I/O Systems (3): Clocks and Timers. CSE 2431: Introduction to Operating Systems
|
|
|
- Diana Willis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 I/O Systems (3): Clocks and Timers CSE 2431: Introduction to Operating Systems 1
2 Outline Clock Hardware Clock Software Soft Timers 2
3 Two Types of Clocks Simple clock: tied to the 110- or 220-volt power line and causes an interrupt on every voltage cycle, at 50 or 60 Hz. The other type, used in modern computers, is based on crystal oscillator. High accuracy, in the range of several hundred megahertz 3
4 Clock Hardware A programmable clock 4
5 Programmable Clocks Two modes One-shot mode vs. Square-wave mode Periodic interrupts are called clock ticks Interrupt frequency can be controlled by software E.g., with 500-MHz crystal and unsigned 32-bit registers, we can generate interrupts at intervals from 2 ns to 8.6 s. 5
6 Battery-powered Backup Clock To prevent the current time from being lost when power is off This clock is read at startup The time is translated into the number of clock ticks since a certain point of origin Jan. 01, 1970 for UNIX Jan. 01, 1980 for Windows At every clock tick, the real time is incremented by one count 6
7 Clock Software Common duties of clock software Maintaining the time of day Preventing processes from running longer than they are allowed to Accounting for CPU usage Handling the alarm system call made by user processes Providing watchdog timers for parts of the system itself Doing profiling, monitoring, and statistics gathering 7
8 Maintaining the Time of Day With a clock rate of 60 Hz, a 32-bit counter will overflow in just over 2 years. What should we do? 8
9 Preventing Processes from Running Too Long When a process is started, the scheduler initializes a counter to the value of that process s quantum in clock ticks At every clock interrupt, the clock driver decrements the quantum counter by 1. When the counter gets to zero, the clock driver calls the scheduler to set up another process 9
10 CPU Accounting The most accurate way is to use a second timer, distinct from the main system timer. A less accurate, but simpler, way is to charge the running process at the time of tick. What if many interrupts occur during a process run? 10
11 Handling Alarm System Calls A process requests OS to give it a warning after a certain interval E.g., time out for network packet transmission OS simulates virtual clocks with a single physical clock, each virtual clock for one process Using a table to store signal times Using a linked list to store signal times 11
12 Simulate Multiple Timers On each tick, the value in Next signal is decremented by one 12
13 Watchdog Timers Part of the operating system also need to set timers (called watchdog timers) A process reads data from an idle floppy disk The mechanism for watchdog timers is the same as that for user signals The only difference is the clock driver calls a procedure supplied by the caller, rather than causing a signal when a timer goes off 13
14 Profiling A mechanism to build up a histogram of its program counter so that a user program can see where it is spending its time At every tick, the driver checks to see if the current process is being profiled, if so, computes the bin# (a range of addresses) corresponding to the current program counter. It then increments that bin by one. This mechanism can also be used to profile the system itself 14
15 Motivation for Soft Timers A second clock available for timer interrupts Specified by applications No problems if interrupt frequency is low Two ways to manage I/O Interrupt: low latency, but overhead due to context switching and their influence on the pipeline, TLB, and cache is high Polling: high latency 15
16 Soft Timers Soft timers avoid interrupts Kernel checks for soft timer expiration before it exits to user mode If the timer expires, the scheduled event (.e.g, packet transmission) is performed, with no context switch Then the soft timer is reset to go off again How well this works depends on rate of kernel entries 16
17 Reasons for Kernel Entries System calls TLB misses Page faults I/O interrupts CPU going idle 17
18 An Example for Soft Timers Gigabit Ethernet accepting or delivering a full-size packet every 12 µs An interrupt takes 4.45 µs on a 300 MHz, 35% overhead [AD99] Intervals of kernel entry are 2 18 µs with several CPU loads [AD99] It is doable with a soft timer go off every 12 µs (with an occasional missed deadline) [AD99] M. Aron and P. Druschel, Soft Timers, ACM Trans. Comput. Syst., vol. 18, no. 3, 1999, pp
19 Summary Clock Hardware Clock Software Soft Timers 19
19: I/O Devices: Clocks, Power Management
 19: I/O Devices: Clocks, Power Management Mark Handley Clock Hardware: A Programmable Clock Pulses Counter, decremented on each pulse Crystal Oscillator On zero, generate interrupt and reload from holding
19: I/O Devices: Clocks, Power Management Mark Handley Clock Hardware: A Programmable Clock Pulses Counter, decremented on each pulse Crystal Oscillator On zero, generate interrupt and reload from holding
Lecture 21 Disk Devices and Timers
 CS 423 Operating Systems Design Lecture 21 Disk Devices and Timers Klara Nahrstedt Fall 2011 Based on slides by YY Zhou and Andrew S. Tanenbaum CS 423 - Fall 2011 Overview Administrative announcements
CS 423 Operating Systems Design Lecture 21 Disk Devices and Timers Klara Nahrstedt Fall 2011 Based on slides by YY Zhou and Andrew S. Tanenbaum CS 423 - Fall 2011 Overview Administrative announcements
I/O. Fall Tore Larsen. Including slides from Pål Halvorsen, Tore Larsen, Kai Li, and Andrew S. Tanenbaum)
 I/O Fall 2011 Tore Larsen Including slides from Pål Halvorsen, Tore Larsen, Kai Li, and Andrew S. Tanenbaum) Big Picture Today we talk about I/O characteristics interconnection devices & controllers (disks
I/O Fall 2011 Tore Larsen Including slides from Pål Halvorsen, Tore Larsen, Kai Li, and Andrew S. Tanenbaum) Big Picture Today we talk about I/O characteristics interconnection devices & controllers (disks
I/O. Fall Tore Larsen. Including slides from Pål Halvorsen, Tore Larsen, Kai Li, and Andrew S. Tanenbaum)
 I/O Fall 2010 Tore Larsen Including slides from Pål Halvorsen, Tore Larsen, Kai Li, and Andrew S. Tanenbaum) Big Picture Today we talk about I/O characteristics interconnection devices & controllers (disks
I/O Fall 2010 Tore Larsen Including slides from Pål Halvorsen, Tore Larsen, Kai Li, and Andrew S. Tanenbaum) Big Picture Today we talk about I/O characteristics interconnection devices & controllers (disks
Computer-System Structures
 Computer-System Structures Computer System Operation I/O Structure Storage Structure Storage Hierarchy Hardware Protection Network Structure 2.1 Sana a University, Dr aimen A Modern Computer System 2.2
Computer-System Structures Computer System Operation I/O Structure Storage Structure Storage Hierarchy Hardware Protection Network Structure 2.1 Sana a University, Dr aimen A Modern Computer System 2.2
Common Computer-System and OS Structures
 Common Computer-System and OS Structures Computer System Operation I/O Structure Storage Structure Storage Hierarchy Hardware Protection General System Architecture Oct-03 1 Computer-System Architecture
Common Computer-System and OS Structures Computer System Operation I/O Structure Storage Structure Storage Hierarchy Hardware Protection General System Architecture Oct-03 1 Computer-System Architecture
I/O Devices. Chapter 5 Input/Output. Memory-Mapped I/O (2) Memory-Mapped I/O (1) Interrupts Revisited. Direct Memory Access (DMA) 11/26/2013
 MODERN OPERATING SYSTEMS I/O Devices Third Edition ANDREW S. TANENBAUM Chapter 5 Input/Output Figure 5-1. Some typical device, network, and bus data rates. Memory-Mapped I/O (1) Memory-Mapped I/O (2) Figure
MODERN OPERATING SYSTEMS I/O Devices Third Edition ANDREW S. TANENBAUM Chapter 5 Input/Output Figure 5-1. Some typical device, network, and bus data rates. Memory-Mapped I/O (1) Memory-Mapped I/O (2) Figure
Brief tour of hardware
 Brief tour of hardware Only the basic aspects are covered here. The hardware is divided into entities ( things ) and features ( actions also called mechanisms ); the main distinction is that you can see
Brief tour of hardware Only the basic aspects are covered here. The hardware is divided into entities ( things ) and features ( actions also called mechanisms ); the main distinction is that you can see
OPERATING SYSTEMS CS136
 OPERATING SYSTEMS CS136 Jialiang LU Jialiang.lu@sjtu.edu.cn Based on Lecture Notes of Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, 1 Chapter 5 INPUT/OUTPUT 2 Overview o OS controls I/O devices => o Issue commands,
OPERATING SYSTEMS CS136 Jialiang LU Jialiang.lu@sjtu.edu.cn Based on Lecture Notes of Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, 1 Chapter 5 INPUT/OUTPUT 2 Overview o OS controls I/O devices => o Issue commands,
Computer-System Architecture
 Chapter 2: Computer-System Structures Computer System Operation I/O Structure Storage Structure Storage Hierarchy Hardware Protection General System Architecture 2.1 Computer-System Architecture 2.2 1
Chapter 2: Computer-System Structures Computer System Operation I/O Structure Storage Structure Storage Hierarchy Hardware Protection General System Architecture 2.1 Computer-System Architecture 2.2 1
Computer-System Architecture. Common Functions of Interrupts. Computer-System Operation. Interrupt Handling. Chapter 2: Computer-System Structures
 Chapter 2: Computer-System Structures Computer-System Architecture Computer System Operation I/O Structure Storage Structure Storage Hierarchy Hardware Protection General System Architecture 2.1 2.2 Computer-System
Chapter 2: Computer-System Structures Computer-System Architecture Computer System Operation I/O Structure Storage Structure Storage Hierarchy Hardware Protection General System Architecture 2.1 2.2 Computer-System
Chapter 5 - Input / Output
 Chapter 5 - Input / Output Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 5 - Input / Output 1 / 90 1 Motivation 2 Principle of I/O Hardware I/O Devices Device Controllers Memory-Mapped
Chapter 5 - Input / Output Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 5 - Input / Output 1 / 90 1 Motivation 2 Principle of I/O Hardware I/O Devices Device Controllers Memory-Mapped
Introduction to Operating Systems Prof. Chester Rebeiro Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Introduction to Operating Systems Prof. Chester Rebeiro Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Week - 04 Lecture 17 CPU Context Switching Hello. In this video
Introduction to Operating Systems Prof. Chester Rebeiro Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Week - 04 Lecture 17 CPU Context Switching Hello. In this video
CSCI-GA Operating Systems I/O. Hubertus Franke
 Operating Systems I/O CSCI-GA.2250-001 Hubertus Franke frankeh@cs.nyu.edu External devices that engage in I/O with computer systems can be grouped into three categories: Human readable suitable for communicating
Operating Systems I/O CSCI-GA.2250-001 Hubertus Franke frankeh@cs.nyu.edu External devices that engage in I/O with computer systems can be grouped into three categories: Human readable suitable for communicating
Instruction Cycle. Computer-System Architecture. Computer-System Operation. Common Functions of Interrupts. Chapter 2: Computer-System Structures
 Summary Operating Systems evolved through stages Resident monitors Multiprogrammed batch systems Time-shared multiuser systems Desktop systems Specialized operating systems (real-time, handheld, parallel
Summary Operating Systems evolved through stages Resident monitors Multiprogrammed batch systems Time-shared multiuser systems Desktop systems Specialized operating systems (real-time, handheld, parallel
Module 2: Computer-System Structures. Computer-System Architecture
 Module 2: Computer-System Structures Computer-System Operation I/O Structure Storage Structure Storage Hierarchy Hardware Protection General System Architecture Operating System Concepts 2.1 Silberschatz
Module 2: Computer-System Structures Computer-System Operation I/O Structure Storage Structure Storage Hierarchy Hardware Protection General System Architecture Operating System Concepts 2.1 Silberschatz
Real-Time Concepts for Embedded Systems Author: Qing Li with Caroline Yao
 Real-Time Concepts for Embedded Systems Author: Qing Li with Caroline Yao ISBN: 1-57820-124-1 CMPBooks Chapter 11 Timer and Timer Services Outline 11.1 Introduction 11.2 Real-Time Clocks and System Clocks
Real-Time Concepts for Embedded Systems Author: Qing Li with Caroline Yao ISBN: 1-57820-124-1 CMPBooks Chapter 11 Timer and Timer Services Outline 11.1 Introduction 11.2 Real-Time Clocks and System Clocks
Virtual Memory Outline
 Virtual Memory Outline Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations Operating-System Examples
Virtual Memory Outline Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations Operating-System Examples
A Global Operating System for HPC Clusters
 A Global Operating System Emiliano Betti 1 Marco Cesati 1 Roberto Gioiosa 2 Francesco Piermaria 1 1 System Programming Research Group, University of Rome Tor Vergata 2 BlueGene Software Division, IBM TJ
A Global Operating System Emiliano Betti 1 Marco Cesati 1 Roberto Gioiosa 2 Francesco Piermaria 1 1 System Programming Research Group, University of Rome Tor Vergata 2 BlueGene Software Division, IBM TJ
Operating System Review
 COP 4225 Advanced Unix Programming Operating System Review Chi Zhang czhang@cs.fiu.edu 1 About the Course Prerequisite: COP 4610 Concepts and Principles Programming System Calls Advanced Topics Internals,
COP 4225 Advanced Unix Programming Operating System Review Chi Zhang czhang@cs.fiu.edu 1 About the Course Prerequisite: COP 4610 Concepts and Principles Programming System Calls Advanced Topics Internals,
Optimal Algorithm. Replace page that will not be used for longest period of time Used for measuring how well your algorithm performs
 Optimal Algorithm Replace page that will not be used for longest period of time Used for measuring how well your algorithm performs page 1 Least Recently Used (LRU) Algorithm Reference string: 1, 2, 3,
Optimal Algorithm Replace page that will not be used for longest period of time Used for measuring how well your algorithm performs page 1 Least Recently Used (LRU) Algorithm Reference string: 1, 2, 3,
Chapter 1: Introduction. Operating System Concepts 8th Edition,
 Chapter 1: Introduction, Administrivia Reading: Chapter 1. Next time: Continued Grand Tour. 1.2 Outline Common computer system devices. Parallelism within an operating system. Interrupts. Storage operation,
Chapter 1: Introduction, Administrivia Reading: Chapter 1. Next time: Continued Grand Tour. 1.2 Outline Common computer system devices. Parallelism within an operating system. Interrupts. Storage operation,
Interrupt response times on Arduino and Raspberry Pi. Tomaž Šolc
 Interrupt response times on Arduino and Raspberry Pi Tomaž Šolc tomaz.solc@ijs.si Introduction Full-featured Linux-based systems are replacing microcontrollers in some embedded applications for low volumes,
Interrupt response times on Arduino and Raspberry Pi Tomaž Šolc tomaz.solc@ijs.si Introduction Full-featured Linux-based systems are replacing microcontrollers in some embedded applications for low volumes,
ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.9 Timer Programming
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.9 Timer Programming Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Programming 8051 Timers Counter programming Timer programming
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.9 Timer Programming Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Programming 8051 Timers Counter programming Timer programming
Timers 1 / 46. Jiffies. Potent and Evil Magic
 Timers 1 / 46 Jiffies Each timer tick, a variable called jiffies is incremented It is thus (roughly) the number of HZ since system boot A 32-bit counter incremented at 1000 Hz wraps around in about 50
Timers 1 / 46 Jiffies Each timer tick, a variable called jiffies is incremented It is thus (roughly) the number of HZ since system boot A 32-bit counter incremented at 1000 Hz wraps around in about 50
Timers and Counters. LISHA/UFSC Prof. Dr. Antônio Augusto Fröhlich Fauze Valério Polpeta Lucas Francisco Wanner.
 Timers and Counters LISHA/UFSC Prof. Dr. Antônio Augusto Fröhlich Fauze Valério Polpeta Lucas Francisco Wanner http://www.lisha.ufsc.br/~guto March 2009 March 2009 http://www.lisha.ufsc.br/ 103 Timers
Timers and Counters LISHA/UFSC Prof. Dr. Antônio Augusto Fröhlich Fauze Valério Polpeta Lucas Francisco Wanner http://www.lisha.ufsc.br/~guto March 2009 March 2009 http://www.lisha.ufsc.br/ 103 Timers
ò mm_struct represents an address space in kernel ò task represents a thread in the kernel ò A task points to 0 or 1 mm_structs
 Last time We went through the high-level theory of scheduling algorithms Scheduling Today: View into how Linux makes its scheduling decisions Don Porter CSE 306 Lecture goals Understand low-level building
Last time We went through the high-level theory of scheduling algorithms Scheduling Today: View into how Linux makes its scheduling decisions Don Porter CSE 306 Lecture goals Understand low-level building
Scheduling. Don Porter CSE 306
 Scheduling Don Porter CSE 306 Last time ò We went through the high-level theory of scheduling algorithms ò Today: View into how Linux makes its scheduling decisions Lecture goals ò Understand low-level
Scheduling Don Porter CSE 306 Last time ò We went through the high-level theory of scheduling algorithms ò Today: View into how Linux makes its scheduling decisions Lecture goals ò Understand low-level
Introduction. Operating Systems. Outline. Hardware. I/O Device Types. Device Controllers. One OS function is to control devices
 Introduction Operating Systems Input/Output Devices (Ch12.1-12.3, 12.7; 13.1-13.3, 13.7) One OS function is to control devices significant fraction of code (80-90% of Linux) Want all devices to be simple
Introduction Operating Systems Input/Output Devices (Ch12.1-12.3, 12.7; 13.1-13.3, 13.7) One OS function is to control devices significant fraction of code (80-90% of Linux) Want all devices to be simple
15: OS Scheduling and Buffering
 15: OS Scheduling and ing Mark Handley Typical Audio Pipeline (sender) Sending Host Audio Device Application A->D Device Kernel App Compress Encode for net RTP ed pending DMA to host (~10ms according to
15: OS Scheduling and ing Mark Handley Typical Audio Pipeline (sender) Sending Host Audio Device Application A->D Device Kernel App Compress Encode for net RTP ed pending DMA to host (~10ms according to
Introduction. Operating Systems. Outline. Hardware. I/O Device Types. Device Controllers. One OS function is to control devices
 Introduction Operating Systems Input/Output Devices (Ch12.1-12.3, 12.7; 13.1-13.3, 13.7) One OS function is to control devices significant fraction of code (80-90% of Linux) Want all devices to be simple
Introduction Operating Systems Input/Output Devices (Ch12.1-12.3, 12.7; 13.1-13.3, 13.7) One OS function is to control devices significant fraction of code (80-90% of Linux) Want all devices to be simple
Introduction. Operating Systems. Outline. Hardware. I/O Device Types. Device Controllers. (done)
 Introduction Operating Systems Input/Output Devices (Ch 13.3, 13.5; 14.1-14.3) One OS function is to control devices significant fraction of code (80-90% of Linux) Want all devices to be simple to use
Introduction Operating Systems Input/Output Devices (Ch 13.3, 13.5; 14.1-14.3) One OS function is to control devices significant fraction of code (80-90% of Linux) Want all devices to be simple to use
I/O Systems (4): Power Management. CSE 2431: Introduction to Operating Systems
 I/O Systems (4): Power Management CSE 2431: Introduction to Operating Systems 1 Outline Overview Hardware Issues OS Issues Application Issues 2 Why Power Management? Desktop PCs Battery-powered Computers
I/O Systems (4): Power Management CSE 2431: Introduction to Operating Systems 1 Outline Overview Hardware Issues OS Issues Application Issues 2 Why Power Management? Desktop PCs Battery-powered Computers
instruction is 6 bytes, might span 2 pages 2 pages to handle from 2 pages to handle to Two major allocation schemes
 Allocation of Frames How should the OS distribute the frames among the various processes? Each process needs minimum number of pages - at least the minimum number of pages required for a single assembly
Allocation of Frames How should the OS distribute the frames among the various processes? Each process needs minimum number of pages - at least the minimum number of pages required for a single assembly
Operating Systems. Introduction & Overview. Outline for today s lecture. Administrivia. ITS 225: Operating Systems. Lecture 1
 ITS 225: Operating Systems Operating Systems Lecture 1 Introduction & Overview Jan 15, 2004 Dr. Matthew Dailey Information Technology Program Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat
ITS 225: Operating Systems Operating Systems Lecture 1 Introduction & Overview Jan 15, 2004 Dr. Matthew Dailey Information Technology Program Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat
EMBEDDED SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT. George Hadley 2017, Images Property of their Respective Owners
 EMBEDDED SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT George Hadley 2017, Images Property of their Respective Owners OUTLINE Embedded vs. General Purpose Programming Layers of Abstraction (Hardware, Interface, Application) Embedded
EMBEDDED SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT George Hadley 2017, Images Property of their Respective Owners OUTLINE Embedded vs. General Purpose Programming Layers of Abstraction (Hardware, Interface, Application) Embedded
Architectural Support for Operating Systems
 OS and Architectures Architectural Support for Operating Systems Emin Gun Sirer What an OS can do is dictated, at least in part, by the architecture. Architecture support can greatly simplify (or complicate)
OS and Architectures Architectural Support for Operating Systems Emin Gun Sirer What an OS can do is dictated, at least in part, by the architecture. Architecture support can greatly simplify (or complicate)
Processes. Sanzheng Qiao. December, Department of Computing and Software
 Processes Sanzheng Qiao Department of Computing and Software December, 2012 What is a process? The notion of process is an abstraction. It has been given many definitions. Program in execution is the most
Processes Sanzheng Qiao Department of Computing and Software December, 2012 What is a process? The notion of process is an abstraction. It has been given many definitions. Program in execution is the most
AVR XMEGA Product Line Introduction AVR XMEGA TM. Product Introduction.
 AVR XMEGA TM Product Introduction 32-bit AVR UC3 AVR Flash Microcontrollers The highest performance AVR in the world 8/16-bit AVR XMEGA Peripheral Performance 8-bit megaavr The world s most successful
AVR XMEGA TM Product Introduction 32-bit AVR UC3 AVR Flash Microcontrollers The highest performance AVR in the world 8/16-bit AVR XMEGA Peripheral Performance 8-bit megaavr The world s most successful
ANALYSIS OF A DYNAMIC FREQUENCY SCALING ALGORTIHM ON XSCALE.
 ANALYSIS OF A DYNAMIC FREQUENCY SCALING ALGORTIHM ON XSCALE. Group 9 Ishdeep Singh Sawhney (issawhne@unity.ncsu.edu) Shobhit Kanaujia (sokanauj@unity.ncsu.edu) Prasanth Ganesan (pganesa@unity.ncsu.edu)
ANALYSIS OF A DYNAMIC FREQUENCY SCALING ALGORTIHM ON XSCALE. Group 9 Ishdeep Singh Sawhney (issawhne@unity.ncsu.edu) Shobhit Kanaujia (sokanauj@unity.ncsu.edu) Prasanth Ganesan (pganesa@unity.ncsu.edu)
Application Note One Wire Digital Output. 1 Introduction. 2 Electrical Parameters for One Wire Interface. 3 Start and Data Transmission
 Application Note One Wire Digital Output 1 Introduction The pressure transmitter automatically outputs pressure data, and when appropriate temperature data, in a fixed interval. The host simply waits for
Application Note One Wire Digital Output 1 Introduction The pressure transmitter automatically outputs pressure data, and when appropriate temperature data, in a fixed interval. The host simply waits for
This section will cover the core initialization process.
 This section will cover the core initialization process. 1 There are three steps to initializing a system, CPU, Boot device and OS initialization + CPU initialization initializes the CPU to a known state.
This section will cover the core initialization process. 1 There are three steps to initializing a system, CPU, Boot device and OS initialization + CPU initialization initializes the CPU to a known state.
Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture 16 Exceptions and Processor Management
 Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture 16 Exceptions and Processor Management Boris Grot School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Class party! When: Friday, Dec 1 @ 8pm Where: Bar 50 on Cowgate Inf2C Computer
Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture 16 Exceptions and Processor Management Boris Grot School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Class party! When: Friday, Dec 1 @ 8pm Where: Bar 50 on Cowgate Inf2C Computer
8254 is a programmable interval timer. Which is widely used in clock driven digital circuits. with out timer there will not be proper synchronization
 8254 is a programmable interval timer. Which is widely used in clock driven digital circuits. with out timer there will not be proper synchronization between two devices. So it is very useful chip. The
8254 is a programmable interval timer. Which is widely used in clock driven digital circuits. with out timer there will not be proper synchronization between two devices. So it is very useful chip. The
TCPivo A High-Performance Packet Replay Engine. Wu-chang Feng Ashvin Goel Abdelmajid Bezzaz Wu-chi Feng Jonathan Walpole
 TCPivo A High-Performance Packet Replay Engine Wu-chang Feng Ashvin Goel Abdelmajid Bezzaz Wu-chi Feng Jonathan Walpole Motivation Many methods for evaluating network devices Simulation Device simulated,
TCPivo A High-Performance Packet Replay Engine Wu-chang Feng Ashvin Goel Abdelmajid Bezzaz Wu-chi Feng Jonathan Walpole Motivation Many methods for evaluating network devices Simulation Device simulated,
Real Time Embedded Systems. Lecture 1 January 17, 2012
 Low-Power & Reset Real Time Embedded Systems www.atomicrhubarb.com/embedded Lecture 1 January 17, 2012 Topic Section Topic Where in the books Catsoulis chapter/page Simon chapter/page Zilog UM197 (ZNEO
Low-Power & Reset Real Time Embedded Systems www.atomicrhubarb.com/embedded Lecture 1 January 17, 2012 Topic Section Topic Where in the books Catsoulis chapter/page Simon chapter/page Zilog UM197 (ZNEO
Computer Science Window-Constrained Process Scheduling for Linux Systems
 Window-Constrained Process Scheduling for Linux Systems Richard West Ivan Ganev Karsten Schwan Talk Outline Goals of this research DWCS background DWCS implementation details Design of the experiments
Window-Constrained Process Scheduling for Linux Systems Richard West Ivan Ganev Karsten Schwan Talk Outline Goals of this research DWCS background DWCS implementation details Design of the experiments
Operating Systems Design Fall 2010 Exam 1 Review. Paul Krzyzanowski
 Operating Systems Design Fall 2010 Exam 1 Review Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 Question 1 To a programmer, a system call looks just like a function call. Explain the difference in the underlying
Operating Systems Design Fall 2010 Exam 1 Review Paul Krzyzanowski pxk@cs.rutgers.edu 1 Question 1 To a programmer, a system call looks just like a function call. Explain the difference in the underlying
Section 10. Watchdog Timer and Power Saving Modes
 Section 10. Watchdog Timer and Power Saving Modes HIGHLIGHTS This section of the manual contains the following topics: 10.1 Introduction... 10-2 10.2 Power Saving Modes... 10-2 10.3 Sleep Mode...10-2 10.4
Section 10. Watchdog Timer and Power Saving Modes HIGHLIGHTS This section of the manual contains the following topics: 10.1 Introduction... 10-2 10.2 Power Saving Modes... 10-2 10.3 Sleep Mode...10-2 10.4
Network performance. slide 1 gaius. Network performance
 slide 1 historically much network performance research was based on the assumption that network traffic was random apoisson distribution of traffic Paxson and Floyd 1994, Willinger 1995 found this assumption
slide 1 historically much network performance research was based on the assumption that network traffic was random apoisson distribution of traffic Paxson and Floyd 1994, Willinger 1995 found this assumption
PC-CARD-DAS16/12 Specifications
 Specifications Document Revision 1.1, February, 2010 Copyright 2010, Measurement Computing Corporation Typical for 25 C unless otherwise specified. Specifications in italic text are guaranteed by design.
Specifications Document Revision 1.1, February, 2010 Copyright 2010, Measurement Computing Corporation Typical for 25 C unless otherwise specified. Specifications in italic text are guaranteed by design.
ECE 3055: Final Exam
 ECE 3055: Final Exam Instructions: You have 2 hours and 50 minutes to complete this quiz. The quiz is closed book and closed notes, except for one 8.5 x 11 sheet. No calculators are allowed. Multiple Choice
ECE 3055: Final Exam Instructions: You have 2 hours and 50 minutes to complete this quiz. The quiz is closed book and closed notes, except for one 8.5 x 11 sheet. No calculators are allowed. Multiple Choice
Ricardo Rocha. Department of Computer Science Faculty of Sciences University of Porto
 Ricardo Rocha Department of Computer Science Faculty of Sciences University of Porto Slides based on the book Operating System Concepts, 9th Edition, Abraham Silberschatz, Peter B. Galvin and Greg Gagne,
Ricardo Rocha Department of Computer Science Faculty of Sciences University of Porto Slides based on the book Operating System Concepts, 9th Edition, Abraham Silberschatz, Peter B. Galvin and Greg Gagne,
BOOST YOUR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE USING THE ZILOG ESCC CONTROLLER
 BOOST YOUR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE USING THE ZILOG ESCC CONTROLLER AN030001-0509 For greater testability, larger interface flexibility, and increased CPU/ DMA offloading, replace the SCC with the ESCC Controller...
BOOST YOUR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE USING THE ZILOG ESCC CONTROLLER AN030001-0509 For greater testability, larger interface flexibility, and increased CPU/ DMA offloading, replace the SCC with the ESCC Controller...
PC-CARD-DAS16/16 Specifications
 Specifications Document Revision 2.1, February, 2010 Copyright 2010, Measurement Computing Corporation Typical for 25 C unless otherwise specified. Specifications in italic text are guaranteed by design.
Specifications Document Revision 2.1, February, 2010 Copyright 2010, Measurement Computing Corporation Typical for 25 C unless otherwise specified. Specifications in italic text are guaranteed by design.
Lecture 2 - Fundamental Concepts
 Lecture 2 - Fundamental Concepts Instructor : Bibhas Ghoshal (bibhas.ghoshal@iiita.ac.in) Autumn Semester, 2015 Bibhas Ghoshal IOSY 332C & IOPS 332C: OS Autumn Semester, 2015 1 / 43 Lecture Outline Operating
Lecture 2 - Fundamental Concepts Instructor : Bibhas Ghoshal (bibhas.ghoshal@iiita.ac.in) Autumn Semester, 2015 Bibhas Ghoshal IOSY 332C & IOPS 332C: OS Autumn Semester, 2015 1 / 43 Lecture Outline Operating
MCS-51 Serial Port A T 8 9 C 5 2 1
 MCS-51 Serial Port AT89C52 1 Introduction to Serial Communications Serial vs. Parallel transfer of data Simplex, Duplex and half-duplex modes Synchronous, Asynchronous UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter.
MCS-51 Serial Port AT89C52 1 Introduction to Serial Communications Serial vs. Parallel transfer of data Simplex, Duplex and half-duplex modes Synchronous, Asynchronous UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter.
CS 341l Fall 2008 Test #4 NAME: Key
 CS 341l all 2008 est #4 NAME: Key CS3411 est #4, 21 November 2008. 100 points total, number of points each question is worth is indicated in parentheses. Answer all questions. Be as concise as possible
CS 341l all 2008 est #4 NAME: Key CS3411 est #4, 21 November 2008. 100 points total, number of points each question is worth is indicated in parentheses. Answer all questions. Be as concise as possible
Even coarse architectural trends impact tremendously the design of systems
 CSE 451: Operating Systems Spring 2006 Module 2 Architectural Support for Operating Systems John Zahorjan zahorjan@cs.washington.edu 534 Allen Center Even coarse architectural trends impact tremendously
CSE 451: Operating Systems Spring 2006 Module 2 Architectural Support for Operating Systems John Zahorjan zahorjan@cs.washington.edu 534 Allen Center Even coarse architectural trends impact tremendously
Chapter 2. Overview of Architecture and Microcontroller-Resources
 Chapter 2 Overview of Architecture and Microcontroller-Resources Lesson 4 Timers, Real Time Clock Interrupts and Watchdog Timer 2 Microcontroller-resources Port P1 Port P0 Port P2 PWM Timers Internal Program
Chapter 2 Overview of Architecture and Microcontroller-Resources Lesson 4 Timers, Real Time Clock Interrupts and Watchdog Timer 2 Microcontroller-resources Port P1 Port P0 Port P2 PWM Timers Internal Program
Power Management for Embedded Systems
 Power Management for Embedded Systems Minsoo Ryu Hanyang University Why Power Management? Battery-operated devices Smartphones, digital cameras, and laptops use batteries Power savings and battery run
Power Management for Embedded Systems Minsoo Ryu Hanyang University Why Power Management? Battery-operated devices Smartphones, digital cameras, and laptops use batteries Power savings and battery run
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
 CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 1: Overview and Introduction Prof. Alan Mislove (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) What is an Operating System? 2 What is an Operating System? A program
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 1: Overview and Introduction Prof. Alan Mislove (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) What is an Operating System? 2 What is an Operating System? A program
POWER MANAGEMENT AND ENERGY EFFICIENCY
 POWER MANAGEMENT AND ENERGY EFFICIENCY * Adopted Power Management for Embedded Systems, Minsoo Ryu 2017 Operating Systems Design Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Power Management Power consumption
POWER MANAGEMENT AND ENERGY EFFICIENCY * Adopted Power Management for Embedded Systems, Minsoo Ryu 2017 Operating Systems Design Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Power Management Power consumption
CS 31: Intro to Systems Operating Systems Overview. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 31, 2015
 CS 31: Intro to Systems Operating Systems Overview Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 31, 2015 Reading Quiz OS: Turn undesirable into desirable Turn undesirable inconveniences: reality Complexity of hardware
CS 31: Intro to Systems Operating Systems Overview Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 31, 2015 Reading Quiz OS: Turn undesirable into desirable Turn undesirable inconveniences: reality Complexity of hardware
ECE 7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture ---- A Systems Perspective. Part I: Operating system overview: Processes and threads
 ECE 7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture ---- A Systems Perspective Part I: Operating system overview: Processes and threads 1 Overview Process concept Process scheduling Thread
ECE 7650 Scalable and Secure Internet Services and Architecture ---- A Systems Perspective Part I: Operating system overview: Processes and threads 1 Overview Process concept Process scheduling Thread
Last 2 Classes: Introduction to Operating Systems & C++ tutorial. Today: OS and Computer Architecture
 Last 2 Classes: Introduction to Operating Systems & C++ tutorial User apps OS Virtual machine interface hardware physical machine interface An operating system is the interface between the user and the
Last 2 Classes: Introduction to Operating Systems & C++ tutorial User apps OS Virtual machine interface hardware physical machine interface An operating system is the interface between the user and the
Asynchronous Events on Linux
 Asynchronous Events on Linux Frederic.Rossi@Ericsson.CA Open System Lab Systems Research June 25, 2002 Ericsson Research Canada Introduction Linux performs well as a general purpose OS but doesn t satisfy
Asynchronous Events on Linux Frederic.Rossi@Ericsson.CA Open System Lab Systems Research June 25, 2002 Ericsson Research Canada Introduction Linux performs well as a general purpose OS but doesn t satisfy
High level scheduling: Medium level scheduling: Low level scheduling. Scheduling 0 : Levels
 Scheduling 0 : Levels High level scheduling: Deciding whether another process can run is process table full? user process limit reached? load to swap space or memory? Medium level scheduling: Balancing
Scheduling 0 : Levels High level scheduling: Deciding whether another process can run is process table full? user process limit reached? load to swap space or memory? Medium level scheduling: Balancing
General Purpose Programmable Peripheral Devices. Assistant Professor, EC Dept., Sankalchand Patel College of Engg.,Visnagar
 Chapter 15 General Purpose Programmable Peripheral Devices by Rahul Patel, Assistant Professor, EC Dept., Sankalchand Patel College of Engg.,Visnagar Microprocessor & Interfacing (140701) Rahul Patel 1
Chapter 15 General Purpose Programmable Peripheral Devices by Rahul Patel, Assistant Professor, EC Dept., Sankalchand Patel College of Engg.,Visnagar Microprocessor & Interfacing (140701) Rahul Patel 1
CS399 New Beginnings. Jonathan Walpole
 CS399 New Beginnings Jonathan Walpole OS-Related Hardware & Software The Process Concept 2 Lecture 2 Overview OS-Related Hardware & Software - complications in real systems - brief introduction to memory
CS399 New Beginnings Jonathan Walpole OS-Related Hardware & Software The Process Concept 2 Lecture 2 Overview OS-Related Hardware & Software - complications in real systems - brief introduction to memory
Swapping. Operating Systems I. Swapping. Motivation. Paging Implementation. Demand Paging. Active processes use more physical memory than system has
 Swapping Active processes use more physical memory than system has Operating Systems I Address Binding can be fixed or relocatable at runtime Swap out P P Virtual Memory OS Backing Store (Swap Space) Main
Swapping Active processes use more physical memory than system has Operating Systems I Address Binding can be fixed or relocatable at runtime Swap out P P Virtual Memory OS Backing Store (Swap Space) Main
CS370: System Architecture & Software [Fall 2014] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS370: System Architecture & Software [Fall 2014] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS370: System Architecture & Software [Fall 2014] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/81/82824425.jpg) Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey CS 370: SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE & SOFTWARE [CPU SCHEDULING] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University OpenMP compiler directives
Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey CS 370: SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE & SOFTWARE [CPU SCHEDULING] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University OpenMP compiler directives
Lecture 6: Real-Time Timing + Real-Time Objects
 Lecture 6: Real-Time Timing + Real-Time Objects 1 Lecture: RT Timing (30) Lab Exercise: Watchdog + auxiliary clock timers (25) Lecture: RT Objects-Events (15) Lab Exercise: Events (30) Project Work (rest
Lecture 6: Real-Time Timing + Real-Time Objects 1 Lecture: RT Timing (30) Lab Exercise: Watchdog + auxiliary clock timers (25) Lecture: RT Objects-Events (15) Lab Exercise: Events (30) Project Work (rest
Micrium µc/os II RTOS Introduction EE J. E. Lumpp
 Micrium µc/os II RTOS Introduction (by Jean Labrosse) EE599 001 Fall 2012 J. E. Lumpp μc/os II μc/os II is a highly portable, ROMable, very scalable, preemptive real time, deterministic, multitasking kernel
Micrium µc/os II RTOS Introduction (by Jean Labrosse) EE599 001 Fall 2012 J. E. Lumpp μc/os II μc/os II is a highly portable, ROMable, very scalable, preemptive real time, deterministic, multitasking kernel
Memory Management Outline. Operating Systems. Motivation. Paging Implementation. Accessing Invalid Pages. Performance of Demand Paging
 Memory Management Outline Operating Systems Processes (done) Memory Management Basic (done) Paging (done) Virtual memory Virtual Memory (Chapter.) Motivation Logical address space larger than physical
Memory Management Outline Operating Systems Processes (done) Memory Management Basic (done) Paging (done) Virtual memory Virtual Memory (Chapter.) Motivation Logical address space larger than physical
CENG-336 Introduction to Embedded Systems Development. Timers
 CENG-336 Introduction to Embedded Systems Development Timers Definitions A counter counts (possibly asynchronous) input pulses from an external signal A timer counts pulses of a fixed, known frequency
CENG-336 Introduction to Embedded Systems Development Timers Definitions A counter counts (possibly asynchronous) input pulses from an external signal A timer counts pulses of a fixed, known frequency
18-349: Introduction to Embedded Real-Time Systems
 18-349: Introduction to Embedded Real-Time Systems Embedded Real-Time Systems Lecture 6: Timers and Interrupts Anthony Rowe Electrical and Computer Engineering Carnegie Mellon University Embedded Real-Time
18-349: Introduction to Embedded Real-Time Systems Embedded Real-Time Systems Lecture 6: Timers and Interrupts Anthony Rowe Electrical and Computer Engineering Carnegie Mellon University Embedded Real-Time
I/O Hardwares. Some typical device, network, and data base rates
 Input/Output 1 I/O Hardwares Some typical device, network, and data base rates 2 Device Controllers I/O devices have components: mechanical component electronic component The electronic component is the
Input/Output 1 I/O Hardwares Some typical device, network, and data base rates 2 Device Controllers I/O devices have components: mechanical component electronic component The electronic component is the
Multics Technical Bulletin MTB-488. To: Distribution From: John J. Bongiovanni Date: 01/20/81 CPU Time Accounting
 Multics Technical Bulletin MTB-488 To: Distribution From: John J. Bongiovanni Date: 01/20/81 Subject: CPU Time Accounting 1. INTRODUCTION The intent of this MTB is to describe a method for measuring CPU
Multics Technical Bulletin MTB-488 To: Distribution From: John J. Bongiovanni Date: 01/20/81 Subject: CPU Time Accounting 1. INTRODUCTION The intent of this MTB is to describe a method for measuring CPU
Page Replacement. 3/9/07 CSE 30341: Operating Systems Principles
 Page Replacement page 1 Page Replacement Algorithms Want lowest page-fault rate Evaluate algorithm by running it on a particular string of memory references (reference string) and computing the number
Page Replacement page 1 Page Replacement Algorithms Want lowest page-fault rate Evaluate algorithm by running it on a particular string of memory references (reference string) and computing the number
Process Scheduling Queues
 Process Control Process Scheduling Queues Job queue set of all processes in the system. Ready queue set of all processes residing in main memory, ready and waiting to execute. Device queues set of processes
Process Control Process Scheduling Queues Job queue set of all processes in the system. Ready queue set of all processes residing in main memory, ready and waiting to execute. Device queues set of processes
A Smart Port Card Tutorial --- Hardware
 A Smart Port Card Tutorial --- Hardware John DeHart Washington University jdd@arl.wustl.edu http://www.arl.wustl.edu/~jdd 1 References: New Links from Kits References Page Intel Embedded Module: Data Sheet
A Smart Port Card Tutorial --- Hardware John DeHart Washington University jdd@arl.wustl.edu http://www.arl.wustl.edu/~jdd 1 References: New Links from Kits References Page Intel Embedded Module: Data Sheet
ECE 477 Digital Systems Senior Design Project. Module 10 Embedded Software Development
 2011 by D. G. Meyer ECE 477 Digital Systems Senior Design Project Module 10 Embedded Software Development Outline Memory Models Memory Sections Discussion Application Code Organization Memory Models -
2011 by D. G. Meyer ECE 477 Digital Systems Senior Design Project Module 10 Embedded Software Development Outline Memory Models Memory Sections Discussion Application Code Organization Memory Models -
Operating Systems (2INC0) 2018/19. Introduction (01) Dr. Tanir Ozcelebi. Courtesy of Prof. Dr. Johan Lukkien. System Architecture and Networking Group
 Operating Systems (2INC0) 20/19 Introduction (01) Dr. Courtesy of Prof. Dr. Johan Lukkien System Architecture and Networking Group Course Overview Introduction to operating systems Processes, threads and
Operating Systems (2INC0) 20/19 Introduction (01) Dr. Courtesy of Prof. Dr. Johan Lukkien System Architecture and Networking Group Course Overview Introduction to operating systems Processes, threads and
Architectural design proposal for real time clock for wireless microcontroller unit
 Architectural design proposal for real time clock for wireless microcontroller unit Muhammad Nor Azwan Mohd Alias 1, *, and Shaiful Nizam Mohyar 1 1 School of Microelectronic Engineering, University Malaysia
Architectural design proposal for real time clock for wireless microcontroller unit Muhammad Nor Azwan Mohd Alias 1, *, and Shaiful Nizam Mohyar 1 1 School of Microelectronic Engineering, University Malaysia
Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Basic Concepts Scheduling Criteria Scheduling Algorithms Thread Scheduling Multiple-Processor Scheduling Real-Time
Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Basic Concepts Scheduling Criteria Scheduling Algorithms Thread Scheduling Multiple-Processor Scheduling Real-Time
Real-Time Operating Systems (Working Draft) What is an Operating System (OS)?
 Real-Time Operating Systems (Working Draft) Originally Prepared by Sebastian Fischemeister Modified by Insup Lee CIS 541, Spring 2010 What is an Operating System (OS)? A program that acts as an intermediary
Real-Time Operating Systems (Working Draft) Originally Prepared by Sebastian Fischemeister Modified by Insup Lee CIS 541, Spring 2010 What is an Operating System (OS)? A program that acts as an intermediary
Section 9. Watchdog Timer and Power-up Timer
 Section 9. Watchdog Timer and Power-up Timer HIGHLIGHTS This section of the manual contains the following topics: 9.1 Introduction... 9-2 9.2 Watchdog Timer and Power-up Timer Control Registers... 9-3
Section 9. Watchdog Timer and Power-up Timer HIGHLIGHTS This section of the manual contains the following topics: 9.1 Introduction... 9-2 9.2 Watchdog Timer and Power-up Timer Control Registers... 9-3
e-pg Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Interrupt Programming in Embedded C Module No: CS/ES/20 Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Interrupt Programming in Embedded C Module No: CS/ES/20 Quadrant 1 e-text In this lecture embedded C program for interrupt handling
e-pg Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Interrupt Programming in Embedded C Module No: CS/ES/20 Quadrant 1 e-text In this lecture embedded C program for interrupt handling
Section I Section Real Time Systems. Processes. 1.6 Input/Output Management. (Textbook: A. S. Tanenbaum Modern OS - ch. 5)
 EE206: Software Engineering IV 1.6 Input/Output page 1 of 9 Section I Section Real Time Systems. Processes 1.6 Input/Output Management (Textbook: A. S. Tanenbaum Modern OS - ch. 5) Input/Output Overview
EE206: Software Engineering IV 1.6 Input/Output page 1 of 9 Section I Section Real Time Systems. Processes 1.6 Input/Output Management (Textbook: A. S. Tanenbaum Modern OS - ch. 5) Input/Output Overview
Unit 2 : Computer and Operating System Structure
 Unit 2 : Computer and Operating System Structure Lesson 1 : Interrupts and I/O Structure 1.1. Learning Objectives On completion of this lesson you will know : what interrupt is the causes of occurring
Unit 2 : Computer and Operating System Structure Lesson 1 : Interrupts and I/O Structure 1.1. Learning Objectives On completion of this lesson you will know : what interrupt is the causes of occurring
Virtual Memory Review. Page faults. Paging system summary (so far)
 Lecture 22 (Wed 11/19/2008) Virtual Memory Review Lab #4 Software Simulation Due Fri Nov 21 at 5pm HW #3 Cache Simulator & code optimization Due Mon Nov 24 at 5pm More Virtual Memory 1 2 Paging system
Lecture 22 (Wed 11/19/2008) Virtual Memory Review Lab #4 Software Simulation Due Fri Nov 21 at 5pm HW #3 Cache Simulator & code optimization Due Mon Nov 24 at 5pm More Virtual Memory 1 2 Paging system
MODERN OPERATING SYSTEMS. Chapter 3 Memory Management
 MODERN OPERATING SYSTEMS Chapter 3 Memory Management No Memory Abstraction Figure 3-1. Three simple ways of organizing memory with an operating system and one user process. Base and Limit Registers Figure
MODERN OPERATING SYSTEMS Chapter 3 Memory Management No Memory Abstraction Figure 3-1. Three simple ways of organizing memory with an operating system and one user process. Base and Limit Registers Figure
Four Components of a Computer System
 Four Components of a Computer System Operating System Concepts Essentials 2nd Edition 1.1 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Operating System Definition OS is a resource allocator Manages all resources
Four Components of a Computer System Operating System Concepts Essentials 2nd Edition 1.1 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Operating System Definition OS is a resource allocator Manages all resources
Scheduling Mar. 19, 2018
 15-410...Everything old is new again... Scheduling Mar. 19, 2018 Dave Eckhardt Brian Railing Roger Dannenberg 1 Outline Chapter 5 (or Chapter 7): Scheduling Scheduling-people/textbook terminology note
15-410...Everything old is new again... Scheduling Mar. 19, 2018 Dave Eckhardt Brian Railing Roger Dannenberg 1 Outline Chapter 5 (or Chapter 7): Scheduling Scheduling-people/textbook terminology note
CS510 Operating System Foundations. Jonathan Walpole
 CS510 Operating System Foundations Jonathan Walpole OS-Related Hardware & Software 2 Lecture 2 Overview OS-Related Hardware & Software - complications in real systems - brief introduction to memory protection,
CS510 Operating System Foundations Jonathan Walpole OS-Related Hardware & Software 2 Lecture 2 Overview OS-Related Hardware & Software - complications in real systems - brief introduction to memory protection,
CS 471 Operating Systems. Yue Cheng. George Mason University Fall 2017
 CS 471 Operating Systems Yue Cheng George Mason University Fall 2017 Outline o Process concept o Process creation o Process states and scheduling o Preemption and context switch o Inter-process communication
CS 471 Operating Systems Yue Cheng George Mason University Fall 2017 Outline o Process concept o Process creation o Process states and scheduling o Preemption and context switch o Inter-process communication
CS 326: Operating Systems. CPU Scheduling. Lecture 6
 CS 326: Operating Systems CPU Scheduling Lecture 6 Today s Schedule Agenda? Context Switches and Interrupts Basic Scheduling Algorithms Scheduling with I/O Symmetric multiprocessing 2/7/18 CS 326: Operating
CS 326: Operating Systems CPU Scheduling Lecture 6 Today s Schedule Agenda? Context Switches and Interrupts Basic Scheduling Algorithms Scheduling with I/O Symmetric multiprocessing 2/7/18 CS 326: Operating
Memory management units
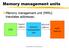 Memory management units Memory management unit (MMU) translates addresses: CPU logical address memory management unit physical address main memory Computers as Components 1 Access time comparison Media
Memory management units Memory management unit (MMU) translates addresses: CPU logical address memory management unit physical address main memory Computers as Components 1 Access time comparison Media
Memory management, part 2: outline. Operating Systems, 2017, Danny Hendler and Amnon Meisels
 Memory management, part 2: outline 1 Page Replacement Algorithms Page fault forces choice o which page must be removed to make room for incoming page? Modified page must first be saved o unmodified just
Memory management, part 2: outline 1 Page Replacement Algorithms Page fault forces choice o which page must be removed to make room for incoming page? Modified page must first be saved o unmodified just
