Lecture 7 Java SE Multithreading
|
|
|
- Melvin McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 7 Java SE Multithreading presentation Java Programming Software App Development Cristian Toma D.I.C.E/D.E.I.C Department of Economic Informatics & Cybernetics
2 Cristian Toma Business Card
3 Agenda for Lecture 7 JSE Multi-threading IPC Multithreading vs. Multi-process Java Multithreading Exchange Ideas & Parallelism Intro
4 Multi-threading models, features, atomic operations, JVM and OS threads Multi-threading vs. Multi-process
5 1.1 Summary of MS Windows Memory Native EXE File on HDD MS Windows: RAM Memory Layout MS Windows: Load EXE IMAGE Module Firefox EXE File Beginning MZ or.com/blog/2007/03/d ude-wheres-my-4- gigabytes-of-ram.html EXE 16, 32 bits Headers EXE IMAGE Load Adobe Module Reader References / pointers to the segments Relocation Pointer Table PRO CESS PROCESS IPC Optional Thread 1 Optional Thread 2 Optional Thread n
6 1.2 Summary of Processes & IPC in Linux Before understanding a thread, one first needs to understand a UNIX process. A process is created by the operating system, and requires a fair amount of "overhead". Processes contain information about program resources & program execution state, including: Process ID, process group ID, user ID, and group ID; Environment; Working directory; Program instructions; Registers; Stack; Heap; File descriptors; Signal actions; Shared libraries; Inter-process communication tools (such as message queues, pipes, semaphores, or shared memory)
7 1.2 Summary of Multi-threading in C vs. Java Multi-threadingvs. Multi-process development in UNIX/Linux:
8 1.2 Summary of Multi-threading in C vs. Java Threads Features: Thread operations include thread creation, termination, synchronization (joins, blocking), scheduling, data management and process interaction. A thread does not maintain a list of created threads, nor does it know the thread that created it. All threads within a process share the same address space. Threads in the same process share: Process instructions Most data open files (descriptors) signals and signal handlers current working directory User and group id Each thread has a unique: Thread ID set of registers, stack pointer stack for local variables, return addresses signal mask priority Return value: errno pthread functions return "0" if OK.
9 1.2 Summary of Race Condition Race Condition Feature Family Bank Account: Copyright: Secure Applications Programming - Boja)
10 1.2 Summary of Race Condition Race Condition Feature Family Bank Account: Copyright: Secure Applications Programming - Boja)
11 1.2 Summary of Multi-threading in C vs. Java Multi-threading in C/C++ with pthread (Is counter++ an atomic operation?):
12 1.2 Summary of Multi-threading in C vs. Java Multi-threading vs. Multi-process quite good/imperfect analogies & terms: USE MULTI-THREADING for PARALLELISM (e.g. adding 2 matrixes in parallel) and/or; CONCURENCY (e.g. handling GUI on one thread & business processing on other thread / even on mono-processor PC, handling multiple HTTP requests from the network) Mutexes are used to prevent data inconsistencies due to race conditions. A race condition often occurs when two or more threads need to perform operations on the same memory area, but the results of computations depends on the order in which these operations are performed. Mutexes are used for serializing shared resources. Anytime a global resource is accessed by more than one thread the resource should have a Mutex associated with it. One can apply a mutex to protect a segment of memory ("critical region") from other threads. Mutexes can be applied only to threads in a single process and do not work between processes as do semaphores in Linux IPC. In Java Mutex is quite ó synchronized (also please see java.util.concurrent.*)
13 1.2 Summary of Multi-threading in C vs. Java Multi-threading Models: A thread One-to-one Mapping A scheduler
14 1.2 Summary of Multi-threading in C vs. Java Multi-threading Models: Many-to-one Mapping Many-to-many Mapping
15 1.2 Summary of Multi-threading in C vs. Java JVM Multi-threading Model mapping to OS native threads: Native C/C++ JVM Kernel Space User Space
16 1.2 Summary of Multi-threading in C vs. Java JVM Multi-threading Model mapping to OS native threads: Inside the Java Virtual Machine, Bill Venners
17 1.2 Summary of Multi-threading in Java JVM Multi-threading Concept: Multiple threads on multiple CPUs Thread 1 Thread 2 Thread 3 Multiple threads sharing a single CPU Thread 1 Thread 2 Thread 3 Different processes do not share memory space. A thread can execute concurrently with other threads within a single process. All threads managed by the JVM share memory space and can communicate with each other.
18 Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Seventh Edition, (c) 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved Threads Issues Thread: Thread: single sequential flow of control within a program Single-threaded program can handleone task at any time. Multitasking allows single processor to run several concurrent threads. Most modern operating systems support multitasking.
19 1.3 Threads Issues Advantages of Multithreading: Reactive systems constantly monitoring More responsive to user input GUI application can interrupt a time-consuming task Server can handle multiple clients simultaneously Can take advantage of parallel processing When Multithreading?: Concurrency and/or Parallelism Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Seventh Edition, (c) 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
20 Section Conclusion Fact: Multi-threading vs. Multi-process In few samples it is easy to understand: Necessity: Parallelism vs. Concurrency Multi-Process vs. Multi-Threading Atomic operations (counter++) Multi-threading model mapping
21 Java API for multi-threading, Java Multi-threading issues Singleton vs. Immutable Objects Multi-threading in Java & OS Linux
22 2.1 Java Multi-threading API Java Multi-threadingAPI Option 1 Java API for Multi-Threading Programming class MyT extends Thread { public void run() { MyT f = new MyT (); f.start(); Defining the classes: Option 2 Java API for Multi-Threading Programming class MyT extends SomeC implements Runnable { public void run() { Instantiates the objects MyT obf = new MyT(); Thread f = new Thread(obf); Set the thread in Runnable state f.start(); public void run() { Thread.sleep( ); String fname = this.getname(); Specific Thread methods calls public void run() { Thread.sleep( ); Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); String fname = t.getname();
23 2.1 Java Multi-threading API Java Threads API Creating Tasks & Threads // Custom task class public class TaskClass implements Runnable {... public TaskClass(...) {... java.lang.runnable TaskClass // Implement the run method in Runnable public void run() { // Tell system how to run custom thread // Client class public class Client {... public void somemethod() {... // Create an instance of TaskClass TaskClass task = new TaskClass(...); // Create a thread Thread thread = new Thread(task); // Start a thread thread.start(); Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Seventh Edition, (c) 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
24 Java Thread Class 2.1 Java Multi-threading API «interface» java.lang.runnable java.lang.thread +Thread() +Thread(task: Runnable) +start(): void +isalive(): boolean +setpriority(p: int): void +join(): void +sleep(millis: long): void +yield(): void +interrupt(): void Creates a default thread. Creates a thread for a specified task. Starts the thread that causes the run() method to be invoked by the JVM. Tests whether the thread is currently running. Sets priority p (ranging from 1 to 10) for this thread. Waits for this thread to finish. Puts the runnable object to sleep for a specified time in milliseconds. Causes this thread to temporarily pause and allow other threads to execute. Interrupts this thread. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Seventh Edition, (c) 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
25 Java Thread States 2.1 Java Multi-threading API CISCO Copyright
26 2.2 Is Java Singleton pattern Thread Safe? class ASingleton { // Version 1 private static ASingleton instance = null; private ASingleton() { public static ASingleton getinstance() { if (instance == null) { instance = new ASingleton(); return instance; class ASingleton{ // Version 2 - what if we are expecting some parameters // like DB URL, User, Pass to be passed in the getinstance private static ASingleton instance = new ASingleton(); private ASingleton(){ public static synchronized ASingleton getinstance(){ return instance;
27 2.2 Is Java Singleton pattern Thread Safe? class ASingleton { // Version 3 Now is quite safe private static ASingleton instance = null; private static Object mutex = new Object(); private ASingleton(){ public static ASingleton getinstance() { if(instance==null) { synchronized (mutex) { if(instance == null) instance = new ASingleton(); return instance;
28 2.2 Is Java Immutable Objects (see previous OOP lecture) Java Class Pattern Thread Safe? Immutable Classes and Objects. If the contents of an object cannot be changed once the object is created, the object is called an immutable object and its class is called an immutable class. If you delete the set method in the Circle class, the class would be immutable because radius is private and cannot be changed without a set method. A class with all private data fields and without mutators is not necessarily immutable. For example, the following class Student has all private data fields and no mutators, but it is mutable. What Class is immutable? For a class to be immutable, it must mark all data fields private and provide no mutator methods and no accessor methods that would return a reference to a mutable data field object. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved :
29 2.2 Is Java Immutable Objects (see previous OOP lecture) Java Class Pattern Thread Safe? Immutable Classes and Objects. 1) All the fields must be private and preferably final 2) Ensure the class cannot be overridden - make the class final, or use static factories and keep constructors private 3) Fields must be populated from the Constructor/Factory 4) Don't provide any setters for the fields 5) Watch out for collections. Use Collections.unmodifiable*. Also, collections should contain only immutable Objects 6) All the getters must provide immutable objects or use defensive copying 7) Don't provide any methods that change the internal state of the Object Read more:
30 2.2 Is Java Immutable Objects (see previous OOP lecture) Java Class Pattern Thread Safe? Immutable Classes and Objects. public class Student { private int id; private BirthDate birthdate; public class BirthDate { private int year; private int month; private int day; public Student(int ssn, int year, int month, int day) { id = ssn; birthdate = new BirthDate(year, month, day); public int getid() { return id; public BirthDate getbirthdate() { return birthdate; public BirthDate(int newyear, int newmonth, int newday) { year = newyear; month = newmonth; day = newday; public void setyear(int newyear) { year = newyear; public Date getdateofbirth() { return new Date(dateOfBirth.getTime()); //defensive copy instead of original meth. public class Test { public static void main(string[] args) { Student student = new Student( , 1970, 5, 3); BirthDate date = student.getbirthdate(); date.setyear(2010); // Now the student birth year is changed! Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved :
31 2.2 Is Java Immutable Objects (see previous OOP lecture) Java Class Pattern Thread Safe? Immutable Classes and Objects Are THREAD-SAFE? An object is considered immutable if its state cannot change after it is constructed. Maximum reliance on immutable objects is widely accepted as a sound strategy for creating simple, reliable code. Immutable objects are particularly useful in concurrent applications. Since they cannot change state, they cannot be corrupted by thread interference or observed in an inconsistentstate. Programmers are often reluctant to employ immutable objects, because they worry about the cost of creating a new object as opposed to updating an object in place. The impact of object creation is often overestimated, and can be offset by some of the efficiencies associated with immutable objects. These include decreased overhead due to garbage collection, and the elimination of code needed to protect mutable objects from corruption.
32 2.2 What Software Design Pattern is impacted by Multithreading?
33 2.2 What Software Design Pattern is impacted by Multithreading?
34 2.2 What Software Design Pattern is impacted by Multithreading?
35 2.2 What Software Design Pattern is impacted by Multithreading?
36 Section Conclusions All threads in a program must run the same executable. A child process, on the other hand, may run a different executable by calling an execfunction. An errant thread can harm other threads in the same process because threads share the same virtual memory space and other resources. Forinstance, a wild memory write through an uninitialized pointer in one thread can corrupt memory visible to another thread. An errant process, on the other hand, cannot do so because each process has a copy of the program s memory space. Multi-threading & IPC Summary for easy sharing Copying memory for a new process adds an additional performance overhead relative to creating a new thread. However, the copy is performed only when the memory is changed, so the penalty is minimal if the child process only reads memory. Threads should be used for programs that need fine-grained parallelism. For example, if a problem can be broken into multiple, nearly identical tasks, threads may be a good choice. Processes should be used for programs that need coarser parallelism. Sharing data among threads is trivial because threads share the same memory. However, great care must be taken to avoid race conditions. Sharing data among processes requires the use of IPC mechanisms. This can be more cumbersome but makes multiple processes less likelyto suffer from concurrency bugs.
37 Share knowledge, Empowering Minds Communicate & Exchange Ideas
38 ? Questions & Answers! But wait There s More!
39 What s Your Message? Thanks! Java Programming Software App Development End of Lecture 7 Java SE Multithreading
ECOM 2324 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING II
 ECOM 2324 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING II Object Oriented Programming with JAVA Instructor: Ruba A. Salamh Islamic University of Gaza 2 CHAPTER 9 OBJECTS AND CLASSES Motivations 3 After learning the preceding
ECOM 2324 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING II Object Oriented Programming with JAVA Instructor: Ruba A. Salamh Islamic University of Gaza 2 CHAPTER 9 OBJECTS AND CLASSES Motivations 3 After learning the preceding
Advanced Programming Methods. Lecture 6 - Concurrency in Java (1)
 Advanced Programming Methods Lecture 6 - Concurrency in Java (1) Overview Introduction Java threads Java.util.concurrent References NOTE: The slides are based on the following free tutorials. You may want
Advanced Programming Methods Lecture 6 - Concurrency in Java (1) Overview Introduction Java threads Java.util.concurrent References NOTE: The slides are based on the following free tutorials. You may want
OO Programming Concepts. Classes. Objects. Chapter 8 User-Defined Classes and ADTs
 Chapter 8 User-Defined Classes and ADTs Objectives To understand objects and classes and use classes to model objects To learn how to declare a class and how to create an object of a class To understand
Chapter 8 User-Defined Classes and ADTs Objectives To understand objects and classes and use classes to model objects To learn how to declare a class and how to create an object of a class To understand
THREADS & CONCURRENCY
 27/04/2018 Sorry for the delay in getting slides for today 2 Another reason for the delay: Yesterday: 63 posts on the course Piazza yesterday. A7: If you received 100 for correctness (perhaps minus a late
27/04/2018 Sorry for the delay in getting slides for today 2 Another reason for the delay: Yesterday: 63 posts on the course Piazza yesterday. A7: If you received 100 for correctness (perhaps minus a late
Chapter 9 Objects and Classes. OO Programming Concepts. Classes. Objects. Motivations. Objectives. CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University
 Chapter 9 Objects and Classes CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations After learning the preceding chapters, you are capable of solving many programming problems using selections, loops,
Chapter 9 Objects and Classes CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations After learning the preceding chapters, you are capable of solving many programming problems using selections, loops,
Computation Abstractions. Processes vs. Threads. So, What Is a Thread? CMSC 433 Programming Language Technologies and Paradigms Spring 2007
 CMSC 433 Programming Language Technologies and Paradigms Spring 2007 Threads and Synchronization May 8, 2007 Computation Abstractions t1 t1 t4 t2 t1 t2 t5 t3 p1 p2 p3 p4 CPU 1 CPU 2 A computer Processes
CMSC 433 Programming Language Technologies and Paradigms Spring 2007 Threads and Synchronization May 8, 2007 Computation Abstractions t1 t1 t4 t2 t1 t2 t5 t3 p1 p2 p3 p4 CPU 1 CPU 2 A computer Processes
Chapter 9 Objects and Classes. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eleventh Edition, (c) 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 9 Objects and Classes 1 Motivations After learning the preceding chapters, you are capable of solving many programming problems using selections, loops, methods, and arrays. However, these Java
Chapter 9 Objects and Classes 1 Motivations After learning the preceding chapters, you are capable of solving many programming problems using selections, loops, methods, and arrays. However, these Java
Chapter 4: Threads. Operating System Concepts. Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne
 Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues Operating System Examples Linux Threads 4.2 Silberschatz, Galvin and
Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues Operating System Examples Linux Threads 4.2 Silberschatz, Galvin and
Threads & Timers. CSE260, Computer Science B: Honors Stony Brook University
 Threads & Timers CSE260, Computer Science B: Honors Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse260 Multi-tasking When you re working, how many different applications do you have open at one
Threads & Timers CSE260, Computer Science B: Honors Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse260 Multi-tasking When you re working, how many different applications do you have open at one
INF 212 ANALYSIS OF PROG. LANGS CONCURRENCY. Instructors: Crista Lopes Copyright Instructors.
 INF 212 ANALYSIS OF PROG. LANGS CONCURRENCY Instructors: Crista Lopes Copyright Instructors. Basics Concurrent Programming More than one thing at a time Examples: Network server handling hundreds of clients
INF 212 ANALYSIS OF PROG. LANGS CONCURRENCY Instructors: Crista Lopes Copyright Instructors. Basics Concurrent Programming More than one thing at a time Examples: Network server handling hundreds of clients
THREADS AND CONCURRENCY
 THREADS AND CONCURRENCY Lecture 22 CS2110 Spring 2013 Graphs summary 2 Dijkstra: given a vertex v, finds shortest path from v to x for each vertex x in the graph Key idea: maintain a 5-part invariant on
THREADS AND CONCURRENCY Lecture 22 CS2110 Spring 2013 Graphs summary 2 Dijkstra: given a vertex v, finds shortest path from v to x for each vertex x in the graph Key idea: maintain a 5-part invariant on
CS 475. Process = Address space + one thread of control Concurrent program = multiple threads of control
 Processes & Threads Concurrent Programs Process = Address space + one thread of control Concurrent program = multiple threads of control Multiple single-threaded processes Multi-threaded process 2 1 Concurrent
Processes & Threads Concurrent Programs Process = Address space + one thread of control Concurrent program = multiple threads of control Multiple single-threaded processes Multi-threaded process 2 1 Concurrent
EPL372 Lab Exercise 2: Threads and pthreads. Εργαστήριο 2. Πέτρος Παναγή
 EPL372 Lab Exercise 2: Threads and pthreads Εργαστήριο 2 Πέτρος Παναγή 1 Threads Vs Processes 2 Process A process is created by the operating system, and requires a fair amount of "overhead". Processes
EPL372 Lab Exercise 2: Threads and pthreads Εργαστήριο 2 Πέτρος Παναγή 1 Threads Vs Processes 2 Process A process is created by the operating system, and requires a fair amount of "overhead". Processes
Quiz on Tuesday April 13. CS 361 Concurrent programming Drexel University Fall 2004 Lecture 4. Java facts and questions. Things to try in Java
 CS 361 Concurrent programming Drexel University Fall 2004 Lecture 4 Bruce Char and Vera Zaychik. All rights reserved by the author. Permission is given to students enrolled in CS361 Fall 2004 to reproduce
CS 361 Concurrent programming Drexel University Fall 2004 Lecture 4 Bruce Char and Vera Zaychik. All rights reserved by the author. Permission is given to students enrolled in CS361 Fall 2004 to reproduce
4. Concurrency via Threads
 CSC400 - Operating Systems 4. Concurrency via Threads J. Sumey Overview Multithreading Concept Background Implementations Thread States & Thread Switching Thread Operations Case Study: pthreads CSC400
CSC400 - Operating Systems 4. Concurrency via Threads J. Sumey Overview Multithreading Concept Background Implementations Thread States & Thread Switching Thread Operations Case Study: pthreads CSC400
7. MULTITHREDED PROGRAMMING
 7. MULTITHREDED PROGRAMMING What is thread? A thread is a single sequential flow of control within a program. Thread is a path of the execution in a program. Muti-Threading: Executing more than one thread
7. MULTITHREDED PROGRAMMING What is thread? A thread is a single sequential flow of control within a program. Thread is a path of the execution in a program. Muti-Threading: Executing more than one thread
Agenda. Threads. Single and Multi-threaded Processes. What is Thread. CSCI 444/544 Operating Systems Fall 2008
 Agenda Threads CSCI 444/544 Operating Systems Fall 2008 Thread concept Thread vs process Thread implementation - user-level - kernel-level - hybrid Inter-process (inter-thread) communication What is Thread
Agenda Threads CSCI 444/544 Operating Systems Fall 2008 Thread concept Thread vs process Thread implementation - user-level - kernel-level - hybrid Inter-process (inter-thread) communication What is Thread
Virtual Machine Design
 Virtual Machine Design Lecture 4: Multithreading and Synchronization Antero Taivalsaari September 2003 Session #2026: J2MEPlatform, Connected Limited Device Configuration (CLDC) Lecture Goals Give an overview
Virtual Machine Design Lecture 4: Multithreading and Synchronization Antero Taivalsaari September 2003 Session #2026: J2MEPlatform, Connected Limited Device Configuration (CLDC) Lecture Goals Give an overview
Chapter 9. Objects and Classes
 Chapter 9 Objects and Classes 1 OO Programming in Java Other than primitive data types (byte, short, int, long, float, double, char, boolean), everything else in Java is of type object. Objects we already
Chapter 9 Objects and Classes 1 OO Programming in Java Other than primitive data types (byte, short, int, long, float, double, char, boolean), everything else in Java is of type object. Objects we already
CS 5523 Operating Systems: Midterm II - reivew Instructor: Dr. Tongping Liu Department Computer Science The University of Texas at San Antonio
 CS 5523 Operating Systems: Midterm II - reivew Instructor: Dr. Tongping Liu Department Computer Science The University of Texas at San Antonio Fall 2017 1 Outline Inter-Process Communication (20) Threads
CS 5523 Operating Systems: Midterm II - reivew Instructor: Dr. Tongping Liu Department Computer Science The University of Texas at San Antonio Fall 2017 1 Outline Inter-Process Communication (20) Threads
Multithreaded Programming
 Multithreaded Programming Multithreaded programming basics Concurrency is the ability to run multiple parts of the program in parallel. In Concurrent programming, there are two units of execution: Processes
Multithreaded Programming Multithreaded programming basics Concurrency is the ability to run multiple parts of the program in parallel. In Concurrent programming, there are two units of execution: Processes
COURSE 11 PROGRAMMING III OOP. JAVA LANGUAGE
 COURSE 11 PROGRAMMING III OOP. JAVA LANGUAGE PREVIOUS COURSE CONTENT Input/Output Streams Text Files Byte Files RandomAcessFile Exceptions Serialization NIO COURSE CONTENT Threads Threads lifecycle Thread
COURSE 11 PROGRAMMING III OOP. JAVA LANGUAGE PREVIOUS COURSE CONTENT Input/Output Streams Text Files Byte Files RandomAcessFile Exceptions Serialization NIO COURSE CONTENT Threads Threads lifecycle Thread
Introduction to Java Threads
 Object-Oriented Programming Introduction to Java Threads RIT CS 1 "Concurrent" Execution Here s what could happen when you run this Java program and launch 3 instances on a single CPU architecture. The
Object-Oriented Programming Introduction to Java Threads RIT CS 1 "Concurrent" Execution Here s what could happen when you run this Java program and launch 3 instances on a single CPU architecture. The
CPS221 Lecture: Threads
 Objectives CPS221 Lecture: Threads 1. To introduce threads in the context of processes 2. To introduce UML Activity Diagrams last revised 9/5/12 Materials: 1. Diagram showing state of memory for a process
Objectives CPS221 Lecture: Threads 1. To introduce threads in the context of processes 2. To introduce UML Activity Diagrams last revised 9/5/12 Materials: 1. Diagram showing state of memory for a process
Motivation. Threads. Multithreaded Server Architecture. Thread of execution. Chapter 4
 Motivation Threads Chapter 4 Most modern applications are multithreaded Threads run within application Multiple tasks with the application can be implemented by separate Update display Fetch data Spell
Motivation Threads Chapter 4 Most modern applications are multithreaded Threads run within application Multiple tasks with the application can be implemented by separate Update display Fetch data Spell
THREADS & CONCURRENCY
 4/26/16 Announcements BRING YOUR CORNELL ID TO THE PRELIM. 2 You need it to get in THREADS & CONCURRENCY Prelim 2 is next Tonight BRING YOUR CORNELL ID! A7 is due Thursday. Our Heap.java: on Piazza (A7
4/26/16 Announcements BRING YOUR CORNELL ID TO THE PRELIM. 2 You need it to get in THREADS & CONCURRENCY Prelim 2 is next Tonight BRING YOUR CORNELL ID! A7 is due Thursday. Our Heap.java: on Piazza (A7
Le L c e t c ur u e e 7 To T p o i p c i s c t o o b e b e co c v o e v r e ed e Multithreading
 Course Name: Advanced Java Lecture 7 Topics to be covered Multithreading Thread--An Introduction Thread A thread is defined as the path of execution of a program. It is a sequence of instructions that
Course Name: Advanced Java Lecture 7 Topics to be covered Multithreading Thread--An Introduction Thread A thread is defined as the path of execution of a program. It is a sequence of instructions that
Threads & Concurrency
 2 Due date of A7 Due d About A5-A6 We have changed the due date of A7 Friday, 28 April. Threads & Concurrency But the last date to submit A7 remains the same: 29 April. We make the last date be 29 April
2 Due date of A7 Due d About A5-A6 We have changed the due date of A7 Friday, 28 April. Threads & Concurrency But the last date to submit A7 remains the same: 29 April. We make the last date be 29 April
Threads & Concurrency
 Threads & Concurrency Lecture 24 CS2110 Spring 2017 Due date of A7 Due d About A5-A6 2 We have changed the due date of A7 Friday, 28 April. But the last date to submit A7 remains the same: 29 April. We
Threads & Concurrency Lecture 24 CS2110 Spring 2017 Due date of A7 Due d About A5-A6 2 We have changed the due date of A7 Friday, 28 April. But the last date to submit A7 remains the same: 29 April. We
CS 450 Operating System Week 4 Lecture Notes
 CS 450 Operating System Week 4 Lecture Notes Reading: Operating System Concepts (7 th Edition) - Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Chapter 5 - Pages 129 147 Objectives: 1. Explain the main Objective of Threads
CS 450 Operating System Week 4 Lecture Notes Reading: Operating System Concepts (7 th Edition) - Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Chapter 5 - Pages 129 147 Objectives: 1. Explain the main Objective of Threads
CMSC 433 Programming Language Technologies and Paradigms. Concurrency
 CMSC 433 Programming Language Technologies and Paradigms Concurrency What is Concurrency? Simple definition Sequential programs have one thread of control Concurrent programs have many Concurrency vs.
CMSC 433 Programming Language Technologies and Paradigms Concurrency What is Concurrency? Simple definition Sequential programs have one thread of control Concurrent programs have many Concurrency vs.
Chapter 5: Threads. Overview Multithreading Models Threading Issues Pthreads Windows XP Threads Linux Threads Java Threads
 Chapter 5: Threads Overview Multithreading Models Threading Issues Pthreads Windows XP Threads Linux Threads Java Threads 5.1 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2003 More About Processes A process encapsulates
Chapter 5: Threads Overview Multithreading Models Threading Issues Pthreads Windows XP Threads Linux Threads Java Threads 5.1 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2003 More About Processes A process encapsulates
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Multithreading Multiprocessors Description Multiple processing units (multiprocessor) From single microprocessor to large compute clusters Can perform multiple
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Multithreading Multiprocessors Description Multiple processing units (multiprocessor) From single microprocessor to large compute clusters Can perform multiple
CS420: Operating Systems
 Threads James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania Based on Operating System Concepts, 9th Edition by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Threads A thread is a basic unit of processing
Threads James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania Based on Operating System Concepts, 9th Edition by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Threads A thread is a basic unit of processing
Chapter 4: Threads. Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues Operating System Examples Windows XP Threads Linux Threads
 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues Operating System Examples Windows XP Threads Linux Threads Chapter 4: Threads Objectives To introduce the notion of a
Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues Operating System Examples Windows XP Threads Linux Threads Chapter 4: Threads Objectives To introduce the notion of a
Process Characteristics. Threads Chapter 4. Process Characteristics. Multithreading vs. Single threading
 Process Characteristics Threads Chapter 4 Reading: 4.1,4.4, 4.5 Unit of resource ownership - process is allocated: a virtual address space to hold the process image control of some resources (files, I/O
Process Characteristics Threads Chapter 4 Reading: 4.1,4.4, 4.5 Unit of resource ownership - process is allocated: a virtual address space to hold the process image control of some resources (files, I/O
Threads Chapter 4. Reading: 4.1,4.4, 4.5
 Threads Chapter 4 Reading: 4.1,4.4, 4.5 1 Process Characteristics Unit of resource ownership - process is allocated: a virtual address space to hold the process image control of some resources (files,
Threads Chapter 4 Reading: 4.1,4.4, 4.5 1 Process Characteristics Unit of resource ownership - process is allocated: a virtual address space to hold the process image control of some resources (files,
Multithreaded Programming
 Multithreaded Programming The slides do not contain all the information and cannot be treated as a study material for Operating System. Please refer the text book for exams. September 4, 2014 Topics Overview
Multithreaded Programming The slides do not contain all the information and cannot be treated as a study material for Operating System. Please refer the text book for exams. September 4, 2014 Topics Overview
Chapter 3 Process Description and Control
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 3 Process Description and Control Seventh Edition By William Stallings Process Control Block Structure of Process Images in Virtual Memory How
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 3 Process Description and Control Seventh Edition By William Stallings Process Control Block Structure of Process Images in Virtual Memory How
Overview. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Concurrency. Multiprocessors. Processes vs. Threads. Computation Abstractions
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Multithreaded Programming Patterns in Java CMSC 330 2 Multiprocessors Description Multiple processing units (multiprocessor) From single microprocessor to
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Multithreaded Programming Patterns in Java CMSC 330 2 Multiprocessors Description Multiple processing units (multiprocessor) From single microprocessor to
What is a thread anyway?
 Concurrency in Java What is a thread anyway? Smallest sequence of instructions that can be managed independently by a scheduler There can be multiple threads within a process Threads can execute concurrently
Concurrency in Java What is a thread anyway? Smallest sequence of instructions that can be managed independently by a scheduler There can be multiple threads within a process Threads can execute concurrently
Threads. Definitions. Process Creation. Process. Thread Example. Thread. From Volume II
 Definitions A glossary Threads From Volume II Copyright 1998-2002 Delroy A. Brinkerhoff. All Rights Reserved. Threads Slide 1 of 30 PMultitasking: (concurrent ramming, multiramming) the illusion of running
Definitions A glossary Threads From Volume II Copyright 1998-2002 Delroy A. Brinkerhoff. All Rights Reserved. Threads Slide 1 of 30 PMultitasking: (concurrent ramming, multiramming) the illusion of running
Object Oriented Programming. Week 10 Part 1 Threads
 Object Oriented Programming Week 10 Part 1 Threads Lecture Concurrency, Multitasking, Process and Threads Thread Priority and State Java Multithreading Extending the Thread Class Defining a Class that
Object Oriented Programming Week 10 Part 1 Threads Lecture Concurrency, Multitasking, Process and Threads Thread Priority and State Java Multithreading Extending the Thread Class Defining a Class that
CS 351 Design of Large Programs Threads and Concurrency
 CS 351 Design of Large Programs Threads and Concurrency Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Concurrency in Java Java has basic concurrency support built into the language. Also has high-level
CS 351 Design of Large Programs Threads and Concurrency Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Concurrency in Java Java has basic concurrency support built into the language. Also has high-level
Concurrency & Parallelism. Threads, Concurrency, and Parallelism. Multicore Processors 11/7/17
 Concurrency & Parallelism So far, our programs have been sequential: they do one thing after another, one thing at a. Let s start writing programs that do more than one thing at at a. Threads, Concurrency,
Concurrency & Parallelism So far, our programs have been sequential: they do one thing after another, one thing at a. Let s start writing programs that do more than one thing at at a. Threads, Concurrency,
Contents. G53SRP: Java Threads. Definition. Why we need it. A Simple Embedded System. Why we need it. Java Threads 24/09/2009 G53SRP 1 ADC
 Contents G53SRP: Java Threads Chris Greenhalgh School of Computer Science 1 Definition Motivations Threads Java threads Example embedded process Java Thread API & issues Exercises Book: Wellings 1.1 &
Contents G53SRP: Java Threads Chris Greenhalgh School of Computer Science 1 Definition Motivations Threads Java threads Example embedded process Java Thread API & issues Exercises Book: Wellings 1.1 &
Threads Chapter 5 1 Chapter 5
 Threads Chapter 5 1 Chapter 5 Process Characteristics Concept of Process has two facets. A Process is: A Unit of resource ownership: a virtual address space for the process image control of some resources
Threads Chapter 5 1 Chapter 5 Process Characteristics Concept of Process has two facets. A Process is: A Unit of resource ownership: a virtual address space for the process image control of some resources
Overview. Processes vs. Threads. Computation Abstractions. CMSC 433, Fall Michael Hicks 1
 CMSC 433 Programming Language Technologies and Paradigms Spring 2003 Threads and Synchronization April 1, 2003 Overview What are threads? Thread scheduling, data races, and synchronization Thread mechanisms
CMSC 433 Programming Language Technologies and Paradigms Spring 2003 Threads and Synchronization April 1, 2003 Overview What are threads? Thread scheduling, data races, and synchronization Thread mechanisms
Threads Assistant Professor DCS Operating System Concepts
 Threads Rab Nawaz Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Assistant Professor COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Operating System Concepts Definitions Threads In the previous discussion, a process
Threads Rab Nawaz Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Assistant Professor COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Operating System Concepts Definitions Threads In the previous discussion, a process
Process Concepts. CSC400 - Operating Systems. 3. Process Concepts. J. Sumey
 CSC400 - Operating Systems 3. Process Concepts J. Sumey Overview Concurrency Processes & Process States Process Accounting Interrupts & Interrupt Processing Interprocess Communication CSC400 - Process
CSC400 - Operating Systems 3. Process Concepts J. Sumey Overview Concurrency Processes & Process States Process Accounting Interrupts & Interrupt Processing Interprocess Communication CSC400 - Process
Review: Easy Piece 1
 CS 537 Lecture 10 Threads Michael Swift 10/9/17 2004-2007 Ed Lazowska, Hank Levy, Andrea and Remzi Arpaci-Dussea, Michael Swift 1 Review: Easy Piece 1 Virtualization CPU Memory Context Switch Schedulers
CS 537 Lecture 10 Threads Michael Swift 10/9/17 2004-2007 Ed Lazowska, Hank Levy, Andrea and Remzi Arpaci-Dussea, Michael Swift 1 Review: Easy Piece 1 Virtualization CPU Memory Context Switch Schedulers
Inter-Process Communication and Synchronization of Processes, Threads and Tasks: Lesson-1: PROCESS
 Inter-Process Communication and Synchronization of Processes, Threads and Tasks: Lesson-1: PROCESS 1 Process Concepts 2 Process A process consists of executable program (codes), state of which is controlled
Inter-Process Communication and Synchronization of Processes, Threads and Tasks: Lesson-1: PROCESS 1 Process Concepts 2 Process A process consists of executable program (codes), state of which is controlled
Concurrent Programming. Copyright 2017 by Robert M. Dondero, Ph.D. Princeton University
 Concurrent Programming Copyright 2017 by Robert M. Dondero, Ph.D. Princeton University 1 Objectives You will learn/review: What a process is How to fork and wait for processes What a thread is How to spawn
Concurrent Programming Copyright 2017 by Robert M. Dondero, Ph.D. Princeton University 1 Objectives You will learn/review: What a process is How to fork and wait for processes What a thread is How to spawn
JAVA and J2EE UNIT - 4 Multithreaded Programming And Event Handling
 JAVA and J2EE UNIT - 4 Multithreaded Programming And Event Handling Multithreaded Programming Topics Multi Threaded Programming What are threads? How to make the classes threadable; Extending threads;
JAVA and J2EE UNIT - 4 Multithreaded Programming And Event Handling Multithreaded Programming Topics Multi Threaded Programming What are threads? How to make the classes threadable; Extending threads;
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II. Threads in Java
 CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II Threads in Java 1 Problem Multiple tasks for computer Draw & display images on screen Check keyboard & mouse input Send & receive data on network Read & write files
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II Threads in Java 1 Problem Multiple tasks for computer Draw & display images on screen Check keyboard & mouse input Send & receive data on network Read & write files
Chapter 4: Multi-Threaded Programming
 Chapter 4: Multi-Threaded Programming Chapter 4: Threads 4.1 Overview 4.2 Multicore Programming 4.3 Multithreading Models 4.4 Thread Libraries Pthreads Win32 Threads Java Threads 4.5 Implicit Threading
Chapter 4: Multi-Threaded Programming Chapter 4: Threads 4.1 Overview 4.2 Multicore Programming 4.3 Multithreading Models 4.4 Thread Libraries Pthreads Win32 Threads Java Threads 4.5 Implicit Threading
Outline. Threads. Single and Multithreaded Processes. Benefits of Threads. Eike Ritter 1. Modified: October 16, 2012
 Eike Ritter 1 Modified: October 16, 2012 Lecture 8: Operating Systems with C/C++ School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham, UK 1 Based on material by Matt Smart and Nick Blundell Outline 1 Concurrent
Eike Ritter 1 Modified: October 16, 2012 Lecture 8: Operating Systems with C/C++ School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham, UK 1 Based on material by Matt Smart and Nick Blundell Outline 1 Concurrent
Concurrency, Thread. Dongkun Shin, SKKU
 Concurrency, Thread 1 Thread Classic view a single point of execution within a program a single PC where instructions are being fetched from and executed), Multi-threaded program Has more than one point
Concurrency, Thread 1 Thread Classic view a single point of execution within a program a single PC where instructions are being fetched from and executed), Multi-threaded program Has more than one point
Threads Questions Important Questions
 Threads Questions Important Questions https://dzone.com/articles/threads-top-80-interview https://www.journaldev.com/1162/java-multithreading-concurrency-interviewquestions-answers https://www.javatpoint.com/java-multithreading-interview-questions
Threads Questions Important Questions https://dzone.com/articles/threads-top-80-interview https://www.journaldev.com/1162/java-multithreading-concurrency-interviewquestions-answers https://www.javatpoint.com/java-multithreading-interview-questions
Threads, Concurrency, and Parallelism
 Threads, Concurrency, and Parallelism Lecture 24 CS2110 Spring 2017 Concurrency & Parallelism So far, our programs have been sequential: they do one thing after another, one thing at a time. Let s start
Threads, Concurrency, and Parallelism Lecture 24 CS2110 Spring 2017 Concurrency & Parallelism So far, our programs have been sequential: they do one thing after another, one thing at a time. Let s start
Agenda Process Concept Process Scheduling Operations on Processes Interprocess Communication 3.2
 Lecture 3: Processes Agenda Process Concept Process Scheduling Operations on Processes Interprocess Communication 3.2 Process in General 3.3 Process Concept Process is an active program in execution; process
Lecture 3: Processes Agenda Process Concept Process Scheduling Operations on Processes Interprocess Communication 3.2 Process in General 3.3 Process Concept Process is an active program in execution; process
CST242 Concurrency Page 1
 CST242 Concurrency Page 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 Concurrency CST242 Concurrent Processing (Page 1) Only computers with multiple processors can truly execute multiple instructions concurrently On single-processor
CST242 Concurrency Page 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 Concurrency CST242 Concurrent Processing (Page 1) Only computers with multiple processors can truly execute multiple instructions concurrently On single-processor
Chapter 19 Multithreading
 Chapter 19 Multithreading Prerequisites for Part VI Chapter 14 Applets, Images, and Audio Chapter 19 Multithreading Chapter 20 Internationalization 1 Objectives To understand the concept of multithreading
Chapter 19 Multithreading Prerequisites for Part VI Chapter 14 Applets, Images, and Audio Chapter 19 Multithreading Chapter 20 Internationalization 1 Objectives To understand the concept of multithreading
Java Threads. COMP 585 Noteset #2 1
 Java Threads The topic of threads overlaps the boundary between software development and operation systems. Words like process, task, and thread may mean different things depending on the author and the
Java Threads The topic of threads overlaps the boundary between software development and operation systems. Words like process, task, and thread may mean different things depending on the author and the
Process Characteristics
 Threads 1 Chapter 4 2 Process Characteristics We ve mentioned a process as having two characteristics Unit of resource ownership: processes have their own dedicated memory address space processes temporarily
Threads 1 Chapter 4 2 Process Characteristics We ve mentioned a process as having two characteristics Unit of resource ownership: processes have their own dedicated memory address space processes temporarily
Unit - IV Multi-Threading
 Unit - IV Multi-Threading 1 Uni Processing In the early days of computer only one program will occupy the memory. The second program must be in waiting. The second program will be entered whenever first
Unit - IV Multi-Threading 1 Uni Processing In the early days of computer only one program will occupy the memory. The second program must be in waiting. The second program will be entered whenever first
Chapter 4: Threads. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edit9on
 Chapter 4: Threads Operating System Concepts 9 th Edit9on Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads 1. Overview 2. Multicore Programming 3. Multithreading Models 4. Thread Libraries 5. Implicit
Chapter 4: Threads Operating System Concepts 9 th Edit9on Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads 1. Overview 2. Multicore Programming 3. Multithreading Models 4. Thread Libraries 5. Implicit
3. Multithreading. Chuanhai Liu. Department of Statistics, Purdue University /29
 /29 3. Multithreading Chuanhai Liu Department of Statistics, Purdue University 2016 2/29 Table of Contents 3.1 Simple SupR additions................................... 3 3.2 Parallel computing.......................................
/29 3. Multithreading Chuanhai Liu Department of Statistics, Purdue University 2016 2/29 Table of Contents 3.1 Simple SupR additions................................... 3 3.2 Parallel computing.......................................
System Call. Preview. System Call. System Call. System Call 9/7/2018
 Preview Operating System Structure Monolithic Layered System Microkernel Virtual Machine Process Management Process Models Process Creation Process Termination Process State Process Implementation Operating
Preview Operating System Structure Monolithic Layered System Microkernel Virtual Machine Process Management Process Models Process Creation Process Termination Process State Process Implementation Operating
Introduction to PThreads and Basic Synchronization
 Introduction to PThreads and Basic Synchronization Michael Jantz, Dr. Prasad Kulkarni Dr. Douglas Niehaus EECS 678 Pthreads Introduction Lab 1 Introduction In this lab, we will learn about some basic synchronization
Introduction to PThreads and Basic Synchronization Michael Jantz, Dr. Prasad Kulkarni Dr. Douglas Niehaus EECS 678 Pthreads Introduction Lab 1 Introduction In this lab, we will learn about some basic synchronization
Lecture 2 summary of Java SE section 1
 Lecture 2 summary of Java SE section 1 presentation DAD Distributed Applications Development Cristian Toma D.I.C.E/D.E.I.C Department of Economic Informatics & Cybernetics www.dice.ase.ro Cristian Toma
Lecture 2 summary of Java SE section 1 presentation DAD Distributed Applications Development Cristian Toma D.I.C.E/D.E.I.C Department of Economic Informatics & Cybernetics www.dice.ase.ro Cristian Toma
POSIX Threads: a first step toward parallel programming. George Bosilca
 POSIX Threads: a first step toward parallel programming George Bosilca bosilca@icl.utk.edu Process vs. Thread A process is a collection of virtual memory space, code, data, and system resources. A thread
POSIX Threads: a first step toward parallel programming George Bosilca bosilca@icl.utk.edu Process vs. Thread A process is a collection of virtual memory space, code, data, and system resources. A thread
Performance Throughput Utilization of system resources
 Concurrency 1. Why concurrent programming?... 2 2. Evolution... 2 3. Definitions... 3 4. Concurrent languages... 5 5. Problems with concurrency... 6 6. Process Interactions... 7 7. Low-level Concurrency
Concurrency 1. Why concurrent programming?... 2 2. Evolution... 2 3. Definitions... 3 4. Concurrent languages... 5 5. Problems with concurrency... 6 6. Process Interactions... 7 7. Low-level Concurrency
EECS 482 Introduction to Operating Systems
 EECS 482 Introduction to Operating Systems Winter 2018 Harsha V. Madhyastha Monitors vs. Semaphores Monitors: Custom user-defined conditions Developer must control access to variables Semaphores: Access
EECS 482 Introduction to Operating Systems Winter 2018 Harsha V. Madhyastha Monitors vs. Semaphores Monitors: Custom user-defined conditions Developer must control access to variables Semaphores: Access
CS 333 Introduction to Operating Systems. Class 3 Threads & Concurrency. Jonathan Walpole Computer Science Portland State University
 CS 333 Introduction to Operating Systems Class 3 Threads & Concurrency Jonathan Walpole Computer Science Portland State University 1 The Process Concept 2 The Process Concept Process a program in execution
CS 333 Introduction to Operating Systems Class 3 Threads & Concurrency Jonathan Walpole Computer Science Portland State University 1 The Process Concept 2 The Process Concept Process a program in execution
W4118 Operating Systems. Junfeng Yang
 W4118 Operating Systems Junfeng Yang What is a process? Outline Process dispatching Common process operations Inter-process Communication What is a process Program in execution virtual CPU Process: an
W4118 Operating Systems Junfeng Yang What is a process? Outline Process dispatching Common process operations Inter-process Communication What is a process Program in execution virtual CPU Process: an
Multithread Computing
 Multithread Computing About This Lecture Purpose To learn multithread programming in Java What You Will Learn ¾ Benefits of multithreading ¾ Class Thread and interface Runnable ¾ Thread methods and thread
Multithread Computing About This Lecture Purpose To learn multithread programming in Java What You Will Learn ¾ Benefits of multithreading ¾ Class Thread and interface Runnable ¾ Thread methods and thread
Chapter 9 Objects and Classes. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, (c) 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 9 Objects and Classes rights reserved. 1 Motivations After learning the preceding chapters, you are capable of solving many programming problems using selections, loops, methods, and arrays. However,
Chapter 9 Objects and Classes rights reserved. 1 Motivations After learning the preceding chapters, you are capable of solving many programming problems using selections, loops, methods, and arrays. However,
Multi-threading in Java. Jeff HUANG
 Multi-threading in Java Jeff HUANG Software Engineering Group @HKUST Do you use them? 2 Do u know their internals? 3 Let s see File DB How can they service so many clients simultaneously? l 4 Multi-threading
Multi-threading in Java Jeff HUANG Software Engineering Group @HKUST Do you use them? 2 Do u know their internals? 3 Let s see File DB How can they service so many clients simultaneously? l 4 Multi-threading
Programmazione Avanzata e Paradigmi Ingegneria e Scienze Informatiche - UNIBO a.a 2013/2014 Lecturer: Alessandro Ricci
 v1.0 20130323 Programmazione Avanzata e Paradigmi Ingegneria e Scienze Informatiche - UNIBO a.a 2013/2014 Lecturer: Alessandro Ricci [module lab 2.1] CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING IN JAVA: INTRODUCTION 1 CONCURRENT
v1.0 20130323 Programmazione Avanzata e Paradigmi Ingegneria e Scienze Informatiche - UNIBO a.a 2013/2014 Lecturer: Alessandro Ricci [module lab 2.1] CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING IN JAVA: INTRODUCTION 1 CONCURRENT
Shared-Memory and Multithread Programming
 Shared-Memory and Multithread Programming Pruet Boonma pruet@eng.cmu.ac.th Department of Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Chiang Mai University Based on a material by: Bryan Carpenter Pervasive
Shared-Memory and Multithread Programming Pruet Boonma pruet@eng.cmu.ac.th Department of Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Chiang Mai University Based on a material by: Bryan Carpenter Pervasive
The Java Memory Model
 The Java Memory Model What is it and why would I want one? Jörg Domaschka. ART Group, Institute for Distributed Systems Ulm University, Germany December 14, 2009 public class WhatDoIPrint{ static int x
The Java Memory Model What is it and why would I want one? Jörg Domaschka. ART Group, Institute for Distributed Systems Ulm University, Germany December 14, 2009 public class WhatDoIPrint{ static int x
CS 333 Introduction to Operating Systems. Class 3 Threads & Concurrency. Jonathan Walpole Computer Science Portland State University
 CS 333 Introduction to Operating Systems Class 3 Threads & Concurrency Jonathan Walpole Computer Science Portland State University 1 Process creation in UNIX All processes have a unique process id getpid(),
CS 333 Introduction to Operating Systems Class 3 Threads & Concurrency Jonathan Walpole Computer Science Portland State University 1 Process creation in UNIX All processes have a unique process id getpid(),
Chapter 4: Threads. Chapter 4: Threads
 Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples
Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples
Chapter 4: Multithreaded
 Chapter 4: Multithreaded Programming Chapter 4: Multithreaded Programming Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues Operating-System Examples 2009/10/19 2 4.1 Overview A thread is
Chapter 4: Multithreaded Programming Chapter 4: Multithreaded Programming Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues Operating-System Examples 2009/10/19 2 4.1 Overview A thread is
Threads (light weight processes) Chester Rebeiro IIT Madras
 Threads (light weight processes) Chester Rebeiro IIT Madras 1 Processes Separate streams of execution Each process isolated from the other Process state contains Process ID Environment Working directory.
Threads (light weight processes) Chester Rebeiro IIT Madras 1 Processes Separate streams of execution Each process isolated from the other Process state contains Process ID Environment Working directory.
Last class: Today: Thread Background. Thread Systems
 1 Last class: Thread Background Today: Thread Systems 2 Threading Systems 3 What kind of problems would you solve with threads? Imagine you are building a web server You could allocate a pool of threads,
1 Last class: Thread Background Today: Thread Systems 2 Threading Systems 3 What kind of problems would you solve with threads? Imagine you are building a web server You could allocate a pool of threads,
Threads and Too Much Milk! CS439: Principles of Computer Systems January 31, 2018
 Threads and Too Much Milk! CS439: Principles of Computer Systems January 31, 2018 Last Time CPU Scheduling discussed the possible policies the scheduler may use to choose the next process (or thread!)
Threads and Too Much Milk! CS439: Principles of Computer Systems January 31, 2018 Last Time CPU Scheduling discussed the possible policies the scheduler may use to choose the next process (or thread!)
Concurrency: State Models & Design Patterns
 Concurrency: State Models & Design Patterns Practical Session Week 02 1 / 13 Exercises 01 Discussion Exercise 01 - Task 1 a) Do recent central processing units (CPUs) of desktop PCs support concurrency?
Concurrency: State Models & Design Patterns Practical Session Week 02 1 / 13 Exercises 01 Discussion Exercise 01 - Task 1 a) Do recent central processing units (CPUs) of desktop PCs support concurrency?
CS 5523: Operating Systems
 CS 5523: Operating Systems Instructor: Dr. Tongping Liu Midterm Exam: Oct 6, 2015, Tuesday 7:15pm 8:30pm CS5523: Operating Systems @ UTSA 1 Lecture1: OS Overview Operating System: what is it?! Evolution
CS 5523: Operating Systems Instructor: Dr. Tongping Liu Midterm Exam: Oct 6, 2015, Tuesday 7:15pm 8:30pm CS5523: Operating Systems @ UTSA 1 Lecture1: OS Overview Operating System: what is it?! Evolution
User Space Multithreading. Computer Science, University of Warwick
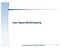 User Space Multithreading 1 Threads Thread short for thread of execution/control B efore create Global During create Global Data Data Executing Code Code Stack Stack Stack A fter create Global Data Executing
User Space Multithreading 1 Threads Thread short for thread of execution/control B efore create Global During create Global Data Data Executing Code Code Stack Stack Stack A fter create Global Data Executing
Processes and Threads
 TDDI04 Concurrent Programming, Operating Systems, and Real-time Operating Systems Processes and Threads [SGG7] Chapters 3 and 4 Copyright Notice: The lecture notes are mainly based on Silberschatz s, Galvin
TDDI04 Concurrent Programming, Operating Systems, and Real-time Operating Systems Processes and Threads [SGG7] Chapters 3 and 4 Copyright Notice: The lecture notes are mainly based on Silberschatz s, Galvin
Chapter 4: Threads. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples
Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples
CPSC/ECE 3220 Fall 2017 Exam Give the definition (note: not the roles) for an operating system as stated in the textbook. (2 pts.
 CPSC/ECE 3220 Fall 2017 Exam 1 Name: 1. Give the definition (note: not the roles) for an operating system as stated in the textbook. (2 pts.) Referee / Illusionist / Glue. Circle only one of R, I, or G.
CPSC/ECE 3220 Fall 2017 Exam 1 Name: 1. Give the definition (note: not the roles) for an operating system as stated in the textbook. (2 pts.) Referee / Illusionist / Glue. Circle only one of R, I, or G.
Chapter 4: Threads. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples
Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples
Thread. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1
 Thread Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1 IPC Shared memory Recap share a memory region between processes read or write to the shared memory region fast
Thread Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from the book authors slides with permission 1 IPC Shared memory Recap share a memory region between processes read or write to the shared memory region fast
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING THREAD S BASICS. Introduction Thread basics. Thread states. Sequence diagrams
 SUMMARY CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING THREAD S BASICS PROGRAMMAZIONE CONCORRENTE E DISTR. Introduction Thread basics Thread properties Thread states Thread interruption Sequence diagrams Università degli Studi
SUMMARY CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING THREAD S BASICS PROGRAMMAZIONE CONCORRENTE E DISTR. Introduction Thread basics Thread properties Thread states Thread interruption Sequence diagrams Università degli Studi
Interoperation of tasks
 Operating systems (vimia219) Interoperation of tasks Tamás Kovácsházy, PhD 4 th topic, Implementation of tasks, processes and threads Budapest University of Technology and Economics Department of Measurement
Operating systems (vimia219) Interoperation of tasks Tamás Kovácsházy, PhD 4 th topic, Implementation of tasks, processes and threads Budapest University of Technology and Economics Department of Measurement
OPERATING SYSTEM. Chapter 4: Threads
 OPERATING SYSTEM Chapter 4: Threads Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples Objectives To
OPERATING SYSTEM Chapter 4: Threads Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples Objectives To
Thread Concept. Thread. No. 3. Multiple single-threaded Process. One single-threaded Process. Process vs. Thread. One multi-threaded Process
 EECS 3221 Operating System Fundamentals What is thread? Thread Concept No. 3 Thread Difference between a process and a thread Prof. Hui Jiang Dept of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, York University
EECS 3221 Operating System Fundamentals What is thread? Thread Concept No. 3 Thread Difference between a process and a thread Prof. Hui Jiang Dept of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, York University
