? Did you notice any difference among the previous simulations? How can you relate your findings to the theory studied in class? Please remember the requirements for the application of the central limit theorem Chapter 6 Page 11
12 Now, let s do a simulation using JMP, we are going to generate an integer uniform distribution using the numbers 1 to 10 and we are going to obtain samples from this distribution First, let s open a new data table: Figure 6.23 then, right click over the heading of Column 1 and select Column Info, Figure 6.24 choose Formula from Column Properties and select Edit Formula Chapter 6 Page 12
13 Figure 6.25 select Random and Random Integer as follows, Figure 6.26 type 1 inside the red box, and hit enter, type, and 10, you should see the following window Chapter 6 Page 13
14 Figure 6.27 then hit enter, click OK on this window and click OK again in the next window. You are not going to see any changes at the data window as we still have to add some columns. To do this, right click over the cell below the red triangle and select Add Rows as follows Figure 6.28 type 200 inside the box Chapter 6 Page 14
15 Figure 6.29 you can see randomly generated numbers from 1 to 10, Figure 6.30 then left click twice over the space to the right of Column 1 and keep doing that until you generate 4 new columns as follows Figure 6.31 Chapter 6 Page 15
16 Figure 6.32 next, right click over the heading of Column 1 and select, Copy Column Properties then go over the heading of each new column and right click over the heading and select Paste Column Properties, repeat this procedure for each column Figure 6.33 you are going to see 5 columns with integer random numbers ranging from 1 to 10 Chapter 6 Page 16
17 Figure 6.34 now, let s compute the mean for each row, and put these results in column 6. Let s generate a new column by double clicking on the space right to the heading of Column 5. Then, right click over the heading of the new column and as we have done before. Select Column info, then select Formula from Column Properties and click over Edit Formula (as in Figures 6.1 to 6.4), then choose Statistical from Functions and select Mean from the menu as follows, Figure 6.35 then, click inside the parenthesis and click twice over Column 1 under Table Columns, type a comma and click over Column 2 and so on, until you add all columns until Column 5, your formula should look like this: Chapter 6 Page 17
18 Figure 6.36 click over OK on this window and in the next window, now you can see the mean computed for every row. The interesting thing about the new column is that it contains the sampling distribution of the means from a uniform probability distribution of integers ranging from 1 to 10. It will be interesting to take a look at the properties of the sampling distribution of the means that we got on column 6. With that purpose in mind, let s choose the Analyze menu and select Distribution, then click over Column 6 and next, click over Y, Columns, and click over OK. You are going to obtain a histogram for the sampling distribution of the means. You can see a bell shaped distribution with a mean of and a standard deviation of (results may vary). You can get a horizontal layout by choosing this option from the Display Options located under the second red triangle. Notice that the mean of your sampling distribution approximates the mean of the uniform distribution of the integers (the mean is 5.5). Figure 6.37 Chapter 6 Page 18
19 Also, you should observe that the sampling distribution of the means approximates a normal distribution even that the original population is uniform with integers ranging from 1 to 10 and we used a small sample size. The next step is to check your sampling distribution of the means for normality. Class Exercise: Assessing normality, Using results from the previous exercise we will assess normality of the sampling distribution of the means located on Column 6. Let s proceed as follows: click over the lower right triangle on the window shown in Figure 6.37 and select Continuous Fit, then select Normal Figure 6.38 This option overlaps a normal shape over the histogram as shown below, but probably this is not enough to assess normality, Figure 6.39 then select from the lower right triangle, and choose the option Normal Quantile Plot Chapter 6 Page 19
20 Figure 6.40 At this point, you can see a Q-Q plot (normal quantile plot) for the data in Column 6 as shown bellow Figure 6.41 we can see that the Q-Q plot follows a straight line pattern (more or less) and the dots are located within the curves described with red dots. There is no presence of an obvious pattern on the Q-Q plot, therefore we can accept normality of the sampling distribution of the means as predicted by the central limit theorem (even that in this case the sample size was small). Chapter 6 Page 20
21 Class Exercises: 1- Probability functions: Consider that women s heights are normally distributed with a mean of 63.6 and a standard deviation of 2.5 then, answer the following questions using the function Normal Distribution as in class example 1 (shown at the beginning of this Chapter). a. Find the probability that a woman selected at random is between the heights of 60 and 66. b. Find the probability that a woman selected at random is taller than Simulations: Solve the previous problems using a simulation (Generate a sequence of 10,000 normally distributed random numbers). Compare the simulated results with the computed probabilities from problem Central Limit Theorem: Generate 4 columns with 250 numbers in each column, using a random normal distribution with a mean of 63.6 and a standard deviation of 2.5 a. Compute the mean for each row on the fifth column b. Analyze the sampling distribution of the means on the fifth column, obtain summary statistics, describe the shape of the distribution and make comments c. Compare the population mean with the mean from the sample means at Column 6, Are they similar? d. Compare the standard deviation of Column 6, with the standard deviation of the population, how they are related? (Hint: take a look at the CLT) e. Discuss your findings with your classmates Team Assignment: Assessing Normality Use your random sample that you obtained from the file Small Town.xls and do the following: 1- Assess normality using a Q-Q plot (Normal Probability Plot) for all numeric variables 2- Write a report showing your findings: a. Show a histogram for each continuous variable b. Show a Q-Q plot (normal probability plot) for each numeric continuous variable c. Based on the previous graphs discuss if normality is acceptable for each variable, write briefly the reasons that support your conclusion d. Explore transformations for those variables that normality was not acceptable, that is: apply a mathematical function such as the logarithmic function or the square root to transform every value, and discuss if the results are different (better) than before e. Summarize your findings on a table, showing which variables can be considered normally distributed and which variables can t be considered normally distributed, specify if a transformation was applied to achieve normality 3- Choose a variable that is normally distributed, compute the mean and standard deviation and simulate the results an equivalent normal distribution. Simulate a normal random variable with these parameters, and find the probability that one observation is between 1.5 standard deviations below the mean and 1.2 standard deviations around the mean, compare the result obtained by simulation with the probability for a standard normal distribution P(-1.5< z <1.2) Chapter 6 Page 21
Prepare a stem-and-leaf graph for the following data. In your final display, you should arrange the leaves for each stem in increasing order.
 Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Distributions of Continuous Data
 C H A P T ER Distributions of Continuous Data New cars and trucks sold in the United States average about 28 highway miles per gallon (mpg) in 2010, up from about 24 mpg in 2004. Some of the improvement
C H A P T ER Distributions of Continuous Data New cars and trucks sold in the United States average about 28 highway miles per gallon (mpg) in 2010, up from about 24 mpg in 2004. Some of the improvement
Density Curve (p52) Density curve is a curve that - is always on or above the horizontal axis.
 1.3 Density curves p50 Some times the overall pattern of a large number of observations is so regular that we can describe it by a smooth curve. It is easier to work with a smooth curve, because the histogram
1.3 Density curves p50 Some times the overall pattern of a large number of observations is so regular that we can describe it by a smooth curve. It is easier to work with a smooth curve, because the histogram
Week 7: The normal distribution and sample means
 Week 7: The normal distribution and sample means Goals Visualize properties of the normal distribution. Learning the Tools Understand the Central Limit Theorem. Calculate sampling properties of sample
Week 7: The normal distribution and sample means Goals Visualize properties of the normal distribution. Learning the Tools Understand the Central Limit Theorem. Calculate sampling properties of sample
BIOL Gradation of a histogram (a) into the normal curve (b)
 (التوزيع الطبيعي ( Distribution Normal (Gaussian) One of the most important distributions in statistics is a continuous distribution called the normal distribution or Gaussian distribution. Consider the
(التوزيع الطبيعي ( Distribution Normal (Gaussian) One of the most important distributions in statistics is a continuous distribution called the normal distribution or Gaussian distribution. Consider the
Ch6: The Normal Distribution
 Ch6: The Normal Distribution Introduction Review: A continuous random variable can assume any value between two endpoints. Many continuous random variables have an approximately normal distribution, which
Ch6: The Normal Distribution Introduction Review: A continuous random variable can assume any value between two endpoints. Many continuous random variables have an approximately normal distribution, which
Organizing and Summarizing Data
 1 Organizing and Summarizing Data Key Definitions Frequency Distribution: This lists each category of data and how often they occur. : The percent of observations within the one of the categories. This
1 Organizing and Summarizing Data Key Definitions Frequency Distribution: This lists each category of data and how often they occur. : The percent of observations within the one of the categories. This
Chapter 3 Analyzing Normal Quantitative Data
 Chapter 3 Analyzing Normal Quantitative Data Introduction: In chapters 1 and 2, we focused on analyzing categorical data and exploring relationships between categorical data sets. We will now be doing
Chapter 3 Analyzing Normal Quantitative Data Introduction: In chapters 1 and 2, we focused on analyzing categorical data and exploring relationships between categorical data sets. We will now be doing
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
Lecture Slides. Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition. by Mario F. Triola. and the Triola Statistics Series. Section 6.2-1
 Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Section 6.2-1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard
Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Section 6.2-1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard
8: Statistics. Populations and Samples. Histograms and Frequency Polygons. Page 1 of 10
 8: Statistics Statistics: Method of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data, as well as drawing conclusions based on the data. Methodology is divided into two main areas. Descriptive Statistics:
8: Statistics Statistics: Method of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data, as well as drawing conclusions based on the data. Methodology is divided into two main areas. Descriptive Statistics:
MAT 142 College Mathematics. Module ST. Statistics. Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015
 MAT 142 College Mathematics Statistics Module ST Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015 2 Statistics Data Organization and Visualization Basic Terms. A population is the set of all objects under study, a sample
MAT 142 College Mathematics Statistics Module ST Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015 2 Statistics Data Organization and Visualization Basic Terms. A population is the set of all objects under study, a sample
23.2 Normal Distributions
 1_ Locker LESSON 23.2 Normal Distributions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: S-ID.4 Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate
1_ Locker LESSON 23.2 Normal Distributions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: S-ID.4 Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate
Chapter 6. The Normal Distribution. McGraw-Hill, Bluman, 7 th ed., Chapter 6 1
 Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution McGraw-Hill, Bluman, 7 th ed., Chapter 6 1 Bluman, Chapter 6 2 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Distributions 6-2 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-3
Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution McGraw-Hill, Bluman, 7 th ed., Chapter 6 1 Bluman, Chapter 6 2 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Distributions 6-2 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-3
Chapter 2 - Graphical Summaries of Data
 Chapter 2 - Graphical Summaries of Data Data recorded in the sequence in which they are collected and before they are processed or ranked are called raw data. Raw data is often difficult to make sense
Chapter 2 - Graphical Summaries of Data Data recorded in the sequence in which they are collected and before they are processed or ranked are called raw data. Raw data is often difficult to make sense
Math 120 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency
 Math 1 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency lowest value + highest value midrange The word average: is very ambiguous and can actually refer to the mean,
Math 1 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency lowest value + highest value midrange The word average: is very ambiguous and can actually refer to the mean,
Example how not to do it: JMP in a nutshell 1 HR, 17 Apr Subject Gender Condition Turn Reactiontime. A1 male filler
 JMP in a nutshell 1 HR, 17 Apr 2018 The software JMP Pro 14 is installed on the Macs of the Phonetics Institute. Private versions can be bought from
JMP in a nutshell 1 HR, 17 Apr 2018 The software JMP Pro 14 is installed on the Macs of the Phonetics Institute. Private versions can be bought from
Frequency Distributions
 Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
Measures of Dispersion
 Lesson 7.6 Objectives Find the variance of a set of data. Calculate standard deviation for a set of data. Read data from a normal curve. Estimate the area under a curve. Variance Measures of Dispersion
Lesson 7.6 Objectives Find the variance of a set of data. Calculate standard deviation for a set of data. Read data from a normal curve. Estimate the area under a curve. Variance Measures of Dispersion
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe
 Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe Section 1.3 Homework Answers Assignment 5 1.80 If you ask a computer to generate "random numbers between 0 and 1, you uniform will
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe Section 1.3 Homework Answers Assignment 5 1.80 If you ask a computer to generate "random numbers between 0 and 1, you uniform will
Applied Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences
 Applied Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences Chapter 2 Frequency Distributions and Graphs Chapter 2 Outline Organization of Data Simple Frequency Distributions Grouped Frequency Distributions Graphs
Applied Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences Chapter 2 Frequency Distributions and Graphs Chapter 2 Outline Organization of Data Simple Frequency Distributions Grouped Frequency Distributions Graphs
Overview. Frequency Distributions. Chapter 2 Summarizing & Graphing Data. Descriptive Statistics. Inferential Statistics. Frequency Distribution
 Chapter 2 Summarizing & Graphing Data Slide 1 Overview Descriptive Statistics Slide 2 A) Overview B) Frequency Distributions C) Visualizing Data summarize or describe the important characteristics of a
Chapter 2 Summarizing & Graphing Data Slide 1 Overview Descriptive Statistics Slide 2 A) Overview B) Frequency Distributions C) Visualizing Data summarize or describe the important characteristics of a
Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach
 i Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach Computer software help: SAS SAS (originally Statistical Analysis Software ) is a commercial statistical software package based on a powerful programming
i Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach Computer software help: SAS SAS (originally Statistical Analysis Software ) is a commercial statistical software package based on a powerful programming
CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA
 CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA This presentation is based on material and graphs from Open Stax and is copyrighted by Open Stax and Georgia Highlands College. OUTLINE 2.1 Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots),
CHAPTER 2: SAMPLING AND DATA This presentation is based on material and graphs from Open Stax and is copyrighted by Open Stax and Georgia Highlands College. OUTLINE 2.1 Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots),
6-1 THE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 6-1 THE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION The major focus of this chapter is the concept of a normal probability distribution, but we begin with a uniform distribution so that we can see the following two very
6-1 THE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION The major focus of this chapter is the concept of a normal probability distribution, but we begin with a uniform distribution so that we can see the following two very
Lecture Slides. Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition. by Mario F. Triola. and the Triola Statistics Series. Section 2.1- #
 Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data 2-1 Review and Preview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Histograms
Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data 2-1 Review and Preview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Histograms
Central Limit Theorem Sample Means
 Date Central Limit Theorem Sample Means Group Member Names: Part One Review of Types of Distributions Consider the three graphs below. Match the histograms with the distribution description. Write the
Date Central Limit Theorem Sample Means Group Member Names: Part One Review of Types of Distributions Consider the three graphs below. Match the histograms with the distribution description. Write the
The Normal Distribution & z-scores
 & z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
& z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
Measures of Position
 Measures of Position In this section, we will learn to use fractiles. Fractiles are numbers that partition, or divide, an ordered data set into equal parts (each part has the same number of data entries).
Measures of Position In this section, we will learn to use fractiles. Fractiles are numbers that partition, or divide, an ordered data set into equal parts (each part has the same number of data entries).
Female Brown Bear Weights
 CC-20 Normal Distributions Common Core State Standards MACC.92.S-ID..4 Use the mean and standard of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate population percentages. Recognize that
CC-20 Normal Distributions Common Core State Standards MACC.92.S-ID..4 Use the mean and standard of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate population percentages. Recognize that
Graphical Analysis of Data using Microsoft Excel [2016 Version]
![Graphical Analysis of Data using Microsoft Excel [2016 Version] Graphical Analysis of Data using Microsoft Excel [2016 Version]](/thumbs/72/67574169.jpg) Graphical Analysis of Data using Microsoft Excel [2016 Version] Introduction In several upcoming labs, a primary goal will be to determine the mathematical relationship between two variable physical parameters.
Graphical Analysis of Data using Microsoft Excel [2016 Version] Introduction In several upcoming labs, a primary goal will be to determine the mathematical relationship between two variable physical parameters.
Microscopic Measurement
 Microscopic Measurement Estimating Specimen Size : The area of the slide that you see when you look through a microscope is called the " field of view ". If you know the diameter of your field of view,
Microscopic Measurement Estimating Specimen Size : The area of the slide that you see when you look through a microscope is called the " field of view ". If you know the diameter of your field of view,
Basic Statistical Terms and Definitions
 I. Basics Basic Statistical Terms and Definitions Statistics is a collection of methods for planning experiments, and obtaining data. The data is then organized and summarized so that professionals can
I. Basics Basic Statistical Terms and Definitions Statistics is a collection of methods for planning experiments, and obtaining data. The data is then organized and summarized so that professionals can
Chapter 2 Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Data
 Slide 1 Chapter 2 Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Data Slide 2 2-1 Overview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Visualizing Data 2-4 Measures of Center 2-5 Measures of Variation 2-6 Measures of Relative
Slide 1 Chapter 2 Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Data Slide 2 2-1 Overview 2-2 Frequency Distributions 2-3 Visualizing Data 2-4 Measures of Center 2-5 Measures of Variation 2-6 Measures of Relative
The main issue is that the mean and standard deviations are not accurate and should not be used in the analysis. Then what statistics should we use?
 Chapter 4 Analyzing Skewed Quantitative Data Introduction: In chapter 3, we focused on analyzing bell shaped (normal) data, but many data sets are not bell shaped. How do we analyze quantitative data when
Chapter 4 Analyzing Skewed Quantitative Data Introduction: In chapter 3, we focused on analyzing bell shaped (normal) data, but many data sets are not bell shaped. How do we analyze quantitative data when
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers
 IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
MAT 110 WORKSHOP. Updated Fall 2018
 MAT 110 WORKSHOP Updated Fall 2018 UNIT 3: STATISTICS Introduction Choosing a Sample Simple Random Sample: a set of individuals from the population chosen in a way that every individual has an equal chance
MAT 110 WORKSHOP Updated Fall 2018 UNIT 3: STATISTICS Introduction Choosing a Sample Simple Random Sample: a set of individuals from the population chosen in a way that every individual has an equal chance
Spreadsheet View and Basic Statistics Concepts
 Spreadsheet View and Basic Statistics Concepts GeoGebra 3.2 Workshop Handout 9 Judith and Markus Hohenwarter www.geogebra.org Table of Contents 1. Introduction to GeoGebra s Spreadsheet View 2 2. Record
Spreadsheet View and Basic Statistics Concepts GeoGebra 3.2 Workshop Handout 9 Judith and Markus Hohenwarter www.geogebra.org Table of Contents 1. Introduction to GeoGebra s Spreadsheet View 2 2. Record
Chapter 2. Descriptive Statistics: Organizing, Displaying and Summarizing Data
 Chapter 2 Descriptive Statistics: Organizing, Displaying and Summarizing Data Objectives Student should be able to Organize data Tabulate data into frequency/relative frequency tables Display data graphically
Chapter 2 Descriptive Statistics: Organizing, Displaying and Summarizing Data Objectives Student should be able to Organize data Tabulate data into frequency/relative frequency tables Display data graphically
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions
 Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
Excel 2010 with XLSTAT
 Excel 2010 with XLSTAT J E N N I F E R LE W I S PR I E S T L E Y, PH.D. Introduction to Excel 2010 with XLSTAT The layout for Excel 2010 is slightly different from the layout for Excel 2007. However, with
Excel 2010 with XLSTAT J E N N I F E R LE W I S PR I E S T L E Y, PH.D. Introduction to Excel 2010 with XLSTAT The layout for Excel 2010 is slightly different from the layout for Excel 2007. However, with
courtesy 1
 1 The Normal Distribution 2 Topic Overview Introduction Normal Distributions Applications of the Normal Distribution The Central Limit Theorem 3 Objectives 1. Identify the properties of a normal distribution.
1 The Normal Distribution 2 Topic Overview Introduction Normal Distributions Applications of the Normal Distribution The Central Limit Theorem 3 Objectives 1. Identify the properties of a normal distribution.
Pre-Lab Excel Problem
 Pre-Lab Excel Problem Read and follow the instructions carefully! Below you are given a problem which you are to solve using Excel. If you have not used the Excel spreadsheet a limited tutorial is given
Pre-Lab Excel Problem Read and follow the instructions carefully! Below you are given a problem which you are to solve using Excel. If you have not used the Excel spreadsheet a limited tutorial is given
Continuous Improvement Toolkit. Normal Distribution. Continuous Improvement Toolkit.
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Normal Distribution The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Normal Distribution The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
Using Large Data Sets Workbook Version A (MEI)
 Using Large Data Sets Workbook Version A (MEI) 1 Index Key Skills Page 3 Becoming familiar with the dataset Page 3 Sorting and filtering the dataset Page 4 Producing a table of summary statistics with
Using Large Data Sets Workbook Version A (MEI) 1 Index Key Skills Page 3 Becoming familiar with the dataset Page 3 Sorting and filtering the dataset Page 4 Producing a table of summary statistics with
Excel Functions & Tables
 Excel Functions & Tables Winter 2012 Winter 2012 CS130 - Excel Functions & Tables 1 Review of Functions Quick Mathematics Review As it turns out, some of the most important mathematics for this course
Excel Functions & Tables Winter 2012 Winter 2012 CS130 - Excel Functions & Tables 1 Review of Functions Quick Mathematics Review As it turns out, some of the most important mathematics for this course
Page 1. Graphical and Numerical Statistics
 TOPIC: Description Statistics In this tutorial, we show how to use MINITAB to produce descriptive statistics, both graphical and numerical, for an existing MINITAB dataset. The example data come from Exercise
TOPIC: Description Statistics In this tutorial, we show how to use MINITAB to produce descriptive statistics, both graphical and numerical, for an existing MINITAB dataset. The example data come from Exercise
Part I, Chapters 4 & 5. Data Tables and Data Analysis Statistics and Figures
 Part I, Chapters 4 & 5 Data Tables and Data Analysis Statistics and Figures Descriptive Statistics 1 Are data points clumped? (order variable / exp. variable) Concentrated around one value? Concentrated
Part I, Chapters 4 & 5 Data Tables and Data Analysis Statistics and Figures Descriptive Statistics 1 Are data points clumped? (order variable / exp. variable) Concentrated around one value? Concentrated
Fathom Dynamic Data TM Version 2 Specifications
 Data Sources Fathom Dynamic Data TM Version 2 Specifications Use data from one of the many sample documents that come with Fathom. Enter your own data by typing into a case table. Paste data from other
Data Sources Fathom Dynamic Data TM Version 2 Specifications Use data from one of the many sample documents that come with Fathom. Enter your own data by typing into a case table. Paste data from other
How individual data points are positioned within a data set.
 Section 3.4 Measures of Position Percentiles How individual data points are positioned within a data set. P k is the value such that k% of a data set is less than or equal to P k. For example if we said
Section 3.4 Measures of Position Percentiles How individual data points are positioned within a data set. P k is the value such that k% of a data set is less than or equal to P k. For example if we said
Activity: page 1/10 Introduction to Excel. Getting Started
 Activity: page 1/10 Introduction to Excel Excel is a computer spreadsheet program. Spreadsheets are convenient to use for entering and analyzing data. Although Excel has many capabilities for analyzing
Activity: page 1/10 Introduction to Excel Excel is a computer spreadsheet program. Spreadsheets are convenient to use for entering and analyzing data. Although Excel has many capabilities for analyzing
Statistics with a Hemacytometer
 Statistics with a Hemacytometer Overview This exercise incorporates several different statistical analyses. Data gathered from cell counts with a hemacytometer is used to explore frequency distributions
Statistics with a Hemacytometer Overview This exercise incorporates several different statistical analyses. Data gathered from cell counts with a hemacytometer is used to explore frequency distributions
LAB #2: SAMPLING, SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONS, AND THE CLT
 NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL LAB #2: SAMPLING, SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONS, AND THE CLT Statistics (OA3102) Lab #2: Sampling, Sampling Distributions, and the Central Limit Theorem Goal: Use R to demonstrate sampling
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL LAB #2: SAMPLING, SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONS, AND THE CLT Statistics (OA3102) Lab #2: Sampling, Sampling Distributions, and the Central Limit Theorem Goal: Use R to demonstrate sampling
Frequency Distributions and Descriptive Statistics in SPS
 230 Combs Building 859.622.3050 studentcomputing.eku.edu studentcomputing@eku.edu Frequency Distributions and Descriptive Statistics in SPSS In this tutorial, we re going to work through a sample problem
230 Combs Building 859.622.3050 studentcomputing.eku.edu studentcomputing@eku.edu Frequency Distributions and Descriptive Statistics in SPSS In this tutorial, we re going to work through a sample problem
= 3 + (5*4) + (1/2)*(4/2)^2.
 Physics 100 Lab 1: Use of a Spreadsheet to Analyze Data by Kenneth Hahn and Michael Goggin In this lab you will learn how to enter data into a spreadsheet and to manipulate the data in meaningful ways.
Physics 100 Lab 1: Use of a Spreadsheet to Analyze Data by Kenneth Hahn and Michael Goggin In this lab you will learn how to enter data into a spreadsheet and to manipulate the data in meaningful ways.
Excel Functions & Tables
 Excel Functions & Tables Fall 2014 Fall 2014 CS130 - Excel Functions & Tables 1 Review of Functions Quick Mathematics Review As it turns out, some of the most important mathematics for this course revolves
Excel Functions & Tables Fall 2014 Fall 2014 CS130 - Excel Functions & Tables 1 Review of Functions Quick Mathematics Review As it turns out, some of the most important mathematics for this course revolves
a. divided by the. 1) Always round!! a) Even if class width comes out to a, go up one.
 Probability and Statistics Chapter 2 Notes I Section 2-1 A Steps to Constructing Frequency Distributions 1 Determine number of (may be given to you) a Should be between and classes 2 Find the Range a The
Probability and Statistics Chapter 2 Notes I Section 2-1 A Steps to Constructing Frequency Distributions 1 Determine number of (may be given to you) a Should be between and classes 2 Find the Range a The
Chapter 12: Quadratic and Cubic Graphs
 Chapter 12: Quadratic and Cubic Graphs Section 12.1 Quadratic Graphs x 2 + 2 a 2 + 2a - 6 r r 2 x 2 5x + 8 2y 2 + 9y + 2 All the above equations contain a squared number. They are therefore called quadratic
Chapter 12: Quadratic and Cubic Graphs Section 12.1 Quadratic Graphs x 2 + 2 a 2 + 2a - 6 r r 2 x 2 5x + 8 2y 2 + 9y + 2 All the above equations contain a squared number. They are therefore called quadratic
0 Graphical Analysis Use of Excel
 Lab 0 Graphical Analysis Use of Excel What You Need To Know: This lab is to familiarize you with the graphing ability of excels. You will be plotting data set, curve fitting and using error bars on the
Lab 0 Graphical Analysis Use of Excel What You Need To Know: This lab is to familiarize you with the graphing ability of excels. You will be plotting data set, curve fitting and using error bars on the
Normal Distribution. 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution
 Normal Distribution 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution 1 /20 Homework Read Sec 6-4. Discussion question p316 Do p316 probs 1-10, 16-22, 31, 32, 34-37, 39 2 /20 3 /20 Objective Find the probabilities
Normal Distribution 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution 1 /20 Homework Read Sec 6-4. Discussion question p316 Do p316 probs 1-10, 16-22, 31, 32, 34-37, 39 2 /20 3 /20 Objective Find the probabilities
Please consider the environment before printing this tutorial. Printing is usually a waste.
 Ortiz 1 ESCI 1101 Excel Tutorial Fall 2011 Please consider the environment before printing this tutorial. Printing is usually a waste. Many times when doing research, the graphical representation of analyzed
Ortiz 1 ESCI 1101 Excel Tutorial Fall 2011 Please consider the environment before printing this tutorial. Printing is usually a waste. Many times when doing research, the graphical representation of analyzed
+ Statistical Methods in
 + Statistical Methods in Practice STA/MTH 3379 + Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Discovering Statistics 2nd Edition
+ Statistical Methods in Practice STA/MTH 3379 + Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Discovering Statistics 2nd Edition
Data organization. So what kind of data did we collect?
 Data organization Suppose we go out and collect some data. What do we do with it? First we need to figure out what kind of data we have. To illustrate, let s do a simple experiment and collect the height
Data organization Suppose we go out and collect some data. What do we do with it? First we need to figure out what kind of data we have. To illustrate, let s do a simple experiment and collect the height
Further Maths Notes. Common Mistakes. Read the bold words in the exam! Always check data entry. Write equations in terms of variables
 Further Maths Notes Common Mistakes Read the bold words in the exam! Always check data entry Remember to interpret data with the multipliers specified (e.g. in thousands) Write equations in terms of variables
Further Maths Notes Common Mistakes Read the bold words in the exam! Always check data entry Remember to interpret data with the multipliers specified (e.g. in thousands) Write equations in terms of variables
Homework 1 Excel Basics
 Homework 1 Excel Basics Excel is a software program that is used to organize information, perform calculations, and create visual displays of the information. When you start up Excel, you will see the
Homework 1 Excel Basics Excel is a software program that is used to organize information, perform calculations, and create visual displays of the information. When you start up Excel, you will see the
Section 6.3: Measures of Position
 Section 6.3: Measures of Position Measures of position are numbers showing the location of data values relative to the other values within a data set. They can be used to compare values from different
Section 6.3: Measures of Position Measures of position are numbers showing the location of data values relative to the other values within a data set. They can be used to compare values from different
Pivot Tables, Lookup Tables and Scenarios
 Introduction Format and manipulate data using pivot tables. Using a grading sheet as and example you will be shown how to set up and use lookup tables and scenarios. Contents Introduction Contents Pivot
Introduction Format and manipulate data using pivot tables. Using a grading sheet as and example you will be shown how to set up and use lookup tables and scenarios. Contents Introduction Contents Pivot
MATH NATION SECTION 9 H.M.H. RESOURCES
 MATH NATION SECTION 9 H.M.H. RESOURCES SPECIAL NOTE: These resources were assembled to assist in student readiness for their upcoming Algebra 1 EOC. Although these resources have been compiled for your
MATH NATION SECTION 9 H.M.H. RESOURCES SPECIAL NOTE: These resources were assembled to assist in student readiness for their upcoming Algebra 1 EOC. Although these resources have been compiled for your
Unit I Supplement OpenIntro Statistics 3rd ed., Ch. 1
 Unit I Supplement OpenIntro Statistics 3rd ed., Ch. 1 KEY SKILLS: Organize a data set into a frequency distribution. Construct a histogram to summarize a data set. Compute the percentile for a particular
Unit I Supplement OpenIntro Statistics 3rd ed., Ch. 1 KEY SKILLS: Organize a data set into a frequency distribution. Construct a histogram to summarize a data set. Compute the percentile for a particular
Bar Charts and Frequency Distributions
 Bar Charts and Frequency Distributions Use to display the distribution of categorical (nominal or ordinal) variables. For the continuous (numeric) variables, see the page Histograms, Descriptive Stats
Bar Charts and Frequency Distributions Use to display the distribution of categorical (nominal or ordinal) variables. For the continuous (numeric) variables, see the page Histograms, Descriptive Stats
Rockefeller College MPA Excel Workshop: Clinton Impeachment Data Example
 Rockefeller College MPA Excel Workshop: Clinton Impeachment Data Example This exercise is a follow-up to the MPA admissions example used in the Excel Workshop. This document contains detailed solutions
Rockefeller College MPA Excel Workshop: Clinton Impeachment Data Example This exercise is a follow-up to the MPA admissions example used in the Excel Workshop. This document contains detailed solutions
Raw Data is data before it has been arranged in a useful manner or analyzed using statistical techniques.
 Section 2.1 - Introduction Graphs are commonly used to organize, summarize, and analyze collections of data. Using a graph to visually present a data set makes it easy to comprehend and to describe the
Section 2.1 - Introduction Graphs are commonly used to organize, summarize, and analyze collections of data. Using a graph to visually present a data set makes it easy to comprehend and to describe the
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
LAB 1 INSTRUCTIONS DESCRIBING AND DISPLAYING DATA
 LAB 1 INSTRUCTIONS DESCRIBING AND DISPLAYING DATA This lab will assist you in learning how to summarize and display categorical and quantitative data in StatCrunch. In particular, you will learn how to
LAB 1 INSTRUCTIONS DESCRIBING AND DISPLAYING DATA This lab will assist you in learning how to summarize and display categorical and quantitative data in StatCrunch. In particular, you will learn how to
Release notes for StatCrunch mid-march 2015 update
 Release notes for StatCrunch mid-march 2015 update A major StatCrunch update was made on March 18, 2015. This document describes the content of the update including major additions to StatCrunch that were
Release notes for StatCrunch mid-march 2015 update A major StatCrunch update was made on March 18, 2015. This document describes the content of the update including major additions to StatCrunch that were
IQR = number. summary: largest. = 2. Upper half: Q3 =
 Step by step box plot Height in centimeters of players on the 003 Women s Worldd Cup soccer team. 157 1611 163 163 164 165 165 165 168 168 168 170 170 170 171 173 173 175 180 180 Determine the 5 number
Step by step box plot Height in centimeters of players on the 003 Women s Worldd Cup soccer team. 157 1611 163 163 164 165 165 165 168 168 168 170 170 170 171 173 173 175 180 180 Determine the 5 number
Using Excel for Graphical Analysis of Data
 EXERCISE Using Excel for Graphical Analysis of Data Introduction In several upcoming experiments, a primary goal will be to determine the mathematical relationship between two variable physical parameters.
EXERCISE Using Excel for Graphical Analysis of Data Introduction In several upcoming experiments, a primary goal will be to determine the mathematical relationship between two variable physical parameters.
2) familiarize you with a variety of comparative statistics biologists use to evaluate results of experiments;
 A. Goals of Exercise Biology 164 Laboratory Using Comparative Statistics in Biology "Statistics" is a mathematical tool for analyzing and making generalizations about a population from a number of individual
A. Goals of Exercise Biology 164 Laboratory Using Comparative Statistics in Biology "Statistics" is a mathematical tool for analyzing and making generalizations about a population from a number of individual
Distributions of random variables
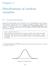 Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Chapter 5: The standard deviation as a ruler and the normal model p131
 Chapter 5: The standard deviation as a ruler and the normal model p131 Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12? Is it fair to say: 67 is
Chapter 5: The standard deviation as a ruler and the normal model p131 Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12? Is it fair to say: 67 is
4. TANGENTS AND NORMALS
 4. TANGENTS AND NORMALS 4. Equation of the Tangent at a Point Recall that the slope of a curve at a point is the slope of the tangent at that point. The slope of the tangent is the value of the derivative
4. TANGENTS AND NORMALS 4. Equation of the Tangent at a Point Recall that the slope of a curve at a point is the slope of the tangent at that point. The slope of the tangent is the value of the derivative
appstats6.notebook September 27, 2016
 Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model Objectives: 1.Students will calculate and interpret z scores. 2.Students will compare/contrast values from different distributions using
Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model Objectives: 1.Students will calculate and interpret z scores. 2.Students will compare/contrast values from different distributions using
8. MINITAB COMMANDS WEEK-BY-WEEK
 8. MINITAB COMMANDS WEEK-BY-WEEK In this section of the Study Guide, we give brief information about the Minitab commands that are needed to apply the statistical methods in each week s study. They are
8. MINITAB COMMANDS WEEK-BY-WEEK In this section of the Study Guide, we give brief information about the Minitab commands that are needed to apply the statistical methods in each week s study. They are
SAT Released Test 8 Problem #28
 SAT Released Test 8 Problem #28 28.) The 22 students in a health class conducted an experiment in which they each recorded their pulse rates, in beats per minute, before and after completing a light exercise
SAT Released Test 8 Problem #28 28.) The 22 students in a health class conducted an experiment in which they each recorded their pulse rates, in beats per minute, before and after completing a light exercise
Excel Functions & Tables
 Excel Functions & Tables SPRING 2016 Spring 2016 CS130 - EXCEL FUNCTIONS & TABLES 1 Review of Functions Quick Mathematics Review As it turns out, some of the most important mathematics for this course
Excel Functions & Tables SPRING 2016 Spring 2016 CS130 - EXCEL FUNCTIONS & TABLES 1 Review of Functions Quick Mathematics Review As it turns out, some of the most important mathematics for this course
Chapter 6: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
 Chapter 6: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Random Sampling Numerical Summaries Stem-n-Leaf plots Histograms, and Box plots Time Sequence Plots Normal Probability Plots Sections 6-1 to 6-5, and 6-7 Random Sampling
Chapter 6: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Random Sampling Numerical Summaries Stem-n-Leaf plots Histograms, and Box plots Time Sequence Plots Normal Probability Plots Sections 6-1 to 6-5, and 6-7 Random Sampling
3/31/2016. Spreadsheets. Spreadsheets. Spreadsheets and Data Management. Unit 3. Can be used to automatically
 MICROSOFT EXCEL and Data Management Unit 3 Thursday March 31, 2016 Allow users to perform simple and complex sorting Allow users to perform calculations quickly Organizes and presents figures that can
MICROSOFT EXCEL and Data Management Unit 3 Thursday March 31, 2016 Allow users to perform simple and complex sorting Allow users to perform calculations quickly Organizes and presents figures that can
CHAPTER 1. Introduction. Statistics: Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, presenting and interpreting data.
 1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction Statistics: Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, presenting and interpreting data. Variable: Any characteristic of a person or thing that can be expressed
1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction Statistics: Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, presenting and interpreting data. Variable: Any characteristic of a person or thing that can be expressed
The Normal Distribution & z-scores
 & z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
& z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
How to Use a Statistical Package
 APPENDIX D How to Use a Statistical Package Candace M. Evans, Lisa M. Gilman, Jeffrey Xavier, Joan Saxton Weber Computers and statistical software such as the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences
APPENDIX D How to Use a Statistical Package Candace M. Evans, Lisa M. Gilman, Jeffrey Xavier, Joan Saxton Weber Computers and statistical software such as the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences
Make sure to keep all graphs in same excel file as your measures.
 Project Part 2 Graphs. I. Use Excel to make bar graph for questions 1, and 5. II. Use Excel to make histograms for questions 2, and 3. III. Use Excel to make pie graphs for questions 4, and 6. IV. Use
Project Part 2 Graphs. I. Use Excel to make bar graph for questions 1, and 5. II. Use Excel to make histograms for questions 2, and 3. III. Use Excel to make pie graphs for questions 4, and 6. IV. Use
9 POINTS TO A GOOD LINE GRAPH
 NAME: PD: DATE: 9 POINTS TO A GOOD LINE GRAPH - 2013 1. Independent Variable on the HORIZONTAL (X) AXIS RANGE DIVIDED BY SPACES and round up to nearest usable number to spread out across the paper. LABELED
NAME: PD: DATE: 9 POINTS TO A GOOD LINE GRAPH - 2013 1. Independent Variable on the HORIZONTAL (X) AXIS RANGE DIVIDED BY SPACES and round up to nearest usable number to spread out across the paper. LABELED
Your Name: Section: 2. To develop an understanding of the standard deviation as a measure of spread.
 Your Name: Section: 36-201 INTRODUCTION TO STATISTICAL REASONING Computer Lab #3 Interpreting the Standard Deviation and Exploring Transformations Objectives: 1. To review stem-and-leaf plots and their
Your Name: Section: 36-201 INTRODUCTION TO STATISTICAL REASONING Computer Lab #3 Interpreting the Standard Deviation and Exploring Transformations Objectives: 1. To review stem-and-leaf plots and their
Ms Nurazrin Jupri. Frequency Distributions
 Frequency Distributions Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and simplify the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results.
Frequency Distributions Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and simplify the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results.
For a walkthrough on how to install this ToolPak, please follow the link below.
 Using histograms to display turntable data On the explore page there is an option to produce a histogram using the data your students gather as they work their way through each of the different sources
Using histograms to display turntable data On the explore page there is an option to produce a histogram using the data your students gather as they work their way through each of the different sources
Lastly, in case you don t already know this, and don t have Excel on your computers, you can get it for free through IT s website under software.
 Welcome to Basic Excel, presented by STEM Gateway as part of the Essential Academic Skills Enhancement, or EASE, workshop series. Before we begin, I want to make sure we are clear that this is by no means
Welcome to Basic Excel, presented by STEM Gateway as part of the Essential Academic Skills Enhancement, or EASE, workshop series. Before we begin, I want to make sure we are clear that this is by no means
Unit 7 Statistics. AFM Mrs. Valentine. 7.1 Samples and Surveys
 Unit 7 Statistics AFM Mrs. Valentine 7.1 Samples and Surveys v Obj.: I will understand the different methods of sampling and studying data. I will be able to determine the type used in an example, and
Unit 7 Statistics AFM Mrs. Valentine 7.1 Samples and Surveys v Obj.: I will understand the different methods of sampling and studying data. I will be able to determine the type used in an example, and
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
Week 2: Frequency distributions
 Types of data Health Sciences M.Sc. Programme Applied Biostatistics Week 2: distributions Data can be summarised to help to reveal information they contain. We do this by calculating numbers from the data
Types of data Health Sciences M.Sc. Programme Applied Biostatistics Week 2: distributions Data can be summarised to help to reveal information they contain. We do this by calculating numbers from the data
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
 CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is how the data is spread or distributed over the range of the data values. This is one of
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is how the data is spread or distributed over the range of the data values. This is one of
