Conic Solution of Euler s Triangle Determination Problem
|
|
|
- Christine Sullivan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 12 (2008), o. 1, 1 6. Conic Solution of Euler s Triangle Determination Problem Paul Yiu Dept. of Mathematical Sciences, Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida, 33431, USA yiu@fau.edu Abstract. We study Euler s problem of determination of a triangle from its circumcenter, orthocenter, and incenter as a problem of geometric construction. While it cannot be solved using ruler and compass, we construct the vertices by intersecting a circle with a rectangular hyperbola, both easily constructed from the given triangle centers. Keywords: circumcenter, orthocenter, incenter, Feuerbach point, rectangular hyperbola MSC 2007: 51M05, 51M15 1. Euler s triangle determination problem Leonhard Euler studied in his famous paper [2] the problem of determining a triangle ABC from its circumcenter, orthocenter, and incenter. Euler constructed a cubic polynomial whose roots are the lengths of the sides, and whose coefficients are rational functions of the distances among the three given triangle centers. e showed that when =, the cubic polynomial factors nontrivially, and gave the roots explicitly. With a numerical example, Euler showed that in the general case, the solution reduces to the trisection of an angle. n this note, we address Euler s determination problem as a construction problem. While the problem cannot be solved with the traditional restriction to ruler and compass, we shall nevertheless give the vertices as the intersections of two conics, one a circle and the other a rectangular hyperbola easily constructed from,, and. Let G and be the points which divide in the ratio G : G : = 2 : 1 : 3. These are the centroid and the nine-point center of the required triangle (if it exists). A necessary and sufficient condition for the existence of ABC is given by the following theorem. For details, see [4, 5, 6, 7]. Theorem 1 [A. Guinand] Let D be the open circular disk with diameter G. A triangle ABC exists with circumcenter, orthocenter, and incenter if and only if D \ {}. SS /$ 2.50 c 2008 eldermann Verlag
2 2 P. Yiu: Euler s Triangle Determination Problem 2. Ruler and compass construction of circumcircle and incircle Let R and r denote respectively the circumradius and inradius of triangle ABC. n [2], Euler established, among other things, the famous relation 2 = R(R 2r). (1) With the help of the famous Feuerbach theorem [3], discovered half a century after Euler s paper [2], that the nine-point circle of a triangle is tangent internally to the incircle, we can easily construct the circumcircle, the incircle, the nine-point circle, and their point of tangency. According to the Feuerbach theorem, = R 2 r. (2) Together with (1), this gives 2R = 2, and suggests the following ruler-and-compass construction. See also [5], which studies the same problem from a paper-folding approach. Y F X Figure 1: ncircle from,, Construction 2 Suppose,, satisfy D \ {}. (1) Extend to X such that X = 2 ; construct the circle X, and extend to intersect the circle again at Y. The length of Y is twice the circumradius, and four times the radius of the nine-point circle. (2) Construct the circumcircle () and the nine-point circle (). (3) Construct the intersection F of the circle () with the half line, and the circle, center, passing through F. This is the incircle and F is the (Feuerbach) point of tangency with the nine-point circle (see Fig. 1). Starting with an arbitrary point A on (), by drawing tangents, we can complete a triangle ABC with incircle () and circumcircle (). The locus of the orthocenter of the variable triangle ABC is the circle, center P, passing through. We determine the specific triangle with as orthocenter. First we consider a special case where the constructibility with ruler and compass is evident from Euler s calculations.
3 3. The case = P. Yiu: Euler s Triangle Determination Problem 3 f =, consider the intersection A of the half line with the circumcircle (see Fig. 2). We complete a triangle ABC with () as circumcircle and () as incircle. The orthocenter of triangle ABC lies on the reflection of A in the line A. This is the line A. Since angle A is a right angle, for the midpoint M of A, we have M = 1 2 A = 1 2 A = R 2. This means that M is a point on the nine-point circle. t is the midpoint of the segment joining A to the orthocenter. t follows that the orthocenter must be. Y A C X B Figure 2: Triangle from,, with = Remark: ne referee has kindly pointed us to [1], which shows that in this case the angle BAC must be π, and the Euler line cuts off an equilateral triangle with the sides AB and 3 AC. 4. The general case: construction with the aid of a conic Set up a cartesian coordinate system with origin at. Assume = (k, 0) and = (p, q). Since A = A, and likewise for B and C, the vertices A, B, C are on the locus of the point P for which P = P. f P = (x, y), a routine calculation shows that the locus of P is a curve K: K(x, y) = 0, where K(x, y) := 2qx 3 (2p k)x 2 y + 2qxy 2 (2p k)y 3 2(p + k)qx 2 + 2(p 2 q 2 )xy + 2(p k)qy 2 + 2kpqx k(p 2 q 2 )y.
4 4 P. Yiu: Euler s Triangle Determination Problem ote that K(k, 0) = 0, i.e., K contains the point. By computing the circumradius R, we easily obtain the equation of the circumcircle () : G(x, y) = 0, where G(x, y) := x 2 + y 2 (p2 + q 2 ) 2 (2p k) 2 + 4q 2. t is possible to find a linear function L(x, y) such that Q(x, y) := K(x, y) L(x, y)g(x, y) does not contain third degree terms. For example, by choosing we have L(x, y) := 2qx (2p k)y 2qk, Q(x, y) = 2pqx 2 + 2(p 2 q 2 )xy + 2pqy 2 k2 (k 4p)(p 2 q 2 ) + k(3p 2 5q 2 )(p 2 + q 2 ) + 2p(p 2 + q 2 ) 2 (2p k) 2 + 4q 2 x + 2q(kp((2p k)2 + 4q 2 ) + (p 2 + q 2 ) 2 ) (2p k) 2 + 4q 2 y 2k(p2 + q 2 ) 2 q (2p k) 2 + 4q 2. The finite intersections of () with K are precisely the same with the conic C defined by Q(x, y) = 0. ote that the coefficients of x and y in L are dictated by the elimination of the third degree terms in K L G. We have chosen the constant term such that L(k, 0) = 0, so that L(x, y) = 0 represents the line P parallel to. t follows that Q(k, 0) = 0, and the conic C contains the vertices and the orthocenter of the required triangle ABC. t is necessarily a rectangular hyperbola. This fact also follows from the factorization of the quadratic part of Q, namely, 2(px + qy)(qx py). This means that C is a rectangular hyperbola whose asymptotes have slopes q/p and p/q. These are parallel and perpendicular to the segment. To construct the rectangular hyperbola C, we identify its center. This is the point with coordinates (u, v) for which the quadratic polynomial Q(x u, y v) has no first degree terms in x and y. A routine calculation gives ( ) k((2p k) = 2 p 2 + 5q 2 ) + 2p(p 2 + q 2 ) (p, 2 + q 2 kp)q 2((2p k) 2 + 4q 2 ) (2p k) 2 + 4q ( 2 k = 2 + (2p k)(p2 + q 2 ) + 2kq 2, 2((2p k) 2 + 4q 2 ) (p 2 + q 2 )q kpq (2p k) 2 + 4q 2 ). (3) Since C is a rectangular hyperbola, its center lies on the nine-point circle (). The following observation leads to a very simple construction of the center. Proposition 3 The Feuerbach point F lies on the asymptote perpendicular to. Proof: The nine-point circle has the equation ( x k 2 + y 2) 2 (p 2 + q 2 ) 2 = 0. (4) 4((2p k) 2 + 4q 2 )
5 P. Yiu: Euler s Triangle Determination Problem 5 F F Figure 3: Center of rectangular hyperbola C This intersects the line at two points, the Feuerbach point and its antipode (on the nine-point circle). The Feuerbach point is the point ( k F = 2 + (2p ) k)(p2 + q 2 ) 2((2p k) 2 + 4q 2 ), (p 2 + q 2 )q. (2p k) 2 + 4q 2 t is easy to see that the line F has slope p, and is perpendicular to the line. q Corollary 4 The center of the rectangular hyperbola C is the second intersection of the nine-point circle () with the perpendicular from F to (Fig. 3). t is well known that if C is a rectangular hyperbola passes through the vertices of a triangle ABC, its fourth intersection with the circumcircle at the reflection of the orthocenter of the triangle in the center of the hyperbola. Therefore, one of the intersections of C with the circle () is the reflection of in. The other three are the vertices of the required triangle (see Fig. 4). References [1]. Dirnböck: Der Zusammenhang zwischen der Gestalt eines Dreieckes und der Lage der Eulerschen Geraden. Die Allgemeinbildende öhere Schule, r. 8/1965. [2] L. Euler: Solutio facilis problematum quorundam geometricorum difficillimorum. ovi Comm. Acad. Scie. Petropolitanae 11 (1765); reprinted in pera omnia, serie prima, vol. 26 (ed. by A. Speiser), (n. 325) [3] K.W. Feuerbach: Eigenschaften einiger merkwürdigen Punkte des geradlinigen Dreiecks, und mehrerer durch sie bestimmten Linien und Figuren. 1822; English translation by R.A. Johnson, in D.E. Smith (ed.), A Source Book in Mathematics, 1929; Dover reprint, 1959; pp
6 6 P. Yiu: Euler s Triangle Determination Problem A F F C B Figure 4: Triangle ABC with given,, [4] A. Guinand: Euler lines, tritangent centers, and their triangles. Amer. Math. Monthly 91, (1984). [5] B. Scimemi: Paper-folding and Euler s theorem revisited. Forum Geom. 2, (2002). [6] G.C. Smith: Statics and moduli space of triangles. Forum Geom. 5, (2005). [7] J. Stern: Euler s triangle determination problem. Forum Geom. 7, 1 9 (2007). Received ctober 10, 2007; final form May 13, 2008
Chapter 7. Some triangle centers. 7.1 The Euler line Inferior and superior triangles
 hapter 7 Some triangle centers 7.1 The Euler line 7.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,. The two triangles
hapter 7 Some triangle centers 7.1 The Euler line 7.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,. The two triangles
SOAR2001 GEOMETRY SUMMER 2001
 SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
SOME PROPERTIES OF PARABOLAS TANGENT TO TWO SIDES OF A TRIANGLE
 Journal of Mathematical Sciences: Advances and Applications Volume 48, 017, Pages 47-5 Available at http://scientificadvances.co.in DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1864/jmsaa_710011907 SOME PROPERTIES OF PARABOLAS
Journal of Mathematical Sciences: Advances and Applications Volume 48, 017, Pages 47-5 Available at http://scientificadvances.co.in DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1864/jmsaa_710011907 SOME PROPERTIES OF PARABOLAS
Forum Geometricorum Volume 3 (2003) FORUM GEOM ISSN Harcourt s Theorem. Nikolaos Dergiades and Juan Carlos Salazar
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 3 (2003) 117 124. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Harcourt s Theorem Nikolaos Dergiades and Juan arlos Salazar bstract. We give a proof of Harcourt s theorem that if the signed distances
Forum Geometricorum Volume 3 (2003) 117 124. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Harcourt s Theorem Nikolaos Dergiades and Juan arlos Salazar bstract. We give a proof of Harcourt s theorem that if the signed distances
A Conic Associated with Euler Lines
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) 17 23. FRU GE ISSN 1534-1178 onic ssociated with Euler Lines Juan Rodríguez, Paula anuel, and Paulo Semião bstract. We study the locus of a point for which the Euler
Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) 17 23. FRU GE ISSN 1534-1178 onic ssociated with Euler Lines Juan Rodríguez, Paula anuel, and Paulo Semião bstract. We study the locus of a point for which the Euler
On the Complement of the Schiffler Point
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 5 (005) 149 164. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On the omplement of the Schiffler Point Khoa Lu Nguyen bstract. onsider a triangle with excircles (), ( ), (), tangent to the nine-point
Forum Geometricorum Volume 5 (005) 149 164. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On the omplement of the Schiffler Point Khoa Lu Nguyen bstract. onsider a triangle with excircles (), ( ), (), tangent to the nine-point
THE TRIANGLE OF REFLECTIONS. Jesus Torres. A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of. The Charles E. Schmidt College of Science
 THE TRIANGLE OF REFLECTIONS by Jesus Torres A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of The Charles E. Schmidt College of Science in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science
THE TRIANGLE OF REFLECTIONS by Jesus Torres A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of The Charles E. Schmidt College of Science in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science
Solutions to the Test. Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written?
 Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011
 MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011 Open the document Getting Started with GeoGebra and follow the instructions either to download and install it on your computer or to run it as a Webstart
MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011 Open the document Getting Started with GeoGebra and follow the instructions either to download and install it on your computer or to run it as a Webstart
On the Cyclic Quadrilaterals with the Same Varignon Parallelogram
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 18 (2018) 103 113. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On the Cyclic Quadrilaterals with the Same Varignon Parallelogram Sándor Nagydobai Kiss Abstract. The circumcenters and anticenters
Forum Geometricorum Volume 18 (2018) 103 113. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On the Cyclic Quadrilaterals with the Same Varignon Parallelogram Sándor Nagydobai Kiss Abstract. The circumcenters and anticenters
The Orthic-of-Intouch and Intouch-of-Orthic Triangles
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (006 171 177 FRUM GEM SSN 1534-1178 The rthic-of-ntouch and ntouch-of-rthic Triangles Sándor Kiss bstract arycentric coordinates are used to prove that the othic of intouch
Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (006 171 177 FRUM GEM SSN 1534-1178 The rthic-of-ntouch and ntouch-of-rthic Triangles Sándor Kiss bstract arycentric coordinates are used to prove that the othic of intouch
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra
 Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
Exterior Region Interior Region
 Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited
 230 Chapter 5. AREAS 5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited 259. Theorem. The areas of squares constructed on the legs of a right triangle add up to the area of the square constructed on its hypotenuse. This
230 Chapter 5. AREAS 5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited 259. Theorem. The areas of squares constructed on the legs of a right triangle add up to the area of the square constructed on its hypotenuse. This
MST Topics in the History of Mathematics
 MST Topics in the History of Mathematics Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Summer 2011 3B: Euclid s Book VI (Similar triangles) Euclide VI.1,2 VI.1. Triangles and parallelograms
MST Topics in the History of Mathematics Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Summer 2011 3B: Euclid s Book VI (Similar triangles) Euclide VI.1,2 VI.1. Triangles and parallelograms
Some Constructions Related to the Kiepert Hyperbola
 Forum eometricorum Volume 6 2006 343 357. FORUM EOM ISSN 534-78 Some onstructions Related to the Kiepert yperbola Paul Yiu bstract. iven a reference triangle and its Kiepert hyperbola K, we study several
Forum eometricorum Volume 6 2006 343 357. FORUM EOM ISSN 534-78 Some onstructions Related to the Kiepert yperbola Paul Yiu bstract. iven a reference triangle and its Kiepert hyperbola K, we study several
Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips
 & present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
& present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
Plane Geometry. Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2011
 lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) FORUM GEOM ISSN Pseudo-Incircles. Stanley Rabinowitz
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) 107 115. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Pseudo-Incircles Stanley Rabinowitz bstract. This paper generalizes properties of mixtilinear incircles. Let (S) be any circle in
Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) 107 115. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Pseudo-Incircles Stanley Rabinowitz bstract. This paper generalizes properties of mixtilinear incircles. Let (S) be any circle in
The uses of homogeneous barycentric coordinates in plane euclidean geometry
 The uses of homogeneous barycentric coordinates in plane euclidean geometry Paul Yiu Abstract. The notion of homogeneous barycentric coordinates provides a powerful tool of analysing problems in plane
The uses of homogeneous barycentric coordinates in plane euclidean geometry Paul Yiu Abstract. The notion of homogeneous barycentric coordinates provides a powerful tool of analysing problems in plane
CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE
 CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE ARSENIY V. AKOPYAN Abstract. Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE ARSENIY V. AKOPYAN Abstract. Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
September 23,
 1. In many ruler and compass constructions it is important to know that the perpendicular bisector of a secant to a circle is a diameter of that circle. In particular, as a limiting case, this obtains
1. In many ruler and compass constructions it is important to know that the perpendicular bisector of a secant to a circle is a diameter of that circle. In particular, as a limiting case, this obtains
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
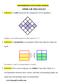 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined
 MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
CONSTRUCTIONS Introduction Division of a Line Segment
 216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle
 Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle Arseniy V. Akopyan Abstract Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle Arseniy V. Akopyan Abstract Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures
 MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
Figure 1. The centroid and the symmedian point of a triangle
 ISOGONAL TRANSFORMATIONS REVISITED WITH GEOGEBRA Péter KÖRTESI, Associate Professor Ph.D., University of Miskolc, Miskolc, Hungary Abstract: The symmedian lines and the symmedian point of a given triangle
ISOGONAL TRANSFORMATIONS REVISITED WITH GEOGEBRA Péter KÖRTESI, Associate Professor Ph.D., University of Miskolc, Miskolc, Hungary Abstract: The symmedian lines and the symmedian point of a given triangle
Chapter 10 Similarity
 Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
On a Geometric Locus in Taxicab Geometry
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 14 014) 117 11 FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On a Geometric Locus in Taxicab Geometry Bryan Brzycki Abstract In axiomatic geometry, the taxicab model of geometry is important as
Forum Geometricorum Volume 14 014) 117 11 FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On a Geometric Locus in Taxicab Geometry Bryan Brzycki Abstract In axiomatic geometry, the taxicab model of geometry is important as
The Monge Point and the 3(n+1) Point Sphere of an n-simplex
 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 9 (2005), No. 1, 31 36. The Monge Point and the 3(n+1) Point Sphere of an n-simplex Ma lgorzata Buba-Brzozowa Department of Mathematics and Information Sciences,
Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 9 (2005), No. 1, 31 36. The Monge Point and the 3(n+1) Point Sphere of an n-simplex Ma lgorzata Buba-Brzozowa Department of Mathematics and Information Sciences,
Forum Geometricorum Volume 13 (2013) FORUM GEOM ISSN Pedal Polygons. Daniela Ferrarello, Maria Flavia Mammana, and Mario Pennisi
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 13 (2013) 153 164. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 edal olygons Daniela Ferrarello, Maria Flavia Mammana, and Mario ennisi Abstract. We study the pedal polygon H n of a point with
Forum Geometricorum Volume 13 (2013) 153 164. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 edal olygons Daniela Ferrarello, Maria Flavia Mammana, and Mario ennisi Abstract. We study the pedal polygon H n of a point with
Vectors in Geometry. 1.5 The diagram below shows vector v 7, 4 drawn in standard position. Draw 3 vectors equivalent to vector v.
 Vectors in Geometry 1. Draw the following segments using an arrow to indicate direction: a. from (3, 1) to (10, 3) b. from ( 5, 5) to (2, 9) c. from ( 4.2, 6.1) to (2.8, 2.1) d. What do they have in common?
Vectors in Geometry 1. Draw the following segments using an arrow to indicate direction: a. from (3, 1) to (10, 3) b. from ( 5, 5) to (2, 9) c. from ( 4.2, 6.1) to (2.8, 2.1) d. What do they have in common?
PARABOLA SYNOPSIS 1.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP
 PARABOLA SYNOPSIS.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP PM = where PM is perpendicular to the directrix, then the locus of P is a parabola... S ax + hxy
PARABOLA SYNOPSIS.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP PM = where PM is perpendicular to the directrix, then the locus of P is a parabola... S ax + hxy
The computer program Discoverer as a tool of mathematical investigation
 Journal of Computer-Generated Mathematics The computer program Discoverer as a tool of mathematical investigation Sava Grozdev, Deko Dekov Submitted: 1 December 2013. Publication date: 30 June 2014 Abstract.
Journal of Computer-Generated Mathematics The computer program Discoverer as a tool of mathematical investigation Sava Grozdev, Deko Dekov Submitted: 1 December 2013. Publication date: 30 June 2014 Abstract.
Geometry Rules. Triangles:
 Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS, Glossary
 TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS, 2003 2004 Glossary Absolute value The size of a number with its + or sign removed. The absolute value of 3.2 is 3.2, the absolute value of +4.6 is 4.6. We write this: 3.2 = 3.2
TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS, 2003 2004 Glossary Absolute value The size of a number with its + or sign removed. The absolute value of 3.2 is 3.2, the absolute value of +4.6 is 4.6. We write this: 3.2 = 3.2
CLASSICAL THEOREMS IN PLANE GEOMETRY. September 2007 BC 1 AC 1 CA 1 BA 1 = 1.
 SSI THEORES I E GEOETRY ZVEZEI STKOV September 2007 ote: ll objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual plane. We say that several points are collinear if they lie on a line. Similarly,
SSI THEORES I E GEOETRY ZVEZEI STKOV September 2007 ote: ll objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual plane. We say that several points are collinear if they lie on a line. Similarly,
Cyclic Quadrilaterals Associated With Squares
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 11 (2011) 223 229. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Cyclic Quadrilaterals Associated With Squares Mihai Cipu Abstract. We discuss a family of problems asking to find the geometrical
Forum Geometricorum Volume 11 (2011) 223 229. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Cyclic Quadrilaterals Associated With Squares Mihai Cipu Abstract. We discuss a family of problems asking to find the geometrical
5.4 Medians and Altitudes in Triangles
 5.4. Medians and Altitudes in Triangles www.ck12.org 5.4 Medians and Altitudes in Triangles Learning Objectives Define median and find their point of concurrency in a triangle. Apply medians to the coordinate
5.4. Medians and Altitudes in Triangles www.ck12.org 5.4 Medians and Altitudes in Triangles Learning Objectives Define median and find their point of concurrency in a triangle. Apply medians to the coordinate
Construction of Malfatti Squares
 Forum eometricorum Volume 8 (008) 49 59. FORUM EOM ISSN 534-78 onstruction of Malfatti Squares Floor van Lamoen and Paul Yiu bstract. We give a very simple construction of the Malfatti squares of a triangle,
Forum eometricorum Volume 8 (008) 49 59. FORUM EOM ISSN 534-78 onstruction of Malfatti Squares Floor van Lamoen and Paul Yiu bstract. We give a very simple construction of the Malfatti squares of a triangle,
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Geometry. Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 G.CO.2. Common Core Institute
 Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry
 8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry 8.1 The circum-center Figure 8.1: In hyperbolic geometry, the perpendicular bisectors can be parallel as shown but this figure is impossible in Euclidean geometry.
8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry 8.1 The circum-center Figure 8.1: In hyperbolic geometry, the perpendicular bisectors can be parallel as shown but this figure is impossible in Euclidean geometry.
Recreational Mathematics
 Recreational Mathematics Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Summer 2003 Chapters 1 4 Version 030627 Please note that p.110 has been replaced. Chapter 1 Lattice polygons 1 Pick
Recreational Mathematics Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Summer 2003 Chapters 1 4 Version 030627 Please note that p.110 has been replaced. Chapter 1 Lattice polygons 1 Pick
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Topics in geometry Exam 1 Solutions 7/8/4
 Topics in geometry Exam 1 Solutions 7/8/4 Question 1 Consider the following axioms for a geometry: There are exactly five points. There are exactly five lines. Each point lies on exactly three lines. Each
Topics in geometry Exam 1 Solutions 7/8/4 Question 1 Consider the following axioms for a geometry: There are exactly five points. There are exactly five lines. Each point lies on exactly three lines. Each
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS
 NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students. Francis Joseph H. Campeña, De La Salle University Manila
 KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila January 26, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila January 26, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
2. A straightedge can create straight line, but can't measure. A ruler can create straight lines and measure distances.
 5.1 Copies of Line Segments and Angles Answers 1. A drawing is a rough sketch and a construction is a process to create an exact and accurate geometric figure. 2. A straightedge can create straight line,
5.1 Copies of Line Segments and Angles Answers 1. A drawing is a rough sketch and a construction is a process to create an exact and accurate geometric figure. 2. A straightedge can create straight line,
Suggested List of Mathematical Language. Geometry
 Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Section Congruence Through Constructions
 Section 10.1 - Congruence Through Constructions Definitions: Similar ( ) objects have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Congruent ( =) objects have the same size as well as the same shape.
Section 10.1 - Congruence Through Constructions Definitions: Similar ( ) objects have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Congruent ( =) objects have the same size as well as the same shape.
Along the Euler Line Berkeley Math Circle Intermediate
 Along the Euler Line Berkeley Math Circle Intermediate by Zvezdelina Stankova Berkeley Math Circle Director October 11, 17 2011 Note: We shall work on the problems below over the next two circle sessions
Along the Euler Line Berkeley Math Circle Intermediate by Zvezdelina Stankova Berkeley Math Circle Director October 11, 17 2011 Note: We shall work on the problems below over the next two circle sessions
Postulates, Theorems, and Corollaries. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
0811ge. Geometry Regents Exam
 0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 9 8 3 6 2 In the diagram below,. 4 Pentagon PQRST has parallel to. After a translation of, which line
0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 9 8 3 6 2 In the diagram below,. 4 Pentagon PQRST has parallel to. After a translation of, which line
Custom Tools and Customizing the Toolbar
 Custom Tools and Customizing the Toolbar GeoGebra Workshop Handout 7 Judith and Markus Hohenwarter www.geogebra.org Table of Contents 1. The Theorem of Phythagoras 2 2. Creating Custom Tools 4 3. Saving
Custom Tools and Customizing the Toolbar GeoGebra Workshop Handout 7 Judith and Markus Hohenwarter www.geogebra.org Table of Contents 1. The Theorem of Phythagoras 2 2. Creating Custom Tools 4 3. Saving
Look up partial Decomposition to use for problems #65-67 Do Not solve problems #78,79
 Franklin Township Summer Assignment 2017 AP calculus AB Summer assignment Students should use the Mathematics summer assignment to identify subject areas that need attention in preparation for the study
Franklin Township Summer Assignment 2017 AP calculus AB Summer assignment Students should use the Mathematics summer assignment to identify subject areas that need attention in preparation for the study
Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence
 Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definition ABC =
Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definition ABC =
MATHEMATICS Geometry Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations
 Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations Number and Number A. Connect physical, verbal and symbolic representations of 1. Connect physical, verbal and symbolic representations of Systems integers,
Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations Number and Number A. Connect physical, verbal and symbolic representations of 1. Connect physical, verbal and symbolic representations of Systems integers,
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
 Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry 1 Mark Questions 1. Where do these following points lie (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) A. Given points (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) The x coordinates of each point is zero.
Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry 1 Mark Questions 1. Where do these following points lie (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) A. Given points (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) The x coordinates of each point is zero.
Quadrilaterals. MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 23
 Quadrilaterals MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 23 Theorems 1. A convex quadrilateral is cyclic if and only if opposite angles are supplementary. (Circumcircle, maltitudes, anticenter) 2. A convex quadrilateral
Quadrilaterals MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 23 Theorems 1. A convex quadrilateral is cyclic if and only if opposite angles are supplementary. (Circumcircle, maltitudes, anticenter) 2. A convex quadrilateral
Centres of a Triangle. Teacher Notes
 Introduction Centres of a Triangle Teacher Notes Centres of a Triangle The aim of this activity is to investigate some of the centres of a triangle and to discover the Euler Line. The activity enables
Introduction Centres of a Triangle Teacher Notes Centres of a Triangle The aim of this activity is to investigate some of the centres of a triangle and to discover the Euler Line. The activity enables
Select the best answer. Bubble the corresponding choice on your scantron. Team 13. Geometry
 Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
UNIT 5 GEOMETRY TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 5
 UNIT 5 GEOMETRY TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 5 Geometry Unit 5 Overview: Circles With and Without Coordinates In this unit, students prove basic theorems about circles, with particular attention
UNIT 5 GEOMETRY TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 5 Geometry Unit 5 Overview: Circles With and Without Coordinates In this unit, students prove basic theorems about circles, with particular attention
GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA
 GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA PART ONE: TRIANGLES Notations AB ( AB ) [ AB ] ] AB [ [ AB ) distance between the points A and B line through the points A and B segment between the two points A and B (A and B included)
GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA PART ONE: TRIANGLES Notations AB ( AB ) [ AB ] ] AB [ [ AB ) distance between the points A and B line through the points A and B segment between the two points A and B (A and B included)
Introduction to Geometry (Autumn Tertm 2012) Exercises 3. Section A. Figure 1
 Introduction to Geometry (utumn ertm 2012) Exercises 3 Section 1. Show that in Figure 1(i) below, = (Euclid III.35). p (i) (ii) Figure 1 (iii) 2. What is the angle-sum in a quadrilateral on the sphere,
Introduction to Geometry (utumn ertm 2012) Exercises 3 Section 1. Show that in Figure 1(i) below, = (Euclid III.35). p (i) (ii) Figure 1 (iii) 2. What is the angle-sum in a quadrilateral on the sphere,
TImath.com. Geometry. Special Segments in Triangles
 Special Segments in Triangles ID: 8672 Time required 90 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore medians, altitudes, angle bisectors, and perpendicular bisectors of triangles. They
Special Segments in Triangles ID: 8672 Time required 90 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore medians, altitudes, angle bisectors, and perpendicular bisectors of triangles. They
Make geometric constructions. (Formalize and explain processes)
 Standard 5: Geometry Pre-Algebra Plus Algebra Geometry Algebra II Fourth Course Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Part 3 Draw construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships
Standard 5: Geometry Pre-Algebra Plus Algebra Geometry Algebra II Fourth Course Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Part 3 Draw construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships
Special Quartics with Triple Points
 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 6 (2002), No. 2, 111 119. Special Quartics with Triple Points Sonja Gorjanc Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Zagreb V. Holjevca 15, 10010 Zagreb, Croatia
Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 6 (2002), No. 2, 111 119. Special Quartics with Triple Points Sonja Gorjanc Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Zagreb V. Holjevca 15, 10010 Zagreb, Croatia
Narrowing the Gap between Computer Algebra and Dynamic Geometry
 Narrowing the Gap between Computer Algebra and Dynamic Geometry 1 Directrix Josef Böhm, ACDCA & DUG, Austria Some examples It is well known that the parabola is defined as the locus of all points which
Narrowing the Gap between Computer Algebra and Dynamic Geometry 1 Directrix Josef Böhm, ACDCA & DUG, Austria Some examples It is well known that the parabola is defined as the locus of all points which
Exploring Analytic Geometry with Mathematica Donald L. Vossler
 Exploring Analytic Geometry with Mathematica Donald L. Vossler BME, Kettering University, 1978 MM, Aquinas College, 1981 Anaheim, California USA, 1999 Copyright 1999-2007 Donald L. Vossler Preface The
Exploring Analytic Geometry with Mathematica Donald L. Vossler BME, Kettering University, 1978 MM, Aquinas College, 1981 Anaheim, California USA, 1999 Copyright 1999-2007 Donald L. Vossler Preface The
Cevians, Symmedians, and Excircles. Cevian. Cevian Triangle & Circle 10/5/2011. MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16
 Cevians, Symmedians, and MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16 Cevian A cevian is a line segment which joins a vertex of a triangle with a point on the opposite side (or its extension). B cevian A D C 05-Oct-2011
Cevians, Symmedians, and MA 341 Topics in Geometry Lecture 16 Cevian A cevian is a line segment which joins a vertex of a triangle with a point on the opposite side (or its extension). B cevian A D C 05-Oct-2011
Construction Instructions. Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment.
 Construction Instructions Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1.) Begin with line segment XY. 2.) Place the compass at point X. Adjust
Construction Instructions Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1.) Begin with line segment XY. 2.) Place the compass at point X. Adjust
From nested Miquel triangles to Miquel distances
 Published in Math Gazette, Nov 2002, 86(507), pp. 390-395. Copyright Mathematical Association. From nested Miquel triangles to Miquel distances MICHAEL DE VILLIERS This article presents interesting generalizations
Published in Math Gazette, Nov 2002, 86(507), pp. 390-395. Copyright Mathematical Association. From nested Miquel triangles to Miquel distances MICHAEL DE VILLIERS This article presents interesting generalizations
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 11: Coordinate Geometry Proofs Review Sheet
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 11: Coordinate Geometry Proofs Review Sheet Complete the entire review sheet (on here, or separate paper as indicated) h in on test day for 5 bonus points! Part 1 The Quadrilateral
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 11: Coordinate Geometry Proofs Review Sheet Complete the entire review sheet (on here, or separate paper as indicated) h in on test day for 5 bonus points! Part 1 The Quadrilateral
Investigating Properties of Kites
 Investigating Properties of Kites Definition: Kite a quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive equal sides (Figure 1). Construct and Investigate: 1. Determine three ways to construct a kite
Investigating Properties of Kites Definition: Kite a quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive equal sides (Figure 1). Construct and Investigate: 1. Determine three ways to construct a kite
Isoparametric Curve of Quadratic F-Bézier Curve
 J. of the Chosun Natural Science Vol. 6, No. 1 (2013) pp. 46 52 Isoparametric Curve of Quadratic F-Bézier Curve Hae Yeon Park 1 and Young Joon Ahn 2, Abstract In this thesis, we consider isoparametric
J. of the Chosun Natural Science Vol. 6, No. 1 (2013) pp. 46 52 Isoparametric Curve of Quadratic F-Bézier Curve Hae Yeon Park 1 and Young Joon Ahn 2, Abstract In this thesis, we consider isoparametric
Unit Number of Days Dates. 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/ Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9
 8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
Special sextics with a quadruple line
 MATHEMATICAL COMMUNICATIONS 85 Math. Commun., Vol. 14, No. 1, pp. 85-102 2009) Special sextics with a quadruple line Sonja Gorjanc 1, and Vladimir Benić 1 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of
MATHEMATICAL COMMUNICATIONS 85 Math. Commun., Vol. 14, No. 1, pp. 85-102 2009) Special sextics with a quadruple line Sonja Gorjanc 1, and Vladimir Benić 1 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of
Agile Mind Geometry Scope and Sequence, Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
 Students began their study of geometric concepts in middle school mathematics. They studied area, surface area, and volume and informally investigated lines, angles, and triangles. Students in middle school
Students began their study of geometric concepts in middle school mathematics. They studied area, surface area, and volume and informally investigated lines, angles, and triangles. Students in middle school
VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER)
 BY PROF. RAHUL MISHRA VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER) CONSTRUCTIONS Class :- X Subject :- Maths Total Time :- SET A Total Marks :- 240 QNo. General Instructions Questions 1 Divide
BY PROF. RAHUL MISHRA VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER) CONSTRUCTIONS Class :- X Subject :- Maths Total Time :- SET A Total Marks :- 240 QNo. General Instructions Questions 1 Divide
MANHATTAN HUNTER SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY CURRICULUM
 COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
History of Mathematics
 History of Mathematics Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Spring 2014 1: Pythagoras Theorem in Euclid s Elements Euclid s Elements n ancient Greek mathematical classic compiled
History of Mathematics Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Spring 2014 1: Pythagoras Theorem in Euclid s Elements Euclid s Elements n ancient Greek mathematical classic compiled
Mth 97 Winter 2013 Sections 4.3 and 4.4
 Section 4.3 Problem Solving Using Triangle Congruence Isosceles Triangles Theorem 4.5 In an isosceles triangle, the angles opposite the congruent sides are congruent. A Given: ABC with AB AC Prove: B C
Section 4.3 Problem Solving Using Triangle Congruence Isosceles Triangles Theorem 4.5 In an isosceles triangle, the angles opposite the congruent sides are congruent. A Given: ABC with AB AC Prove: B C
MST Topics in History of Mathematics
 MST Topics in History of Mathematics Euclid s Elements and the Works of rchimedes Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2014 June 30 2.6 ngle properties 11 2.6 ngle properties
MST Topics in History of Mathematics Euclid s Elements and the Works of rchimedes Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2014 June 30 2.6 ngle properties 11 2.6 ngle properties
1 Points and Distances
 Ale Zorn 1 Points and Distances 1. Draw a number line, and plot and label these numbers: 0, 1, 6, 2 2. Plot the following points: (A) (3,1) (B) (2,5) (C) (-1,1) (D) (2,-4) (E) (-3,-3) (F) (0,4) (G) (-2,0)
Ale Zorn 1 Points and Distances 1. Draw a number line, and plot and label these numbers: 0, 1, 6, 2 2. Plot the following points: (A) (3,1) (B) (2,5) (C) (-1,1) (D) (2,-4) (E) (-3,-3) (F) (0,4) (G) (-2,0)
NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry
 NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and
NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and
Standards-Based Curriculum Support!
 Coach is the leader in standards-based, state-customized instruction for grades K 12 in English language arts, mathematics, science, and social studies. Our student texts deliver everything you need to
Coach is the leader in standards-based, state-customized instruction for grades K 12 in English language arts, mathematics, science, and social studies. Our student texts deliver everything you need to
fall08ge Geometry Regents Exam Test Sampler fall08 4 The diagram below shows the construction of the perpendicular bisector of AB.
 fall08ge 1 Isosceles trapezoid ABCD has diagonals AC and BD. If AC = 5x + 13 and BD = 11x 5, what is the value of x? 1) 8 4 The diagram below shows the construction of the perpendicular bisector of AB.
fall08ge 1 Isosceles trapezoid ABCD has diagonals AC and BD. If AC = 5x + 13 and BD = 11x 5, what is the value of x? 1) 8 4 The diagram below shows the construction of the perpendicular bisector of AB.
Correlation of Discovering Geometry 5th Edition to Florida State Standards
 Correlation of 5th Edition to Florida State s MAFS content is listed under three headings: Introduced (I), Developed (D), and Applied (A). Developed standards are the focus of the lesson, and are being
Correlation of 5th Edition to Florida State s MAFS content is listed under three headings: Introduced (I), Developed (D), and Applied (A). Developed standards are the focus of the lesson, and are being
Geometry. Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section.
 Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
 SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS A system of linear equations is a set of two equations of lines. A solution of a system of linear equations is the set of ordered pairs that makes each equation true. That is
SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS A system of linear equations is a set of two equations of lines. A solution of a system of linear equations is the set of ordered pairs that makes each equation true. That is
The focus and the median of a non-tangential quadrilateral in the isotropic plane
 MATHEMATICAL COMMUNICATIONS 117 Math. Commun., Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 117-17 (010) The focus and the median of a non-tangential quadrilateral in the isotropic plane Vladimir Volenec 1,, Jelena Beban-Brkić
MATHEMATICAL COMMUNICATIONS 117 Math. Commun., Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 117-17 (010) The focus and the median of a non-tangential quadrilateral in the isotropic plane Vladimir Volenec 1,, Jelena Beban-Brkić
How to Project Spherical Conics into the Plane
 How to Project pherical Conics into the Plane Yoichi Maeda maeda@keyakiccu-tokaiacjp Department of Mathematics Tokai University Japan Abstract: In this paper, we will introduce a method how to draw the
How to Project pherical Conics into the Plane Yoichi Maeda maeda@keyakiccu-tokaiacjp Department of Mathematics Tokai University Japan Abstract: In this paper, we will introduce a method how to draw the
Conic Sections and Locii
 Lesson Summary: Students will investigate the ellipse and the hyperbola as a locus of points. Activity One addresses the ellipse and the hyperbola is covered in lesson two. Key Words: Locus, ellipse, hyperbola
Lesson Summary: Students will investigate the ellipse and the hyperbola as a locus of points. Activity One addresses the ellipse and the hyperbola is covered in lesson two. Key Words: Locus, ellipse, hyperbola
Common Core State Standards High School Geometry Constructions
 ommon ore State Standards High School Geometry onstructions HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying a line segment HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying an angle HSG.O..12 onstruction: isecting a line segment HSG.O..12
ommon ore State Standards High School Geometry onstructions HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying a line segment HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying an angle HSG.O..12 onstruction: isecting a line segment HSG.O..12
Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles
 1 Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles or contains a right angle. D D 2 Solution to Example
1 Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles or contains a right angle. D D 2 Solution to Example
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions. 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH6 2.1 Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system Coordinate axes: Two perpendicular lines that intersect at the origin O on each line.
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH6 2.1 Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system Coordinate axes: Two perpendicular lines that intersect at the origin O on each line.
