Cinematic Rendering - A New 3D Imaging Technique for Computed Tomography
|
|
|
- Cameron Alice Chapman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cinematic Rendering - A New 3D Imaging Technique for Computed Tomography Poster No.: C-0100 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Dappa, K. Higashigaito, J. Fornaro, S. Leschka, S Wildermuth, H. Alkadhi ; Zürich/CH, St. Gallen/CH, Zurich/CH Keywords: Tissue characterisation, Image registration, Arteriovenous malformations, Computer Applications-3D, Image manipulation / Reconstruction, CT, Computer applications, Anatomy DOI: /ecr2016/C-0100 Any information contained in this pdf file is automatically generated from digital material submitted to EPOS by third parties in the form of scientific presentations. References to any names, marks, products, or services of third parties or hypertext links to thirdparty sites or information are provided solely as a convenience to you and do not in any way constitute or imply ECR's endorsement, sponsorship or recommendation of the third party, information, product or service. ECR is not responsible for the content of these pages and does not make any representations regarding the content or accuracy of material in this file. As per copyright regulations, any unauthorised use of the material or parts thereof as well as commercial reproduction or multiple distribution by any traditional or electronically based reproduction/publication method ist strictly prohibited. You agree to defend, indemnify, and hold ECR harmless from and against any and all claims, damages, costs, and expenses, including attorneys' fees, arising from or related to your use of these pages. Please note: Links to movies, ppt slideshows and any other multimedia files are not available in the pdf version of presentations. Page 1 of 13
2 Learning objectives 1. To give a concise overview about standard volume rendering (VR) and a new threedimensional (3D) technique labelled cinematic rendering (CR). 2. To illustrate the image appearance and potential value of CR in comparison with conventional VR. Background Current computed tomography (CT) scanners provide isotropic submillimeter resolution enabling the utilization of various 2D and 3D post-processing techniques with excellent spatial resolution. Whereas 2D techniques such as planar or curved multiplanar reformations (MPR) can be considered part of daily radiological routine [1], 3D imaging postprocessing techniques such as volume rendering (VR) are used more rarely for visualizing complex anatomical information. This holds particularly true for CT angiography examinations and for orthopedic as well as oncological imaging. 3D visualizations of CT image data can offer additional information compared with 2D axial images in both preoperative planning and post-treatment follow-up, including applications in otorhinolaryngiology [2], neurosurgery [3], management of foreign body extractions [4], visualization of complex tumor [5] and vessel [6; 7] anatomy. Nowadays, VR is used as the standard technique for the 3D visualization of CT image data. The main advantages of VR lie in a relatively simple evaluation of different body structures at the same time, which can be useful in patients with vascular malformations [8] and acute vascular syndromes [9]. Moreover, VR enables the display of CT image data in a colored fashion, which helps visualizing complex anatomy [10]. While the generation of VR images in early days was hampered by high computational demands and often was associated with long post-processing times, today's powerful computers allow for a nearreal time and automatic rendering of 3D images in a fast, clinically compatible manner. Recently, a new technique for 3D visualization of cross-sectional image data from CT has been introduced, which is entitled cinematic rendering (CR). CR works with random sampling computational algorithms and uses different light maps to generate a realistic depiction of medical data. Page 2 of 13
3 VOLUME RENDERING VR technique represents a computer algorithm used to transform cross-sectional image datasets (from e.g. CT) into 3D images. The volume rendering technique consists of the following two steps: classification of each voxel and image projection. First, the tissue represented in each voxel of the volume dataset is determined by using predefined attenuation threshold levels and assigned to a specific color and opacity. Then, weighted sum of the percentage of each tissue type represented in the voxel is calculated to determine the overall color and transparency of each voxel. This step is performed for each voxel of the whole volume dataset. Second, the 3D volume is displayed by using a projection technique. This is done by simulating rays of light which are projected through the 3D volume that contains the classified voxels. Each voxel which is passed by the simulated rays modulate the color of the light depending on the assigned color and transparency and contribute to the final projection and final image. Finally, 3D perception in the projected image can be enhanced by implementing additional effects such as reflection and shadows on the surface of the rendered image. CINEMATIC RENDERING CR is currently available only as a research tool on an open research environment containing various prototype software (Frontier, version 1.0.0, syngo.via, version VB10A) and has so far no approval for clinical use. The CR technique introduces a new paradigm to render volumetric medical image data by using a path tracing-based technique. As opposed to conventional rendering methods such as VR that model only one light ray per pixel, path tracing integrates a huge number of light rays, each with different paths to form each pixel of the rendered image. Since the number of light paths which can be traced is in theory infinite, and tracing of light paths is computationally expensive, Monte-Carlo simulations are used to generate a randomized subset of light paths with an adequate distribution. High dynamic range (HDR) rendering light maps are used for illumination, which lead to a natural illumination of the rendered data, in contrast to synthetic light sources used in conventional rendering methods such as VR [13]. As a result, the complex physics of lighting effect can model shadows, ambient occlusion, multi-scattering, and color transmittance as well as sophisticated camera models, which Page 3 of 13
4 include concepts such as aperture, exposure and shutter speed. This novel approach leads to a natural and physically accurate presentation of the medical data, which considerably enhances depth and shape perception. Findings and procedure details Both VR and CR post-processing techniques have the same general rendering concept in common, which includes the segmentation of data based on voxel attenuation and using colour look-up tables taking into account opacity and brightness. As a consequence, both VR and CR share the same problem of potentially masking findings in the dataset by inappropriate use of the rendering parameters. Albeit CR currently is only provided by a single vendor in a pre-clinical research tool with still limited display options, CR can provide the same advanced display functions such as VR including flying-through, flyingaround and multiple views of the volume data with independent parameters in equal segments of the displayed window [11; 12]. Due to the above mentioned similarities between CR and VR, there are no major differences in the visualization of CT image data when regarding the diagnostic value of the presentation. Similar to VR, we found that particularly high-contrast structures such as contrast-enhanced vessels and bones can be depicted with high quality also with CR. However, we also found a major improvement of CR in the perception of depth and soft tissue structures. In general, lighting in 3D rendered images such as VR and CR is a function of ambient, diffuse and specular light properties. In both techniques, the brightness of each voxel is defined by the distribution of these light properties which results in different lighting of different body parts relative to the artificial light source introduced into the volume, giving rise to 3D impressions of the images. In VR, the differences in light emitted to the voxels are rather small. In contrast, CR uses a more complex lighting model taking into account the effect of lighting to other voxels and subsequent reflections as well. Also the effect of body parts blocking the trace from the artificial light source to other structures introduces shadowing into the images. As a result of the differences in lighting functions - as being illustrated in the representative image examples of this pictorial review - CR images go along with a more natural image impression as compared to conventional VR. Despite of the potential benefits of CR compared to VR in the visualization of volume datasets, there is a higher computational power demand required for the CR technique because of the more complex lighting model. Therefore, real-time display of for instance rotating the CR image is currently interrupted by repetitive recalculation processes. In Page 4 of 13
5 addition, there is currently no proven added clinical value of CR in terms of accuracy to neither conventional VR nor cross-sectional 2D image interpretation such as MPR [14]. Representative image examples of vascular anatomy and pathology are provided in Fig. 1 on page 5, Fig. 2 on page 5, Fig. 3 on page 6, and Fig. 4 on page 6, representative images illustrating the quality for depiction of bones and skeletal disease are provided in Fig. 5 on page 7, Fig. 6 on page 8, and Fig. 7 on page 9, and the quality of CR for the visualization of soft tissue anatomy and tumors is shown in Fig. 8 on page 9, Fig. 9 on page 9, and Fig. 10 on page 10. Images for this section: Fig. 1: Malignant type coronary anomaly with origin of the right coronary artery (RCA) from the left coronary sinus and interarterial course (arrows). Cinematic rendering (CR) (a) shows the RCA coursing ventrally to the aortic root to the right side. The volume rendered (VR)image (b) depicts the same anomaly from a similar perspective. Universitätsspital Zürich - Zürich/CH Page 5 of 13
6 Fig. 2: Basilar artery aneurysm. CR (a) and conventional VR (b) depict the base of the skull with the cerebral arteries of the circle of Willis, as well as the fusiform dilation of the basilar artery. Universitätsspital Zürich - Zürich/CH Fig. 3: Endovascular stent graft treatment of the abdominal aorta with visceral debranching in a patient with infrarenal aortic and splenic artery aneurysm. Coronal 3D images showing the dilatation of the splenic artery with CR (a) and VR (b). Universitätsspital Zürich - Zürich/CH Page 6 of 13
7 Fig. 4: Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) in the upper pole of the left kidney. CR (a) and VR (b) images and close-up view (c, d) images allow for more detailed depiction of the AVM. Universitätsspital Zürich - Zürich/CH Page 7 of 13
8 Fig. 5: Cervical spine injury with luxation of C3/4. 3D rendering using CR (a) and VR (b)technique shows anterior subluxation of the cervical spine (arrows). Department of Radiology, Kantonsspital St. Gallen, St. Gallen/CH 2015 Fig. 6: Polytrauma patient with multiple fractures of the axial skeleton. Back side view of the osseous structures of the spine and pelvis using CR (a) and VR (b) reveals multiple fractures of the ribs, lumbal transverse processes, sacrum, and pubic bones. Page 8 of 13
9 Universitätsspital Zürich - Zürich/CH Fig. 7: Head shot injury. CR (a) and VR (b) showing the bullets and the extensive damage of the skull base. Department of Radiology, Kantonsspital St. Gallen, St. Gallen/CH 2015 Fig. 8: Neuroendocrine tumor of the duodenum. CR (a) and VR (b) showing the large vascularized mass in the upper abdomen with dilated arterial feeders and draining veins (arrows). Department of Radiology, Kantonsspital St. Gallen, St. Gallen/CH 2015 Page 9 of 13
10 Fig. 9: Herniation of small bowel through the anterior abdominal wall caused by blunt trauma. CR (a) and VR (b) showing the soft tissue of the abdominal wall and upper thigh along with the herniating bowel loops (arrows). Department of Radiology, Kantonsspital St. Gallen, St. Gallen/CH 2015 Page 10 of 13
11 Fig. 10: Whole body CT in a patient with polytrauma. CR (a) and VR (b) visualize the soft tissues of the head, neck, chest and abdomen. Department of Radiology, Kantonsspital St. Gallen, St. Gallen/CH 2015 Page 11 of 13
12 Conclusion Our aim was to give a first demonstration of a new post-processing technique for the 3D visualization of CT image data. Our first experience indicates that CR of CT images is particularly impressive when high contrast structures such as bones and vessels after the administration of contrast media are to be visualized. The main innovations as compared to conventional VR appear to be a more natural representation of the CT image data, with an enhanced depth and shape perception. Personal information References Petik B (2015) Inferior vena cava anomalies and variations: imaging and rare clinical findings. Insights Imaging /s z Guo Y, Liu Y, Lu QH, Zheng KH, Shi LJ, Wang QJ (2013) CT twodimensional reformation versus three-dimensional volume rendering with regard to surgical findings in the preoperative assessment of the ossicular chain in chronic suppurative otitis media. Eur J Radiol 82: Sun W, Jia L, Dong Y et al (2014) Morphological study of surgical approach by superior temporal sulcus-temporal horn of lateral ventricle approach using volume rendering. J Craniofac Surg 25: Yang XJ, Xing GF, Shi CW, Li W (2013) Value of 3-dimensional CT virtual anatomy imaging in complex foreign body retrieval from soft tissues. Korean J Radiol 14: Li Y, Zheng Y, Chen J et al (2015) Determining the organ of origin of large pelvic masses in females using multidetector CT angiography and threedimensional volume rendering CT angiography. Eur Radiol 25: Hammer S, Kroft LJ, Hidalgo AL, Leta R, de Roos A (2015) Chest CT examinations in patients presenting with acute chest pain: a pictorial review. Insights Imaging /s Zampakis P, Panagiotopoulos V, Petsas T, Kalogeropoulou C (2015) Common and uncommon intracranial arterial anatomic variations in multidetector computed tomography angiography (MDCTA). What radiologists should be aware of. Insights Imaging 6:33-42 Hatzidakis A, Rossi M, Mamoulakis C et al (2014) Management of renal arteriovenous malformations: A pictorial review. Insights Imaging 5: Vu KN, Kaitoukov Y, Morin-Roy F et al (2014) Rupture signs on computed tomography, treatment, and outcome of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Insights Imaging 5: Page 12 of 13
13 10. Fishman EK, Ney DR, Heath DG, Corl FM, Horton KM, Johnson PT (2006) Volume rendering versus maximum intensity projection in CT angiography: what works best, when, and why. Radiographics 26: Calhoun PS, Kuszyk BS, Heath DG, Carley JC, Fishman EK (1999) Threedimensional Volume Rendering of Spiral CT Data: Theory and Method. RadioGraphics 19: Fishman EK, Ney DR, Heath DG, Corl FM, Horton KM, Johnson PT (2006) Volume Rendering versus Maximum Intensity Projection in CT Angiography: What Works Best, When, and Why. RadioGraphics 26: Debevec ZH (1998) Rendering Synthetic Objects into Real Scenes: Bridging Traditional and Image-based Graphics with Global Illumination and High Dynamic Range Photography. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH '98: Zheng L, Chaudhari AJ, Badawi RD, Ma KL (2014) Using global illumination in volume visualization of rheumatoid arthritis CT data. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 34:16-23 Page 13 of 13
Dedifferentiated chondrosarcomas: A comprehensive review of imaging and pathologic features
 Dedifferentiated chondrosarcomas: A comprehensive review of imaging and pathologic features Poster No.: C-2187 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal - Bone Authors: G. Bierry,
Dedifferentiated chondrosarcomas: A comprehensive review of imaging and pathologic features Poster No.: C-2187 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal - Bone Authors: G. Bierry,
A client-server architecture for semi-automatic segmentation of peripheral vessels in CTA data
 A client-server architecture for semi-automatic segmentation of peripheral vessels in CTA data Poster No.: C-2174 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Grünauer, E. Vuçini,
A client-server architecture for semi-automatic segmentation of peripheral vessels in CTA data Poster No.: C-2174 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Grünauer, E. Vuçini,
3D temporal subtraction on chest MDCT images using nonlinear image registration technique
 3D temporal subtraction on chest MDCT images using nonlinear image registration technique Poster No.: C-1072 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Computer Applications
3D temporal subtraction on chest MDCT images using nonlinear image registration technique Poster No.: C-1072 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Computer Applications
Learning knee MRI the easy way: A multimedial online program for teaching multiplanar MRI anatomy of the knee
 Learning knee MRI the easy way: A multimedial online program for teaching multiplanar MRI anatomy of the knee Poster No.: C-2225 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors:
Learning knee MRI the easy way: A multimedial online program for teaching multiplanar MRI anatomy of the knee Poster No.: C-2225 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors:
3D imaging with SPACE vs 2D TSE in MR guided prostate biopsy
 3D imaging with SPACE vs 2D TSE in MR guided prostate biopsy Poster No.: C-2004 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper M. Garmer, S. Mateiescu, M. Busch, D. Groenemeyer; Bochum/
3D imaging with SPACE vs 2D TSE in MR guided prostate biopsy Poster No.: C-2004 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper M. Garmer, S. Mateiescu, M. Busch, D. Groenemeyer; Bochum/
Using a local Dose Index Registry system to determine Notification Values for the MITA XR 25 (Dose Check) Standard in CT
 Using a local Dose Index Registry system to determine Notification Values for the MITA XR 25 (Dose Check) Standard in CT Poster No.: C-0913 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit M. Shinozaki
Using a local Dose Index Registry system to determine Notification Values for the MITA XR 25 (Dose Check) Standard in CT Poster No.: C-0913 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit M. Shinozaki
Detector Noise evaluation by means of Continue Wavelet Transform. Comparison with Fourier Transform methods
 Detector Noise evaluation by means of Continue Wavelet Transform. Comparison with Fourier Transform methods Poster No.: C-0215 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Kalyvas 1, S. Angelakis
Detector Noise evaluation by means of Continue Wavelet Transform. Comparison with Fourier Transform methods Poster No.: C-0215 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Kalyvas 1, S. Angelakis
Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) the new parameter of 2D texture analysis for the evaluation of 3D bone micro architecture status.
 Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) the new parameter of 2D texture analysis for the evaluation of 3D bone micro architecture status. Poster No.: C-1961 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) the new parameter of 2D texture analysis for the evaluation of 3D bone micro architecture status. Poster No.: C-1961 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
A validation of the biexponential model in diffusion MRI signal attenuation using diffusion Monte Carlo simulator
 A validation of the biexponential model in diffusion MRI signal attenuation using diffusion Monte Carlo simulator Poster No.: C-0331 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Nishigake, S.
A validation of the biexponential model in diffusion MRI signal attenuation using diffusion Monte Carlo simulator Poster No.: C-0331 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Nishigake, S.
Digital breast tomosynthesis: comparison of different methods to calculate patient doses
 Digital breast tomosynthesis: comparison of different methods to calculate patient doses Poster No.: C-2220 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: A. Jacobs 1, L. Cockmartin 1, D. R. Dance
Digital breast tomosynthesis: comparison of different methods to calculate patient doses Poster No.: C-2220 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: A. Jacobs 1, L. Cockmartin 1, D. R. Dance
EVERNOTE: How radiologists can improve their productivity
 EVERNOTE: How radiologists can improve their productivity Poster No.: C-0122 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. D. Monedero Picazo, M. R. Pastor Juan, M. Villar Garcia, 1 1 1 1 1
EVERNOTE: How radiologists can improve their productivity Poster No.: C-0122 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. D. Monedero Picazo, M. R. Pastor Juan, M. Villar Garcia, 1 1 1 1 1
Clarify behavioral factor of X-ray scatter in MDCT scanners based on evaluation data by a wide variety of MDCT scanners
 Clarify behavioral factor of X-ray scatter in MDCT scanners based on evaluation data by a wide variety of MDCT scanners Poster No.: C-1748 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Miyashita
Clarify behavioral factor of X-ray scatter in MDCT scanners based on evaluation data by a wide variety of MDCT scanners Poster No.: C-1748 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Miyashita
Evaluation of 3D shearwave(tm) elastography and its benefits for the characterization of breast lesions
 Evaluation of 3D shearwave(tm) elastography and its benefits for the characterization of breast lesions Poster No.: C-2280 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: D. AMY; Aix en Provence/FR
Evaluation of 3D shearwave(tm) elastography and its benefits for the characterization of breast lesions Poster No.: C-2280 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: D. AMY; Aix en Provence/FR
AN EVALUATION OF IMSIMQA AS A TOOL FOR COMMISSIONING 4DCT
 AN EVALUATION OF IMSIMQA AS A TOOL FOR COMMISSIONING 4DCT e-poster: 12474 Congress: ESTRO 2011 Type: eposter Topic: 11th Biennial / QA: of software Authors: N. Whilde; Any information contained in this
AN EVALUATION OF IMSIMQA AS A TOOL FOR COMMISSIONING 4DCT e-poster: 12474 Congress: ESTRO 2011 Type: eposter Topic: 11th Biennial / QA: of software Authors: N. Whilde; Any information contained in this
Dynalog data tool for IMRT plan verification
 Dynalog data tool for IMRT plan verification Poster No.: R-0051 Congress: 2014 CSM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Sashin; FOOTSCRAY/AU Keywords: Computer applications, Radiation physics, Experimental,
Dynalog data tool for IMRT plan verification Poster No.: R-0051 Congress: 2014 CSM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Sashin; FOOTSCRAY/AU Keywords: Computer applications, Radiation physics, Experimental,
Artefacts in body and breast MRI: lessons learned from second reading
 Artefacts in body and breast MRI: lessons learned from second reading Poster No.: C-0573 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nadrljanski, P. Jovanovic, A. Jankovic, Z. C. Milosevic
Artefacts in body and breast MRI: lessons learned from second reading Poster No.: C-0573 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nadrljanski, P. Jovanovic, A. Jankovic, Z. C. Milosevic
Artefacts in body and breast MRI: lessons learned from second reading
 Artefacts in body and breast MRI: lessons learned from second reading Poster No.: C-0573 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nadrljanski, P. Jovanovic, A. Jankovic, Z. C. Milosevic
Artefacts in body and breast MRI: lessons learned from second reading Poster No.: C-0573 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nadrljanski, P. Jovanovic, A. Jankovic, Z. C. Milosevic
Purpose. Methods and Materials
 A systematic approach for the objective evaluation of low-contrast performance in MDCT: combination of a fullreference image fidelity metric and a software phantom Poster No.: C-1496 Congress: ECR 2012
A systematic approach for the objective evaluation of low-contrast performance in MDCT: combination of a fullreference image fidelity metric and a software phantom Poster No.: C-1496 Congress: ECR 2012
Integrating information in Radiology: Teaching File System (TFS) implementation in a third-level hospital using MIRC
 Integrating information in Radiology: Teaching File System (TFS) implementation in a third-level hospital using MIRC Poster No.: C-2964 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Ibáñez Caturla,
Integrating information in Radiology: Teaching File System (TFS) implementation in a third-level hospital using MIRC Poster No.: C-2964 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Ibáñez Caturla,
Accelerated quantitative multi-material beam hardening correction(bhc) in cone-beam CT
 Accelerated quantitative multi-material beam hardening correction(bhc) in cone-beam CT Award: Poster No.: C-2161 Certificate of Merit Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Q. Yang, M. Elter,
Accelerated quantitative multi-material beam hardening correction(bhc) in cone-beam CT Award: Poster No.: C-2161 Certificate of Merit Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Q. Yang, M. Elter,
Medical Image Processing: Image Reconstruction and 3D Renderings
 Medical Image Processing: Image Reconstruction and 3D Renderings 김보형 서울대학교컴퓨터공학부 Computer Graphics and Image Processing Lab. 2011. 3. 23 1 Computer Graphics & Image Processing Computer Graphics : Create,
Medical Image Processing: Image Reconstruction and 3D Renderings 김보형 서울대학교컴퓨터공학부 Computer Graphics and Image Processing Lab. 2011. 3. 23 1 Computer Graphics & Image Processing Computer Graphics : Create,
Functional analysis with DTI and diffusion-neurography of cranial nerves
 Functional analysis with DTI and diffusion-neurography of cranial nerves Poster No.: C-1942 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. P. Martínez Barbero, T. Martín Noguerol, A. Luna Alcalá;
Functional analysis with DTI and diffusion-neurography of cranial nerves Poster No.: C-1942 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. P. Martínez Barbero, T. Martín Noguerol, A. Luna Alcalá;
11/18/ CPT Preauthorization Groupings Effective January 1, Computerized Tomography (CT) Abdomen 6. CPT Description SEGR CT01
 Computerized Tomography (CT) 6 & 101 5 Upper Extremity 11 Lower Extremity 12 Head 3 Orbit 1 Sinus 2 Neck 4 7 Cervical Spine 8 Thoracic Spine 9 Lumbar Spine 10 Colon 13 CPT Description SEGR 74150 74160
Computerized Tomography (CT) 6 & 101 5 Upper Extremity 11 Lower Extremity 12 Head 3 Orbit 1 Sinus 2 Neck 4 7 Cervical Spine 8 Thoracic Spine 9 Lumbar Spine 10 Colon 13 CPT Description SEGR 74150 74160
The VesselGlyph: Focus & Context Visualization in CT-Angiography
 The VesselGlyph: Focus & Context Visualization in CT-Angiography Matúš Straka M. Šrámek, A. La Cruz E. Gröller, D. Fleischmann Contents Motivation:» Why again a new visualization method for vessel data?
The VesselGlyph: Focus & Context Visualization in CT-Angiography Matúš Straka M. Šrámek, A. La Cruz E. Gröller, D. Fleischmann Contents Motivation:» Why again a new visualization method for vessel data?
Storage optimization of multi-slice computed tomographic data on PACS systems
 Storage optimization of multi-slice computed tomographic data on PACS systems Poster No.: C-3033 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Radiographers Authors: B. Begenau, C. Beigelman, O. Lucidarme,
Storage optimization of multi-slice computed tomographic data on PACS systems Poster No.: C-3033 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Radiographers Authors: B. Begenau, C. Beigelman, O. Lucidarme,
CT Basics Principles of Spiral CT Dose. Always Thinking Ahead.
 1 CT Basics Principles of Spiral CT Dose 2 Who invented CT? 1963 - Alan Cormack developed a mathematical method of reconstructing images from x-ray projections Sir Godfrey Hounsfield worked for the Central
1 CT Basics Principles of Spiral CT Dose 2 Who invented CT? 1963 - Alan Cormack developed a mathematical method of reconstructing images from x-ray projections Sir Godfrey Hounsfield worked for the Central
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 4: Image Visualization
 Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 4: Image Visualization Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington,
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 4: Image Visualization Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington,
Automatic Ascending Aorta Detection in CTA Datasets
 Automatic Ascending Aorta Detection in CTA Datasets Stefan C. Saur 1, Caroline Kühnel 2, Tobias Boskamp 2, Gábor Székely 1, Philippe Cattin 1,3 1 Computer Vision Laboratory, ETH Zurich, 8092 Zurich, Switzerland
Automatic Ascending Aorta Detection in CTA Datasets Stefan C. Saur 1, Caroline Kühnel 2, Tobias Boskamp 2, Gábor Székely 1, Philippe Cattin 1,3 1 Computer Vision Laboratory, ETH Zurich, 8092 Zurich, Switzerland
The effect of automatic exposure control with inappropriate scout image on radiation dose: a chest phantom experiment with three different CT machines
 The effect of automatic exposure control with inappropriate scout image on radiation dose: a chest phantom experiment with three different CT machines Poster No.: C-0891 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors:
The effect of automatic exposure control with inappropriate scout image on radiation dose: a chest phantom experiment with three different CT machines Poster No.: C-0891 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors:
GPU Based Region Growth and Vessel Tracking. Supratik Moulik M.D. Jason Walsh
 GPU Based Region Growth and Vessel Tracking Supratik Moulik M.D. (supratik@moulik.com) Jason Walsh Conflict of Interest Dr. Supratik Moulik does not have a significant financial stake in any company, nor
GPU Based Region Growth and Vessel Tracking Supratik Moulik M.D. (supratik@moulik.com) Jason Walsh Conflict of Interest Dr. Supratik Moulik does not have a significant financial stake in any company, nor
Computed tomography (CT) has
 CE CT Image Visualization: A Conceptual Introduction Bryant Furlow, BA Computed tomography (CT) postprocessing produces information-rich diagnostic images, transforming enormous amounts of x-ray attenuation
CE CT Image Visualization: A Conceptual Introduction Bryant Furlow, BA Computed tomography (CT) postprocessing produces information-rich diagnostic images, transforming enormous amounts of x-ray attenuation
US 1.
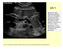 US 1 Sample image: Normal pancreas seen on sonogram. Looking up from abdomen toward the head of the patient. The liver is in front of the pancreas. A vein draining the spleen is behind the pancreas http://www.radiologyinfo.org/photocat/photos.cfm?image=abdo-us-pancr.jpg&&subcategory=abdomen&&stop=9
US 1 Sample image: Normal pancreas seen on sonogram. Looking up from abdomen toward the head of the patient. The liver is in front of the pancreas. A vein draining the spleen is behind the pancreas http://www.radiologyinfo.org/photocat/photos.cfm?image=abdo-us-pancr.jpg&&subcategory=abdomen&&stop=9
Technician s role in the postprocessing of CT and MRI images.
 Technician s role in the postprocessing of CT and MRI images. Poster No.: C-1628 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Fraga Piñeiro, M. Centeno, M. González Vázquez, D. Castellón Plaza,
Technician s role in the postprocessing of CT and MRI images. Poster No.: C-1628 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Fraga Piñeiro, M. Centeno, M. González Vázquez, D. Castellón Plaza,
Shadow casting. What is the problem? Cone Beam Computed Tomography THE OBJECTIVES OF DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING IDEAL DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING STUDY LIMITATIONS
 Cone Beam Computed Tomography THE OBJECTIVES OF DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Reveal pathology Reveal the anatomic truth Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu IDEAL DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING STUDY Provides desired diagnostic
Cone Beam Computed Tomography THE OBJECTIVES OF DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Reveal pathology Reveal the anatomic truth Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu IDEAL DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING STUDY Provides desired diagnostic
Non-rigid 2D-3D image registration for use in Endovascular repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms.
 RAHEEM ET AL.: IMAGE REGISTRATION FOR EVAR IN AAA. 1 Non-rigid 2D-3D image registration for use in Endovascular repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Ali Raheem 1 ali.raheem@kcl.ac.uk Tom Carrell 2 tom.carrell@gstt.nhs.uk
RAHEEM ET AL.: IMAGE REGISTRATION FOR EVAR IN AAA. 1 Non-rigid 2D-3D image registration for use in Endovascular repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Ali Raheem 1 ali.raheem@kcl.ac.uk Tom Carrell 2 tom.carrell@gstt.nhs.uk
Medical Image Analysis
 Computer assisted Image Analysis VT04 29 april 2004 Medical Image Analysis Lecture 10 (part 1) Xavier Tizon Medical Image Processing Medical imaging modalities XRay,, CT Ultrasound MRI PET, SPECT Generic
Computer assisted Image Analysis VT04 29 april 2004 Medical Image Analysis Lecture 10 (part 1) Xavier Tizon Medical Image Processing Medical imaging modalities XRay,, CT Ultrasound MRI PET, SPECT Generic
Teleradiology in Italy: results of an online survey
 Teleradiology in Italy: results of an online survey Poster No.: B-1044 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: F. Coppola, E. Neri, D. Regge ; Bologna/IT, Pisa/IT, Turin/IT Keywords: Computer
Teleradiology in Italy: results of an online survey Poster No.: B-1044 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: F. Coppola, E. Neri, D. Regge ; Bologna/IT, Pisa/IT, Turin/IT Keywords: Computer
RSNA, /rg
 RSNA, 2015 10.1148/rg.2015140320 Appendix As noted in the main article, DICOM image files cannot be used directly for 3D printing; further steps are necessary to make them readable by 3D printers. The
RSNA, 2015 10.1148/rg.2015140320 Appendix As noted in the main article, DICOM image files cannot be used directly for 3D printing; further steps are necessary to make them readable by 3D printers. The
Anatomic measurement accuracy: CT parameters and 3D rendering effects
 Anatomic measurement accuracy: CT parameters and 3D rendering effects Brian J Whyms a, E Michael Schimek a, Houri K Vorperian a, Lindell R Gentry b, and Edward T Bersu c University of Wisconsin-Madison
Anatomic measurement accuracy: CT parameters and 3D rendering effects Brian J Whyms a, E Michael Schimek a, Houri K Vorperian a, Lindell R Gentry b, and Edward T Bersu c University of Wisconsin-Madison
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis. A. Criminisi
 Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi Overview Introduction to machine learning Decision forests Applications in medical image analysis Anatomy localization in CT Scans Spine Detection
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi Overview Introduction to machine learning Decision forests Applications in medical image analysis Anatomy localization in CT Scans Spine Detection
Automated segmentation methods for liver analysis in oncology applications
 University of Szeged Department of Image Processing and Computer Graphics Automated segmentation methods for liver analysis in oncology applications Ph. D. Thesis László Ruskó Thesis Advisor Dr. Antal
University of Szeged Department of Image Processing and Computer Graphics Automated segmentation methods for liver analysis in oncology applications Ph. D. Thesis László Ruskó Thesis Advisor Dr. Antal
USER MANUAL VP PLANNING
 USER MANUAL VP PLANNING 1.0 Mobile application ios Visible Patient SAS RCS Strasbourg TI 794 458 125 1 place de l'ho pital 67000 Strasbourg, FRANCE Share capital: 58330 Tel.: 33 (0)3 88 11 90 00 Fax: 33
USER MANUAL VP PLANNING 1.0 Mobile application ios Visible Patient SAS RCS Strasbourg TI 794 458 125 1 place de l'ho pital 67000 Strasbourg, FRANCE Share capital: 58330 Tel.: 33 (0)3 88 11 90 00 Fax: 33
VieW 3D. 3D Post-Processing WorKstation THE THIRD DIMENSION. Version 3.1
 VieW 3D 3D Post-Processing WorKstation THE THIRD DIMENSION Version 3.1 iq-view 3D THE FULLY-FEATURED 3D MEDICAL IMAGING SOLUTION FOR RADIOLOGISTS iq-view 3D contains all components of iq-view with the
VieW 3D 3D Post-Processing WorKstation THE THIRD DIMENSION Version 3.1 iq-view 3D THE FULLY-FEATURED 3D MEDICAL IMAGING SOLUTION FOR RADIOLOGISTS iq-view 3D contains all components of iq-view with the
USER MANUAL VP PLANNING
 USER MANUAL VP PLANNING 1.0 Mobile application Android Visible Patient SAS RCS Strasbourg TI 794 458 125 1 place de l'ho pital 67000 Strasbourg, FRANCE Share capital: 58330 Tel.: 33 (0)3 88 11 90 00 Fax:
USER MANUAL VP PLANNING 1.0 Mobile application Android Visible Patient SAS RCS Strasbourg TI 794 458 125 1 place de l'ho pital 67000 Strasbourg, FRANCE Share capital: 58330 Tel.: 33 (0)3 88 11 90 00 Fax:
Medical Image Segmentation
 Medical Image Segmentation Xin Yang, HUST *Collaborated with UCLA Medical School and UCSB Segmentation to Contouring ROI Aorta & Kidney 3D Brain MR Image 3D Abdominal CT Image Liver & Spleen Caudate Nucleus
Medical Image Segmentation Xin Yang, HUST *Collaborated with UCLA Medical School and UCSB Segmentation to Contouring ROI Aorta & Kidney 3D Brain MR Image 3D Abdominal CT Image Liver & Spleen Caudate Nucleus
Automatic Cerebral Aneurysm Detection in Multimodal Angiographic Images
 Automatic Cerebral Aneurysm Detection in Multimodal Angiographic Images Clemens M. Hentschke, Oliver Beuing, Rosa Nickl and Klaus D. Tönnies Abstract We propose a system to automatically detect cerebral
Automatic Cerebral Aneurysm Detection in Multimodal Angiographic Images Clemens M. Hentschke, Oliver Beuing, Rosa Nickl and Klaus D. Tönnies Abstract We propose a system to automatically detect cerebral
Anatomy 1 st Paper. Past Papers
 Anatomy 1 st Paper Past Papers September 2010 April 2010 September 2009 April 2009 September 2008 April 2008 September 2007 April 2007 September 2006 May 2006 September 2005 April 2005 September 2004 April
Anatomy 1 st Paper Past Papers September 2010 April 2010 September 2009 April 2009 September 2008 April 2008 September 2007 April 2007 September 2006 May 2006 September 2005 April 2005 September 2004 April
RADIOLOGY AND DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING
 Day 2 part 2 RADIOLOGY AND DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Dr hab. Zbigniew Serafin, MD, PhD serafin@cm.umk.pl 2 3 4 5 CT technique CT technique 6 CT system Kanal K: RSNA/AAPM web module: CT Systems & CT Image Quality
Day 2 part 2 RADIOLOGY AND DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Dr hab. Zbigniew Serafin, MD, PhD serafin@cm.umk.pl 2 3 4 5 CT technique CT technique 6 CT system Kanal K: RSNA/AAPM web module: CT Systems & CT Image Quality
Development and Evaluation of a New Method for Measuring of Signal-to-Noise Ratio in Magnetic Resonance Images
 Development and Evaluation of a New Method for Measuring of Signal-to-Noise Ratio in Magnetic Resonance Images Poster No.: C-0707 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Fukuyama, K. Imai,
Development and Evaluation of a New Method for Measuring of Signal-to-Noise Ratio in Magnetic Resonance Images Poster No.: C-0707 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Fukuyama, K. Imai,
Utility of 3D magnetic resonance imaging in preoperative evaluation of hepatobiliary diseases
 HPB, 2006; 8: 311317 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Utility of 3D magnetic resonance imaging in preoperative evaluation of hepatobiliary diseases R. TONGDEE 1, V.R. NARRA 1, E.P. OLIVEIRA 1, W. CHAPMAN 2, K.M. ELSAYES
HPB, 2006; 8: 311317 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Utility of 3D magnetic resonance imaging in preoperative evaluation of hepatobiliary diseases R. TONGDEE 1, V.R. NARRA 1, E.P. OLIVEIRA 1, W. CHAPMAN 2, K.M. ELSAYES
e-anatomy User Guide IMAIOS - e-anatomy
 e-anatomy User Guide IMAIOS - e-anatomy 3.1.5 Content 1 3 Chapter 1 : The IMAIOS site 4 How the site works 4 The color coding system 4 Princing system 5 Chapter 2 : e-anatomy 5 Presentation 6 The modules
e-anatomy User Guide IMAIOS - e-anatomy 3.1.5 Content 1 3 Chapter 1 : The IMAIOS site 4 How the site works 4 The color coding system 4 Princing system 5 Chapter 2 : e-anatomy 5 Presentation 6 The modules
Vessel Explorer: a tool for quantitative measurements in CT and MR angiography
 Clinical applications Vessel Explorer: a tool for quantitative measurements in CT and MR angiography J. Oliván Bescós J. Sonnemans R. Habets J. Peters H. van den Bosch T. Leiner Healthcare Informatics/Patient
Clinical applications Vessel Explorer: a tool for quantitative measurements in CT and MR angiography J. Oliván Bescós J. Sonnemans R. Habets J. Peters H. van den Bosch T. Leiner Healthcare Informatics/Patient
B-230 Skeletal maturity assessment web application
 B-230 Skeletal maturity assessment web application Scientific Paper B-230 Skeletal maturity assessment web application S. D. Bolboaca (Cluj Napoca/RO) Topic: Computer Applications 1 Purpose In pediatrics,
B-230 Skeletal maturity assessment web application Scientific Paper B-230 Skeletal maturity assessment web application S. D. Bolboaca (Cluj Napoca/RO) Topic: Computer Applications 1 Purpose In pediatrics,
31 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY GAYLE K. WRIGHT
 31 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY GAYLE K. WRIGHT Thorax 3D reconstruction from 64-slice CT scanner. OUTLINE Fundamentals of computed tomography, 304 Computed tomography and conventional radiography, 304 Historical
31 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY GAYLE K. WRIGHT Thorax 3D reconstruction from 64-slice CT scanner. OUTLINE Fundamentals of computed tomography, 304 Computed tomography and conventional radiography, 304 Historical
A Study of Medical Image Analysis System
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(25), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i25/80492, October 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study of Medical Image Analysis System Kim Tae-Eun
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(25), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i25/80492, October 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study of Medical Image Analysis System Kim Tae-Eun
Frequency split metal artifact reduction (FSMAR) in computed tomography
 The Johns Hopkins University Advanced Computer Integrated Surgery Group 4 Metal Artifact Removal in C-arm Cone-Beam CT Paper Seminar Critical Review of Frequency split metal artifact reduction (FSMAR)
The Johns Hopkins University Advanced Computer Integrated Surgery Group 4 Metal Artifact Removal in C-arm Cone-Beam CT Paper Seminar Critical Review of Frequency split metal artifact reduction (FSMAR)
Fundamentals of CT imaging
 SECTION 1 Fundamentals of CT imaging I History In the early 1970s Sir Godfrey Hounsfield s research produced the first clinically useful CT scans. Original scanners took approximately 6 minutes to perform
SECTION 1 Fundamentals of CT imaging I History In the early 1970s Sir Godfrey Hounsfield s research produced the first clinically useful CT scans. Original scanners took approximately 6 minutes to perform
Metal Artifact Reduction CT Techniques. Tobias Dietrich University Hospital Balgrist University of Zurich Switzerland
 Metal Artifact Reduction CT Techniques R S S S Tobias Dietrich University Hospital Balgrist University of Zurich Switzerland N. 1 v o 4 1 0 2. Postoperative CT Metal Implants CT is accurate for assessment
Metal Artifact Reduction CT Techniques R S S S Tobias Dietrich University Hospital Balgrist University of Zurich Switzerland N. 1 v o 4 1 0 2. Postoperative CT Metal Implants CT is accurate for assessment
Building soft-tissue constraints through a mass spring system for liver surgical simulations
 Building soft-tissue constraints through a mass spring system for liver surgical simulations e-poster (content for oral presentation): 754 Congress: ESMRMB 2008 Type: Scientific Paper Topic: Magnetic Resonance
Building soft-tissue constraints through a mass spring system for liver surgical simulations e-poster (content for oral presentation): 754 Congress: ESMRMB 2008 Type: Scientific Paper Topic: Magnetic Resonance
Interactive Boundary Detection for Automatic Definition of 2D Opacity Transfer Function
 Interactive Boundary Detection for Automatic Definition of 2D Opacity Transfer Function Martin Rauberger, Heinrich Martin Overhoff Medical Engineering Laboratory, University of Applied Sciences Gelsenkirchen,
Interactive Boundary Detection for Automatic Definition of 2D Opacity Transfer Function Martin Rauberger, Heinrich Martin Overhoff Medical Engineering Laboratory, University of Applied Sciences Gelsenkirchen,
IMPAX Volume Viewing 3D Visualization & Segmentation
 Getting started guide IMPAX Volume Viewing 3D Visualization & Segmentation This guide outlines the basic steps to perform and manipulate a 3D reconstruction of volumetric image data using IMPAX Volume
Getting started guide IMPAX Volume Viewing 3D Visualization & Segmentation This guide outlines the basic steps to perform and manipulate a 3D reconstruction of volumetric image data using IMPAX Volume
Volume rendering for interactive 3-d segmentation
 Volume rendering for interactive 3-d segmentation Klaus D. Toennies a, Claus Derz b a Dept. Neuroradiology, Inst. Diagn. Radiology, Inselspital Bern, CH-3010 Berne, Switzerland b FG Computer Graphics,
Volume rendering for interactive 3-d segmentation Klaus D. Toennies a, Claus Derz b a Dept. Neuroradiology, Inst. Diagn. Radiology, Inselspital Bern, CH-3010 Berne, Switzerland b FG Computer Graphics,
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class III
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class III 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class III 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
A comparison of different VNA philosophies, their associated configurations and respective properties in deployment
 A comparison of different VNA philosophies, their associated configurations and respective properties in deployment Poster No.: C-2178 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit
A comparison of different VNA philosophies, their associated configurations and respective properties in deployment Poster No.: C-2178 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit
Introduction to 3D Concepts
 PART I Introduction to 3D Concepts Chapter 1 Scene... 3 Chapter 2 Rendering: OpenGL (OGL) and Adobe Ray Tracer (ART)...19 1 CHAPTER 1 Scene s0010 1.1. The 3D Scene p0010 A typical 3D scene has several
PART I Introduction to 3D Concepts Chapter 1 Scene... 3 Chapter 2 Rendering: OpenGL (OGL) and Adobe Ray Tracer (ART)...19 1 CHAPTER 1 Scene s0010 1.1. The 3D Scene p0010 A typical 3D scene has several
Modeling and preoperative planning for kidney surgery
 Modeling and preoperative planning for kidney surgery Refael Vivanti Computer Aided Surgery and Medical Image Processing Lab Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel Advisor: Prof. Leo Joskowicz Clinical
Modeling and preoperative planning for kidney surgery Refael Vivanti Computer Aided Surgery and Medical Image Processing Lab Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel Advisor: Prof. Leo Joskowicz Clinical
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Velocity. Information. Joe Lee. April 4, 2000
 Locating Arteriovenous Malformations using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Velocity Information Joe Lee April 4, 2000 1 Introduction An arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is a congenital vascular defect where
Locating Arteriovenous Malformations using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Velocity Information Joe Lee April 4, 2000 1 Introduction An arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is a congenital vascular defect where
Computational Radiology Lab, Children s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA.
 Shape prior integration in discrete optimization segmentation algorithms M. Freiman Computational Radiology Lab, Children s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA. Email: moti.freiman@childrens.harvard.edu
Shape prior integration in discrete optimization segmentation algorithms M. Freiman Computational Radiology Lab, Children s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA. Email: moti.freiman@childrens.harvard.edu
Edge Detection for Dental X-ray Image Segmentation using Neural Network approach
 Volume 1, No. 7, September 2012 ISSN 2278-1080 The International Journal of Computer Science & Applications (TIJCSA) RESEARCH PAPER Available Online at http://www.journalofcomputerscience.com/ Edge Detection
Volume 1, No. 7, September 2012 ISSN 2278-1080 The International Journal of Computer Science & Applications (TIJCSA) RESEARCH PAPER Available Online at http://www.journalofcomputerscience.com/ Edge Detection
Human Heart Coronary Arteries Segmentation
 Human Heart Coronary Arteries Segmentation Qian Huang Wright State University, Computer Science Department Abstract The volume information extracted from computed tomography angiogram (CTA) datasets makes
Human Heart Coronary Arteries Segmentation Qian Huang Wright State University, Computer Science Department Abstract The volume information extracted from computed tomography angiogram (CTA) datasets makes
Improved Navigated Spine Surgery Utilizing Augmented Reality Visualization
 Improved Navigated Spine Surgery Utilizing Augmented Reality Visualization Zein Salah 1,2, Bernhard Preim 1, Erck Elolf 3, Jörg Franke 4, Georg Rose 2 1Department of Simulation and Graphics, University
Improved Navigated Spine Surgery Utilizing Augmented Reality Visualization Zein Salah 1,2, Bernhard Preim 1, Erck Elolf 3, Jörg Franke 4, Georg Rose 2 1Department of Simulation and Graphics, University
The use of the modulation transfer function for comparison and image quality assessment of commercially available hybrid PET-CT scanners
 The use of the modulation transfer function for comparison and image quality assessment of commercially available hybrid PET-CT scanners Poster No.: C-2943 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit
The use of the modulation transfer function for comparison and image quality assessment of commercially available hybrid PET-CT scanners Poster No.: C-2943 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit
icatvision Quick Reference
 icatvision Quick Reference Navigating the i-cat Interface This guide shows how to: View reconstructed images Use main features and tools to optimize an image. REMINDER Images are displayed as if you are
icatvision Quick Reference Navigating the i-cat Interface This guide shows how to: View reconstructed images Use main features and tools to optimize an image. REMINDER Images are displayed as if you are
Prostate Detection Using Principal Component Analysis
 Prostate Detection Using Principal Component Analysis Aamir Virani (avirani@stanford.edu) CS 229 Machine Learning Stanford University 16 December 2005 Introduction During the past two decades, computed
Prostate Detection Using Principal Component Analysis Aamir Virani (avirani@stanford.edu) CS 229 Machine Learning Stanford University 16 December 2005 Introduction During the past two decades, computed
FOREWORD TO THE SPECIAL ISSUE ON MOTION DETECTION AND COMPENSATION
 Philips J. Res. 51 (1998) 197-201 FOREWORD TO THE SPECIAL ISSUE ON MOTION DETECTION AND COMPENSATION This special issue of Philips Journalof Research includes a number of papers presented at a Philips
Philips J. Res. 51 (1998) 197-201 FOREWORD TO THE SPECIAL ISSUE ON MOTION DETECTION AND COMPENSATION This special issue of Philips Journalof Research includes a number of papers presented at a Philips
AORTA CTA VPMC-12419
 AORTA CTA VPMC-12419 Workflow Overview: The Aorta can be post-processed in various ways. Auto Bone Removal and Vessel Pick provide a quick overview of the entire Aorta. Vessel Probe creates a centerline
AORTA CTA VPMC-12419 Workflow Overview: The Aorta can be post-processed in various ways. Auto Bone Removal and Vessel Pick provide a quick overview of the entire Aorta. Vessel Probe creates a centerline
Ch. 4 Physical Principles of CT
 Ch. 4 Physical Principles of CT CLRS 408: Intro to CT Department of Radiation Sciences Review: Why CT? Solution for radiography/tomography limitations Superimposition of structures Distinguishing between
Ch. 4 Physical Principles of CT CLRS 408: Intro to CT Department of Radiation Sciences Review: Why CT? Solution for radiography/tomography limitations Superimposition of structures Distinguishing between
[PDR03] RECOMMENDED CT-SCAN PROTOCOLS
![[PDR03] RECOMMENDED CT-SCAN PROTOCOLS [PDR03] RECOMMENDED CT-SCAN PROTOCOLS](/thumbs/72/66454100.jpg) SURGICAL & PROSTHETIC DESIGN [PDR03] RECOMMENDED CT-SCAN PROTOCOLS WORK-INSTRUCTIONS DOCUMENT (CUSTOMER) RECOMMENDED CT-SCAN PROTOCOLS [PDR03_V1]: LIVE 1 PRESCRIBING SURGEONS Patient-specific implants,
SURGICAL & PROSTHETIC DESIGN [PDR03] RECOMMENDED CT-SCAN PROTOCOLS WORK-INSTRUCTIONS DOCUMENT (CUSTOMER) RECOMMENDED CT-SCAN PROTOCOLS [PDR03_V1]: LIVE 1 PRESCRIBING SURGEONS Patient-specific implants,
Towards Projector-based Visualization for Computer-assisted CABG at the Open Heart
 Towards Projector-based Visualization for Computer-assisted CABG at the Open Heart Christine Hartung 1, Claudia Gnahm 1, Stefan Sailer 1, Marcel Schenderlein 1, Reinhard Friedl 2, Martin Hoffmann 3, Klaus
Towards Projector-based Visualization for Computer-assisted CABG at the Open Heart Christine Hartung 1, Claudia Gnahm 1, Stefan Sailer 1, Marcel Schenderlein 1, Reinhard Friedl 2, Martin Hoffmann 3, Klaus
FINDING THE TRUE EDGE IN CTA
 FINDING THE TRUE EDGE IN CTA by: John A. Rumberger, PhD, MD, FACC Your patient has chest pain. The Cardiac CT Angiography shows plaque in the LAD. You adjust the viewing window trying to evaluate the stenosis
FINDING THE TRUE EDGE IN CTA by: John A. Rumberger, PhD, MD, FACC Your patient has chest pain. The Cardiac CT Angiography shows plaque in the LAD. You adjust the viewing window trying to evaluate the stenosis
INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL IMAGING- 3D LOCALIZATION LAB MANUAL 1. Modifications for P551 Fall 2013 Medical Physics Laboratory
 INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL IMAGING- 3D LOCALIZATION LAB MANUAL 1 Modifications for P551 Fall 2013 Medical Physics Laboratory Introduction Following the introductory lab 0, this lab exercise the student through
INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL IMAGING- 3D LOCALIZATION LAB MANUAL 1 Modifications for P551 Fall 2013 Medical Physics Laboratory Introduction Following the introductory lab 0, this lab exercise the student through
Functional Analysis of the Vertebral Column Based on MR and Direct Volume Rendering
 Functional Analysis of the Vertebral Column Based on MR and Direct Volume Rendering P. Hastreiter 1, C. Rezk-Salama 2,K.Eberhardt 3 and B. Tomandl 3,andT.Ertl 4 1 Neurocenter, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg,
Functional Analysis of the Vertebral Column Based on MR and Direct Volume Rendering P. Hastreiter 1, C. Rezk-Salama 2,K.Eberhardt 3 and B. Tomandl 3,andT.Ertl 4 1 Neurocenter, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg,
Integrating Ontologies with Three-Dimensional Models of Anatomy
 Integrating Ontologies with Three-Dimensional Models of Anatomy Daniel L. Rubin Yasser Bashir David Grossman Parvati Dev Mark A. Musen Stanford Medical Informatics Stanford University Projectile Injury
Integrating Ontologies with Three-Dimensional Models of Anatomy Daniel L. Rubin Yasser Bashir David Grossman Parvati Dev Mark A. Musen Stanford Medical Informatics Stanford University Projectile Injury
rscriptor Tutorial 1 Introduction Table of Contents
 rscriptor Tutorial sales@scriptorsoftware.com www.scriptorsoftware.com 1-844-230-0455 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Tutorial #1 rscriptor header... 2 3 Tutorial #2 Narrative Reporting... 3 4
rscriptor Tutorial sales@scriptorsoftware.com www.scriptorsoftware.com 1-844-230-0455 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Tutorial #1 rscriptor header... 2 3 Tutorial #2 Narrative Reporting... 3 4
Evaluation of surface and volume rendering in 3D-CT of facial fractures
 (2006) 35, 227 231 q 2006 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Evaluation of surface and volume rendering in 3D-CT of facial fractures T Rodt*,1, SO Bartling 2, JE Zajaczek
(2006) 35, 227 231 q 2006 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Evaluation of surface and volume rendering in 3D-CT of facial fractures T Rodt*,1, SO Bartling 2, JE Zajaczek
Image Analysis, Geometrical Modelling and Image Synthesis for 3D Medical Imaging
 Image Analysis, Geometrical Modelling and Image Synthesis for 3D Medical Imaging J. SEQUEIRA Laboratoire d'informatique de Marseille - FRE CNRS 2246 Faculté des Sciences de Luminy, 163 avenue de Luminy,
Image Analysis, Geometrical Modelling and Image Synthesis for 3D Medical Imaging J. SEQUEIRA Laboratoire d'informatique de Marseille - FRE CNRS 2246 Faculté des Sciences de Luminy, 163 avenue de Luminy,
Scalar Data. Visualization Torsten Möller. Weiskopf/Machiraju/Möller
 Scalar Data Visualization Torsten Möller Weiskopf/Machiraju/Möller Overview Basic strategies Function plots and height fields Isolines Color coding Volume visualization (overview) Classification Segmentation
Scalar Data Visualization Torsten Möller Weiskopf/Machiraju/Möller Overview Basic strategies Function plots and height fields Isolines Color coding Volume visualization (overview) Classification Segmentation
Chapter 48 3D video reconstructions of normal and abnormal human vocal folds
 405 48 3D video reconstructions of normal and abnormal human vocal folds Chapter 48 3D video reconstructions of normal and abnormal human vocal folds Jarosław Sova, Joanna Cieszyńska, Jarosław Kijewski
405 48 3D video reconstructions of normal and abnormal human vocal folds Chapter 48 3D video reconstructions of normal and abnormal human vocal folds Jarosław Sova, Joanna Cieszyńska, Jarosław Kijewski
Available Online through
 Available Online through www.ijptonline.com ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Research Article ANALYSIS OF CT LIVER IMAGES FOR TUMOUR DIAGNOSIS BASED ON CLUSTERING TECHNIQUE AND TEXTURE FEATURES M.Krithika
Available Online through www.ijptonline.com ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Research Article ANALYSIS OF CT LIVER IMAGES FOR TUMOUR DIAGNOSIS BASED ON CLUSTERING TECHNIQUE AND TEXTURE FEATURES M.Krithika
Image Acquisition Systems
 Image Acquisition Systems Goals and Terminology Conventional Radiography Axial Tomography Computer Axial Tomography (CAT) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) PET, SPECT Ultrasound Microscopy Imaging ITCS
Image Acquisition Systems Goals and Terminology Conventional Radiography Axial Tomography Computer Axial Tomography (CAT) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) PET, SPECT Ultrasound Microscopy Imaging ITCS
Evaluation of Diffusion Techniques for Improved Vessel Visualization and Quantification in Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography
 Evaluation of Diffusion Techniques for Improved Vessel Visualization and Quantification in Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography Erik Meijering 1, Wiro Niessen 1, Joachim Weickert 2, and Max Viergever
Evaluation of Diffusion Techniques for Improved Vessel Visualization and Quantification in Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography Erik Meijering 1, Wiro Niessen 1, Joachim Weickert 2, and Max Viergever
Probabilistic Tracking and Model-based Segmentation of 3D Tubular Structures
 Probabilistic Tracking and Model-based Segmentation of 3D Tubular Structures Stefan Wörz, William J. Godinez, Karl Rohr University of Heidelberg, BIOQUANT, IPMB, and DKFZ Heidelberg, Dept. Bioinformatics
Probabilistic Tracking and Model-based Segmentation of 3D Tubular Structures Stefan Wörz, William J. Godinez, Karl Rohr University of Heidelberg, BIOQUANT, IPMB, and DKFZ Heidelberg, Dept. Bioinformatics
3/27/2012 WHY SPECT / CT? SPECT / CT Basic Principles. Advantages of SPECT. Advantages of CT. Dr John C. Dickson, Principal Physicist UCLH
 3/27/212 Advantages of SPECT SPECT / CT Basic Principles Dr John C. Dickson, Principal Physicist UCLH Institute of Nuclear Medicine, University College London Hospitals and University College London john.dickson@uclh.nhs.uk
3/27/212 Advantages of SPECT SPECT / CT Basic Principles Dr John C. Dickson, Principal Physicist UCLH Institute of Nuclear Medicine, University College London Hospitals and University College London john.dickson@uclh.nhs.uk
Interactive segmentation of vascular structures in CT images for liver surgery planning
 Interactive segmentation of vascular structures in CT images for liver surgery planning L. Wang¹, C. Hansen¹, S.Zidowitz¹, H. K. Hahn¹ ¹ Fraunhofer MEVIS, Institute for Medical Image Computing, Bremen,
Interactive segmentation of vascular structures in CT images for liver surgery planning L. Wang¹, C. Hansen¹, S.Zidowitz¹, H. K. Hahn¹ ¹ Fraunhofer MEVIS, Institute for Medical Image Computing, Bremen,
Scalar Data. CMPT 467/767 Visualization Torsten Möller. Weiskopf/Machiraju/Möller
 Scalar Data CMPT 467/767 Visualization Torsten Möller Weiskopf/Machiraju/Möller Overview Basic strategies Function plots and height fields Isolines Color coding Volume visualization (overview) Classification
Scalar Data CMPT 467/767 Visualization Torsten Möller Weiskopf/Machiraju/Möller Overview Basic strategies Function plots and height fields Isolines Color coding Volume visualization (overview) Classification
An approach to calculate and visualize intraoperative scattered radiation exposure
 Peter L. Reicertz Institut für Medizinische Informatik An approach to calculate and visualize intraoperative scattered radiation exposure Markus Wagner University of Braunschweig Institute of Technology
Peter L. Reicertz Institut für Medizinische Informatik An approach to calculate and visualize intraoperative scattered radiation exposure Markus Wagner University of Braunschweig Institute of Technology
TECHNICAL REPORT. Smart Linking of 2D and 3D Views in Medical Applications
 Institut für Computergraphik und Algorithmen Technische Universität Wien Karlsplatz 13/186/2 A-1040 Wien AUSTRIA Tel: +43 (1) 58801-18601 Fax: +43 (1) 58801-18698 Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms
Institut für Computergraphik und Algorithmen Technische Universität Wien Karlsplatz 13/186/2 A-1040 Wien AUSTRIA Tel: +43 (1) 58801-18601 Fax: +43 (1) 58801-18698 Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms
SAMPLING AND NOISE. Increasing the number of samples per pixel gives an anti-aliased image which better represents the actual scene.
 SAMPLING AND NOISE When generating an image, Mantra must determine a color value for each pixel by examining the scene behind the image plane. Mantra achieves this by sending out a number of rays from
SAMPLING AND NOISE When generating an image, Mantra must determine a color value for each pixel by examining the scene behind the image plane. Mantra achieves this by sending out a number of rays from
Computer-Tomography II: Image reconstruction and applications
 Computer-Tomography II: Image reconstruction and applications Prof. Dr. U. Oelfke DKFZ Heidelberg Department of Medical Physics (E040) Im Neuenheimer Feld 280 69120 Heidelberg, Germany u.oelfke@dkfz.de
Computer-Tomography II: Image reconstruction and applications Prof. Dr. U. Oelfke DKFZ Heidelberg Department of Medical Physics (E040) Im Neuenheimer Feld 280 69120 Heidelberg, Germany u.oelfke@dkfz.de
MRI Visualisation by Digitally Reconstructed Radiographs
 Antoine Serrurier *a1, Andrea Bönsch b, Robert Lau a, Thomas M. Deserno (né Lehmann) a a Department of Medical Informatics, Uniklinik RWTH Aachen, Germany; b Virtual Reality Group, RWTH Aachen University,
Antoine Serrurier *a1, Andrea Bönsch b, Robert Lau a, Thomas M. Deserno (né Lehmann) a a Department of Medical Informatics, Uniklinik RWTH Aachen, Germany; b Virtual Reality Group, RWTH Aachen University,
