A Framework for Real-Time Resource Allocation in IP Multimedia Subsystem Network
|
|
|
- Coleen Hart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 I. J. Computer Network and Information Security, 2013, 3, Published Online March 2013 in MECS ( DOI: /ijcnis A Framework for Real-Time Resource Allocation in IP Multimedia Subsystem Network Muhammad Naeem Department of Computer Science, Mohammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad, Pakistan naeems.naeem@gmail.com Sheneela Naz and Saira Gillani Centre of Research in Networks & Telecom, Mohammad Ali Jinnah University Islamabad, Pakistan shahneela.cs@gmail.com, sairagilani@yahoo.com Abstract IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) is designed to provide multiple-services and can be accessed from any access network. With the advent of new multimedia services; user requirement also changed and required delay tolerant services from the service providers. The new multimedia services demands the restrictions on network parameters and this can be achieved by analyzing the traffic flow from the core as well as access network capabilities. As access and core IMS network are independent of each other and does not exchange user SLA with each other. In this paper we proposed framework based on Session border controller (SBC) that proactively monitored the traffic statistics as well as interact with access network operator for getting user s SLA and reserve resources accordingly. We are also proposing alterations in SIP invite and re-invite message to incorporate requested information. These alterations will be useful in ensuring availability of user s handset capabilities to IMS core network. Index Terms quality of service, IP multimedia subsystem, SIP, RTCP, SBC I. INTRODUCTION Next Generation Network is getting attraction from the service providers. In order to provide multiple services over a single converged network, most of Mobile and fixed network operator had already moved their Telecommunication infrastructure to All IP converged network. IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) standardized by 3GPP is getting attention for replacing the legacy circuit switched network with All IP network [1]. IMS provides Multiple services independent of underlying access network. The user can access the services of IMS using any of access technology which is DSL, Wi-Fi, Wi- Max, GPRS etc. IMS is multi service network and user requirement may vary from simple voice call to high multimedia applications. These requirements introduce the significant challenges as network operator must manage real time services across the more complex Multivendor, multiaccess and multi service environment to continuously fulfill the requirement of customers. For providing on demand services to end-user most of the network operator signed SLA agreement with end-user to ensure there required service demands. In this paper we provide a mechanism for resource reservation by analyzing the traffic stats of end-user. For allocating the resources and QOS services to end-user; we are using Session Border Controller (SBC) that continuously monitored the real-time traffic and RTCP packets for QoS decisions [2]. The SBC also analyzed the SLA of access and core IMS network and enforce polices according to signed SLA and feedback from RTCP packets. As SIP/SDP is core protocol for exchange of signaling information [3] [4] [5]; we are proposing change in invite and re-invite SIP messages for including user specific information s. As IMS services can be accessed from any of access network and SLA s of both access and IMS network are different for this we recommended that the user s access level SLA exchanged with core IMS network and IMS enforce policies accordingly. The rest of the paper is organized as in section 1 we will discuss the QoS challenges, basic QoS Metrics and provide QoS requirement for different applications. In section 2 we will detail out the functional architecture of IMS and different protocols used in IMS network. In section 3 we will discuss the based architecture for IMS network and State of the art, in section 4. In section 5 we will discuss real-time resource allocation based on session border controller (SBC) with final conclusion retrieved from this study. II. BACKGROUND In order to highlight the framework for real time resource allocation in IP Multimedia Subsystem Network; it is useful to elaborate the preliminary concepts related to these technologies. We have divided this section into four sub sections to explain each of the subsection in detail. A. QOS CHALLENGES IMS is multi-service network that provide data, video, and voice service to end user regardless of under lying access network. The applications are varied from simple
2 A Framework for Real-Time Resource Allocation in IP Multimedia Subsystem Network 33 low quality voice call to high quality multimedia application and require the acceptable service quality from operators. As Multimedia applications are becoming richer day by day and required more bandwidth to fulfill the needs of end-user. In order to meet this; network operator adds more bandwidth to their network but addition of bandwidth does not means that the multimedia application will get the better services from network operators. Besides adding more bandwidth to the network it is also required to provide some strong policing, traffic reshaping, and queuing methods that provides uninterrupted service to end user. In order to provide the good services to customer the aim of Operator is to minimize the jitter, delay, packet loss and maximize the Throughput. The operators ensure the services to end-user within the signed SLA and QOS benchmark. Table 1 provides the QOS bench mark for different applications. Table 1: QoS Bench Mark (Bandwidth, Delay, Jitter) Applications QoS Benchmark (Sensitive to) Bandwidth Delay Jitter VoIP High Delay Low VOD High Delay Low IP TV High Delay Low Web Medium Medium Medium s Medium Medium Medium IM Messaging Low Delay Low Conferencing High Delay Low PoT Medium Delay Low Database Moderate Delay Medium Banking Medium Delay Low E-Government Medium Delay Low Signaling Low Low Low Table 2: QoS Bench Mark (Packet Loss, Throughput, Availability) Applications QoS Benchmark (Sensitive to) Availability Packet Throughput Loss VoIP Low High High VOD Low High High IP TV Low High High Web Low High Medium s Low High Medium IM Low High High Messaging Conferencing Low High High PoT Low High High Database Low High High Banking Low High High E- Low High High Government Signaling Low High High B. STATIC VERSUS ONLINE QOS Static QoS requires manual setup and reserve the bandwidth as expected by the end user. This will result in degradation when more bandwidth is required as well as wastage of bandwidth when it cannot be used. The main drawback of this approach is that it requires end to end configuration of network to reserve the resources at all network nodes. In contrast, Dynamic QoS does not reserve any bandwidth instead it dynamically processes voice, video, and data traffic on the basis of current needs, optimizing the bandwidth resources. C. IP MULTIMEIDA SUBSYSTEM 3GPP defines number of components for IMS network [6], [7], [8]. 3GPP provide the IMS framework for its 3 rd generation UMTS network. In conjunction with 3GPP ETSI working group TISPAN [14], [15] provides working architecture for fixed network. The main functional component of IMS is Call Session Control Function (CSCF) Session controller manages SIP session and coordinates with other network entities for session control, service control and resource allocation. To fulfill such functionalities, the CSCF can act as Proxy CSCF (P- CSCF), Serving CSCF (S-CSCF) or Interrogating CSCF (I-CSCF). P-CSCF is the first point for contact for end user, end user registers with P-CSCF to access the network resources. S-CSCF control and maintains services requested by the user. S-CSCF is also responsible for enforcing the policies and finds which application server to be contacted to fulfill the user requirement. I-CSCF acts as initial point of contact to the IMS home network from other networks. It routes received SIP requests to the S-CSCF assigned to the user or selects an S-CSCF if one is not currently assigned. Call Session control functions uses the SIP protocol for exchange of session information between different call session entities as well as with user. SDP is used along with SIP to provide the information about the session and RTP is used for real time traffic. The Home subscriber server (HSS) provides the authentication, authorization and contains the information about end user and their subscription profiles. HSS use the diameter protocol for authorization, authentication and accounting. Decision Function (PDF) provides QoS policy and resource admission control for the IMS network. PDF uses the services of COPS for exchange of policy information between PEP and PDF. Other core component of IMS are MGCF that provides interworking with other circuit switched PSTN and PLMN network it controls the Media Gateway that control the user traffic to circuit switched network and signaling gateway that controls signaling exchange with PSTN and PLMN network. MGCF make use of MGCP for signaling to Media gateway and Sigtran for exchange of SS7 Signaling with PSTN. Application server provides services like VOD, presences services, gaming capability, Value added services and IPTV service. MRF provides multiparty conferencing and announcement services.
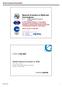
3 34 A Framework for Real-Time Resource Allocation in IP Multimedia Subsystem Network D. POLICY BASED QOS IN IMS IMS adopted the based QOS model proposed by IETF RFC [7] to provide the Quality of services for its UMTS based IMS network. The based network is based on two elements, the Decision Point (PDP) and the Enforcement Point (PEP). The role of PEP is to enforce that only authorized IP flows can pass through the network. The PEP send the policy requirement to PDP, the PDP checked the policy rules for the request and extract a set of policies that has been implemented. The PDP responds back the PEP with the set of rules that has been implemented and PEP enforces the rules that have been extracted from PDP. The flow of call using policy based network is as under 1. The user send invite message to P-CSCF with SDP information, the S-CSCF routes this to HSS for initial filtration and user authentication and call is routed to the second user. 2. The Second user replies the SIP invite message with SDP information, The P-CSCF examines the SDP information responded by User B to determine the QoS of service requirement for session. The P-CSCF send request to PCF for token authorization, PDP in IMS serves as a PCF. The PCF replies with token identifying the authorized session and resources. The P-CSCF sends this authorization token to caller. Management Tool Decision point Decision Point Enforcement Enforcement Point Store Policies to be enforce Retrieve Polices for Enforcement Figure 1. Base Network [8] Database/SLA 3. The caller sends the PDP context activation and token to GSGN and reserve resources 4. PCF check the validity of session after receiving the COPS message of from GGSN. 5. The PCF sends resource reservation information to GGSN. The PEF in the GGSN act as a gate that it controls the flow of packets. It only allows the packets to cross the network that are authorized by the PCF and block the rest of the packets. The IMS session setup starts with exchange of signaling information to Proxy call session controller, once the signaling setup is completed then media channel is open for the exchange of actual multimedia traffic. The path for signaling and real time traffic is different from each other. As the access to IMS network can be made by using any of the access technology that is Wimax, wifi, GPRS, DSL technologies. Initially 3GPP designed IMS network for UMTS network but later ETSI TISPAN recommends the IMS network for it All IP NGN network. User A SGSN PEP Media To User B P-CSCF Enforcement Go Inf Request SLA/ Database Information PDP User B Diameter CORE IMS Figure 2. Base Architecture for IMS III. RELATED WORK HSS As stated earlier 3GPP adopted the IETF policy based QoS for its IMS network. Different proposal has been made to provide the QoS. For UMTS based access to IMS network the [8] proposed the policy based admission control architecture for IMS network. The architecture only take care of Qos requirements for UMTS based end user.3gpp release 6 and release 7 introduce the WLAN access an DSL access to IMS network. [9] Proposed QOS service architecture for WLAN based access to IMS core network. It introduces the implementation of PDP for WLAN network. There are two segments of network, one is core network and other access network [10]. The proposed packet data gateway is designed on such architecuter to keep both of them separte by means of inclusion of entry points into IMS network. The PDG interfaces with PDF for controlling the resources of network irrespective of access technology. Managing resources for the end-user during mobility is very difficult task and require much of researcher s attentions. The [11] provides the framework for QOS management for mobile user as well as for all type of access network. The framework introduced the local PDP and PEP nodes in all access networks. The feedback of quality perceived by user to network also is an important factor for providing better QOS and resource allocation to end user. [12] propose a set-top box architecture that provides the perceived quality of end user to IMS network. The framework did not consider any under lying access network. The SIP protocol is main signaling protocol for session setup in IMS network. The [13] make use of information
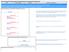
4 A Framework for Real-Time Resource Allocation in IP Multimedia Subsystem Network 35 in SIP messages and proposed almost similar architecture as proposed by. The author proposes to setup local policy decision in access network controlled by border gateways of access network. In addition to functional architecture the author also proposed the changes in SIP messages to incorporate some end user related information i.e., the user access network information, battery timing of mobile, received signal strength from access network etc. IV. DYNAMIC QOS FRAMEWORK FOR IMS Session controller in our architecture is shown in Fig. 4 is B2B user agent. The Main function of session border controller is to provide access of IMS network to end user, monitored traffic and analysis of QOS parameters received by end user. It means Session Border Controller (SBC) provides the two type of functionality. First, analyzed the SLA of access and core IMS network and enforce polices according to signed SLA. The SBC also act as PEP and negotiate with access network as well as IMS PDP for SLA signed policies. As IMS network can be accessed from different access network and we ensured that the providers of access network agrees to provide SLA of their users. SBC use COPS protocol for getting information about user access SLA. The second functionality is to continuously monitor the real-time traffic and RTCP feedback packets for QoS decisions. QoS decisions are based on QoS parameters in which to minimize the jitter, delay, packet loss and maximize the throughput. The SBC continuously monitored the flow of traffic and analyzed the stats received by end user by analyzing the RTCP packet and adjust the resources according to signed SLA. The Signaling flow for call setup using resource reservation is shown in Fig Initially user sends invite message to P-CSCF with SDP information. Session border controller relays the request to P-CSCF for initial filtering. 2. P-CSCF sends invite message to S-CSCF. The S-CSCF routes this to HSS for initial filtration and user authentication. 3. After filtration and authentication, S-CSCF sends the SIP invite message to the second user. 4. The Second user replies the SIP invite message with SDP information. 5. The P-CSCF examines the SDP information responded by User B to determine the QoS of service requirement for session. 6. The P-CSCF responded back with SDP information of the called user. a. The P-CSCF send request to PCF for token authorization, PDP in IMS serves as a PCF. b. PCF replies with token identifying the authorized session and resources. c. The P-CSCF sends this authorization token to caller. 7. The SBC enquires the PDP for policies which the PDP response back and the SBC with required resources for Session. a. The PEP uses the COPS protocol for negotiating policies from access network and IMS PDP. The caller sends the PDP context activation and token to GSGN and reserve resources. PCF check the validity of session after receiving the COPS message of from GGSN. The PCF sends resource reservation information to GGSN. The PEF in the GGSN act as a gate that it controls the flow of packets. It only allows the packets to cross the network that are authorized by the PCF and block the rest of the packets. 8. After reservation of resources for session the two media session was open between the end users. 9. After the session establishment, if the end user requirements are changed during the transmission especially in mobility cases then end user sends the SIP re-invite message which contains the user new required data. The SBC relays the real time traffic between the end user continuously monitor the RTCP packets for getting the perceived quality of flows and QOS stats. The SBC drops the packets that are not according the policies provided by the PDP. If the resources for particular session need to be changed the SBC directly request the PDP for resource reservation and PDP respond back result after negotiating the HSS and server. The end-user capabilities help IMS network efficient allocation of resources. Mani et al., [13] proposed an alteration in SIP messages to incorporate the user related information during resource allocation. We suggest inclusion of user access network information in SIP invite message. During the conversation and mobility the network resources are changed then the new resource allocations are required so, the IP re-invite message is sent containing user information about access network and battery timing.
5 36 A Framework for Real-Time Resource Allocation in IP Multimedia Subsystem Network Signaling Media Games PTT VOD PS HSS MGCF SGW PSTN Wimax WLAN P-CSCF Gq Go S-CSCF I-CSCF BGCF MGW SBC DSLAM PDP IP Network IP Network SGSN GGSN And SLA Figure 3. Real Time Resource Allocations
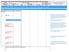
6 A Framework for Real-Time Resource Allocation in IP Multimedia Subsystem Network 37 SBC PDP Data P-CSCF HSS S-CSCF BGCF MGCF MGW Initial Filteration Filteration Respons H248 Add Req H248 resp Authorize QOS Resources Session Progress Session Progress Session Progress Session Progress H248 Add Req/ resp ISUP Req data base Response Authorization Enforcement PRACK PRACK PRACK ISUP Ring back MEDIA Figure 4. Call Flow for Resource Allocation Conclusion V. CONCLUSIONS In this study, we proposed a architecture which based on Session border controller (SBC) that interact with access network operator for getting user s SLA and reserve resources accordingly. We also introduced a real time resource allocation mechanism depending upon the network RTCP feedback report.
7 38 A Framework for Real-Time Resource Allocation in IP Multimedia Subsystem Network SBC continuously monitored the RTCP packet and allocate resources to end user in conjunction with information received from access network and IMS SLA. We also proposed an alteration in SIP invite and re-invite message to include user specific information during resource allocation process. Moreover, we have also shown that how this framework is useful for Real-Time Resource Allocation in IP Multimedia Subsystem Network REFERENCES [1] 3rd Generation Partnership Project, TS : Release 7, IP Multimedia.Subsystem (IMS) ( [2] Schulzrinne H., Casner S. RTP Profile for Audio and Video Conferences with Minimal Control. Request for comments 3551, Internet Engineering Task Force, 2003 [3] Rosenberg, J., et al., SIP:Session Initiation Protocol, IETF RFC 3261, June 2002 [4] Rosenberg, J. and H. Schulzrinne, An Offer/Answer Model with Session Description Protocol (SDP), IETF RFC 3264, June 2002 [5] Magedanz, T., and De Gouveia, F. C. (2006). IMS the IP multimedia system as NGN service delivery platform. e & i Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik, 123(7), [6] Knightson, K., Morita, N., & Towle, T. (2005). NGN architecture: generic principles, functional architecture, and implementation. Communications Magazine, IEEE, 43(10), [7] IETF RFC 2753, A Framework for -Based Admission Control, [8] Zhuang, W., S. G. Yung, K. J. Loh, and K. C. Chua., -based QoS architecture in the IP multimedia subsystem of UMTS.IEEE Network, 17(3):51 57, May/June 2003 [9] Zhuang, W., Y. Gan, K. Loh, and K. Chua, based QoS management Architecture in an integrated UMTS and WLAN environment, IEEE Communications Magazine, pp , November 2003 [10] An End to End QoS Management Framework for the 3GPP IP Multimedia Subsystem R. Good, N. Ventura Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Telecommunications and Malaysia International Conference on Communications, May 2007, Penang, Malaysia [11] De Gouveia, F. C., & Magedanz, T. (2005, December). A framework to improve QoS and mobility management for multimedia applications in the IMS. In Multimedia, Seventh IEEE International Symposium on (pp. 7-pp). IEEE. [12] Siddiqui, M. S., Amin, S. O., & Hong, C. S. (2009). A set-top box for end-to-end QoS management and home network gateway in IMS. Consumer Electronics, IEEE Transactions on, 55(2), [13] Mani, M., and N. Crespi. New QoS control mechanism based on extension to SIP for access to UMTS core network via different kinds of access networks. In Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications, (WiMob 2005), IEEE International Conference on, volume 2, pages , August 2005 [14] Blum, N., Boldea, I., Magedanz, T., & Margaria, T. (2010). Service-oriented Access to Next Generation Networks from Service Creation to Execution. Mobile networks and applications, 15(3), [15] Cruz, R. A. S., Nunes, M. S., Menezes, L., & Domingues, J. (2011). IPTV architecture for an IMS environment with dynamic QoS adaptation. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 53(3), Muhammad Naeem: Research scholar at department of computer science, M. A. Jinnah University Islamabad Pakistan. His research area includes computer networks, machine learning, semantic computing, text retrieval and data mining. Shahneela Naz: Research scholar at department of computer science, M. A. Jinnah University Islamabad Pakistan. Her research area includes Clustering Classification, Semantic engineering, Text retrieval, Adaptive Real-time Video Multicast Techniques, Layered Video Multicast, Multimedia protocols, Routing and Multimedia Streaming. Saira Gilani: She received her M.IT degree in Information Technology from Balochistan University, Quetta, Pakistan in She is an MS student at M.A. Jinnah University, Islamabad, Pakistan and is a member of Center of Research in Networks and Telecommunication (CoReNeT). Her current research activities include investigation of MAC layer schemes, network security for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks and data mining and semantic computing.
Status of IMS-Based Next Generation Networks for Fixed Mobile Convergence
 Status of IMS-Based Next Generation Networks for Fixed Mobile Convergence Prepared for: WOCC 2007 Fuchun Joseph Lin Chief Scientist fjlin@research.telcordia.com Telcordia Technologies, Inc. April 28, 2007
Status of IMS-Based Next Generation Networks for Fixed Mobile Convergence Prepared for: WOCC 2007 Fuchun Joseph Lin Chief Scientist fjlin@research.telcordia.com Telcordia Technologies, Inc. April 28, 2007
IMS signalling for multiparty services based on network level multicast
 IMS signalling for multiparty services based on network level multicast Ivan Vidal, Ignacio Soto, Francisco Valera, Jaime Garcia, Arturo Azcorra UniversityCarlosIIIofMadrid Av.Universidad,30 E-28911, Madrid,
IMS signalling for multiparty services based on network level multicast Ivan Vidal, Ignacio Soto, Francisco Valera, Jaime Garcia, Arturo Azcorra UniversityCarlosIIIofMadrid Av.Universidad,30 E-28911, Madrid,
IP Multimedia Subsystem Application Servers
 IP Multimedia Subsystem Application Servers Second part of the project Presented by: Masood Khosroshahy B E G I N N I N G 1 June 2006 Project supervisor: Prof. Elie Najm IMS Application Servers HSS IMS
IP Multimedia Subsystem Application Servers Second part of the project Presented by: Masood Khosroshahy B E G I N N I N G 1 June 2006 Project supervisor: Prof. Elie Najm IMS Application Servers HSS IMS
What is NGN? Hamid R. Rabiee Mostafa Salehi, Fatemeh Dabiran, Hoda Ayatollahi Spring 2011
 What is NGN? Hamid R. Rabiee Mostafa Salehi, Fatemeh Dabiran, Hoda Ayatollahi Spring 2011 Outlines Next Generation Network (NGN) Definition Applications Requirements Network Architecture QoS Issues 2 What
What is NGN? Hamid R. Rabiee Mostafa Salehi, Fatemeh Dabiran, Hoda Ayatollahi Spring 2011 Outlines Next Generation Network (NGN) Definition Applications Requirements Network Architecture QoS Issues 2 What
Mobile Computing #MC05 Internet Protocol and Mobile Computing
 Mobile Computing #MC05 Internet Protocol and Mobile Computing CS60002: Distributed Systems Winter 2006-2007 Where we left off... Device databases Flash, OR/direct Synchronization Algorithms Push/notifications
Mobile Computing #MC05 Internet Protocol and Mobile Computing CS60002: Distributed Systems Winter 2006-2007 Where we left off... Device databases Flash, OR/direct Synchronization Algorithms Push/notifications
8.4 IMS Network Architecture A Closer Look
 8.4 IMS Network Architecture A Closer Look 243 The anchoring of the media in TrGW also has an implicit topology-hiding effect. Without anchoring, the SDP answer provided to the other network would contain
8.4 IMS Network Architecture A Closer Look 243 The anchoring of the media in TrGW also has an implicit topology-hiding effect. Without anchoring, the SDP answer provided to the other network would contain
IP Multimedia Subsystem(IMS) and Its Applications
 KNOM Conference April 26 ~ 27 2007 IP Multimedia Subsystem(IMS) and Its Applications 2007. 4. 26 Jun-Won Lee 1 Contents IMS Overview IMS Architecture Contents IMS Applications IMS Enablers & Clients 2
KNOM Conference April 26 ~ 27 2007 IP Multimedia Subsystem(IMS) and Its Applications 2007. 4. 26 Jun-Won Lee 1 Contents IMS Overview IMS Architecture Contents IMS Applications IMS Enablers & Clients 2
ETSI TR V1.1.1 ( )
 TR 102 422 V1.1.1 (2005-04) Technical Report Methods for Testing and Specification (MTS) IMS Integration Testing Infrastructure Testing Methodology 2 TR 102 422 V1.1.1 (2005-04) Reference DTR/MTS-00099
TR 102 422 V1.1.1 (2005-04) Technical Report Methods for Testing and Specification (MTS) IMS Integration Testing Infrastructure Testing Methodology 2 TR 102 422 V1.1.1 (2005-04) Reference DTR/MTS-00099
Overview and Status of NGN Standardization Activities. Naotaka Morita Vice Chairman of SG13, ITU-T NTT Service Integration Laboratories
 Overview and Status of NGN Standardization Activities Naotaka Morita Vice Chairman of SG13, ITU-T NTT Service Integration Laboratories Contents 1. Outline of NGN 2. Key Technologies of NGN 3. Summary and
Overview and Status of NGN Standardization Activities Naotaka Morita Vice Chairman of SG13, ITU-T NTT Service Integration Laboratories Contents 1. Outline of NGN 2. Key Technologies of NGN 3. Summary and
Proposal Architecture For Quality of Service Provisioning Within Inter-domain IP Multimedia Subsystem Context
 Proposal Architecture For Quality of Service Provisioning Within Inter-domain IP Multimedia Subsystem Context Mosbah Ageal Computer Engineering Department, Higher Polytechnic Institute of Zliten, Zliten,
Proposal Architecture For Quality of Service Provisioning Within Inter-domain IP Multimedia Subsystem Context Mosbah Ageal Computer Engineering Department, Higher Polytechnic Institute of Zliten, Zliten,
Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN):
 ITU-BDT Regional Seminar on Fixed Mobile Convergence and new network architecture for the Arab Region Tunis (Tunisia), 21-24 November 2005 Day 1 Session 1.2: International Framework Telecommunications
ITU-BDT Regional Seminar on Fixed Mobile Convergence and new network architecture for the Arab Region Tunis (Tunisia), 21-24 November 2005 Day 1 Session 1.2: International Framework Telecommunications
In Next-Generation Networks. The Role of TISPAN. Graham Finnie. A Light Reading Webinar. Thursday, March 9, Senior Analyst.
 A Light Reading Webinar The Role of TISPAN In Next-Generation Networks Thursday, March 9, 2006 Hosted by Graham Finnie Senior Analyst Speakers Simon Spraggs Cisco Systems Jared Rosoff Tazz Networks Agenda
A Light Reading Webinar The Role of TISPAN In Next-Generation Networks Thursday, March 9, 2006 Hosted by Graham Finnie Senior Analyst Speakers Simon Spraggs Cisco Systems Jared Rosoff Tazz Networks Agenda
IMS Migrations IMS Enabling Common Network Convergence. Michael Coward CTO and Co-founder
 IMS Migrations IMS Enabling Common Network Convergence Michael Coward CTO and Co-founder Introduction New wave of telecom infrastructure $4B IMS New generation of Fixed/Mobile Convergence 3G-LTE Equipment
IMS Migrations IMS Enabling Common Network Convergence Michael Coward CTO and Co-founder Introduction New wave of telecom infrastructure $4B IMS New generation of Fixed/Mobile Convergence 3G-LTE Equipment
Chapter 3: IP Multimedia Subsystems and Application-Level Signaling
 Chapter 3: IP Multimedia Subsystems and Application-Level Signaling Jyh-Cheng Chen and Tao Zhang IP-Based Next-Generation Wireless Networks Published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. January 2004 Outline 3.1
Chapter 3: IP Multimedia Subsystems and Application-Level Signaling Jyh-Cheng Chen and Tao Zhang IP-Based Next-Generation Wireless Networks Published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. January 2004 Outline 3.1
Experiences and hopes of an IMS based approach to FMC
 Experiences and hopes of an IMS based approach to FMC Enrico Scarrone Telecom Italia Standards and IPR Department Chairman 3GPP TSG SA WG1 Enrico.Scarrone@TelecomItalia.It +39 3356121214 1 IP Multimedia
Experiences and hopes of an IMS based approach to FMC Enrico Scarrone Telecom Italia Standards and IPR Department Chairman 3GPP TSG SA WG1 Enrico.Scarrone@TelecomItalia.It +39 3356121214 1 IP Multimedia
A Framework to Improve QoS and Mobility Management for Multimedia Applications in the IMS
 A Framework to Improve QoS and Mobility Management for Multimedia Applications in the IMS Fabricio Carvalho de Gouveia Technical University of Berlin Franklinstr. 28-29, D-10587 Faculty IV / Next Generation
A Framework to Improve QoS and Mobility Management for Multimedia Applications in the IMS Fabricio Carvalho de Gouveia Technical University of Berlin Franklinstr. 28-29, D-10587 Faculty IV / Next Generation
IMS in the Next Generation Network
 Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on COMMUNICATIONS, Agios Nikolaos, Crete Island, Greece, July 26-28, 2007 45 IMS in the Next Generation Network TATIANA KOVACIKOVA, PAVOL SEGEC, MILAN
Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on COMMUNICATIONS, Agios Nikolaos, Crete Island, Greece, July 26-28, 2007 45 IMS in the Next Generation Network TATIANA KOVACIKOVA, PAVOL SEGEC, MILAN
End-to-End QoS Support for SIP Sessions in CDMA2000 Networks. M. Ali Siddiqui, Katherine Guo, Sampath Rangarajan and Sanjoy Paul
 End-to-End QoS Support for SIP Sessions in CDMA2000 Networks M. Ali Siddiqui, Katherine Guo, Sampath Rangarajan and Sanjoy Paul M. Ali Siddiqui Lucent Technologies Room 4F-606A 101 Crawfords Corner Road,
End-to-End QoS Support for SIP Sessions in CDMA2000 Networks M. Ali Siddiqui, Katherine Guo, Sampath Rangarajan and Sanjoy Paul M. Ali Siddiqui Lucent Technologies Room 4F-606A 101 Crawfords Corner Road,
Sh Gy. Ro Gx. Cx Ici. Mr Mj
 Sh Ro Cx Ici SIP UT IMS Sv LTE Mr Mj Mi Mg ISC Mw LTE / VoLTE IMS Protocols Interfaces LTE Protocol Stack IMS Protocol Stack LTE (4G) IMS PSTN / LTE Ex : S1, S5, SGi LTE Control Plane Ex : S1, S10, S11,
Sh Ro Cx Ici SIP UT IMS Sv LTE Mr Mj Mi Mg ISC Mw LTE / VoLTE IMS Protocols Interfaces LTE Protocol Stack IMS Protocol Stack LTE (4G) IMS PSTN / LTE Ex : S1, S5, SGi LTE Control Plane Ex : S1, S10, S11,
Support for End-to-End QoS
 GPP S.R00-A Version.0 Version Date: June, 00 0 0 Support for End-to-End QoS Stage Requirements COPYRIGHT NOTICE GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational
GPP S.R00-A Version.0 Version Date: June, 00 0 0 Support for End-to-End QoS Stage Requirements COPYRIGHT NOTICE GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational
The IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS)
 The IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Miguel A. Garcia Martin Nokia Siemens Networks Application and Services in Internet Helsinki University of Technology October 24, 2007 1 Nokia Siemens Networks IMS / Miguel
The IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Miguel A. Garcia Martin Nokia Siemens Networks Application and Services in Internet Helsinki University of Technology October 24, 2007 1 Nokia Siemens Networks IMS / Miguel
Analyzing the Internal Processing of IMS-based and traditional VoIP systems
 Analyzing the Internal Processing of IMS-based and traditional VoIP systems Yuheng He 1, Johannes Veerkamp 1, Attila Bilgic 1,2 1 Institute for Integrated Systems, Ruhr University Bochum, 44780 Bochum,
Analyzing the Internal Processing of IMS-based and traditional VoIP systems Yuheng He 1, Johannes Veerkamp 1, Attila Bilgic 1,2 1 Institute for Integrated Systems, Ruhr University Bochum, 44780 Bochum,
IPv6 the Catalyst for Convergence
 International Telecommunication Union IPv6 the Catalyst for Convergence Bosco Eduardo Fernandes Siemens Ag Agenda o IP the glue to convergence of multimedia content and mobility. o Benefits and Advantages
International Telecommunication Union IPv6 the Catalyst for Convergence Bosco Eduardo Fernandes Siemens Ag Agenda o IP the glue to convergence of multimedia content and mobility. o Benefits and Advantages
Interworking of Wimax and 3GPP Networks based on IMS
 IP MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS (IMS) INFRASTRUCTURE AND SERVICES Interworking of Wimax and 3GPP Networks based on IMS Fangmin Xu, Luyong Zhang, and Zheng Zhou, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications
IP MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS (IMS) INFRASTRUCTURE AND SERVICES Interworking of Wimax and 3GPP Networks based on IMS Fangmin Xu, Luyong Zhang, and Zheng Zhou, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications
Introduction to 3G 1
 Introduction to 3G 1 References [1] Carrier Grade Voice over IP, D. Collins, McGraw-Hill, Second Edition, 2003. [2] 3GPP TS 23.228 [3] 3GPP TS 24.228 [4] 3GPP TS 23.102 2 Outline Mobile Technology Evolution
Introduction to 3G 1 References [1] Carrier Grade Voice over IP, D. Collins, McGraw-Hill, Second Edition, 2003. [2] 3GPP TS 23.228 [3] 3GPP TS 24.228 [4] 3GPP TS 23.102 2 Outline Mobile Technology Evolution
Mobile Network Evolution to NGN
 Network Evolution to NGN and Convergence 2.1.1: Mobile Network Evolution to NGN ITU-BDT Regional Seminar on Fixed Mobile Convergence and Guidelines on the smooth transition of existing mobile networks
Network Evolution to NGN and Convergence 2.1.1: Mobile Network Evolution to NGN ITU-BDT Regional Seminar on Fixed Mobile Convergence and Guidelines on the smooth transition of existing mobile networks
All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain
 1 2 3 3GPP2 X.S0013-000-0 Version 1.0 Version Date: December, 2003 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 All-IP Core Multimedia Domain Overview 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 COPYRIGHT NOTICE 3GPP2 and its Organizational Partners
1 2 3 3GPP2 X.S0013-000-0 Version 1.0 Version Date: December, 2003 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 All-IP Core Multimedia Domain Overview 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 COPYRIGHT NOTICE 3GPP2 and its Organizational Partners
Improved One-Pass IP Multimedia Subsystem Authentication for UMTS
 Improved One-Pass IP Multimedia Subsystem Authentication for UMTS Lili Gu RMIT University Melbourne, Australia l.gu@student.rmit.edu.au Abstract As defined in the 3GPP specifications, a UMTS user device
Improved One-Pass IP Multimedia Subsystem Authentication for UMTS Lili Gu RMIT University Melbourne, Australia l.gu@student.rmit.edu.au Abstract As defined in the 3GPP specifications, a UMTS user device
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Contents. 1 Short Message Service and IP Network Integration 1. 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS 39
 Acknowledgments Introduction xv xvii 1 Short Message Service and IP Network Integration 1 1.1 SMS-IP Integration with SM-SC 3 1.1.1 NCTU Short Message System 4 1.1.2 Statistics for SMS Delivery 7 1.2 isms
Acknowledgments Introduction xv xvii 1 Short Message Service and IP Network Integration 1 1.1 SMS-IP Integration with SM-SC 3 1.1.1 NCTU Short Message System 4 1.1.2 Statistics for SMS Delivery 7 1.2 isms
3GPP support for IP based Emergency Calls - April 2007 Status
 3GPP support for IP based Emergency Calls - April 2007 Status 2 nd SDO Emergency Services Coordination Workshop (ESW07) Library of Congress, Washington, DC, USA April 10-12, 2007 Stephen Edge, Qualcomm,
3GPP support for IP based Emergency Calls - April 2007 Status 2 nd SDO Emergency Services Coordination Workshop (ESW07) Library of Congress, Washington, DC, USA April 10-12, 2007 Stephen Edge, Qualcomm,
This sequence diagram was generated with EventStudio System Designer (
 This call flow covers the handling of a CS network originated call with ISUP. In the diagram the MGCF requests seizure of the IM CN subsystem side termination and CS network side bearer termination. When
This call flow covers the handling of a CS network originated call with ISUP. In the diagram the MGCF requests seizure of the IM CN subsystem side termination and CS network side bearer termination. When
Adaptive Quality of Service Management for Next Generation Residential Gateways
 Adaptive Quality of Service Management for Next Generation Residential Gateways Iván Vidal, Jaime García, Francisco Valera, Ignacio Soto, and Arturo Azcorra Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Avda. Universidad
Adaptive Quality of Service Management for Next Generation Residential Gateways Iván Vidal, Jaime García, Francisco Valera, Ignacio Soto, and Arturo Azcorra Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Avda. Universidad
IP Multimedia Subsystem Part 3 Marek Średniawa
 IP Multimedia Subsystem Part 3 Marek Średniawa mareks@tele.pw.edu.pl Institute of Telecommunications Project is co-financed by European Union within the European Social Fund Charging in IMS IMS charging
IP Multimedia Subsystem Part 3 Marek Średniawa mareks@tele.pw.edu.pl Institute of Telecommunications Project is co-financed by European Union within the European Social Fund Charging in IMS IMS charging
Medical Sensor Application Framework Based on IMS/SIP Platform
 Medical Sensor Application Framework Based on IMS/SIP Platform I. Markota, I. Ćubić Research & Development Centre, Ericsson Nikola Tesla d.d. Poljička cesta 39, 21000 Split, Croatia Phone: +38521 305 656,
Medical Sensor Application Framework Based on IMS/SIP Platform I. Markota, I. Ćubić Research & Development Centre, Ericsson Nikola Tesla d.d. Poljička cesta 39, 21000 Split, Croatia Phone: +38521 305 656,
 Pilsung AB Taegyun A Fathur AB Afif A Hari A Gary A Dhika AB April AB Mulya AB Yusuf AB Anin A Rizka B Dion AB Siska AB Mirel AB Hani AB Airita AB List of countries by number of Internet users 100,00%
Pilsung AB Taegyun A Fathur AB Afif A Hari A Gary A Dhika AB April AB Mulya AB Yusuf AB Anin A Rizka B Dion AB Siska AB Mirel AB Hani AB Airita AB List of countries by number of Internet users 100,00%
3G TS V2.0.0 ( )
 Technical Specification 3 rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia (IM) Subsystem - Stage 2 (3G TS 23.228 version 2.0.0) The present document
Technical Specification 3 rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia (IM) Subsystem - Stage 2 (3G TS 23.228 version 2.0.0) The present document
This sequence diagram was generated with EventStudio System Designer (http://www.eventhelix.com/eventstudio).
 10-Jan-13 16:23 (Page 1) This call flow covers the handling of a CS network originated call with ISUP. In the diagram the MGCF requests seizure of the IM CN subsystem side termination and CS network side
10-Jan-13 16:23 (Page 1) This call flow covers the handling of a CS network originated call with ISUP. In the diagram the MGCF requests seizure of the IM CN subsystem side termination and CS network side
PTT + IMS = PTM - Towards Community/Presence-based IMS Multimedia Services
 PTT + IMS = PTM - Towards Community/Presence-based IMS Multimedia Services Niklas Blum Fraunhofer Institute FOKUS Next Generation Network Integration Kaiserin-Augusta-Allee 31, 10589 Berlin, Germany niklas.blum@fokus.fraunhofer.de
PTT + IMS = PTM - Towards Community/Presence-based IMS Multimedia Services Niklas Blum Fraunhofer Institute FOKUS Next Generation Network Integration Kaiserin-Augusta-Allee 31, 10589 Berlin, Germany niklas.blum@fokus.fraunhofer.de
Review Article How IMS Enables Converged Services for Cable and 3G Technologies: A Survey
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURA Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking Volume 2008, Article ID 589623, 14 pages doi:10.1155/2008/589623 Review Article How IMS Enables Converged Services
Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURA Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking Volume 2008, Article ID 589623, 14 pages doi:10.1155/2008/589623 Review Article How IMS Enables Converged Services
ETSI TS V1.1.1 ( )
 TS 183 028 V1.1.1 (2006-04) Technical Specification Telecommunications and Internet Converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); Common basic communication procedures; Protocol specification
TS 183 028 V1.1.1 (2006-04) Technical Specification Telecommunications and Internet Converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); Common basic communication procedures; Protocol specification
Access to IP Multimedia Subsystem of UMTS via PacketCable Network
 Access to IP Multimedia Subsystem of UMTS via PacketCable Network Mehdi Mani, Student Member, IEEE, Noël Crespi {mehdi.mani,noel.crespi}@int-evry.fr Institut National des Telecommunications (INT) Mobile
Access to IP Multimedia Subsystem of UMTS via PacketCable Network Mehdi Mani, Student Member, IEEE, Noël Crespi {mehdi.mani,noel.crespi}@int-evry.fr Institut National des Telecommunications (INT) Mobile
Business Considerations for Migration to IMT-2000
 Business Considerations for Migration to IMT-2000 Bosco Eduardo Fernandes Siemens AG, ICM N PG SP NI IB Vice President International Affairs Email:bosco.fernandes@siemens.com ontent The Services Delivery
Business Considerations for Migration to IMT-2000 Bosco Eduardo Fernandes Siemens AG, ICM N PG SP NI IB Vice President International Affairs Email:bosco.fernandes@siemens.com ontent The Services Delivery
IMS Mapping of QoS Requirements on the Network Level
 IMS Mapping of QoS Requirements on the Network Level Tomáš Mácha 1, Luboš Nagy 1, Zdeněk Martinásek 1, Vít Novotný 1 1 Fakulta elektrotechniky a komunikačních technologií VUT v Brně Email: {tomas.macha,
IMS Mapping of QoS Requirements on the Network Level Tomáš Mácha 1, Luboš Nagy 1, Zdeněk Martinásek 1, Vít Novotný 1 1 Fakulta elektrotechniky a komunikačních technologií VUT v Brně Email: {tomas.macha,
Open Standards and Interoperability for IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS)
 Open Standards and Interoperability for IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Jonas SUNDBORG Director of Standardization and Regulation Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson Group Function R&D, Standardization Standards,
Open Standards and Interoperability for IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Jonas SUNDBORG Director of Standardization and Regulation Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson Group Function R&D, Standardization Standards,
Resource authorization in IMS with known multimedia service adaptation capabilities
 Resource authorization in IMS with known multimedia service adaptation capabilities Tomislav Grgic, Vedran Huskic, and Maja Matijasevic University of Zagreb, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing,
Resource authorization in IMS with known multimedia service adaptation capabilities Tomislav Grgic, Vedran Huskic, and Maja Matijasevic University of Zagreb, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing,
Convergence of Policy based Resource Management Framework in Next Generation Networks
 Convergence of Policy based Resource Management Framework in Next Generation Networks Dong Sun Bell Laboraries, Alcatel-Lucent Agenda Challenges Review of current works Converged model Summary 2 Challenges
Convergence of Policy based Resource Management Framework in Next Generation Networks Dong Sun Bell Laboraries, Alcatel-Lucent Agenda Challenges Review of current works Converged model Summary 2 Challenges
3GPP TS V7.0.0 ( )
 TS 23.417 V7.0.0 (2007-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Telecommunications and Internet
TS 23.417 V7.0.0 (2007-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Telecommunications and Internet
Nairobi (Kenya), 9-12 May 2005 Session 1.2 "International Framework"
 Regional Seminar for Africa on Fixed Mobile Convergence and Guidelines on the smooth transition of existing mobile networks to IMT-2000 for Developing Countries Nairobi (Kenya), 9-12 May 2005 Session 1.2
Regional Seminar for Africa on Fixed Mobile Convergence and Guidelines on the smooth transition of existing mobile networks to IMT-2000 for Developing Countries Nairobi (Kenya), 9-12 May 2005 Session 1.2
IMS: Lessons Learned. Brough Turner SVP & CTO
 IMS: Lessons Learned Brough Turner SVP & CTO Tomorrow s Communications Network One core network with any access Based on IP Wireline and wireless transparency Standardized signaling based on extensions
IMS: Lessons Learned Brough Turner SVP & CTO Tomorrow s Communications Network One core network with any access Based on IP Wireline and wireless transparency Standardized signaling based on extensions
Network Architectures for Evolving 3G LTE and Mobile WiMAX
 Network Architectures for Evolving 3G LTE and Mobile WiMAX All-IP networking is the ultimate goal of 4G mobile networks, but 3G LTE and mobile WiMAX systems have designed semi all-ip network architectures
Network Architectures for Evolving 3G LTE and Mobile WiMAX All-IP networking is the ultimate goal of 4G mobile networks, but 3G LTE and mobile WiMAX systems have designed semi all-ip network architectures
IP MULTIMEDIA SUBSYSTEM (IMS) SECURITY MODEL
 International Journal of Advance Research, IJOAR.org ISSN 2320-9194 1 International Journal of Advance Research, IJOAR.org Volume 1, Issue 3, March 2013, Online: ISSN 2320-9194 IP MULTIMEDIA SUBSYSTEM
International Journal of Advance Research, IJOAR.org ISSN 2320-9194 1 International Journal of Advance Research, IJOAR.org Volume 1, Issue 3, March 2013, Online: ISSN 2320-9194 IP MULTIMEDIA SUBSYSTEM
3GPP TS V6.1.0 ( )
 TS 29.161 V6.1.0 (2005-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Interworking between the Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN)
TS 29.161 V6.1.0 (2005-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Interworking between the Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN)
Delivering Quadruple Play with IPTV over IMS
 Delivering Quadruple Play with IPTV over IMS Bruno Chatras, Mikhaël Saïd France Telecom Research & Development 38-40 rue du Général Leclerc F-92794 Issy Moulineaux Cedex 9 Email: {bruno.chatras,mikhael.said}@orange-ftgroup.com
Delivering Quadruple Play with IPTV over IMS Bruno Chatras, Mikhaël Saïd France Telecom Research & Development 38-40 rue du Général Leclerc F-92794 Issy Moulineaux Cedex 9 Email: {bruno.chatras,mikhael.said}@orange-ftgroup.com
ETSI TS V ( ) Technical Specification
 TS 124 628 V10.3.0 (2011-06) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Common Basic Communication procedures
TS 124 628 V10.3.0 (2011-06) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Common Basic Communication procedures
IP multimedia in 3G. Structure. Author: MartinHarris Orange. Understanding IP multimedia in 3G. Developments in 3GPP. IP multimedia services
 IP multimedia in 3G Author: MartinHarris Orange slide 1 Structure Understanding IP multimedia in 3G Developments in 3GPP IP multimedia services IMS challenges and open issues IP multimedia roadmap slide
IP multimedia in 3G Author: MartinHarris Orange slide 1 Structure Understanding IP multimedia in 3G Developments in 3GPP IP multimedia services IMS challenges and open issues IP multimedia roadmap slide
MED: Voice over IP systems
 Course aim: Online course specification MED: Voice over IP systems This course describes the functional components and operation of telephony systems based on the Internet Protocol (IP) with emphasis on
Course aim: Online course specification MED: Voice over IP systems This course describes the functional components and operation of telephony systems based on the Internet Protocol (IP) with emphasis on
IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS)
 PART 5 Multimedia & Multimedia Networking MSCEG442 IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) 1 IMS started as a technology for 3 rd Generation mobile networks (under the auspices of the 3 rd Generation Partnership
PART 5 Multimedia & Multimedia Networking MSCEG442 IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) 1 IMS started as a technology for 3 rd Generation mobile networks (under the auspices of the 3 rd Generation Partnership
QoS based vertical handoff method between UMTS systems and wireless LAN networks
 QoS based vertical handoff method between UMTS systems and wireless LAN networks Sungkwan Jung and Dong-ho Cho Div. of EE, Dept. of EECS Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Daejeon, Rep.
QoS based vertical handoff method between UMTS systems and wireless LAN networks Sungkwan Jung and Dong-ho Cho Div. of EE, Dept. of EECS Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Daejeon, Rep.
3GPP TS V7.2.0 ( )
 TS 23.167 V7.2.0 (2006-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (Release
TS 23.167 V7.2.0 (2006-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (Release
The Future Wireless Internet
 The Future Wireless Internet Presented by Bosco Eduardo Fernandes V.President Siemens Ag,, UMTSF Chair ICTG, IPv6 SUMMIT 1 OUTLINE INTRODUCTION CELLULAR & INTERNET IP MULTIMEDIA SUBSYSTEM SUMMARY IPv6
The Future Wireless Internet Presented by Bosco Eduardo Fernandes V.President Siemens Ag,, UMTSF Chair ICTG, IPv6 SUMMIT 1 OUTLINE INTRODUCTION CELLULAR & INTERNET IP MULTIMEDIA SUBSYSTEM SUMMARY IPv6
Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE 13 年 5 月 27 日星期 一
 Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE 1. The Market for Voice and SMS 2. Third Party Voice over IP 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem 4. Circuit Switched Fallback 5. VoLGA LTE was designed as a data
Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE 1. The Market for Voice and SMS 2. Third Party Voice over IP 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem 4. Circuit Switched Fallback 5. VoLGA LTE was designed as a data
V. Mancuso, I. Tinnirello
 UMTS Core Network GSM/GPRS Network Architecture Radio access network BSS GSM/GPRS core network MS BTS BSC MSC VLR GMSC HLR PSTN, ISDN BTS PCU SGSN AuC EIR IP Backbone GGSN database Internet 3GPP Rel. 99
UMTS Core Network GSM/GPRS Network Architecture Radio access network BSS GSM/GPRS core network MS BTS BSC MSC VLR GMSC HLR PSTN, ISDN BTS PCU SGSN AuC EIR IP Backbone GGSN database Internet 3GPP Rel. 99
End-to-end IP Service Quality and Mobility - Lecture #6 -
 End-to-end IP Quality and Mobility - Lecture #6 - Special Course in Networking Technology S-38.215 vilho.raisanen@nokia.com Planned contents & draft schedule 1. Introduction Jan 13th 2. Characteristics
End-to-end IP Quality and Mobility - Lecture #6 - Special Course in Networking Technology S-38.215 vilho.raisanen@nokia.com Planned contents & draft schedule 1. Introduction Jan 13th 2. Characteristics
Enabling FMC: Airvana Universal Access Gateway
 Enabling FMC: Airvana Universal Access Gateway 2006 3G CDMA Latin America Regional Conference May 25 th, 2006 Sao Paulo, Brazil Michael McFarland Director, Marketing & Business Development Airvana, Inc
Enabling FMC: Airvana Universal Access Gateway 2006 3G CDMA Latin America Regional Conference May 25 th, 2006 Sao Paulo, Brazil Michael McFarland Director, Marketing & Business Development Airvana, Inc
Integration of a QoS aware end user network within the TISPAN NGN solutions
 Integration of a QoS aware end user network within the TISPAN NGN solutions I. Vidal, J. Garcia, F. Valera, I. Soto, A. Azcorra University Carlos III of Madrid, Telematic Engineering Department {ividal,
Integration of a QoS aware end user network within the TISPAN NGN solutions I. Vidal, J. Garcia, F. Valera, I. Soto, A. Azcorra University Carlos III of Madrid, Telematic Engineering Department {ividal,
Emergency Services and Priority Signaling
 ITU-T / ATIS Workshop Next Generation Technology and Standardization Emergency Services and Priority Signaling Martin Dolly AT&T (With credit to Percy Tarapore (AT&T) for Priority contributions) ITU-T
ITU-T / ATIS Workshop Next Generation Technology and Standardization Emergency Services and Priority Signaling Martin Dolly AT&T (With credit to Percy Tarapore (AT&T) for Priority contributions) ITU-T
ETSI TS V5.8.0 ( )
 TS 129 208 V5.8.0 (2004-06) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); End to end Quality of Service (QoS) signalling
TS 129 208 V5.8.0 (2004-06) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); End to end Quality of Service (QoS) signalling
Integration of the IMS/PCC Framework into the Mobile WiMAX Network
 WIMAX: A TECHNOLOGY UPDATE Integration of the IMS/PCC Framework into the Mobile WiMAX Network Suma S. Cherian and Peretz Feder, Alcatel-Lucent Bahareh Sadeghi, Intel Corporation Richard Wisenöcker, Nokia
WIMAX: A TECHNOLOGY UPDATE Integration of the IMS/PCC Framework into the Mobile WiMAX Network Suma S. Cherian and Peretz Feder, Alcatel-Lucent Bahareh Sadeghi, Intel Corporation Richard Wisenöcker, Nokia
NG40 IMS Emulator. Key features: IMS Registration VoLTE Basic SRVCC (one-way HO of single active speech session from 4G PS to 3G CS)
 NG40 IMS Emulator IMS Emulation for LTE has been added to the ng4t portfolio. The NG40 IMS Emulator is an extension to the NG40 eutran and to the NG40 EPC Emulator. The NG40 eutran Emulator simulates the
NG40 IMS Emulator IMS Emulation for LTE has been added to the ng4t portfolio. The NG40 IMS Emulator is an extension to the NG40 eutran and to the NG40 EPC Emulator. The NG40 eutran Emulator simulates the
Name of Course : E1-E2 CFA. Chapter 7A. Topic : SIP. Date of Creation :
 E1-E2(CFA)/SIP Rev Date 28.03.2011 Name of Course : E1-E2 CFA Chapter 7A Topic : SIP Date of Creation : 28.03.2011 For internal circulation of BSNL only Page 1 E1-E2(CFA)/SIP Rev Date 28.03.2011 Session
E1-E2(CFA)/SIP Rev Date 28.03.2011 Name of Course : E1-E2 CFA Chapter 7A Topic : SIP Date of Creation : 28.03.2011 For internal circulation of BSNL only Page 1 E1-E2(CFA)/SIP Rev Date 28.03.2011 Session
The Role of IMS Functional Architecture in Next Generation Network. Sheyda Kiani Mehr. Shomal University, Amol, Iran
 The Role of IMS Functional Architecture in Next Generation Network Sheyda Kiani Mehr Shomal University, Amol, Iran Abstract: The migration to Next Generation Networks is a sea change, a fundamental transformation
The Role of IMS Functional Architecture in Next Generation Network Sheyda Kiani Mehr Shomal University, Amol, Iran Abstract: The migration to Next Generation Networks is a sea change, a fundamental transformation
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 23.167 V7.11.0 (2008-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (Release
TS 23.167 V7.11.0 (2008-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (Release
3GPP TR V7.0.0 ( )
 TR 24.930 V7.0.0 (2006-12) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Signalling flows for the session setup in the IP Multimedia core
TR 24.930 V7.0.0 (2006-12) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Signalling flows for the session setup in the IP Multimedia core
ETSI TS V2.0.4 ( ) Technical Specification
 TS 182 006 V2.0.4 (2008-05) Technical Specification Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2 description
TS 182 006 V2.0.4 (2008-05) Technical Specification Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2 description
GPRS billing: getting ready for UMTS
 GPRS billing: getting ready for UMTS In his first article about UMTS, Lucas Baugé looks into the key challenges of GPRS billing. He seeks to show how solving these challenges will help operators succeed
GPRS billing: getting ready for UMTS In his first article about UMTS, Lucas Baugé looks into the key challenges of GPRS billing. He seeks to show how solving these challenges will help operators succeed
3GPP TS V7.3.0 ( )
 TS 23.167 V7.3.0 (2006-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (Release
TS 23.167 V7.3.0 (2006-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (Release
3GPP TR V ( )
 TR 24.930 V10.1.0 (2011-12) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Signalling flows for the session setup in the IP Multimedia core
TR 24.930 V10.1.0 (2011-12) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Signalling flows for the session setup in the IP Multimedia core
VoIP Protocols and QoS
 Announcements I. Times have been posted for demo slots VoIP Protocols and QoS II. HW5 and HW6 solutions have been posted HW6 being graded Internet Protocols CSC / ECE 573 Fall, 2005 N. C. State University
Announcements I. Times have been posted for demo slots VoIP Protocols and QoS II. HW5 and HW6 solutions have been posted HW6 being graded Internet Protocols CSC / ECE 573 Fall, 2005 N. C. State University
NGN interconnection: technology challenges. Dr. Rochdi ZOUAKIA.
 ITU/ Arab Regional Workshop on NGN interconnection: technology challenges Dr. Rochdi ZOUAKIA zouakia@anrt.net.ma TODAY We have different networks offering different services. Networks with Different architectures.
ITU/ Arab Regional Workshop on NGN interconnection: technology challenges Dr. Rochdi ZOUAKIA zouakia@anrt.net.ma TODAY We have different networks offering different services. Networks with Different architectures.
ETSI TS V8.2.0 ( ) Technical Specification
 TS 124 147 V8.2.0 (2009-01) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Conferencing using the IP Multimedia (IM)
TS 124 147 V8.2.0 (2009-01) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Conferencing using the IP Multimedia (IM)
4G: Convergence, Openness for Excellence and Opportunity Cisco Systems, Inc
 4G: Convergence, Openness for Excellence and Opportunity, Inc 1 4G Not Just for Mobility This next generation of mobility networks will have over the air throughput speeds that will approach those of wireless
4G: Convergence, Openness for Excellence and Opportunity, Inc 1 4G Not Just for Mobility This next generation of mobility networks will have over the air throughput speeds that will approach those of wireless
Multi-Service Access and Next Generation Voice Service
 Hands-On Multi-Service Access and Next Generation Voice Service Course Description The next generation of telecommunications networks is being deployed using VoIP technology and soft switching replacing
Hands-On Multi-Service Access and Next Generation Voice Service Course Description The next generation of telecommunications networks is being deployed using VoIP technology and soft switching replacing
Seamless Interoperability Across LTE And WiMAX Using Vertical Handover Mechanism
 Seamless Interoperability Across LTE And WiMAX Using Vertical Handover Mechanism Bharatesh Chakravarthi S. B M.Tech. Dept of ISE The Oxford College of Engineering Bangalore, India Prof. D. Jayaramaiah
Seamless Interoperability Across LTE And WiMAX Using Vertical Handover Mechanism Bharatesh Chakravarthi S. B M.Tech. Dept of ISE The Oxford College of Engineering Bangalore, India Prof. D. Jayaramaiah
ETSI ES V1.1.1 ( )
 ES 282 001 V1.1.1 (2005-08) Standard Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); NGN Functional Architecture Release 1 2 ES 282 001 V1.1.1 (2005-08)
ES 282 001 V1.1.1 (2005-08) Standard Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); NGN Functional Architecture Release 1 2 ES 282 001 V1.1.1 (2005-08)
MEA: Telephony systems MEB: Voice over IP MED: VoIP systems MEC: C7 signalling systems MEE: Video principles MEF: Video over IP
 learntelecoms interactive e-learning suite of courses from PTT: MediaNet v3 Voice and video service delivery MediaNet is a suite of interactive, online e-learning courses that provides training in the
learntelecoms interactive e-learning suite of courses from PTT: MediaNet v3 Voice and video service delivery MediaNet is a suite of interactive, online e-learning courses that provides training in the
ETSI NGN Work: TISPAN Status
 ITU-T International Telecommunication Union International Multimedia Telecommunications Consortium ETSI NGN Work: TISPAN Status Richard Brennan Vice-Chair ETSI TISPAN Joint ITU-T Workshop and IMTC Forum
ITU-T International Telecommunication Union International Multimedia Telecommunications Consortium ETSI NGN Work: TISPAN Status Richard Brennan Vice-Chair ETSI TISPAN Joint ITU-T Workshop and IMTC Forum
UNIVERSAL MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATIONS
 IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 23, NO. 6, JUNE 2005 1233 One-Pass GPRS and IMS Authentication Procedure for UMTS Yi-Bing Lin, Fellow, IEEE, Ming-Feng Chang, Meng-Ta Hsu, and Lin-Yi
IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 23, NO. 6, JUNE 2005 1233 One-Pass GPRS and IMS Authentication Procedure for UMTS Yi-Bing Lin, Fellow, IEEE, Ming-Feng Chang, Meng-Ta Hsu, and Lin-Yi
IP Multimedia Subsystem and its protocols: a step to convergence
 IP Multimedia Subsystem and its protocols: a step to convergence Ewa Gałczyńska, Wojciech Zabierowski, Andrzej Napieralski Abstract- Today s world has been changing drastically over few past years in aspect
IP Multimedia Subsystem and its protocols: a step to convergence Ewa Gałczyńska, Wojciech Zabierowski, Andrzej Napieralski Abstract- Today s world has been changing drastically over few past years in aspect
3GPP TS V8.0.0 ( )
 TS 23.517 V8.0.0 (2007-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Protocols for Advanced Networking
TS 23.517 V8.0.0 (2007-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Protocols for Advanced Networking
CRITICAL ISSUES FOR ROAMING IN 3G ANDERS ROOS, MAGNUS HARTMAN, AND STEPHEN DUTNALL, NORTHSTREAM AB
 3G MOBILE N ETWORK T ECHNOLOGIES AND E XPERIENCES CRITICAL ISSUES FOR ROAMING IN 3G ANDERS ROOS, MAGNUS HARTMAN, AND STEPHEN DUTNALL, NORTHSTREAM AB UE Applications and services Node B RNC UTRAN (PS) SCP
3G MOBILE N ETWORK T ECHNOLOGIES AND E XPERIENCES CRITICAL ISSUES FOR ROAMING IN 3G ANDERS ROOS, MAGNUS HARTMAN, AND STEPHEN DUTNALL, NORTHSTREAM AB UE Applications and services Node B RNC UTRAN (PS) SCP
Overview of the Session Initiation Protocol
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides an overview of SIP. It includes the following sections: Introduction to SIP, page 1-1 Components of SIP, page 1-2 How SIP Works, page 1-3 SIP Versus H.323, page 1-8 Introduction
CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides an overview of SIP. It includes the following sections: Introduction to SIP, page 1-1 Components of SIP, page 1-2 How SIP Works, page 1-3 SIP Versus H.323, page 1-8 Introduction
TSIN02 - Internetworking
 Lecture 8: SIP and H323 Litterature: 2004 Image Coding Group, Linköpings Universitet Lecture 8: SIP and H323 Goals: After this lecture you should Understand the basics of SIP and it's architecture Understand
Lecture 8: SIP and H323 Litterature: 2004 Image Coding Group, Linköpings Universitet Lecture 8: SIP and H323 Goals: After this lecture you should Understand the basics of SIP and it's architecture Understand
ETSI ES V2.0.0 ( ) ETSI Standard
 ES 282 007 V2.0.0 (2008-05) Standard Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Functional architecture 2 ES 282 007
ES 282 007 V2.0.0 (2008-05) Standard Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Functional architecture 2 ES 282 007
VoIP. ALLPPT.com _ Free PowerPoint Templates, Diagrams and Charts
 VoIP ALLPPT.com _ Free PowerPoint Templates, Diagrams and Charts VoIP System Gatekeeper: A gatekeeper is useful for handling VoIP call connections includes managing terminals, gateways and MCU's (multipoint
VoIP ALLPPT.com _ Free PowerPoint Templates, Diagrams and Charts VoIP System Gatekeeper: A gatekeeper is useful for handling VoIP call connections includes managing terminals, gateways and MCU's (multipoint
Satellites in Next Generation Networks QoS issues Stéphane Combes, R&D, Alcatel Space
 Satellites in Next Generation s QoS issues Stéphane Combes, R&D, Alcatel Space ITU-T workshop on Satellites in IP and Multimedia Geneva, 9-11 December 2002 Content > What NGN and QoS mean? End-to-end QoS
Satellites in Next Generation s QoS issues Stéphane Combes, R&D, Alcatel Space ITU-T workshop on Satellites in IP and Multimedia Geneva, 9-11 December 2002 Content > What NGN and QoS mean? End-to-end QoS
ETSI TS V5.2.0 ( )
 Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); End to end Quality of Service (QoS) signalling flows () GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR
Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); End to end Quality of Service (QoS) signalling flows () GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR
3GPP TS V ( )
 Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Policy and charging control signalling flows and Quality of Service (QoS) parameter
Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Policy and charging control signalling flows and Quality of Service (QoS) parameter
TS-3GB-S.R0079-0v1.0 Support for End-to-End QoS Stage 1 Requirements
 TS-GB-S.R00-0v.0 Support for End-to-End QoS Stage Requirements Sep,00 THE TELECOMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY COMMITTEE TS-GB-S.R00-0v.0 Support for End-to-End QoS Stage Requirements . Application level
TS-GB-S.R00-0v.0 Support for End-to-End QoS Stage Requirements Sep,00 THE TELECOMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY COMMITTEE TS-GB-S.R00-0v.0 Support for End-to-End QoS Stage Requirements . Application level
ETSI TR V1.1.1 ( )
 Technical Report Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); Organization of user data 2 Reference DTR/TISPAN-02027-NGN-R1 Keywords architecture,
Technical Report Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); Organization of user data 2 Reference DTR/TISPAN-02027-NGN-R1 Keywords architecture,
Timmins Training Consulting
 VoLTE Core Network Course Outline Short Description VoLTE stands for voice over Long-Term Evolution. It is a combination of LTE and IMS technology which enables processing of digital packet voice service
VoLTE Core Network Course Outline Short Description VoLTE stands for voice over Long-Term Evolution. It is a combination of LTE and IMS technology which enables processing of digital packet voice service
