Operation Instructions (Ver )
|
|
|
- Vincent Mosley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Operation Instructions (Ver ) 1
2
3 i-dixel One Volume Viewer: Conditions of Use 1. Data Export Conditions This application can be used for any CT data which is compatible with i-dixel software. However, the CT volume data must still be saved. The computer must have both the i-dixel application and the i-dixel One Data Viewer Plus software (option) in order to export data to be used with the i-dixel One Volume Viewer. When exporting CT data, you must specify either Volume or Slice. Also, the option of exporting data for version or earlier must be turned off. 2. Hardware and Software i-dixel One Volume Viewer requires the following: Operating System (OS) Windows 2000 Professional SP4 Windows XP Professional SP2/SP3 Windows Vista Business 32 bit * It has not been confirmed if other operating systems can be used. Computer Specifications The chart below shows the minimum and recommended specifications. For especially large amounts of data, the recommended specifications should be considered the minimum specifications. Minimum Recommended CPU Pentium 4 1.7GHz, min., Intel CPU Core 2 Duo, min., Intel CPU RAM Memory 2GB, min. 1 3GB, min. HDD Free Space 1GB, min. 10GB, min. Display Colors 16 bit Color, min. 32 bit Color Display Resolution , min , min. 1 Depends on volume data size. Minimum should be at least 2 times the volume data size. 3. Cautionary Remarks Proper operation cannot be guaranteed if running under virtual environments. Data cannot be used if it is in a folder with a network path. It must be in a folder on a local or mapped network drive. Refer to the Windows Help Files for how to map a network drive. Depending on computer settings, i-dixel One Volume viewer may not work even if specified computer conditions have been met. If this happens, check with the computer administrator. For large amounts of data, data read-in and processing may take a long time. Therefore, even if the specified minimum computer conditions have been met, the application may not run smoothly. Windows Vista Business 32 bit requires an especially high level of processing power. Do not run or start up any other applications while using i-dixel One Volume Viewer. This could result in a shortage of memory for proper operation. Do not eject a medium with recorded data or shut down any data read-in devices while i-dixel One Volume Viewer is running. This could damage data or the computer. Data output may take a long time under the following circumstances. In these cases, it is better to first copy the data on the computer s hard drive and then run the program. For data saved on a device connected with a slow connection such as USB 1.1. For data recorded on CD, DVD, MO disks which are used with a slow reading drive. For data saved on a computer network. Anti-virus software can cause the application to run extremely slowly.
4
5 "Windows 2000 Professional SP4," "Windows XP Professional SP2," and "Windows Vista Business 32bit" are registered trademarks of Microsoft Inc., U.S.A. i-dixel One Volume Viewer is a registered trademark whose right to use is owned by J. MORITA MFG. CORP. The volume rendering related functions of this software are based on collaborative research by Professor Kensaku Mori of the Graduate School of Information Science, Nagoya University, and J. MORITA MFG. Corp. i-dixel One Volume Viewer Operation Instructions (Ver.2.0.0) June 2010 J. MORITA MFG. CORP. All rights reserved Do Not Fail to Observe the Following Cautionry Remarks J. Morita Mfg. Corp. is the legal registered owner of the i-dixel One Volume Viewer and does not permit unauthorized reproduction of it. J. Morita Mfg. Corp. cannot be held liable for problems or malfunctions attributable to the OS (operating system). J. Morita Mfg. Corp. bears no responsibility for problems attributable to factors arising from the operating environment established by the user. This software is not compliant with the Windows standby mode or with the unique standby modes for notebook computers. Do not use a screen saver; screen savers may prevent the software from running smoothly. Do not use controls for automatically turning off the display and hard disk which are in the screen saver section of the display control panel. These should both be disabled and not used; otherwise the software may not run smoothly. Do not use Sleep or Suspend functions; the software may not run smoothly if these are turned on. The J. Morita Mfg. Corp. bears no responsibility for problems and defects originating with hardware items such as the computer itself or peripheral devices or for problems and defects which seem to originate with such hardware items. This software has been confirmed to operate without problems on a computer with a Pentium 4 CPU or better, CPU clock speed of 1.7 GHz or faster, minimum RAM of 2 GB, and at least 1 GB of hard disk space, running Microsoft Windows XP Professional SP2, Windows 2000 Professional SP4 or Windows Vista Business 32bit. J. Morita Mfg. Corp. does not warrant that the software will operate correctly on a computer not meeting the above requirements. When operations are performed using high definition or wide scope data, as loading and processing of data can take time, even if the minimum recommended environment is used, operation may not be smooth. In particular, when using "Windows Vista Business 32 bit," high performance is necessary. The warranty for this software will not extend more than 1 year after the manufacturer of the operating system (OS), which has been proven to work, has discontinued sales of the operating system regardless of the original valid period of the warrantee. 1
6 CONTENTS 1. Introduction Start Up i-dixel One Volume Viewer Shut Down the Application Display Window Main Window View Menu Status Bar X Image Inversion, Z Image Inversion Switch Display of Z Slice Images, Cross Section Images, and Panorama Images Histogram Cursor :1 Pixel Magnification Magnifying Glass Tool Menu Select Eraser (Clear) Length Measurement Angle Measurement Annotation (Comments) Carve Images Magnifying Glass Section Volumes Add Rulers to Images Being Output Synchronize the Viewpoint with VoIR Unsynchronize the Viewpoint XYZ View and CMPR View XYZ View Display Window Volume Rendering Histogram Window Part Names Volume Rendering Settings Rotate and Move the Image Show X, Y, and Z Cursor Planes Partial Slicing Cut Plane Display Carve Images Movie Align the Volume to the Selected Implant CMPR View How to Create Image Data Slice Curve Adjustment Cross Section Image Adjustment Cross-sectional View Browsing CMPR Image Display Change-over Measurement of Distance and Angle Partial Slicing Image Saving Version Information
7 1. Introduction i-dixel One Volume Viewer is a single user application for viewing CT data exported from i-dixel databases. It is only designed to open exported CT data. The user bears all responsibility resulting from use of this software. CT does not provide absolutely accurate biological information, so caution is necessary. Please use an adequate amount of time when observing images. Users of i-dixel-3dx are supported. Enquiries resulting from distribution of data to people other than users are not supported and cannot be answered. 3
8 Keyboard Input Usage Ctrl+A This means you hold down the Ctrl Key and press A. Back Space The key in the upper right corner of the keyboard. Tab The key on the far left side with arrows pointing to the right and left. Shift The two keys in the lower left and right corners with a larger arrow pointing up. Used to type in capital letters. Enter The large key on the right side of the main part of the keyboard used for typing, designated by the word "Enter" or "Return" with a curved arrow on it. Space Bar The wide key at the bottom and in the middle of the keyboard. 4
9 Standard Terms Used in This Manual To avoid needless repetition, the meaning of terms related to operations using the mouse and other terms are defined below. Click (Left Click) Locate the mouse pointer on the object and then click the left button on the mouse once. For example, if the instruction is click the file, put the mouse pointer on the file and click the left button once. Right Click Click the button on the right side of the mouse Double Click Click the mouse button twice in quick succession. For example, Double click the icon, means to move the mouse s pointer onto the icon and then click the left button twice in quick succession. It is possible to adjust the length of time between clicks which will distinguish between a double click and two, separate single clicks. Go to the Windows Control Panels. Drag and Drop with the Mouse This means to locate the mouse s pointer on top of an icon or other object, hold down the left button and then move the icon or object to some other place. Release the left button when the object is at the desired location. For example, this is used to put an image in the image Arrangement Window. Windows Desk Top This refers to the view in the monitor right after Windows has been started up where various program icons are displayed. Double click a program icon to start it up. With Windows, more than one program can be used at the same time. Pop-up Menu A menu which is displayed by clicking with the right mouse button. Radio Button On-and-off switches for various functions and features. 5
10 1.1. Start Up i-dixel One Volume Viewer Double click the One Volume Viewer icon in the export data folder. If there is no One Volume Viewer icon, check the settings of the software used to export the data, and confirm that Volume, Slice, and OneDataViewer have been selected. (*Confirm that export was not performed with "Pre-1.72 versions..." selected.) Please do not use VIEW One Volume Viewer and i-dixel software at the same time. There is a possibility that i-dixel One Volume Viewer will not operate correctly. A dialog indicating cautions about usage will be displayed. Please check the contents of the dialog and click "OK" if you agree to the conditions. i-dixel One Volume Viewer is configured to start in the same folder as the export data. Please be aware that if the content of the folder in which the program was saved is changed, the program cannot be started. 6
11 After completing pre-processing, data is displayed in the XYZ view. (*Pre-processing may take several minutes.) 1.2. Shut Down the Application Use this command to exit the i-dixel One Volume Viewer. The application can be shut down by selecting [File]-[Exit] from the menu or clicking the "x" in the upper right of the window. 7
12 2. Display Window 2.1. Main Window This window is displayed when i-dixel One Volume Viewer is started. Menu Bar Panel Controller Panel Display Area Histogram Window Menu Bar Menue Bar displays the various functions of i-dixel One Volume Viewer. The display and order of buttons is changeable. Panel Controller Clicking the buttons on the Panel Controller allows switching of panels. The Main button displays the main panel, the Data button displays the data panel, and the Settings button displays the settings panel. Main button, Data button, Settings button 8
13 Panel Display Area Each tool is used to perform processing of images displayed in the XYZ View and the CurvedMPR View. Data Panel The data panel displays additional information related to exported images. This includes patient names, i-dixel database patient IDs, image dates, rotation histories, and comments. Comments and patient information are not displayed under the initial settings. To display data, click the "+" button on the left of the "Information" displayed on the data table. To display comments, click the "+" button on the left of the "Private" displayed on the data table. 9
14 Settings Panel Setting of [Volume Rendering Settings] and [Application Settings] can be performed. [Volume Rendering Settings] Adjustment of volume rendering images on the XYZ view can be performed. [Application Settings] Values of image display settings can be checked. In regards to thickness when displaying XYZ slice images and cross section images, if spike noise and artifacts stand out, increasing the thickness will reduce the effects. Histogram Window Histogram window displays a histogram of the displayed image. In order to improve the visibility of images, adjust the contrast and brightness of images. (For details, please refer to [2.2.4 Histogram].) Selecting [View]-[Histogram] from the menu, or clicking the displaying and hiding the histogram window. button on the main panel, switches between 10
15 2.2. View Menu Status Bar Selecting [View]-[Status Bar] from the menu switches between displaying and hiding the status bar. Status Bar X Image Inversion, Z Image Inversion By selecting [View]-[XYZ View Layout]-[X Invert] from the menu it is possible to invert images in the X-axis direction on the X,Y,Z slice view and volume rendering view. Inversion of the Z-axis is possible by selecting [Z Invert]. Inversion is also possible by pressing the XYZ View layout or buttons on the main panel. <<Example: When the X image inversion button: is selected>> The initial display positions of each view are the same as those used when CT data was exported from i-dixel. The next time the application is started, there are reset to the initial positions. 11
16 Switch Display of Z Slice Images, Cross Section Images, and Panorama Images Please refer to [3.2.5 CMPR Image Display Change-over] Histogram Selecting [View]-[Histogram] from the menu, or clicking the [Histogram] button: switches between displaying and hiding the histogram panel. The size of the histogram window can be adjusted by dragging the edge of the window. on the main panel, Cursor Selecting [View]-[Cursor] from the menu, or clicking the [Cursor] button: on the main panel, switches between displaying and hiding the cursor line on slice images. (When operating cursor lines, all cursor lines will be displayed regardless of the settings.) :1 Pixel Magnification Images are shown on the display at a 1:1 pixel ratio. Clicking the [1:1 Pixel Magnification] button: on the main panel turns 1:1 pixel magnification ON and OFF. The size of displayed slice images will be magnified/reduced. If images are too large for the display area, scroll bars will be displayed. 12
17 Magnifying Glass Magnifying glass displays the selected area at double resolution. Clicking the [Magnifying Glass] button: on the main panel, or selecting [Tools]-[Magnify] from the menu enables the magnifying glass and changes the shape of the pointer to a magnifying glass. Display of the selected area is magnified. While using the magnifying glass it is not possible to move cursor lines. To disable the magnifying glass, either click the [Magnifying Glass] button again, click another measuring tool, or right click with the mouse. 13
18 2.3. Tool Menu Select You can measure distances and angles or draw graphics and character strings on CT slice image in the XYZ view and Z slice image, panoramic image, and cross-sectional image in the CurvedMPR view. It is enabled by either selecting [Tools]-[Select] from the menu, or clicking the [Tool] button: panel. * Please be aware that clicking this button during measurement will stop the measurement process. on the task Eraser (Clear) You can delete measurement data added to slice images. It is enabled by either selecting [Tools]-[Erase] from the menu, or clicking the [Eraser] button: panel, and changes the pointer into an eraser. on the task Clicking on lines of measurement data or text boxes will delete them. Please be careful, as deleted items cannot be undeleted. When using the keyboard, deletion is possible by clicking a line of measurement data or a text box, and then pressing the Delete key on the keyboard. Right clicking on an image will revert to the selection tool Length Measurement Performs measurement of distance. Either selecting [Tools]-[Length Measurement] from the menu, or clicking the [Measure Length] button: on the task panel will change the pointer to a "+." (Clicking this button during measurement will stop the measurement process.) Cursor The first position clicked is the starting point of the distance measured, and each position clicked is maintained until you double click. The double clicked position is the end point, and the measured distance from the start to the end is displayed in a text box. This text box can be moved as desired. When measuring, clicking the next slice image has no effect. When measurement of distance is complete, the next measurement can be performed. 14
19 The points (measurement points) clicked when measuring can be moved by dragging them. By dragging a measurement line it is possible to move the entire line, and when the positions of points or lines are changed the measurement data is updated. Measurement data The location being changed is displayed is blue. By right clicking with the mouse before releasing the left mouse button it is possible to stop adjustment. If a measurement line is clicked once, it will remain selected until something other than a line is clicked, or another line is selected. Measurement results other than rotations on the same plane will remain even if the displayed direction or position of slice images are changed. Please execute measurement after defining the display direction and position of slice images. 15
20 Angle Measurement Angle measurement performs measurement of angles. Either selecting [Tools]-[Angle Measurement] from the menu, or clicking the [Measure Angle] button: on the task panel will change the pointer to a "+." (Clicking this button during measurement will stop the measurement process.) The first position clicked becomes the start point for angle measurement, and the angle is displayed on the fourth point clicked. The angle of the straight lines connecting points 1 & 2, and 3 & 4 is calculated and the measurement data is displayed in a text box. This text box can be moved as desired. While measuring the angle, clicking another measurement tool or right clicking with the mouse reverts to the selection tool. Measured Angle φ Parallel When angle measurement is complete, the selection tool is automatically restored. The points (measurement points) clicked when measuring can be moved by dragging them. By dragging a measurement line it is possible to move the entire line, and when the positions of points or lines are changed the measurement data is updated. When moving measurement lines or measurement points, it is possible to stop the movement by right clicking before releasing the left mouse button. If a measurement line is clicked once, it will remain selected until something other than a line is clicked, or another line is selected. Measurement results other than rotations on the same plane will remain even if the displayed direction or position of slice images are changed. Please execute measurement after defining the display direction and position of slice images. 16
21 Annotation (Comments) Annotations (comments) can be added to slice images. Selecting [Tools]-[Annotations] from the menu displays the 5 annotations (Straight line, rectangle, ellipse, arrow, and text). Straight line, rectangle, ellipse, and arrow annotations can be added by dragging them. With text annotations, drag to create a quadrilateral frame, and then enter text. To exit, click another location. Added annotations can be moved using the Selection tool: on the tool panel. Annotations can be deleted by selecting either the Eraser tool: or the Selection tool:, and pressing the Delete key on the keyboard. 17
22 Carve Images You can carve CT slice image or volume rendering image. Selecting [Tools]-[VolR Carver] from the menu, or clicking the "Carving the volume" button: on the task panel will enable slicing and change the pointer to a hand piece. Please refer to [3.1.9 Carve Images] Magnifying Glass Please refer to [2.2.7 Magnifying Glass] Section Volumes Please refer to [ Cut Place Display] Add Rulers to Images Being Output Select [Tools]-[Copy Rulers on Image] from the menu and the image will be output with a ruler in it Synchronize the Viewpoint with VoIR Please refer to [ Visual point lock] Unsynchronize the Viewpoint Please refer to [ Visual point lock]. 18
23 3. XYZ View and CMPR View In i-dixel One Volume View it is possible to switch between displaying the XYZ view and the CurvedMPR view. Switch by selecting the XYZ tab or the CurvedMPR tab XYZ View CurvedMPR View 1. Z Slice Image 5. Z Slice Image 2. Y Slice Image 6. Section Image 3. Volume Rendering Image 7. Panorama Image 4. X, Slice Image 19
24 What is Volume Rendering Volume rendering is a method of creating images based on data distributed in a 3-dimensional space. It is enables visibility of internal structures as well as the surface. Through display of volume rendered images: It is possible to display 3-dimensional images of both the surface and interior. It is possible to observe sections of 3-dimensional images. It is possible to make intuitive explanations to patients. Please use i-dixel Volume Rendering volume rendering images for giving explanations to patients. For making diagnoses, please use i-dixel or One Data Viewer Plus slice image data. Volume rendering makes it possible to render both the surface and interior of objects, similar to looking at something inside a glass bottle. What is CurvedMPR CurvedMPR creates slice images from prepared (saved) CT volumes, by selecting a plane and creating images from the 2 planes that cross it perpendicularly. It is also possible to create panoramic images of selected curved surfaces. Features of CurvedMPR Creation and changing of slice curves 3D volume rotation for obtaining optimal images Measurement of distance and angles on individual section images Export of measurement data and orientation data 20
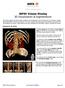
25 3.1. XYZ View Display Window Z Slice Image Stereoscopic CT Image Patient Direction Indicator Y Slice Image Ruler X Slice Image X Cursor Line Y Cursor Line Z Cursor Line X, Y, Z Slice Images Section images generated in real-time from reconstructed CT volumes. The X cursor line indicates the position on the X slice, the Y cursor line indicates the position on the Y slice, and the Z cursor line indicates the position on the Z slice. Dragging each of the cursors is reflected on the displayed X, Y, and Z slices. Scale marks on the edges of the 3 images are a ruler (diminishing scale) indicating the plain scale of the image in millimeters. In a VolR image, X, Y, Z slice planes are shown so you can identify the position of an X, Y or Z slice image currently displayed three-dimensionally. * X slice plane: the cross section of an X slice image * Y slice plane: the cross section of a Y slice image * Z slice plane: the cross section of a Z slice image Stereoscopic CT Images * Images (Volume rendering image, MIP image, or RaySum image) of reconstructed CT volume data displayed stereoscopically. Patient Direction Indicator Patient Direction Indicator indicates the direction of the patient. Updated automatically when the directions of images are changed. 21
26 * Volume rendering image, MIP image, and RaySum image are switched as shown below: Volume rendering image Click MIP Image RaySum Image Volume rendering image: The anatomical site scanned with CT is visualized three-dimensionally. This is useful to check the anatomical site three-dimensionally. MIP image: * MIP: Maximum Intensity Projection The three-dimensional structure of the anatomical site scanned with CT is displayed as the projection onto the plane facing the observer. This is useful to check the status of implants and prosthetics. RaySum image: * RaySum: Ray Summation The three-dimensional structure of the anatomical site scanned with CT is displayed as the image taken with the plain X-ray. This is useful to check the internal structure of the anatomical site. 22
27 Volume Rendering The 3 Tools Composing Volume Rendering: VOI, Opacity, and Color Volume rendering is a method for creating stereographic displays of reconstructed CT volumes using 3 tools; "Threshold values," "Opacity (Opaqueness)," and "Color." This software uses ray casting to provide clear display of volume rendering images. VOI (Volume of Interest) A VOI is space that is divided by the scope of a gray-scale. This gray-scale is decided by 2 threshold values. Opacity Opacity is the level of opaqueness, and the opacity graph is referred to as the "Opacity Curve." Opaqueness is reached when the value of the opacity curve is 100% (the maximum value). Transparency is reached at 0% (the minimum value). Color The color of the Volume of Interest can be changed using the [Change Color] tool. There are two types of Histogram Window: one for gray-scale images and one for volume rendering images. You can switch them by clicking the GS LUT (gray-scale) / C LUT (color) button. The threshold values and opacity and color adjustment tools in the histogram window are as below. (For gray-scale images) Color button (For volume rendering images) Adjustment of opacity (OP: Opaqueness) Opacity Curve Adjustment of the threshold value (WW) Adjustment of the threshold value (WL) The gray-scale images refer to CT slice images, MIP images, and RaySum images displayed in the XYZ view and Z slice images, panoramic images, and cross-sectional images displayed in the CurvedMPR view. 23
28 The gray-scale distribution of each system is a set width that is centered on the value on the histogram. (Figure a below) Considering the volume data that is the region in the scope of the maximum and minimum thresholds of distribution on the histogram, this is the region corresponding to the 3-dimensional space of the target systems. This region (without distinction between the histogram and 3-dimensional space) is called the VOI (Volume of Interest). Volume rendering is the function that enables selective allocation of colors and opacity for display of each VOI. The most important factor of VOI is the maximums and minimums of the gray level. The maximum and minimum are decided in WL (Window Level) and WW (Window Width). The area encompassed by the maximum and minimum is frequently called the window, and WL is the central position on the histogram in the window, and WW is the width of the window. The density distributions of multiple systems often overlap. (Figure b below) Accordingly, when a specific color is allocated to the overlapping section (area II in figure c below) and a figure drawn, the 2 systems will be displayed intermixed. This situation can be avoided by changing the gray level of the opacity value. In other words, in regions with contributions from multiple systems (area II in figure c below), configure a lower opacity value than in either of the regions with contributions from only one system (areas I and III in figure c below). In this case, consecutively changing the opacity (Figure d below) will result in generation of a natural image. The means of changing the opacity is called "opacity curve," and is set using the [Opacity Curve Selection Button] [Opacity(Op)] [Sh]. Frequency Frequency Gray-scale Gray-scale Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum Figure a: Maximum and Minimum of VOI Figure b: With Multiple Systems Frequency Frequency Opaqueness Gray-scale Gray-scale Figure c: Contribution of Multiple Systems to VOI Figure d: Opacity Curve Settings 24
29 Histogram Window Part Names In Histogram Window, you can check the histogram for CT volume data, adjust the quality of gray-scale image and set VOI (Volume of Interest) to be shown in the volume rendering image. [Feasures of the histogram window for gray-scale images] In gray-scale images, it is possible to adjust WW (Window Width), WL (Window Level), the slope of the contrast curve, and the brightness while checking the histogram shown on the histogram window. 1. Histogram of Voxel Values: The distribution of the voxel values in the CT volume data is displayed. From the histogram, it is possible to distinguish what level of hard tissues such as teeth and bone, and soft tissues such as gums are included in the CT volume data. 2. Contrast Curve: The contrast is adjusted by changing the slope of the contrast curve. The size of WW (Window Width) changes with the slope of the contrast curve. 3. WL (Window Level): Setting WL sets the voxel value of the center of WW. You can enter the value directly or set the value by sliding the vertical line on the histogram left or right. 4. Brightness Level: The brightness can be adjusted by sliding the horizontal line on the histogram up or down. 5. Opacity Level Slider: Opacity Level Slide is disabled in Histogram Window for gray-scale images. 6. Vertical Axis Scale Toggle Switch (Linear / Log): You can switch the scale of the vertical axis of the histogram between linear (Linear button) or logarithmic (Log button). 25
30 7. Overflow: You can specify the color for the voxels with the value exceeding the voxel value set for WW. 8. Underflow: You can specify the color for the voxels with the value below the voxel value set for WW. 9. WW (Window Width): Window Width represents the range of voxel values to be displayed as gray scale. You can set the value by directly entering the value or changing the slope of the contrast curve. 10: C LUT (Color): Clicking the button changes the window to the histogram window for volume rendering images. 11: Auto: Clicking this button sets WW, WL, and the brightness level for the image to the optimal values automatically. 12. Reset: This button resets the values for WL, WW, and the brightness level to 3999, 7999, and 128, respectively. Histogram The histogram is the graph showing the distribution of the voxel values of CT volume data, and the horizontal axis and vertical axis represent the voxel value and voxel count for each voxel value, respectively. Voxel Count Voxel Value * The voxels containing the elements of tooth, bone, and prosthetics are mainly shown on the right side of the histogram. 26
31 Settings for WW (Window Width), WL (Window Level), and the brightness level: WW (Window Width): Window Width is set by dragging and dropping the contrast curve to change the slope of the curve. Increasing the slope narrows the width and increases the contrast. WL (Window Level): Window Level is set by sliding the vertical line on the histogram. Moving to the left makes the image brighter, and moving to the right makes the image darker. Brightness Level: Brightness Level is set by sliding the horizontal line on the histogram. Moving upwards makes the image brighter, and moving downwards makes the image darker. Brightness WL Slope of Contrast Curve Brightness level WW Voxel Value Switch the scale for the vertical axis of histogram: The scale of the vertical axis of the histogram can be switched between linear or logarithmic. Linear display Clicking the Linear button shows the histogram in the linear form. Logarithmic display Clicking the Log button shows the histogram in the logarithmic form. Comparing to the linear from, it is easier to see the distributions of the voxels at the right and left edges of the histogram. (See below) 27
32 [Adjust the image quality of gray-scale images] <<Example: Displaying prosthetics clearly in CT slice images and MIP images>> [1] Click the Log button to show the histogram in the logarithmic form and check the distribution of the voxels with the elements of tooth, bone, and prosthetics in the CT volume data. The voxels with the elements of tooth, bone, and prosthetics are mainly shown on the right side of the histogram. [2] Setting WL (Window Level) to the right side of the histogram shows teeth, bones, and prosthetics clearly. WL [3] Adjusting the slope of the contrast to narrow WW (Window Width) shows teeth, bones, and prosthetics clearly. WW 28
33 [4] Adjust the brightness level as needed. You can adjust this by sliding the green horizontal line on the histogram window up and down. 29
34 [Features of the histogram window for volume rendering images] Volume rendering images are displayed in accordance with the predetermined volume of interest (VOI). CT volume data includes many voxels with the elements of hard tissues such as teeth, bones, etc. and soft tissues such as gingiva. Therefore, to show a specific object such as teeth, bones, etc., it is necessary to set the volume of interest. You can set the volume of interest by adjusting the shape of the opacity curve, WW (Window Width), WL (Window Level), and the opacity level while checking the histogram shown on the histogram window. 1. Histogram of Voxel Values The distribution of the voxel values in the CT volume data is displayed. You can find out the portion of the hard tissue elements such as teeth, bones, etc. and the soft tissue elements such as gingiva in the CT volume data from the histogram. 2. Opacity Curve You can adjust the WW (Window Width), WL (Window Level), and the opacity level by changing the shape of the opacity curve with drag & drop. 3. VOI You can register, delete, show, and hide the volumes of interest and set the display color (color coding). The priority for displaying multiple volumes of interest is set. 4. WW (Window Width) Window Width represents the range of voxel values of objects to be displayed. You can set the value by directly entering the value or changing the shape of the opacity curve. 5. WL (Window Level) Window Level represents the reference point of the opacity curve. opacity curve is selected, this represents its center. However, if the trapezoid shape The reference point of the opacity curve varies with the shape of opacity curve selected. 30
35 6. Sh This is enabled only if the trapezoid shape opacity curve is selected. Sh is the value equivalent to the shape of trapezoid. If Sh is 0, the opacity curve becomes an isosceles triangle, and if Sh is 1, the curve becomes a rectangle. You can set Sh by directly entering the value or changing the shape of the opacity curve. 7. GS LUT Clicking this button changes the window to the histogram window for gray-scale images. 8. Opacity Level Slider You can adjust the opacity level of the image by moving the slide up or down. You can adjust the opacity for only the voxel values within the range of WW (Window Width). Moving the slider downwards decreases the opacity revealing the internal structures of the volume rendering image. 9. Types of Opacity Curve You can select the basic shape of the opacity curve. Increasing Select this shape to show the objects such as teeth, bones, etc. with the relatively :, large voxel value. Trapezoid : Select this shape to show multiple objects such as hard tissues, soft tissues, etc. Decreasing, : Select this shape to show the objects such as air, etc. with the relatively small voxel value. Set WW (Window Width), WL (Window Level), and the opacity level You can set WW (Window Width), WL (Window Level), and the opacity level by dragging the opacity curve to change the shape of the curve. WW (Window Width), WL (Window Level), and the opacity level for the increasing shape WL is the voxel value for the starting point of WW. Opacity Level Opacity WL WW Voxel Value 31
36 WW (Window Width), WL (Window Level), and the opacity level for the increasing shape WL is the voxel value for the starting point of WW. Opacity Opacity Level WW WL Voxel Value WW (Window Width), WL (Window Level), the opacity level, and WS for the trapezoid shape WL is the voxel value for the median value of WW. Opacity Level Opacity WL WW Voxel Value The shape of trapezoid can be changed with the value of WS. You can set the value for WS between 0 and 1. If WS is 0, the opacity curve becomes an isosceles triangle, and if WS is 1, the curve becomes a rectangle. WS = 0 WS = 0.5 WS = 1 WW WL WW WL WW WL 32
37 WW (Window Width), WL (Window Level), and the opacity level for the decreasing shape Opacity Opacity Level WL is the voxel value for the starting point of WW. WW WL Voxel value WW (Window Width), WL (Window Level), and the opacity level for the decreasing shape Opacity WL is the voxel value for the starting point of WW. Opacity Level WW WL Voxel Value * You can adjust the transparency of the image by adjusting the opacity level slider. Moving the opacity level slider downwards increases the transparency of the image revealing the internal structures such as roots of teeth. 33
38 [Display the volume of interest of the volume rendering image] The steps differ with the number of volumes of interest. <Display hard tissues such as bones, teeth, etc. for a single volume of interest> [1] Check the distribution of the voxels with the elements of teeth and bones in the CT volume data. The voxels with the elements of teeth and bones are mainly shown on the right side of the histogram. [2] To show the objects such as teeth, bones, etc., with the relatively large voxel value, select the increasing opacity curve. [3] Drag the opacity curve to set WL (Window Level) to the right side of the histogram so that objects are shown. WL [4] Drag the opacity curve to adjust WL (Window Level) so that hard tissues such as teeth and bones are targeted. Narrowing the width of WW shows hard tissues such as teeth and bones clearly. WW is set using WL (Window Level) as the reference point. WW 34
39 [5] Set the name and the color of the object to be displayed and register the volume of interest. Double-click the name ( new VOI for initial setting) to enter changes. In addition, click the color (blue for initial setting) to select an optional color from the color setting dialog. <<By setting a plurality of VOIs, tooth section, gum, and other soft tissues are displayed.>> In order to display a plurality of VOIs, a plurality of VOIs must be set and the display priority must be decided. [1] Set the VOI of the tooth section and register the color and the name. 35
40 [2] Click the VOI new creation button to add a VOI, and set VOIs for the gum and other soft tissues, and register the color and the name. VOI new creation button [3] A ticked VOI is displayed on the volume rendering image. Set the display priority of the VOI. Select the VOI which you want to display on the foreground, click the Move to the next level button to display on the highest step of the VOI item list box. Unrequired VOIs can be deleted by selecting an unwanted VOI and clicking the Delete VOI button. Move to the next level button Delete VOI button A plurality of VOIs are displayed in accordance with the priority. 36
41 Volume Rendering Settings Selecting Volume Rendering Settings on the setting panel allows you to set Specular Reflection, Light Attenuation, Blending Ratio, Projection Method, etc. Adjust while confirming images. <Draw Tomography on Cutting Plane> Tick <Draw Tomography on Cutting Plane> to allow a tomographic view to be displayed for the cutting plane of the volume rendering image. <Specular Reflection> If you check the Specular Reflection checkbox, the effects of light reflection will appear strongly around the center of images. Without specular reflection With specular reflection <Resolution> Moving the slider to the right increases the resolution, and images are displayed at the higher resolution. 37
42 <Sampling> Increasing Sampling improves the image display speed, but this may result in laminar artifacts. Decreasing Sampling slows down the display speed, but the images will be displayed with more details. The image display speed depends on the performance of the i-dixel computer when decreasing Sampling. <Light Attenuation> You can reduce the diffused light by checking the Light Attenuation checkbox. Moving the slider to the left decreases the light attenuation. Without light attenuation With light attenuation <Blending Ratio> Blending Ratio represents the ratio of ambient light and diffuse light. Moving the slider to the right increases the blending ratio emphasizing convex and concave. Small blending ratio Large blending ratio 38
43 <Projection> You can select either Perspective projection or Parallel projection. With the perspective projection, changing the angle of view results in the apparent changes in the distance from the point of view. Parallel projection Perspective projection (Angle of View: 10 ) Perspective projection (Angle of View: 20 ) Perspective projection (Angle of View: 80 ) 39
44 Rotate and Move the Image Volume rendered, MIP, and Raysun images can be rotated and shifted Rotate of the volume rendering image Drag the image up and down or left and right with the mouse. If you drag with the Ctrl key held down, you can rotate the image clockwise or counterclockwise. The head at the lower left shows the orientation of the image. Drag mouse pointer with Ctrl held depressed Move the volume rendering image Dragging the mouse pointer with the Shift key held down on the volume rendering image shifts the volume rendered image vertically or horizontally. Drag mouse pointer with Shift held depressed. To zoom in or zoom out the image Placing the mouse pointer on the volume rendering image and moving the mouse wheel longitudinally zooms in or zooms out the volume rendering image. 40
45 Rotate the slice image Dragging the mouse pointer on each slice image (any point other than the cursor line) rotates the slice plane. Optional slice plane are able to be observed. In such event, each slice image rotates around the intersection of slice cursor lines Move the slice image Dragging the cursor line can move the slice plane corresponding to that cursor line. X-cursor line Y-cursor line Z-cursor line 41
46 To achieve linkage between the volume rendering image and the slice image Rotating or moving each slice image causes the volume rendering image to rotate or move in linkage with the slice image. * Clicking the Original Position button turns the volume rendering image to face the front and X, Y, and Z cursors return to the home (0, 0, 0) position, respectively. 42
47 Visual point lock This will link and synchronize the volume rendered, MIP, or Raysum image with the X, Y and Z slice images or vice versa. Selecting [Tool]-[Synchronize to Volume Rendering] on the menu or clicking the [Synchronize the visual point to VoIR] button : on the main panel turns the CT slice image in such a manner as to match the direction of the volume rendering image in display. In addition, clicking the [Synchronize the visual point to X, Y, and Z slices] button: on the main panel turns the volume rendering image in such a manner as to match the direction of CT slice image in display. <<Example: To rotate the volume rendering image with the visual point in synchronism with VoIR.>> Rotating the volume rendering image rotates the slice image in synchronism with the rotating direction of the volume rendering image. To bring the visual point to be asynchronized. Either selecting [Tool]-[Decouple Volume Rendering] on the menu or clicking the [Visual Point Unlock] button: on the main panel prevents the volume rendering image from turning even if the CT slice image is turned. In addition, even when the volume rendering image is turned, the CT slice image is not turned. <<Example: To rotate the volume rendering image>> Even if the volume rendering image is rotated, the slice image is not turned. 43
48 Show X, Y, and Z Cursor Planes You can show the X, Y, and Z cursor planes by clicking the [Show XYZ cursor planes] button. Clicking again hides them. You can show the X, Y, and Z cursor planes on volume rendering image, MIP image, or RaySum image. Showing the X, Y, and Z cursor planes helps you understand the positions of the CT slice images three-dimensionally. Unlocking Point of View allows you to show the X, Y, and Z cursor planes in arbitrary orientation. Therefore, you can understand the position of the CT slice images displayed easily. In addition, moving the X, Y, and Z cursor lines moves the X, Y, and Z cursor planes accordingly. * If Point of View is locked, the X and Z cursor planes will not be displayed. 44
49 Partial Slicing The partial slicing is a useful tool for showing only the volume of interest in CT slice image in XYZ view. Executing the partial slice displays the CT slice image using the specified FOV (Field of View) area, but FOV will not be used for the volume rendering images, MIP images, and RaySum images. To limit to the volume of interest, it is necessary to execute the zoom reconstruction. However, the zoom reconstruction is an option feature, and it is available only with the i-dixel capture computer for 3DX MULTI-IMAGE MICRO CT Type F8. <Partial slicing of CT slice image in XYZ View> [1] Move the X, Y, and Z cursor lines to the center of volume of interest. [2] Clicking the "Show / Hide FOV for partial slicing" button shows the frame of field of view (FOV) area on the CT slice image. 45
50 [3] Select the field of view area for the partial slicing. You can set it by dragging the frame of the field of view area. The size of the field of view area is equivalent to the volume of interest. [4] Double-clicking the frame of the field of view area performs the partial slicing, and the results are reflected to the CT slice image. On the volume rendering image, the field of view area is shown as a wireframe cube. Once the field of view volume (cube) is shown on the volume rendering image by the execution of the partial slicing, the record of the field of view volume is added to the Measurements, Annotations & Implants list. On the list, the show / hide toggle checkbox for the object will be checked. (* Removing the check mark hides the field of view volume from the volume rendering image.) Checkbox 46
51 Cut Plane Display Volume rendering image, MIP image, or RaySum image are cut by X, Y, and Z cursor planes and their cross sections are able to be observed. Select either [Tool]-[Volume Cutter] of the menu or click the [Volume Cut] button on the task panel to select the plane you want to cut. Cut by the X-cursor plane. Cut by the Y-cursor plane. Cut by the Z-cursor plane. <Example: Cutting the volume rendering image at the X cursor plane> [1] Move the X cursor line to the cutting plane. X cursor line [2] Click the [Cut the volume] button and click the [Cut at the X cursor plane] button. 47
52 [3] The volume will be cut at the X cursor plane. [4] To view the cutting plane, rotate the volume rendering image. * You can cancel the cut by clicking the "Cancel the cut" button:. [Y plane dynamic cut] You can view the changes of the Y cutting plane for volume rendering image, MIP image, or RaySum image by moving the Y cursor line. [1] Clicking the [Y plane dynamic cut] button cut the volume at the Y cursor plane and display the cutting plane. 48
53 [2] Moving the Y cursor line changes the cutting planes displayed on the screen accordingly. [3] To end the Y plane dynamic cut, click the [Select an object] button. * You can cancel the cut by clicking the "Cancel the cut" button:. 49
54 Carve Images You can carve CT slice image or volume rendering image. Carving images is effective for removing artifacts, etc. If you carve an image, all images shown in 3D Viewer are updated accordingly. <Example: Carving the right lower 30> * In this example, to show the right mandibular first molar clearly, the intersection of X, Y, and Z cursor lines were moved to the right mandibular first molar to cut at the Z cursor plane, and the volume rendering image was rotated toward the anterior-inferior direction. [1] Click the [Settings] button from Panel Controller and enter the value for Carving Tool Diameter [mm] of "Other" under "Application Settings" of the settings panel. [2] Click the "Main" button of Panel Controller and click the "Carving the volume" button from "Tools" of the main panel. The mouse pointer changes to the handpiece shape. [3] Move the pointer to the right mandibular first molar on the volume rendering image and right-click the image to carve the tooth. The CT slice images are updated automatically. CT slice images are updated automatically. 50
55 To carve the tooth deeper, repeat the right-click. [4] To end carving the tooth, click the [Select an object] button. 51
56 Movie Clicking the Create movie button:, you can create the movie of volume rendering image. The created movie can be saved in the internal or the external media Align the Volume to the Selected Implant Clicking the "Align the volume to the selected implant" button, the implant drawn on the CT slice image will be displayed vertical to the Z slice plane at the intersection of cursor lines. Overlaying the image of the proposed implants on the patient s dental image using the Implant Presentation feature is for patient presentation and educational purposes only. The proposed implant imagery may not exactly match real clinical conditions, and proper professional care must be taken when performing actual surgery. Do not rely on the Implant Presentation feature when performing surgery. 52
57 3.2. CMPR View How to Create Image Data On the CurvedMPR (cmpr) view, Z slice image, panorama image, and cross section image are displayed. [Create and display panorama image and cross section image] [1] On the XYZ view, move the Z-cursor line to a target position, and the Z slice image is decided to draw a spline curve. *Spline curve: The panorama image and the cross section image are created along this curve. [2] Click the CurvedMPR tab and change over the view to the CurvedMPR view. 53
58 [3] Click the MPR spline button on the operation panel and click the mouse pointer on the drawing start point. The mouse cursor will change to a plus sign. Click along the dental arch in the Z slice image. The points will be connected by short lines. Double dlick to mark the end of the spline. Pointer MPR spline [4] After you finish drawing the spline, the panorama image and the cross section image are displayed (the defined curve is called the slice curve). The time before the image is displayed conforms to the processing speed of the computer you use (*while the image is being created, a progress bar may be displayed on the panorama or the cross section image window). Z slice Panorama Slice curve Cross section image On the Z slice image, the spline curve (slice curve) and a line that crosses the spline (slice) curve at right angles (orthogonal line) are drawn. The number of orthogonal lines indicates the total number of cross section images. In addition, the drawing position of the orthogonal line indicates the cross-sectional position of the cross section image and the length of the orthogonal line indicates the lateral width when the cross section image is displayed. See the next page for fine-adjustment of the slice curve. 54
59 Slice Curve Adjustment On the slice curve, red points (clicked points) are displayed. Dragging this point can change the point position. In addition, dragging the line that connects the point can move the whole slice curve. These changes are reflected to the panorama image and the cross section image (either pressing the ESC key or right-clicking before releasing the left button of the mouse can cancel the move). While the pointer is being operated, the tracking line moves in accordance with the mouse operation. Tracking line Dragging the end of the cross-section indicating line can adjust the width in the buccolingual direction of the cross section image. End of cross-section indicating line 55
60 Carrying out the foregoing operations can change the panorama image as follows: 56
61 Cross Section Image Adjustment Dragging the red line on the panorama image can change the display range of the cross section image. Moving the red line is reflected to the Z slice image. In such event, the slice curve is temporarily not displayed. Drag the red line. You can drag the spline curve (yellow line) in the Z slice image to change the cross sections. Drag Spline 57
62 Cross-sectional View Browsing Drag the green line on the panorama image and designate the target cross section image. In such event, the cross section image is automatically selected from the cross section image table and a green frame is indicated. In addition, the cross-section indicating line on the Z slice image, which indicates the cross section image position, is displayed in the green color (*the initial setting color of the frame and the line is green but can be changed by right-clicking). Drag. 58
63 To select a plurality of cross section images Dragging a selected image on the Z slice image displays the selected cross-section indicating line in the blue color. The cross section image of the selected portion is indicated by a blue frame, and in the panorama image, it is indicated by a blue perpendicular line. (*The initial setting color of the frame and the line is blue but it can be changed.) In addition, a plurality of cross section images can be selected by clicking the mouse pointer while pressing the Ctrl key. Drag selected image. 59
64 To adjust the display range of the cross section image Selecting the red line on the panorama image displays a red broken line above and below the red line. Dragging either the upper or the lower broken line can change the vertical display range of the cross section image. Moving the red broken line recreates the cross section image and changes the vertical width. Drag red broken line To make cross sections wider or narrower, drag the end of one of the cross section lines. Drag end of cross section line 60
65 To display a cross section image by a different window Double-clicking the selected cross section image displays the selected cross section image on a new window. Double-click. Even on a new window, tool menu functions are able to be used, and the results are reflected to the original cross section image. In addition, clicking the zoom button: displayed on the upper part of the new window can select the display magnification of the cross section image. *For the detailed tool menu, see [2.3 Tool Menu]. 61
66 CMPR Image Display Change-over Selecting [Axial Image] from [View] of the menu switches between display and non-display of the [axial image]. This applies to [Cross section Image] and [Panorama Image]. Incidentally, these can be switched by the relevant button of the tool bar, too; provided, however, that all the images are unable to be non-displayed simultaneously. * For the details of other display menu, see [2.2 View Menu] Measurement of Distance and Angle Distance and angle can be measured. *For the operating methods, see [2.3.3 Length Measurement] and [2.3.4 Angle Measurement]. 62
67 Partial Slicing The partial slicing is a useful tool for showing only the volume of interest in panoramic image / Z slice image in CurvedMPR View. Executing the partial slice displays the CT slice image using the specified FOV (Field of View) area, but FOV will not be used for the volume rendering images, MIP images, and RaySum images. To limit to the volume of interest, it is necessary to execute the zoom reconstruction. However, the zoom reconstruction is an option feature, and it is available only with the i-dixel capture computer for 3DX MULTI-IMAGE MICRO CT Type F8. < Partial slicing of panoramic images and Z slice images in CurvedMPR View> [1] Move the cursor lines on the panoramic image to the center of volume of interest. Moving the cursor line of the horizontal axis (red cursor line) automatically executes CurvedMPR and updates the cross-sectional image and Z slice image based on the movement of the cursor line. [2] Clicking the show / hide FOV for partial slicing button shows the frame of field of view (FOV) area for the partial slicing on the panoramic image and the Z slice image. FOV of the partial slicing 63
68 [3] Select the field of view area for the partial slicing. You can set it by dragging the frame of field of view area. The size of the field of view area is equivalent to the volume of interest. [4] Double-clicking the frame of the field of view area performs the partial slicing. Then, the partially sliced CT slice image is displayed (See below). On the panoramic image, a rectangular frame representing the field of view area is displayed. 64
69 You can switch the CT slice image by moving the X, Y, and Z cursor lines. Once the field of view area is shown on the panoramic image by the execution of the partial slicing, the record of the field of view area is added to the Measurements, Annotations & Implants list. On the list, the show / hide toggle checkbox for the object will be checked. (* Removing the check mark hides the field of view area from the panoramic image.) Checkbox 65
70 Image Saving Each image is able to be saved by the following method. For the cross section image, selecting multiple images in advance can save all the selected images. *For the method to select multiple images, see [3.2.4 Cross-sectional View Browsing]. To save from the right-clicking menu. Right-click the image and select [Export]. Select the file format * and save. *Kind of file formats JPEG File Interchange Format The image data format with emphasis placed on the data compression ratio. With degraded image quality allowed, data compression is performed. The file size is reduced but the image quality is degraded. Windows Bitmap Windows Bitmap is a standard image saving system in Windows. No data compression is conducted. Practically 8 bits are used for the black-and-white density scale. The picture quality is not degraded but the file size increases. 66
71 To save picture images by dragging and dropping the images. With the Alt key held depressed, drag and drop the image into the folder to be saved. The image is saved by BMP (bitmap). 67
72 4. Version Information Selecting [Help]-[Version information] of the menu displays the following windows. The version of the i-dixel One Volume Viewer can be confirmed. Notify us of this information whey you make any inquiries on the operation of the i-dixel One Volume Viewer. 68
Virtual MODELA USER'S MANUAL
 Virtual MODELA USER'S MANUAL Virtual MODELA is a program that simulates the movement of the tool on the screen. Contents Contents Part 1 Introduction 1-1 System Requirements... 4 1-2 Overview of Virtual
Virtual MODELA USER'S MANUAL Virtual MODELA is a program that simulates the movement of the tool on the screen. Contents Contents Part 1 Introduction 1-1 System Requirements... 4 1-2 Overview of Virtual
VXvue User Manual (For Human Use)
 VXvue User Manual (For Human Use) Page 2 of 90 Revision History Version Date Description 1.0 2012-03-20 Initial Release Page 3 of 90 Contents Safety and Regulatory... 8 Safety Notice... 8 1. Introduction...
VXvue User Manual (For Human Use) Page 2 of 90 Revision History Version Date Description 1.0 2012-03-20 Initial Release Page 3 of 90 Contents Safety and Regulatory... 8 Safety Notice... 8 1. Introduction...
icatvision Quick Reference
 icatvision Quick Reference Navigating the i-cat Interface This guide shows how to: View reconstructed images Use main features and tools to optimize an image. REMINDER Images are displayed as if you are
icatvision Quick Reference Navigating the i-cat Interface This guide shows how to: View reconstructed images Use main features and tools to optimize an image. REMINDER Images are displayed as if you are
14 July Ver CRView V3 User Guide. 1 P a g e
 Ver. 080707 CRView V3 User Guide 1 P a g e Contents Copyright notice... 3 Trademarks... 3 System requirements... 4 Required hardware... 4 Recommended hardware... 4 Installing CRView... 5 Installing from
Ver. 080707 CRView V3 User Guide 1 P a g e Contents Copyright notice... 3 Trademarks... 3 System requirements... 4 Required hardware... 4 Recommended hardware... 4 Installing CRView... 5 Installing from
JAZZ HARMONY User Manual
 JAZZ HARMONY User Manual Copyright 2017 Imaging. All rights reserved. This manual and the software described herein are protected by copyright laws and international copyright treaties, as well as other
JAZZ HARMONY User Manual Copyright 2017 Imaging. All rights reserved. This manual and the software described herein are protected by copyright laws and international copyright treaties, as well as other
ViewONE User Manual. Genazim. The Friedberg Geniza Project. Daeja Image Systems. All Rights Reserved.
 Genazim The Friedberg Geniza Project ViewONE User Manual Daeja Image Systems. All Rights Reserved. Email: info@daeja.com Web site: http://www.daeja.com 1 Contents Introduction 3 The User interface 3 Toolbars
Genazim The Friedberg Geniza Project ViewONE User Manual Daeja Image Systems. All Rights Reserved. Email: info@daeja.com Web site: http://www.daeja.com 1 Contents Introduction 3 The User interface 3 Toolbars
MIMAKI ENGINEERING CO., LTD.
 CAMLINK Instruction manual MIMAKI ENGINEERING CO., LTD. TKB Gotenyama Building, 5-9-41, Kitashinagawa, Shinagawa-ku, Tokyo 141-0001, Japan Phone: +81-3-5420-8671 Fax: +81-3-5420-8687 URL: http://www.mimaki.co.jp/
CAMLINK Instruction manual MIMAKI ENGINEERING CO., LTD. TKB Gotenyama Building, 5-9-41, Kitashinagawa, Shinagawa-ku, Tokyo 141-0001, Japan Phone: +81-3-5420-8671 Fax: +81-3-5420-8687 URL: http://www.mimaki.co.jp/
Sending image(s) to report Click Send Snapshot on any screen in Dolphin3D and choose the Send to Report option
 Dolphin 3D Reports Sending image(s) to report Click Send Snapshot on any screen in Dolphin3D and choose the Send to Report option Creating a report step by step 1. Generate the desired images in Dolphin3D
Dolphin 3D Reports Sending image(s) to report Click Send Snapshot on any screen in Dolphin3D and choose the Send to Report option Creating a report step by step 1. Generate the desired images in Dolphin3D
Gamepad Controls. Figure 1: A diagram of an Xbox controller. Figure 2: A screenshot of the BodyViz Controller Panel. BodyViz 3 User Manual 1
 BodyViz User Manual Gamepad Controls The first step in becoming an expert BodyViz user is to get acquainted with the Xbox gamepad, also known as a controller, and the BodyViz Controller Panel. These can
BodyViz User Manual Gamepad Controls The first step in becoming an expert BodyViz user is to get acquainted with the Xbox gamepad, also known as a controller, and the BodyViz Controller Panel. These can
GCC vinyl cutter, cutting plotter for sign making
 Plotter Setup In "Plotter Setup," you can choose "Plotter List," "Environment," "Pen," and so on. [Plotter list] In this area, you can choose the machine type and set some basic information for your plotter
Plotter Setup In "Plotter Setup," you can choose "Plotter List," "Environment," "Pen," and so on. [Plotter list] In this area, you can choose the machine type and set some basic information for your plotter
Table of Contents. Logos Imaging Application User s Manual Version Page 1
 Table of Contents About... 4 System Requirements... 5 Uninstall Previous Versions... 5 Install LIA 6.0... 6 Install the Device Drivers... 13 Register... 14 Getting Help... 14 Technical Support... 14 Workspace
Table of Contents About... 4 System Requirements... 5 Uninstall Previous Versions... 5 Install LIA 6.0... 6 Install the Device Drivers... 13 Register... 14 Getting Help... 14 Technical Support... 14 Workspace
Contents... 1 Installation... 3
 Contents Contents... 1 Installation... 3 1 Prerequisites (check for.net framework 3.5)... 3 Install Doctor Eye... 3 Start Using Doctor Eye... 4 How to create a new user... 4 The Main Window... 4 Open a
Contents Contents... 1 Installation... 3 1 Prerequisites (check for.net framework 3.5)... 3 Install Doctor Eye... 3 Start Using Doctor Eye... 4 How to create a new user... 4 The Main Window... 4 Open a
A QUICK TOUR OF ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CC (2018 RELEASE)
 A QUICK TOUR OF ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CC (2018 RELEASE) Lesson overview In this interactive demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CC (2018 release), you ll get an overview of the main features of the application.
A QUICK TOUR OF ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CC (2018 RELEASE) Lesson overview In this interactive demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CC (2018 release), you ll get an overview of the main features of the application.
IMAGE STUDIO LITE. Tutorial Guide Featuring Image Studio Analysis Software Version 3.1
 IMAGE STUDIO LITE Tutorial Guide Featuring Image Studio Analysis Software Version 3.1 Notice The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice. LI-COR MAKES NO WARRANTY OF
IMAGE STUDIO LITE Tutorial Guide Featuring Image Studio Analysis Software Version 3.1 Notice The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice. LI-COR MAKES NO WARRANTY OF
3DMMVR REFERENCE MANUAL V 0.81
 3DMMVR REFERENCE MANUAL V 0.81 Page 1 of 30 Index: 1.0 System Requirements...5 1.1 System Processor...5 1.2 System RAM...5 1.3 Graphics Card...5 1.4 Operating System...5 2.0 Conventions...6 2.1 Typographic
3DMMVR REFERENCE MANUAL V 0.81 Page 1 of 30 Index: 1.0 System Requirements...5 1.1 System Processor...5 1.2 System RAM...5 1.3 Graphics Card...5 1.4 Operating System...5 2.0 Conventions...6 2.1 Typographic
User Guide Belltech Systems, LLC
 User Guide Belltech Systems, LLC http://www.belltechsystems.com May, 2006 1. Introducing Belltech CaptureXT 2. Installation and Uninstallation Installation Running the Application Uninstallation 3. User
User Guide Belltech Systems, LLC http://www.belltechsystems.com May, 2006 1. Introducing Belltech CaptureXT 2. Installation and Uninstallation Installation Running the Application Uninstallation 3. User
4 TRANSFORMING OBJECTS
 4 TRANSFORMING OBJECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Add, edit, rename, and reorder artboards in an existing document. Navigate artboards. Select individual objects,
4 TRANSFORMING OBJECTS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Add, edit, rename, and reorder artboards in an existing document. Navigate artboards. Select individual objects,
2 SELECTING AND ALIGNING
 2 SELECTING AND ALIGNING Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Differentiate between the various selection tools and employ different selection techniques. Recognize Smart
2 SELECTING AND ALIGNING Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Differentiate between the various selection tools and employ different selection techniques. Recognize Smart
MiBio Reference Manual
 MiBio Reference Manual www.microtek.com Copyright 2012 by Microtek International, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks Microtek, ScanMaker, ArtixScan, ScanWizard and ColoRescue are trademarks or registered
MiBio Reference Manual www.microtek.com Copyright 2012 by Microtek International, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks Microtek, ScanMaker, ArtixScan, ScanWizard and ColoRescue are trademarks or registered
OPERATION MANUAL. MV-410HS Layout Editor. Version higher. Command
 OPERATION MANUAL MV-410HS Layout Editor Version 3.0 - higher Command Command Table of Contents 1. Setup... 1 1-1. Overview... 1 1-2. System Requirements... 1 1-3. Operation Flow... 1 1-4. Installing MV-410HS
OPERATION MANUAL MV-410HS Layout Editor Version 3.0 - higher Command Command Table of Contents 1. Setup... 1 1-1. Overview... 1 1-2. System Requirements... 1 1-3. Operation Flow... 1 1-4. Installing MV-410HS
PHOTOSHOP WORKSPACE. Interface Overview. Menus. The Tools. Palettes. Presets and Preferences PHOTOSHOP WORKSPACE UNIVERSAL TASKS PHOTO AND VIDEO TASKS
 12/30/03 2:19 PM Page 1 CHAPTER 1 Interface Overview 3 AL Menus RI 13 27 CHAPTER 4 59 ED Palettes CHAPTER 5 87 PRINT TASKS PY R IG HT Presets and Preferences PHOTO AND VIDEO TASKS MA TE CHAPTER 3 The Tools
12/30/03 2:19 PM Page 1 CHAPTER 1 Interface Overview 3 AL Menus RI 13 27 CHAPTER 4 59 ED Palettes CHAPTER 5 87 PRINT TASKS PY R IG HT Presets and Preferences PHOTO AND VIDEO TASKS MA TE CHAPTER 3 The Tools
Display. Introduction page 67 2D Images page 68. All Orientations page 69 Single Image page 70 3D Images page 71
 Display Introduction page 67 2D Images page 68 All Orientations page 69 Single Image page 70 3D Images page 71 Intersecting Sections page 71 Cube Sections page 72 Render page 73 1. Tissue Maps page 77
Display Introduction page 67 2D Images page 68 All Orientations page 69 Single Image page 70 3D Images page 71 Intersecting Sections page 71 Cube Sections page 72 Render page 73 1. Tissue Maps page 77
Adobe Photoshop Sh S.K. Sublania and Sh. Naresh Chand
 Adobe Photoshop Sh S.K. Sublania and Sh. Naresh Chand Photoshop is the software for image processing. With this you can manipulate your pictures, either scanned or otherwise inserted to a great extant.
Adobe Photoshop Sh S.K. Sublania and Sh. Naresh Chand Photoshop is the software for image processing. With this you can manipulate your pictures, either scanned or otherwise inserted to a great extant.
Guide to WB Annotations
 Guide to WB Annotations 04 May 2016 Annotations are a powerful new feature added to Workbench v1.2.0 (Released May 2016) for placing text and symbols within wb_view tabs and windows. They enable generation
Guide to WB Annotations 04 May 2016 Annotations are a powerful new feature added to Workbench v1.2.0 (Released May 2016) for placing text and symbols within wb_view tabs and windows. They enable generation
How to...create a Video VBOX Gauge in Inkscape. So you want to create your own gauge? How about a transparent background for those text elements?
 BASIC GAUGE CREATION The Video VBox setup software is capable of using many different image formats for gauge backgrounds, static images, or logos, including Bitmaps, JPEGs, or PNG s. When the software
BASIC GAUGE CREATION The Video VBox setup software is capable of using many different image formats for gauge backgrounds, static images, or logos, including Bitmaps, JPEGs, or PNG s. When the software
Feature-based CAM software for mills, multi-tasking lathes and wire EDM. Getting Started
 Feature-based CAM software for mills, multi-tasking lathes and wire EDM www.featurecam.com Getting Started FeatureCAM 2015 R3 Getting Started FeatureCAM Copyright 1995-2015 Delcam Ltd. All rights reserved.
Feature-based CAM software for mills, multi-tasking lathes and wire EDM www.featurecam.com Getting Started FeatureCAM 2015 R3 Getting Started FeatureCAM Copyright 1995-2015 Delcam Ltd. All rights reserved.
W-E
 Signage Suite V2.20 User Guide 605220-02-01-W-E-051613-02 Trademarks Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, and Microsoft are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other trademarks are the
Signage Suite V2.20 User Guide 605220-02-01-W-E-051613-02 Trademarks Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, and Microsoft are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other trademarks are the
4) Finish the spline here. To complete the spline, double click the last point or select the spline tool again.
 1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
SI-100 Digital Microscope. User Manual
 SI-100 Digital Microscope User Manual Read this manual before use Keep for future reference Content 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 About The SI-100... 3 1.2 Advantage of SI-100... 3 1.3 Product Specification...
SI-100 Digital Microscope User Manual Read this manual before use Keep for future reference Content 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 About The SI-100... 3 1.2 Advantage of SI-100... 3 1.3 Product Specification...
ezimagex2 User s Guide Version 1.0
 ezimagex2 User s Guide Version 1.0 Copyright and Trademark Information The products described in this document are copyrighted works of AVEN, Inc. 2015 AVEN, Inc. 4595 Platt Rd Ann Arbor, MI 48108 All
ezimagex2 User s Guide Version 1.0 Copyright and Trademark Information The products described in this document are copyrighted works of AVEN, Inc. 2015 AVEN, Inc. 4595 Platt Rd Ann Arbor, MI 48108 All
BDM s Annotation User Guide
 ETS :Foothill De Anza CC District April 17, 2014 1 BDM s Annotation User Guide Users with Read/Write access can annotate (markup) documents if they retrieve the document using Microsoft s Internet Explorer
ETS :Foothill De Anza CC District April 17, 2014 1 BDM s Annotation User Guide Users with Read/Write access can annotate (markup) documents if they retrieve the document using Microsoft s Internet Explorer
Copyright (C) 2001 Roland DG Corporation
 User's Manual Unauthorized copying or transferal, in whole or in part, of this manual is prohibited. The contents of this operation manual and the specifications of this product are subject to change without
User's Manual Unauthorized copying or transferal, in whole or in part, of this manual is prohibited. The contents of this operation manual and the specifications of this product are subject to change without
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide
 Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
IMAGE VIEWER. Following is the explanation of different settings and features: Page. First Page
 IMAGE VIEWER All scanned and or imported documents can be seen in Image Viewer. SequelMed image viewer is a powerful viewer where you can manipulate scanned documents. It has basic features starting from
IMAGE VIEWER All scanned and or imported documents can be seen in Image Viewer. SequelMed image viewer is a powerful viewer where you can manipulate scanned documents. It has basic features starting from
intelligent Touch Manager
 Commissioning Manual Supplementary Volume intelligent Touch Manager Layout Screen Creation Tool Model DCM601A51 MONITOR SERVICE LAN LAN SW FRONT BACK ON SLAVE BACKUP D MASTER OFF MASTER CPU ALIVE LAN LINK
Commissioning Manual Supplementary Volume intelligent Touch Manager Layout Screen Creation Tool Model DCM601A51 MONITOR SERVICE LAN LAN SW FRONT BACK ON SLAVE BACKUP D MASTER OFF MASTER CPU ALIVE LAN LINK
ImageVis3D User's Manual
 ImageVis3D User's Manual 1 1. The current state of ImageVis3D Remember : 1. If ImageVis3D causes any kind of trouble, please report this to us! 2. We are still in the process of adding features to the
ImageVis3D User's Manual 1 1. The current state of ImageVis3D Remember : 1. If ImageVis3D causes any kind of trouble, please report this to us! 2. We are still in the process of adding features to the
Panaboard Overlayer User's Guide. Image Capture Software for Electronic Whiteboard (Panaboard)
 Panaboard Overlayer User's Guide Image Capture Software for Electronic Whiteboard (Panaboard) Contents Introduction... 3 Functional Overview... 3 Operation Flow... 3 Abbreviations... 4 Trademarks... 4
Panaboard Overlayer User's Guide Image Capture Software for Electronic Whiteboard (Panaboard) Contents Introduction... 3 Functional Overview... 3 Operation Flow... 3 Abbreviations... 4 Trademarks... 4
Drawing shapes and lines
 Fine F Fi i Handmade H d d Ch Chocolates l Hours Mon Sat 10am 6pm In this demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CS6, you will be introduced to new and exciting application features, like gradients on a stroke
Fine F Fi i Handmade H d d Ch Chocolates l Hours Mon Sat 10am 6pm In this demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CS6, you will be introduced to new and exciting application features, like gradients on a stroke
Tach Facts V3.0 Software
 Tach Facts V3.0 Software Download runs from your Auto Meter Playback Tach with Tach-Facts Software. Instr. No. 2650-978 Tach Facts provides complete race analysis on your personal computer. Introduction
Tach Facts V3.0 Software Download runs from your Auto Meter Playback Tach with Tach-Facts Software. Instr. No. 2650-978 Tach Facts provides complete race analysis on your personal computer. Introduction
A Study of Angles & Curves
 A Study of Angles & Curves Method 1: Cutting Quilt Shapes/Using the Shapes Tools Open BERNINA CutWork Software. Make sure that Create New is selected. Click Next. Place a dot in front of New Graphic. Select
A Study of Angles & Curves Method 1: Cutting Quilt Shapes/Using the Shapes Tools Open BERNINA CutWork Software. Make sure that Create New is selected. Click Next. Place a dot in front of New Graphic. Select
Operating Instructions
 Providing presentation solutions V iewer Software Program Operating Instructions NIPPON AVIONICS CO., LTD. 1 This manual describes the functions and operations for conducting presentations using ip Viewer.
Providing presentation solutions V iewer Software Program Operating Instructions NIPPON AVIONICS CO., LTD. 1 This manual describes the functions and operations for conducting presentations using ip Viewer.
B-Works 2 User s Guide
 B-Works 2 User s Guide UMBWORKS 011413V1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. System Requirements... 2 3. Install B-Works 2... 3 4. Connection to the Hardware... 7 5. Start to Use B-Works 2... 7 6.
B-Works 2 User s Guide UMBWORKS 011413V1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. System Requirements... 2 3. Install B-Works 2... 3 4. Connection to the Hardware... 7 5. Start to Use B-Works 2... 7 6.
IMPAX Volume Viewing 3D Visualization & Segmentation
 Getting started guide IMPAX Volume Viewing 3D Visualization & Segmentation This guide outlines the basic steps to perform and manipulate a 3D reconstruction of volumetric image data using IMPAX Volume
Getting started guide IMPAX Volume Viewing 3D Visualization & Segmentation This guide outlines the basic steps to perform and manipulate a 3D reconstruction of volumetric image data using IMPAX Volume
Modify Panel. Flatten Tab
 AFM Image Processing Most images will need some post acquisition processing. A typical procedure is to: i) modify the image by flattening, using a planefit, and possibly also a mask, ii) analyzing the
AFM Image Processing Most images will need some post acquisition processing. A typical procedure is to: i) modify the image by flattening, using a planefit, and possibly also a mask, ii) analyzing the
1 ZoomBrowser EX Software User Guide 5.0
 1 ZoomBrowser EX Software User Guide 5.0 Table of Contents (1/2) Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 What is ZoomBrowser EX? What Can ZoomBrowser EX Do?... 4 Guide to the ZoomBrowser EX Windows... 5 Task Buttons
1 ZoomBrowser EX Software User Guide 5.0 Table of Contents (1/2) Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 What is ZoomBrowser EX? What Can ZoomBrowser EX Do?... 4 Guide to the ZoomBrowser EX Windows... 5 Task Buttons
efilm Workstation Quick Reference
 efilm Workstation Quick Reference Toolbar Features Customizing the Toolbar Toolbar Properties NOTE: Some tools have function key shortcuts, which can be adjusted. You can alter the mouse button selection
efilm Workstation Quick Reference Toolbar Features Customizing the Toolbar Toolbar Properties NOTE: Some tools have function key shortcuts, which can be adjusted. You can alter the mouse button selection
Using IPACS Webserver:
 Using IPACS Webserver: Logging On: The IPACS Webserver can be accessed from any PC with internet connectivity. 1. Open Internet Explorer or your internet service provider. 2. Type the IPACS web address
Using IPACS Webserver: Logging On: The IPACS Webserver can be accessed from any PC with internet connectivity. 1. Open Internet Explorer or your internet service provider. 2. Type the IPACS web address
1 Filter the search by entering search criteria; 2 Enter a range of dates in which to search. 3 You can filter the search by modality type.
 efilm / Managing Studies STUDY MANAGER How to use the study manager The Study Manager can search for four different types of exams: Local Exams: studies stored on your workstation s hard drive. Remote
efilm / Managing Studies STUDY MANAGER How to use the study manager The Study Manager can search for four different types of exams: Local Exams: studies stored on your workstation s hard drive. Remote
5.2. Click these tabs to jump to the Table of Contents, Index or start of each chapter.
 5.2 Click these tabs to jump to the, or start of each chapter. Click this button to advance to the next page. Click this button to return to the previous page. (Since this is the starting page, the [Back]
5.2 Click these tabs to jump to the, or start of each chapter. Click this button to advance to the next page. Click this button to return to the previous page. (Since this is the starting page, the [Back]
Instructions for Display of Imaging Studies Using Stentor isite
 Instructions for Display of Imaging Studies Using Stentor isite Open http://isite.rad.tju.edu in Internet Explorer Log-In: Enter your user name (case Sensitive) and password (case sensitive) and press
Instructions for Display of Imaging Studies Using Stentor isite Open http://isite.rad.tju.edu in Internet Explorer Log-In: Enter your user name (case Sensitive) and password (case sensitive) and press
Beginning Paint 3D A Step by Step Tutorial. By Len Nasman
 A Step by Step Tutorial By Len Nasman Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Paint 3D User Interface...4 Creating 2D Shapes...5 Drawing Lines with Paint 3D...6 Straight Lines...6 Multi-Point Curves...6
A Step by Step Tutorial By Len Nasman Table of Contents Introduction... 3 The Paint 3D User Interface...4 Creating 2D Shapes...5 Drawing Lines with Paint 3D...6 Straight Lines...6 Multi-Point Curves...6
VSPlayer Software User Manual
 VSPlayer Software User Manual UD03888B User Manual COPYRIGHT 2016 Hangzhou Hikvision Digital Technology Co., Ltd. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. Any and all information, including, among others, wordings, pictures,
VSPlayer Software User Manual UD03888B User Manual COPYRIGHT 2016 Hangzhou Hikvision Digital Technology Co., Ltd. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. Any and all information, including, among others, wordings, pictures,
BoA Tools Page 1 / 31
 BoA Tools Page 1 / 31 Standard tools Overview 2 Work pane 3 3D-2D file Main palette 6 Layout Main Palette 9 Navigation tools 11 Workplane Palette 14 Cursor Palette 21 Numeric control 24 Selection by Criteria
BoA Tools Page 1 / 31 Standard tools Overview 2 Work pane 3 3D-2D file Main palette 6 Layout Main Palette 9 Navigation tools 11 Workplane Palette 14 Cursor Palette 21 Numeric control 24 Selection by Criteria
CellaVision Proficiency Software
 CellaVision Proficiency USER S MANUAL 2.3 CellaVision Proficiency Preface CellaVision is a trademark of CellaVision AB. All other trademarks used in this document are property of their respective owners.
CellaVision Proficiency USER S MANUAL 2.3 CellaVision Proficiency Preface CellaVision is a trademark of CellaVision AB. All other trademarks used in this document are property of their respective owners.
Keyboard Shortcuts. Command Windows Macintosh
 S00ILCS5.qxp 3/19/2010 1:11 AM Page 477 Keyboard Shortcuts k Adobe Illustrator CS5 If a command on a menu includes a keyboard reference, known as a keyboard shortcut, to the right of the command name,
S00ILCS5.qxp 3/19/2010 1:11 AM Page 477 Keyboard Shortcuts k Adobe Illustrator CS5 If a command on a menu includes a keyboard reference, known as a keyboard shortcut, to the right of the command name,
Lens Selection Software. User Manual
 Lens Selection Software User Manual Legal Information User Manual 2018 Hangzhou Hikvision Digital Technology Co., Ltd. About this Manual This Manual is subject to domestic and international copyright protection.
Lens Selection Software User Manual Legal Information User Manual 2018 Hangzhou Hikvision Digital Technology Co., Ltd. About this Manual This Manual is subject to domestic and international copyright protection.
The Fundamentals. Document Basics
 3 The Fundamentals Opening a Program... 3 Similarities in All Programs... 3 It's On Now What?...4 Making things easier to see.. 4 Adjusting Text Size.....4 My Computer. 4 Control Panel... 5 Accessibility
3 The Fundamentals Opening a Program... 3 Similarities in All Programs... 3 It's On Now What?...4 Making things easier to see.. 4 Adjusting Text Size.....4 My Computer. 4 Control Panel... 5 Accessibility
Guidelines for Legible and Readable Text, page 2-1 Visual Density Transparent, Translucent, or Opaque?, page 2-3
 CHAPTER 2 Revised: November 15, 2011 Concepts, page 2-1 s, page 2-4 Reference, page 2-25 Concepts Guidelines for Legible and Readable Text, page 2-1 Visual Density Transparent, Translucent, or Opaque?,
CHAPTER 2 Revised: November 15, 2011 Concepts, page 2-1 s, page 2-4 Reference, page 2-25 Concepts Guidelines for Legible and Readable Text, page 2-1 Visual Density Transparent, Translucent, or Opaque?,
ENVI Classic Tutorial: 3D SurfaceView and Fly- Through
 ENVI Classic Tutorial: 3D SurfaceView and Fly- Through 3D SurfaceView and Fly-Through 2 Files Used in this Tutorial 2 3D Visualization in ENVI Classic 2 Load a 3D SurfaceView 3 Open and Display Landsat
ENVI Classic Tutorial: 3D SurfaceView and Fly- Through 3D SurfaceView and Fly-Through 2 Files Used in this Tutorial 2 3D Visualization in ENVI Classic 2 Load a 3D SurfaceView 3 Open and Display Landsat
Česky. Introduction... E-1 Minimum system requirements for PC... E-1 Using the AVerVision Application for PC.. E-3
 Table of Contents Introduction... E-1 Minimum system requirements for PC... E-1 Using the AVerVision Application for PC.. E-3 Video Screen... E-3 Control Panel... E-3 Document Camera Control Panel... E-4
Table of Contents Introduction... E-1 Minimum system requirements for PC... E-1 Using the AVerVision Application for PC.. E-3 Video Screen... E-3 Control Panel... E-3 Document Camera Control Panel... E-4
Medical Image Viewer Guide
 Cloud Medical Image Management Medical Image Viewer Guide March 2016 Table of Contents Indications for Use 3 Browser Requirements 3 User Interface Overview 4-5 Study Page 6 Main Toolbar 7 Sub-Toolbars
Cloud Medical Image Management Medical Image Viewer Guide March 2016 Table of Contents Indications for Use 3 Browser Requirements 3 User Interface Overview 4-5 Study Page 6 Main Toolbar 7 Sub-Toolbars
Getting Started with ShowcaseChapter1:
 Chapter 1 Getting Started with ShowcaseChapter1: In this chapter, you learn the purpose of Autodesk Showcase, about its interface, and how to import geometry and adjust imported geometry. Objectives After
Chapter 1 Getting Started with ShowcaseChapter1: In this chapter, you learn the purpose of Autodesk Showcase, about its interface, and how to import geometry and adjust imported geometry. Objectives After
Keynote 08 Basics Website:
 Website: http://etc.usf.edu/te/ Keynote is Apple's presentation application. Keynote is installed as part of the iwork suite, which also includes the word processing program Pages and the spreadsheet program
Website: http://etc.usf.edu/te/ Keynote is Apple's presentation application. Keynote is installed as part of the iwork suite, which also includes the word processing program Pages and the spreadsheet program
CTvox Quick Start Guide
 CTvox Quick Start Guide For Software Version 3.0 CTvox Quick Start Guide (for Software Version 3.0) Page 1 Contents Version history... 3 Introduction... 4 Loading a dataset... 5 Navigating the scene...
CTvox Quick Start Guide For Software Version 3.0 CTvox Quick Start Guide (for Software Version 3.0) Page 1 Contents Version history... 3 Introduction... 4 Loading a dataset... 5 Navigating the scene...
3ds Max Cottage Step 1. Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch.
 3ds Max Cottage Step 1 Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch. File/Import the CAD drawing Be sure Files of Type is set to all formats
3ds Max Cottage Step 1 Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch. File/Import the CAD drawing Be sure Files of Type is set to all formats
Motic Images Plus 3.0 ML Software. Windows OS User Manual
 Motic Images Plus 3.0 ML Software Windows OS User Manual Motic Images Plus 3.0 ML Software Windows OS User Manual CONTENTS (Linked) Introduction 05 Menus and tools 05 File 06 New 06 Open 07 Save 07 Save
Motic Images Plus 3.0 ML Software Windows OS User Manual Motic Images Plus 3.0 ML Software Windows OS User Manual CONTENTS (Linked) Introduction 05 Menus and tools 05 File 06 New 06 Open 07 Save 07 Save
Figure 1: NC > 2 Axis menu > Options
 Click To See: How to Use Online Documents SURFCAM Online Documents J 685)&$0Ã5HIHUHQFHÃ0DQXDO 7 &21),*85$7,21722/6 7.1 INTRODUCTION SURFCAM s default configuration parameters are contained in the SURFCAM.INI
Click To See: How to Use Online Documents SURFCAM Online Documents J 685)&$0Ã5HIHUHQFHÃ0DQXDO 7 &21),*85$7,21722/6 7.1 INTRODUCTION SURFCAM s default configuration parameters are contained in the SURFCAM.INI
Work with Shapes. Concepts CHAPTER. Concepts, page 3-1 Procedures, page 3-5
 3 CHAPTER Revised: November 15, 2011 Concepts, page 3-1, page 3-5 Concepts The Shapes Tool is Versatile, page 3-2 Guidelines for Shapes, page 3-2 Visual Density Transparent, Translucent, or Opaque?, page
3 CHAPTER Revised: November 15, 2011 Concepts, page 3-1, page 3-5 Concepts The Shapes Tool is Versatile, page 3-2 Guidelines for Shapes, page 3-2 Visual Density Transparent, Translucent, or Opaque?, page
OPERATION MANUAL MIMAKI ENGINEERING CO., LTD. D200652
 OPERATION MANUAL MIMAKI ENGINEERING CO., LTD. http://www.mimaki.co.jp E-mail:traiding@mimaki.co.jp D200652 About FineCut Thank you very much for purchasing a product of Mimaki. FineCut, a plug-in software
OPERATION MANUAL MIMAKI ENGINEERING CO., LTD. http://www.mimaki.co.jp E-mail:traiding@mimaki.co.jp D200652 About FineCut Thank you very much for purchasing a product of Mimaki. FineCut, a plug-in software
HOUR 12. Adding a Chart
 HOUR 12 Adding a Chart The highlights of this hour are as follows: Reasons for using a chart The chart elements The chart types How to create charts with the Chart Wizard How to work with charts How to
HOUR 12 Adding a Chart The highlights of this hour are as follows: Reasons for using a chart The chart elements The chart types How to create charts with the Chart Wizard How to work with charts How to
Panoramic Quickvision S0MANUVSMQV/GB. Panoramic QuickVision. User s Guide. Version /05/2012. Panoramic Quickvision
 S0MANUVSMQV/GB Panoramic QuickVision User s Guide Version 1.05 11/05/2012 Panoramic Quickvision Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 INSTALLATION OF PANORAMIC QUICKVISION... 5 PROGRAM INSTALLATION
S0MANUVSMQV/GB Panoramic QuickVision User s Guide Version 1.05 11/05/2012 Panoramic Quickvision Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 INSTALLATION OF PANORAMIC QUICKVISION... 5 PROGRAM INSTALLATION
Impress Guide Chapter 11 Setting Up and Customizing Impress
 Impress Guide Chapter 11 Setting Up and Customizing Impress This PDF is designed to be read onscreen, two pages at a time. If you want to print a copy, your PDF viewer should have an option for printing
Impress Guide Chapter 11 Setting Up and Customizing Impress This PDF is designed to be read onscreen, two pages at a time. If you want to print a copy, your PDF viewer should have an option for printing
Saturn User Manual. Rubén Cárdenes. 29th January 2010 Image Processing Laboratory, University of Valladolid. Abstract
 Saturn User Manual Rubén Cárdenes 29th January 2010 Image Processing Laboratory, University of Valladolid Abstract Saturn is a software package for DTI processing and visualization, provided with a graphic
Saturn User Manual Rubén Cárdenes 29th January 2010 Image Processing Laboratory, University of Valladolid Abstract Saturn is a software package for DTI processing and visualization, provided with a graphic
DentMILL. Basic Quick Guide. Copyright 2011.Roland DG Corporation R
 DentMILL Basic Quick Guide R1-111221 Copyright 2011.Roland DG Corporation Table of Contents User Interface... 2 Workflow from the preparation to exporting data... 3 Basic operation procedures... 4 Step
DentMILL Basic Quick Guide R1-111221 Copyright 2011.Roland DG Corporation Table of Contents User Interface... 2 Workflow from the preparation to exporting data... 3 Basic operation procedures... 4 Step
OrthoAnalyzer 2012 User Manual
 OrthoAnalyzer 2012 User Manual Table of Contents Preface... 3 1 Getting Started... 4 1.1 Executing OrthoAnalyzer... 4 1.2 Creating a New Database Entry... 5 1.2.1 New Patient... 5 1.2.2 New Model Set...
OrthoAnalyzer 2012 User Manual Table of Contents Preface... 3 1 Getting Started... 4 1.1 Executing OrthoAnalyzer... 4 1.2 Creating a New Database Entry... 5 1.2.1 New Patient... 5 1.2.2 New Model Set...
Photoshop / Editing paths
 Photoshop / Editing paths Path segments, components, and points Select a path Adjust path segments Add or delete anchor points Convert between smooth points and corner points Adjust path components Path
Photoshop / Editing paths Path segments, components, and points Select a path Adjust path segments Add or delete anchor points Convert between smooth points and corner points Adjust path components Path
Press the Plus + key to zoom in. Press the Minus - key to zoom out. Scroll the mouse wheel away from you to zoom in; towards you to zoom out.
 Navigate Around the Map Interactive maps provide many choices for displaying information, searching for more details, and moving around the map. Most navigation uses the mouse, but at times you may also
Navigate Around the Map Interactive maps provide many choices for displaying information, searching for more details, and moving around the map. Most navigation uses the mouse, but at times you may also
User Manual Version 1.1 January 2015
 User Manual Version 1.1 January 2015 - 2 / 112 - V1.1 Variegator... 7 Variegator Features... 7 1. Variable elements... 7 2. Static elements... 7 3. Element Manipulation... 7 4. Document Formats... 7 5.
User Manual Version 1.1 January 2015 - 2 / 112 - V1.1 Variegator... 7 Variegator Features... 7 1. Variable elements... 7 2. Static elements... 7 3. Element Manipulation... 7 4. Document Formats... 7 5.
Controlling the Drawing Display
 Controlling the Drawing Display In This Chapter 8 AutoCAD provides many ways to display views of your drawing. As you edit your drawing, you can control the drawing display and move quickly to different
Controlling the Drawing Display In This Chapter 8 AutoCAD provides many ways to display views of your drawing. As you edit your drawing, you can control the drawing display and move quickly to different
Work with RSS Feeds. Procedures. Add an RSS Text Object CHAPTER. Procedures, page 7-1
 CHAPTER 7 Revised: November 15, 2011 s, page 7-1 s Add an RSS Text Object, page 7-1 Rename an RSS Text Object, page 7-2 Delete or Restore an RSS Text Object, page 7-4 Manipulate an RSS Text Object, page
CHAPTER 7 Revised: November 15, 2011 s, page 7-1 s Add an RSS Text Object, page 7-1 Rename an RSS Text Object, page 7-2 Delete or Restore an RSS Text Object, page 7-4 Manipulate an RSS Text Object, page
Using the Markup Commands
 Using SoftPlan review 1 Using the Markup Commands The Markup menu supplies various commands that allow you to add changes, comments, and suggestions to a drawing or to specific areas of a drawing. To open
Using SoftPlan review 1 Using the Markup Commands The Markup menu supplies various commands that allow you to add changes, comments, and suggestions to a drawing or to specific areas of a drawing. To open
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL PHOTOSHOP WORKSPACE. Interface Overview 3. Menus 15. The Toolbox 29. Palettes 61. Presets and Preferences 83 WEB TASKS
 PHOTOSHOP WORKSPACE CHAPTER 1 Interface Overview 3 CHAPTER 2 Menus 15 CHAPTER 3 The Toolbox 29 CHAPTER 4 Palettes 61 CHAPTER 5 Presets and Preferences 83 COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL PHOTOSHOP WORK SPACE UNIVERSAL
PHOTOSHOP WORKSPACE CHAPTER 1 Interface Overview 3 CHAPTER 2 Menus 15 CHAPTER 3 The Toolbox 29 CHAPTER 4 Palettes 61 CHAPTER 5 Presets and Preferences 83 COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL PHOTOSHOP WORK SPACE UNIVERSAL
June 05, 2018, Version 3.0.6
 June 05, 2018, Version 3.0.6 VolViCon is an advanced application for reconstruction of computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance (MR), ultrasound, and x-rays images. It gives features for exporting
June 05, 2018, Version 3.0.6 VolViCon is an advanced application for reconstruction of computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance (MR), ultrasound, and x-rays images. It gives features for exporting
Insight: Measurement Tool. User Guide
 OMERO Beta v2.2: Measurement Tool User Guide - 1 - October 2007 Insight: Measurement Tool User Guide Open Microscopy Environment: http://www.openmicroscopy.org OMERO Beta v2.2: Measurement Tool User Guide
OMERO Beta v2.2: Measurement Tool User Guide - 1 - October 2007 Insight: Measurement Tool User Guide Open Microscopy Environment: http://www.openmicroscopy.org OMERO Beta v2.2: Measurement Tool User Guide
ANALYSIS SOFTWARE. CAmReport
 ANALYSIS SOFTWARE CAmReport ENGLISH User Manual CONTENTS 1. INSTALLATION... 3 2. GETTING STARTED... 4 2.1 Starting and Exiting CAmReport... 4 2.2 Setup... 4 2.2.1 Language... 4 2.2.2 Units... 4 2.2.3 CAmReport
ANALYSIS SOFTWARE CAmReport ENGLISH User Manual CONTENTS 1. INSTALLATION... 3 2. GETTING STARTED... 4 2.1 Starting and Exiting CAmReport... 4 2.2 Setup... 4 2.2.1 Language... 4 2.2.2 Units... 4 2.2.3 CAmReport
INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL IMAGING- 3D LOCALIZATION LAB MANUAL 1. Modifications for P551 Fall 2013 Medical Physics Laboratory
 INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL IMAGING- 3D LOCALIZATION LAB MANUAL 1 Modifications for P551 Fall 2013 Medical Physics Laboratory Introduction Following the introductory lab 0, this lab exercise the student through
INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL IMAGING- 3D LOCALIZATION LAB MANUAL 1 Modifications for P551 Fall 2013 Medical Physics Laboratory Introduction Following the introductory lab 0, this lab exercise the student through
Intermediate/Advanced. Faculty Development Workshop FSE Faculty retreat April 18, 2012
 Intermediate/Advanced Faculty Development Workshop FSE Faculty retreat April 18, 2012 Remote Desktop Sharing Quick Reference Guide for Moderators The Moderator or a Participant may request control of another
Intermediate/Advanced Faculty Development Workshop FSE Faculty retreat April 18, 2012 Remote Desktop Sharing Quick Reference Guide for Moderators The Moderator or a Participant may request control of another
Enhanced material contrast by dual-energy microct imaging
 Enhanced material contrast by dual-energy microct imaging Method note Page 1 of 12 2 Method note: Dual-energy microct analysis 1. Introduction 1.1. The basis for dual energy imaging Micro-computed tomography
Enhanced material contrast by dual-energy microct imaging Method note Page 1 of 12 2 Method note: Dual-energy microct analysis 1. Introduction 1.1. The basis for dual energy imaging Micro-computed tomography
Avid FX Tutorials. Understanding the Tutorial Exercises
 Avid FX Tutorials Understanding the Tutorial Exercises The following tutorial exercises provide step-by-step instructions for creating various kinds of effects, while exploring many aspects of the Avid
Avid FX Tutorials Understanding the Tutorial Exercises The following tutorial exercises provide step-by-step instructions for creating various kinds of effects, while exploring many aspects of the Avid
Using TeraRecon intuition Viewer with STAT Quick Reference Guide
 Using TeraRecon intuition Viewer with STAT Quick Reference Guide 1. Launching intuition 2. 3D Assessment of Coronary Arteries for Stenosis 3. Time Volume Analysis (TVA) for Determination of Left Ventricular
Using TeraRecon intuition Viewer with STAT Quick Reference Guide 1. Launching intuition 2. 3D Assessment of Coronary Arteries for Stenosis 3. Time Volume Analysis (TVA) for Determination of Left Ventricular
Quick Guide for Photoshop CC Basics April 2016 Training:
 Photoshop CC Basics Creating a New File 1. Click File > New 2. Keep Default Photoshop Size selected in the Preset drop-down list. 3. Click OK. Showing Rulers 1. On the Menu bar, click View. 2. Click Rulers.
Photoshop CC Basics Creating a New File 1. Click File > New 2. Keep Default Photoshop Size selected in the Preset drop-down list. 3. Click OK. Showing Rulers 1. On the Menu bar, click View. 2. Click Rulers.
R2CAD User Guide V1.7. Copyright All rights reserved.
 R2CAD User Guide V1.7 Copyright All rights reserved. Table of Contents 1. About R2CAD... 1 1.1 System Requirements... 1 2. User Interface... 2 2.1 Main menu... 2 2.2 Mouse Operation... 2 2.3 Setting...
R2CAD User Guide V1.7 Copyright All rights reserved. Table of Contents 1. About R2CAD... 1 1.1 System Requirements... 1 2. User Interface... 2 2.1 Main menu... 2 2.2 Mouse Operation... 2 2.3 Setting...
Edupen Pro User Manual
 Edupen Pro User Manual (software for interactive LCD/LED displays and monitors) Ver. 3 www.ahatouch.com Some services in Edupen Pro require dual touch capability. In order to use dual touch, your computer
Edupen Pro User Manual (software for interactive LCD/LED displays and monitors) Ver. 3 www.ahatouch.com Some services in Edupen Pro require dual touch capability. In order to use dual touch, your computer
MANUAL NO. OPS647-UM-151 USER S MANUAL
 MANUAL NO. OPS647-UM-151 USER S MANUAL Software Usage Agreement Graphtec Corporation ( Graphtec ) hereby grants the purchaser and authorized User (the User ) the right to use the software (the Software
MANUAL NO. OPS647-UM-151 USER S MANUAL Software Usage Agreement Graphtec Corporation ( Graphtec ) hereby grants the purchaser and authorized User (the User ) the right to use the software (the Software
Contents. - i - Ver.:2
 Contents 1 Accessories of D-Point 2... 2 2 Connecting Projector to PC... 4 3 Pen Action... 4 4 Driver Installation... 5 5 Configuration Setting... 8 6 D-Point 2 Pull-up Menu... 12 7 DT02 Multi-touch Interactive
Contents 1 Accessories of D-Point 2... 2 2 Connecting Projector to PC... 4 3 Pen Action... 4 4 Driver Installation... 5 5 Configuration Setting... 8 6 D-Point 2 Pull-up Menu... 12 7 DT02 Multi-touch Interactive
IUL Flash & Go User Manual
 IUL Flash & Go User Manual 1 Index Flash & Go User Manual... 1 Index... 2 1-Installation Prerequisites... 3 1.1-Minimum Requirements for the Host PC... 3 1.2-Recommended Requirements for the Host PC...
IUL Flash & Go User Manual 1 Index Flash & Go User Manual... 1 Index... 2 1-Installation Prerequisites... 3 1.1-Minimum Requirements for the Host PC... 3 1.2-Recommended Requirements for the Host PC...
GEOCIRRUS 3D Viewer. User Manual: GEOCIRRUS 3D Viewer Document version 1.6 Page 1
 GEOCIRRUS 3D Viewer Page 1 Table of Contents 3D Viewer Functionality... 3 Line of Sight (LoS)... 4 Identify... 8 Measurement... 9 3D Line Measure Tool... 10 3D Area Measure Tool... 11 Environment... 12
GEOCIRRUS 3D Viewer Page 1 Table of Contents 3D Viewer Functionality... 3 Line of Sight (LoS)... 4 Identify... 8 Measurement... 9 3D Line Measure Tool... 10 3D Area Measure Tool... 11 Environment... 12
XRADIA microxct Manual
 XRADIA microxct Manual Multiscale CT Lab Table of Contents 1. Introduction and Basics 1.1 Instrument Parts 1.2 Powering up the system 1.3 Preparing your sample 2. TXM Controller 2.1 Starting up 2.2 Finding
XRADIA microxct Manual Multiscale CT Lab Table of Contents 1. Introduction and Basics 1.1 Instrument Parts 1.2 Powering up the system 1.3 Preparing your sample 2. TXM Controller 2.1 Starting up 2.2 Finding
Keynote Basics Website:
 Keynote Basics Website: http://etc.usf.edu/te/ Keynote is Apple's presentation application. Keynote is installed as part of the iwork suite, which also includes the word processing program Pages. If you
Keynote Basics Website: http://etc.usf.edu/te/ Keynote is Apple's presentation application. Keynote is installed as part of the iwork suite, which also includes the word processing program Pages. If you
Adobe Acrobat Reader 4.05
 Adobe Acrobat Reader 4.05 1. Installing Adobe Acrobat Reader 4.05 If you already have Adobe Acrobat Reader installed on your computer, please ensure that it is version 4.05 and that it is Adobe Acrobat
Adobe Acrobat Reader 4.05 1. Installing Adobe Acrobat Reader 4.05 If you already have Adobe Acrobat Reader installed on your computer, please ensure that it is version 4.05 and that it is Adobe Acrobat
