Stereotypes. Stereotype: recurring combination of elements in an object or class. Example: <<signal>> mouse_click :
|
|
|
- Alberta Lloyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stereotypes Stereotype: recurring combination of elements in an object or class. Example: <<signal>> mouse_click : Mouse_click (x,y,button) A communication mechanism in Fig 1.11 Computers as Components 1
2 Signal event <<signal>> mouse_click leftorright: button x, y: position Signal event declaration a mouse_click(x,y,button) b event description Computers as Components 2
3 Behavioral description Several ways to describe behavior: internal view; external view. Computers as Components 3
4 State machines transition a b state state name Computers as Components 4
5 Event-driven state machines Behavioral descriptions are written as event-driven state machines. Machine changes state when receiving an input. An event may come from inside or outside of the system. Computers as Components 5
6 Types of events Three types of event defined by UML Signal: asynchronous event. Call: synchronized communication. Timer: activated by time. Computers as Components 6
7 Signal event <<signal>> mouse_click leftorright: button x, y: position Signal event declaration a mouse_click(x,y,button) b event description Computers as Components 7
8 Call event draw_box(10,5,3,2,blue) c d Computers as Components 8
9 Timer event tm(time-value) e f Computers as Components 9
10 Example: state machine start mouse_click(x,y,button)/ find_region(region) region found region = menu/ which_menu(i) got menu item call_menu(i) input/output called menu item region = drawing/ find_object(objid) found object highlight(objid) object highlighted finish Computers as Components 10
11 Sequence diagram Shows sequence of operations over time. Relates behaviors of multiple objects. Designed to show a particular scenario or choice of events Computers as Components 11
12 Sequence diagram Object m: Mouse d1: Display u: Menu Focus of control When the object is actively proccessing mouse_click(x,y,button) time which_menu(x,y,i) call_menu(i) Lifeline Computers as Components 12
13 Summary Object-oriented design helps us organize a design. UML is a transportable system design language. Provides structural and behavioral description primitives. Computers as Components 13
14 1.4 model train controller. Follow a design through several levels of abstraction. Gain experience with UML. Computers as Components 14
15 Model train setup rcvr motor console power supply ECC command address header Computers as Components 좌우바뀌었음 15
16 Requirements Console can control 8 trains on 1 track. Throttle has at least 63 levels. Inertia control adjusts responsiveness with at least 8 levels. Emergency stop button. Error detection scheme on messages. Computers as Components 16
17 Requirements form name purpose inputs outputs functions model train controller control speed of <= 8 model trains throttle, inertia, emergency stop, train # train control signals set engine speed w. inertia; emergency stop performance can update train speed at least 10 times/sec manufacturing cost $50 power physical size/weight 10 W (wall powered) console comfortable for 2 hands; < 2 lbs. Computers as Components 17
18 Digital Command Control DCC created by model railroad hobbyists, picked up by industry. Defines way in which model trains, controllers communicate. Leaves many system design aspects open, allowing competition. This is a simple example of a big trend: Cell phones, digital TV rely on standards. Computers as Components 18
19 DCC documents Standard S-9.1, DCC Electrical Standard. Defines how bits are encoded on the rails. Standard S-9.2, DCC Communication Standard. Defines packet format and semantics. Computers as Components 19
20 DCC electrical standard Voltage moves around the power supply voltage; adds no DC component. 1 is 58 ms, 0 is at least 100 ms. logic 1 logic 0 time 58 ms >= 100 ms Computers as Components 20
21 DCC communication standard Basic packet format: PSA(sD) + E. P: preamble = S: packet start bit = 0. A: address data byte. s: data byte start bit = 0. D: data byte (data payload). E: packet end bit = 1. A packet include one or more data byte start bit/ data byte combination. Computers as Components 21
22 DCC packet types A baseline packet: minimum packet that must be accepted by all DCC implementations, which has three data bytes. an address data byte gives receiver address. an instruction data byte gives basic instruction. an error correction data byte gives ECC. Computers as Components 22
23 Instruction data bits 0-3: a 4-bit speed value bit 4 : an additional speed bit (interpreted as a LSB of speed) bit 5 : forward (1), backward (0) bits 7-8:(01) instruction for speed/direction Computers as Components 23
24 Conceptual specification Before we create a detailed specification, we will make an initial, simplified specification. Gives us practice in specification and UML. Good idea in general to identify potential problems before investing too much effort in detail. Commands and packets may not be generated in a 1-to-1 ratio. Computers as Components 24
25 Basic system commands command name set-speed set-inertia estop parameters speed (positive/negative) inertia-value (nonnegative) none Computers as Components 25
26 Typical control sequence :console set-inertia set-speed :train_rcvr set-speed estop set-speed Computers as Components 26
27 Message classes command set-speed value: integer set-inertia value: unsignedinteger estop Class diagram for the train controller messages Computers as Components 27
28 Roles of message classes Implemented message classes derived from message class. Attributes and operations will be filled in for detailed specification. Implemented message classes specify message type by their class. May have to add type as parameter to data structure in implementation Wayne Wolf Overheads for Computers as Computers Components as Components 28
29 Collaboration diagram Interaction diagram Shows relationship between console and receiver (ignores role of track): 1..n: command :console :receiver 2008 Wayne Wolf Overheads for Computers as Computers Components as Components 2 nd ed. 29
30 System structure modeling Some classes define non-computer components (physical objects). Denote by name*. Choose important systems at this point to show basic relationships. Computers as Components 30
31 Major subsystem roles Console: read state of front panel; format messages; transmit messages. Train: receive message; interpret message; control the train. Computers as Components 31
32 Console system classes 1 1 console panel formatter transmitter 1 knob* sender* Computers as Components 32
33 Console class roles panel: describes analog knobs and interface hardware. formatter: turns knob settings into bit streams. transmitter: sends data on track. Computers as Components 33
34 Train system classes train set receiver t 1 train motor interface 1 1 detector* controller 1 1 pulser* Computers as Components 34
35 Train class roles receiver: digitizes signal from track. controller: interprets received commands and makes control decisions. motor interface: generates signals required by motor. Computers as Components 35
36 Detailed specification We can now fill in the details of the conceptual specification: more classes; behaviors. Sketching out the spec first helps us understand the basic relationships in the system. Computers as Components 36
37 Train speed control Motor controlled by pulse width modulation: duty cycle + V - Computers as Components 37
38 Physical object classes in console and trains knobs* train-knob: integer speed-knob: integer inertia-knob: unsignedinteger emergency-stop: boolean set-nobs() sender* pulser* pulse-width: unsignedinteger direction: boolean detector* send-bit() read-bit() : integer Computers as Components 38
39 Panel and motor interface classes panel train-number() : integer speed() : integer inertia() : integer estop() : boolean new-settings() motor-interface speed: integer new-settings(): use the set-knobs behavior of the Knobs* class to read the knobs settings whenever the train number setting is changed Computers as Components 39
40 Class descriptions panel class defines the controls. new-settings() behavior reads the controls. motor-interface class defines the motor speed held as state. Computers as Components 40
41 Transmitter and receiver classes transmitter send-speed(adrs: integer, speed: integer) send-inertia(adrs: integer, val: integer) set-estop(adrs: integer) receiver current: command new: boolean read-cmd() new-cmd() : boolean rcv-type(msg-type: command) rcv-speed(val: integer) rcv-inertia(val:integer) Computers as Components 41
42 Class descriptions transmitter class has one behavior for each type of message sent. receiver function provides methods to: detect a new message; determine its type; read its parameters (estop has no parameters). Computers as Components 42
43 Formatter class formatter current-train: integer current-speed[ntrains]: integer current-inertia[ntrains]: unsigned-integer current-estop[ntrains]: boolean send-command() panel-active() : boolean operate() Computers as Components 43
44 Formatter class description Formatter class holds state for each train, setting for current train. The operate() operation performs the basic formatting task. Computers as Components 44
Example: Model Train Controller
 Example: Model Train Controller Purposes of example: Follow a design through several levels of abstraction. Gain experience with UML. Text: Section 1.4 Model train setup rcvr motor power supply console
Example: Model Train Controller Purposes of example: Follow a design through several levels of abstraction. Gain experience with UML. Text: Section 1.4 Model train setup rcvr motor power supply console
Formal System Design Process with UML
 Formal System Design Process with UML Use a formal process & tools to facilitate and automate design steps: Requirements Specification System architecture Coding/chip design Testing Text: Chapter 1.4 Other
Formal System Design Process with UML Use a formal process & tools to facilitate and automate design steps: Requirements Specification System architecture Coding/chip design Testing Text: Chapter 1.4 Other
Embedded computing system
 Unit-1 EMBEDDED COMPUTING SYSTEM 1.1 COMPLEX SYSTEMS AND MICROPROCESSORS Embedded computer system is any device that includes a programmable computer but is not itself intended to be a general-purpose
Unit-1 EMBEDDED COMPUTING SYSTEM 1.1 COMPLEX SYSTEMS AND MICROPROCESSORS Embedded computer system is any device that includes a programmable computer but is not itself intended to be a general-purpose
UNIT 1 (ECS-10CS72) VTU Question paper solutions
 UNIT 1 (ECS-10CS72) VTU Question paper solutions 1. Give the characteristics and constraint of embedded system? Jun 14 Embedded computing is in many ways much more demanding than the sort of programs that
UNIT 1 (ECS-10CS72) VTU Question paper solutions 1. Give the characteristics and constraint of embedded system? Jun 14 Embedded computing is in many ways much more demanding than the sort of programs that
EE Embedded Systems Design
 EE4800-03 Embedded Systems Design Lesson 2 Structured Design, Documentation, and Laboratory Notebooks 1 Overview - Structured Design The divide-and-conquer technique Requirements Partitioning - The Black
EE4800-03 Embedded Systems Design Lesson 2 Structured Design, Documentation, and Laboratory Notebooks 1 Overview - Structured Design The divide-and-conquer technique Requirements Partitioning - The Black
6.033 Computer System Engineering
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.033 Computer System Engineering Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 6.033 Lecture 10:
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.033 Computer System Engineering Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 6.033 Lecture 10:
Signal Analyzer for Infrared Remote Control
 More products at http://www.sunrom.com Document: Datasheet Date: 26-Jul-13 Model #: 1145 Product s Page: www.sunrom.com/178 Signal Analyzer for Infrared Remote Control The board receives IR signals from
More products at http://www.sunrom.com Document: Datasheet Date: 26-Jul-13 Model #: 1145 Product s Page: www.sunrom.com/178 Signal Analyzer for Infrared Remote Control The board receives IR signals from
Network Working Group. Obsoletes: 3452, 3695 March 2009 Category: Standards Track
 Network Working Group M. Watson Request for Comments: 5445 Digital Fountain Obsoletes: 3452, 3695 March 2009 Category: Standards Track Status of This Memo Basic Forward Error Correction (FEC) Schemes This
Network Working Group M. Watson Request for Comments: 5445 Digital Fountain Obsoletes: 3452, 3695 March 2009 Category: Standards Track Status of This Memo Basic Forward Error Correction (FEC) Schemes This
Data Communications & Networks. Session 3 Main Theme Data Encoding and Transmission. Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti
 Data Communications & Networks Session 3 Main Theme Data Encoding and Transmission Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences
Data Communications & Networks Session 3 Main Theme Data Encoding and Transmission Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences
Advantages and disadvantages
 Advantages and disadvantages Advantages Disadvantages Asynchronous transmission Simple, doesn't require synchronization of both communication sides Cheap, timing is not as critical as for synchronous transmission,
Advantages and disadvantages Advantages Disadvantages Asynchronous transmission Simple, doesn't require synchronization of both communication sides Cheap, timing is not as critical as for synchronous transmission,
Embedded Computing System. Sub Code: 10CS72 IA Marks :25 Hrs/Week: 04 Exam Hours :03 Total Hrs: 52 Exam Marks :100 PART- A
 Sub Code: IA Marks :25 Hrs/Week: 04 Exam Hours :03 Total Hrs: 52 Exam Marks :100 PART- A UNIT 1 6 Hours Embedded Computing: Introduction, Complex Systems and Microprocessors, Embedded Systems Design Process,
Sub Code: IA Marks :25 Hrs/Week: 04 Exam Hours :03 Total Hrs: 52 Exam Marks :100 PART- A UNIT 1 6 Hours Embedded Computing: Introduction, Complex Systems and Microprocessors, Embedded Systems Design Process,
Links, clocks, optics and radios
 Links, clocks, optics and radios end IP addresses Source Destination Data 171.64.74.55 176.22.45.66 176 10110000 start Example of On-Off Keying +5V 0V Volts 1 0 time Data 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0
Links, clocks, optics and radios end IP addresses Source Destination Data 171.64.74.55 176.22.45.66 176 10110000 start Example of On-Off Keying +5V 0V Volts 1 0 time Data 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0
ANSI E Architecture for Control Networks Device Management Protocol Entertainment Services and Technology Association Abstract
 ANSI E1.17-2006 Architecture for Control Networks Device Management Protocol This document forms part of ANSI E1.17-2006, Entertainment Technology - Architecture for Control Networks, which was approved
ANSI E1.17-2006 Architecture for Control Networks Device Management Protocol This document forms part of ANSI E1.17-2006, Entertainment Technology - Architecture for Control Networks, which was approved
Lab 01 Arduino 程式設計實驗. Essential Arduino Programming and Digital Signal Process
 Lab 01 Arduino 程式設計實驗 Essential Arduino Programming and Digital Signal Process Arduino Arduino is an open-source electronics prototyping platform based on flexible, easy-to-use hardware and software. It's
Lab 01 Arduino 程式設計實驗 Essential Arduino Programming and Digital Signal Process Arduino Arduino is an open-source electronics prototyping platform based on flexible, easy-to-use hardware and software. It's
MIDI CPU Firmware V User Manual
 MIDI CPU Firmware V..2 MIDI CPU Firmware Version.2 User Manual Updated 23-5-3 Additional documentation available at: http://highlyliquid.com/support/ 23 Sonarcana LLC Page / 55 MIDI CPU Firmware V..2 Table
MIDI CPU Firmware V..2 MIDI CPU Firmware Version.2 User Manual Updated 23-5-3 Additional documentation available at: http://highlyliquid.com/support/ 23 Sonarcana LLC Page / 55 MIDI CPU Firmware V..2 Table
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING UML FUNDAMENTALS. Saulius Ragaišis.
 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING UML FUNDAMENTALS Saulius Ragaišis saulius.ragaisis@mif.vu.lt Information source Slides are prepared on the basis of Bernd Oestereich, Developing Software with UML: Object- Oriented
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING UML FUNDAMENTALS Saulius Ragaišis saulius.ragaisis@mif.vu.lt Information source Slides are prepared on the basis of Bernd Oestereich, Developing Software with UML: Object- Oriented
Data Communications & Networks. Session 3 Main Theme Data Encoding and Transmission. Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti
 Data Communications & Networks Session 3 Main Theme Data Encoding and Transmission Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences
Data Communications & Networks Session 3 Main Theme Data Encoding and Transmission Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences
EMBEDDED COMPUTING SYSTEMS Sub Code: 10CS72 IA Marks :25 Hrs/Week: 04 Exam Hours :03 Total Hrs: 52 Exam Marks :100 PART- A
 EMBEDDED COMPUTING SYSTEMS Sub Code: 10CS72 IA Marks :25 Hrs/Week: 04 Exam Hours :03 Total Hrs: 52 Exam Marks :100 PART- A UNIT 1 6 Hours Embedded Computing: Introduction, Complex Systems and Microprocessors,
EMBEDDED COMPUTING SYSTEMS Sub Code: 10CS72 IA Marks :25 Hrs/Week: 04 Exam Hours :03 Total Hrs: 52 Exam Marks :100 PART- A UNIT 1 6 Hours Embedded Computing: Introduction, Complex Systems and Microprocessors,
Mobile Transport Layer Lesson 10 Timeout Freezing, Selective Retransmission, Transaction Oriented TCP and Explicit Notification Methods
 Mobile Transport Layer Lesson 10 Timeout Freezing, Selective Retransmission, Transaction Oriented TCP and Explicit Notification Methods 1 Timeout freezing of transmission (TFT) Used in situations where
Mobile Transport Layer Lesson 10 Timeout Freezing, Selective Retransmission, Transaction Oriented TCP and Explicit Notification Methods 1 Timeout freezing of transmission (TFT) Used in situations where
EE4390 Microprocessors. Lessons 2, 3 68HC12 Hardware Overview, Subsystems, and memory System
 EE4390 Microprocessors Lessons 2, 3 68HC12 Hardware Overview, Subsystems, and memory System 1 Overview 68HC12 hardware overview Subsystems Memory System 2 68HC12 Hardware Overview "Copyright of Motorola,
EE4390 Microprocessors Lessons 2, 3 68HC12 Hardware Overview, Subsystems, and memory System 1 Overview 68HC12 hardware overview Subsystems Memory System 2 68HC12 Hardware Overview "Copyright of Motorola,
Pretty Good Protocol - Design Specification
 Document # Date effective October 23, 2006 Author(s) Ryan Herbst Supersedes Draft Revision 0.02 January 12, 2007 Document Title Pretty Good Protocol - Design Specification CHANGE HISTORY LOG Revision Effective
Document # Date effective October 23, 2006 Author(s) Ryan Herbst Supersedes Draft Revision 0.02 January 12, 2007 Document Title Pretty Good Protocol - Design Specification CHANGE HISTORY LOG Revision Effective
Problem 7. Problem 8. Problem 9
 Problem 7 To best answer this question, consider why we needed sequence numbers in the first place. We saw that the sender needs sequence numbers so that the receiver can tell if a data packet is a duplicate
Problem 7 To best answer this question, consider why we needed sequence numbers in the first place. We saw that the sender needs sequence numbers so that the receiver can tell if a data packet is a duplicate
NEV Spec. Document Version R01838_07
 NEV Spec Salt Lake City, UT, USA Document Version R01838_07 Contents File Format Overview... 3 NEV File Format... 3 NEV Basic Header... NEURALEV... NEV Extended Headers... 5 NEUEVWAV... 5 NEUEVFLT... 6
NEV Spec Salt Lake City, UT, USA Document Version R01838_07 Contents File Format Overview... 3 NEV File Format... 3 NEV Basic Header... NEURALEV... NEV Extended Headers... 5 NEUEVWAV... 5 NEUEVFLT... 6
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 th Edition Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All rights reserved.
 + William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 th Edition 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All rights reserved. 2 + Chapter 3 A Top-Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection
+ William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 th Edition 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All rights reserved. 2 + Chapter 3 A Top-Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection
The OSI Model. Open Systems Interconnection (OSI). Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
 Network Models The OSI Model Open Systems Interconnection (OSI). Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Model for understanding and developing computer-to-computer communication
Network Models The OSI Model Open Systems Interconnection (OSI). Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Model for understanding and developing computer-to-computer communication
plc numbers Encoded values; BCD and ASCII Error detection; parity, gray code and checksums
 plc numbers - 3. 3. NUMBERS AND DATA Topics: Number bases; binary, octal,, hexa Binary calculations; s compliments, addition, subtraction and Boolean operations Encoded values; BCD and ASCII Error detection;
plc numbers - 3. 3. NUMBERS AND DATA Topics: Number bases; binary, octal,, hexa Binary calculations; s compliments, addition, subtraction and Boolean operations Encoded values; BCD and ASCII Error detection;
PIC-I/O Multifunction I/O Controller
 J R KERR AUTOMATION ENGINEERING PIC-I/O Multifunction I/O Controller The PIC-I/O multifunction I/O controller is compatible with the PIC-SERVO and PIC-STEP motor control modules and provides the following
J R KERR AUTOMATION ENGINEERING PIC-I/O Multifunction I/O Controller The PIC-I/O multifunction I/O controller is compatible with the PIC-SERVO and PIC-STEP motor control modules and provides the following
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 36 I/O : Networks 2008-04-25 TA Brian Zimmer CS61C L36 I/O : Networks (1) inst.eecs/~cs61c-th NASA To Develop Small Satellites NASA has
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 36 I/O : Networks 2008-04-25 TA Brian Zimmer CS61C L36 I/O : Networks (1) inst.eecs/~cs61c-th NASA To Develop Small Satellites NASA has
Lecture 8: February 19
 CMPSCI 677 Operating Systems Spring 2013 Lecture 8: February 19 Lecturer: Prashant Shenoy Scribe: Siddharth Gupta 8.1 Server Architecture Design of the server architecture is important for efficient and
CMPSCI 677 Operating Systems Spring 2013 Lecture 8: February 19 Lecturer: Prashant Shenoy Scribe: Siddharth Gupta 8.1 Server Architecture Design of the server architecture is important for efficient and
Table of Contents. Appendix. Table of Figures. Document Change Log
 Definition of the Telemetry Parameter Exchange Protocol All information is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of. Release 1.09 (October 1999) Table of Contents
Definition of the Telemetry Parameter Exchange Protocol All information is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of. Release 1.09 (October 1999) Table of Contents
FlashFlex MCU SST89C58RC
 Introduction This document provides the instructions to help programming vendors qualify SST FlashFlex microcontrollers. Functional Blocks 051 CPU Core ALU, ACC, B-Register, Instruction Register, Program
Introduction This document provides the instructions to help programming vendors qualify SST FlashFlex microcontrollers. Functional Blocks 051 CPU Core ALU, ACC, B-Register, Instruction Register, Program
Direct Link Networks. Lecture - Encoding & Framing 1. Areas for Discussion. Problems
 Areas for Discussion Direct Link s Joseph Spring School of Computer Science 3COM0088 Computer Protocols & Architecture s Based on Chapter 2, Peterson & Davie, Computer s: A Systems Approach, 3 rd Ed Problems
Areas for Discussion Direct Link s Joseph Spring School of Computer Science 3COM0088 Computer Protocols & Architecture s Based on Chapter 2, Peterson & Davie, Computer s: A Systems Approach, 3 rd Ed Problems
Logosol Joystick Node LS-731
 Features 2 and 3 axis models Travel ±20 deg Non contact hall effect joystick Mechanical MTBF 15,000,000 cycles 3 pushbuttons Up to 2 stick pushbuttons 8 LEDs Member of Logosol s distributed motion control
Features 2 and 3 axis models Travel ±20 deg Non contact hall effect joystick Mechanical MTBF 15,000,000 cycles 3 pushbuttons Up to 2 stick pushbuttons 8 LEDs Member of Logosol s distributed motion control
Acu-Trac Ultrasonic Level Sensors
 General SSI s Acu-Trac ultrasonic level sensors broadcast and receive commands over a standard TIA/EIA RS- 485 serial data bus enabling the sensors to communicate and share data with other modules located
General SSI s Acu-Trac ultrasonic level sensors broadcast and receive commands over a standard TIA/EIA RS- 485 serial data bus enabling the sensors to communicate and share data with other modules located
file:///c:/users/hpguo/dropbox/website/teaching/fall 2017/CS4470/H...
 1 of 9 11/26/2017, 11:28 AM Homework 3 solutions 1. A window holds bytes 2001 to 5000. The next byte to be sent is 3001. Draw a figure to show the situation of the window after the following two events:
1 of 9 11/26/2017, 11:28 AM Homework 3 solutions 1. A window holds bytes 2001 to 5000. The next byte to be sent is 3001. Draw a figure to show the situation of the window after the following two events:
Nubotics Device Interface DLL
 Nubotics Device Interface DLL ver-1.1 Generated by Doxygen 1.5.5 Mon Mar 2 17:01:02 2009 Contents Chapter 1 Module Index 1.1 Modules Here is a list of all modules: Initialization Functions.............................??
Nubotics Device Interface DLL ver-1.1 Generated by Doxygen 1.5.5 Mon Mar 2 17:01:02 2009 Contents Chapter 1 Module Index 1.1 Modules Here is a list of all modules: Initialization Functions.............................??
RIP Version 2. The Classless Brother
 RIP Version 2 The Classless Brother (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 1 Why RIPv2 Need for subnet information and VLSM Need for Next Hop addresses for each route entry Need for external route tags Need for multicast
RIP Version 2 The Classless Brother (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 1 Why RIPv2 Need for subnet information and VLSM Need for Next Hop addresses for each route entry Need for external route tags Need for multicast
Packet/Frame, Error Detection How to send data efficiently & reliably?
 Packet/Frame, Error Detection How to send data efficiently & reliably? Packet and Packet Communication - Shared Network Resource, Fairness, Reliability Frame - Byte Oriented Frame and Bit Oriented Frame
Packet/Frame, Error Detection How to send data efficiently & reliably? Packet and Packet Communication - Shared Network Resource, Fairness, Reliability Frame - Byte Oriented Frame and Bit Oriented Frame
c. If the sum contains a zero, the receiver knows there has been an error.
 ENSC-37 Fall 27 Assignment#3 Due Date 6 Oct. 27 Problem-:[4] UDP and TCP use s complement for their checksums. Suppose you have the following three 8-bit bytes:,, and. a. [6] What is the s complement of
ENSC-37 Fall 27 Assignment#3 Due Date 6 Oct. 27 Problem-:[4] UDP and TCP use s complement for their checksums. Suppose you have the following three 8-bit bytes:,, and. a. [6] What is the s complement of
CS433 Homework 6. Problem 1 [15 points] Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017
![CS433 Homework 6. Problem 1 [15 points] Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017 CS433 Homework 6. Problem 1 [15 points] Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017](/thumbs/86/93964159.jpg) CS433 Homework 6 Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration.
CS433 Homework 6 Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration.
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 36 I/O : Networks TA Sameer The Yellow Dart Iyengar inst.eecs/~cs61c-ti Next year: Forget Elmo Get a Robot buddy New human-like robots that
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 36 I/O : Networks TA Sameer The Yellow Dart Iyengar inst.eecs/~cs61c-ti Next year: Forget Elmo Get a Robot buddy New human-like robots that
CS61C : Machine Structures
 CS61C L36 I/O : Networks (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 36 I/O : Networks TA Sameer The Yellow Dart Iyengar inst.eecs/~cs61c-ti Next year: Forget Elmo Get a Robot
CS61C L36 I/O : Networks (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 36 I/O : Networks TA Sameer The Yellow Dart Iyengar inst.eecs/~cs61c-ti Next year: Forget Elmo Get a Robot
Transport Protocol (IEX-TP)
 Transport Protocol (IEX-TP) Please contact IEX Market Operations at 646.568.2330 or marketops@iextrading.com, or your IEX onboarding contact with any questions. Version: 1.1 Updated: December 22, 2014
Transport Protocol (IEX-TP) Please contact IEX Market Operations at 646.568.2330 or marketops@iextrading.com, or your IEX onboarding contact with any questions. Version: 1.1 Updated: December 22, 2014
FrTime: A Language for Reactive Programs
 FrTime: A Language for Reactive Programs Version 7.2.0.12 Greg Cooper April 1, 2019 #lang frtime package: frtime The frtime language supports declarative construction of reactive systems in a syntax very
FrTime: A Language for Reactive Programs Version 7.2.0.12 Greg Cooper April 1, 2019 #lang frtime package: frtime The frtime language supports declarative construction of reactive systems in a syntax very
MR175 ERGONOMIC HAND-HELD SERIAL PENDANT
 Applications Features Products MR175 ERGONOMIC HAND-HELD SERIAL PENDANT MICRONOR automation components The MR175 Hand-Held Serial Pendant/ HMI offers a superb ergonomic form factor, a full complement of
Applications Features Products MR175 ERGONOMIC HAND-HELD SERIAL PENDANT MICRONOR automation components The MR175 Hand-Held Serial Pendant/ HMI offers a superb ergonomic form factor, a full complement of
Problem Statement. Physical and Data Link Layer Overview. Five Tasks Encoding. Make two computers talk to each other
 Physical and Data Link Layer Overview Problem Statement Make two talk to each other Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur Physical media transmit Analog signals Modulate/demodulate
Physical and Data Link Layer Overview Problem Statement Make two talk to each other Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur Physical media transmit Analog signals Modulate/demodulate
The trace file is here: https://kevincurran.org/com320/labs/wireshark/trace-udp.pcap
 Lab Exercise UDP Objective To look at the details of UDP (User Datagram Protocol). UDP is a transport protocol used throughout the Internet as an alternative to TCP when reliability is not required. It
Lab Exercise UDP Objective To look at the details of UDP (User Datagram Protocol). UDP is a transport protocol used throughout the Internet as an alternative to TCP when reliability is not required. It
DCC Industry Quality Metrics
 DCC Industry Quality Metrics These quality metrics represent typical industry practice, and are used in conjunction with the NMRA Standards and Recommended Practices for Conformance and Inspection testing.
DCC Industry Quality Metrics These quality metrics represent typical industry practice, and are used in conjunction with the NMRA Standards and Recommended Practices for Conformance and Inspection testing.
Direct Link Networks. Framing. Lecture - Encoding & Framing 1. Problems. Areas for Discussion
 Areas for Discussion Direct Link s Joseph Spring School of Computer Science 3COM0271 Computer Protocols & Architecture s Based on Chapter 2, Peterson & Davie, Computer s: A Systems Approach, 4 th Ed Problems
Areas for Discussion Direct Link s Joseph Spring School of Computer Science 3COM0271 Computer Protocols & Architecture s Based on Chapter 2, Peterson & Davie, Computer s: A Systems Approach, 4 th Ed Problems
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32 Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter Interface. It covers the main features
 Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32 Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter Interface. It covers the main features of this USART interface, which is widely used for serial
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32 Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter Interface. It covers the main features of this USART interface, which is widely used for serial
Computer Network Programming
 Computer Network Programming SCTP Overview Dr. Sam Hsu Computer Science & Engineering Florida Atlantic University SCTP Overview Introduction Motivations Architectural & Functional Views Packet & Chunk
Computer Network Programming SCTP Overview Dr. Sam Hsu Computer Science & Engineering Florida Atlantic University SCTP Overview Introduction Motivations Architectural & Functional Views Packet & Chunk
What is a Class Diagram? A diagram that shows a set of classes, interfaces, and collaborations and their relationships
 Class Diagram What is a Class Diagram? A diagram that shows a set of classes, interfaces, and collaborations and their relationships Why do we need Class Diagram? Focus on the conceptual and specification
Class Diagram What is a Class Diagram? A diagram that shows a set of classes, interfaces, and collaborations and their relationships Why do we need Class Diagram? Focus on the conceptual and specification
What is a Class Diagram? Class Diagram. Why do we need Class Diagram? Class - Notation. Class - Semantic 04/11/51
 What is a Class Diagram? Class Diagram A diagram that shows a set of classes, interfaces, and collaborations and their relationships Why do we need Class Diagram? Focus on the conceptual and specification
What is a Class Diagram? Class Diagram A diagram that shows a set of classes, interfaces, and collaborations and their relationships Why do we need Class Diagram? Focus on the conceptual and specification
Overview. Performance metrics - Section 1.5 Direct link networks Hardware building blocks - Section 2.1 Encoding - Section 2.2 Framing - Section 2.
 Overview Performance metrics - Section 1.5 Direct link networks Hardware building blocks - Section 2.1 Encoding - Section 2.2 Framing - Section 2.3 Performance Metrics Bandwidth Amount of data that can
Overview Performance metrics - Section 1.5 Direct link networks Hardware building blocks - Section 2.1 Encoding - Section 2.2 Framing - Section 2.3 Performance Metrics Bandwidth Amount of data that can
Fig 1 Changing Pipe Wall Thicknesses in the Master Files, and making these changes available to use in the spec.
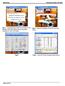 Fig 1 Changing Pipe Wall Thicknesses in the Master Files, and making these changes available to use in the spec. Fig 2 Select the Master Files from the Edit menu Fig 3 Fig 4 Click the Show Unused Rows
Fig 1 Changing Pipe Wall Thicknesses in the Master Files, and making these changes available to use in the spec. Fig 2 Select the Master Files from the Edit menu Fig 3 Fig 4 Click the Show Unused Rows
Internet II. CS10 : Beauty and Joy of Computing. cs10.berkeley.edu. !!Senior Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia!!! Garcia UCB!
 cs10.berkeley.edu CS10 : Beauty and Joy of Computing Internet II!!Senior Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia!!!www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia CS10 L17 Internet II (1)! Why Networks?! Originally sharing I/O devices
cs10.berkeley.edu CS10 : Beauty and Joy of Computing Internet II!!Senior Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia!!!www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia CS10 L17 Internet II (1)! Why Networks?! Originally sharing I/O devices
ELECTRICINEMA Connect IP Projection Screen
 ELECTRICINEMA Connect IP Projection Screen Thank you for purchasing a Screen Technics Projection Screen, please ensure that you read the following instructions fully before to install this product. Wall
ELECTRICINEMA Connect IP Projection Screen Thank you for purchasing a Screen Technics Projection Screen, please ensure that you read the following instructions fully before to install this product. Wall
InfoTag KE28xx Communications for 186 CPU Firmware Version 4
 InfoTag KE28xx Communications for 186 CPU Firmware Version 4 *KE28xx models include: KE2800, KE2852, KE2853, KE2856 This document applies to printer firmware versions 4.x only. Note that changes made to
InfoTag KE28xx Communications for 186 CPU Firmware Version 4 *KE28xx models include: KE2800, KE2852, KE2853, KE2856 This document applies to printer firmware versions 4.x only. Note that changes made to
Hard Disk Drive. Controller
 II Controller 2 tj Electronics HDA Head Disk Assembly AEM Arm Electronics Module VCM Voice Coil Module * Jacob et.al. 3 tj Controller * Jacob et.al. 4 tj Controller Processor Microcontroller (Arm Mx) Manages
II Controller 2 tj Electronics HDA Head Disk Assembly AEM Arm Electronics Module VCM Voice Coil Module * Jacob et.al. 3 tj Controller * Jacob et.al. 4 tj Controller Processor Microcontroller (Arm Mx) Manages
SV3C DPRX MIPI D-PHY Analyzer. Data Sheet
 SV3C DPRX MIPI D-PHY Analyzer Data Sheet Table of Contents Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 List of Figures... 2 List of Tables... 3 Introduction... 4 Overview... 4 Key Benefits... 4 Applications...
SV3C DPRX MIPI D-PHY Analyzer Data Sheet Table of Contents Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 List of Figures... 2 List of Tables... 3 Introduction... 4 Overview... 4 Key Benefits... 4 Applications...
UNIT-II 1. Discuss the issues in the data link layer. Answer:
 UNIT-II 1. Discuss the issues in the data link layer. Answer: Data Link Layer Design Issues: The data link layer has a number of specific functions it can carry out. These functions include 1. Providing
UNIT-II 1. Discuss the issues in the data link layer. Answer: Data Link Layer Design Issues: The data link layer has a number of specific functions it can carry out. These functions include 1. Providing
Ad hoc and Sensor Networks Chapter 6: Link layer protocols. Holger Karl
 Ad hoc and Sensor Networks Chapter 6: Link layer protocols Holger Karl Goals of this chapter Link layer tasks in general Framing group bit sequence into packets/frames Important: format, size Error control
Ad hoc and Sensor Networks Chapter 6: Link layer protocols Holger Karl Goals of this chapter Link layer tasks in general Framing group bit sequence into packets/frames Important: format, size Error control
Ch 9 Discrete Control Using PLCs and PCs
 Ch 9 Discrete Control Using PLCs and PCs Sections: 1. Discrete Process Control 2. Ladder Logic Diagrams 3. Programmable Logic Controllers 4. Personal Computers Using Soft Logic Discrete Process Control
Ch 9 Discrete Control Using PLCs and PCs Sections: 1. Discrete Process Control 2. Ladder Logic Diagrams 3. Programmable Logic Controllers 4. Personal Computers Using Soft Logic Discrete Process Control
SV3C DPRX MIPI D-PHY Analyzer. Data Sheet
 SV3C DPRX MIPI D-PHY Analyzer Data Sheet Table of Contents Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 List of Figures... 2 List of Tables... 2 Introduction... 3 Overview... 3 Key Benefits... 3 Applications...
SV3C DPRX MIPI D-PHY Analyzer Data Sheet Table of Contents Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 List of Figures... 2 List of Tables... 2 Introduction... 3 Overview... 3 Key Benefits... 3 Applications...
This document is for information purposes only and is subject to change without notice.
 Notice WALCHEM, Iwaki America Inc. (hereinafter Walchem ) Boynton Road, Holliston, MA USA () - All Rights Reserved Printed in USA Proprietary Material The information and descriptions contained herein
Notice WALCHEM, Iwaki America Inc. (hereinafter Walchem ) Boynton Road, Holliston, MA USA () - All Rights Reserved Printed in USA Proprietary Material The information and descriptions contained herein
Fig.12.5 Serial Data Line during Serial Communication
 Lecture-66 Asynchronous Serial Data Communication A serial data signal is divided into time intervals called bit times as shown in fig.2.5. During each bit time interval (T B ), the signal is either a
Lecture-66 Asynchronous Serial Data Communication A serial data signal is divided into time intervals called bit times as shown in fig.2.5. During each bit time interval (T B ), the signal is either a
11 ASYNCHRONOUS SERIAL PORTS
 11 ASYNCHRONOUS SERIAL PORTS 11.1 General The ETRAX 100LX contains four complete asynchronous serial receivers/ transmitters with full buffering and parity control. Each asynchronous serial port has one
11 ASYNCHRONOUS SERIAL PORTS 11.1 General The ETRAX 100LX contains four complete asynchronous serial receivers/ transmitters with full buffering and parity control. Each asynchronous serial port has one
Framing and Stuffing. Advanced Computer Networks
 Framing and Stuffing Advanced Computer Networks Framing & Stuffing Outline Synchronous vs Asynchronous Transmissions Asynchronous Character Transmissions Framing Identifying Synchronous Block Boundaries
Framing and Stuffing Advanced Computer Networks Framing & Stuffing Outline Synchronous vs Asynchronous Transmissions Asynchronous Character Transmissions Framing Identifying Synchronous Block Boundaries
[MC-SMP]: Session Multiplex Protocol. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation
![[MC-SMP]: Session Multiplex Protocol. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation [MC-SMP]: Session Multiplex Protocol. Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation](/thumbs/75/71746808.jpg) [MC-SMP]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for protocols,
[MC-SMP]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for protocols,
FrTime: A Language for Reactive Programs
 FrTime: A Language for Reactive Programs Version 5.3.6 Greg Cooper August 9, 2013 #lang frtime The frtime language supports declarative construction of reactive systems in a syntax very similar to that
FrTime: A Language for Reactive Programs Version 5.3.6 Greg Cooper August 9, 2013 #lang frtime The frtime language supports declarative construction of reactive systems in a syntax very similar to that
Decoder Installation:
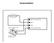 Decoder Installation: MOTOR Right Track Power Pickup Motor + Motor - RIGHT RAIL (Engineer's Side) Left Track Power Pickup LEFT RAIL (Fireman's Side) **Last revised: 15 February 2010 Page 2 TRKCAR-A Decoder
Decoder Installation: MOTOR Right Track Power Pickup Motor + Motor - RIGHT RAIL (Engineer's Side) Left Track Power Pickup LEFT RAIL (Fireman's Side) **Last revised: 15 February 2010 Page 2 TRKCAR-A Decoder
2008 JINST 3 S Online System. Chapter System decomposition and architecture. 8.2 Data Acquisition System
 Chapter 8 Online System The task of the Online system is to ensure the transfer of data from the front-end electronics to permanent storage under known and controlled conditions. This includes not only
Chapter 8 Online System The task of the Online system is to ensure the transfer of data from the front-end electronics to permanent storage under known and controlled conditions. This includes not only
Hands-on course Mobile Communications
 Hands-on course Mobile Communications Summer 2008 Material and Assignments in the areas of: Medium Access in Wireless Networks Freie Universität Berlin Institute of Computer Systems & Telematics A. Liers,
Hands-on course Mobile Communications Summer 2008 Material and Assignments in the areas of: Medium Access in Wireless Networks Freie Universität Berlin Institute of Computer Systems & Telematics A. Liers,
EECS 122: Introduction to Communication Networks Final Exam Solutions
 EECS 22: Introduction to Communication Networks Final Exam Solutions Problem. (6 points) How long does it take for a 3000-byte IP packet to go from host A to host B in the figure below. Assume the overhead
EECS 22: Introduction to Communication Networks Final Exam Solutions Problem. (6 points) How long does it take for a 3000-byte IP packet to go from host A to host B in the figure below. Assume the overhead
Internet transport-layer protocols. Transport services and protocols. Sending and receiving. Connection-oriented (TCP) Connection-oriented
 Transport services and protocols Internet -layer protocols logical communication between processes protocols run in end systems send side: breaks app messages into segments, passes to layer rcv side: reassembles
Transport services and protocols Internet -layer protocols logical communication between processes protocols run in end systems send side: breaks app messages into segments, passes to layer rcv side: reassembles
TCP/IP Transport Layer Protocols, TCP and UDP
 TCP/IP Transport Layer Protocols, TCP and UDP Learning Objectives Identify TCP header fields and operation using a Wireshark FTP session capture. Identify UDP header fields and operation using a Wireshark
TCP/IP Transport Layer Protocols, TCP and UDP Learning Objectives Identify TCP header fields and operation using a Wireshark FTP session capture. Identify UDP header fields and operation using a Wireshark
3. Except for strings, double quotes, identifiers, and keywords, C++ ignores all white space.
 Chapter 2: Problem Solving Using C++ TRUE/FALSE 1. Modular programs are easier to develop, correct, and modify than programs constructed in some other manner. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 45 2. One important requirement
Chapter 2: Problem Solving Using C++ TRUE/FALSE 1. Modular programs are easier to develop, correct, and modify than programs constructed in some other manner. ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: 45 2. One important requirement
Groups of two-state devices are used to represent data in a computer. In general, we say the states are either: high/low, on/off, 1/0,...
 Chapter 9 Computer Arithmetic Reading: Section 9.1 on pp. 290-296 Computer Representation of Data Groups of two-state devices are used to represent data in a computer. In general, we say the states are
Chapter 9 Computer Arithmetic Reading: Section 9.1 on pp. 290-296 Computer Representation of Data Groups of two-state devices are used to represent data in a computer. In general, we say the states are
FlashFlex MCU SST89E54RD2A/RDA / SST89E58RD2A/RDA
 Introduction This document provides instructions to help programming vendors qualify the SST FlashFlex microcontrollers. Functional Blocks 8051 CPU Core ALU, ACC, B-Register, Instruction Register, Program
Introduction This document provides instructions to help programming vendors qualify the SST FlashFlex microcontrollers. Functional Blocks 8051 CPU Core ALU, ACC, B-Register, Instruction Register, Program
ESE250: Digital Audio Basics. Week 13: April 2nd, 2013 Networking
 1 ESE250: Digital Audio Basics Week 13: April 2nd, 2013 Networking 2 Teaser 2006 Debate Former Senator Stevens Jon Stewart Reporting 2010 Ruling U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Decision
1 ESE250: Digital Audio Basics Week 13: April 2nd, 2013 Networking 2 Teaser 2006 Debate Former Senator Stevens Jon Stewart Reporting 2010 Ruling U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Decision
Adapted from a lab originally written by Simon Hastings and Bill Ashmanskas
 Physics 364 Arduino Lab 1 Adapted from a lab originally written by Simon Hastings and Bill Ashmanskas Vithayathil/Kroll Introduction Last revised: 2014-11-12 This lab introduces you to an electronic development
Physics 364 Arduino Lab 1 Adapted from a lab originally written by Simon Hastings and Bill Ashmanskas Vithayathil/Kroll Introduction Last revised: 2014-11-12 This lab introduces you to an electronic development
EVENTS AND SIGNALS. Figure 1: Events. kinds of events Signal Event
 EVENTS AND SIGNALS Events An event is the specification of a significant occurrence that has a location in time and space. Any thing that happens is modeled as an event in UML. In the context of state
EVENTS AND SIGNALS Events An event is the specification of a significant occurrence that has a location in time and space. Any thing that happens is modeled as an event in UML. In the context of state
Operating Manual. Inferface. CANopen. English
 Operating Manual Inferface CANopen English Disclaimer The information in this brochure corresponds to our current state of knowledge. However, it is not to be understood as a warranty for certain characteristics
Operating Manual Inferface CANopen English Disclaimer The information in this brochure corresponds to our current state of knowledge. However, it is not to be understood as a warranty for certain characteristics
Architectural Styles: Definitions
 Component-Based Software Engineering ECE493-Topic 4 Winter 2006 Lecture 7 Architectural Styles in CBSE (Part A) Ladan Tahvildari Assistant Professor Dept. of Elect. & Comp. Eng. University of Waterloo
Component-Based Software Engineering ECE493-Topic 4 Winter 2006 Lecture 7 Architectural Styles in CBSE (Part A) Ladan Tahvildari Assistant Professor Dept. of Elect. & Comp. Eng. University of Waterloo
Computer and Network Security
 CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2009 Lecture 6 Announcements First project: Due: 6 Feb. 2009 at 11:59 p.m. http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~cis551/project1.html Plan for Today: Networks:
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2009 Lecture 6 Announcements First project: Due: 6 Feb. 2009 at 11:59 p.m. http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~cis551/project1.html Plan for Today: Networks:
hipecs-cio55 CANopen I/O module with 4 analog inputs
 General The hipecs-cio55 is a low-cost CANopen module with 4 analog input lines. The I/O are isolated from power supply and the CAN bus sub system. Furthermore, the module has an input resolution of 16
General The hipecs-cio55 is a low-cost CANopen module with 4 analog input lines. The I/O are isolated from power supply and the CAN bus sub system. Furthermore, the module has an input resolution of 16
Signature: 1. (10 points) Basic Microcontroller Concepts
 EE 109 Practice Final Exam Last name: First name: Signature: The practice final is one hour, ten minutes long, closed book, closed notes, calculators allowed. To receive full credit on a question show
EE 109 Practice Final Exam Last name: First name: Signature: The practice final is one hour, ten minutes long, closed book, closed notes, calculators allowed. To receive full credit on a question show
NWEN 243. Networked Applications. Layer 4 TCP and UDP
 NWEN 243 Networked Applications Layer 4 TCP and UDP 1 About the second lecturer Aaron Chen Office: AM405 Phone: 463 5114 Email: aaron.chen@ecs.vuw.ac.nz Transport layer and application layer protocols
NWEN 243 Networked Applications Layer 4 TCP and UDP 1 About the second lecturer Aaron Chen Office: AM405 Phone: 463 5114 Email: aaron.chen@ecs.vuw.ac.nz Transport layer and application layer protocols
Last Lecture. Network Architecture: Layers. This Lecture. In the sending host (2) In the sending host
 Chapter 7.B and 7.C Architecture: Layers Prof. Dina Katabi Last Lecture We learned how to share the network infrastructure between many connections/flows We also learned about the implications of the sharing
Chapter 7.B and 7.C Architecture: Layers Prof. Dina Katabi Last Lecture We learned how to share the network infrastructure between many connections/flows We also learned about the implications of the sharing
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017
 ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Lecture 5.1: Link Layer Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527 Computer
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Lecture 5.1: Link Layer Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527 Computer
Chapter 8 Memory Basics
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 8 Memory Basics Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview Memory definitions Random Access
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 8 Memory Basics Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode) Overview Memory definitions Random Access
Advanced Computer Networks. Rab Nawaz Jadoon DCS. Assistant Professor COMSATS University, Lahore Pakistan. Department of Computer Science
 Advanced Computer Networks Rab Nawaz Jadoon Department of Computer Science DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Assistant Professor COMSATS University, Lahore Pakistan Advanced Computer Networks
Advanced Computer Networks Rab Nawaz Jadoon Department of Computer Science DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Assistant Professor COMSATS University, Lahore Pakistan Advanced Computer Networks
XYO Network: Network Implementation
 XYO Network: Network Implementation Erik Saberski, Carter Harrison, Arie Trouw August, 2018 The XY Oracle Network utilizes a novel blockchain protocol to provide a trustless, cryptographic network of decentralized
XYO Network: Network Implementation Erik Saberski, Carter Harrison, Arie Trouw August, 2018 The XY Oracle Network utilizes a novel blockchain protocol to provide a trustless, cryptographic network of decentralized
SpaceWire-R DRAFT. SCDHA Issue September 2013
 SpaceWire-R DRAFT SCDHA 151-0.3 Issue 0.3 13 September 2013 Takahiro Yamada Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS) 1 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 3
SpaceWire-R DRAFT SCDHA 151-0.3 Issue 0.3 13 September 2013 Takahiro Yamada Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS) 1 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 3
Version. Table of Contents
 NAP Protocol 1.0 Version Version Date By Comment v1.0 24.01.2011 JP Release version of NAP documentation. Table of Contents 1 Basic concepts...3 1.1 Usage info...3 1.2 Length byte...3 1.3 Literal characters...4
NAP Protocol 1.0 Version Version Date By Comment v1.0 24.01.2011 JP Release version of NAP documentation. Table of Contents 1 Basic concepts...3 1.1 Usage info...3 1.2 Length byte...3 1.3 Literal characters...4
Nabto Serial Link Protocol
 Nabto Serial Link Protocol Nabto TM Nabto Serial Link Protocol Page 1 of 22 Contents Vocabulary... 4 Introduction... 5 Access Control... 5 Connection type... 5 Access Control List... 5 Protocol details...
Nabto Serial Link Protocol Nabto TM Nabto Serial Link Protocol Page 1 of 22 Contents Vocabulary... 4 Introduction... 5 Access Control... 5 Connection type... 5 Access Control List... 5 Protocol details...
CS433 Homework 6. Problem 1 [15 points] Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017
![CS433 Homework 6. Problem 1 [15 points] Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017 CS433 Homework 6. Problem 1 [15 points] Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017](/thumbs/86/93964184.jpg) CS433 Homework 6 Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration.
CS433 Homework 6 Assigned on 11/28/2017 Due in class on 12/12/2017 Instructions: 1. Please write your name and NetID clearly on the first page. 2. Refer to the course fact sheet for policies on collaboration.
Operating Omega ATS and Lynx ATS. QUOTE TRANSFER PROTOCOL (QTP) SPECIFICATION v 1.05
 Operating Omega ATS and Lynx ATS QUOTE TRANSFER PROTOCOL (QTP) SPECIFICATION v 1.05 Revision History Date Revision Description of Change April 15, 2016 1.00 Created April 27, 2016 1.01 Edits made to document.
Operating Omega ATS and Lynx ATS QUOTE TRANSFER PROTOCOL (QTP) SPECIFICATION v 1.05 Revision History Date Revision Description of Change April 15, 2016 1.00 Created April 27, 2016 1.01 Edits made to document.
PLC AUTOMATION SYSTEM LABORATORY. Manual
 MRS AVN COLLEGE POLYTECHNIC VISAKHAPATNAM DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING PLC AUTOMATION SYSTEM LABORATORY Manual PLC Automation System Laboratory Lab 1 : Getting familiar with Step 7-
MRS AVN COLLEGE POLYTECHNIC VISAKHAPATNAM DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING PLC AUTOMATION SYSTEM LABORATORY Manual PLC Automation System Laboratory Lab 1 : Getting familiar with Step 7-
EtherCAT User Manual. For SS EtherCAT
 EtherCAT User Manual For SS EtherCAT Table of Contents Introduction to EtherCAT... 3 Commonly Used Acronyms... 3 Protocol... 4 Logical Addressing... 4 Auto Increment Addressing... 4 Fixed Node Addressing...
EtherCAT User Manual For SS EtherCAT Table of Contents Introduction to EtherCAT... 3 Commonly Used Acronyms... 3 Protocol... 4 Logical Addressing... 4 Auto Increment Addressing... 4 Fixed Node Addressing...
