STATISTICS FOR PSYCHOLOGISTS
|
|
|
- Osborn Webb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STATISTICS FOR PSYCHOLOGISTS SECTION: JAMOVI CHAPTER: USING THE SOFTWARE Section Abstract: This section provides step-by-step instructions on how to obtain basic statistical output using JAMOVI, both visually with screenshots and via written instructions. Simple examples for most undergraduate-level between-subjects and within-subjects research designs are provided. Keywords: JAMOVI, screenshots, directions for use Section Updated: October 2017 This document is part of an online statistics textbook. A browser-friendly viewing platform for the textbook is available: All individual files are available via the Open Science Framework:
2 Table of Contents for This Section ENTERING ONE SAMPLE AND REPEATED MEASURES DATA... 2 ENTERING MULTIPLE SAMPLE AND MIXED DESIGN DATA... 5 DESCRIPTIVES (FREQUENCIES AND DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS)... 7 CORRELATION MATRIX (BIVARIATE)... 9 REGRESSION (BIVARIATE) ONE SAMPLE T TEST PAIRED SAMPLES T TEST INDEPENDENT SAMPLES T TEST ONE-WAY ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE REPEATED MEASURES ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE FACTORIAL ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE MIXED DESIGN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE... 23
3 ENTERING ONE SAMPLE AND REPEATED MEASURES DATA Steps for Defining Variables 1. First, click on the Data tab on the top of the window. Generally speaking, this is where you will enter the data for all of the variables in the data set. 2. Click on a cell in the column (i.e., variable) that you wish to define. Click on Setup from the menu. This will bring up a new set of options. Steps for Setting Variable Properties 3. Type in the name of the variable in the top box (previously labeled A ). 4. Define the level of measurement for the variables by choosing the appropriate option. In this example, score (an outcome variable) is continuous. 5. To save the changes you have made, click the large check mark on the right side of the options. To hide the setup menu, click on the large up arrow button in that same location. Page 2 of 25
4 Steps for Entering Data 6. Enter the data in the individual cells of the column for the variable. Note that each cell should contain a single score for an individual person. There will be as many rows as people. Steps for Entering Additional Variables 7. If you wish to add data for additional variables, simply repeat the steps described above. Return to the Setup and define the next variable (which is, in this example, called outcome ). 8. Then enter the scores for each of the same participants on this second variable. Notice that each individual (i.e., the rows) have values for each variable (i.e., the columns). Page 3 of 25
5 Steps for Entering Repeated Measurements 9. If you wish to add data for repeated measurements of variables, simply modify the steps above. Return to the Setup and define the next measurement instance (not shown here). 10. For repeated measures data, the columns really represent the different instances of the within-subjects variable. In the example here, each variable column is a measurement of the quiz outcome variable. 11. Notice that each participant has scores on both variables. In this example, each of the five participants has a score on for the Time 1 measurement ( t1score ) and one for the Time 2 measurement ( t2score ). Your data are now ready to be analyzed! Page 4 of 25
6 ENTERING MULTIPLE SAMPLE AND MIXED DESIGN DATA Steps for Defining Variables 1. First, click on the Data tab on the top of the window. Generally speaking, this is where you will enter the data for all of the variables in the data set. 2. Click on a cell in the column (i.e., variable) that you wish to define. Click on Setup from the menu. This will bring up a new set of options. Steps for Setting Variable Properties 3. You will need to define multiple variables. One variable will represent the Factor (Independent Variable) and the other will represent the Outcome (Dependent) Variable. 4. Provide a name and define the level of measurement for the variables by choosing the appropriate options. In this example, group (the Factor) is nominal. The Outcome variable ( score ) is continuous. 5. To save the changes you have made, click the large check mark on the right side of the options. To hide the setup menu, click on the large up arrow button in that same location. Page 5 of 25
7 Steps for Entering Data 6. Enter the data for all of the participants. Notice that each participant has scores on both the Factor and Outcome Variables. There will be as many rows as people. 7. On the categorical Factor, you will use numbers to represent the two categories (or levels ) of the variable. 8. If your data set has more than two groups, simply be sure to add a group indicator (a value on the group variable) and a score for each additional person. Steps for Adding Variables and Data 9. If you wish to add data for additional variables, simply repeat the steps described above. Return to Setup and define the next variable and the level of measurement for that variable (not shown here). 10. Then enter the scores for each of the same participants on the new variables. Notice that each individual (i.e., the rows) will still have values for each variable (i.e., the columns). 11. On the categorical Factors, use the numerical values associated with the categories or groups. Note that the combination of values in the Factors will define the multiple groups of the factorial design. 12. If your data have multiple outcome variables, simply add additional columns for each instance of the outcome. You can define these as needed in the Setup. Your data are now ready to be analyzed! Page 6 of 25
8 DESCRIPTIVES (FREQUENCIES AND DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS) Steps for Obtaining Frequency-Related Statistics 1. First, enter the data (described elsewhere). 2. On the Analyses tab, select the Exploration Descriptives option. Steps for Obtaining a Frequency Distribution 3. A set of options will then appear for you to choose the variables and statistics of interest. 4. Select the variables you wish to analyze by clicking on them in the left-hand box and then the arrow to move them into the right-hand box. 5. Be sure that Frequency tables is checked. Without this checked, you will not get a frequency distribution. 6. Output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Page 7 of 25
9 Steps for Obtaining Summary Statistics 7. Though some basic summary statistics are displayed by default, you can make changes by expanding the Statistics drop-down menu. 8. As you select the desired statistics, the output on the right side of the window will be automatically updated. 9. Individual tables (or even the whole section of Output) can be copied using the drop-down arrow options in the output. These can be pasted into other word processing software for printing purposes. Your data have now been analyzed! Page 8 of 25
10 CORRELATION MATRIX (BIVARIATE) Steps for Obtaining Correlational Statistics 1. First, enter data involving multiple variables (described elsewhere). 2. On the Analyses tab, select the Regression Correlation Matrix option. Steps for Obtaining the Correlations (and Significance Tests) 3. A set of options will then appear for you to choose the variables and statistics of interest. 4. Select the variables you wish to analyze by clicking on them in the left-hand box and then the arrow to move them into the right-hand box. 5. Output (with no descriptive statistics) will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. 6. If you wish descriptive statistics associated with each variable, follow the Descriptives procedures described earlier in this manual. Your data have now been analyzed! Page 9 of 25
11 REGRESSION (BIVARIATE) Steps for Obtaining Regression Statistics 1. First, enter data involving multiple variables (described elsewhere). 2. On the Analyses tab, select the Regression Linear Regression option. Steps for Obtaining the Regression Coefficients 3. A set of options will then appear for you to choose the variables and statistics of interest. 4. Select the outcome variable (i.e., criterion) and clicking the arrow to move it into the Dependent Variable box. 5. Move the predictor variable to the Covariates box. [In regression, it is possible to have multiple predictors but this is not addressed in this tutorial.] 6. Output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Your data have now been analyzed! Page 10 of 25
12 ONE SAMPLE T TEST Steps for Obtaining One-Sample Inferential Statistics 1. First, enter the data (described elsewhere). 2. On the Analysis tab, select the T-Tests One Sample T-Test option. Steps for Obtaining the Significance Test 3. A set of options will then appear for you to choose the variables and statistics of interest. 4. Select the variable you wish to analyze by clicking on it in the left-hand box and then the arrow to move it into the right-hand box. 5. Output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Page 11 of 25
13 Steps for Obtaining Additional Statistics 6. Be sure to enter a known or hypothesized mean into the Test Value field. If you do not enter a value here, JAMOVI will automatically use zero as the comparison mean. 7. If you wish to view (and alter) the width of the confidence interval, check the Confidence Interval box. 8. Similarly, select other options that are important for you: Mean Difference will display the size of the difference between the two means; Effect size will display Cohen s d; and Descriptives will offer a mean and standard deviation for the group. 9. Updated output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Your data have now been analyzed! Page 12 of 25
14 PAIRED SAMPLES T TEST Steps for Obtaining Paired-Sample Inferential Statistics 1. First, enter paired samples or repeated measures data (described elsewhere). 2. On the Analysis tab, Select the T-Tests Paired Samples T-Test option. Steps for Obtaining the Significance Test 3. A set of options will then appear for you to choose the variables and statistics of interest. 4. Select the variables you wish to analyze by clicking on both of them while holding down the CTRL key. Then click on the arrow to move the pair of variables to the right-hand box. 5. Output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Page 13 of 25
15 Steps for Obtaining Additional Statistics 6. If you wish to view (and alter) the width of the confidence interval, check the Confidence Interval box. 7. Similarly, select other options that are important for you: Mean Difference will display the size of the difference between the two means; Effect size will display Cohen s d; and Descriptives will offer means and standard deviations for each variable. 8. Updated output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Your data have now been analyzed! Page 14 of 25
16 Steps for Obtaining Two-Sample Inferential Statistics 1. First, enter two sample data (described elsewhere). 2. On the Analysis tab, select the T-Tests Independent Samples T-Test option. INDEPENDENT SAMPLES T TEST Steps for Obtaining the Significance Test 3. A set of options will then appear for you to choose the variables and statistics of interest. 4. Select the outcome variable and click the arrow to move it into the Dependent Variables box. 5. Move the Independent Variable to the Grouping Variable box. 6. Output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Page 15 of 25
17 Steps for Obtaining Additional Statistics 7. If you wish to view (and alter) the width of the confidence interval, check the Confidence Interval box. 8. Similarly, select other options that are important for you: Mean Difference will display the size of the difference between the two group s means; Effect size will display Cohen s d; and Descriptives will offer means and standard deviations for each group. 9. Updated output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Your data have now been analyzed! Page 16 of 25
18 Steps for Obtaining Multiple-Sample Inferential Statistics 1. First, enter multiple group data (described elsewhere). 2. On the Analysis tab, select the ANOVA ANOVA option. ONE-WAY ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE Steps for Obtaining the Significance Test 3. A set of options will then appear for you to choose the variables and statistics of interest. 4. Select the outcome variable and click the arrow to move it into the Dependent Variable box. 5. Move the Factor (Independent Variable) to the Fixed Factors box. 6. Output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Page 17 of 25
19 Steps for Obtaining Additional Statistics 7. Choose an effect size measure from the Effect Size list. 8. Though some basic summary statistics are displayed by default, you can make changes by expanding the Additional Options drop-down menu. 9. Select Descriptive statistics to get means and standard deviations for each group. 10. Updated output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Steps for Obtaining Post Hoc Tests 11. If you wish to obtain post hoc tests for the purpose of making comparisons between groups, click the Post Hoc Tests drop-down button. 12. Move the factor (Independent Variable) name from the left-hand box to the right-hand box. 13. Select Tukey to get Tukey HSD post hoc tests (or whatever option you prefer). 14. Updated output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Your data have now been analyzed! Page 18 of 25
20 Steps for Obtaining Repeated Measures Inferential Statistics 1. First, enter repeated measures data (described elsewhere). 2. On the Analysis tab, select the ANOVA Repeated Measures ANOVA option. REPEATED MEASURES ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE Steps for Labeling the Within-Subjects Variable/Factor 3. A set of options will then appear for you to choose the variables and statistics of interest. 4. In the Repeated Measures Factors box, you will define the repeated measures factor. This box is necessary for labeling the repeated measurements of the same underlying factor. 5. Click on RM Factor 1 and type in the name you wish to give to the repeated measures factor. In this example, the measurements/columns reflect quizzes at two different times so Time is used as the name. 6. Below that, click on Level 1 to type the name of the individual level of the repeated measures factor. You may do the same for each level. In this example, the quiz was given twice, so there were only 2 levels of the factor. Page 19 of 25
21 Steps for Obtaining the Significance Test 7. In the Repeated Measures Cells box, you will indicate which measurements/columns in the data set reflect the instances of the repeated measurements. 8. Select the instances you wish to associate with the factor by clicking on them and then arrow to move them. In this example, t1score reflects the first level of the factor and t2score reflects the second level of the factor. 9. Note that this factor only exists in the computer s memory. For examples, nowhere in the data set will you see a variable called Time. 10. Output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Steps for Obtaining Additional Statistics 11. Choose an effect size measure from the Effect Size list. 12. Updated output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. 13. If you wish descriptive statistics associated with each variable, follow the Descriptives procedures described earlier in this manual. Your data have now been analyzed! Page 20 of 25
22 Steps for Obtaining Factorial Inferential Statistics 1. First, enter factorial data (described elsewhere). 2. On the Analysis tab, select the ANOVA ANOVA option. FACTORIAL ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE Steps for Obtaining the Significance Test 3. A set of options will then appear for you to choose the variables and statistics of interest. 4. Select the outcome variable and click the arrow to move it into the Dependent Variable box. 5. Move the multiple Factors (Independent Variables) to the Fixed Factors box. (The interaction term will be automatically generated in the output.) 6. Output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Page 21 of 25
23 Steps for Obtaining Additional Statistics 7. Choose an effect size measure from the Effect Size list. 8. Though some basic summary statistics are displayed by default, you can make changes by expanding the Additional Options drop-down menu. 9. Select Descriptive statistics to get means and standard deviations for each group. 10. Updated output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Your data have now been analyzed! Page 22 of 25
24 Steps for Obtaining Repeated Measures Inferential Statistics 1. First, enter mixed design data (described elsewhere). 2. On the Analysis tab, select the ANOVA Repeated Measures ANOVA option. MIXED DESIGN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE Steps for Labeling the Within-Subjects Variable/Factor 3. A set of options will then appear for you to choose the variables and statistics of interest. 4. In the Repeated Measures Factors box, you will define the repeated measures factor. This box is necessary for labeling the repeated measurements of the same underlying factor. 5. Click on RM Factor 1 and type in the name you wish to give to the repeated measures factor. In this example, the measurements/columns reflect quizzes at two different times so Time is used as the name. 6. Below that, click on Level 1 to type the name of the individual level of the repeated measures factor. You may do the same for each level. In this example, the quiz was given twice, so there were only 2 levels of the factor. Page 23 of 25
25 Steps for Obtaining the Significance Test 7. In the Repeated Measures Cells box, you will indicate which measurements/columns in the data set reflect the instances of the repeated measurements. 8. Select the instances you wish to associate with the factor by clicking on them and then arrow to move them. In this example, t1score reflects the first level of the factor and t2score reflects the second level of the factor. 9. Click on the between-subjects variable on the left-hand side and then the arrow to move it into the Between Subjects Factors box on the right-hand side box. 10. Output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. Steps for Obtaining Additional Statistics 11. Choose an effect size measure from the Effect Size list. 12. Updated output will automatically appear on the right side of the window. Output can be copied and pasted into other documents for printing. 13. If you wish descriptive statistics associated with each variable, follow the Descriptives procedures described earlier in this manual. Your data have now been analyzed! Page 24 of 25
Psychology 282 Lecture #21 Outline Categorical IVs in MLR: Effects Coding and Contrast Coding
 Psychology 282 Lecture #21 Outline Categorical IVs in MLR: Effects Coding and Contrast Coding In the previous lecture we learned how to incorporate a categorical research factor into a MLR model by using
Psychology 282 Lecture #21 Outline Categorical IVs in MLR: Effects Coding and Contrast Coding In the previous lecture we learned how to incorporate a categorical research factor into a MLR model by using
Also, for all analyses, two other files are produced upon program completion.
 MIXOR for Windows Overview MIXOR is a program that provides estimates for mixed-effects ordinal (and binary) regression models. This model can be used for analysis of clustered or longitudinal (i.e., 2-level)
MIXOR for Windows Overview MIXOR is a program that provides estimates for mixed-effects ordinal (and binary) regression models. This model can be used for analysis of clustered or longitudinal (i.e., 2-level)
Quick Start Guide Jacob Stolk PhD Simone Stolk MPH November 2018
 Quick Start Guide Jacob Stolk PhD Simone Stolk MPH November 2018 Contents Introduction... 1 Start DIONE... 2 Load Data... 3 Missing Values... 5 Explore Data... 6 One Variable... 6 Two Variables... 7 All
Quick Start Guide Jacob Stolk PhD Simone Stolk MPH November 2018 Contents Introduction... 1 Start DIONE... 2 Load Data... 3 Missing Values... 5 Explore Data... 6 One Variable... 6 Two Variables... 7 All
Minitab Study Card J ENNIFER L EWIS P RIESTLEY, PH.D.
 Minitab Study Card J ENNIFER L EWIS P RIESTLEY, PH.D. Introduction to Minitab The interface for Minitab is very user-friendly, with a spreadsheet orientation. When you first launch Minitab, you will see
Minitab Study Card J ENNIFER L EWIS P RIESTLEY, PH.D. Introduction to Minitab The interface for Minitab is very user-friendly, with a spreadsheet orientation. When you first launch Minitab, you will see
E-Campus Inferential Statistics - Part 2
 E-Campus Inferential Statistics - Part 2 Group Members: James Jones Question 4-Isthere a significant difference in the mean prices of the stores? New Textbook Prices New Price Descriptives 95% Confidence
E-Campus Inferential Statistics - Part 2 Group Members: James Jones Question 4-Isthere a significant difference in the mean prices of the stores? New Textbook Prices New Price Descriptives 95% Confidence
Introduction. About this Document. What is SPSS. ohow to get SPSS. oopening Data
 Introduction About this Document This manual was written by members of the Statistical Consulting Program as an introduction to SPSS 12.0. It is designed to assist new users in familiarizing themselves
Introduction About this Document This manual was written by members of the Statistical Consulting Program as an introduction to SPSS 12.0. It is designed to assist new users in familiarizing themselves
Bluman & Mayer, Elementary Statistics, A Step by Step Approach, Canadian Edition
 Bluman & Mayer, Elementary Statistics, A Step by Step Approach, Canadian Edition Online Learning Centre Technology Step-by-Step - Minitab Minitab is a statistical software application originally created
Bluman & Mayer, Elementary Statistics, A Step by Step Approach, Canadian Edition Online Learning Centre Technology Step-by-Step - Minitab Minitab is a statistical software application originally created
STATS PAD USER MANUAL
 STATS PAD USER MANUAL For Version 2.0 Manual Version 2.0 1 Table of Contents Basic Navigation! 3 Settings! 7 Entering Data! 7 Sharing Data! 8 Managing Files! 10 Running Tests! 11 Interpreting Output! 11
STATS PAD USER MANUAL For Version 2.0 Manual Version 2.0 1 Table of Contents Basic Navigation! 3 Settings! 7 Entering Data! 7 Sharing Data! 8 Managing Files! 10 Running Tests! 11 Interpreting Output! 11
MIXREG for Windows. Overview
 MIXREG for Windows Overview MIXREG is a program that provides estimates for a mixed-effects regression model (MRM) including autocorrelated errors. This model can be used for analysis of unbalanced longitudinal
MIXREG for Windows Overview MIXREG is a program that provides estimates for a mixed-effects regression model (MRM) including autocorrelated errors. This model can be used for analysis of unbalanced longitudinal
Creating a data file and entering data
 4 Creating a data file and entering data There are a number of stages in the process of setting up a data file and analysing the data. The flow chart shown on the next page outlines the main steps that
4 Creating a data file and entering data There are a number of stages in the process of setting up a data file and analysing the data. The flow chart shown on the next page outlines the main steps that
Product Catalog. AcaStat. Software
 Product Catalog AcaStat Software AcaStat AcaStat is an inexpensive and easy-to-use data analysis tool. Easily create data files or import data from spreadsheets or delimited text files. Run crosstabulations,
Product Catalog AcaStat Software AcaStat AcaStat is an inexpensive and easy-to-use data analysis tool. Easily create data files or import data from spreadsheets or delimited text files. Run crosstabulations,
Predict Outcomes and Reveal Relationships in Categorical Data
 PASW Categories 18 Specifications Predict Outcomes and Reveal Relationships in Categorical Data Unleash the full potential of your data through predictive analysis, statistical learning, perceptual mapping,
PASW Categories 18 Specifications Predict Outcomes and Reveal Relationships in Categorical Data Unleash the full potential of your data through predictive analysis, statistical learning, perceptual mapping,
STAT 311 (3 CREDITS) VARIANCE AND REGRESSION ANALYSIS ELECTIVE: ALL STUDENTS. CONTENT Introduction to Computer application of variance and regression
 STAT 311 (3 CREDITS) VARIANCE AND REGRESSION ANALYSIS ELECTIVE: ALL STUDENTS. CONTENT Introduction to Computer application of variance and regression analysis. Analysis of Variance: one way classification,
STAT 311 (3 CREDITS) VARIANCE AND REGRESSION ANALYSIS ELECTIVE: ALL STUDENTS. CONTENT Introduction to Computer application of variance and regression analysis. Analysis of Variance: one way classification,
Example Using Missing Data 1
 Ronald H. Heck and Lynn N. Tabata 1 Example Using Missing Data 1 Creating the Missing Data Variable (Miss) Here is a data set (achieve subset MANOVAmiss.sav) with the actual missing data on the outcomes.
Ronald H. Heck and Lynn N. Tabata 1 Example Using Missing Data 1 Creating the Missing Data Variable (Miss) Here is a data set (achieve subset MANOVAmiss.sav) with the actual missing data on the outcomes.
Example 5.25: (page 228) Screenshots from JMP. These examples assume post-hoc analysis using a Protected LSD or Protected Welch strategy.
 JMP Output from Chapter 5 Factorial Analysis through JMP Example 5.25: (page 228) Screenshots from JMP. These examples assume post-hoc analysis using a Protected LSD or Protected Welch strategy. Fitting
JMP Output from Chapter 5 Factorial Analysis through JMP Example 5.25: (page 228) Screenshots from JMP. These examples assume post-hoc analysis using a Protected LSD or Protected Welch strategy. Fitting
Both the polynomial must meet and give same value at t=4 and should look like this
 Polymath Regression tutorial on Polynomial fitting of data The following table shows the raw data for experimental tracer concentration from a reactor which you need to fit using Polymath (refer Example
Polymath Regression tutorial on Polynomial fitting of data The following table shows the raw data for experimental tracer concentration from a reactor which you need to fit using Polymath (refer Example
An introduction to SPSS
 An introduction to SPSS To open the SPSS software using U of Iowa Virtual Desktop... Go to https://virtualdesktop.uiowa.edu and choose SPSS 24. Contents NOTE: Save data files in a drive that is accessible
An introduction to SPSS To open the SPSS software using U of Iowa Virtual Desktop... Go to https://virtualdesktop.uiowa.edu and choose SPSS 24. Contents NOTE: Save data files in a drive that is accessible
Minitab 17 commands Prepared by Jeffrey S. Simonoff
 Minitab 17 commands Prepared by Jeffrey S. Simonoff Data entry and manipulation To enter data by hand, click on the Worksheet window, and enter the values in as you would in any spreadsheet. To then save
Minitab 17 commands Prepared by Jeffrey S. Simonoff Data entry and manipulation To enter data by hand, click on the Worksheet window, and enter the values in as you would in any spreadsheet. To then save
Nuts and Bolts Research Methods Symposium
 Organizing Your Data Jenny Holcombe, PhD UT College of Medicine Nuts & Bolts Conference August 16, 3013 Topics to Discuss: Types of Variables Constructing a Variable Code Book Developing Excel Spreadsheets
Organizing Your Data Jenny Holcombe, PhD UT College of Medicine Nuts & Bolts Conference August 16, 3013 Topics to Discuss: Types of Variables Constructing a Variable Code Book Developing Excel Spreadsheets
8. MINITAB COMMANDS WEEK-BY-WEEK
 8. MINITAB COMMANDS WEEK-BY-WEEK In this section of the Study Guide, we give brief information about the Minitab commands that are needed to apply the statistical methods in each week s study. They are
8. MINITAB COMMANDS WEEK-BY-WEEK In this section of the Study Guide, we give brief information about the Minitab commands that are needed to apply the statistical methods in each week s study. They are
Bivariate (Simple) Regression Analysis
 Revised July 2018 Bivariate (Simple) Regression Analysis This set of notes shows how to use Stata to estimate a simple (two-variable) regression equation. It assumes that you have set Stata up on your
Revised July 2018 Bivariate (Simple) Regression Analysis This set of notes shows how to use Stata to estimate a simple (two-variable) regression equation. It assumes that you have set Stata up on your
Introduction to SPSS Faiez Mossa 2 nd Class
 Introduction to SPSS 16.0 Faiez Mossa 2 nd Class 1 Outline Review of Concepts (stats and scales) Data entry (the workspace and labels) By hand Import Excel Running an analysis- frequency, central tendency,
Introduction to SPSS 16.0 Faiez Mossa 2 nd Class 1 Outline Review of Concepts (stats and scales) Data entry (the workspace and labels) By hand Import Excel Running an analysis- frequency, central tendency,
Data Analysis and Solver Plugins for KSpread USER S MANUAL. Tomasz Maliszewski
 Data Analysis and Solver Plugins for KSpread USER S MANUAL Tomasz Maliszewski tmaliszewski@wp.pl Table of Content CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1. ABOUT DATA ANALYSIS PLUGIN... 3 1.3. ABOUT SOLVER PLUGIN...
Data Analysis and Solver Plugins for KSpread USER S MANUAL Tomasz Maliszewski tmaliszewski@wp.pl Table of Content CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1. ABOUT DATA ANALYSIS PLUGIN... 3 1.3. ABOUT SOLVER PLUGIN...
Handling Your Data in SPSS. Columns, and Labels, and Values... Oh My! The Structure of SPSS. You should think about SPSS as having three major parts.
 Handling Your Data in SPSS Columns, and Labels, and Values... Oh My! You might think that simple intuition will guide you to a useful organization of your data. If you follow that path, you might find
Handling Your Data in SPSS Columns, and Labels, and Values... Oh My! You might think that simple intuition will guide you to a useful organization of your data. If you follow that path, you might find
The Solution to the Factorial Analysis of Variance
 The Solution to the Factorial Analysis of Variance As shown in the Excel file, Howell -2, the ANOVA analysis (in the ToolPac) yielded the following table: Anova: Two-Factor With Replication SUMMARYCounting
The Solution to the Factorial Analysis of Variance As shown in the Excel file, Howell -2, the ANOVA analysis (in the ToolPac) yielded the following table: Anova: Two-Factor With Replication SUMMARYCounting
DATA DEFINITION PHASE
 Twoway Analysis of Variance Unlike previous problems in the manual, the present problem involves two independent variables (gender of juror and type of crime committed by defendant). There are two levels
Twoway Analysis of Variance Unlike previous problems in the manual, the present problem involves two independent variables (gender of juror and type of crime committed by defendant). There are two levels
Orientation Assignment for Statistics Software (nothing to hand in) Mary Parker,
 Orientation to MINITAB, Mary Parker, mparker@austincc.edu. Last updated 1/3/10. page 1 of Orientation Assignment for Statistics Software (nothing to hand in) Mary Parker, mparker@austincc.edu When you
Orientation to MINITAB, Mary Parker, mparker@austincc.edu. Last updated 1/3/10. page 1 of Orientation Assignment for Statistics Software (nothing to hand in) Mary Parker, mparker@austincc.edu When you
Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach
 i Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach Computer software help: SPSS SPSS (originally Statistical Package for the Social Sciences ) is a commercial statistical software package with an easy-to-use
i Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach Computer software help: SPSS SPSS (originally Statistical Package for the Social Sciences ) is a commercial statistical software package with an easy-to-use
Introduction to Statistical Analyses in SAS
 Introduction to Statistical Analyses in SAS Programming Workshop Presented by the Applied Statistics Lab Sarah Janse April 5, 2017 1 Introduction Today we will go over some basic statistical analyses in
Introduction to Statistical Analyses in SAS Programming Workshop Presented by the Applied Statistics Lab Sarah Janse April 5, 2017 1 Introduction Today we will go over some basic statistical analyses in
Organizing Your Data. Jenny Holcombe, PhD UT College of Medicine Nuts & Bolts Conference August 16, 3013
 Organizing Your Data Jenny Holcombe, PhD UT College of Medicine Nuts & Bolts Conference August 16, 3013 Learning Objectives Identify Different Types of Variables Appropriately Naming Variables Constructing
Organizing Your Data Jenny Holcombe, PhD UT College of Medicine Nuts & Bolts Conference August 16, 3013 Learning Objectives Identify Different Types of Variables Appropriately Naming Variables Constructing
STATA 13 INTRODUCTION
 STATA 13 INTRODUCTION Catherine McGowan & Elaine Williamson LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE DECEMBER 2013 0 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 Versions of STATA... 1 OPENING STATA... 1 THE STATA
STATA 13 INTRODUCTION Catherine McGowan & Elaine Williamson LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE DECEMBER 2013 0 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 Versions of STATA... 1 OPENING STATA... 1 THE STATA
Fathom Dynamic Data TM Version 2 Specifications
 Data Sources Fathom Dynamic Data TM Version 2 Specifications Use data from one of the many sample documents that come with Fathom. Enter your own data by typing into a case table. Paste data from other
Data Sources Fathom Dynamic Data TM Version 2 Specifications Use data from one of the many sample documents that come with Fathom. Enter your own data by typing into a case table. Paste data from other
Year 10 General Mathematics Unit 2
 Year 11 General Maths Year 10 General Mathematics Unit 2 Bivariate Data Chapter 4 Chapter Four 1 st Edition 2 nd Edition 2013 4A 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 2F (FM) 1,
Year 11 General Maths Year 10 General Mathematics Unit 2 Bivariate Data Chapter 4 Chapter Four 1 st Edition 2 nd Edition 2013 4A 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 2F (FM) 1,
Generalized least squares (GLS) estimates of the level-2 coefficients,
 Contents 1 Conceptual and Statistical Background for Two-Level Models...7 1.1 The general two-level model... 7 1.1.1 Level-1 model... 8 1.1.2 Level-2 model... 8 1.2 Parameter estimation... 9 1.3 Empirical
Contents 1 Conceptual and Statistical Background for Two-Level Models...7 1.1 The general two-level model... 7 1.1.1 Level-1 model... 8 1.1.2 Level-2 model... 8 1.2 Parameter estimation... 9 1.3 Empirical
1. Basic Steps for Data Analysis Data Editor. 2.4.To create a new SPSS file
 1 SPSS Guide 2009 Content 1. Basic Steps for Data Analysis. 3 2. Data Editor. 2.4.To create a new SPSS file 3 4 3. Data Analysis/ Frequencies. 5 4. Recoding the variable into classes.. 5 5. Data Analysis/
1 SPSS Guide 2009 Content 1. Basic Steps for Data Analysis. 3 2. Data Editor. 2.4.To create a new SPSS file 3 4 3. Data Analysis/ Frequencies. 5 4. Recoding the variable into classes.. 5 5. Data Analysis/
Chemical Reaction dataset ( https://stat.wvu.edu/~cjelsema/data/chemicalreaction.txt )
 JMP Output from Chapter 9 Factorial Analysis through JMP Chemical Reaction dataset ( https://stat.wvu.edu/~cjelsema/data/chemicalreaction.txt ) Fitting the Model and checking conditions Analyze > Fit Model
JMP Output from Chapter 9 Factorial Analysis through JMP Chemical Reaction dataset ( https://stat.wvu.edu/~cjelsema/data/chemicalreaction.txt ) Fitting the Model and checking conditions Analyze > Fit Model
Instructions for Using ABCalc James Alan Fox Northeastern University Updated: August 2009
 Instructions for Using ABCalc James Alan Fox Northeastern University Updated: August 2009 Thank you for using ABCalc, a statistical calculator to accompany several introductory statistics texts published
Instructions for Using ABCalc James Alan Fox Northeastern University Updated: August 2009 Thank you for using ABCalc, a statistical calculator to accompany several introductory statistics texts published
CDAA No. 4 - Part Two - Multiple Regression - Initial Data Screening
 CDAA No. 4 - Part Two - Multiple Regression - Initial Data Screening Variables Entered/Removed b Variables Entered GPA in other high school, test, Math test, GPA, High school math GPA a Variables Removed
CDAA No. 4 - Part Two - Multiple Regression - Initial Data Screening Variables Entered/Removed b Variables Entered GPA in other high school, test, Math test, GPA, High school math GPA a Variables Removed
Multivariate Normal Random Numbers
 Multivariate Normal Random Numbers Revised: 10/11/2017 Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Analysis Options... 4 Analysis Summary... 5 Matrix Plot... 6 Save Results... 8 Calculations... 9 Summary This procedure
Multivariate Normal Random Numbers Revised: 10/11/2017 Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Analysis Options... 4 Analysis Summary... 5 Matrix Plot... 6 Save Results... 8 Calculations... 9 Summary This procedure
Statistical Analysis Using SPSS for Windows Getting Started (Ver. 2018/10/30) The numbers of figures in the SPSS_screenshot.pptx are shown in red.
 Statistical Analysis Using SPSS for Windows Getting Started (Ver. 2018/10/30) The numbers of figures in the SPSS_screenshot.pptx are shown in red. 1. How to display English messages from IBM SPSS Statistics
Statistical Analysis Using SPSS for Windows Getting Started (Ver. 2018/10/30) The numbers of figures in the SPSS_screenshot.pptx are shown in red. 1. How to display English messages from IBM SPSS Statistics
MegaStat User s Guide
 MegaStat User s Guide J. B. Orris Butler University Copyright 2015 by J. B. Orris Table of Contents 1. Basic Procedures... 2 Buttons... 4 Data Selection... 5 Entering values... 6 Data Labels... 6 Output...
MegaStat User s Guide J. B. Orris Butler University Copyright 2015 by J. B. Orris Table of Contents 1. Basic Procedures... 2 Buttons... 4 Data Selection... 5 Entering values... 6 Data Labels... 6 Output...
StatCalc User Manual. Version 9 for Mac and Windows. Copyright 2018, AcaStat Software. All rights Reserved.
 StatCalc User Manual Version 9 for Mac and Windows Copyright 2018, AcaStat Software. All rights Reserved. http://www.acastat.com Table of Contents Introduction... 4 Getting Help... 4 Uninstalling StatCalc...
StatCalc User Manual Version 9 for Mac and Windows Copyright 2018, AcaStat Software. All rights Reserved. http://www.acastat.com Table of Contents Introduction... 4 Getting Help... 4 Uninstalling StatCalc...
Source df SS MS F A a-1 [A] [T] SS A. / MS S/A S/A (a)(n-1) [AS] [A] SS S/A. / MS BxS/A A x B (a-1)(b-1) [AB] [A] [B] + [T] SS AxB
![Source df SS MS F A a-1 [A] [T] SS A. / MS S/A S/A (a)(n-1) [AS] [A] SS S/A. / MS BxS/A A x B (a-1)(b-1) [AB] [A] [B] + [T] SS AxB Source df SS MS F A a-1 [A] [T] SS A. / MS S/A S/A (a)(n-1) [AS] [A] SS S/A. / MS BxS/A A x B (a-1)(b-1) [AB] [A] [B] + [T] SS AxB](/thumbs/96/128510119.jpg) Keppel, G. Design and Analysis: Chapter 17: The Mixed Two-Factor Within-Subjects Design: The Overall Analysis and the Analysis of Main Effects and Simple Effects Keppel describes an Ax(BxS) design, which
Keppel, G. Design and Analysis: Chapter 17: The Mixed Two-Factor Within-Subjects Design: The Overall Analysis and the Analysis of Main Effects and Simple Effects Keppel describes an Ax(BxS) design, which
Correctly Compute Complex Samples Statistics
 SPSS Complex Samples 15.0 Specifications Correctly Compute Complex Samples Statistics When you conduct sample surveys, use a statistics package dedicated to producing correct estimates for complex sample
SPSS Complex Samples 15.0 Specifications Correctly Compute Complex Samples Statistics When you conduct sample surveys, use a statistics package dedicated to producing correct estimates for complex sample
Part I, Chapters 4 & 5. Data Tables and Data Analysis Statistics and Figures
 Part I, Chapters 4 & 5 Data Tables and Data Analysis Statistics and Figures Descriptive Statistics 1 Are data points clumped? (order variable / exp. variable) Concentrated around one value? Concentrated
Part I, Chapters 4 & 5 Data Tables and Data Analysis Statistics and Figures Descriptive Statistics 1 Are data points clumped? (order variable / exp. variable) Concentrated around one value? Concentrated
Laboratory for Two-Way ANOVA: Interactions
 Laboratory for Two-Way ANOVA: Interactions For the last lab, we focused on the basics of the Two-Way ANOVA. That is, you learned how to compute a Brown-Forsythe analysis for a Two-Way ANOVA, as well as
Laboratory for Two-Way ANOVA: Interactions For the last lab, we focused on the basics of the Two-Way ANOVA. That is, you learned how to compute a Brown-Forsythe analysis for a Two-Way ANOVA, as well as
Tier III Data Collection
 Tier III Data Collection What is it? The Tier III Data Collection tool is designed to measure progress for individual students before and during interventions. The tool can measure several different types
Tier III Data Collection What is it? The Tier III Data Collection tool is designed to measure progress for individual students before and during interventions. The tool can measure several different types
REALCOM-IMPUTE: multiple imputation using MLwin. Modified September Harvey Goldstein, Centre for Multilevel Modelling, University of Bristol
 REALCOM-IMPUTE: multiple imputation using MLwin. Modified September 2014 by Harvey Goldstein, Centre for Multilevel Modelling, University of Bristol This description is divided into two sections. In the
REALCOM-IMPUTE: multiple imputation using MLwin. Modified September 2014 by Harvey Goldstein, Centre for Multilevel Modelling, University of Bristol This description is divided into two sections. In the
APPENDIX B EXCEL BASICS 1
 APPENDIX B EXCEL BASICS 1 Microsoft Excel is a powerful application for education researchers and students studying educational statistics. Excel worksheets can hold data for a variety of uses and therefore
APPENDIX B EXCEL BASICS 1 Microsoft Excel is a powerful application for education researchers and students studying educational statistics. Excel worksheets can hold data for a variety of uses and therefore
Getting Started with MegaStat
 Getting Started with MegaStat J. B. Orris Butler University Copyright 2005 by J. B. Orris Table of Contents 1. Basic Procedures... 2 Buttons... 3 Data Selection... 3 Data Labels... 5 Output... 5 Repeat
Getting Started with MegaStat J. B. Orris Butler University Copyright 2005 by J. B. Orris Table of Contents 1. Basic Procedures... 2 Buttons... 3 Data Selection... 3 Data Labels... 5 Output... 5 Repeat
Basic concepts and terms
 CHAPTER ONE Basic concepts and terms I. Key concepts Test usefulness Reliability Construct validity Authenticity Interactiveness Impact Practicality Assessment Measurement Test Evaluation Grading/marking
CHAPTER ONE Basic concepts and terms I. Key concepts Test usefulness Reliability Construct validity Authenticity Interactiveness Impact Practicality Assessment Measurement Test Evaluation Grading/marking
2016 SPSS Workshop UBC Research Commons
 " 2016 SPSS Workshop #2 @ UBC Research Commons Part 1: Data Management The Select Cases Command Menu: Data Select Cases 1. Option 1- randomly selecting cases Select Random sample of cases, click on Sample,
" 2016 SPSS Workshop #2 @ UBC Research Commons Part 1: Data Management The Select Cases Command Menu: Data Select Cases 1. Option 1- randomly selecting cases Select Random sample of cases, click on Sample,
JMP Book Descriptions
 JMP Book Descriptions The collection of JMP documentation is available in the JMP Help > Books menu. This document describes each title to help you decide which book to explore. Each book title is linked
JMP Book Descriptions The collection of JMP documentation is available in the JMP Help > Books menu. This document describes each title to help you decide which book to explore. Each book title is linked
How to Make APA Format Tables Using Microsoft Word
 How to Make APA Format Tables Using Microsoft Word 1 I. Tables vs. Figures - See APA Publication Manual p. 147-175 for additional details - Tables consist of words and numbers where spatial relationships
How to Make APA Format Tables Using Microsoft Word 1 I. Tables vs. Figures - See APA Publication Manual p. 147-175 for additional details - Tables consist of words and numbers where spatial relationships
CHAPTER 7 EXAMPLES: MIXTURE MODELING WITH CROSS- SECTIONAL DATA
 Examples: Mixture Modeling With Cross-Sectional Data CHAPTER 7 EXAMPLES: MIXTURE MODELING WITH CROSS- SECTIONAL DATA Mixture modeling refers to modeling with categorical latent variables that represent
Examples: Mixture Modeling With Cross-Sectional Data CHAPTER 7 EXAMPLES: MIXTURE MODELING WITH CROSS- SECTIONAL DATA Mixture modeling refers to modeling with categorical latent variables that represent
Show how the LG-Syntax can be generated from a GUI model. Modify the LG-Equations to specify a different LC regression model
 Tutorial #S1: Getting Started with LG-Syntax DemoData = 'conjoint.sav' This tutorial introduces the use of the LG-Syntax module, an add-on to the Advanced version of Latent GOLD. In this tutorial we utilize
Tutorial #S1: Getting Started with LG-Syntax DemoData = 'conjoint.sav' This tutorial introduces the use of the LG-Syntax module, an add-on to the Advanced version of Latent GOLD. In this tutorial we utilize
MegaStat User s Guide
 MegaStat User s Guide for Mac Excel 2016 Copyright 2017 by J. B. Orris Table of Contents 1. Basic Procedures... 2 Buttons... 4 Data Selection... 5 Entering values... 6 Data Labels... 6 Output... 7 Repeat
MegaStat User s Guide for Mac Excel 2016 Copyright 2017 by J. B. Orris Table of Contents 1. Basic Procedures... 2 Buttons... 4 Data Selection... 5 Entering values... 6 Data Labels... 6 Output... 7 Repeat
Me Learning User Guide
 Royal Borough of Greenwich Me Learning User Guide Last Updated: 3 July 2012 Page 1 of 15 Purpose and Scope This guide will detail how to login and navigate around Me Learning. Click the activity listed
Royal Borough of Greenwich Me Learning User Guide Last Updated: 3 July 2012 Page 1 of 15 Purpose and Scope This guide will detail how to login and navigate around Me Learning. Click the activity listed
Categorical Data in a Designed Experiment Part 2: Sizing with a Binary Response
 Categorical Data in a Designed Experiment Part 2: Sizing with a Binary Response Authored by: Francisco Ortiz, PhD Version 2: 19 July 2018 Revised 18 October 2018 The goal of the STAT COE is to assist in
Categorical Data in a Designed Experiment Part 2: Sizing with a Binary Response Authored by: Francisco Ortiz, PhD Version 2: 19 July 2018 Revised 18 October 2018 The goal of the STAT COE is to assist in
IBM SPSS Categories. Predict outcomes and reveal relationships in categorical data. Highlights. With IBM SPSS Categories you can:
 IBM Software IBM SPSS Statistics 19 IBM SPSS Categories Predict outcomes and reveal relationships in categorical data Highlights With IBM SPSS Categories you can: Visualize and explore complex categorical
IBM Software IBM SPSS Statistics 19 IBM SPSS Categories Predict outcomes and reveal relationships in categorical data Highlights With IBM SPSS Categories you can: Visualize and explore complex categorical
Table of Contents (As covered from textbook)
 Table of Contents (As covered from textbook) Ch 1 Data and Decisions Ch 2 Displaying and Describing Categorical Data Ch 3 Displaying and Describing Quantitative Data Ch 4 Correlation and Linear Regression
Table of Contents (As covered from textbook) Ch 1 Data and Decisions Ch 2 Displaying and Describing Categorical Data Ch 3 Displaying and Describing Quantitative Data Ch 4 Correlation and Linear Regression
Your Name: Section: INTRODUCTION TO STATISTICAL REASONING Computer Lab #4 Scatterplots and Regression
 Your Name: Section: 36-201 INTRODUCTION TO STATISTICAL REASONING Computer Lab #4 Scatterplots and Regression Objectives: 1. To learn how to interpret scatterplots. Specifically you will investigate, using
Your Name: Section: 36-201 INTRODUCTION TO STATISTICAL REASONING Computer Lab #4 Scatterplots and Regression Objectives: 1. To learn how to interpret scatterplots. Specifically you will investigate, using
Table of Contents. Help/Information Help System System Information About MegaStat... 11
 MegaStat User s Guide Windows version Copyright 2017 by J. B. Orris Table of Contents 1. Basic Procedures... 2 Buttons... 4 Data Selection... 5 Entering values... 6 Data Labels... 6 Output... 7 Repeat
MegaStat User s Guide Windows version Copyright 2017 by J. B. Orris Table of Contents 1. Basic Procedures... 2 Buttons... 4 Data Selection... 5 Entering values... 6 Data Labels... 6 Output... 7 Repeat
Tutorial 4 - Data Analysis
 Tutorial 4 - Data Analysis The iatgen internet application cleans and analyzes the data quickly and easily. Users of the R version of the tool are presumed to know how to download and import data into
Tutorial 4 - Data Analysis The iatgen internet application cleans and analyzes the data quickly and easily. Users of the R version of the tool are presumed to know how to download and import data into
Chapter 1: Random Intercept and Random Slope Models
 Chapter 1: Random Intercept and Random Slope Models This chapter is a tutorial which will take you through the basic procedures for specifying a multilevel model in MLwiN, estimating parameters, making
Chapter 1: Random Intercept and Random Slope Models This chapter is a tutorial which will take you through the basic procedures for specifying a multilevel model in MLwiN, estimating parameters, making
SAS Structural Equation Modeling 1.3 for JMP
 SAS Structural Equation Modeling 1.3 for JMP SAS Documentation The correct bibliographic citation for this manual is as follows: SAS Institute Inc. 2012. SAS Structural Equation Modeling 1.3 for JMP. Cary,
SAS Structural Equation Modeling 1.3 for JMP SAS Documentation The correct bibliographic citation for this manual is as follows: SAS Institute Inc. 2012. SAS Structural Equation Modeling 1.3 for JMP. Cary,
Tutorial for Windows and Macintosh SNP Hunting
 Tutorial for Windows and Macintosh SNP Hunting 2010 Gene Codes Corporation Gene Codes Corporation 775 Technology Drive, Ann Arbor, MI 48108 USA 1.800.497.4939 (USA) +1.734.769.7249 (elsewhere) +1.734.769.7074
Tutorial for Windows and Macintosh SNP Hunting 2010 Gene Codes Corporation Gene Codes Corporation 775 Technology Drive, Ann Arbor, MI 48108 USA 1.800.497.4939 (USA) +1.734.769.7249 (elsewhere) +1.734.769.7074
Enter your UID and password. Make sure you have popups allowed for this site.
 Log onto: https://apps.csbs.utah.edu/ Enter your UID and password. Make sure you have popups allowed for this site. You may need to go to preferences (right most tab) and change your client to Java. I
Log onto: https://apps.csbs.utah.edu/ Enter your UID and password. Make sure you have popups allowed for this site. You may need to go to preferences (right most tab) and change your client to Java. I
Step by Step Instructions for Using TestGenerator to Import Test Questions into Moodle
 Step by Step Instructions for Using TestGenerator to Import Test Questions into Moodle 1. Open Test Generator by double clicking on TestGenerator Icon. 2. Choose A Test for the Web option. Choose A Test
Step by Step Instructions for Using TestGenerator to Import Test Questions into Moodle 1. Open Test Generator by double clicking on TestGenerator Icon. 2. Choose A Test for the Web option. Choose A Test
Tests of difference for two sample designs. Bivariate and multiple regression. Analysis of covariance and multivariate analysis of variance
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Chapter 10 Chapter 11 Chapter 12 Chapter 13 Data entry in SPSS Exploring data in SPSS Data handling
Chapter 1 Introduction 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Chapter 10 Chapter 11 Chapter 12 Chapter 13 Data entry in SPSS Exploring data in SPSS Data handling
Conducting a Path Analysis With SPSS/AMOS
 Conducting a Path Analysis With SPSS/AMOS Download the PATH-INGRAM.sav data file from my SPSS data page and then bring it into SPSS. The data are those from the research that led to this publication: Ingram,
Conducting a Path Analysis With SPSS/AMOS Download the PATH-INGRAM.sav data file from my SPSS data page and then bring it into SPSS. The data are those from the research that led to this publication: Ingram,
1 Introduction to Using Excel Spreadsheets
 Survey of Math: Excel Spreadsheet Guide (for Excel 2007) Page 1 of 6 1 Introduction to Using Excel Spreadsheets This section of the guide is based on the file (a faux grade sheet created for messing with)
Survey of Math: Excel Spreadsheet Guide (for Excel 2007) Page 1 of 6 1 Introduction to Using Excel Spreadsheets This section of the guide is based on the file (a faux grade sheet created for messing with)
Correctly Compute Complex Samples Statistics
 PASW Complex Samples 17.0 Specifications Correctly Compute Complex Samples Statistics When you conduct sample surveys, use a statistics package dedicated to producing correct estimates for complex sample
PASW Complex Samples 17.0 Specifications Correctly Compute Complex Samples Statistics When you conduct sample surveys, use a statistics package dedicated to producing correct estimates for complex sample
The Mplus modelling framework
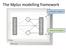 The Mplus modelling framework Continuous variables Categorical variables 1 Mplus syntax structure TITLE: a title for the analysis (not part of the syntax) DATA: (required) information about the data set
The Mplus modelling framework Continuous variables Categorical variables 1 Mplus syntax structure TITLE: a title for the analysis (not part of the syntax) DATA: (required) information about the data set
Opening a Data File in SPSS. Defining Variables in SPSS
 Opening a Data File in SPSS To open an existing SPSS file: 1. Click File Open Data. Go to the appropriate directory and find the name of the appropriate file. SPSS defaults to opening SPSS data files with
Opening a Data File in SPSS To open an existing SPSS file: 1. Click File Open Data. Go to the appropriate directory and find the name of the appropriate file. SPSS defaults to opening SPSS data files with
Using the Design Tool for Inventory & Monitoring (DTIM) Chip Scott October 6, 2009
 Using the Design Tool for Inventory & Monitoring (DTIM) Chip Scott October 6, 2009 The Design Tool for Inventory and Monitoring (DTIM) is an MS Excel spreadsheet that assists you in meeting your inventory
Using the Design Tool for Inventory & Monitoring (DTIM) Chip Scott October 6, 2009 The Design Tool for Inventory and Monitoring (DTIM) is an MS Excel spreadsheet that assists you in meeting your inventory
Using Large Data Sets Workbook Version A (MEI)
 Using Large Data Sets Workbook Version A (MEI) 1 Index Key Skills Page 3 Becoming familiar with the dataset Page 3 Sorting and filtering the dataset Page 4 Producing a table of summary statistics with
Using Large Data Sets Workbook Version A (MEI) 1 Index Key Skills Page 3 Becoming familiar with the dataset Page 3 Sorting and filtering the dataset Page 4 Producing a table of summary statistics with
STATISTICS (STAT) Statistics (STAT) 1
 Statistics (STAT) 1 STATISTICS (STAT) STAT 2013 Elementary Statistics (A) Prerequisites: MATH 1483 or MATH 1513, each with a grade of "C" or better; or an acceptable placement score (see placement.okstate.edu).
Statistics (STAT) 1 STATISTICS (STAT) STAT 2013 Elementary Statistics (A) Prerequisites: MATH 1483 or MATH 1513, each with a grade of "C" or better; or an acceptable placement score (see placement.okstate.edu).
SPSS QM II. SPSS Manual Quantitative methods II (7.5hp) SHORT INSTRUCTIONS BE CAREFUL
 SPSS QM II SHORT INSTRUCTIONS This presentation contains only relatively short instructions on how to perform some statistical analyses in SPSS. Details around a certain function/analysis method not covered
SPSS QM II SHORT INSTRUCTIONS This presentation contains only relatively short instructions on how to perform some statistical analyses in SPSS. Details around a certain function/analysis method not covered
Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach
 i Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach Computer software help: SAS SAS (originally Statistical Analysis Software ) is a commercial statistical software package based on a powerful programming
i Applied Regression Modeling: A Business Approach Computer software help: SAS SAS (originally Statistical Analysis Software ) is a commercial statistical software package based on a powerful programming
Excel Assignment 4: Correlation and Linear Regression (Office 2016 Version)
 Economics 225, Spring 2018, Yang Zhou Excel Assignment 4: Correlation and Linear Regression (Office 2016 Version) 30 Points Total, Submit via ecampus by 8:00 AM on Tuesday, May 1, 2018 Please read all
Economics 225, Spring 2018, Yang Zhou Excel Assignment 4: Correlation and Linear Regression (Office 2016 Version) 30 Points Total, Submit via ecampus by 8:00 AM on Tuesday, May 1, 2018 Please read all
An Introduction to Growth Curve Analysis using Structural Equation Modeling
 An Introduction to Growth Curve Analysis using Structural Equation Modeling James Jaccard New York University 1 Overview Will introduce the basics of growth curve analysis (GCA) and the fundamental questions
An Introduction to Growth Curve Analysis using Structural Equation Modeling James Jaccard New York University 1 Overview Will introduce the basics of growth curve analysis (GCA) and the fundamental questions
The Power and Sample Size Application
 Chapter 72 The Power and Sample Size Application Contents Overview: PSS Application.................................. 6148 SAS Power and Sample Size............................... 6148 Getting Started:
Chapter 72 The Power and Sample Size Application Contents Overview: PSS Application.................................. 6148 SAS Power and Sample Size............................... 6148 Getting Started:
Statistics with a Hemacytometer
 Statistics with a Hemacytometer Overview This exercise incorporates several different statistical analyses. Data gathered from cell counts with a hemacytometer is used to explore frequency distributions
Statistics with a Hemacytometer Overview This exercise incorporates several different statistical analyses. Data gathered from cell counts with a hemacytometer is used to explore frequency distributions
SPSS INSTRUCTION CHAPTER 9
 SPSS INSTRUCTION CHAPTER 9 Chapter 9 does no more than introduce the repeated-measures ANOVA, the MANOVA, and the ANCOVA, and discriminant analysis. But, you can likely envision how complicated it can
SPSS INSTRUCTION CHAPTER 9 Chapter 9 does no more than introduce the repeated-measures ANOVA, the MANOVA, and the ANCOVA, and discriminant analysis. But, you can likely envision how complicated it can
In this tutorial, we show how to implement this approach and how to interpret the results with Tanagra.
 Subject Implementing the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) with TANAGRA. The PCA belongs to the factor analysis approaches. It is used to discover the underlying structure of a set of variables. It reduces
Subject Implementing the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) with TANAGRA. The PCA belongs to the factor analysis approaches. It is used to discover the underlying structure of a set of variables. It reduces
CHAPTER 11 EXAMPLES: MISSING DATA MODELING AND BAYESIAN ANALYSIS
 Examples: Missing Data Modeling And Bayesian Analysis CHAPTER 11 EXAMPLES: MISSING DATA MODELING AND BAYESIAN ANALYSIS Mplus provides estimation of models with missing data using both frequentist and Bayesian
Examples: Missing Data Modeling And Bayesian Analysis CHAPTER 11 EXAMPLES: MISSING DATA MODELING AND BAYESIAN ANALYSIS Mplus provides estimation of models with missing data using both frequentist and Bayesian
Chapter One: Getting Started With IBM SPSS for Windows
 Chapter One: Getting Started With IBM SPSS for Windows Using Windows The Windows start-up screen should look something like Figure 1-1. Several standard desktop icons will always appear on start up. Note
Chapter One: Getting Started With IBM SPSS for Windows Using Windows The Windows start-up screen should look something like Figure 1-1. Several standard desktop icons will always appear on start up. Note
Chapter 3: Data Description Calculate Mean, Median, Mode, Range, Variation, Standard Deviation, Quartiles, standard scores; construct Boxplots.
 MINITAB Guide PREFACE Preface This guide is used as part of the Elementary Statistics class (Course Number 227) offered at Los Angeles Mission College. It is structured to follow the contents of the textbook
MINITAB Guide PREFACE Preface This guide is used as part of the Elementary Statistics class (Course Number 227) offered at Los Angeles Mission College. It is structured to follow the contents of the textbook
4. Descriptive Statistics: Measures of Variability and Central Tendency
 4. Descriptive Statistics: Measures of Variability and Central Tendency Objectives Calculate descriptive for continuous and categorical data Edit output tables Although measures of central tendency and
4. Descriptive Statistics: Measures of Variability and Central Tendency Objectives Calculate descriptive for continuous and categorical data Edit output tables Although measures of central tendency and
Both the polynomial must meet and give same value at t=4 and should look like this
 Polymath Regression tutorial on Polynomial fitting of data The following table shows the raw data for experimental tracer concentration from a reactor which you need to fit using Polymath (refer Example
Polymath Regression tutorial on Polynomial fitting of data The following table shows the raw data for experimental tracer concentration from a reactor which you need to fit using Polymath (refer Example
SPSS for Survey Analysis
 STC: SPSS for Survey Analysis 1 SPSS for Survey Analysis STC: SPSS for Survey Analysis 2 SPSS for Surveys: Contents Background Information... 4 Opening and creating new documents... 5 Starting SPSS...
STC: SPSS for Survey Analysis 1 SPSS for Survey Analysis STC: SPSS for Survey Analysis 2 SPSS for Surveys: Contents Background Information... 4 Opening and creating new documents... 5 Starting SPSS...
Intermediate SAS: Statistics
 Intermediate SAS: Statistics OIT TSS 293-4444 oithelp@mail.wvu.edu oit.wvu.edu/training/classmat/sas/ Table of Contents Procedures... 2 Two-sample t-test:... 2 Paired differences t-test:... 2 Chi Square
Intermediate SAS: Statistics OIT TSS 293-4444 oithelp@mail.wvu.edu oit.wvu.edu/training/classmat/sas/ Table of Contents Procedures... 2 Two-sample t-test:... 2 Paired differences t-test:... 2 Chi Square
JMP 10 Student Edition Quick Guide
 JMP 10 Student Edition Quick Guide Instructions presume an open data table, default preference settings and appropriately typed, user-specified variables of interest. RMC = Click Right Mouse Button Graphing
JMP 10 Student Edition Quick Guide Instructions presume an open data table, default preference settings and appropriately typed, user-specified variables of interest. RMC = Click Right Mouse Button Graphing
If the active datasheet is empty when the StatWizard appears, a dialog box is displayed to assist in entering data.
 StatWizard Summary The StatWizard is designed to serve several functions: 1. It assists new users in entering data to be analyzed. 2. It provides a search facility to help locate desired statistical procedures.
StatWizard Summary The StatWizard is designed to serve several functions: 1. It assists new users in entering data to be analyzed. 2. It provides a search facility to help locate desired statistical procedures.
Introduction to Minitab 1
 Introduction to Minitab 1 We begin by first starting Minitab. You may choose to either 1. click on the Minitab icon in the corner of your screen 2. go to the lower left and hit Start, then from All Programs,
Introduction to Minitab 1 We begin by first starting Minitab. You may choose to either 1. click on the Minitab icon in the corner of your screen 2. go to the lower left and hit Start, then from All Programs,
Page 1. Graphical and Numerical Statistics
 TOPIC: Description Statistics In this tutorial, we show how to use MINITAB to produce descriptive statistics, both graphical and numerical, for an existing MINITAB dataset. The example data come from Exercise
TOPIC: Description Statistics In this tutorial, we show how to use MINITAB to produce descriptive statistics, both graphical and numerical, for an existing MINITAB dataset. The example data come from Exercise
Fathom Tutorial. Dynamic Statistical Software. for teachers of Ontario grades 7-10 mathematics courses
 Fathom Tutorial Dynamic Statistical Software for teachers of Ontario grades 7-10 mathematics courses Please Return This Guide to the Presenter at the End of the Workshop if you would like an electronic
Fathom Tutorial Dynamic Statistical Software for teachers of Ontario grades 7-10 mathematics courses Please Return This Guide to the Presenter at the End of the Workshop if you would like an electronic
6:1 LAB RESULTS -WITHIN-S ANOVA
 6:1 LAB RESULTS -WITHIN-S ANOVA T1/T2/T3/T4. SStotal =(1-12) 2 + + (18-12) 2 = 306.00 = SSpill + SSsubj + SSpxs df = 9-1 = 8 P1 P2 P3 Ms Ms-Mg 1 8 15 8.0-4.0 SSsubj= 3x(-4 2 + ) 4 17 15 12.0 0 = 96.0 13
6:1 LAB RESULTS -WITHIN-S ANOVA T1/T2/T3/T4. SStotal =(1-12) 2 + + (18-12) 2 = 306.00 = SSpill + SSsubj + SSpxs df = 9-1 = 8 P1 P2 P3 Ms Ms-Mg 1 8 15 8.0-4.0 SSsubj= 3x(-4 2 + ) 4 17 15 12.0 0 = 96.0 13
Quick Guide FAST HR. For more resources, including a guide on FAST HR codes, visit # Instructions Screenshot
 Tips & tricks This quick guide describes basic navigation within the FAST HR reporting tool, including how to use filter options, format columns and export reports. For more resources, including a guide
Tips & tricks This quick guide describes basic navigation within the FAST HR reporting tool, including how to use filter options, format columns and export reports. For more resources, including a guide
