Objective A Identify the numerator and the denominator of a fraction. When the numerator is less than the denominator, it is a(n) fraction.
|
|
|
- Bridget Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4. Section 4. Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers Complete the outline as you view Lecture Video 4.. Pause the video as needed to fill in all blanks. Circle your answer to each numbered exercise. Then press Play to continue listening to the video. Objective A Identify the numerator and the denominator of a fraction. We can use to represent part of a whole. The number on top is the. The number on bottom is the. The bar between the numbers is the bar. When the numerator is less than the denominator, it is a(n) fraction. When the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator, it is a(n) fraction. Identify the numerator and denominator of the fraction and determine whether the fraction is proper or improper.. 2 Determine whether the fraction is proper or improper
2 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4. Section 4. Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers Objective B Write a fraction to represent parts of figures or real-life data. Represent the shaded portion of each figure with a fraction or mixed number.. 4. Write, in your own words, the definition of a proper fraction. Write, in your own words, the definition of an improper fraction. A(n) has a whole number part and a fraction part. Answer the questions about the application problem. 5. A bag contains 50 red or blue marbles, If 2 marbles are blue, a) What fraction of the marbles are blue? b) How many marbles are red? c) What fraction of the marbles are red? 49
3 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4. Section 4. Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers Objective C Graph fractions on a number line. Graph the following fractions on a number line Objective D Review division properties for 0 and. Simplify each fraction by dividing Let n be any integer except o, n = n n = n 0 0 n = n is undefined 0 50
4 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4. Section 4. Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers Objective E Write mixed numbers as improper fractions. In your own words, write the definition of a mixed number. Write the steps used to write a mixed number as an improper fraction. Write a Mixed Number as an Improper Fraction Step : Step 2: Step : Write each mixed number as an improper fraction The fraction bar means. 5
5 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4. Section 4. Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers Objective F Write improper fractions as mixed numbers or whole numbers. Write the steps used to write improper fractions as a mixed numbers or whole numbers. Writing an Improper Fraction as a Mixed Number or a Whole Number Step : Step 2: Writing each improper fraction as an equivalent mixed number
6 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.2 Section 4.2 Factors and Simplest Form Complete the outline as you view Lecture Video 4.2. Pause the video as needed as you fill in all blanks. Circle your answer to each numbered exercise. Then press Play to continue listening to the video. Objective A Write a number as a product of prime numbers. A(n) is a natural number greater than whose only factors are and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2,, 5, 7,,, 7, 9, 2, 29, A(n) is a natural number greater than that is not prime. When a composite number is written as a product of prime numbers, this product is called the of the number. There is only one prime factorization for each composite number. Find the prime factorization of the whole number using the branching method.. 48 Find the prime factorization of the whole number using another method
7 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.2 Section 4.2 Factors and Simplest Form Objective B Write a fraction in simplest form. A fraction is in when the numerator and denominator have no common factors other than or. Writing a Fraction in Simplest Form To write a fraction in simplest form, write the of the numerator and the denominator and then both by all common factors. Simplify each fraction. Write in simplest form x 2 6x 5. 40xy 64xyz Objective C Determine whether two fractions are equivalent. Use to determine if two fractions are equal. Determine whether or not each pair of fractions are equivalent fractions. 6. 7? 5 = 8 54
8 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.2 Section 4.2 Factors and Simplest Form Pause and work 7.? 6 = 9 8 Objective D Solve problems by writing fractions in simplest form. Write a fraction in simplest form to represent the fraction in the application problem. 8. The outer wall of the Pentagon is 24 inches wide. Ten inches is concrete, 8 inches is brick, and 6 inches is limestone. What fraction of the wall is concrete? 0 in. 8 in. 6 in. 24 in. 55
9 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4. Section 4. Multiplying and Dividing Fractions Complete the outline as you view Lecture Video 4.. Pause the video as needed as you fill in all blanks. Circle your answer to each numbered exercise. Then press Play to continue listening to the video. Objective A Multiply fractions. Multiplying Fractions To multiply two fractions, multiply the numerators and multiply the denominators. If a, b, c, and d represent numbers, and b and d are not 0, we have a c a i c i =. b d b i d Multiply the fractions. Simplify if possible i i 7 8 Write, in your own words, the process used to multiply fractions. Multiply and simplify.. x y 2 i y x 56
10 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4. Section 4. Multiplying and Dividing Fractions Objective B Evaluate exponential expressions with fractional bases. Evaluate the expression Objective C Divide fractions. Reciprocal of a Fraction Two numbers are of each other if their product is. The reciprocal of the fraction a b is b a because a b a i i = b = b a b i a Give the reciprocal of each number. 5. The reciprocal of 7 2 is because 6. The reciprocal of because 5 6 is 57
11 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4. Section 4. Multiplying and Dividing Fractions 7. The reciprocal of is Dividing Fractions To divide two fractions, multiply the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction. If a, b, c, and d represent numbers and b, c, and d are not 0, then a c a d a i d = i = b d b c b i c reciprocal Divide the fractions In your own words, write the process you will use to divide fractions. Divide. Write the quotient in simplest form. 9. y 20 58
12 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4. Section 4. Multiplying and Dividing Fractions Simplify by multiplying and dividing i 2 6 Objective D Multiply and divide given fractional replacement values. Use the given replacement values to evaluate each expression If x = and y =, 5 Find a) xy and b) x y a) xy b) x y Objective E Solve applications that require multiplication of fractions. Solve the application. 2. The radius of a circle is one-half of its diameter. If the diameter of a circle is 8 of an inch, what is the radius? Remember... of means multiplication 59
13 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.4 Section 4.4 Adding and Subtracting Like Fractions, Least Common Denominator, and Equivalent Fractions Complete the outline as you view Lecture Video 4.4. Pause the video as needed as you fill in all blanks. Circle your answer to each numbered exercise. Then press Play to continue listening to the video. Objective A Add or subtract like fractions. Adding or Subtracting Like Fractions (Fractions with the Same Denominator) If a, b, and c are numbers and b is not 0, then a c a+ c + = and b b b also a c a c = b b b In other words, to add or subtract fractions with the same denominator, add or subtract their numerators and write the sum or difference over the common denominator. Add or Subtract In general the following is true: a a a = = as long as b is not 0 b b b Remember... numerator + numerator denominator 60
14 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.4 Section 4.4 Adding and Subtracting Like Fractions, Least Common Denominator, and Equivalent Fractions. 6 7x 5x Subtract. Give the answer in simplest form Objective B Add or subtract given fractional replacement values. 6. Evaluate x yif x = and 5 y = 5 x y = Objective C Solve problems by adding or subtracting like fractions. means distance around. 7. Find the perimeter 5 2 meters 7 2 meters 6
15 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.4 Section 4.4 Adding and Subtracting Like Fractions, Least Common Denominator, and Equivalent Fractions Objective D Find the least common denominator of a list of fractions. The (LCD) of a list of fractions is the smallest positive number divisible by all the denominators in the list. (The least common denominator is also the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators. Write the steps used to find the least common denominator of a list of fractions when using Method. Method : Finding the LCD of a List of fractions Using Multiples of the Largest Number. Step : Step 2: Use Method to find the LCD of the fractions , 9 5 Write the steps used to find the least common denominator when using Method 2. Method 2: Finding the LCD of a list of denominators using prime factorization. Step : Step 2: Step : 62
16 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.4 Section 4.4 Adding and Subtracting Like Fractions, Least Common Denominator, and Equivalent Fractions Use Method 2 to find the least common denominator (LCD) of the fractions ,, 2 56 Objective E Write equivalent fractions. have the same value. Write an equivalent fraction to the first fraction that has the given denominator =. 2 2y = = 9 6a 6
17 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.5 Section 4.5 Adding and Subtracting Unlike Fractions Complete the outline as you view Lecture Video 4.5. Pause the video as needed as you fill in all blanks. Circle your answer to each numbered exercise. Then press Play to continue listening to the video. Objective A Add or subtract unlike fractions. Write the steps used to add or subtract unlike fractions. Adding or Subtracting Unlike Fractions Step : Step 2: Step : Step 4: Add or subtract the fractions y
18 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.5 Section 4.5 Adding and Subtracting Unlike Fractions Objective B Write fractions in order. Insert < or > to form a true statement Objective C Evaluate expressions given fractional replacement values. 6. Evaluate 2 y + x if x = and y = 4. Remember how to Multiply Fractions: numerator i numerator denominator i denominator Objective D Solve problems by adding or subtracting unlike fractions. Remember... Perimeter means distance around. Find the perimeter of the parallelogram cm cm cm 4 5 cm 65
19 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.6 Section 4.6 Complex Fractions and Review of Order of Operations Complete the outline as you view Lecture Video 4.6. Pause the video as needed as you fill in all blanks. Circle your answer to each numbered exercise. Then press Play to continue listening to the video. Objective A Simplify complex fractions. A fraction whose numerator or denominator or both of these contain fractions is called a. Method for Simplifying Complex Fractions The first method makes use of the fact that a fraction bar means division. Simplify the complex fraction using Method To divide fractions: The first fraction times the of the second fraction. To multiply fractions: numerator times over denominator times. Method 2 for Simplifying Complex Fractions The second method for simplifying complex fractions is to multiply the numerator and the denominator of the complex fraction by the of all the fractions in its numerator and its denominator. Use Method 2 to simplify the complex fraction. 2. x
20 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.6 Section 4.6 Complex Fractions and Review of Order of Operations Objective B Review the order of operations. Write the steps in order of the order of operations Step : Order of Operations Step 2: Step : Step 4: Using the order of operations, simplify the expression Objective C Evaluate expressions given replacement values. 2 x 4. Evaluate if x =, yz y = 2 5, and z =
21 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.7 Section 4.7 Operations on Mixed Numbers Complete the outline as you view Lecture Video 4.7. Pause the video as needed as you fill in all blanks. Circle your answer to each numbered exercise. Then press Play to continue listening to the video. Objective A Graph positive and negative fractions and mixed numbers.. Graph the following numbers on the number line: 4,,, 4, Objective B Multiply or divide mixed or whole numbers. Multiplying or Dividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers or Whole Numbers To multiply or divide with mixed numbers or whole numbers, first write any mixed or whole numbers as improper fractions and then multiply or divide as usual. Multiply. Write the final answer as a mixed number i 2 Divide. Write the final answer as a mixed number
22 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.7 Section 4.7 Operations on Mixed Numbers Objective C Add or subtract mixed numbers. Adding or Subtracting Mixed Numbers To add or subtract mixed numbers, add or subtract the fraction parts and then add or subtract the whole number parts. Add Objective D Solve problems containing mixed numbers. Solve the application problem. 5. If Tucson s average rainfall is the average does Tucson get than Yuma? 4 inches and Yuma s is 5 inches, how much more rain, on Objective E Perform operations on negative mixed numbers. Add the mixed numbers Remember... To add numbers with unlike signs, subtract absolute values. The answer has the same sign as the number with the larger absolute value. 69
23 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.8 Section 4.8 Solving Equations Containing Fractions Complete the outline as you view Lecture Video 4.8. Pause the video as needed as you fill in all blanks. Circle your answer to each numbered exercise. Then press Play to continue listening to the video. Objective A Solve equations containing fractions. Equation: expression = expression Solve the equations using the properties of equality.. x 5 = 2 6 To check, replace the variable (in the original equation) with the proposed solution and see that a true statement results z =
24 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.8 Section 4.8 Solving Equations Containing Fractions Objective B Solve equations by multiplying by the LCD. Write the steps used to solve an equation in x. Solving an Equation in x Step : Step 2: Step : Step 4: Step 5: Step 6: Solve the equations x = 6 4 x x =
25 Prealgebra Seventh Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 4.8 Section 4.8 Solving Equations Containing Fractions Objective C Review adding and subtracting fractions. Add the fractions. 5. x x
What is a Fraction? Fractions. One Way To Remember Numerator = North / 16. Example. What Fraction is Shaded? 9/16/16. Fraction = Part of a Whole
 // Fractions Pages What is a Fraction? Fraction Part of a Whole Top Number? Bottom Number? Page Numerator tells how many parts you have Denominator tells how many parts are in the whole Note: the fraction
// Fractions Pages What is a Fraction? Fraction Part of a Whole Top Number? Bottom Number? Page Numerator tells how many parts you have Denominator tells how many parts are in the whole Note: the fraction
Section 2.3 Rational Numbers. A rational number is a number that may be written in the form a b. for any integer a and any nonzero integer b.
 Section 2.3 Rational Numbers A rational number is a number that may be written in the form a b for any integer a and any nonzero integer b. Why is division by zero undefined? For example, we know that
Section 2.3 Rational Numbers A rational number is a number that may be written in the form a b for any integer a and any nonzero integer b. Why is division by zero undefined? For example, we know that
3.1 Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts. 3.1 Dividing a Set into Fractional Parts. 3.2 Identifying Parts of Wholes.
 . Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts Fraction: represents a part of a whole object or unit Numerator: (top number) represents number of parts of the whole Denominator: (bottom number) represents how
. Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts Fraction: represents a part of a whole object or unit Numerator: (top number) represents number of parts of the whole Denominator: (bottom number) represents how
Rational number operations can often be simplified by converting mixed numbers to improper fractions Add EXAMPLE:
 Rational number operations can often be simplified by converting mixed numbers to improper fractions Add ( 2) EXAMPLE: 2 Multiply 1 Negative fractions can be written with the negative number in the numerator
Rational number operations can often be simplified by converting mixed numbers to improper fractions Add ( 2) EXAMPLE: 2 Multiply 1 Negative fractions can be written with the negative number in the numerator
Instructional. Essential Standards. Materials. Envision Topic 1 1-1; 1-2; 1-3; 1-4. Envision Topic 2 2-2; 2-3. Envision Topic 2 2-4; 2-5; 2-6
 Time Frame Period 1 Dates: Sept.4 Oct.26 Big Idea/Topic Essential Standards NS1.1 Estimate, round, and manipulate very large and very small numbers. Materials Envision Topic 1 1-1; 1-2; 1-3; 1-4 Envision
Time Frame Period 1 Dates: Sept.4 Oct.26 Big Idea/Topic Essential Standards NS1.1 Estimate, round, and manipulate very large and very small numbers. Materials Envision Topic 1 1-1; 1-2; 1-3; 1-4 Envision
ADDING AND SUBTRACTING RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS
 ADDING AND SUBTRACTING RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS To Add or Subtract Two Fractions, 0, 0 Example 1 a) Add b) Subtract a) b) The same principles apply when adding or subtracting rational expressions containing
ADDING AND SUBTRACTING RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS To Add or Subtract Two Fractions, 0, 0 Example 1 a) Add b) Subtract a) b) The same principles apply when adding or subtracting rational expressions containing
50 MATHCOUNTS LECTURES (6) OPERATIONS WITH DECIMALS
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE 1. Decimal representation: A decimal is used to represent a portion of whole. It contains three parts: an integer (which indicates the number of wholes), a decimal point (which separates
BASIC KNOWLEDGE 1. Decimal representation: A decimal is used to represent a portion of whole. It contains three parts: an integer (which indicates the number of wholes), a decimal point (which separates
Algebra2go: Working with Fractions and Mixed Numbers
 Algebrago: Working with Fractions and Mixed Numbers Algebrago Review of Fractions. Understand Fractions on a Number Line Fractions are used to represent quantities between the whole numbers on a number
Algebrago: Working with Fractions and Mixed Numbers Algebrago Review of Fractions. Understand Fractions on a Number Line Fractions are used to represent quantities between the whole numbers on a number
HOW TO DIVIDE: MCC6.NS.2 Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE
 MCC6.NS. Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE Dividend A number that is divided by another number. Divisor A number by which another number
MCC6.NS. Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE Dividend A number that is divided by another number. Divisor A number by which another number
 - 0.8.00-0.8. 7 ANSWERS: ) : ) : ) : ) : 8 RATIO WORD PROBLEM EXAMPLES: Ratio Compares two amounts or values; they can be written in ways. As a fraction With a colon : With words to A classroom has girls
- 0.8.00-0.8. 7 ANSWERS: ) : ) : ) : ) : 8 RATIO WORD PROBLEM EXAMPLES: Ratio Compares two amounts or values; they can be written in ways. As a fraction With a colon : With words to A classroom has girls
Integers are whole numbers; they include negative whole numbers and zero. For example -7, 0, 18 are integers, 1.5 is not.
 What is an INTEGER/NONINTEGER? Integers are whole numbers; they include negative whole numbers and zero. For example -7, 0, 18 are integers, 1.5 is not. What is a REAL/IMAGINARY number? A real number is
What is an INTEGER/NONINTEGER? Integers are whole numbers; they include negative whole numbers and zero. For example -7, 0, 18 are integers, 1.5 is not. What is a REAL/IMAGINARY number? A real number is
FUNDAMENTAL ARITHMETIC
 FUNDAMENTAL ARITHMETIC Prime Numbers Prime numbers are any whole numbers greater than that can only be divided by and itself. Below is the list of all prime numbers between and 00: Prime Factorization
FUNDAMENTAL ARITHMETIC Prime Numbers Prime numbers are any whole numbers greater than that can only be divided by and itself. Below is the list of all prime numbers between and 00: Prime Factorization
6 th Grade Math Reference Sheet
 6 th Grade Math Reference Sheet Data Analysis, Statistics, and Probability DATA ANALYSIS DSP 1 GRAPHS DSP 2 PROBABILITY DSP 3 Mean: Average Median: 1 middle number or average of 2 middle number Mode: Most
6 th Grade Math Reference Sheet Data Analysis, Statistics, and Probability DATA ANALYSIS DSP 1 GRAPHS DSP 2 PROBABILITY DSP 3 Mean: Average Median: 1 middle number or average of 2 middle number Mode: Most
6.2 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
 8 CHAPTER 6 Rational Epressions Simplify. Assume that no denominator is 0. 99. p - - p 00. + q n q n + n + k - 9 0. n 0. - 6 + k Perform the indicated operation. Write all answers in lowest terms. 0. 0.
8 CHAPTER 6 Rational Epressions Simplify. Assume that no denominator is 0. 99. p - - p 00. + q n q n + n + k - 9 0. n 0. - 6 + k Perform the indicated operation. Write all answers in lowest terms. 0. 0.
Mini-Lesson 1. Section 1.1: Order of Operations PEMDAS
 Name: Date: 1 Section 1.1: Order of Operations PEMDAS If we are working with a mathematical expression that contains more than one operation, then we need to understand how to simplify. The acronym PEMDAS
Name: Date: 1 Section 1.1: Order of Operations PEMDAS If we are working with a mathematical expression that contains more than one operation, then we need to understand how to simplify. The acronym PEMDAS
Mathematics 700 Unit Lesson Title Lesson Objectives 1 - INTEGERS Represent positive and negative values. Locate integers on the number line.
 Mathematics 700 Unit Lesson Title Lesson Objectives 1 - INTEGERS Integers on the Number Line Comparing and Ordering Integers Absolute Value Adding Integers with the Same Sign Adding Integers with Different
Mathematics 700 Unit Lesson Title Lesson Objectives 1 - INTEGERS Integers on the Number Line Comparing and Ordering Integers Absolute Value Adding Integers with the Same Sign Adding Integers with Different
Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
 Page 1 of 14 Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Attendance Problems. Simplify each expression. Assume all variables are nonzero. x 6 y 2 1. x 5 x 2 2. y 3 y 3 3. 4. x 2 y 5 Factor each expression.
Page 1 of 14 Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Attendance Problems. Simplify each expression. Assume all variables are nonzero. x 6 y 2 1. x 5 x 2 2. y 3 y 3 3. 4. x 2 y 5 Factor each expression.
Lesson 1: Arithmetic Review
 In this lesson we step back and review several key arithmetic topics that are extremely relevant to this course. Before we work with algebraic expressions and equations, it is important to have a good
In this lesson we step back and review several key arithmetic topics that are extremely relevant to this course. Before we work with algebraic expressions and equations, it is important to have a good
Lesson 1: Arithmetic Review
 Lesson 1: Arithmetic Review Topics and Objectives: Order of Operations Fractions o Improper fractions and mixed numbers o Equivalent fractions o Fractions in simplest form o One and zero Operations on
Lesson 1: Arithmetic Review Topics and Objectives: Order of Operations Fractions o Improper fractions and mixed numbers o Equivalent fractions o Fractions in simplest form o One and zero Operations on
Summer Packet 7 th into 8 th grade. Name. Integer Operations = 2. (-7)(6)(-4) = = = = 6.
 Integer Operations Name Adding Integers If the signs are the same, add the numbers and keep the sign. 7 + 9 = 16 - + -6 = -8 If the signs are different, find the difference between the numbers and keep
Integer Operations Name Adding Integers If the signs are the same, add the numbers and keep the sign. 7 + 9 = 16 - + -6 = -8 If the signs are different, find the difference between the numbers and keep
Name: Date: Review Packet: Unit 1 The Number System
 Name: Date: Math 7 Ms. Conway Review Packet: Unit 1 The Number System Key Concepts Module 1: Adding and Subtracting Integers 7.NS.1, 7.NS.1a, 7.NS.1b, 7.NS.1c, 7.NS.1d, 7.NS.3, 7.EE.3 To add integers with
Name: Date: Math 7 Ms. Conway Review Packet: Unit 1 The Number System Key Concepts Module 1: Adding and Subtracting Integers 7.NS.1, 7.NS.1a, 7.NS.1b, 7.NS.1c, 7.NS.1d, 7.NS.3, 7.EE.3 To add integers with
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS. Date: Lesson: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers
 Chapter 3: Portions and Integers CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
Chapter 3: Portions and Integers CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
The Bracket Strategy
 The Bracket Strategy This strategy will show students how common denominators are actually found. This strategy should be done with fraction bars. Step Create a bracket X Step Fill in the bracket with
The Bracket Strategy This strategy will show students how common denominators are actually found. This strategy should be done with fraction bars. Step Create a bracket X Step Fill in the bracket with
Number/Computation. addend Any number being added. digit Any one of the ten symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9
 14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
A) Decimal Notation and Writing Decimals in Words. ecim B) Writing Decimals in Standard Form.
 5.1 Introduction to Decimals A) Decimal Notation and Writing Decimals in Words. Decimals The Place Value System for Decimal Numbers Tens/ ones/ decimal point/ tenths/ hundredths/ thousandths/ ten-thousandths
5.1 Introduction to Decimals A) Decimal Notation and Writing Decimals in Words. Decimals The Place Value System for Decimal Numbers Tens/ ones/ decimal point/ tenths/ hundredths/ thousandths/ ten-thousandths
Fraction to Percents Change the fraction to a decimal (see above) and then change the decimal to a percent (see above).
 PEMDAS This is an acronym for the order of operations. Order of operations is the order in which you complete problems with more than one operation. o P parenthesis o E exponents o M multiplication OR
PEMDAS This is an acronym for the order of operations. Order of operations is the order in which you complete problems with more than one operation. o P parenthesis o E exponents o M multiplication OR
Introduction to Fractions
 Introduction to Fractions Fractions represent parts of a whole. The top part of a fraction is called the numerator, while the bottom part of a fraction is called the denominator. The denominator states
Introduction to Fractions Fractions represent parts of a whole. The top part of a fraction is called the numerator, while the bottom part of a fraction is called the denominator. The denominator states
Mini-Lectures by Section
 Mini-Lectures by Section BEGINNING AND INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA, Mini-Lecture 1.1 1. Learn the definition of factor.. Write fractions in lowest terms.. Multiply and divide fractions.. Add and subtract fractions..
Mini-Lectures by Section BEGINNING AND INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA, Mini-Lecture 1.1 1. Learn the definition of factor.. Write fractions in lowest terms.. Multiply and divide fractions.. Add and subtract fractions..
A triangle that has three acute angles Example:
 1. acute angle : An angle that measures less than a right angle (90 ). 2. acute triangle : A triangle that has three acute angles 3. angle : A figure formed by two rays that meet at a common endpoint 4.
1. acute angle : An angle that measures less than a right angle (90 ). 2. acute triangle : A triangle that has three acute angles 3. angle : A figure formed by two rays that meet at a common endpoint 4.
6th Grade Arithmetic (with QuickTables)
 6th Grade Arithmetic (with QuickTables) This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence
6th Grade Arithmetic (with QuickTables) This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence
CW Middle School. Math RtI 7 A. 4 Pro cient I can add and subtract positive fractions with unlike denominators and simplify the result.
 1. Foundations (14.29%) 1.1 I can add and subtract positive fractions with unlike denominators and simplify the result. 4 Pro cient I can add and subtract positive fractions with unlike denominators and
1. Foundations (14.29%) 1.1 I can add and subtract positive fractions with unlike denominators and simplify the result. 4 Pro cient I can add and subtract positive fractions with unlike denominators and
Unit 1 Integers, Fractions & Order of Operations
 Unit 1 Integers, Fractions & Order of Operations In this unit I will learn Date: I have finished this work! I can do this on the test! Operations with positive and negative numbers The order of operations
Unit 1 Integers, Fractions & Order of Operations In this unit I will learn Date: I have finished this work! I can do this on the test! Operations with positive and negative numbers The order of operations
Number- Algebra. Problem solving Statistics Investigations
 Place Value Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division Fractions Position and Direction Decimals Percentages Algebra Converting units Perimeter, Area and Volume Ratio Properties of Shapes Problem
Place Value Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division Fractions Position and Direction Decimals Percentages Algebra Converting units Perimeter, Area and Volume Ratio Properties of Shapes Problem
absolute value- the absolute value of a number is the distance between that number and 0 on a number line. Absolute value is shown 7 = 7-16 = 16
 Grade Six MATH GLOSSARY absolute value- the absolute value of a number is the distance between that number and 0 on a number line. Absolute value is shown 7 = 7-16 = 16 abundant number: A number whose
Grade Six MATH GLOSSARY absolute value- the absolute value of a number is the distance between that number and 0 on a number line. Absolute value is shown 7 = 7-16 = 16 abundant number: A number whose
Section 1.2 Fractions
 Objectives Section 1.2 Fractions Factor and prime factor natural numbers Recognize special fraction forms Multiply and divide fractions Build equivalent fractions Simplify fractions Add and subtract fractions
Objectives Section 1.2 Fractions Factor and prime factor natural numbers Recognize special fraction forms Multiply and divide fractions Build equivalent fractions Simplify fractions Add and subtract fractions
Rational Numbers CHAPTER Introduction
 RATIONAL NUMBERS Rational Numbers CHAPTER. Introduction In Mathematics, we frequently come across simple equations to be solved. For example, the equation x + () is solved when x, because this value of
RATIONAL NUMBERS Rational Numbers CHAPTER. Introduction In Mathematics, we frequently come across simple equations to be solved. For example, the equation x + () is solved when x, because this value of
Summer Assignment Glossary
 Algebra 1.1 Summer Assignment Name: Date: Hour: Directions: Show all work for full credit using a pencil. Circle your final answer. This assignment is due the first day of school. Use the summer assignment
Algebra 1.1 Summer Assignment Name: Date: Hour: Directions: Show all work for full credit using a pencil. Circle your final answer. This assignment is due the first day of school. Use the summer assignment
Integer Operations. Summer Packet 7 th into 8 th grade 1. Name = = = = = 6.
 Summer Packet 7 th into 8 th grade 1 Integer Operations Name Adding Integers If the signs are the same, add the numbers and keep the sign. 7 + 9 = 16-2 + -6 = -8 If the signs are different, find the difference
Summer Packet 7 th into 8 th grade 1 Integer Operations Name Adding Integers If the signs are the same, add the numbers and keep the sign. 7 + 9 = 16-2 + -6 = -8 If the signs are different, find the difference
For Module 2 SKILLS CHECKLIST. Fraction Notation. George Hartas, MS. Educational Assistant for Mathematics Remediation MAT 025 Instructor
 Last Updated: // SKILLS CHECKLIST For Module Fraction Notation By George Hartas, MS Educational Assistant for Mathematics Remediation MAT 0 Instructor Assignment, Section. Divisibility SKILL: Determine
Last Updated: // SKILLS CHECKLIST For Module Fraction Notation By George Hartas, MS Educational Assistant for Mathematics Remediation MAT 0 Instructor Assignment, Section. Divisibility SKILL: Determine
Algebra II Chapter 8 Part 2: Rational Functions
 Algebra II Chapter 8 Part 2: Rational Functions Chapter 8 Lesson 4 Multiply and Divide Rational Functions Vocabulary Words to Review: Reciprocal The rules of fractions DO NOT change! *When adding and subtracting,
Algebra II Chapter 8 Part 2: Rational Functions Chapter 8 Lesson 4 Multiply and Divide Rational Functions Vocabulary Words to Review: Reciprocal The rules of fractions DO NOT change! *When adding and subtracting,
Math 085 Final Exam Review
 Math 08 Final Exam Review Objective : Use the rules of signed number arithmetic to perform operations on integers. These operations include, but are not limited to, addition, subtraction, multiplication,
Math 08 Final Exam Review Objective : Use the rules of signed number arithmetic to perform operations on integers. These operations include, but are not limited to, addition, subtraction, multiplication,
Rational Number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 10.
 PA Ch 5 Rational Expressions Rational Number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 0. Since decimals are special
PA Ch 5 Rational Expressions Rational Number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 0. Since decimals are special
8 th Grade Math Reference Sheet
 8 th Grade Math Reference Sheet Number Sense DECIMALS NS 1 To change a DECIMAL FRACTION, use the place value of the decimal as the denominator of the fraction; simplify if. 1. Line up decimal points 2.
8 th Grade Math Reference Sheet Number Sense DECIMALS NS 1 To change a DECIMAL FRACTION, use the place value of the decimal as the denominator of the fraction; simplify if. 1. Line up decimal points 2.
Course Outlines. Elementary Mathematics (Grades K-5) Kids and Numbers (Recommended for K-1 students)
 Course Outlines Elementary Mathematics (Grades K-5) Kids and Numbers (Recommended for K-1 students) Shapes and Patterns. Grouping objects by similar properties. Identifying simple figures within a complex
Course Outlines Elementary Mathematics (Grades K-5) Kids and Numbers (Recommended for K-1 students) Shapes and Patterns. Grouping objects by similar properties. Identifying simple figures within a complex
Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
 Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Warm Up Simplify each expression. Assume all variables are nonzero. 1. x 5 x 2 3. x 6 x 2 x 7 Factor each expression. 2. y 3 y 3 y 6 x 4 4. y 2 1 y 5 y 3 5.
Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Warm Up Simplify each expression. Assume all variables are nonzero. 1. x 5 x 2 3. x 6 x 2 x 7 Factor each expression. 2. y 3 y 3 y 6 x 4 4. y 2 1 y 5 y 3 5.
( 3) ( 4 ) 1. Exponents and Radicals ( ) ( xy) 1. MATH 102 College Algebra. still holds when m = n, we are led to the result
 Exponents and Radicals ZERO & NEGATIVE EXPONENTS If we assume that the relation still holds when m = n, we are led to the result m m a m n 0 a = a = a. Consequently, = 1, a 0 n n a a a 0 = 1, a 0. Then
Exponents and Radicals ZERO & NEGATIVE EXPONENTS If we assume that the relation still holds when m = n, we are led to the result m m a m n 0 a = a = a. Consequently, = 1, a 0 n n a a a 0 = 1, a 0. Then
Reteaching. Comparing and Ordering Integers
 - Comparing and Ordering Integers The numbers and - are opposites. The numbers 7 and -7 are opposites. Integers are the set of positive whole numbers, their opposites, and zero. 7 6 4 0 negative zero You
- Comparing and Ordering Integers The numbers and - are opposites. The numbers 7 and -7 are opposites. Integers are the set of positive whole numbers, their opposites, and zero. 7 6 4 0 negative zero You
Grade 6 Math Curriculum Sequence School Year
 Grade 6 Math Curriculum Sequence School Year 2010-2011 QUARTER 1 (Aug 30 Nov 5) 45 days BENCHMARK A (same skills as June Benchmark in previous grade) UNIT 1: Fractions 1 Review Add and Subtract Fractions
Grade 6 Math Curriculum Sequence School Year 2010-2011 QUARTER 1 (Aug 30 Nov 5) 45 days BENCHMARK A (same skills as June Benchmark in previous grade) UNIT 1: Fractions 1 Review Add and Subtract Fractions
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit Five: Rational Numbers and Equations
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit Five: Rational Numbers and Equations Rational Numbers Rational numbers are numbers that can be written as a quotient of two integers. Since decimals are special fractions, all the
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit Five: Rational Numbers and Equations Rational Numbers Rational numbers are numbers that can be written as a quotient of two integers. Since decimals are special fractions, all the
Gateway Regional School District VERTICAL ALIGNMENT OF MATHEMATICS STANDARDS Grades 3-6
 NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS 3.N.1 Exhibit an understanding of the values of the digits in the base ten number system by reading, modeling, writing, comparing, and ordering whole numbers through 9,999. Our
NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS 3.N.1 Exhibit an understanding of the values of the digits in the base ten number system by reading, modeling, writing, comparing, and ordering whole numbers through 9,999. Our
Math Glossary Numbers and Arithmetic
 Math Glossary Numbers and Arithmetic Version 0.1.1 September 1, 200 Next release: On or before September 0, 200. E-mail edu@ezlink.com for the latest version. Copyright 200 by Brad Jolly All Rights Reserved
Math Glossary Numbers and Arithmetic Version 0.1.1 September 1, 200 Next release: On or before September 0, 200. E-mail edu@ezlink.com for the latest version. Copyright 200 by Brad Jolly All Rights Reserved
Accuplacer Arithmetic Study Guide
 Accuplacer Arithmetic Study Guide I. Terms Numerator: which tells how many parts you have (the number on top) Denominator: which tells how many parts in the whole (the number on the bottom) Example: parts
Accuplacer Arithmetic Study Guide I. Terms Numerator: which tells how many parts you have (the number on top) Denominator: which tells how many parts in the whole (the number on the bottom) Example: parts
Decimals. Chapter Five
 Chapter Five Decimals 5.1 Introductions to Decimals 5.2 Adding & Subtracting Decimals 5.3 Multiplying Decimals & Circumference of a Circle 5.4 Dividing Decimals 5.5 Fractions, Decimals, & Order of Operations
Chapter Five Decimals 5.1 Introductions to Decimals 5.2 Adding & Subtracting Decimals 5.3 Multiplying Decimals & Circumference of a Circle 5.4 Dividing Decimals 5.5 Fractions, Decimals, & Order of Operations
Mathematics LV 5 (with QuickTables)
 Mathematics LV 5 (with QuickTables) This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence
Mathematics LV 5 (with QuickTables) This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence
COMPETENCY 1.0 UNDERSTAND THE STRUCTURE OF THE BASE TEN NUMERATION SYSTEM AND NUMBER THEORY
 SUBAREA I. NUMBERS AND OPERATIONS COMPETENCY.0 UNDERSTAND THE STRUCTURE OF THE BASE TEN NUMERATION SYSTEM AND NUMBER THEORY Skill. Analyze the structure of the base ten number system (e.g., decimal and
SUBAREA I. NUMBERS AND OPERATIONS COMPETENCY.0 UNDERSTAND THE STRUCTURE OF THE BASE TEN NUMERATION SYSTEM AND NUMBER THEORY Skill. Analyze the structure of the base ten number system (e.g., decimal and
Grade 4 Fractions. Answer the questions. For more such worksheets visit (1) Convert into a mixed fraction. (2) Convert
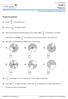 ID : aefractions [1] Grade Fractions For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Convert 63 13 (2) Convert 6 7 12 into a mixed fraction. to improper fraction. (3) Aleser had
ID : aefractions [1] Grade Fractions For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Convert 63 13 (2) Convert 6 7 12 into a mixed fraction. to improper fraction. (3) Aleser had
1-3 Multiplying and Dividing Real Numbers
 Multiplying and Dividing 1-3 Multiplying and Dividing Real Numbers Real Numbers Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 1 2 pts Bell Quiz 1-3 Add or Subtract 1. 3 8 2 pts 2. - 8 + 12 2 pts 3. 4 (-4) 2
Multiplying and Dividing 1-3 Multiplying and Dividing Real Numbers Real Numbers Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 1 2 pts Bell Quiz 1-3 Add or Subtract 1. 3 8 2 pts 2. - 8 + 12 2 pts 3. 4 (-4) 2
Number Mulitplication and Number and Place Value Addition and Subtraction Division
 Number Mulitplication and Number and Place Value Addition and Subtraction Division read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10 000 000 and determine the value of each digit round any whole number to
Number Mulitplication and Number and Place Value Addition and Subtraction Division read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10 000 000 and determine the value of each digit round any whole number to
Mathematics LV 4 (with QuickTables)
 Mathematics LV 4 (with QuickTables) This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence
Mathematics LV 4 (with QuickTables) This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence
Summer 2013 Modules 9-13
 Summer 201 Modules 9-1 Mastering the Fundamentals Chris Millett Copyright 201 All rights reserved. Written permission must be secured from the author to use or reproduce any part of this book. Academic
Summer 201 Modules 9-1 Mastering the Fundamentals Chris Millett Copyright 201 All rights reserved. Written permission must be secured from the author to use or reproduce any part of this book. Academic
6-8 Math Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Lesson Objective: Subobjective 1: Subobjective 2:
 6-8 Math Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Lesson Objective: The student will add and subtract polynomials. Subobjective 1: The student will add polynomials. Subobjective 2: The student will subtract
6-8 Math Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Lesson Objective: The student will add and subtract polynomials. Subobjective 1: The student will add polynomials. Subobjective 2: The student will subtract
Year 6 Maths Long Term Plan
 Week & Focus 1 Number and Place Value Unit 1 2 Subtraction Value Unit 1 3 Subtraction Unit 3 4 Subtraction Unit 5 5 Unit 2 6 Division Unit 4 7 Fractions Unit 2 Autumn Term Objectives read, write, order
Week & Focus 1 Number and Place Value Unit 1 2 Subtraction Value Unit 1 3 Subtraction Unit 3 4 Subtraction Unit 5 5 Unit 2 6 Division Unit 4 7 Fractions Unit 2 Autumn Term Objectives read, write, order
Algebra Homework: Chapter 1 (Homework is listed by date assigned; homework is due the following class period) Day Date In-Class Homework
 Algebra Homework: Chapter 1 (Homework is listed by date assigned; homework is due the following class period) Day Date In-Class Homework 1 T 8/30 Introductions Operations on Decimals Converting Decimals
Algebra Homework: Chapter 1 (Homework is listed by date assigned; homework is due the following class period) Day Date In-Class Homework 1 T 8/30 Introductions Operations on Decimals Converting Decimals
New Swannington Primary School 2014 Year 6
 Number Number and Place Value Number Addition and subtraction, Multiplication and division Number fractions inc decimals & % Ratio & Proportion Algebra read, write, order and compare numbers up to 0 000
Number Number and Place Value Number Addition and subtraction, Multiplication and division Number fractions inc decimals & % Ratio & Proportion Algebra read, write, order and compare numbers up to 0 000
Big Apple Academy 2017 Mathematics Department
 Big Apple Academy 201 Mathematics Department Grade Homework Math Package It is important that you keep practicing your mathematical Knowledge over the summer to be ready for 5 th grade. In this Package
Big Apple Academy 201 Mathematics Department Grade Homework Math Package It is important that you keep practicing your mathematical Knowledge over the summer to be ready for 5 th grade. In this Package
UNIT 4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS
 UNIT 4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS 1 Determine the fraction represented by the area shaded pink using the given unit Unit Fraction 2 Determine the fraction represented by the shaded area using the given unit Unit
UNIT 4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS 1 Determine the fraction represented by the area shaded pink using the given unit Unit Fraction 2 Determine the fraction represented by the shaded area using the given unit Unit
Mathematics Curriculum Objectives Year Six. Trinity Primary
 Mathematics Curriculum Objectives Year Six Trinity Primary Counting Year 6 Number I can count backwards I can count backwards I can find the difference through zero to include through zero to include between
Mathematics Curriculum Objectives Year Six Trinity Primary Counting Year 6 Number I can count backwards I can count backwards I can find the difference through zero to include through zero to include between
Y6 MATHEMATICS TERMLY PATHWAY NUMBER MEASURE GEOMETRY STATISTICS
 Autumn Number & Place value read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10 000 000 and determine the value of each digit round any whole number to a required degree of accuracy use negative numbers in
Autumn Number & Place value read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10 000 000 and determine the value of each digit round any whole number to a required degree of accuracy use negative numbers in
DIOCESE OF HARRISBURG MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM GRADE 5
 5A.Numbers and Operations Read, write, and identify whole numbers to the billions place. a. Demonstrate understanding of place value of whole numbers and decimal numbers. Match standard form to word form
5A.Numbers and Operations Read, write, and identify whole numbers to the billions place. a. Demonstrate understanding of place value of whole numbers and decimal numbers. Match standard form to word form
Mathematics - LV 5 (with QuickTables)
 Mathematics - LV 5 (with QuickTables) Correlation of the ALEKS Course Mathematics LV 5 to the California Mathematics Content Standards for Grade 5 (1998) Number Sense: NS1.1: NS1.2: NS1.3: NS1.4: TD =
Mathematics - LV 5 (with QuickTables) Correlation of the ALEKS Course Mathematics LV 5 to the California Mathematics Content Standards for Grade 5 (1998) Number Sense: NS1.1: NS1.2: NS1.3: NS1.4: TD =
Year 6 Mathematics Overview
 Year 6 Mathematics Overview Term Strand National Curriculum 2014 Objectives Focus Sequence Autumn 1 Number and Place Value read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10 000 000 and determine the value
Year 6 Mathematics Overview Term Strand National Curriculum 2014 Objectives Focus Sequence Autumn 1 Number and Place Value read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10 000 000 and determine the value
Integers and Rational Numbers
 A A Family Letter: Integers Dear Family, The student will be learning about integers and how these numbers relate to the coordinate plane. The set of integers includes the set of whole numbers (0, 1,,,...)
A A Family Letter: Integers Dear Family, The student will be learning about integers and how these numbers relate to the coordinate plane. The set of integers includes the set of whole numbers (0, 1,,,...)
Chapter 4 Section 2 Operations on Decimals
 Chapter 4 Section 2 Operations on Decimals Addition and subtraction of decimals To add decimals, write the numbers so that the decimal points are on a vertical line. Add as you would with whole numbers.
Chapter 4 Section 2 Operations on Decimals Addition and subtraction of decimals To add decimals, write the numbers so that the decimal points are on a vertical line. Add as you would with whole numbers.
Study Guide For use with pages
 . GOAL For use with pages Write fractions as decimals and vice versa. VOCABULARY A rational number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. In a terminating decimal, the division
. GOAL For use with pages Write fractions as decimals and vice versa. VOCABULARY A rational number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. In a terminating decimal, the division
Fractions. There are several terms that are commonly used when working with fractions.
 Chapter 0 Review of Arithmetic Fractions There are several terms that are commonly used when working with fractions. Fraction: The ratio of two numbers. We use a division bar to show this ratio. The number
Chapter 0 Review of Arithmetic Fractions There are several terms that are commonly used when working with fractions. Fraction: The ratio of two numbers. We use a division bar to show this ratio. The number
Final Exam Review 114 Questions Fall 2011 math 0301 prealgebra
 Final Exam Review 114 Questions 12-11-11 Fall 2011 math 0301 prealgebra Name atfm0301car28yes website www.alvarezmathhelp.com PROGRAMS: ALVAREZLAB AND INTERACTMATH (CARSON PREALGEBRA 3RD EDITION) MULTIPLE
Final Exam Review 114 Questions 12-11-11 Fall 2011 math 0301 prealgebra Name atfm0301car28yes website www.alvarezmathhelp.com PROGRAMS: ALVAREZLAB AND INTERACTMATH (CARSON PREALGEBRA 3RD EDITION) MULTIPLE
Number System. Introduction. Natural Numbers (N) Whole Numbers (W) Integers (Z) Prime Numbers (P) Face Value. Place Value
 1 Number System Introduction In this chapter, we will study about the number system and number line. We will also learn about the four fundamental operations on whole numbers and their properties. Natural
1 Number System Introduction In this chapter, we will study about the number system and number line. We will also learn about the four fundamental operations on whole numbers and their properties. Natural
Need more help with decimal subtraction? See T23. Note: The inequality sign is reversed only when multiplying or dividing by a negative number.
 . (D) According to the histogram, junior boys sleep an average of.5 hours on a daily basis and junior girls sleep an average of. hours. To find how many more hours the average junior boy sleeps than the
. (D) According to the histogram, junior boys sleep an average of.5 hours on a daily basis and junior girls sleep an average of. hours. To find how many more hours the average junior boy sleeps than the
CIV Module Unit Session Learning Objectives
 CIV Module Unit Session Learning Objectives C IV Module: Essentials of Recognizing a Fraction 1. Learning that a fraction is a part of a whole through the use of area models C IV Module: Essentials of
CIV Module Unit Session Learning Objectives C IV Module: Essentials of Recognizing a Fraction 1. Learning that a fraction is a part of a whole through the use of area models C IV Module: Essentials of
SINGAPORE CORE COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS BOY ASSESSMENT UNIT 1: BILLIONS. -recognize place value up to billions
 5 TH GRADE MATH CURRICULUM MAP Approximate Month AUG. SEPT. SINGAPORE CORE COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS BOY ASSESSMENT UNIT 1: BILLIONS -Write very large s in -read and write s (in digits and Standard 1.1,
5 TH GRADE MATH CURRICULUM MAP Approximate Month AUG. SEPT. SINGAPORE CORE COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS BOY ASSESSMENT UNIT 1: BILLIONS -Write very large s in -read and write s (in digits and Standard 1.1,
MAT 003 Brian Killough s Instructor Notes Saint Leo University
 MAT 003 Brian Killough s Instructor Notes Saint Leo University Success in online courses requires self-motivation and discipline. It is anticipated that students will read the textbook and complete sample
MAT 003 Brian Killough s Instructor Notes Saint Leo University Success in online courses requires self-motivation and discipline. It is anticipated that students will read the textbook and complete sample
RtI 7. Curriculum (219 topics additional topics)
 RtI 7 This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs. Curriculum
RtI 7 This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs. Curriculum
Solving Algebraic Equations
 Lesson 4. Solving Algebraic Equations 3 3 3 3 3 8 8 4 Add 3 to both sides. Divide both sides by. 4 gives the solution of the equation 3. Check: Substitute 4 for x into the original equation. 3 4 3 When
Lesson 4. Solving Algebraic Equations 3 3 3 3 3 8 8 4 Add 3 to both sides. Divide both sides by. 4 gives the solution of the equation 3. Check: Substitute 4 for x into the original equation. 3 4 3 When
Odd-Numbered Answers to Exercise Set 1.1: Numbers
 Odd-Numbered Answers to Exercise Set.: Numbers. (a) Composite;,,, Prime Neither (d) Neither (e) Composite;,,,,,. (a) 0. 0. 0. (d) 0. (e) 0. (f) 0. (g) 0. (h) 0. (i) 0.9 = (j). (since = ) 9 9 (k). (since
Odd-Numbered Answers to Exercise Set.: Numbers. (a) Composite;,,, Prime Neither (d) Neither (e) Composite;,,,,,. (a) 0. 0. 0. (d) 0. (e) 0. (f) 0. (g) 0. (h) 0. (i) 0.9 = (j). (since = ) 9 9 (k). (since
Teacher: CORE Math Grade 6 Year: Content Skills VocabularyAssessments Lessons Resources Standards. Diagnostic Math 6 Test 9/10/2011
 Teacher: CORE Math Grade 6 Year: 2010-11 Course: Math Grade 6 Month: All Months S e p Essential t Questions e m b e r NUMBER SENSE AND OPERATIONS Content Skills VocabularyAssessments Lessons Resources
Teacher: CORE Math Grade 6 Year: 2010-11 Course: Math Grade 6 Month: All Months S e p Essential t Questions e m b e r NUMBER SENSE AND OPERATIONS Content Skills VocabularyAssessments Lessons Resources
Digits. Value The numbers a digit. Standard Form. Expanded Form. The symbols used to show numbers: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
 Digits The symbols used to show numbers: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 Value The numbers a digit represents, which is determined by the position of the digits Standard Form Expanded Form A common way of the writing
Digits The symbols used to show numbers: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 Value The numbers a digit represents, which is determined by the position of the digits Standard Form Expanded Form A common way of the writing
Algebra II Chapter 6: Rational Exponents and Radical Functions
 Algebra II Chapter 6: Rational Exponents and Radical Functions Chapter 6 Lesson 1 Evaluate nth Roots and Use Rational Exponents Vocabulary 1 Example 1: Find nth Roots Note: and Example 2: Evaluate Expressions
Algebra II Chapter 6: Rational Exponents and Radical Functions Chapter 6 Lesson 1 Evaluate nth Roots and Use Rational Exponents Vocabulary 1 Example 1: Find nth Roots Note: and Example 2: Evaluate Expressions
TOPIC 2 DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3
 TOPIC DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3 Association between Fractions and Decimals is a fraction. It means divided by. If we divide by the result is not a whole number. It is a half of whole
TOPIC DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3 Association between Fractions and Decimals is a fraction. It means divided by. If we divide by the result is not a whole number. It is a half of whole
6 th Grade Enriched Math to 7 th Grade Pre-Algebra
 Summer Work 2018 6 th Grade Enriched Math to 7 th Grade Pre-Algebra 6 th Grade Skills that are necessary for success in 7 th grade and beyond: - ability to add subtract, multiply and divide decimals, fractions
Summer Work 2018 6 th Grade Enriched Math to 7 th Grade Pre-Algebra 6 th Grade Skills that are necessary for success in 7 th grade and beyond: - ability to add subtract, multiply and divide decimals, fractions
MATH EXPRESSIONS GRADE 5 SCOPE AND SEQUENCE
 UNIT 1: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION WORD PROBLEMS Math Expressions (teach all lessons) 10 --- 15 days (assuming a 60 minute lesson) Algebra & Functions: Solve for a missing number (blank, question mark,
UNIT 1: MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION WORD PROBLEMS Math Expressions (teach all lessons) 10 --- 15 days (assuming a 60 minute lesson) Algebra & Functions: Solve for a missing number (blank, question mark,
Basic and Intermediate Math Vocabulary Spring 2017 Semester
 Digit A symbol for a number (1-9) Whole Number A number without fractions or decimals. Place Value The value of a digit that depends on the position in the number. Even number A natural number that is
Digit A symbol for a number (1-9) Whole Number A number without fractions or decimals. Place Value The value of a digit that depends on the position in the number. Even number A natural number that is
York Public Schools Subject Area: Mathematics Course: 6 th Grade Math NUMBER OF DAYS TAUGHT DATE
 6.1.1.d 6.EE.A.1 Represent large numbers using exponential notation (i.e.. 10x10x10x10x10) (Review PV chart first) Write evaluate numerical expressions involving whole number exponents 5 days August, Lesson
6.1.1.d 6.EE.A.1 Represent large numbers using exponential notation (i.e.. 10x10x10x10x10) (Review PV chart first) Write evaluate numerical expressions involving whole number exponents 5 days August, Lesson
Adding and Subtracting Integers
 Quarterly 1 Review Sheet (NOTE: This may not include everything you need to know for tomorrow about every topic. It is student created and I am just sharing it in case you find it helpful) Page 1: Adding
Quarterly 1 Review Sheet (NOTE: This may not include everything you need to know for tomorrow about every topic. It is student created and I am just sharing it in case you find it helpful) Page 1: Adding
Chapter 5 DECIMAL NOTATION
 Name: Instructor: Date: Section: Chapter 5 DECIMAL NOTATION 5.1 Decimal Notation, Order, and Rounding Learning Objectives A Given decimal notation, write a word name. B Convert between decimal notation
Name: Instructor: Date: Section: Chapter 5 DECIMAL NOTATION 5.1 Decimal Notation, Order, and Rounding Learning Objectives A Given decimal notation, write a word name. B Convert between decimal notation
NFC ACADEMY MATH 600 COURSE OVERVIEW
 NFC ACADEMY MATH 600 COURSE OVERVIEW Math 600 is a full-year elementary math course focusing on number skills and numerical literacy, with an introduction to rational numbers and the skills needed for
NFC ACADEMY MATH 600 COURSE OVERVIEW Math 600 is a full-year elementary math course focusing on number skills and numerical literacy, with an introduction to rational numbers and the skills needed for
Math 083 Final Exam Practice
 Math 083 Final Exam Practice Name: 1. Simplify the expression. Remember, negative exponents give reciprocals.. Combine the expressions. 3. Write the expression in simplified form. (Assume the variables
Math 083 Final Exam Practice Name: 1. Simplify the expression. Remember, negative exponents give reciprocals.. Combine the expressions. 3. Write the expression in simplified form. (Assume the variables
Table of Contents. Foundations 5p Vocabulary List
 Table of Contents Objective 1: Review (Natural Numbers)... 3 Objective 2: Reading and Writing Natural Numbers... 5 Objective 3: Lines: Rays, and Line Segments... 6 Objective 4: Comparing Natural Numbers...
Table of Contents Objective 1: Review (Natural Numbers)... 3 Objective 2: Reading and Writing Natural Numbers... 5 Objective 3: Lines: Rays, and Line Segments... 6 Objective 4: Comparing Natural Numbers...
MAT 090 Brian Killough s Instructor Notes Strayer University
 MAT 090 Brian Killough s Instructor Notes Strayer University Success in online courses requires self-motivation and discipline. It is anticipated that students will read the textbook and complete sample
MAT 090 Brian Killough s Instructor Notes Strayer University Success in online courses requires self-motivation and discipline. It is anticipated that students will read the textbook and complete sample
Rules of Exponents Part 1[Algebra 1](In Class Version).notebook. August 22, 2017 WARM UP. Simplify using order of operations. SOLUTION.
.notebook. August 22, 2017 WARM UP. Simplify using order of operations. SOLUTION. Rules of Exponents Part 1[Algebra 1](In Class Version).notebook. August 22, 2017 WARM UP. Simplify using order of operations. SOLUTION.](/thumbs/95/124127108.jpg) WARM UP Simplify using order of operations. Aug 22 3:22 PM 1 Aug 22 4:09 PM 2 WARM UP a) The equation 3(4x) = (4x)3 illustrates which property? b) Which property of real numbers is illustrated by the equation
WARM UP Simplify using order of operations. Aug 22 3:22 PM 1 Aug 22 4:09 PM 2 WARM UP a) The equation 3(4x) = (4x)3 illustrates which property? b) Which property of real numbers is illustrated by the equation
Year 6.1- Number and Place Value 2 weeks- Autumn 1 Read, write, order and compare numbers up to and determine the value of each digit.
 Year 6.1- Number and Place Value 2 weeks- Autumn 1 Read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10 000 000 and determine the value of each digit. Round any whole number to a required degree of accuracy.
Year 6.1- Number and Place Value 2 weeks- Autumn 1 Read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10 000 000 and determine the value of each digit. Round any whole number to a required degree of accuracy.
