We P9 16 Eigenray Tracing in 3D Heterogeneous Media
|
|
|
- Loraine Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 We P9 Eigenray Traing in 3D Heterogeneous Media Z. Koren* (Emerson), I. Ravve (Emerson) Summary Conventional two-point ray traing in a general 3D heterogeneous medium is normally performed by a shooting method. The loation and the slowness omponents are speified at the start point, and the ray path is the solution of ODEs with the initial onditions. The ray arrives to some proximity of the destination, and the start diretion is then suessively refined, so that the ray path eventually inludes the destination point. Eigenray traing, however, is a boundary-value problem, rather than an initial-value problem. The boundary onditions are two endpoint loations, and the ray trajetory satisfies Fermat's priniple of least traveltime. In this study, we apply the non-linear Finite Element Analysis to find the least-time ray path. The ray trajetory is split into a number of three-nodal segments with quadrati interpolation of trajetory points, traveltime and other funtions between the nodes. For eah segment, we ompute the traveltime, and its first and seond derivatives with respet to the nodal loations. The loal derivatives (related to a single segment) are ombined into the global derivatives of the entire path. For the least time, the first derivatives vanish. Knowledge of the seond derivatives makes it possible to apply the Newton method for ray path optimization. 8th EAGE Conferene & Exhibition 8 - June 8, Copenhagen, Denmark
2 Introdution Conventional two-point ray traing in general 3D heterogeneous media is normally performed using the so-alled shooting method. In this method, a fan of rays is traed from a given starting point, where the rays arriving in the viinity of the target loation, with lose take-off angles, are used to onverge to the atual end point. By overing a wide range of take-off angles, multi-pathing stationary solutions an be found. However, in omplex geologial areas, the solution to the initial-value problem assoiated with the individual rays is highly sensitive to small hanges in the take-off angles at the starting point, resulting in shadow zones whih the numerial rays annot penetrate. The proposed Eigenray method (also known as the ray bending method) is a diret solution of the boundary-value problem, rather than the initial-value problem. The boundary onditions are the two endpoint loations, and the ray trajetory satisfies Fermat s priniple of stationary traveltime. This method is partiularly attrative for areas that involve sharp veloity variations or loal veloity anomalies. The ase of simulating head waves is an extreme example of Eigenrays providing stable solutions where onventional ray traing fails. Ray bending methods have been extensively studied. Westwood and Vidmar (987) applied the method to simulate the signals interating with a layered oean bottom. Waltham (988) studied models onsisting of onstant-veloity layers separated by urved interfaes and omputed ray paths whose traveltimes are stationary with respet to hanges in ray/interfae intersetion positions. The amplitude of the resulting event is related to the seond derivative of the traveltime with respet to hanges in the position of the ray/interfae intersetion. Moser (99) used this method to ompute the traveltime between the soure point and all points of a network. Moser et al. (99) improved the onventional ray bending approah by applying a) gradient searh methods and b) interpolation by beta-splines between the nodes. Farra (99) applied the Hamiltonian formulation to the ray bending approah. Shashidhar and Anand (995) solved the problem of three-dimensional Eigenray traing in an oean hannel. Bona et al. (9) demonstrated that Fermat s priniple of stationary traveltime holds for general heterogeneous anisotropi media using stohasti simulated annealing global searh methods. Reently, Sripanih and Fomel () presented an effiient algorithm for two-point seismi ray traing in layered media by means of the bending method, where the ray paths are disretized at the intersetion of the rays with the struture s interfaes. In this study, we demonstrate the power of applying this type of ray traing by using a non-linear spetral element method to effiiently find aurate least-time ray paths in omplex geologial areas, providing solutions beyond onventional ray traing. Model and Method Consider an initial ray trajetory that is divided into a number of multi-nodal segments (spetral finite elements) with a Legendre polynomial interpolation. Eah segment inludes two endpoints and a number of internal points plaed along the internal flow parameter aording to the Gauss-Lobatto quadrature. The quadrature also assoiates definite weights for all points of a segment. The simplest spetral element is a three-nodal segment whih we use to demonstrate the syntheti examples. The nodes are loated at, and + of the flow parameter. For eah segment, we ompute the traveltime and its first and seond derivatives with respet to the nodal loations. The loal derivatives (related to a single segment) are ombined into the global derivatives of the entire path. The loal derivatives are vetors of size 3n, and the loal seond derivatives are matries of the same size, where n is the number of segment nodes, inluding its endpoints. The global matrix of the seond derivatives has a band struture with a narrow band width 3n. This matrix is symmetri, and if the stationary traveltime is minimum (the most pratial ase), it is also positive-definite in the proximity of the stationary ray. For the least-time solution, the first derivatives vanish. Knowledge of the seond derivatives makes it possible to apply the Newton method for Eigenray optimization. The seond derivatives of the traveltime depend on the loations of the nodes, and thus the minimization problem is nonlinear. In addition, the seond derivatives may be used to ompute the geometrial spreading when the stationary ray path is found. We note that the least traveltime (or generally, the stationary traveltime) fully defines the ray path, but it still allows moving the nodes along the ray. Therefore, we apply an additional onstraint on the lengths between the suessive nodes. The nodes are loated more densely in regions where the veloity hanges rapidly. Thus, the onstraints are the ratios between the ar lengths onneting suessive nodes. There are, in general, two ways to implement the onstraints: stiff onstraints (e.g., applying Lagrangian multipliers method) and soft or relaxed 8th EAGE Conferene & Exhibition 8 - June 8, Copenhagen, Denmark
3 onstraints, adding a penalty term to the target funtion to be minimized. The soft onstraint method is simpler, does not lead to additional unknown parameters, does not inrease the bandwidth of the resolving matrix, and still provides exellent auray. Sine the onstraints only affet the loation of the nodes along the stationary ray, the omputational formulae are essentially simplified if the hords (i.e., the distanes between the suessive nodes) are applied instead of the ar lengths. Syntheti Examples Three examples of ray bending solutions are presented. Example : High-veloity half-spae under onstant veloity layer (head wave). Consider a D veloity model whose profile and gradient are shown in Figure, to the left. Eigenray Trae for Two Initial Guesses Eigenray Init Init 8 distane (km) Figure High-veloity half-spae under onstant veloity layer: Veloity model and stationary ray The smoothed veloity model is depth-dependent and desribed by, v z z v vo tanh t, () zo where vo km/s is the veloity of the homogeneous layer above the half-spae, v km/s is the differene between the veloity of the half-spae and that of the overlying layer; thus, the halfspae veloity is vh vo v km/s. Atually, neither the overlying layer nor the half-spae is homogeneous due to the transition zone. Parameter zt.5km is the mid-level of the transition zone, and parameter zo.km is the harateristi distane that shows the width of the transition zone. The offset h = km. Figure, to the right, shows the initial guesses and the stationary ray. We applied the initial guess twie: first with the floor depth km (whih is approximately the lower end of the transition zone), then with the over-estimated floor depth 5 km (red and blue lines, respetively). Both initial guesses onverge to a unique head wave solution (blak line). In the next example we show that in the ase of multi-arrivals, the final solution is sensitive to the initial guess. Example : One-way path in a medium with low-veloity ellipti anomaly. Consider a onstant bakground veloity with an ellipti anomaly region of a lower veloity, as shown in Figure. Loation of the ellipse enter is x, z, and the semi-axes of the ellipse are rx, r z. The veloity field is desribed by an analyti funtion, 8th EAGE Conferene & Exhibition 8 - June 8, Copenhagen, Denmark
4 x x z z v vx, z vb tanh A, A, () s rx rz where v b is the bakground veloity outside the ellipse, and v b v is the anomalous low veloity inside the ellipse. Negative v leads to anomalous high veloity inside the ellipse. Parameter s is the smoothing sale: the smaller s is, the sharper the veloity hange. For infinitesimal s, the veloity funtion beomes disontinuous. We aept the following parameters, v 5km/s, v 3km/s, x 5km, z 3km, r 3km, r km, s.. (3) b x z The soure is loated at the subsurfae point with zero horizontal oordinate and depth dz km, and the reeiver is on the surfae, with the one-way offset ds km. Three different initial guesses shown in Figure left, by green, blak and blue lines, lead to three different solutions shown in Figure right. The red ellipse is the ontour of the veloity anomaly. Traing with Low Veloity Ellipse 3 5 Contour Trae Trae Trae distane (km) Figure One-way path in a medium with low-veloity ellipti anomaly For rays and (blak and green lines), the resulting (minimum) traveltime is t.8s, and for ray 3 (blue line), the traveltime is t 3.79s. Rays and are symmetri solutions, where the ray bypasses the low-veloity inlusion and almost avoids penetration into the transition zone. These rays travel ompletely through the high-veloity bakground. For ray 3, refration ours twie, upon entry to and exit from the low-veloity ellipse. Thus, we deal with a multi-arrival ase, haraterized by three loal minima, two of whih are also global. Example 3: Veloity field with two ellipti anomalies. Consider a model that ombines slow- and high-veloity anomalies and fast half-spae. It an be analytially desribed by, v v v vx, z v tanh tanh h b A A tanh A3, () where x x z z x x z z z z A o, A, A 3 s r s z x r z rx r z d. (5) Parameters x and x are horizontal oordinates of entral points of ellipti anomalies, z is their ommon vertial oordinate, z o is the floor depth of the high-veloity half-spae. Parameters s and z d govern the width of the transition zones, vb km/s, v km/s, vh 3km/s, x km, x km, z km, r km, r km, z km, z.km, s., () x z o d 8th EAGE Conferene & Exhibition 8 - June 8, Copenhagen, Denmark
5 and the offset h = km. Figure 3 shows the veloity field (left) and the ray traing results (right). The distanes in the veloity field plot are in km, and veloity is in km/s. Eigenray Traing with High & Low Veloity Ellipses & Fast Half-Spae 8 Trae Init Slow Fast Floor 8 distane (km) Figure 3 Ray traing in a medium with two ellipti anomalies and high-veloity half-spae In the right subplot, the blue and red ellipses show the low-veloity and high-veloity anomalies, respetively. The gray line is the loation of the half-spae floor midline. The green line is the initial guess, where the depth of the floor was deliberately overestimated, in order to demonstrate onvergene to a orret result even with an initial error. The blak line is the least-time ray path. Conlusions A ray bending algorithm, referred to as the Eigenray method, has been developed for two-point traing in a general 3D heterogeneous medium. The method uses spetral elements with Legendre polynomial interpolation between the nodes and Gauss-Lobatto quadrature. Additional soft onstraints related to the segment lengths govern the loations of the nodes along the stationary ray. Expliit expressions for the traveltime and its first and seond derivatives allow the implementation of the Newton method optimization, whih also yields the geometrial spreading. We demonstrated the attrativeness of the method in ases of loal low/high veloity anomalies and for solving the ray trajetory of head waves. For multi-arrivals, the final solution is obviously sensitive to the initial guess. A strategy of ombining the global ray shooting method with the proposed Eigenray method seems very attrative. Referenes Bona, A., Slawinski, M., and Smith, P. [9]. Ray traing by simulated annealing: Bending method. Geophysis, 7, no., T5 T3. Farra, V. [99]. Bending method revisited: a Hamiltonian approah. Geophysial Journal International, 9, no., Moser, T. [99]. Shortest path alulation of seismi rays, Geophysis, 5, no., Moser, T., Nolet, G., and Snieder, R. [99]. Ray bending revisited, Bulletin of the Seismologial Soiety of Ameria, 8, no., Shashidhar, N., and Anand, G. [995]. Eigenray traing in an oean using Fermat s priniple. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 8, no., 3-3. Sripanih, Y., and Fomel, S. []. Two-point seismi ray traing in layered media using bending, SEG Tehnial Program Expanded Abstrats, Waltham, D. [988]. Two-point ray traing using Fermat s priniple. Geophysial Journal International, 93, no. 3, Westwood, E., and Vidmar, P. [987]. Eigenray funding and time series simulation in a layeredbottom oean. The Journal of the Aoustial Soiety of Ameria, 8, no., th EAGE Conferene & Exhibition 8 - June 8, Copenhagen, Denmark
Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ow.mit.edu 1.510 Introdution to Seismology Spring 008 For information about iting these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ow.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Leture Notes 3.3.007
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ow.mit.edu 1.510 Introdution to Seismology Spring 008 For information about iting these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ow.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Leture Notes 3.3.007
Smooth Trajectory Planning Along Bezier Curve for Mobile Robots with Velocity Constraints
 Smooth Trajetory Planning Along Bezier Curve for Mobile Robots with Veloity Constraints Gil Jin Yang and Byoung Wook Choi Department of Eletrial and Information Engineering Seoul National University of
Smooth Trajetory Planning Along Bezier Curve for Mobile Robots with Veloity Constraints Gil Jin Yang and Byoung Wook Choi Department of Eletrial and Information Engineering Seoul National University of
Travel-time sensitivity kernels versus diffraction patterns obtained through double beam-forming in shallow water
 Travel-time sensitivity kernels versus diffration patterns obtained through double beam-forming in shallow water Ion Iturbe a GIPSA Laboratory, INPG CNRS, 96 rue de la Houille Blanhe, Domaine Universitaire,
Travel-time sensitivity kernels versus diffration patterns obtained through double beam-forming in shallow water Ion Iturbe a GIPSA Laboratory, INPG CNRS, 96 rue de la Houille Blanhe, Domaine Universitaire,
And, the (low-pass) Butterworth filter of order m is given in the frequency domain by
 Problem Set no.3.a) The ideal low-pass filter is given in the frequeny domain by B ideal ( f ), f f; =, f > f. () And, the (low-pass) Butterworth filter of order m is given in the frequeny domain by B
Problem Set no.3.a) The ideal low-pass filter is given in the frequeny domain by B ideal ( f ), f f; =, f > f. () And, the (low-pass) Butterworth filter of order m is given in the frequeny domain by B
Plot-to-track correlation in A-SMGCS using the target images from a Surface Movement Radar
 Plot-to-trak orrelation in A-SMGCS using the target images from a Surfae Movement Radar G. Golino Radar & ehnology Division AMS, Italy ggolino@amsjv.it Abstrat he main topi of this paper is the formulation
Plot-to-trak orrelation in A-SMGCS using the target images from a Surfae Movement Radar G. Golino Radar & ehnology Division AMS, Italy ggolino@amsjv.it Abstrat he main topi of this paper is the formulation
Pre-Critical incidence
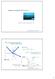 Seismi methods: Refration I Refration reading: Sharma p58-86 Pre-Critial inidene Refletion and refration Snell s Law: sin i sin R sin r P P P P P P where p is the ray parameter and is onstant along eah
Seismi methods: Refration I Refration reading: Sharma p58-86 Pre-Critial inidene Refletion and refration Snell s Law: sin i sin R sin r P P P P P P where p is the ray parameter and is onstant along eah
Drawing lines. Naïve line drawing algorithm. drawpixel(x, round(y)); double dy = y1 - y0; double dx = x1 - x0; double m = dy / dx; double y = y0;
 Naïve line drawing algorithm // Connet to grid points(x0,y0) and // (x1,y1) by a line. void drawline(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1) { int x; double dy = y1 - y0; double dx = x1 - x0; double m = dy / dx;
Naïve line drawing algorithm // Connet to grid points(x0,y0) and // (x1,y1) by a line. void drawline(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1) { int x; double dy = y1 - y0; double dx = x1 - x0; double m = dy / dx;
Detection and Recognition of Non-Occluded Objects using Signature Map
 6th WSEAS International Conferene on CIRCUITS, SYSTEMS, ELECTRONICS,CONTROL & SIGNAL PROCESSING, Cairo, Egypt, De 9-31, 007 65 Detetion and Reognition of Non-Oluded Objets using Signature Map Sangbum Park,
6th WSEAS International Conferene on CIRCUITS, SYSTEMS, ELECTRONICS,CONTROL & SIGNAL PROCESSING, Cairo, Egypt, De 9-31, 007 65 Detetion and Reognition of Non-Oluded Objets using Signature Map Sangbum Park,
with respect to the normal in each medium, respectively. The question is: How are θ
 Prof. Raghuveer Parthasarathy University of Oregon Physis 35 Winter 8 3 R EFRACTION When light travels from one medium to another, it may hange diretion. This phenomenon familiar whenever we see the bent
Prof. Raghuveer Parthasarathy University of Oregon Physis 35 Winter 8 3 R EFRACTION When light travels from one medium to another, it may hange diretion. This phenomenon familiar whenever we see the bent
A Novel Validity Index for Determination of the Optimal Number of Clusters
 IEICE TRANS. INF. & SYST., VOL.E84 D, NO.2 FEBRUARY 2001 281 LETTER A Novel Validity Index for Determination of the Optimal Number of Clusters Do-Jong KIM, Yong-Woon PARK, and Dong-Jo PARK, Nonmembers
IEICE TRANS. INF. & SYST., VOL.E84 D, NO.2 FEBRUARY 2001 281 LETTER A Novel Validity Index for Determination of the Optimal Number of Clusters Do-Jong KIM, Yong-Woon PARK, and Dong-Jo PARK, Nonmembers
Orientation of the coordinate system
 Orientation of the oordinate system Right-handed oordinate system: -axis by a positive, around the -axis. The -axis is mapped to the i.e., antilokwise, rotation of The -axis is mapped to the -axis by a
Orientation of the oordinate system Right-handed oordinate system: -axis by a positive, around the -axis. The -axis is mapped to the i.e., antilokwise, rotation of The -axis is mapped to the -axis by a
A {k, n}-secret Sharing Scheme for Color Images
 A {k, n}-seret Sharing Sheme for Color Images Rastislav Luka, Konstantinos N. Plataniotis, and Anastasios N. Venetsanopoulos The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Dept. of Eletrial and Computer Engineering, University
A {k, n}-seret Sharing Sheme for Color Images Rastislav Luka, Konstantinos N. Plataniotis, and Anastasios N. Venetsanopoulos The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Dept. of Eletrial and Computer Engineering, University
Time delay estimation of reverberant meeting speech: on the use of multichannel linear prediction
 University of Wollongong Researh Online Faulty of Informatis - apers (Arhive) Faulty of Engineering and Information Sienes 7 Time delay estimation of reverberant meeting speeh: on the use of multihannel
University of Wollongong Researh Online Faulty of Informatis - apers (Arhive) Faulty of Engineering and Information Sienes 7 Time delay estimation of reverberant meeting speeh: on the use of multihannel
Vertex Unfoldings of Orthogonal Polyhedra: Positive, Negative, and Inconclusive Results
 CCCG 2018, Winnipeg, Canada, August 8 10, 2018 Vertex Unfoldings of Orthogonal Polyhedra: Positive, Negative, and Inonlusive Results Luis A. Garia Andres Gutierrrez Isaa Ruiz Andrew Winslow Abstrat We
CCCG 2018, Winnipeg, Canada, August 8 10, 2018 Vertex Unfoldings of Orthogonal Polyhedra: Positive, Negative, and Inonlusive Results Luis A. Garia Andres Gutierrrez Isaa Ruiz Andrew Winslow Abstrat We
Exploring the Commonality in Feature Modeling Notations
 Exploring the Commonality in Feature Modeling Notations Miloslav ŠÍPKA Slovak University of Tehnology Faulty of Informatis and Information Tehnologies Ilkovičova 3, 842 16 Bratislava, Slovakia miloslav.sipka@gmail.om
Exploring the Commonality in Feature Modeling Notations Miloslav ŠÍPKA Slovak University of Tehnology Faulty of Informatis and Information Tehnologies Ilkovičova 3, 842 16 Bratislava, Slovakia miloslav.sipka@gmail.om
Supplementary Material: Geometric Calibration of Micro-Lens-Based Light-Field Cameras using Line Features
 Supplementary Material: Geometri Calibration of Miro-Lens-Based Light-Field Cameras using Line Features Yunsu Bok, Hae-Gon Jeon and In So Kweon KAIST, Korea As the supplementary material, we provide detailed
Supplementary Material: Geometri Calibration of Miro-Lens-Based Light-Field Cameras using Line Features Yunsu Bok, Hae-Gon Jeon and In So Kweon KAIST, Korea As the supplementary material, we provide detailed
Chapter 2: Introduction to Maple V
 Chapter 2: Introdution to Maple V 2-1 Working with Maple Worksheets Try It! (p. 15) Start a Maple session with an empty worksheet. The name of the worksheet should be Untitled (1). Use one of the standard
Chapter 2: Introdution to Maple V 2-1 Working with Maple Worksheets Try It! (p. 15) Start a Maple session with an empty worksheet. The name of the worksheet should be Untitled (1). Use one of the standard
RANGE DOPPLER ALGORITHM FOR BISTATIC SAR PROCESSING BASED ON THE IMPROVED LOFFELD S BISTATIC FORMULA
 Progress In Eletromagnetis Researh Letters, Vol. 27, 161 169, 2011 RANGE DOPPLER ALGORITHM FOR ISTATIC SAR PROCESSING ASED ON THE IMPROVED LOFFELD S ISTATIC FORMULA X. Wang 1, * and D. Y. Zhu 2 1 Nanjing
Progress In Eletromagnetis Researh Letters, Vol. 27, 161 169, 2011 RANGE DOPPLER ALGORITHM FOR ISTATIC SAR PROCESSING ASED ON THE IMPROVED LOFFELD S ISTATIC FORMULA X. Wang 1, * and D. Y. Zhu 2 1 Nanjing
NONLINEAR BACK PROJECTION FOR TOMOGRAPHIC IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION. Ken Sauer and Charles A. Bouman
 NONLINEAR BACK PROJECTION FOR TOMOGRAPHIC IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION Ken Sauer and Charles A. Bouman Department of Eletrial Engineering, University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556, (219) 631-6999 Shool of
NONLINEAR BACK PROJECTION FOR TOMOGRAPHIC IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION Ken Sauer and Charles A. Bouman Department of Eletrial Engineering, University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556, (219) 631-6999 Shool of
Video Data and Sonar Data: Real World Data Fusion Example
 14th International Conferene on Information Fusion Chiago, Illinois, USA, July 5-8, 2011 Video Data and Sonar Data: Real World Data Fusion Example David W. Krout Applied Physis Lab dkrout@apl.washington.edu
14th International Conferene on Information Fusion Chiago, Illinois, USA, July 5-8, 2011 Video Data and Sonar Data: Real World Data Fusion Example David W. Krout Applied Physis Lab dkrout@apl.washington.edu
HIGHER ORDER full-wave three-dimensional (3-D) large-domain techniques in
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NIŠ) SER.: ELEC. ENERG. vol. 21, no. 2, August 2008, 209-220 Comparison of Higher Order FEM and MoM/SIE Approahes in Analyses of Closed- and Open-Region Eletromagneti Problems Milan
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NIŠ) SER.: ELEC. ENERG. vol. 21, no. 2, August 2008, 209-220 Comparison of Higher Order FEM and MoM/SIE Approahes in Analyses of Closed- and Open-Region Eletromagneti Problems Milan
Self-Adaptive Parent to Mean-Centric Recombination for Real-Parameter Optimization
 Self-Adaptive Parent to Mean-Centri Reombination for Real-Parameter Optimization Kalyanmoy Deb and Himanshu Jain Department of Mehanial Engineering Indian Institute of Tehnology Kanpur Kanpur, PIN 86 {deb,hjain}@iitk.a.in
Self-Adaptive Parent to Mean-Centri Reombination for Real-Parameter Optimization Kalyanmoy Deb and Himanshu Jain Department of Mehanial Engineering Indian Institute of Tehnology Kanpur Kanpur, PIN 86 {deb,hjain}@iitk.a.in
INTERPOLATED AND WARPED 2-D DIGITAL WAVEGUIDE MESH ALGORITHMS
 Proeedings of the COST G-6 Conferene on Digital Audio Effets (DAFX-), Verona, Italy, Deember 7-9, INTERPOLATED AND WARPED -D DIGITAL WAVEGUIDE MESH ALGORITHMS Vesa Välimäki Lab. of Aoustis and Audio Signal
Proeedings of the COST G-6 Conferene on Digital Audio Effets (DAFX-), Verona, Italy, Deember 7-9, INTERPOLATED AND WARPED -D DIGITAL WAVEGUIDE MESH ALGORITHMS Vesa Välimäki Lab. of Aoustis and Audio Signal
Simulation of Crystallographic Texture and Anisotropie of Polycrystals during Metal Forming with Respect to Scaling Aspects
 Raabe, Roters, Wang Simulation of Crystallographi Texture and Anisotropie of Polyrystals during Metal Forming with Respet to Saling Aspets D. Raabe, F. Roters, Y. Wang Max-Plank-Institut für Eisenforshung,
Raabe, Roters, Wang Simulation of Crystallographi Texture and Anisotropie of Polyrystals during Metal Forming with Respet to Saling Aspets D. Raabe, F. Roters, Y. Wang Max-Plank-Institut für Eisenforshung,
Trajectory Tracking Control for A Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Fuzzy Logic Controller
 Trajetory Traking Control for A Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Fuzzy Logi Controller K N FARESS 1 M T EL HAGRY 1 A A EL KOSY 2 1 Eletronis researh institute, Cairo, Egypt 2 Faulty of Engineering, Cairo University,
Trajetory Traking Control for A Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Fuzzy Logi Controller K N FARESS 1 M T EL HAGRY 1 A A EL KOSY 2 1 Eletronis researh institute, Cairo, Egypt 2 Faulty of Engineering, Cairo University,
Particle Swarm Optimization for the Design of High Diffraction Efficient Holographic Grating
 Original Artile Partile Swarm Optimization for the Design of High Diffration Effiient Holographi Grating A.K. Tripathy 1, S.K. Das, M. Sundaray 3 and S.K. Tripathy* 4 1, Department of Computer Siene, Berhampur
Original Artile Partile Swarm Optimization for the Design of High Diffration Effiient Holographi Grating A.K. Tripathy 1, S.K. Das, M. Sundaray 3 and S.K. Tripathy* 4 1, Department of Computer Siene, Berhampur
the data. Structured Principal Component Analysis (SPCA)
 Strutured Prinipal Component Analysis Kristin M. Branson and Sameer Agarwal Department of Computer Siene and Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 9193-114 Abstrat Many tasks involving
Strutured Prinipal Component Analysis Kristin M. Branson and Sameer Agarwal Department of Computer Siene and Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 9193-114 Abstrat Many tasks involving
PARAMETRIC SAR IMAGE FORMATION - A PROMISING APPROACH TO RESOLUTION-UNLIMITED IMAGING. Yesheng Gao, Kaizhi Wang, Xingzhao Liu
 20th European Signal Proessing Conferene EUSIPCO 2012) Buharest, Romania, August 27-31, 2012 PARAMETRIC SAR IMAGE FORMATION - A PROMISING APPROACH TO RESOLUTION-UNLIMITED IMAGING Yesheng Gao, Kaizhi Wang,
20th European Signal Proessing Conferene EUSIPCO 2012) Buharest, Romania, August 27-31, 2012 PARAMETRIC SAR IMAGE FORMATION - A PROMISING APPROACH TO RESOLUTION-UNLIMITED IMAGING Yesheng Gao, Kaizhi Wang,
timestamp, if silhouette(x, y) 0 0 if silhouette(x, y) = 0, mhi(x, y) = and mhi(x, y) < timestamp - duration mhi(x, y), else
 3rd International Conferene on Multimedia Tehnolog(ICMT 013) An Effiient Moving Target Traking Strateg Based on OpenCV and CAMShift Theor Dongu Li 1 Abstrat Image movement involved bakground movement and
3rd International Conferene on Multimedia Tehnolog(ICMT 013) An Effiient Moving Target Traking Strateg Based on OpenCV and CAMShift Theor Dongu Li 1 Abstrat Image movement involved bakground movement and
Lecture Notes of Möbuis Transformation in Hyperbolic Plane
 Applied Mathematis, 04, 5, 6-5 Published Online August 04 in SiRes http://wwwsirporg/journal/am http://dxdoiorg/0436/am04555 Leture Notes of Möbuis Transformation in Hyperboli Plane Rania B M Amer Department
Applied Mathematis, 04, 5, 6-5 Published Online August 04 in SiRes http://wwwsirporg/journal/am http://dxdoiorg/0436/am04555 Leture Notes of Möbuis Transformation in Hyperboli Plane Rania B M Amer Department
The Mathematics of Simple Ultrasonic 2-Dimensional Sensing
 The Mathematis of Simple Ultrasoni -Dimensional Sensing President, Bitstream Tehnology The Mathematis of Simple Ultrasoni -Dimensional Sensing Introdution Our ompany, Bitstream Tehnology, has been developing
The Mathematis of Simple Ultrasoni -Dimensional Sensing President, Bitstream Tehnology The Mathematis of Simple Ultrasoni -Dimensional Sensing Introdution Our ompany, Bitstream Tehnology, has been developing
1. Introduction. 2. The Probable Stope Algorithm
 1. Introdution Optimization in underground mine design has reeived less attention than that in open pit mines. This is mostly due to the diversity o underground mining methods and omplexity o underground
1. Introdution Optimization in underground mine design has reeived less attention than that in open pit mines. This is mostly due to the diversity o underground mining methods and omplexity o underground
MPhys Final Year Project Dissertation by Andrew Jackson
 Development of software for the omputation of the properties of eletrostati eletro-optial devies via both the diret ray traing and paraxial approximation tehniques. MPhys Final Year Projet Dissertation
Development of software for the omputation of the properties of eletrostati eletro-optial devies via both the diret ray traing and paraxial approximation tehniques. MPhys Final Year Projet Dissertation
On - Line Path Delay Fault Testing of Omega MINs M. Bellos 1, E. Kalligeros 1, D. Nikolos 1,2 & H. T. Vergos 1,2
 On - Line Path Delay Fault Testing of Omega MINs M. Bellos, E. Kalligeros, D. Nikolos,2 & H. T. Vergos,2 Dept. of Computer Engineering and Informatis 2 Computer Tehnology Institute University of Patras,
On - Line Path Delay Fault Testing of Omega MINs M. Bellos, E. Kalligeros, D. Nikolos,2 & H. T. Vergos,2 Dept. of Computer Engineering and Informatis 2 Computer Tehnology Institute University of Patras,
SEGMENTATION OF IMAGERY USING NETWORK SNAKES
 SEGMENTATION OF IMAGERY USING NETWORK SNAKES Matthias Butenuth Institute of Photogrammetry and GeoInformation, Leibniz Universität Hannover Nienburger Str. 1, 30167 Hannover, Germany butenuth@ipi.uni-hannover.de
SEGMENTATION OF IMAGERY USING NETWORK SNAKES Matthias Butenuth Institute of Photogrammetry and GeoInformation, Leibniz Universität Hannover Nienburger Str. 1, 30167 Hannover, Germany butenuth@ipi.uni-hannover.de
特集 Road Border Recognition Using FIR Images and LIDAR Signal Processing
 デンソーテクニカルレビュー Vol. 15 2010 特集 Road Border Reognition Using FIR Images and LIDAR Signal Proessing 高木聖和 バーゼル ファルディ Kiyokazu TAKAGI Basel Fardi ヘンドリック ヴァイゲル Hendrik Weigel ゲルド ヴァニーリック Gerd Wanielik This paper
デンソーテクニカルレビュー Vol. 15 2010 特集 Road Border Reognition Using FIR Images and LIDAR Signal Proessing 高木聖和 バーゼル ファルディ Kiyokazu TAKAGI Basel Fardi ヘンドリック ヴァイゲル Hendrik Weigel ゲルド ヴァニーリック Gerd Wanielik This paper
Outline: Software Design
 Outline: Software Design. Goals History of software design ideas Design priniples Design methods Life belt or leg iron? (Budgen) Copyright Nany Leveson, Sept. 1999 A Little History... At first, struggling
Outline: Software Design. Goals History of software design ideas Design priniples Design methods Life belt or leg iron? (Budgen) Copyright Nany Leveson, Sept. 1999 A Little History... At first, struggling
The Implementation of RRTs for a Remote-Controlled Mobile Robot
 ICCAS5 June -5, KINEX, Gyeonggi-Do, Korea he Implementation of RRs for a Remote-Controlled Mobile Robot Chi-Won Roh*, Woo-Sub Lee **, Sung-Chul Kang *** and Kwang-Won Lee **** * Intelligent Robotis Researh
ICCAS5 June -5, KINEX, Gyeonggi-Do, Korea he Implementation of RRs for a Remote-Controlled Mobile Robot Chi-Won Roh*, Woo-Sub Lee **, Sung-Chul Kang *** and Kwang-Won Lee **** * Intelligent Robotis Researh
Learning Convention Propagation in BeerAdvocate Reviews from a etwork Perspective. Abstract
 CS 9 Projet Final Report: Learning Convention Propagation in BeerAdvoate Reviews from a etwork Perspetive Abstrat We look at the way onventions propagate between reviews on the BeerAdvoate dataset, and
CS 9 Projet Final Report: Learning Convention Propagation in BeerAdvoate Reviews from a etwork Perspetive Abstrat We look at the way onventions propagate between reviews on the BeerAdvoate dataset, and
ICCGLU. A Fortran IV subroutine to solve large sparse general systems of linear equations. J.J. Dongarra, G.K. Leaf and M. Minkoff.
 http://www.netlib.org/linalg/ig-do 1 of 8 12/7/2009 11:14 AM ICCGLU A Fortran IV subroutine to solve large sparse general systems of linear equations. J.J. Dongarra, G.K. Leaf and M. Minkoff July, 1982
http://www.netlib.org/linalg/ig-do 1 of 8 12/7/2009 11:14 AM ICCGLU A Fortran IV subroutine to solve large sparse general systems of linear equations. J.J. Dongarra, G.K. Leaf and M. Minkoff July, 1982
CleanUp: Improving Quadrilateral Finite Element Meshes
 CleanUp: Improving Quadrilateral Finite Element Meshes Paul Kinney MD-10 ECC P.O. Box 203 Ford Motor Company Dearborn, MI. 8121 (313) 28-1228 pkinney@ford.om Abstrat: Unless an all quadrilateral (quad)
CleanUp: Improving Quadrilateral Finite Element Meshes Paul Kinney MD-10 ECC P.O. Box 203 Ford Motor Company Dearborn, MI. 8121 (313) 28-1228 pkinney@ford.om Abstrat: Unless an all quadrilateral (quad)
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 6
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 6 Unit 6 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS MATH 1206 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS INTRODUCTION 3 1. TRIGONOMETRY OF OBLIQUE TRIANGLES 5 LAW OF SINES 5 AMBIGUITY AND AREA OF A TRIANGLE
MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 6 Unit 6 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS MATH 1206 TRIGONOMETRIC APPLICATIONS INTRODUCTION 3 1. TRIGONOMETRY OF OBLIQUE TRIANGLES 5 LAW OF SINES 5 AMBIGUITY AND AREA OF A TRIANGLE
COMBINATION OF INTERSECTION- AND SWEPT-BASED METHODS FOR SINGLE-MATERIAL REMAP
 Combination of intersetion- and swept-based methods for single-material remap 11th World Congress on Computational Mehanis WCCM XI) 5th European Conferene on Computational Mehanis ECCM V) 6th European
Combination of intersetion- and swept-based methods for single-material remap 11th World Congress on Computational Mehanis WCCM XI) 5th European Conferene on Computational Mehanis ECCM V) 6th European
3D Ideal Flow For Non-Lifting Bodies
 3D Ideal Flow For Non-Lifting Bodies 3D Doublet Panel Method 1. Cover body with 3D onstant strength doublet panels of unknown strength (N panels) 2. Plae a ontrol point at the enter of eah panel (N ontrol
3D Ideal Flow For Non-Lifting Bodies 3D Doublet Panel Method 1. Cover body with 3D onstant strength doublet panels of unknown strength (N panels) 2. Plae a ontrol point at the enter of eah panel (N ontrol
A Numerical optimization technique for the design of airfoils in viscous flows
 Rohester Institute of Tehnology RIT Sholar Works Theses Thesis/Dissertation Colletions 7-1-1995 A Numerial optimization tehnique for the design of airfoils in visous flows Robert MaNeill Follow this and
Rohester Institute of Tehnology RIT Sholar Works Theses Thesis/Dissertation Colletions 7-1-1995 A Numerial optimization tehnique for the design of airfoils in visous flows Robert MaNeill Follow this and
Extracting Partition Statistics from Semistructured Data
 Extrating Partition Statistis from Semistrutured Data John N. Wilson Rihard Gourlay Robert Japp Mathias Neumüller Department of Computer and Information Sienes University of Strathlyde, Glasgow, UK {jnw,rsg,rpj,mathias}@is.strath.a.uk
Extrating Partition Statistis from Semistrutured Data John N. Wilson Rihard Gourlay Robert Japp Mathias Neumüller Department of Computer and Information Sienes University of Strathlyde, Glasgow, UK {jnw,rsg,rpj,mathias}@is.strath.a.uk
Sequential Incremental-Value Auctions
 Sequential Inremental-Value Autions Xiaoming Zheng and Sven Koenig Department of Computer Siene University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-0781 {xiaominz,skoenig}@us.edu Abstrat We study the
Sequential Inremental-Value Autions Xiaoming Zheng and Sven Koenig Department of Computer Siene University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-0781 {xiaominz,skoenig}@us.edu Abstrat We study the
Adaptive Implicit Surface Polygonization using Marching Triangles
 Volume 20 (2001), Number 2 pp. 67 80 Adaptive Impliit Surfae Polygonization using Marhing Triangles Samir Akkouhe Eri Galin L.I.G.I.M L.I.G.I.M Eole Centrale de Lyon Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1 B.P.
Volume 20 (2001), Number 2 pp. 67 80 Adaptive Impliit Surfae Polygonization using Marhing Triangles Samir Akkouhe Eri Galin L.I.G.I.M L.I.G.I.M Eole Centrale de Lyon Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1 B.P.
arxiv: v1 [cs.db] 13 Sep 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cs.db] 13 Sep 2017 arxiv: v1 [cs.db] 13 Sep 2017](/thumbs/96/126543346.jpg) An effiient lustering algorithm from the measure of loal Gaussian distribution Yuan-Yen Tai (Dated: May 27, 2018) In this paper, I will introdue a fast and novel lustering algorithm based on Gaussian distribution
An effiient lustering algorithm from the measure of loal Gaussian distribution Yuan-Yen Tai (Dated: May 27, 2018) In this paper, I will introdue a fast and novel lustering algorithm based on Gaussian distribution
The Alpha Torque and Quantum Physics
 The Alpha Torque and Quantum Physis Zhiliang Cao, Henry Cao williamao15000@yahoo.om, henry.gu.ao@gmail.om July 18, 010 Abstrat In the enter of the unierse, there isn t a super massie blak hole or any speifi
The Alpha Torque and Quantum Physis Zhiliang Cao, Henry Cao williamao15000@yahoo.om, henry.gu.ao@gmail.om July 18, 010 Abstrat In the enter of the unierse, there isn t a super massie blak hole or any speifi
Unsupervised Stereoscopic Video Object Segmentation Based on Active Contours and Retrainable Neural Networks
 Unsupervised Stereosopi Video Objet Segmentation Based on Ative Contours and Retrainable Neural Networks KLIMIS NTALIANIS, ANASTASIOS DOULAMIS, and NIKOLAOS DOULAMIS National Tehnial University of Athens
Unsupervised Stereosopi Video Objet Segmentation Based on Ative Contours and Retrainable Neural Networks KLIMIS NTALIANIS, ANASTASIOS DOULAMIS, and NIKOLAOS DOULAMIS National Tehnial University of Athens
Detecting Moving Targets in Clutter in Airborne SAR via Keystoning and Multiple Phase Center Interferometry
 Deteting Moving Targets in Clutter in Airborne SAR via Keystoning and Multiple Phase Center Interferometry D. M. Zasada, P. K. Sanyal The MITRE Corp., 6 Eletroni Parkway, Rome, NY 134 (dmzasada, psanyal)@mitre.org
Deteting Moving Targets in Clutter in Airborne SAR via Keystoning and Multiple Phase Center Interferometry D. M. Zasada, P. K. Sanyal The MITRE Corp., 6 Eletroni Parkway, Rome, NY 134 (dmzasada, psanyal)@mitre.org
Chemical, Biological and Radiological Hazard Assessment: A New Model of a Plume in a Complex Urban Environment
 hemial, Biologial and Radiologial Haard Assessment: A New Model of a Plume in a omplex Urban Environment Skvortsov, A.T., P.D. Dawson, M.D. Roberts and R.M. Gailis HPP Division, Defene Siene and Tehnology
hemial, Biologial and Radiologial Haard Assessment: A New Model of a Plume in a omplex Urban Environment Skvortsov, A.T., P.D. Dawson, M.D. Roberts and R.M. Gailis HPP Division, Defene Siene and Tehnology
Acoustic Links. Maximizing Channel Utilization for Underwater
 Maximizing Channel Utilization for Underwater Aousti Links Albert F Hairris III Davide G. B. Meneghetti Adihele Zorzi Department of Information Engineering University of Padova, Italy Email: {harris,davide.meneghetti,zorzi}@dei.unipd.it
Maximizing Channel Utilization for Underwater Aousti Links Albert F Hairris III Davide G. B. Meneghetti Adihele Zorzi Department of Information Engineering University of Padova, Italy Email: {harris,davide.meneghetti,zorzi}@dei.unipd.it
Using Augmented Measurements to Improve the Convergence of ICP
 Using Augmented Measurements to Improve the onvergene of IP Jaopo Serafin, Giorgio Grisetti Dept. of omputer, ontrol and Management Engineering, Sapienza University of Rome, Via Ariosto 25, I-0085, Rome,
Using Augmented Measurements to Improve the onvergene of IP Jaopo Serafin, Giorgio Grisetti Dept. of omputer, ontrol and Management Engineering, Sapienza University of Rome, Via Ariosto 25, I-0085, Rome,
3D Model Based Pose Estimation For Omnidirectional Stereovision
 3D Model Based Pose Estimation For Omnidiretional Stereovision Guillaume Caron, Eri Marhand and El Mustapha Mouaddib Abstrat Robot vision has a lot to win as well with wide field of view indued by atadioptri
3D Model Based Pose Estimation For Omnidiretional Stereovision Guillaume Caron, Eri Marhand and El Mustapha Mouaddib Abstrat Robot vision has a lot to win as well with wide field of view indued by atadioptri
A RAY TRACING SIMULATION OF SOUND DIFFRACTION BASED ON ANALYTIC SECONDARY SOURCE MODEL
 19th European Signal Proessing Conferene (EUSIPCO 211) Barelona, Spain, August 29 - September 2, 211 A RAY TRACING SIMULATION OF SOUND DIFFRACTION BASED ON ANALYTIC SECONDARY SOURCE MODEL Masashi Okada,
19th European Signal Proessing Conferene (EUSIPCO 211) Barelona, Spain, August 29 - September 2, 211 A RAY TRACING SIMULATION OF SOUND DIFFRACTION BASED ON ANALYTIC SECONDARY SOURCE MODEL Masashi Okada,
Rotation Invariant Spherical Harmonic Representation of 3D Shape Descriptors
 Eurographis Symposium on Geometry Proessing (003) L. Kobbelt, P. Shröder, H. Hoppe (Editors) Rotation Invariant Spherial Harmoni Representation of 3D Shape Desriptors Mihael Kazhdan, Thomas Funkhouser,
Eurographis Symposium on Geometry Proessing (003) L. Kobbelt, P. Shröder, H. Hoppe (Editors) Rotation Invariant Spherial Harmoni Representation of 3D Shape Desriptors Mihael Kazhdan, Thomas Funkhouser,
Design of tree-type support structure of free-form shell generated using fractal geometry
 6 30 September, 06, Too, Japan K. Kawaguhi, M. Ohsai, T. Taeuhi (eds.) Design of tree-tpe support struture of free-form shell generated using fratal geometr Jinglan CUI*, Guanghun ZHOU a, Maoto OHSAKI
6 30 September, 06, Too, Japan K. Kawaguhi, M. Ohsai, T. Taeuhi (eds.) Design of tree-tpe support struture of free-form shell generated using fratal geometr Jinglan CUI*, Guanghun ZHOU a, Maoto OHSAKI
Measurement of the stereoscopic rangefinder beam angular velocity using the digital image processing method
 Measurement of the stereosopi rangefinder beam angular veloity using the digital image proessing method ROMAN VÍTEK Department of weapons and ammunition University of defense Kouniova 65, 62 Brno CZECH
Measurement of the stereosopi rangefinder beam angular veloity using the digital image proessing method ROMAN VÍTEK Department of weapons and ammunition University of defense Kouniova 65, 62 Brno CZECH
Stable Road Lane Model Based on Clothoids
 Stable Road Lane Model Based on Clothoids C Gakstatter*, S Thomas**, Dr P Heinemann*, Prof Gudrun Klinker*** *Audi Eletronis Venture GmbH, **Leibniz Universität Hannover, ***Tehnishe Universität Münhen
Stable Road Lane Model Based on Clothoids C Gakstatter*, S Thomas**, Dr P Heinemann*, Prof Gudrun Klinker*** *Audi Eletronis Venture GmbH, **Leibniz Universität Hannover, ***Tehnishe Universität Münhen
End mills are widely used in industry for high-speed machining. End milling cutters are C H A P T E R 2
 C H A P T E R End Mill End mills are widely used in industry for high-speed mahining. End milling utters are multi-point milling utters with utting edges both on the fae end as well as on the periphery,
C H A P T E R End Mill End mills are widely used in industry for high-speed mahining. End milling utters are multi-point milling utters with utting edges both on the fae end as well as on the periphery,
Boundary Correct Real-Time Soft Shadows
 Boundary Corret Real-Time Soft Shadows Bjarke Jakobsen Niels J. Christensen Bent D. Larsen Kim S. Petersen Informatis and Mathematial Modelling Tehnial University of Denmark {bj, nj, bdl}@imm.dtu.dk, kim@deadline.dk
Boundary Corret Real-Time Soft Shadows Bjarke Jakobsen Niels J. Christensen Bent D. Larsen Kim S. Petersen Informatis and Mathematial Modelling Tehnial University of Denmark {bj, nj, bdl}@imm.dtu.dk, kim@deadline.dk
Rapid, accurate particle tracking by calculation of radial symmetry centers
 Rapid, aurate partile traing by alulation of radial symmetry enters Raghuveer Parthasarathy Supplementary Text and Figures Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure Supplementary
Rapid, aurate partile traing by alulation of radial symmetry enters Raghuveer Parthasarathy Supplementary Text and Figures Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure Supplementary
Cracked Hole Finite Element Modeling
 Craked Hole Finite Element Modeling (E-20-F72) Researh Report Submitted to: Lokheed Martin, Program Manager: Dr. Stephen P. Engelstad Prinipal Investigator: Dr. Rami M. Haj-Ali Shool of Civil and Environmental
Craked Hole Finite Element Modeling (E-20-F72) Researh Report Submitted to: Lokheed Martin, Program Manager: Dr. Stephen P. Engelstad Prinipal Investigator: Dr. Rami M. Haj-Ali Shool of Civil and Environmental
Face and Facial Feature Tracking for Natural Human-Computer Interface
 Fae and Faial Feature Traking for Natural Human-Computer Interfae Vladimir Vezhnevets Graphis & Media Laboratory, Dept. of Applied Mathematis and Computer Siene of Mosow State University Mosow, Russia
Fae and Faial Feature Traking for Natural Human-Computer Interfae Vladimir Vezhnevets Graphis & Media Laboratory, Dept. of Applied Mathematis and Computer Siene of Mosow State University Mosow, Russia
Finding the Equation of a Straight Line
 Finding the Equation of a Straight Line You should have, before now, ome aross the equation of a straight line, perhaps at shool. Engineers use this equation to help determine how one quantity is related
Finding the Equation of a Straight Line You should have, before now, ome aross the equation of a straight line, perhaps at shool. Engineers use this equation to help determine how one quantity is related
CONSIDERING the high computational load of synthetic
 IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL. 5, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2008 573 Doppler Keystone Transform: An Approah Suitable for Parallel Implementation of SAR Moving Target Imaging Gang Li, Member, IEEE,
IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL. 5, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2008 573 Doppler Keystone Transform: An Approah Suitable for Parallel Implementation of SAR Moving Target Imaging Gang Li, Member, IEEE,
Abstract. Key Words: Image Filters, Fuzzy Filters, Order Statistics Filters, Rank Ordered Mean Filters, Channel Noise. 1.
 Fuzzy Weighted Rank Ordered Mean (FWROM) Filters for Mixed Noise Suppression from Images S. Meher, G. Panda, B. Majhi 3, M.R. Meher 4,,4 Department of Eletronis and I.E., National Institute of Tehnology,
Fuzzy Weighted Rank Ordered Mean (FWROM) Filters for Mixed Noise Suppression from Images S. Meher, G. Panda, B. Majhi 3, M.R. Meher 4,,4 Department of Eletronis and I.E., National Institute of Tehnology,
A Unified Subdivision Scheme for Polygonal Modeling
 EUROGRAPHICS 2 / A. Chalmers and T.-M. Rhyne (Guest Editors) Volume 2 (2), Number 3 A Unified Subdivision Sheme for Polygonal Modeling Jérôme Maillot Jos Stam Alias Wavefront Alias Wavefront 2 King St.
EUROGRAPHICS 2 / A. Chalmers and T.-M. Rhyne (Guest Editors) Volume 2 (2), Number 3 A Unified Subdivision Sheme for Polygonal Modeling Jérôme Maillot Jos Stam Alias Wavefront Alias Wavefront 2 King St.
A radiometric analysis of projected sinusoidal illumination for opaque surfaces
 University of Virginia tehnial report CS-21-7 aompanying A Coaxial Optial Sanner for Synhronous Aquisition of 3D Geometry and Surfae Refletane A radiometri analysis of projeted sinusoidal illumination
University of Virginia tehnial report CS-21-7 aompanying A Coaxial Optial Sanner for Synhronous Aquisition of 3D Geometry and Surfae Refletane A radiometri analysis of projeted sinusoidal illumination
Pipelined Multipliers for Reconfigurable Hardware
 Pipelined Multipliers for Reonfigurable Hardware Mithell J. Myjak and José G. Delgado-Frias Shool of Eletrial Engineering and Computer Siene, Washington State University Pullman, WA 99164-2752 USA {mmyjak,
Pipelined Multipliers for Reonfigurable Hardware Mithell J. Myjak and José G. Delgado-Frias Shool of Eletrial Engineering and Computer Siene, Washington State University Pullman, WA 99164-2752 USA {mmyjak,
3-D IMAGE MODELS AND COMPRESSION - SYNTHETIC HYBRID OR NATURAL FIT?
 3-D IMAGE MODELS AND COMPRESSION - SYNTHETIC HYBRID OR NATURAL FIT? Bernd Girod, Peter Eisert, Marus Magnor, Ekehard Steinbah, Thomas Wiegand Te {girod eommuniations Laboratory, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg
3-D IMAGE MODELS AND COMPRESSION - SYNTHETIC HYBRID OR NATURAL FIT? Bernd Girod, Peter Eisert, Marus Magnor, Ekehard Steinbah, Thomas Wiegand Te {girod eommuniations Laboratory, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg
Improved Vehicle Classification in Long Traffic Video by Cooperating Tracker and Classifier Modules
 Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
Algorithms for External Memory Lecture 6 Graph Algorithms - Weighted List Ranking
 Algorithms for External Memory Leture 6 Graph Algorithms - Weighted List Ranking Leturer: Nodari Sithinava Sribe: Andi Hellmund, Simon Ohsenreither 1 Introdution & Motivation After talking about I/O-effiient
Algorithms for External Memory Leture 6 Graph Algorithms - Weighted List Ranking Leturer: Nodari Sithinava Sribe: Andi Hellmund, Simon Ohsenreither 1 Introdution & Motivation After talking about I/O-effiient
Structural Topology Optimization Based on the Smoothed Finite Element Method
 378 Strutural Topology Optimization Based on the Smoothed Finite Element Method Astrat In this paper, the smoothed finite element method, inorporated with the level set method, is employed to arry out
378 Strutural Topology Optimization Based on the Smoothed Finite Element Method Astrat In this paper, the smoothed finite element method, inorporated with the level set method, is employed to arry out
Fitting conics to paracatadioptric projections of lines
 Computer Vision and Image Understanding 11 (6) 11 16 www.elsevier.om/loate/viu Fitting onis to paraatadioptri projetions of lines João P. Barreto *, Helder Araujo Institute for Systems and Robotis, Department
Computer Vision and Image Understanding 11 (6) 11 16 www.elsevier.om/loate/viu Fitting onis to paraatadioptri projetions of lines João P. Barreto *, Helder Araujo Institute for Systems and Robotis, Department
Accommodations of QoS DiffServ Over IP and MPLS Networks
 Aommodations of QoS DiffServ Over IP and MPLS Networks Abdullah AlWehaibi, Anjali Agarwal, Mihael Kadoh and Ahmed ElHakeem Department of Eletrial and Computer Department de Genie Eletrique Engineering
Aommodations of QoS DiffServ Over IP and MPLS Networks Abdullah AlWehaibi, Anjali Agarwal, Mihael Kadoh and Ahmed ElHakeem Department of Eletrial and Computer Department de Genie Eletrique Engineering
Algorithms, Mechanisms and Procedures for the Computer-aided Project Generation System
 Algorithms, Mehanisms and Proedures for the Computer-aided Projet Generation System Anton O. Butko 1*, Aleksandr P. Briukhovetskii 2, Dmitry E. Grigoriev 2# and Konstantin S. Kalashnikov 3 1 Department
Algorithms, Mehanisms and Proedures for the Computer-aided Projet Generation System Anton O. Butko 1*, Aleksandr P. Briukhovetskii 2, Dmitry E. Grigoriev 2# and Konstantin S. Kalashnikov 3 1 Department
Cluster-Based Cumulative Ensembles
 Cluster-Based Cumulative Ensembles Hanan G. Ayad and Mohamed S. Kamel Pattern Analysis and Mahine Intelligene Lab, Eletrial and Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1,
Cluster-Based Cumulative Ensembles Hanan G. Ayad and Mohamed S. Kamel Pattern Analysis and Mahine Intelligene Lab, Eletrial and Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1,
Graph-Based vs Depth-Based Data Representation for Multiview Images
 Graph-Based vs Depth-Based Data Representation for Multiview Images Thomas Maugey, Antonio Ortega, Pasal Frossard Signal Proessing Laboratory (LTS), Eole Polytehnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) Email:
Graph-Based vs Depth-Based Data Representation for Multiview Images Thomas Maugey, Antonio Ortega, Pasal Frossard Signal Proessing Laboratory (LTS), Eole Polytehnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) Email:
Adapting K-Medians to Generate Normalized Cluster Centers
 Adapting -Medians to Generate Normalized Cluster Centers Benamin J. Anderson, Deborah S. Gross, David R. Musiant Anna M. Ritz, Thomas G. Smith, Leah E. Steinberg Carleton College andersbe@gmail.om, {dgross,
Adapting -Medians to Generate Normalized Cluster Centers Benamin J. Anderson, Deborah S. Gross, David R. Musiant Anna M. Ritz, Thomas G. Smith, Leah E. Steinberg Carleton College andersbe@gmail.om, {dgross,
What are Cycle-Stealing Systems Good For? A Detailed Performance Model Case Study
 What are Cyle-Stealing Systems Good For? A Detailed Performane Model Case Study Wayne Kelly and Jiro Sumitomo Queensland University of Tehnology, Australia {w.kelly, j.sumitomo}@qut.edu.au Abstrat The
What are Cyle-Stealing Systems Good For? A Detailed Performane Model Case Study Wayne Kelly and Jiro Sumitomo Queensland University of Tehnology, Australia {w.kelly, j.sumitomo}@qut.edu.au Abstrat The
 Algebra Lab Investigating Trigonometri Ratios You an use paper triangles to investigate the ratios of the lengths of sides of right triangles. Virginia SOL Preparation for G.8 The student will solve realworld
Algebra Lab Investigating Trigonometri Ratios You an use paper triangles to investigate the ratios of the lengths of sides of right triangles. Virginia SOL Preparation for G.8 The student will solve realworld
One Against One or One Against All : Which One is Better for Handwriting Recognition with SVMs?
 One Against One or One Against All : Whih One is Better for Handwriting Reognition with SVMs? Jonathan Milgram, Mohamed Cheriet, Robert Sabourin To ite this version: Jonathan Milgram, Mohamed Cheriet,
One Against One or One Against All : Whih One is Better for Handwriting Reognition with SVMs? Jonathan Milgram, Mohamed Cheriet, Robert Sabourin To ite this version: Jonathan Milgram, Mohamed Cheriet,
13.1 Numerical Evaluation of Integrals Over One Dimension
 13.1 Numerial Evaluation of Integrals Over One Dimension A. Purpose This olletion of subprograms estimates the value of the integral b a f(x) dx where the integrand f(x) and the limits a and b are supplied
13.1 Numerial Evaluation of Integrals Over One Dimension A. Purpose This olletion of subprograms estimates the value of the integral b a f(x) dx where the integrand f(x) and the limits a and b are supplied
Gray Codes for Reflectable Languages
 Gray Codes for Refletable Languages Yue Li Joe Sawada Marh 8, 2008 Abstrat We lassify a type of language alled a refletable language. We then develop a generi algorithm that an be used to list all strings
Gray Codes for Refletable Languages Yue Li Joe Sawada Marh 8, 2008 Abstrat We lassify a type of language alled a refletable language. We then develop a generi algorithm that an be used to list all strings
3D Shadows: Computer Vision for an Unencumbered Interface
 3D Shadows: Computer Vision for an Unenumbered Interfae Robert Virtue University of British Columbia 356 Main Mall Vanouver, BC Canada 604-8-053 virtue@ee.ub.a ABSTRACT In this paper we desribe a real-time
3D Shadows: Computer Vision for an Unenumbered Interfae Robert Virtue University of British Columbia 356 Main Mall Vanouver, BC Canada 604-8-053 virtue@ee.ub.a ABSTRACT In this paper we desribe a real-time
Automatic Physical Design Tuning: Workload as a Sequence Sanjay Agrawal Microsoft Research One Microsoft Way Redmond, WA, USA +1-(425)
 Automati Physial Design Tuning: Workload as a Sequene Sanjay Agrawal Mirosoft Researh One Mirosoft Way Redmond, WA, USA +1-(425) 75-357 sagrawal@mirosoft.om Eri Chu * Computer Sienes Department University
Automati Physial Design Tuning: Workload as a Sequene Sanjay Agrawal Mirosoft Researh One Mirosoft Way Redmond, WA, USA +1-(425) 75-357 sagrawal@mirosoft.om Eri Chu * Computer Sienes Department University
Segmentation of brain MR image using fuzzy local Gaussian mixture model with bias field correction
 IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Proessing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 2, Issue 2 (Mar. Apr. 2013), PP 35-41 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 Segmentation of brain MR image using fuzzy loal Gaussian mixture
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Proessing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 2, Issue 2 (Mar. Apr. 2013), PP 35-41 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 Segmentation of brain MR image using fuzzy loal Gaussian mixture
Gradient based progressive probabilistic Hough transform
 Gradient based progressive probabilisti Hough transform C.Galambos, J.Kittler and J.Matas Abstrat: The authors look at the benefits of exploiting gradient information to enhane the progressive probabilisti
Gradient based progressive probabilisti Hough transform C.Galambos, J.Kittler and J.Matas Abstrat: The authors look at the benefits of exploiting gradient information to enhane the progressive probabilisti
Chromaticity-matched Superimposition of Foreground Objects in Different Environments
 FCV216, the 22nd Korea-Japan Joint Workshop on Frontiers of Computer Vision Chromatiity-mathed Superimposition of Foreground Objets in Different Environments Yohei Ogura Graduate Shool of Siene and Tehnology
FCV216, the 22nd Korea-Japan Joint Workshop on Frontiers of Computer Vision Chromatiity-mathed Superimposition of Foreground Objets in Different Environments Yohei Ogura Graduate Shool of Siene and Tehnology
A DYNAMIC ACCESS CONTROL WITH BINARY KEY-PAIR
 Malaysian Journal of Computer Siene, Vol 10 No 1, June 1997, pp 36-41 A DYNAMIC ACCESS CONTROL WITH BINARY KEY-PAIR Md Rafiqul Islam, Harihodin Selamat and Mohd Noor Md Sap Faulty of Computer Siene and
Malaysian Journal of Computer Siene, Vol 10 No 1, June 1997, pp 36-41 A DYNAMIC ACCESS CONTROL WITH BINARY KEY-PAIR Md Rafiqul Islam, Harihodin Selamat and Mohd Noor Md Sap Faulty of Computer Siene and
PROBABILISTIC SURFACE DAMAGE TOLERANCE ASSESSMENT OF AIRCRAFT TURBINE ROTORS
 Proeedings of ASE Turbo Expo 2 Power for Land, Sea, and Air June 16 19, 2, Atlanta, Georgia, USA GT2-871 PROBABILISTIC SURFACE DAAGE TOLERANCE ASSESSENT OF AIRCRAFT TURBINE ROTORS ihael P. Enright R. Craig
Proeedings of ASE Turbo Expo 2 Power for Land, Sea, and Air June 16 19, 2, Atlanta, Georgia, USA GT2-871 PROBABILISTIC SURFACE DAAGE TOLERANCE ASSESSENT OF AIRCRAFT TURBINE ROTORS ihael P. Enright R. Craig
KERNEL SPARSE REPRESENTATION WITH LOCAL PATTERNS FOR FACE RECOGNITION
 KERNEL SPARSE REPRESENTATION WITH LOCAL PATTERNS FOR FACE RECOGNITION Cuiui Kang 1, Shengai Liao, Shiming Xiang 1, Chunhong Pan 1 1 National Laboratory of Pattern Reognition, Institute of Automation, Chinese
KERNEL SPARSE REPRESENTATION WITH LOCAL PATTERNS FOR FACE RECOGNITION Cuiui Kang 1, Shengai Liao, Shiming Xiang 1, Chunhong Pan 1 1 National Laboratory of Pattern Reognition, Institute of Automation, Chinese
System-Level Parallelism and Throughput Optimization in Designing Reconfigurable Computing Applications
 System-Level Parallelism and hroughput Optimization in Designing Reonfigurable Computing Appliations Esam El-Araby 1, Mohamed aher 1, Kris Gaj 2, arek El-Ghazawi 1, David Caliga 3, and Nikitas Alexandridis
System-Level Parallelism and hroughput Optimization in Designing Reonfigurable Computing Appliations Esam El-Araby 1, Mohamed aher 1, Kris Gaj 2, arek El-Ghazawi 1, David Caliga 3, and Nikitas Alexandridis
Fuzzy Meta Node Fuzzy Metagraph and its Cluster Analysis
 Journal of Computer Siene 4 (): 9-97, 008 ISSN 549-3636 008 Siene Publiations Fuzzy Meta Node Fuzzy Metagraph and its Cluster Analysis Deepti Gaur, Aditya Shastri and Ranjit Biswas Department of Computer
Journal of Computer Siene 4 (): 9-97, 008 ISSN 549-3636 008 Siene Publiations Fuzzy Meta Node Fuzzy Metagraph and its Cluster Analysis Deepti Gaur, Aditya Shastri and Ranjit Biswas Department of Computer
arxiv: v2 [math.ho] 5 May 2018
![arxiv: v2 [math.ho] 5 May 2018 arxiv: v2 [math.ho] 5 May 2018](/thumbs/80/81138349.jpg) Longest Straight Line Paths on Water or Land on the Earth Rohan Chabukswar 1 and Kushal Mukherjee 1 United Tehnologies Researh Center Ireland IBM Researh India May 8, 018 arxiv:180.07389v [math.ho] 5 May
Longest Straight Line Paths on Water or Land on the Earth Rohan Chabukswar 1 and Kushal Mukherjee 1 United Tehnologies Researh Center Ireland IBM Researh India May 8, 018 arxiv:180.07389v [math.ho] 5 May
arxiv: v1 [cs.gr] 10 Apr 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cs.gr] 10 Apr 2015 arxiv: v1 [cs.gr] 10 Apr 2015](/thumbs/92/109500704.jpg) REAL-TIME TOOL FOR AFFINE TRANSFORMATIONS OF TWO DIMENSIONAL IFS FRACTALS ELENA HADZIEVA AND MARIJA SHUMINOSKA arxiv:1504.02744v1 s.gr 10 Apr 2015 Abstrat. This work introdues a novel tool for interative,
REAL-TIME TOOL FOR AFFINE TRANSFORMATIONS OF TWO DIMENSIONAL IFS FRACTALS ELENA HADZIEVA AND MARIJA SHUMINOSKA arxiv:1504.02744v1 s.gr 10 Apr 2015 Abstrat. This work introdues a novel tool for interative,
Multi-Piece Mold Design Based on Linear Mixed-Integer Program Toward Guaranteed Optimality
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MANUFACTURING AUTOMATION (ICMA200) Multi-Piee Mold Design Based on Linear Mixed-Integer Program Toward Guaranteed Optimality Stephen Stoyan, Yong Chen* Epstein Department of
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MANUFACTURING AUTOMATION (ICMA200) Multi-Piee Mold Design Based on Linear Mixed-Integer Program Toward Guaranteed Optimality Stephen Stoyan, Yong Chen* Epstein Department of
