Spatially selective RF excitation using k-space analysis
|
|
|
- Isabella Payne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spatially selective RF excitation using k-space analysis Dimitrios Pantazis a, a Signal and Image Processing Institute, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA Abstract This project develops spatially selective RF excitation schemes, based on the excitation k- space principle (Pauly et al., 1987). In particular, we develop various k-space trajectories and weighting schemes, in order to excite cylindrical, spherical, and cubical volumes. The excitation pulses are inherenctly refocused, since the trajectories end at the origin of k- space. The analysis is based on a small-tip-angle approximation, but behaves well for larger tip angles.
2 1 Introduction Magnetic reconance imaging reconstruction has been successfully analyzed using the representation of k-space, and frequency sampling. Pauly et al. (1987) used the same idea to analyze spatially selective RF excitation schemes. The excitation k-space is an elegant tool, and greatly simplifies the design of efficient excitation schemes that target specific areas of the body (Morrell and Macovski, 1997; Bornert and Aldefeld, 1998). Using the small-tip approximation, we can find an integral expression for the transverse magnetization produced by a selective excitation pulse. This expression may be interpreted as scanning a path in a spatial frequency space, or k-space: M xy (x) = iγm o where W (k) is a weighting function, defined by: K W (k(t)) = W (k)s(k)e ixk dk (1) B 1(t) g 2π G(t) (2) Further, Sk is a sampling structure, determining the area and the density of k-space representation: S(k) = T 0 { 3 δ(k(t) k) k(t) }dt (3) In this brief report, we present pulse sequences to excite a cylindrical volume, a gaussian-weighted sphere, and a cube. We also investigate the robustness of the excitation schemes to of-resonance. 2 Exciting Cylindrical Volume In order to excite a cylindrical volume in the MR scanner, we choose a spiral trajectory with 20 cycles, shown in Fig. 2. The gradients required to achieve this trajectory (Fig. 2) are estimated using Eq. 4: k(t) = γ T G(s)ds (4) 2π t 2
3 Fig 1: Spiral trajectory is used to excite a cylinder. Fig 2: Gx, Gy, and Gz gradients for the spiral k-space trajectory. In order to excite a cylinder in the spatial domain, we need to weight with a jinc fuction in the spatial frequency domain: W (k) = α jinc(β kx 2 + kz) 2 (5) where α scales the tip angle, and β determines the spatial resolution of the selective volume. Fig 3: Left: Spatial frequency weighting using a jinc function; Right: Jinc funcion at k z = 0. 3
4 g Fig 4: Estimation of RF field using Eq. 2. Left: 2π G(t) for the cylindrical trajectory; Center: wighting function for the cylindrical trajectory; Right: RF field We simulated the pulse sequence to selectively excite a cylinder, and the results are given in Fig. 5 and Fig. 6. Fig 5: Simulation results for the cylinder excitition. The excition region is in great accordance with the theoretical prediction. Fig 6: Mx and Mz components for the cylinder excitation. Mx is nearly zero, as expected. Conversely, the Mz component is only small in the cylindrical region, and remains unaffected elsewhere. 4
5 3 Exciting a Gaussian-Weighted Sphere In order to limit the object domain excitation region in all 3 dimensions, we need to apply 3 gradients (Gx, Gy, and Gz), and develop a 3D trajectory. This trajectory must sufficiently sample the k-space in x,y, and z dimension. We begin by designing a spiral trajectory with n = 50 cycles. Then, we slowly rotate each cycle using Rx and Rz rotating matrices, so that the trajectory traverses all 3 dimentions, as shown in Fig. 7. kx (t) = A(1 t/t ) cos(2πnt/t ); ky (t) = 0; kz (t) = A(1 t/t ) sin(2πnt/t ); (6) Fig. 7: Left: Spiral trajectory used to generate the 3D trajectory; Right: 3D trajectory used to weight the excitation space. Fig 8: Gx, Gy, and Gz gradients for the 3D k-space trajectory. In order to excite a gaussian-weighted sphere in the spatial domain, we need to weight with a gaussian-weighted function in the spatial frequency domain: W (k) = α e β 2 (k 2 +k 2 +k 2 )/A2 x y z (7) where α scales the tip angle, and β determines the spatial resolution of the selective volume. 5
6 Fig 9: Left: Spatial frequency weighting using a Gaussian-weighted function (Eq. 7) ; Right: Profile of the function at k z = 0. Fig 10: Estimation of RF field using Eq. 2. Left: g 2π G(t) for the 3D trajectory; Center: weighting function for the cylindrical trajectory; Right: RF field We simulated the pulse sequence to selectively excite a gaussian-weighted sphere, and the results are given in Fig. 11 and Fig. 12. Fig 11: Mx, My, and Mz components for the Gaussian-sphere excitation. Mx is nearly zero, as expected. My is in great accordance with the theoritical results. The Mz component is only small in the central region, and remains unaffected elsewhere. 6
7 Fig 12: Z-profile of My magnetization component. Only the central region is excited. 4 Exciting a Cube In order to excite a cube in the spatial domain, we need to weight with a sinc function in the spatial frequency domain: W (k) = α sinc(βk x )sinc(βk y )sinc(βk z ); (8) where α = 10 6 scales the tip angle, and β = 8 determines the spatial resolution of the selective volume. Unfortunately, this excitation scheme is only of theoretical interest. The required RF pulse (Fig. 13) is impossible to generate with current hardware limitations. In order to excite a cube, we need to implement a different trajectory, which will lead to a more reasonable RF pulse. We simulated the pulse sequence to selectively excite a cube, and the results are given in Fig
8 Fig 13: RF pulse for excitation of a cube. The pulse is not realizable with current hardware limitations. Fig 14: Sinc profile at k z = 0. The figure does not show the third sinc function, in the z-dimension. Fig 15: Simulation results for the excitation of a cube. 5 Relaxation Effects The pulse sequence for the excitation of a Gaussian-weighted sphere requires 20ms, under current hardware limitations. This is relatively long as compared to other modern sequences, such as SSFP, and therefore 3D excitation is usually avoided. We tested the robustness of the method for various T2 values, when T1 = 100ms. M y magnetization is detectible for up to T2 = 5ms, which is sufficient for most imaging purposes. 8
9 Fig 16: Mx, My, and Mz magnetization under Gaussian-weighted sphere excitation, for various values of T2. T1 was 100ms. 6 Of resonance Effects Unfortunately, due to the long excitation period, the pulse sequence is very sensitive to of resonance. Even 0.25ppm on a 1.5T mashine (1ppm corresponds to df = 63.86Hz) can cause significant artifacts. 9
10 Fig 17: Of resonance behavior of the Gaussian-weighted sphere excitation scheme. References Bornert, P., Aldefeld, B., December On spatially selective rf excitation and its analogy with spiral mr image acquisition. Magma 7 (3), Morrell, G., Macovski, A., March Three-dimensional spectral-spatial excitation. Magn Reson Med 37 (3), Pauly, J., Nishimura, D., Macovski, A., A k-space analysis of small-tip-angle excitation. Journal of Magnetic Resonance 81,
2D spatially selective excitation pulse design and the artifact evaluation
 EE 591 Project 2D spatially selective excitation pulse design and the artifact evaluation 12/08/2004 Zungho Zun Two-dimensional spatially selective excitation is used to excite a volume such as pencil
EE 591 Project 2D spatially selective excitation pulse design and the artifact evaluation 12/08/2004 Zungho Zun Two-dimensional spatially selective excitation is used to excite a volume such as pencil
Evaluations of k-space Trajectories for Fast MR Imaging for project of the course EE591, Fall 2004
 Evaluations of k-space Trajectories for Fast MR Imaging for project of the course EE591, Fall 24 1 Alec Chi-Wah Wong Department of Electrical Engineering University of Southern California 374 McClintock
Evaluations of k-space Trajectories for Fast MR Imaging for project of the course EE591, Fall 24 1 Alec Chi-Wah Wong Department of Electrical Engineering University of Southern California 374 McClintock
Field Maps. 1 Field Map Acquisition. John Pauly. October 5, 2005
 Field Maps John Pauly October 5, 25 The acquisition and reconstruction of frequency, or field, maps is important for both the acquisition of MRI data, and for its reconstruction. Many of the imaging methods
Field Maps John Pauly October 5, 25 The acquisition and reconstruction of frequency, or field, maps is important for both the acquisition of MRI data, and for its reconstruction. Many of the imaging methods
(a Scrhon5 R2iwd b. P)jc%z 5. ivcr3. 1. I. ZOms Xn,s. 1E IDrAS boms. EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2013 Principles of MRI. Assignment 8 Solutions
 EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2013 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Assignment 8 Solutions 1. Nishimura 7.1 P)jc%z 5 ivcr3. 1. I Due Wednesday April 10th, 2013 (a Scrhon5 R2iwd b 0 ZOms Xn,s r cx > qs 4-4 8ni6 4
EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2013 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Assignment 8 Solutions 1. Nishimura 7.1 P)jc%z 5 ivcr3. 1. I Due Wednesday April 10th, 2013 (a Scrhon5 R2iwd b 0 ZOms Xn,s r cx > qs 4-4 8ni6 4
MRI Physics II: Gradients, Imaging
 MRI Physics II: Gradients, Imaging Douglas C., Ph.D. Dept. of Biomedical Engineering University of Michigan, Ann Arbor Magnetic Fields in MRI B 0 The main magnetic field. Always on (0.5-7 T) Magnetizes
MRI Physics II: Gradients, Imaging Douglas C., Ph.D. Dept. of Biomedical Engineering University of Michigan, Ann Arbor Magnetic Fields in MRI B 0 The main magnetic field. Always on (0.5-7 T) Magnetizes
K-Space Trajectories and Spiral Scan
 K-Space and Spiral Scan Presented by: Novena Rangwala nrangw2@uic.edu 1 Outline K-space Gridding Reconstruction Features of Spiral Sampling Pulse Sequences Mathematical Basis of Spiral Scanning Variations
K-Space and Spiral Scan Presented by: Novena Rangwala nrangw2@uic.edu 1 Outline K-space Gridding Reconstruction Features of Spiral Sampling Pulse Sequences Mathematical Basis of Spiral Scanning Variations
Midterm Review
 Midterm Review - 2017 EE369B Concepts Noise Simulations with Bloch Matrices, EPG Gradient Echo Imaging 1 About the Midterm Monday Oct 30, 2017. CCSR 4107 Up to end of C2 1. Write your name legibly on this
Midterm Review - 2017 EE369B Concepts Noise Simulations with Bloch Matrices, EPG Gradient Echo Imaging 1 About the Midterm Monday Oct 30, 2017. CCSR 4107 Up to end of C2 1. Write your name legibly on this
EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2011 Principles of MRI. Assignment 5. Solutions
 EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 211 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Handout Assignment 5 Solutions 1. Matlab Exercise: 2DFT Pulse sequence design. In this assignment we will write functions to design a 2DFT pulse
EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 211 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Handout Assignment 5 Solutions 1. Matlab Exercise: 2DFT Pulse sequence design. In this assignment we will write functions to design a 2DFT pulse
Imaging Notes, Part IV
 BME 483 MRI Notes 34 page 1 Imaging Notes, Part IV Slice Selective Excitation The most common approach for dealing with the 3 rd (z) dimension is to use slice selective excitation. This is done by applying
BME 483 MRI Notes 34 page 1 Imaging Notes, Part IV Slice Selective Excitation The most common approach for dealing with the 3 rd (z) dimension is to use slice selective excitation. This is done by applying
Improved Spatial Localization in 3D MRSI with a Sequence Combining PSF-Choice, EPSI and a Resolution Enhancement Algorithm
 Improved Spatial Localization in 3D MRSI with a Sequence Combining PSF-Choice, EPSI and a Resolution Enhancement Algorithm L.P. Panych 1,3, B. Madore 1,3, W.S. Hoge 1,3, R.V. Mulkern 2,3 1 Brigham and
Improved Spatial Localization in 3D MRSI with a Sequence Combining PSF-Choice, EPSI and a Resolution Enhancement Algorithm L.P. Panych 1,3, B. Madore 1,3, W.S. Hoge 1,3, R.V. Mulkern 2,3 1 Brigham and
Spread Spectrum Using Chirp Modulated RF Pulses for Incoherent Sampling Compressive Sensing MRI
 Spread Spectrum Using Chirp Modulated RF Pulses for Incoherent Sampling Compressive Sensing MRI Sulaiman A. AL Hasani Department of ECSE, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Email: sulaiman.alhasani@monash.edu
Spread Spectrum Using Chirp Modulated RF Pulses for Incoherent Sampling Compressive Sensing MRI Sulaiman A. AL Hasani Department of ECSE, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Email: sulaiman.alhasani@monash.edu
Fast Imaging Trajectories: Non-Cartesian Sampling (1)
 Fast Imaging Trajectories: Non-Cartesian Sampling (1) M229 Advanced Topics in MRI Holden H. Wu, Ph.D. 2018.05.03 Department of Radiological Sciences David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Class Business
Fast Imaging Trajectories: Non-Cartesian Sampling (1) M229 Advanced Topics in MRI Holden H. Wu, Ph.D. 2018.05.03 Department of Radiological Sciences David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Class Business
The SIMRI project A versatile and interactive MRI simulator *
 COST B21 Meeting, Lodz, 6-9 Oct. 2005 The SIMRI project A versatile and interactive MRI simulator * H. Benoit-Cattin 1, G. Collewet 2, B. Belaroussi 1, H. Saint-Jalmes 3, C. Odet 1 1 CREATIS, UMR CNRS
COST B21 Meeting, Lodz, 6-9 Oct. 2005 The SIMRI project A versatile and interactive MRI simulator * H. Benoit-Cattin 1, G. Collewet 2, B. Belaroussi 1, H. Saint-Jalmes 3, C. Odet 1 1 CREATIS, UMR CNRS
Compressed Sensing for Rapid MR Imaging
 Compressed Sensing for Rapid Imaging Michael Lustig1, Juan Santos1, David Donoho2 and John Pauly1 1 Electrical Engineering Department, Stanford University 2 Statistics Department, Stanford University rapid
Compressed Sensing for Rapid Imaging Michael Lustig1, Juan Santos1, David Donoho2 and John Pauly1 1 Electrical Engineering Department, Stanford University 2 Statistics Department, Stanford University rapid
Development of fast imaging techniques in MRI From the principle to the recent development
 980-8575 2-1 2012 10 13 Development of fast imaging techniques in MRI From the principle to the recent development Yoshio MACHIDA and Issei MORI Health Sciences, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine
980-8575 2-1 2012 10 13 Development of fast imaging techniques in MRI From the principle to the recent development Yoshio MACHIDA and Issei MORI Health Sciences, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine
surface Image reconstruction: 2D Fourier Transform
 2/1/217 Chapter 2-3 K-space Intro to k-space sampling (chap 3) Frequenc encoding and Discrete sampling (chap 2) Point Spread Function K-space properties K-space sampling principles (chap 3) Basic Contrast
2/1/217 Chapter 2-3 K-space Intro to k-space sampling (chap 3) Frequenc encoding and Discrete sampling (chap 2) Point Spread Function K-space properties K-space sampling principles (chap 3) Basic Contrast
Computational Algorithm for Estimating the Gradient Isocenter of an MRI Scanner
 Computational Algorithm for Estimating the Gradient Isocenter of an MRI Scanner R Cai 1, KE Schubert 1, R Schulte 2 ritchiecai@r2labsorg, keith@r2labsorg, rschulte@dominionllumcedu 1 School of Computer
Computational Algorithm for Estimating the Gradient Isocenter of an MRI Scanner R Cai 1, KE Schubert 1, R Schulte 2 ritchiecai@r2labsorg, keith@r2labsorg, rschulte@dominionllumcedu 1 School of Computer
Partial k-space Recconstruction
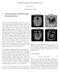 Partial k-space Recconstruction John Pauly September 29, 2005 1 Motivation for Partial k-space Reconstruction a) Magnitude b) Phase In theory, most MRI images depict the spin density as a function of position,
Partial k-space Recconstruction John Pauly September 29, 2005 1 Motivation for Partial k-space Reconstruction a) Magnitude b) Phase In theory, most MRI images depict the spin density as a function of position,
Faster 3D Vocal Tract Real-time MRI Using Constrained Reconstruction
 Faster 3D Vocal Tract Real-time MRI Using Constrained Reconstruction Yinghua Zhu 1, Asterios Toutios 1, Shrikanth Narayanan 1,2, Krishna Nayak 1 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Southern
Faster 3D Vocal Tract Real-time MRI Using Constrained Reconstruction Yinghua Zhu 1, Asterios Toutios 1, Shrikanth Narayanan 1,2, Krishna Nayak 1 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Southern
NUFFT for Medical and Subsurface Image Reconstruction
 NUFFT for Medical and Subsurface Image Reconstruction Qing H. Liu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Duke University Duke Frontiers 2006 May 16, 2006 Acknowledgment Jiayu Song main contributor
NUFFT for Medical and Subsurface Image Reconstruction Qing H. Liu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Duke University Duke Frontiers 2006 May 16, 2006 Acknowledgment Jiayu Song main contributor
A Transmission Line Matrix Model for Shielding Effects in Stents
 A Transmission Line Matrix Model for hielding Effects in tents Razvan Ciocan (1), Nathan Ida (2) (1) Clemson University Physics and Astronomy Department Clemson University, C 29634-0978 ciocan@clemon.edu
A Transmission Line Matrix Model for hielding Effects in tents Razvan Ciocan (1), Nathan Ida (2) (1) Clemson University Physics and Astronomy Department Clemson University, C 29634-0978 ciocan@clemon.edu
FOV. ] are the gradient waveforms. The reconstruction of this signal proceeds by an inverse Fourier Transform as:. [2] ( ) ( )
![FOV. ] are the gradient waveforms. The reconstruction of this signal proceeds by an inverse Fourier Transform as:. [2] ( ) ( ) FOV. ] are the gradient waveforms. The reconstruction of this signal proceeds by an inverse Fourier Transform as:. [2] ( ) ( )](/thumbs/86/94912904.jpg) Gridding Procedures for Non-Cartesian K-space Trajectories Douglas C. Noll and Bradley P. Sutton Dept. of Biomedical Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA 1. Introduction The data collected
Gridding Procedures for Non-Cartesian K-space Trajectories Douglas C. Noll and Bradley P. Sutton Dept. of Biomedical Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA 1. Introduction The data collected
Sampling, Ordering, Interleaving
 Sampling, Ordering, Interleaving Sampling patterns and PSFs View ordering Modulation due to transients Temporal modulations Slice interleaving Sequential, Odd/even, bit-reversed Arbitrary Other considerations:
Sampling, Ordering, Interleaving Sampling patterns and PSFs View ordering Modulation due to transients Temporal modulations Slice interleaving Sequential, Odd/even, bit-reversed Arbitrary Other considerations:
University of Cape Town
 Development of a 3D radial MR Imaging sequence to be used for (self) navigation during the scanning of the fetal brain in utero by Leah Morgan Thesis presented for the degree of Master of Science June
Development of a 3D radial MR Imaging sequence to be used for (self) navigation during the scanning of the fetal brain in utero by Leah Morgan Thesis presented for the degree of Master of Science June
Partial k-space Reconstruction
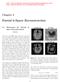 Chapter 2 Partial k-space Reconstruction 2.1 Motivation for Partial k- Space Reconstruction a) Magnitude b) Phase In theory, most MRI images depict the spin density as a function of position, and hence
Chapter 2 Partial k-space Reconstruction 2.1 Motivation for Partial k- Space Reconstruction a) Magnitude b) Phase In theory, most MRI images depict the spin density as a function of position, and hence
MRI Reconstruction using Real-Time Motion Tracking: A Simulation Study
 MRI Reconstruction using Real-Time Motion Tracking: A Simulation Study Jeff Orchard David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo Waterloo, ON Canada, N2L 3G1 e-mail: jorchard@uwaterloo.ca
MRI Reconstruction using Real-Time Motion Tracking: A Simulation Study Jeff Orchard David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo Waterloo, ON Canada, N2L 3G1 e-mail: jorchard@uwaterloo.ca
Correction for EPI Distortions Using Multi-Echo Gradient-Echo Imaging
 Correction for EPI Distortions Using Multi-Echo Gradient-Echo Imaging Nan-kuei Chen and Alice M. Wyrwicz* Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 41:1206 1213 (1999) A novel and effective technique is described
Correction for EPI Distortions Using Multi-Echo Gradient-Echo Imaging Nan-kuei Chen and Alice M. Wyrwicz* Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 41:1206 1213 (1999) A novel and effective technique is described
TOPICS 2/5/2006 8:17 PM. 2D Acquisition 3D Acquisition
 TOPICS 2/5/2006 8:17 PM 2D Acquisition 3D Acquisition 2D Acquisition Involves two main steps : Slice Selection Slice selection is accomplished by spatially saturating (single or multi slice imaging) or
TOPICS 2/5/2006 8:17 PM 2D Acquisition 3D Acquisition 2D Acquisition Involves two main steps : Slice Selection Slice selection is accomplished by spatially saturating (single or multi slice imaging) or
PHASE-SENSITIVE AND DUAL-ANGLE RADIOFREQUENCY MAPPING IN. Steven P. Allen. A senior thesis submitted to the faculty of. Brigham Young University
 PHASE-SENSITIVE AND DUAL-ANGLE RADIOFREQUENCY MAPPING IN 23 NA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING by Steven P. Allen A senior thesis submitted to the faculty of Brigham Young University in partial fulfillment
PHASE-SENSITIVE AND DUAL-ANGLE RADIOFREQUENCY MAPPING IN 23 NA MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING by Steven P. Allen A senior thesis submitted to the faculty of Brigham Young University in partial fulfillment
k y 2k y,max k x 2k x,max
 EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2013 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Assignment 5 Solutions Due March 6th 2012 1. Finish reading Nishimura Ch. 5. 2. For the 16 turn spiral trajectory, plotted below, what is the a)
EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2013 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Assignment 5 Solutions Due March 6th 2012 1. Finish reading Nishimura Ch. 5. 2. For the 16 turn spiral trajectory, plotted below, what is the a)
Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images
 16 Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images 3.1 MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) MRI is a technique of measuring physical structure within the human anatomy. Our proposed research focuses
16 Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images 3.1 MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) MRI is a technique of measuring physical structure within the human anatomy. Our proposed research focuses
MATH203 Calculus. Dr. Bandar Al-Mohsin. School of Mathematics, KSU
 School of Mathematics, KSU Theorem The rectangular coordinates (x, y, z) and the cylindrical coordinates (r, θ, z) of a point P are related as follows: x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ, tan θ = y x, r 2 = x 2
School of Mathematics, KSU Theorem The rectangular coordinates (x, y, z) and the cylindrical coordinates (r, θ, z) of a point P are related as follows: x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ, tan θ = y x, r 2 = x 2
Clinical Importance. Aortic Stenosis. Aortic Regurgitation. Ultrasound vs. MRI. Carotid Artery Stenosis
 Clinical Importance Rapid cardiovascular flow quantitation using sliceselective Fourier velocity encoding with spiral readouts Valve disease affects 10% of patients with heart disease in the U.S. Most
Clinical Importance Rapid cardiovascular flow quantitation using sliceselective Fourier velocity encoding with spiral readouts Valve disease affects 10% of patients with heart disease in the U.S. Most
Steen Moeller Center for Magnetic Resonance research University of Minnesota
 Steen Moeller Center for Magnetic Resonance research University of Minnesota moeller@cmrr.umn.edu Lot of material is from a talk by Douglas C. Noll Department of Biomedical Engineering Functional MRI Laboratory
Steen Moeller Center for Magnetic Resonance research University of Minnesota moeller@cmrr.umn.edu Lot of material is from a talk by Douglas C. Noll Department of Biomedical Engineering Functional MRI Laboratory
Spiral Imaging: A Critical Appraisal
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 21:657 668 (2005) Review Article Spiral Imaging: A Critical Appraisal Kai Tobias Block, MSc and Jens Frahm, PhD* In view of recent applications in cardiovascular and
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 21:657 668 (2005) Review Article Spiral Imaging: A Critical Appraisal Kai Tobias Block, MSc and Jens Frahm, PhD* In view of recent applications in cardiovascular and
Spiral keyhole imaging for MR fingerprinting
 Spiral keyhole imaging for MR fingerprinting Guido Buonincontri 1, Laura Biagi 1,2, Pedro A Gómez 3,4, Rolf F Schulte 4, Michela Tosetti 1,2 1 IMAGO7 Research Center, Pisa, Italy 2 IRCCS Stella Maris,
Spiral keyhole imaging for MR fingerprinting Guido Buonincontri 1, Laura Biagi 1,2, Pedro A Gómez 3,4, Rolf F Schulte 4, Michela Tosetti 1,2 1 IMAGO7 Research Center, Pisa, Italy 2 IRCCS Stella Maris,
SIMULATION D'IRM ANGIOGRAPHIQUE PAR EXTENSION DU LOGICIEL JEMRIS
 SIMULATION D'IRM ANGIOGRAPHIQUE PAR EXTENSION DU LOGICIEL JEMRIS Alexandre FORTIN Supervised by Emmanuel DURAND and Stéphanie SALMON Laboratoire de Mathématiques de Reims Model : clipart-fr.com VIVABRAIN
SIMULATION D'IRM ANGIOGRAPHIQUE PAR EXTENSION DU LOGICIEL JEMRIS Alexandre FORTIN Supervised by Emmanuel DURAND and Stéphanie SALMON Laboratoire de Mathématiques de Reims Model : clipart-fr.com VIVABRAIN
Role of Parallel Imaging in High Field Functional MRI
 Role of Parallel Imaging in High Field Functional MRI Douglas C. Noll & Bradley P. Sutton Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Michigan Supported by NIH Grant DA15410 & The Whitaker Foundation
Role of Parallel Imaging in High Field Functional MRI Douglas C. Noll & Bradley P. Sutton Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Michigan Supported by NIH Grant DA15410 & The Whitaker Foundation
PHASE-ENCODED, RAPID, MULTIPLE-ECHO (PERME) NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
 PHASE-ENCODED, RAPID, MULTIPLE-ECHO (PERME) NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING Mark Steven Lawton Master of Engineering Thesis Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory University of California Berkeley, California
PHASE-ENCODED, RAPID, MULTIPLE-ECHO (PERME) NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING Mark Steven Lawton Master of Engineering Thesis Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory University of California Berkeley, California
White Pixel Artifact. Caused by a noise spike during acquisition Spike in K-space <--> sinusoid in image space
 White Pixel Artifact Caused by a noise spike during acquisition Spike in K-space sinusoid in image space Susceptibility Artifacts Off-resonance artifacts caused by adjacent regions with different
White Pixel Artifact Caused by a noise spike during acquisition Spike in K-space sinusoid in image space Susceptibility Artifacts Off-resonance artifacts caused by adjacent regions with different
Unit Maps: Grade 8 Math
 Real Number Relationships 8.3 Number and operations. The student represents and use real numbers in a variety of forms. Representation of Real Numbers 8.3A extend previous knowledge of sets and subsets
Real Number Relationships 8.3 Number and operations. The student represents and use real numbers in a variety of forms. Representation of Real Numbers 8.3A extend previous knowledge of sets and subsets
IMAGE reconstruction in conventional magnetic resonance
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 24, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 325 Conjugate Phase MRI Reconstruction With Spatially Variant Sample Density Correction Douglas C. Noll*, Member, IEEE, Jeffrey A. Fessler,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 24, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 325 Conjugate Phase MRI Reconstruction With Spatially Variant Sample Density Correction Douglas C. Noll*, Member, IEEE, Jeffrey A. Fessler,
Advanced Imaging Trajectories
 Advanced Imaging Trajectories Cartesian EPI Spiral Radial Projection 1 Radial and Projection Imaging Sample spokes Radial out : from k=0 to kmax Projection: from -kmax to kmax Trajectory design considerations
Advanced Imaging Trajectories Cartesian EPI Spiral Radial Projection 1 Radial and Projection Imaging Sample spokes Radial out : from k=0 to kmax Projection: from -kmax to kmax Trajectory design considerations
EE290T: Advanced Reconstruction Methods for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Martin Uecker
 EE290T: Advanced Reconstruction Methods for Magnetic Resonance Imaging Martin Uecker Tentative Syllabus 01: Jan 27 Introduction 02: Feb 03 Parallel Imaging as Inverse Problem 03: Feb 10 Iterative Reconstruction
EE290T: Advanced Reconstruction Methods for Magnetic Resonance Imaging Martin Uecker Tentative Syllabus 01: Jan 27 Introduction 02: Feb 03 Parallel Imaging as Inverse Problem 03: Feb 10 Iterative Reconstruction
ADVANCED RECONSTRUCTION TECHNIQUES IN MRI - 2
 ADVANCED RECONSTRUCTION TECHNIQUES IN MRI - 2 Presented by Rahil Kothari PARTIAL FOURIER RECONSTRUCTION WHAT IS PARTIAL FOURIER RECONSTRUCTION? In Partial Fourier Reconstruction data is not collected symmetrically
ADVANCED RECONSTRUCTION TECHNIQUES IN MRI - 2 Presented by Rahil Kothari PARTIAL FOURIER RECONSTRUCTION WHAT IS PARTIAL FOURIER RECONSTRUCTION? In Partial Fourier Reconstruction data is not collected symmetrically
Sampling, Ordering, Interleaving
 Sampling, Ordering, Interleaving Sampling patterns and PSFs View ordering Modulation due to transients Temporal modulations Timing: cine, gating, triggering Slice interleaving Sequential, Odd/even, bit-reversed
Sampling, Ordering, Interleaving Sampling patterns and PSFs View ordering Modulation due to transients Temporal modulations Timing: cine, gating, triggering Slice interleaving Sequential, Odd/even, bit-reversed
Information about presenter
 Information about presenter 2013-now Engineer R&D ithera Medical GmbH 2011-2013 M.Sc. in Biomedical Computing (TU München) Thesis title: A General Reconstruction Framework for Constrained Optimisation
Information about presenter 2013-now Engineer R&D ithera Medical GmbH 2011-2013 M.Sc. in Biomedical Computing (TU München) Thesis title: A General Reconstruction Framework for Constrained Optimisation
Module 5: Dynamic Imaging and Phase Sharing. (true-fisp, TRICKS, CAPR, DISTAL, DISCO, HYPR) Review. Improving Temporal Resolution.
 MRES 7005 - Fast Imaging Techniques Module 5: Dynamic Imaging and Phase Sharing (true-fisp, TRICKS, CAPR, DISTAL, DISCO, HYPR) Review Improving Temporal Resolution True-FISP (I) True-FISP (II) Keyhole
MRES 7005 - Fast Imaging Techniques Module 5: Dynamic Imaging and Phase Sharing (true-fisp, TRICKS, CAPR, DISTAL, DISCO, HYPR) Review Improving Temporal Resolution True-FISP (I) True-FISP (II) Keyhole
Chapter 4. Clustering Core Atoms by Location
 Chapter 4. Clustering Core Atoms by Location In this chapter, a process for sampling core atoms in space is developed, so that the analytic techniques in section 3C can be applied to local collections
Chapter 4. Clustering Core Atoms by Location In this chapter, a process for sampling core atoms in space is developed, so that the analytic techniques in section 3C can be applied to local collections
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
 C. A. Bouman: Digital Image Processing - January 12, 215 1 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Can be very high resolution No radiation exposure Very flexible and programable Tends to be expensive, noisy,
C. A. Bouman: Digital Image Processing - January 12, 215 1 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Can be very high resolution No radiation exposure Very flexible and programable Tends to be expensive, noisy,
VD-AUTO-SMASH Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 45:1066 1074 (2001) VD-AUTO-SMASH Imaging Robin M. Heidemann, Mark A. Griswold, Axel Haase, and Peter M. Jakob* Recently a self-calibrating SMASH technique, AUTO-SMASH, was
Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 45:1066 1074 (2001) VD-AUTO-SMASH Imaging Robin M. Heidemann, Mark A. Griswold, Axel Haase, and Peter M. Jakob* Recently a self-calibrating SMASH technique, AUTO-SMASH, was
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Math 11 Fall 2016 Section 1 Monday, October 17, 2016
 Math 11 Fall 16 Section 1 Monday, October 17, 16 First, some important points from the last class: f(x, y, z) dv, the integral (with respect to volume) of f over the three-dimensional region, is a triple
Math 11 Fall 16 Section 1 Monday, October 17, 16 First, some important points from the last class: f(x, y, z) dv, the integral (with respect to volume) of f over the three-dimensional region, is a triple
Unit Maps: Grade 8 Math
 Real Number Relationships 8.3 Number and operations. The student represents and use real numbers in a variety of forms. Representation of Real Numbers 8.3A extend previous knowledge of sets and subsets
Real Number Relationships 8.3 Number and operations. The student represents and use real numbers in a variety of forms. Representation of Real Numbers 8.3A extend previous knowledge of sets and subsets
Lab Location: MRI, B2, Cardinal Carter Wing, St. Michael s Hospital, 30 Bond Street
 Lab Location: MRI, B2, Cardinal Carter Wing, St. Michael s Hospital, 30 Bond Street MRI is located in the sub basement of CC wing. From Queen or Victoria, follow the baby blue arrows and ride the CC south
Lab Location: MRI, B2, Cardinal Carter Wing, St. Michael s Hospital, 30 Bond Street MRI is located in the sub basement of CC wing. From Queen or Victoria, follow the baby blue arrows and ride the CC south
Advanced Image Reconstruction Methods for Photoacoustic Tomography
 Advanced Image Reconstruction Methods for Photoacoustic Tomography Mark A. Anastasio, Kun Wang, and Robert Schoonover Department of Biomedical Engineering Washington University in St. Louis 1 Outline Photoacoustic/thermoacoustic
Advanced Image Reconstruction Methods for Photoacoustic Tomography Mark A. Anastasio, Kun Wang, and Robert Schoonover Department of Biomedical Engineering Washington University in St. Louis 1 Outline Photoacoustic/thermoacoustic
General and Efficient Super-Resolution Method for Multi-slice MRI
 General and Efficient Super-Resolution Method for Multi-slice MRI D.H.J. Poot 1,2,V.VanMeir 2, and J. Sijbers 2 1 BIGR, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam 2 Visionlab, University of Antwerp, Antwerp Abstract.
General and Efficient Super-Resolution Method for Multi-slice MRI D.H.J. Poot 1,2,V.VanMeir 2, and J. Sijbers 2 1 BIGR, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam 2 Visionlab, University of Antwerp, Antwerp Abstract.
MRI image formation 8/3/2016. Disclosure. Outlines. Chen Lin, PhD DABR 3. Indiana University School of Medicine and Indiana University Health
 MRI image formation Indiana University School of Medicine and Indiana University Health Disclosure No conflict of interest for this presentation 2 Outlines Data acquisition Spatial (Slice/Slab) selection
MRI image formation Indiana University School of Medicine and Indiana University Health Disclosure No conflict of interest for this presentation 2 Outlines Data acquisition Spatial (Slice/Slab) selection
2D Fan Beam Reconstruction 3D Cone Beam Reconstruction
 2D Fan Beam Reconstruction 3D Cone Beam Reconstruction Mario Koerner March 17, 2006 1 2D Fan Beam Reconstruction Two-dimensional objects can be reconstructed from projections that were acquired using parallel
2D Fan Beam Reconstruction 3D Cone Beam Reconstruction Mario Koerner March 17, 2006 1 2D Fan Beam Reconstruction Two-dimensional objects can be reconstructed from projections that were acquired using parallel
Motion Robust Magnetic Susceptibility and Field Inhomogeneity Estimation Using Regularized Image Restoration Techniques for fmri
 Motion Robust Magnetic Susceptibility and Field Inhomogeneity Estimation Using Regularized Image Restoration Techniques for fmri Desmond Tec Beng Yeo 1,, Jeffrey A. Fessler 1,, and Bolye Kim 1 1 Department
Motion Robust Magnetic Susceptibility and Field Inhomogeneity Estimation Using Regularized Image Restoration Techniques for fmri Desmond Tec Beng Yeo 1,, Jeffrey A. Fessler 1,, and Bolye Kim 1 1 Department
CHAPTER 9: Magnetic Susceptibility Effects in High Field MRI
 Figure 1. In the brain, the gray matter has substantially more blood vessels and capillaries than white matter. The magnified image on the right displays the rich vasculature in gray matter forming porous,
Figure 1. In the brain, the gray matter has substantially more blood vessels and capillaries than white matter. The magnified image on the right displays the rich vasculature in gray matter forming porous,
Feldkamp-type image reconstruction from equiangular data
 Journal of X-Ray Science and Technology 9 (2001) 113 120 113 IOS Press Feldkamp-type image reconstruction from equiangular data Ben Wang a, Hong Liu b, Shiying Zhao c and Ge Wang d a Department of Elec.
Journal of X-Ray Science and Technology 9 (2001) 113 120 113 IOS Press Feldkamp-type image reconstruction from equiangular data Ben Wang a, Hong Liu b, Shiying Zhao c and Ge Wang d a Department of Elec.
Sources of Distortion in Functional MRI Data
 Human Brain Mapping 8:80 85(1999) Sources of Distortion in Functional MRI Data Peter Jezzard* and Stuart Clare FMRIB Centre, Department of Clinical Neurology, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK Abstract:
Human Brain Mapping 8:80 85(1999) Sources of Distortion in Functional MRI Data Peter Jezzard* and Stuart Clare FMRIB Centre, Department of Clinical Neurology, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK Abstract:
Measuring Lengths The First Fundamental Form
 Differential Geometry Lia Vas Measuring Lengths The First Fundamental Form Patching up the Coordinate Patches. Recall that a proper coordinate patch of a surface is given by parametric equations x = (x(u,
Differential Geometry Lia Vas Measuring Lengths The First Fundamental Form Patching up the Coordinate Patches. Recall that a proper coordinate patch of a surface is given by parametric equations x = (x(u,
Joint design of excitation k-space trajectory and RF pulse for small-tip 3D tailored excitation in MRI
 Joint design of excitation k-space trajectory and RF pulse for small-tip 3D tailored excitation in MRI Hao Sun, Student member, IEEE, Jeffrey A. Fessler, Fellow, IEEE, Douglas C. Noll, Senior member, IEEE,
Joint design of excitation k-space trajectory and RF pulse for small-tip 3D tailored excitation in MRI Hao Sun, Student member, IEEE, Jeffrey A. Fessler, Fellow, IEEE, Douglas C. Noll, Senior member, IEEE,
Tradeoffs and complexities in model-based MR image reconstruction
 Tradeoffs and complexities in model-based MR image reconstruction Jeffrey A. Fessler EECS Dept., The University of Michigan fessler@umich.edu December 6, 2007 Abstract Model-based methods for image reconstruction
Tradeoffs and complexities in model-based MR image reconstruction Jeffrey A. Fessler EECS Dept., The University of Michigan fessler@umich.edu December 6, 2007 Abstract Model-based methods for image reconstruction
Constrained Reconstruction of Sparse Cardiac MR DTI Data
 Constrained Reconstruction of Sparse Cardiac MR DTI Data Ganesh Adluru 1,3, Edward Hsu, and Edward V.R. DiBella,3 1 Electrical and Computer Engineering department, 50 S. Central Campus Dr., MEB, University
Constrained Reconstruction of Sparse Cardiac MR DTI Data Ganesh Adluru 1,3, Edward Hsu, and Edward V.R. DiBella,3 1 Electrical and Computer Engineering department, 50 S. Central Campus Dr., MEB, University
Mean Shift Tracking. CS4243 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Leow Wee Kheng
 CS4243 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Leow Wee Kheng Department of Computer Science School of Computing National University of Singapore (CS4243) Mean Shift Tracking 1 / 28 Mean Shift Mean Shift
CS4243 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Leow Wee Kheng Department of Computer Science School of Computing National University of Singapore (CS4243) Mean Shift Tracking 1 / 28 Mean Shift Mean Shift
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators. Preprocessing
 SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
Regularized Estimation of Main and RF Field Inhomogeneity and Longitudinal Relaxation Rate in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Regularized Estimation of Main and RF Field Inhomogeneity and Longitudinal Relaxation Rate in Magnetic Resonance Imaging by Amanda K. Funai A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Regularized Estimation of Main and RF Field Inhomogeneity and Longitudinal Relaxation Rate in Magnetic Resonance Imaging by Amanda K. Funai A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Sparse sampling in MRI: From basic theory to clinical application. R. Marc Lebel, PhD Department of Electrical Engineering Department of Radiology
 Sparse sampling in MRI: From basic theory to clinical application R. Marc Lebel, PhD Department of Electrical Engineering Department of Radiology Objective Provide an intuitive overview of compressed sensing
Sparse sampling in MRI: From basic theory to clinical application R. Marc Lebel, PhD Department of Electrical Engineering Department of Radiology Objective Provide an intuitive overview of compressed sensing
2D and 3D Far-Field Radiation Patterns Reconstruction Based on Compressive Sensing
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 46, 47 56, 206 2D and 3D Far-Field Radiation Patterns Reconstruction Based on Compressive Sensing Berenice Verdin * and Patrick Debroux Abstract The measurement
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 46, 47 56, 206 2D and 3D Far-Field Radiation Patterns Reconstruction Based on Compressive Sensing Berenice Verdin * and Patrick Debroux Abstract The measurement
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators. Preprocessing. fmri Preprocessing
 SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
Diffusion MRI Acquisition. Karla Miller FMRIB Centre, University of Oxford
 Diffusion MRI Acquisition Karla Miller FMRIB Centre, University of Oxford karla@fmrib.ox.ac.uk Diffusion Imaging How is diffusion weighting achieved? How is the image acquired? What are the limitations,
Diffusion MRI Acquisition Karla Miller FMRIB Centre, University of Oxford karla@fmrib.ox.ac.uk Diffusion Imaging How is diffusion weighting achieved? How is the image acquired? What are the limitations,
Following on from the two previous chapters, which considered the model of the
 Chapter 5 Simulator validation Following on from the two previous chapters, which considered the model of the simulation process and how this model was implemented in software, this chapter is concerned
Chapter 5 Simulator validation Following on from the two previous chapters, which considered the model of the simulation process and how this model was implemented in software, this chapter is concerned
RECOVERY OF PARTIALLY OBSERVED DATA APPEARING IN CLUSTERS. Sunrita Poddar, Mathews Jacob
 RECOVERY OF PARTIALLY OBSERVED DATA APPEARING IN CLUSTERS Sunrita Poddar, Mathews Jacob Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Iowa, IA, USA ABSTRACT We propose a matrix completion
RECOVERY OF PARTIALLY OBSERVED DATA APPEARING IN CLUSTERS Sunrita Poddar, Mathews Jacob Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Iowa, IA, USA ABSTRACT We propose a matrix completion
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
 Name Code Class Branch Page 1 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : ROBOTICS (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 0 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : A7055 : IV B. Tech I Semester : MECHANICAL
Name Code Class Branch Page 1 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : ROBOTICS (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 0 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : A7055 : IV B. Tech I Semester : MECHANICAL
Animating orientation. CS 448D: Character Animation Prof. Vladlen Koltun Stanford University
 Animating orientation CS 448D: Character Animation Prof. Vladlen Koltun Stanford University Orientation in the plane θ (cos θ, sin θ) ) R θ ( x y = sin θ ( cos θ sin θ )( x y ) cos θ Refresher: Homogenous
Animating orientation CS 448D: Character Animation Prof. Vladlen Koltun Stanford University Orientation in the plane θ (cos θ, sin θ) ) R θ ( x y = sin θ ( cos θ sin θ )( x y ) cos θ Refresher: Homogenous
11/1/13. Visualization. Scientific Visualization. Types of Data. Height Field. Contour Curves. Meshes
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 26 Visualization Height Fields and Contours Scalar Fields Volume Rendering Vector Fields [Angel Ch. 2.11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Scientific Visualization
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 26 Visualization Height Fields and Contours Scalar Fields Volume Rendering Vector Fields [Angel Ch. 2.11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Scientific Visualization
Visualization. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 26
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 26 Visualization Height Fields and Contours Scalar Fields Volume Rendering Vector Fields [Angel Ch. 11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Scientific Visualization
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 26 Visualization Height Fields and Contours Scalar Fields Volume Rendering Vector Fields [Angel Ch. 11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Scientific Visualization
COBRE Scan Information
 COBRE Scan Information Below is more information on the directory structure for the COBRE imaging data. Also below are the imaging parameters for each series. Directory structure: var/www/html/dropbox/1139_anonymized/human:
COBRE Scan Information Below is more information on the directory structure for the COBRE imaging data. Also below are the imaging parameters for each series. Directory structure: var/www/html/dropbox/1139_anonymized/human:
Fiber Selection from Diffusion Tensor Data based on Boolean Operators
 Fiber Selection from Diffusion Tensor Data based on Boolean Operators D. Merhof 1, G. Greiner 2, M. Buchfelder 3, C. Nimsky 4 1 Visual Computing, University of Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany 2 Computer Graphics
Fiber Selection from Diffusion Tensor Data based on Boolean Operators D. Merhof 1, G. Greiner 2, M. Buchfelder 3, C. Nimsky 4 1 Visual Computing, University of Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany 2 Computer Graphics
Optimal Sampling Geometries for TV-Norm Reconstruction of fmri Data
 Optimal Sampling Geometries for TV-Norm Reconstruction of fmri Data Oliver M. Jeromin, Student Member, IEEE, Vince D. Calhoun, Senior Member, IEEE, and Marios S. Pattichis, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
Optimal Sampling Geometries for TV-Norm Reconstruction of fmri Data Oliver M. Jeromin, Student Member, IEEE, Vince D. Calhoun, Senior Member, IEEE, and Marios S. Pattichis, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Vectors and the Geometry of Space In Figure 11.43, consider the line L through the point P(x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and parallel to the vector. The vector v is a direction vector for the line L, and a, b, and c
Vectors and the Geometry of Space In Figure 11.43, consider the line L through the point P(x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and parallel to the vector. The vector v is a direction vector for the line L, and a, b, and c
Lecture 15. Lecturer: Prof. Sergei Fedotov Calculus and Vectors. Length of a Curve and Parametric Equations
 Lecture 15 Lecturer: Prof. Sergei Fedotov 10131 - Calculus and Vectors Length of a Curve and Parametric Equations Sergei Fedotov (University of Manchester) MATH10131 2011 1 / 5 Lecture 15 1 Length of a
Lecture 15 Lecturer: Prof. Sergei Fedotov 10131 - Calculus and Vectors Length of a Curve and Parametric Equations Sergei Fedotov (University of Manchester) MATH10131 2011 1 / 5 Lecture 15 1 Length of a
Development of a Simulation Method of Three-Dimensional Ultrafine Processing by Femtosecond Laser Shunsuke Nabetani 1, a, Hideki Aoyama 1, b * 1, 2, c
 Development of a Simulation Method of Three-Dimensional Ultrafine Processing by Femtosecond Laser Shunsuke Nabetani 1, a, Hideki Aoyama 1, b * 1,, c, Masahiro Ueda Yoshinori Ogawa 1,, d 1,, 3, e, and Kazuo
Development of a Simulation Method of Three-Dimensional Ultrafine Processing by Femtosecond Laser Shunsuke Nabetani 1, a, Hideki Aoyama 1, b * 1,, c, Masahiro Ueda Yoshinori Ogawa 1,, d 1,, 3, e, and Kazuo
MRI Imaging Options. Frank R. Korosec, Ph.D. Departments of Radiology and Medical Physics University of Wisconsin Madison
 MRI Imaging Options Frank R. Korosec, Ph.D. Departments of Radiolog and Medical Phsics Universit of Wisconsin Madison f.korosec@hosp.wisc.edu As MR imaging becomes more developed, more imaging options
MRI Imaging Options Frank R. Korosec, Ph.D. Departments of Radiolog and Medical Phsics Universit of Wisconsin Madison f.korosec@hosp.wisc.edu As MR imaging becomes more developed, more imaging options
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Med Phys. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 March 13.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Med Phys. 2008 February ; 35(2): 660 663. Prior image constrained compressed sensing (PICCS): A method to accurately reconstruct dynamic
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Med Phys. 2008 February ; 35(2): 660 663. Prior image constrained compressed sensing (PICCS): A method to accurately reconstruct dynamic
Fast Isotropic Volumetric Coronary MR Angiography Using Free-Breathing 3D Radial Balanced FFE Acquisition
 Fast Isotropic Volumetric Coronary MR Angiography Using Free-Breathing 3D Radial Balanced FFE Acquisition C. Stehning, 1 * P. Börnert, 2 K. Nehrke, 2 H. Eggers, 2 and O. Dössel 1 Magnetic Resonance in
Fast Isotropic Volumetric Coronary MR Angiography Using Free-Breathing 3D Radial Balanced FFE Acquisition C. Stehning, 1 * P. Börnert, 2 K. Nehrke, 2 H. Eggers, 2 and O. Dössel 1 Magnetic Resonance in
Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 16 Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing Ray-Surface Intersection Barycentric Coordinates [Angel Ch. 11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Ray-Surface Intersections
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 16 Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing Ray-Surface Intersection Barycentric Coordinates [Angel Ch. 11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Ray-Surface Intersections
EPI Data Are Acquired Serially. EPI Data Are Acquired Serially 10/23/2011. Functional Connectivity Preprocessing. fmri Preprocessing
 Functional Connectivity Preprocessing Geometric distortion Head motion Geometric distortion Head motion EPI Data Are Acquired Serially EPI Data Are Acquired Serially descending 1 EPI Data Are Acquired
Functional Connectivity Preprocessing Geometric distortion Head motion Geometric distortion Head motion EPI Data Are Acquired Serially EPI Data Are Acquired Serially descending 1 EPI Data Are Acquired
k-space Interpretation of the Rose Model: Noise Limitation on the Detectable Resolution in MRI
 k-space Interpretation of the Rose Model: Noise Limitation on the Detectable Resolution in MRI Richard Watts and Yi Wang* Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 48:550 554 (2002) Noise limitation on the detected
k-space Interpretation of the Rose Model: Noise Limitation on the Detectable Resolution in MRI Richard Watts and Yi Wang* Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 48:550 554 (2002) Noise limitation on the detected
Functional MRI in Clinical Research and Practice Preprocessing
 Functional MRI in Clinical Research and Practice Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization
Functional MRI in Clinical Research and Practice Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization
High Fidelity Brain Connectivity Imaging
 CNI Inauguration Workshop Stanford, March 22 nd, 2012 High Fidelity Brain Connectivity Imaging -Recent Progress on Diffusion Weighted MRI for High Resolution and Low Distortion Allen W. Song, PhD Brain
CNI Inauguration Workshop Stanford, March 22 nd, 2012 High Fidelity Brain Connectivity Imaging -Recent Progress on Diffusion Weighted MRI for High Resolution and Low Distortion Allen W. Song, PhD Brain
Vector Integration : Surface Integrals
 Vector Integration : Surface Integrals P. Sam Johnson April 10, 2017 P. Sam Johnson Vector Integration : Surface Integrals April 10, 2017 1/35 Overview : Surface Area and Surface Integrals You know how
Vector Integration : Surface Integrals P. Sam Johnson April 10, 2017 P. Sam Johnson Vector Integration : Surface Integrals April 10, 2017 1/35 Overview : Surface Area and Surface Integrals You know how
Automatic Correction of Echo-Planar Imaging (EPI) Ghosting Artifacts in Real-Time Interactive Cardiac MRI Using Sensitivity Encoding
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 27:239 245 (2008) Technical Note Automatic Correction of Echo-Planar Imaging (EPI) Ghosting Artifacts in Real-Time Interactive Cardiac MRI Using Sensitivity Encoding
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 27:239 245 (2008) Technical Note Automatic Correction of Echo-Planar Imaging (EPI) Ghosting Artifacts in Real-Time Interactive Cardiac MRI Using Sensitivity Encoding
GRADE 3 GRADE-LEVEL GOALS
 Content Strand: Number and Numeration Understand the Meanings, Uses, and Representations of Numbers Understand Equivalent Names for Numbers Understand Common Numerical Relations Place value and notation
Content Strand: Number and Numeration Understand the Meanings, Uses, and Representations of Numbers Understand Equivalent Names for Numbers Understand Common Numerical Relations Place value and notation
3D z-shim Method for Reduction of Susceptibility Effects in BOLD fmri
 3D z-shim Method for Reduction of Susceptibility Effects in BOLD fmri Gary H. Glover* Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 42:290 299 (1999) Susceptibility-induced magnetic field gradients (SFGs) perpendicular
3D z-shim Method for Reduction of Susceptibility Effects in BOLD fmri Gary H. Glover* Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 42:290 299 (1999) Susceptibility-induced magnetic field gradients (SFGs) perpendicular
Dynamic Image and Fieldmap Joint Estimation Methods for MRI Using Single-Shot Trajectories
 Dynamic Image and Fieldmap Joint Estimation Methods for MRI Using Single-Shot Trajectories by Antonis Matakos A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
Dynamic Image and Fieldmap Joint Estimation Methods for MRI Using Single-Shot Trajectories by Antonis Matakos A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
